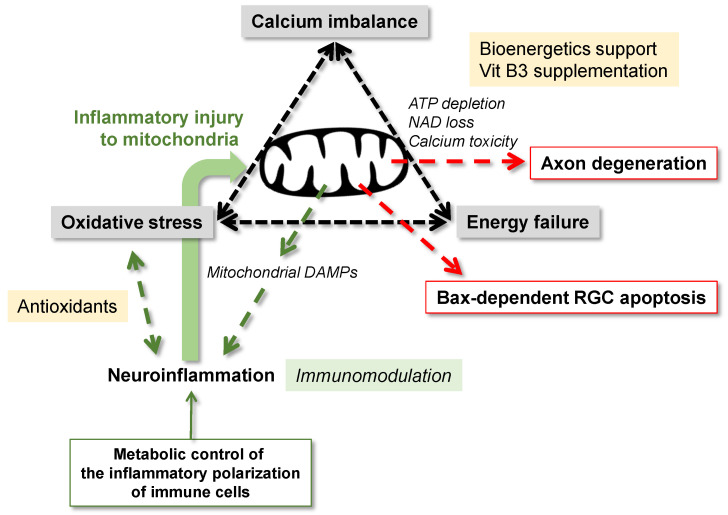
Figure 4.
Interplay between mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in glaucoma. Mitochondria through energy failure, oxidative stress, disturbed calcium homeostasis, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) loss are critically involved in RGC degeneration and neuroinflammation. Mitochondria-generated oxidative stress and the mitochondrial constituents released after increased membrane permeability, including damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), can induce glial inflammatory responses. Mitochondria’s role in neuroinflammation also includes the metabolic control of glial inflammatory polarization. While dysfunctional mitochondria induce neuroinflammation, proinflammatory cytokines may further impair mitochondria. Yellow boxes indicate the related treatment strategies that are being tested in clinical studies. As shown in the green box, immunomodulatory treatments are still explored in preclinical studies.