Abstract
Background: Osteosarcopenia is a recently identified condition caused by the coexistence of osteoporosis and sarcopenia that affects the frail elderly population, leading to an increased risk of falls and fractures. Given the recent socio-economic interest associated with osteosarcopenia, the aim of this meta-analysis is to provide an overview of the factors potentially involved in its pathogenesis, assessing its population type, prevalence, and associated variables. Methods: A comprehensive systematic search for relevant studies, published from 2015 to 2020, was performed by using PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases. We analysed the variables of age, vitamin D, handgrip, and T-score in four different groups: healthy, osteopenic–osteoporotic, sarcopenic, and osteosarcopenic. Results: A total of 6504 patients from 16 studies were included in the final meta-analysis. The analysis of the individual variables reveals a statistically significant correlation between the handgrip test data and T-score (p < 0.001). Conclusions: The correlation between T-score values and handgrip strength suggests a new potential parameter in the development of predictive models that could be used in clinical practice, highlighting its importance for the diagnosis of osteosarcopenia.
Keywords: systematic review, meta-analysis, osteosarcopenia, sarcopenia, osteoporosis, T-score, handgrip strength
1. Introduction
The concept of “osteosarcopenia”, which emerged in 2009 with the first editorial by Binkley and Buehring [1], is currently used to refer to a subgroup of elderly patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia, characterised by an higher risk of falls, fractures, disability, and frailty [2]. Osteoporosis, defined by low bone mass and micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue [3], and sarcopenia, manifested by loss of muscle mass, strength, and function [4], often coexist in the fragile population, leading to significantly worse outcomes than those observed in either condition alone. Several evidences demonstrate considerable overlap in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and sarcopenia, suggesting the possibility of treating the conditions together [5,6,7,8]. Indeed, bone and muscle not only interact mechanically, but also communicate with each other biochemically, via complex paracrine and endocrine mechanisms, to maintain muscle and bone homeostasis [9,10,11]. Many scientists agree that the prevalence of osteosarcopenia increases with age: Fahimfar and colleagues reported that it occurs in 14.3% of men in the 60–64 age group and in 59.4% of men over 75; in women, the disease affects 20.3% of the 60–64 age group and 48.3% of women over 75 [12]. In addition, a higher prevalence of osteosarcopenia has been observed in women (25.5–82.6%) than in men (16.4–32.0%) [13]. Finally, in patients with low-energy trauma fractures, the prevalence of osteosarcopenia is between 17 and 96.3% in both sexes [12]. Sarcopenia is generally defined as a decrease in skeletal muscle mass and muscle strength or motor skills [11]. Several research groups have focused their attention on the study of this disease; among the most important are the EWGSOP2 (European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2) [14] of 2019 and the AWGS (Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia) [15] of 2014. The parameters used to make a diagnosis of sarcopenia are strength, muscle quantity, and physical performance [4]. Accurate measurement of grip strength (handgrip strength test) requires the use of a calibrated handheld dynamometer under well-defined test conditions with interpretative data from appropriate reference populations. Low grip strength is a powerful predictor of adverse patient outcomes, as well as long hospital stay, increased functional limitations, poor quality of life, and mortality. On the other hand, in relation to osteoporosis, the World Health Organisation (WHO) has developed diagnostic criteria using a score based on standard deviations of bone mineral density (BMD), referring to peak bone mass in young healthy women. On this basis, osteoporosis was defined by a BMD T-score of less than −2.5, and osteopenia by a T-score between −1 and −2.5. Undoubtedly, the diagnostic criteria have supported the importance of low BMD in the pathogenesis of fragility fractures and have provided a tool that can be used in epidemiological studies to quantify the prevalence of osteoporosis; however, the usefulness of BMD as a clinical indicator of osteoporosis is limited because it is only one of a number of risk factors related to possible fractures [16]. The focus on research and treatment of pathological conditions that can affect older people is certainly one of the health priorities for the near future. As this is a newly defined pathology, there are no currently valid diagnostic criteria that would allow the rapid elaboration of a diagnosis of osteosarcopenia. In this respect, our meta-analysis aims to analyse the correlation between some variables normally considered for the diagnosis of osteoporosis (T-score) and sarcopenia (handgrip strength test), with the final objective of defining one or more new parameters to refer to for the diagnosis of this pathology.
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
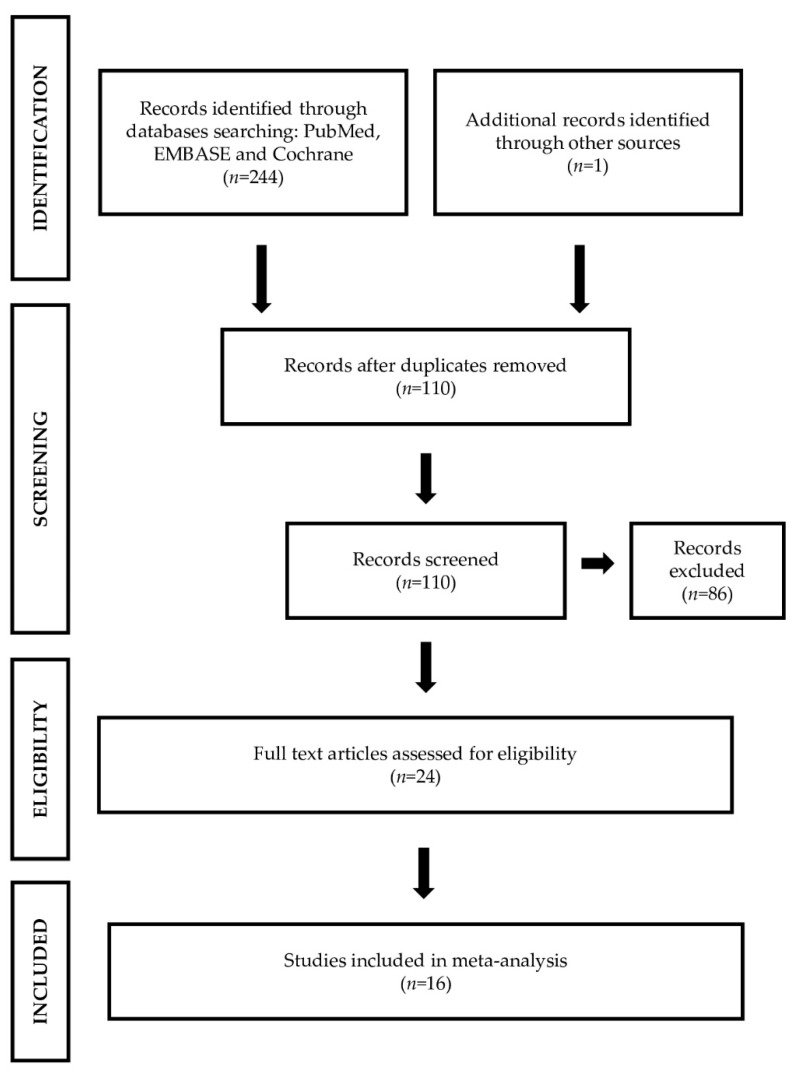
A systematic review was conducted following the recommendations of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Figure 1) [17]. An independent literature search was conducted across PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases. The search strategy was based on combination of following terms: “osteosarcopenia”, “sarco-osteopenia”, “osteopenia”, “osteoporosis”, “sarcopenia”, “fractures”, and “fragility”. Case reports, abstracts, short communications, letters to the editor, dissertations, and studies lacking case and control adequate numbers were also excluded. The main requirements for primary studies were introduced to have the most homogeneous data possible (same type of outcome, presence of clear, and explanatory summary tables as well as the use of statistical methodology), with the aim of searching for relationships between variables and risk groups. For selecting primary studies, we used criteria for classifying patients into clusters or homogeneous groups (Table 1).
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of the literature search and selection process of the included studies.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the studies.
| References | Year | Study Design | Type of Participants | Mean/Median Age | Sample Size | n, Male | n, Female | Osteoporosis Diagnostic Criteria | Sarcopenia Diagnostic Criteria | n, Osteosarcopenic Subjects | %, Osteosarcopenic Subjects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | 2015 | transversal | fragility, falls, fractures | NA | 679 | 224 | 455 | WHO | * p < 0.05 | 258 | 38% |
| [20] | 2015 | observational | hip fracture | 82 | 239 | 72 | 167 | WHO | AWGS | 166 | 69% |
| [21] | 2016 | control cases | hip fracture | NA | 359 | 87 | 272 | WHO | AWGS | NA | NA |
| [22] | 2016 | prospective-observational | community living seniors | 70.5 | 750 | 0 | 750 | WHO | ALM < −DS | NA | NA |
| [23] | 2016 | observational | community living seniors | NA | 68 | 21 | 47 | WHO | EWGSOP | 19 | 28% |
| [24] | 2018 | retrospective | hip fracture | 77.8 | 324 | 78 | 246 | WHO | AWGS | 93 | 29% |
| [25] | 2018 | transversal | consecutively admitted to hospital, first hip fracture | 81.4 | 80 | 80 | 0 | WHO | * p < 0.05 | NA | NA |
| [26] | 2018 | longitudinal | community living seniors | 76.7 | 1575 | 1575 | 0 | WHO | EWGSOP | 131 | 8% |
| [27] | 2019 | transversal | hospitalised | 80.6 | 141 | 57 | 84 | WHO | EWGSOP | 20 | 14% |
| [28] | 2019 | prospective-observational | community living seniors | 78.8 | 106 | 34 | 72 | WHO | * p < 0.05 | NA | NA |
| [29] | 2019 | transversal | fragility, falls, fractures | 77.9 | 253 | 57 | 196 | WHO | EWGSOP2 | 138 | 55% |
| [30] | 2019 | prospective-transversal | postmenopausal subjects | 64.14 | 140 | 0 | 140 | WHO | EWGSOP | 90 | 64% |
| [31] | 2019 | transversal | community living seniors | 76 | 484 | 147 | 337 | WHO | EWGSOP2 | 25 | 5% |
| [32] | 2019 | transversal | healthy subjects | 71.4 | 427 | 205 | 222 | * p < 0.05 | * p < 0.05 | 36 | 8% |
| [13] | 2020 | transversal | community living healthy seniors | 75 | 529 | 232 | 297 | WHO | EWGSOP2 | 8 | 2% |
| [33] | 2020 | transversal | hip fracture | 79.7 | 350 | 0 | 350 | WHO | EWGSOP2 | NA | NA |
2.2. Data Collection, Extraction, and Quality Assessment
Data were collected independently by two reviewers using a standardised data extraction form to summarise characteristics of the studies and outcome data [18]. Discrepancies or difficulties were resolved by consensus. From each individual study, we extracted baseline information: the first author’s name; the year of publication; socio-demographic data (type of population, sex ratio, mean age); sample size; study design; tools used to assess bone and muscle mass (handgrip strength test, gait speed test, timed up and go test); patient characteristics (BMI, BMD, T-score, serum levels of calcium, vitamin D, and PTH). To include as many studies as possible in our systematic review, we contacted authors or co-authors when information was missing in the full-text paper. After collection of the relevant articles, the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to assess their methodological quality.
2.3. Data Analysis
The outcomes provided by the primary studies detected within each cluster were the numerosities and continuous measures such as means and standard deviations, both for clinical covariates (BMI, T-score, vitamin D, handgrip) and demographic covariates (age and gender) (Table 2). The weighted arithmetic averages of the outcomes of the primary studies were then calculated for each group with weights equal to the number of statistical units in the same study, named global outcome. If data were not available, the overall outcome values of the uncategorised group (RG) or the calculated overall outcome were assigned. Statistical analyses were conducted by using R software (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, version 3.6.2; 2019-12-12; Vienna, Austria). Pearson’s chi-squared test for evaluating the independence between covariates in the groups and t-test for Pearson correlation have been used. Differences were considered significant when the p value was <0.05 (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).
Table 2.
Characteristics of the different subgroups of the studies.
| RG | H | OP | SP | OSP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All subjects | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| AGE | 75.5 ± 5.5 | 73.0 ± 9.6 | 75.6 ± 8.9 | 78.0 ± 7.5 | 77.6 ± 8.8 |
| BMI | 25.0 ± 2.3 | 28.1 ± 3.7 | 26.2 ± 3.1 | 25.4 ± 2.6 | 25.3 ± 3.0 |
| T-SCORE | −1.4 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.04 | −2.0 ± 0.4 | −0.8 ± 0.14 | −2.9 ± 0.58 |
| VITAMIN D | 43.9 ± 5.1 | 56.6 ± 11.2 | 56.0 ± 8.8 | 63.6 ± 12.3 | 56.2 ± 7.6 |
| HANDGRIP | 26.6 ± 3.7 | 35.2 ± 7.6 | 30.5 ± 6.13 | 24.0 ± 4.8 | 18.7 ± 2.7 |
| Male | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| AGE | 76.3 ± 13.0 | 75.5 ± 18.9 | 76.6 ± 18.4 | 79.5 ± 16.5 | 79.8 ± 18.7 |
| BMI | 23.1 ± 3.3 | 28.1 ± 7.0 | 26.5 ± 6.6 | 21.7 ± 5.4 | 20.6 ± 5.1 |
| T-SCORE | −1.7 ± 0.21 | 0.1 ± 0.04 | −1.7 ± 0.4 | −0.8 ± 0.2 | −2.9 ± 0.7 |
| VITAMIN D | 43.4 ± 7.6 | 56.6 ± 14.1 | 56.0 ± 14.0 | 63.6 ± 15.9 | 56.2 ± 14.0 |
| HANDGRIP | 35.4 ± 5.0 | 33.7 ± 8.4 | 35.6 ± 8.3 | 31.7 ± 6.9 | 31.0 ± 5.4 |
| Female | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| AGE | 76.2 ± 5.8 | 60.6 ± 15.1 | 69.8 ± 9.5 | 65.6 ± 11.4 | 68.9 ± 11.8 |
| BMI | 24.6 ± 3.4 | 29.0 ± 7.2 | 25.8 ± 5.5 | 23.9 ± 4.2 | 26.7 ± 5.6 |
| T-SCORE | −2.2 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.04 | −1.8 ± 0.45 | −0.7 ± 0.18 | −1.7 ± 0.42 |
| VITAMIN D | 46.6 ± 6.6 | 56.6 ± 14.1 | 51.3 ± 12.8 | 63.6 ±15.9 | 55.5 ± 13.8 |
| HANDGRIP | 19.4 ± 2.3 | 21.4 ± 5.3 | 18.4 ± 2.6 | 18.2 ± 3.4 | 13.5 ± 2.1 |
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
The initial search yielded 245 studies, with duplicate studies removed, resulting in 110 studies remaining. Following the inclusion and exclusion criteria, we selected 16 studies. Figure 1 shows a flow diagram of the literature search and study selection.
3.2. Study Characteristics
The selected studies include different experimental designs: transversal, observational, control cases, prospective, retrospective, and longitudinal. The enrolled subjects were divided into the following categories: healthy (H) (all individuals who were not osteoporotic, not sarcopenic, not osteosarcopenic), osteoporotic (OP) (all individuals with a T-score < −1 SD), sarcopenic (SP) (all individuals who fall within the various definitions of sarcopenia), and osteo-sarcopenic (OSP) (all individuals with osteopenia/osteoporosis and sarcopenia simultaneously). The group of uncategorised (RG) was also considered, i.e., patients who had no direct or clear allocation in the primary study to one of the four previous groups.
3.3. Analysis Outcome
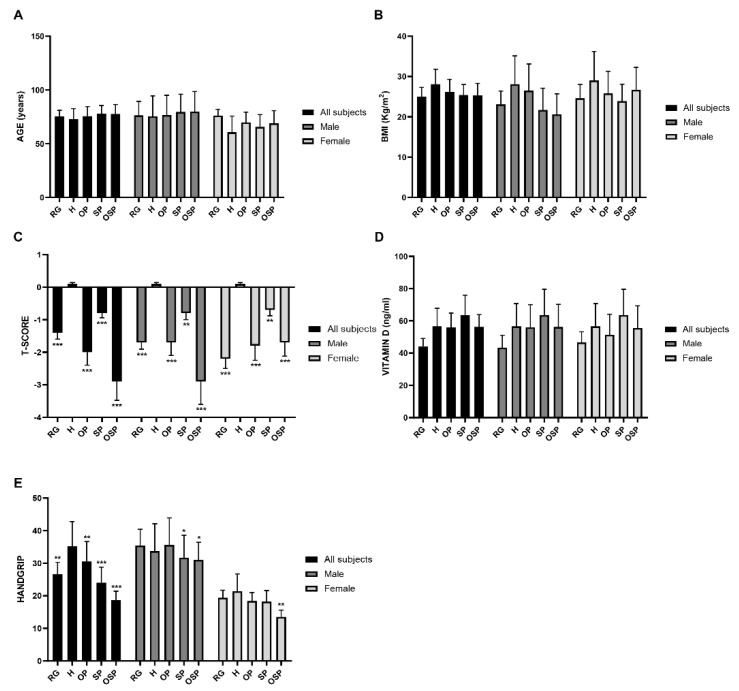
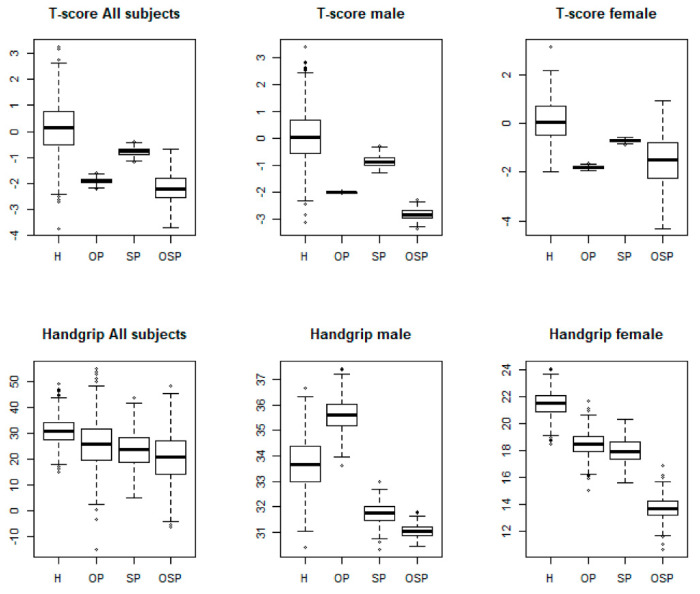
Analyses of the mean values between groups (all subjects, males, and females) showed important differences with respect to age and clinical covariates (Figure 2). Regarding the variables age (panel A), BMI (panel B), and vitamin D (panel D), the analysis showed no significant differences between the five different categories of subjects, nor between males and females. In contrast, we found significant differences for the variable T-score (panel C) and handgrip (panel E) between all groups. We observed a progressively decreasing trend for the T-score values, starting from the H group towards the OSP group, in all subjects (H: 0.1 ± 0.04; OP: −2.0 ± 0.4; SP: −0.8 ± 0.14; OSP: −2.9 ± 0.6) (Table 2). We also obtained the same result by analysing the T-score value separately between males and females (male: H: 0.1 ± 0.04, OP: −1.7 ± 0.4, SP: −0.8 ± 0.2, OSP: −2.9 ± 0.7; female: H: 0.1 ± 0.04, OP: −1.8 ± 0.45, SP: −0.7 ± 0.18, OSP: −1.7 ± 0.42). In relation to the RG group, we found the following T-score values: all subjects, −1.4 ± 0.2; male, −1.7 ± 0.21; female, −2.2 ± 0.3. The same decreasing trend was also observed for the variable handgrip, with significant differences between the different groups: in all subjects: H: 35.2 ± 7.6, OP: 30.5 ± 6.13, SP: 24.0 ± 4.8, OSP: 18.7 ± 2.7; in the male group: H: 33.7 ± 8.4, OP: 35.6 ± 8.3, SP: 31.7 ± 6.9, OSP: 31.0 ± 5.4; in the female group: H: 21.4 ± 5.3, OP: 18.4 ± 2.6, SP: 18.2 ± 3.4, OSP: 13.5 ± 2.1. In relation to the RG group, we found the following handgrip values: all subjects, 26.6 ± 3.7; male, 35.4 ± 5.0; female, 19.4 ± 2.3. After analysing the distribution of the variables considered in this meta-analysis, we determined an integrated database representing a sample of the population under analysis, according to the clusters defined a priori (H, OP, SP, and OSP) and the data-pooling conducted. The purpose of the classification adopted responds to the need to use an elected sample according to the criteria highlighted above to initiate association analyses between the variables under study. This sample was constituted by taking the outcome of the individual primary studies for the selected variables and by risk group where present and inserting the weighted or global outcome for the missing cases. The sample was then reclassified using cut-offs that meet the EWGSOP2 and AWGS criteria for sarcopenia and the criteria established by the WHO for osteoporosis [14,15]. The modalities of the qualitative variables are represented by the outcome estimated from the 16 individual primary studies. From an initial analysis of the sample, a statistically significant correlation was observed between two of the analysed variables, T-score, and handgrip among all groups (rho = 0.47; p < 0.001). Furthermore, this correlation was also found within the individual OSP group (rho = 0.17; p < 0.001). Finally, the association between these variables was analysed by means of the chi-squared independence test, applied to the contingency tables obtained through the classification adopted previously. The results of this statistical analysis confirmed the data obtained previously, showing the existence of a significant association between the two variables, T-score and handgrip, both between groups (χ2 = 188; p < 0.001) and within the single OSP group (χ2 = 278; p < 0.001). The boxplots show the distribution of the two variables, by gender and risk group, obtained from the sample analysed (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Distribution of the variables associated with the subjects of the primary studies. (A) Age variable; (B) BMI variable; (C) T-score variable; (D) Vitamin D; (E) Handgrip variable. All subjects and male and female groups were analysed separately. Differences were considered significant when the p value was < 0.05 (* p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001).
Figure 3.
Boxplot of the statistically significant correlation between the T-score and handgrip variables in all subjects, males, and females between groups (χ2 = 188; ** p < 0.001) and within the single OSP group (χ2 =2 78; ** p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
Osteosarcopenia is a newly defined pathology in which two of the most characteristic diseases of the elderly population, osteoporosis and sarcopenia, coexist [5]. Osteoporosis is characterised by a reduction in bone mineral density (BMD) and a deterioration of the microarchitecture of the bone tissue, while sarcopenia is manifested by a loss of muscle mass, strength, and function (19). While there are already valid criteria on which to base a rapid and accurate diagnosis of osteoporosis and sarcopenia, there is no uniform protocol for diagnosing osteosarcopenia, this being a multifactorial and, as mentioned above, recently defined condition. The aim of this meta-analysis was to identify a correlation between the variables that are usually considered to establish a diagnosis of osteoporosis (T-score and vitamin D) and the result of the main diagnostic test that is carried out to establish a possible condition of sarcopenia (handgrip strength test). The analysis of variables’ trend between the categories of subjects taken into consideration showed significant differences between the different groups for two of the five variables investigated, T-score, and handgrip strength test. This result highlights how the trend of these variables goes hand in hand with the progressive increase in the severity of the osteoporotic and sarcopenic condition, up to osteosarcopenia. Next, the reclassification of the sample through the global size effect confirmed the hypotheses of causal association between the selected groups and the variables, as well as between the variables themselves within the groups. These results enrich the matrix of the meta-analysis by providing different information. In fact, through the calculation of the global effect sizes of the variables, new threshold values were identified, against which different levels of risk attributable to each group defined a priori are associated. These results were tested by reconstructing a sample of individuals and assessing the association between the different variables and between risk groups. Some studies found associations only between some single variables such as BMD [31], chair stand test [23], and handgrip strength [30]. Instead, our meta-analysis showed a very significant association between handgrip strength and T-score (p < 0.001), as well as their mutual influence. This result suggests that poor bone quality, as evidenced by negative T-score values, as well as reduced muscle strength and function, as evidenced by poor handgrip strength test results, may concomitantly lead to osteosarcopenic syndrome. This correlation could therefore represent a potential new parameter that the clinician could use to make a diagnosis of osteosarcopenia, quickly and inexpensively.
4.2. Limitations of This Review
Since osteosarcopenia is a newly defined syndrome, few studies are currently available in the literature. This aspect therefore represents the main limitation of this meta-analysis, in addition to other limitations. Firstly, the analysed studies do not all belong to the same type. Furthermore, there are both prospective and retrospective studies but also longitudinal, cross-sectional, and observational studies and no randomised studies. The population is heterogeneous, comprising healthy volunteers, non-hospitalised or institutionalised (community-dwelling individuals); fracture patients; patients with a history of falls; and hospitalised patients. Additionally, their ethnicity, country or region of origin, risk factors, and treatment were not considered. The purpose of the classification through the global ES responds to the need to use an elected sample according to the considered criteria in order to conduct an association analyses between the variables under study. However, a much larger sample size will be required to confirm the type and level of association measured through the statistics used in this review. In the data collection, different criteria were used in defining sarcopenia, although looking at the cut-offs of the variables under consideration, we considered it legitimate to accept the various groups of sarcopenic patients in each study as such. Moreover, further primary studies are needed to increase the sample size by filling the gaps in the availability of data for specific variables to assess the intensity of this interesting relationship.
4.3. Implications for Clinical Practice
As mentioned above, osteosarcopenia is a recently defined condition for which no protocol has yet been established to allow for a rapid diagnosis. This pathology affects both bone and muscle tissue, which together make up the bone–muscle unit (Figure 4). An impairment in the quality of muscle tissue inevitably leads to degeneration of bone tissue, and vice versa. The results of this study further highlight how bone–muscle crosstalk is implicated in the pathogenesis of osteosarcopenia, suggesting a new diagnostic strategy in which bone and muscle tissue assessment parameters converge. Thus, this study provides a new potential tool that could speed up the elaboration of a diagnosis of osteosarcopenia, immediately highlighting which aspects need to be addressed with therapeutic treatment [34].
Figure 4.
Bone–muscle unit. Characteristics of sarcopenia and osteoporosis diseases, which contribute to the onset of osteosarcopenia (created with BioRender.com).
4.4. Implications for Further Research
It is suggested that future research should be strengthened with the help of these two variables in the context of risk factors associated with osteosarcopenia. For this purpose, multivariate regression models, including logistic models, will be required. Through such models, regression coefficients associated with the variables and their modes will be available: the value and the sign will provide information about the strength and direction of their influence on the risk factors. The final hope is to acquire the capacity to elaborate a predictive, single model, increasingly used in the medical and health field, in order to respond specifically to the needs of the individual, implementing all the tools that can make this possible.
5. Conclusions
Our pilot study identified a new potential predictive model, on the basis of the correlation of the two variables T-score and handgrip strength, for a faster and more targeted diagnosis of osteosarcopenia, increasing the spectrum of clinical investigation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, U.T. and C.C.; methodology, M.A.; data curation, C.G., V.V.V., I.C., M.T., M.F., and R.I.; writing—original draft preparation, C.G., V.V.V., I.C., and M.A.; writing—review and editing, U.T., C.C., and E.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by BRIC-INAIL #23.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Binkley N., Buehring B. Beyond FRAX®: It’s Time to Consider “Sarco-Osteopenia”. J. Clin. Densitom. 2009;12:413–416. doi: 10.1016/j.jocd.2009.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Martin F.C., Ranhoff A.H. Frailty and Sarcopenia. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. pp. 53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Edwards M.H., Dennison E.M., Aihie Sayer A., Fielding R., Cooper C. Osteoporosis and sarcopenia in older age. Bone. 2015;80:126–130. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.04.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fuggle N., Shaw S., Dennison E., Cooper C. Sarcopenia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017;31:218–242. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2017.11.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kirk B., Zanker J., Duque G. Osteosarcopenia: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment—Facts and numbers. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11:609–618. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Paintin J., Cooper C., Dennison E. Proceedings of the British Journal of Hospital Medicine. Volume 79. MA Healthcare Ltd; London, UK: 2018. Osteosarcopenia; pp. 253–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tarantino U., Piccirilli E., Fantini M., Baldi J., Gasbarra E., Bei R. Sarcopenia and fragility fractures: Molecular and clinical evidence of the bone-muscle interaction. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2015;97:429–437. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.N.00648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tarantino U., Baldi J., Celi M., Rao C., Liuni F.M., Iundusi R., Gasbarra E. Osteoporosis and sarcopenia: The connections. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2013;25:93–95. doi: 10.1007/s40520-013-0097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Girgis C.M., Mokbel N., DiGirolamo D.J. Therapies for musculoskeletal disease: Can we treat two birds with one stone? Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2014;12:142–153. doi: 10.1007/s11914-014-0204-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Avin K.G., Moorthi R.N. Bone is Not Alone: The Effects of Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2015;13:173–179. doi: 10.1007/s11914-015-0261-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Scimeca M., Piccirilli E., Mastrangeli F., Rao C., Feola M., Orlandi A., Gasbarra E., Bonanno E., Tarantino U. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and myostatin pathways: Key mediator of human sarcopenia. J. Transl. Med. 2017;15:34. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1143-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fahimfar N., Zahedi Tajrishi F., Gharibzadeh S., Shafiee G., Tanha K., Heshmat R., Nabipour I., Raeisi A., Jalili A., Larijani B., et al. Prevalence of Osteosarcopenia and Its Association with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Iranian Older People: Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) Program. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020;106:364–370. doi: 10.1007/s00223-019-00646-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nielsen B.R., Andersen H.E., Haddock B., Hovind P., Schwarz P., Suetta C. Prevalence of muscle dysfunction concomitant with osteoporosis in a home-dwelling Danish population aged 65–93 years—The Copenhagen Sarcopenia Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2020;138:110974. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2020.110974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cruz-Jentoft A.J., Bahat G., Bauer J., Boirie Y., Bruyère O., Cederholm T., Cooper C., Landi F., Rolland Y., Sayer A.A., et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48:16–31. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afy169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen L.K., Liu L.K., Woo J., Assantachai P., Auyeung T.W., Bahyah K.S., Chou M.Y., Chen L.Y., Hsu P.S., Krairit O., et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus report of the Asian working group for sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014;15:95–101. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.11.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nielsen B.R., Abdulla J., Andersen H.E., Schwarz P., Suetta C. Sarcopenia and osteoporosis in older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018;9:419–434. doi: 10.1007/s41999-018-0079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liberati A., Altman D.G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P.C., Ioannidis J.P.A., Clarke M., Devereaux P.J., Kleijnen J., Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu B., Sui Y., Zhu C., Yang X., Zhou J., Li L., Ren L., Wang X. Music intervention on cognitive dysfunction in healthy older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2017;38:983–992. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-2878-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huo Y.R., Suriyaarachchi P., Gomez F., Curcio C.L., Boersma D., Muir S.W., Montero-Odasso M., Gunawardene P., Demontiero O., Duque G. Phenotype of Osteosarcopenia in Older Individuals With a History of Falling. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015;16:290–295. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2014.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ho A.W.H., Lee M.M.L., Chan E.W.C., Ng H.M.Y., Lee C.W., Ng W.S., Wong S.H. Prevalence of pre-sarcopenia and sarcopenia in Hong Kong chinese geriatric patients with hip fracture and its correlation with different factors. Hong Kong Med. J. 2016;22:23–29. doi: 10.12809/hkmj154570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yoo J.-I., Ha Y.-C., Kwon H.-B., Lee Y.-K., Koo K.-H., Yoo M.-J. High Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Korean Patients after Hip Fracture: A Case-Control Study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 1479;31:1479–1484. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.9.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pasco J.A., Mohebbi M., Holloway K.L., Brennan-Olsen S.L., Hyde N.K., Kotowicz M.A. Musculoskeletal decline and mortality: Prospective data from the Geelong Osteoporosis Study. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8:482–489. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Drey M., Sieber C.C., Bertsch T., Bauer J.M., Schmidmaier R. The FiAT intervention group Osteosarcopenia is more than sarcopenia and osteopenia alone. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2016;28:895–899. doi: 10.1007/s40520-015-0494-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yoo J.I., Kim H., Ha Y.C., Kwon H.B., Koo K.H. Osteosarcopenia in patients with hip fracture is related with high mortality. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018;33:e27. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Di Monaco M., Castiglioni C., Milano E., Massazza G. Is there a definition of low lean mass that captures the associated low bone mineral density? A cross-sectional study of 80 men with hip fracture. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018;30:1429–1435. doi: 10.1007/s40520-018-1058-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Scott D., Seibel M., Cumming R., Naganathan V., Blyth F., Le Couteur D.G., Handelsman D.J., Waite L.M., Hirani V. Does combined osteopenia/osteoporosis and sarcopenia confer greater risk of falls and fracture than either condition alone in older men? The concord health and ageing in men project. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019;74:827–834. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gly162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Reiss J., Iglseder B., Alzner R., Mayr-Pirker B., Pirich C., Kässmann H., Kreutzer M., Dovjak P., Reiter R. Sarcopenia and osteoporosis are interrelated in geriatric inpatients. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019;52:688–693. doi: 10.1007/s00391-019-01553-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gomez F., Curcio C.L., Brennan-Olsen S.L., Boersma D., Phu S., Vogrin S., Suriyaarachchi P., Duque G. Effects of the falls and fractures clinic as an integrated multidisciplinary model of care in Australia: A pre-post study. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e027013. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sepúlveda-Loyola W., Phu S., Hassan E.B., Brennan-Olsen S.L., Zanker J., Vogrin S., Conzade R., Kirk B., Al Saedi A., Probst V., et al. The Joint Occurrence of Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia (Osteosarcopenia): Definitions and Characteristics. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020;21:220–225. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hamad B., Basaran S., Benlidayi I.C. Osteosarcopenia among postmenopausal women and handgrip strength as a practical method for predicting the risk. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020;32:1923–1930. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01399-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kirk B., Phu S., Brennan-Olsen S.L., Hassan E.B., Duque G. Associations between osteoporosis, the severity of sarcopenia and fragility fractures in community-dwelling older adults. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2020;11:443–450. doi: 10.1007/s41999-020-00301-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kobayashi K., Imagama S., Ando K., Machino M., Ota K., Tanaka S., Morozumi M., Kanbara S., Ito S., Ishiguro N., et al. Epidemiology and effect on physical function of osteosarcopenia in community-dwelling elderly people in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020;30:592–597. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2019.1623455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Di Monaco M., Castiglioni C., Bardesono F., Milano E., Massazza G. Sarcopenia, osteoporosis and the burden of prevalent vertebral fractures: A cross-sectional study of 350 women with hip fracture. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020;56:184–190. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.20.05991-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Iolascon G., Moretti A., Toro G., Gimigliano F., Liguori S., Paoletta M. Pharmacological therapy of osteoporosis: What’s new? Clin. Interv. Aging. 2020;15:485–491. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S242038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.