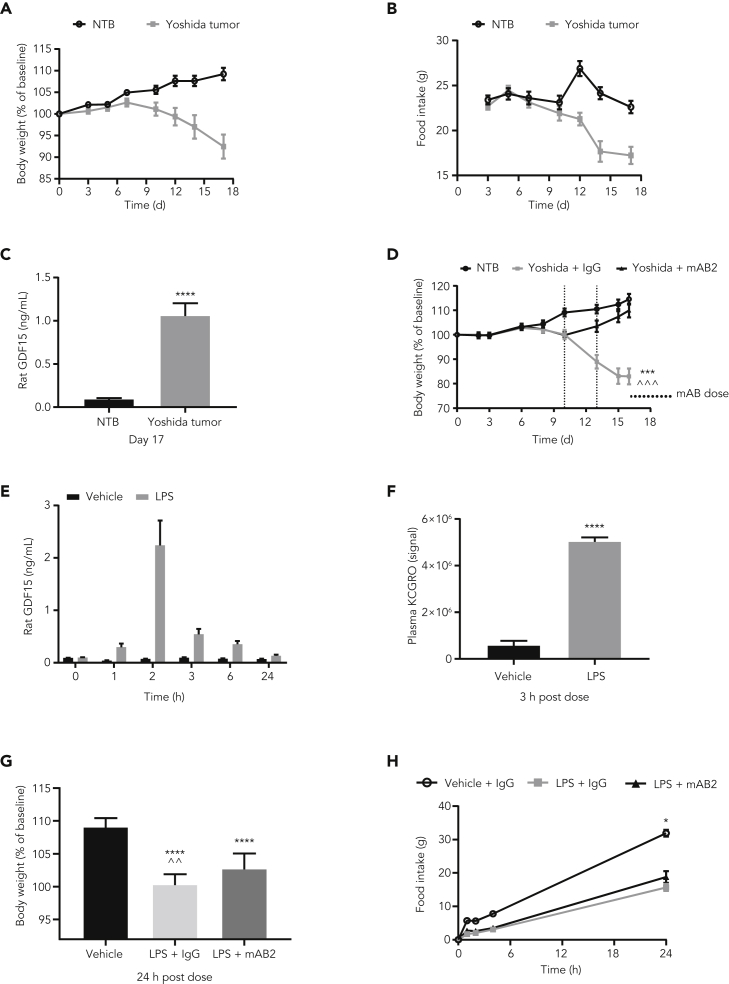
Figure 4.
Neutralization of GDF15 marginally modulates weight loss but not anorexia induced by a low dose of LPS in rats
(A) Body weight, (B) food intake, and (C) plasma GDF15 of nontumor-bearing rats and rats injected with Yoshida tumor cells. ∗∗∗∗ p value < 0.0001 vs. NTB. Data were analyzed using Welch's heteroscedastic F test. (D) Body weights of Yoshida-tumor-bearing rats injected with mAB2 and control IgG. ∗∗∗ p value < 0.001 vs. NTB; ^^^ p value < 0.001 vs. Yoshida + mAB2. Data were analyzed using longitudinal mixed effects ANOVA. (E) Plasma GDF15 levels in rats IP injected with 0.25 mg/kg LPS. (F) Plasma KCGRO levels in rats dosed with 0.25 mg/kg LPS at 3 h after dose. ∗∗∗∗ p value < 0.0001 vs. Vehicle; data were analyzed using an unpaired two-tailed t-test. (G) Body weight and cumulative food intake post LPS dose of 0.25 mg/kg. ∗∗∗∗ p value < 0.0001 vs. Vehicle; ˆˆ p value < 0.004 vs. LPS + mAB2; data were analyzed using ANOVA. (H) Cumulative food intake for rats was measured at 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, and 24 h. ∗ p value < 0.05 vs. LPS + IgG or LPS + mAB2. Data were analyzed using Welch's heteroscedastic F test at 24h timepoint. Data represented as mean ± SEM. N = 12 per group.
GDF15, growth differentiation factor 15; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IP, intraperitoneal; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NTB, nontumor-bearing; SEM, standard error of the mean.