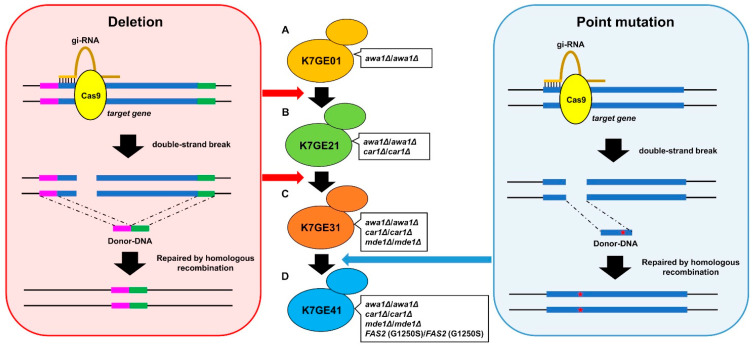
Figure 1.
Serial breeding of a sake yeast strain with eight mutations. A double-strand break was introduced in the target gene by CRISPR-Cas9. Homologous recombination repair was performed using donor DNA (150 bp) to introduce gene deletion (light red region) or point mutation (light blue region). Starting from K7GE01 (yellow) with AWA1 deletion (A), K7GE21 (green) with CAR1 deletion (B), K7GE31 (orange) with MDE1 deletion (C), and K7GE41 (blue) with FAS2 (G1250S) point mutation (D) were generated successively. The final K7GE41 sake yeast strain harbored homozygous eight mutations that confer excellent brewing characteristics.