Abstract
Intracellular free zinc ([Zn2+]i) is mobilized in neuronal and non-neuronal cells under physiological and/or pathophysiological conditions; therefore, [Zn2+]i is a component of cellular signal transduction in biological systems. Although several transporters and ion channels that carry Zn2+ have been identified, proteins that are involved in Zn2+ supply into cells and their expression are poorly understood, particularly under inflammatory conditions. Here, we show that the expression of Zn2+ transporters ZIP8 and ZIP14 is increased via the activation of hypoxia-induced factor 1α (HIF-1α) in inflammation, leading to [Zn2+]i accumulation, which intrinsically activates transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) channel and elevates basal [Zn2+]i. In human fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs), treatment with inflammatory mediators, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1α (IL-1α), evoked TRPA1-dependent intrinsic Ca2+ oscillations. Assays with fluorescent Zn2+ indicators revealed that the basal [Zn2+]i concentration was significantly higher in TRPA1-expressing HEK cells and inflammatory FLSs. Moreover, TRPA1 activation induced an elevation of [Zn2+]i level in the presence of 1 μM Zn2+ in inflammatory FLSs. Among the 17 out of 24 known Zn2+ transporters, FLSs that were treated with TNF-α and IL-1α exhibited a higher expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14. Their expression levels were augmented by transfection with an active component of nuclear factor-κB P65 and HIF-1α expression vectors, and they could be abolished by pretreatment with the HIF-1α inhibitor echinomycin (Echi). The functional expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 in HEK cells significantly increased the basal [Zn2+]i level. Taken together, Zn2+ carrier proteins, TRPA1, ZIP8, and ZIP14, induced under HIF-1α mediated inflammation can synergistically change [Zn2+]i in inflammatory FLSs.
Keywords: TRPA1, ZIP8, ZIP14, intracellular Zn2+ concentration, synoviocytes, inflammation, hypoxia-induced factor 1α (HIF-1α)
1. Introduction
Zinc is an essential dietary metal that mainly functions as a cofactor for carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. In particular, zinc plays an obligatory role in immune function, the regulation of C-C chemokine production [1], and activation of mast cells via FcεRIs [2,3]. Other roles of this metal, in the form of the so-called free zinc (Zn2+), as a component of cellular signal transduction, lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction in monocytes [4], and cytoprotection of lung epithelia in inflammation [5], have been suggested. In addition, the importance of Zn2+ in neuronal cells and its involvement in neuronal death is well-documented [6,7]. Therefore, zinc homeostasis is a major focus of research in biology, and zinc transporters, such as ZnT (ZnT1- ZnT10) and ZIP (ZIP1-ZIP14), respectively, functioning as Zn2+ exporters and importers, have been identified as regulators of this metal ion in a physiological milieu. However, the molecular mechanisms that underlie the regulation of ZnT and ZIP expression remain unclear. Although transcriptional and non-transcriptional regulation of the expression of some zinc transporters have been revealed [5,8,9,10,11,12], the present understanding of this regulatory phenomenon is rather limited. Furthermore, the control of Zn2+ is complex and multiple mechanisms are involved: zinc transporters that are located at intracellular organelles, protein binding, and metallothioneins in a redox sensitive pool of zinc. Therefore, cellular Zn2+ represents a small proportion of the total zinc pool.
TRPA1 is widely expressed in neuronal and non-neuronal cells, and it acts as a biological sensor that is activated by environmental irritants and oxidative- and thiol-reactive compounds [13,14,15,16,17]. Because transgenic mice lacking TRPA1 exhibit suppressed sensitivity to mechanical stimulation, cold stimuli, and TNF-α-induced mechanical hyperalgesia [18,19,20,21,22], TRPA1 has been identified as a nociceptor mediating acute and inflammatory pain [21,22,23,24,25]. On the other hand, a previous study from our group revealed the transcriptional induction of TRPA1 by inflammation via HIF-1α as a mechanism controlling inflammatory cytokine release [26]. A unique property of TRPA1 is that the channel can be activated by a nanomolar concentration range of [Zn2+]i and imports extracellular Zn2+ ([Zn2+]o), which indicates that TRPA1 is a potential Zn2+ transporter regulating zinc homeostasis [27,28]. Indeed, endogenous [Zn2+]i intrinsically activates TRPA1 in inflammatory FLSs [26]. However, whether the [Zn2+]i level in inflammatory cells is high enough to activate TRPA1 remains debatable, even though [Zn2+]i is known to be highly potent against TRPA1 [27,29].
In this study, we show that the expression of Zn2+ transporters ZIP8 and ZIP14 is increased via nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling and the downstream activation of the transcription factor HIF-1α in FLSs pretreated with TNF-α and IL-1α. The resultant intracellular Zn2+ accumulation could activate TRPA1, leading to increased basal [Zn2+]i and evoking Ca2+ oscillations. Assays with fluorescent Zn2+ indicators revealed that the basal [Zn2+]i concentration was significantly higher in TRPA1-expressing HEK cells and inflammatory FLSs. Therefore, inflammatory conditions induce the expression of Zn2+ carrier proteins TRPA1, ZIP8, and ZIP14, which, in turn, synergistically change [Zn2+]i in inflammatory FLSs.
2. Results
2.1. Zn2+-Dependent TRPA1 Activation and [Zn2+]i Components in TRPA1-Expressing Cells
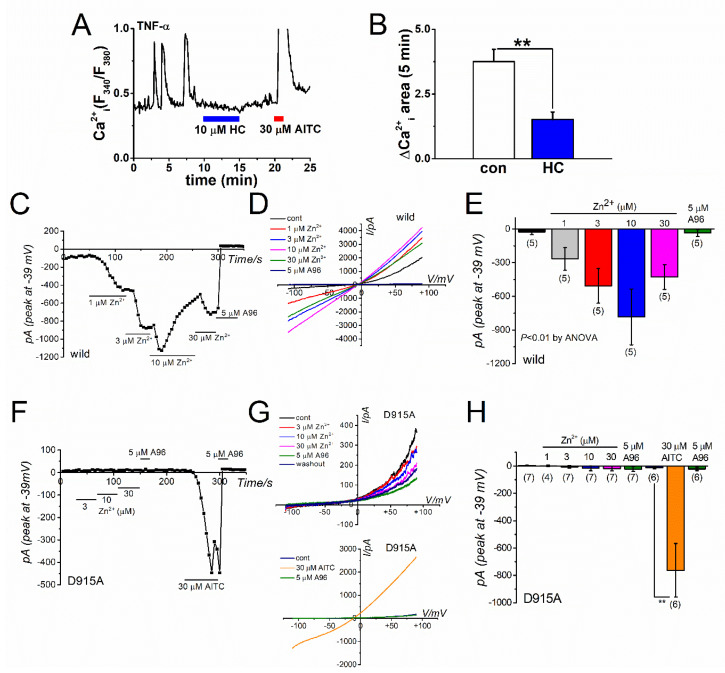
In a previous study, we have shown that TNF-α and IL-1α induce TRPA1 gene expression via NF-κB signaling and the downstream activation of HIF-1α in FLSs. Indeed, 50% FLSs that were treated with 10 U TNF-α for 24 h exhibited intrinsic Ca2+ oscillations, which were inhibited by the TRPA1 antagonist HC-030031 (HC) (Figure 1A shows a representative cell response and Figure 1B plots the overall change; see also [26]). These TRPA1-dependent Ca2+ oscillations were effectively inhibited by a membrane-permeable Zn2+ chelator N,N,N’,N-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine (TPEN, [26]), indicating that [Zn2+]i acts as an endogenous TRPA1 agonist and activates the induced TRPA1. Consistent with these observations, a cumulative application of Zn2+ in the concentration range of 1 to 30 μM activated inward currents in TRPA1 expressing HEK (HEK-TRPA1, wild) cells, which were abolished by the selective TRPA1 antagonist A-967079 (A96, Figure 1C–E). In contrast, Zn2+ did not induce any inward currents in HEK cells that were transfected with a mutant TRPA1 (D915A, Figure 1F–H), in which the channel-pore is rigid against Zn2+, which suggests that active TRPA1 can supply Zn2+ into cells [27,29]. Not being directly evident, these results may suggest that intracellular Zn2+ can activate TRPA1-dependent Ca2+ and Na+ influx through TRPA1.
Figure 1.
Zn2+-dependent TRPA1 activation. (A) Intrinsic Ca2+ oscillations sensitive to the TRPA1 antagonist HC observed on treating inflammatory FLSs with 10 U TNF-α for 24 h. Presence of the TRPA1 agonist AITC (30 μM) evoked a larger Ca2+ response, which was scaled out. (B) Inhibitory effects of 10 μM HC on Ca2+ oscillations in inflammatory FLSs. Mean data of ΔCa2+i response area in a 5-min window with and without HC are pooled (n = 13; three independent experiments; ** p < 0.01). Comparison of Zn2+-induced TRPA1 channel currents in (C–E) wild TRPA1 (wild; five independent experiments; ** p < 0.01 by ANOVA) and (F–H) a mutant TRPA1 (D915A; 4–7 independent experiments; ** p < 0.01 by Tukey-Kramer test) in the channel pore. The mutant TRPA1 was generated by replacing an aspartic acid residue at position 915 of the wild TRPA1 with an alanine residue. Cells expressing the mutant channel were superfused with SBS and dialyzed with Cs-aspartate rich pipette solution including 0.3 μM Ca2+. Ramp waveform voltage pulses from −110 to +90 mV were applied for 100 ms every 5 s at a holding potential of −10 mV. Each cell was exposed to Zn2+ to confirm its effects on membrane currents at −39 mV, whereas the contamination by Cl- currents was negligible. After treatment with the final concentration of Zn2+, 5 μM A-967079 (A96) was applied to assess the TRPA1 channel components giving rise to conductance. To confirm functional expression of the mutant TRPA1, AITC (30 μM) and A96 (5 μM) were used. A representative time-course change and current-voltage relationship of Zn2+- or AITC-induced TRPA1 currents in a HEK cell with (C,D) wild and (F,G) D915A channels. The peak values of inward current induced by (E) Zn2+- or (F) AITC at −39 mV were averaged and plotted.
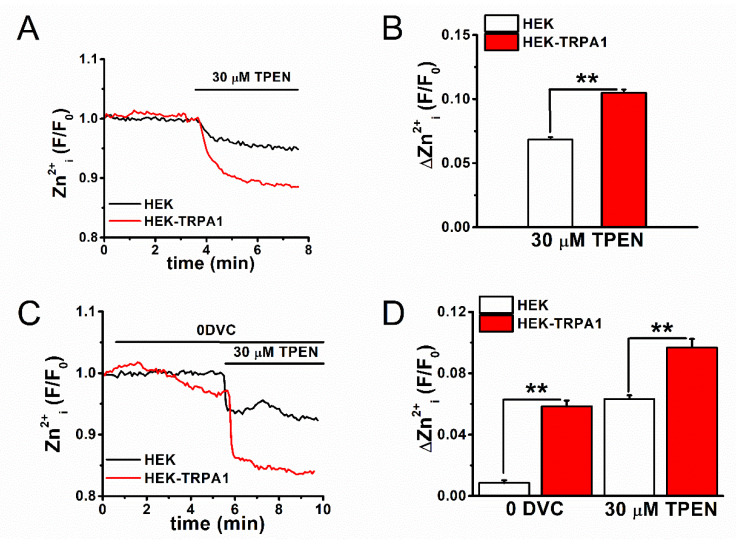
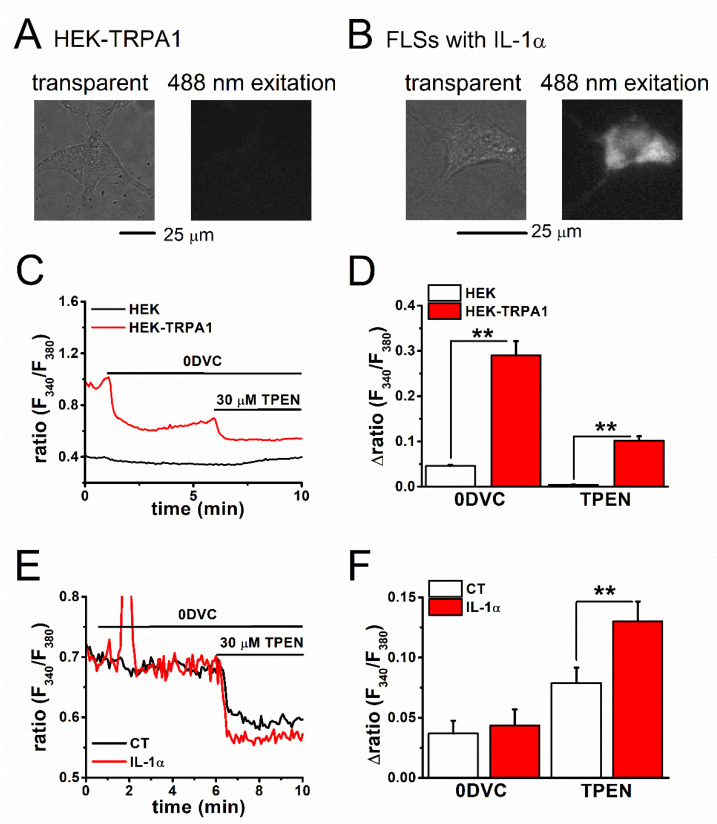
We assayed [Zn2+]i with the fluorescent Zn2+ indicators FluoZin-3 and Fura-2, the zinc chelator TPEN, and the Zn2+ ionophore zinc-pyrithione (Pyr) to further examine the contribution of TRPA1 as a Zn2+ carrier in maintaining [Zn2+]i level and identify other regulators of [Zn2+]i in inflammatory FLSs. First, TPEN-sensitive [Zn2+]i components were assayed using FluoZin-3 (Kd-Zn2+: ~15 nM), which functions as a selective Zn2+ indicator, in cells with and without TRPA1 expression. When the TPEN-sensitive [Zn2+]i components were compared between the control HEK (HEK) and HEK-TRPA1 cells in standard bathing solution (SBS), the [Zn2+]i components were significantly higher in HEK-TRPA1 cells (Figure 2A,B). The control HEK and HEK-TRPA1 cells were treated with 30 μM TPEN after the removal of extracellular divalent cations without EGTA (zero divalent cation; 0DVC), as shown in Figure 2C,D. This induced substantially larger reductions in the [Zn2+]i components in HEK-TRPA1 cells (Figure 2D), suggesting that active rapid Zn2+ influx through TRPA1 (0DVC-dependent) and subsequent basal [Zn2+]i accumulation (TPEN-dependent) were prominent in HEK-TRPA1 cells. In contrast, a quantitative assay of [Zn2+]i components in FLSs with FluoZin-3 offered limited insights, due to the large auto-fluorescence signals of these cells (Figure 3A,B). In particular, this higher background fluorescence in FLSs interacts with the FluoZin-3 signal, affecting the accurate evaluation of [Zn2+]i. When alternatively assayed with Fura-2 (Kd-Zn2+: ~2 nM), which acts as a Ca2+ and Zn2+ indicator, 0DVC-sensitive components were again found to be higher in HEK-TRPA1 cells when compared to that in the control HEK cells, while no appreciable difference was observed between FLSs with and without IL-1α (Figure 3C–F). However, the TPEN-sensitive [Zn2+]i components in 0DVC were significantly larger in both HEK-TRPA1 cells (Figure 3C,D) and FLSs with IL-1α (Figure 3E,F). Therefore, although Ca2+-dependent Fura-2 signals could mask Zn2+-dependent Fura-2 signals under perfusion with SBS, TPEN in the presence of 0DVC is a useful marker for evaluating Zn2+-dependent Fura-2 signals.
Figure 2.
[Zn2+]i components in HEK-TRPA1 cells. (A) Comparative analysis of TPEN-sensitive basal [Zn2+]i components in control HEK and HEK-TRPA1 cells. [Zn2+]i levels in SBS was monitored using FluoZin-3 in the presence of 30 μM TPEN. (B) Peak changes in [Zn2+]i in the presence of TPEN (mean±SEM; n = 184 and n = 293, four and six independent experiments for control HEK and HEK-TRPA1 cells, respectively; ** p < 0.01). (C) Comparison of extracellular divalent cations and TPEN-sensitive basal [Zn2+]i components assayed with FluoZin-3 in control HEK and HEK-TRPA1 cells. The extracellular divalent cations were removed without EGTA (0DVC), followed by exposure to 30 μM TPEN. (D) Peak changes in [Zn2+]i in the presence of 0DVC and TPEN (mean ± SEM; n = 76 and n = 78 for HEK and HEK-TRPA1 cells, respectively; two independent experiments each, ** p < 0.01).
Figure 3.
The assay of [Zn2+]i in TRPA1-expressing cells using a Fura-2 based assay. Auto-fluorescence images of (A) HEK-TRPA1 cells and (B) FLSs with IL-1α in the absence of fluorescence indicators. Fluorescence images acquired in cells excited with light of 488 nm wavelength (right panels) and light-transmitting images (left panels) are shown. Comparison of TPEN-sensitive [Zn2+]i components that were assayed with Fura-2 between (C,D) HEK cells with and without expression of TRPA1 or (E,F) FLSs with and without IL-1α. Cells were treated with 30 μM TPEN in the presence of 0DVC without EGTA. The fluorescence signal measured as a ratio (F340/F380) and the corresponding peak change in the presence of (D) 0DVC and (F) TPEN are plotted (mean ± SEM; n = 101 and n = 111 for HEK and HEK-TRPA1, respectively, and four independent experiments each; n = 33 and n = 31 for CT and 100 U IL-1α, respectively, and four independent experiments each; ** p < 0.01).
2.2. Estimation of Basal [Zn2+]i Concentration in TRPA1-Expressing Cells
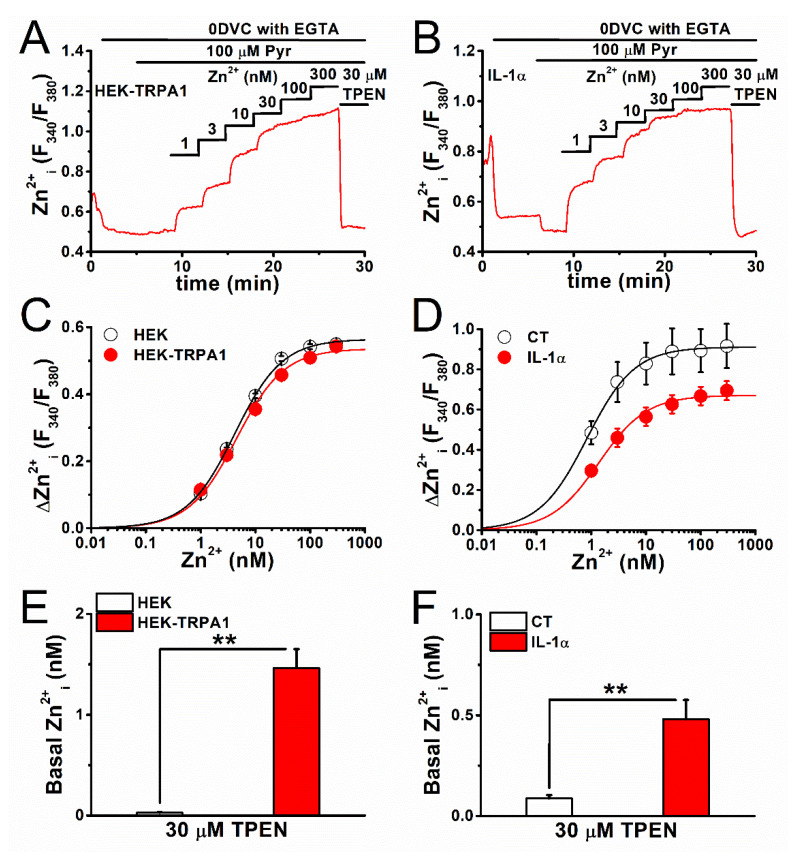
We constructed a dissociation curve of fluorescent signals from Fura-2 (reflecting cellular Zn2+ content) against [Zn2+]i concentration to determine the [Zn2+]i concentration in TRPA1-expressing cells (Figure 4A–H). In 0DVC buffered with EGTA (1 mM), cumulative treatment with Zn2+ at concentrations ranging from 1 to 300 nM was performed on HEK-TRPA1 cells (Figure 4A) and FLSs with IL-1α (Figure 4B), after the permeabilization of these cells with the Zn2+ ionophore Pyr (100 μM). We added 30 μM TPEN at the end of each experiment to verify the changes in Zn2+-dependent Fura-2 signals. The data set obtained this way was fitted to a dissociation curve of Fura-2 vs. Zn2+ concentration (see the Experimental Procedure) and Kd was calculated to be 4.2. 4.5, 0.9, and 1.5 nM for HEK cells, HEK-TRPA1 cells, FLSs without IL-1α (CT), and FLSs with IL-1α, respectively (Figure 4C,D). It is obvious that TRPA1-expressing cells had higher basal [Zn2+]i concentration (see Methods in detail, 1.46 ± 0.19 nM in HEK-TRPA1 cells vs. 0.03 ± 0.01 nM in HEK cells, p < 0.01, Figure 4E; 0.48 ± 0.10 nM in FLSs with IL-1α vs. 0.09 ± 0.01 nM in CT, p < 0.01, Figure 4F), which suggested that TRPA1 is one of the factors to change the basal [Zn2+]i level in TRPA1-expressing cells.
Figure 4.
The identification of basal [Zn2+]i concentration in TRPA1-expressing cells. Relationship between [Zn2+]i-dependent fluorescence ratio (Zn2+i (F340/F380)) and [Zn2+]i concentration was assayed with Fura-2 in (A,C) HEK cells and (B,D) FLSs. In the presence of 0DVC, Zn2+ buffered with 1 mM EGTA was cumulatively applied to (A) HEK-TRPA1 cells and (B) FLSs with 100 U IL-1α for 24 h, after permeabilization with the Zn2+ ionophore Pyr (100 μM). (C,D) [Zn2+]i-dependent change in fluorescence ratio (ΔZn2+i (F340/F380)) is plotted (n = 94 and n = 89 for HEK and HEK-TRPA1 cells, respectively, and two independent experiments for each; n = 22 and n = 30 for CT and 100 U IL-1α, respectively, and three independent experiments for each). The generated dataset was fitted to a dissociation curve of Fura-2 vs. Zn2+ concentration (see Experimental procedures). (E,F) Data in Figure 3 and the dissociation curves (C,D) were utilized to estimate the basal [Zn2+]i concentration in each condition. The pooled data are averaged and represented as bar charts (mean ± SEM; n = 101 and n = 111 for HEK and HEK-TRPA1 cells, respectively, and four independent experiments each; n = 33 and n = 31 for CT and 100 U IL-1α, respectively, and four independent experiments each; ** p < 0.01).
2.3. Mechanism of Elevation of Basal [Zn2+]i Concentration in Inflammatory FLSs
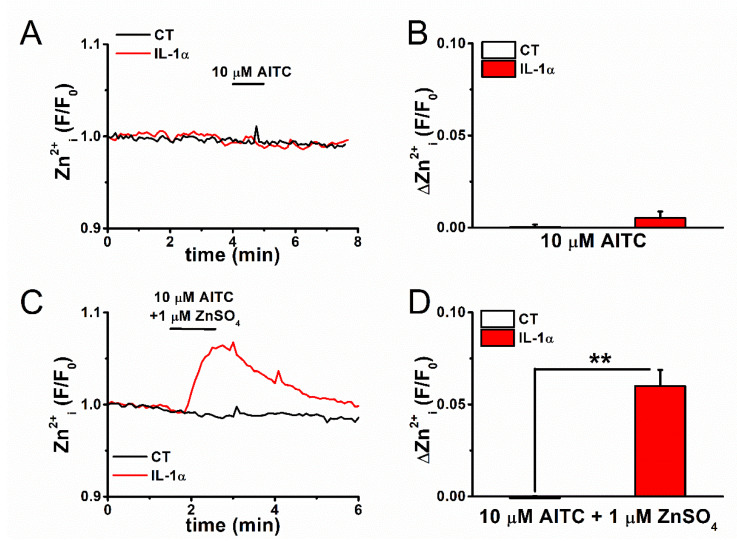
Although the large auto-fluorescence of FLSs complicates the use of FluoZin-3, we nevertheless attempted to detect Zn2+-dependent FluoZin-3 signals in FLSs. Exposure to 10 μM AITC did not induce any change in [Zn2+]i within this short time scale in FLSs stained with FluoZin-3, even though TRPA1 was induced by pretreatment with IL-1α, as shown in Figure 5A,B. In contrast, extracellular free Zn2+ ([Zn2+]e) itself could permeate the TRPA1 pore (see Figure 1C–H), which suggested that [Zn2+]i change is not detectable in FLSs within a short amount of time, even when the corresponding TRPA1 channels are activated by AITC, presumably due to the low expression of TRPA1. In fact, in the presence of 1 μM Zn2+ in SBS, a small but substantial Zn2+ response was elicited by the treatment of inflammatory FLSs with 10 μM AITC (Figure 5C,D). Therefore, TRPA1 in inflammatory FLSs functions as a Zn2+ carrier into cells (Figure 4), while additional Zn2+ carriers and other factors play obligatory roles in the regulation of cellular Zn2+. It is to be noted here that the [Zn2+]e concentration in SBS used under the present experimental conditions was less than 153 nM (Supplementary Figure S1).
Figure 5.
A change in [Zn2+]i by activation of TRPA1 in FLSs. FLSs pretreated with and without 100 U IL-1α for 24 h were exposed to AITC at 10 μM, followed by monitoring of (A) [Zn2+]i assayed by FluoZin-3 and (B) change in [Zn2+]i (mean ± SEM; n = 16 and n = 28 for CT and IL-1α, respectively, and three independent experiments each). (C,D) These experiments were repeated in FLSs the presence of 1 μM ZnSO4 in the SBS to increase the driving force of Zn2+ (mean ± SEM; n = 38 and n = 26 for CT and 100 U IL-1α, respectively, and two independent experiments each; ** p < 0.01).
2.4. Expression and Inflammation-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation of Zn2+ Transporters in FLSs
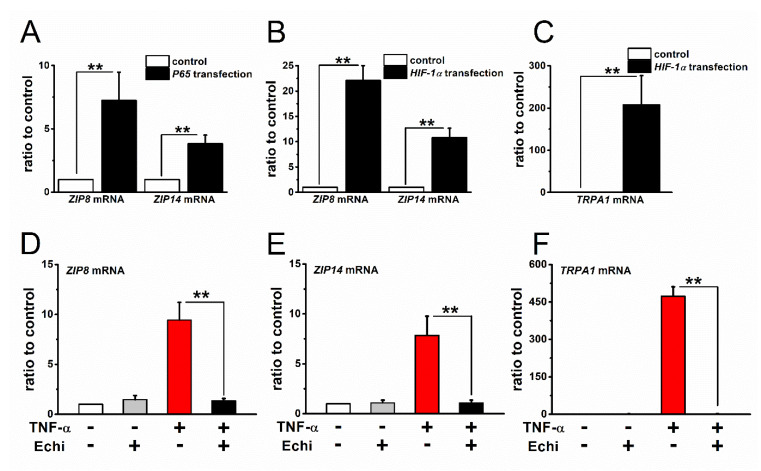
Among multiple cellular Zn2+ regulators, here we focused on plasma membrane-associated Zn2+ carriers that are involved in the observed basal [Zn2+]i elevation in inflammatory FLSs. Among the 17 out of 24 known Zn2+ transporters, which are expressed in plasma membrane, exposure of FLSs to 100 U IL-1α and 10 U TNF-α for 24 h eventually increased the expression of only ZIP8 and ZIP14 mRNA transcripts (Supplementary Figure S2A–D). Because IL-1α and TNF-α can both activate NF-κB signaling cascades that are known to predominantly regulate transcriptional gene expression, we tested the involvement of NF-κB in the upregulation of these genes. To this end, we directly transfected FLSs with a P65 plasmid vector that encodes RelA, an active component of NF-κB (Figure 6A). The transfected FLSs showed a clear increase in the expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 mRNA. In addition, the inflammatory stimulation of FLSs is known to activate the transcriptional factor HIF-1α via NF-κB signaling in a transcriptional and/or post-transcriptional manner [26]. Therefore, we further examined the involvement of HIF-1α in the induction of ZIP8 and ZIP14 mRNA in FLSs. Transfection of FLSs with an HIF-1α plasmid vector effectively increased the expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 mRNA, as well as TRPA1 mRNA (Figure 6C), even without stimulation with TNF-α and IL-1α, as shown in Figure 6B. Moreover, when the FLSs were pretreated with the HIF inhibitor Echi (1 μM), the induction of ZIP8 and ZIP14 as well as TRPA1 by TNF-α was abolished (Figure 6D–F), which suggested that NF-κB signaling and downstream activation of HIF-1α are critical for the inflammatory induction of ZIP8 and ZIP14. Taken together, these results, which are in overall agreement with our previous study on TRPA1 [26], indicate that HIF-1α is a novel transcriptional factor for ZIP8 and ZIP14. It is noteworthy that other Zn2+ regulators, such as organellar Zn2+ transporters and binding proteins, may be involved in inflammation-induced basal [Zn2+]i elevation in FLSs.
Figure 6.
Expression of Zn2+ transporters in FLSs and involvement of transcriptional factors NF-κB and HIF-1α in inflammatory induction. (A) Expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 mRNA in FLSs transfected with and without a P65 expression vector (mean ± SEM; four independent experiments; ** p < 0.01). (B) The expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 mRNA in FLSs transfected with and without an HIF-1α expression vector (mean ± SEM; three independent experiments; ** p < 0.01). (C) As a control, the mRNA expression of TRPA1 was also compared in FLSs with and without HIF-1α expression vector (mean ± SEM; three independent experiments; ** p < 0.01). Effects of Echi (1 μM) on the induction of (D) ZIP8, (E) ZIP14, and (F) TRPA1 mRNA in FLSs stimulated with TNF-α. FLSs were treated with and without 10 U TNF-α for 24 h and the mRNA transcripts of ZIP8, ZIP14, and TRPA1 were compared. Echi treatment was performed for 24 h with and without TNF-α (mean ± SEM; four independent experiments; ** p < 0.01).
2.5. Basal [Zn2+]i Components in ZIP8- and ZIP14-Expressing Cells
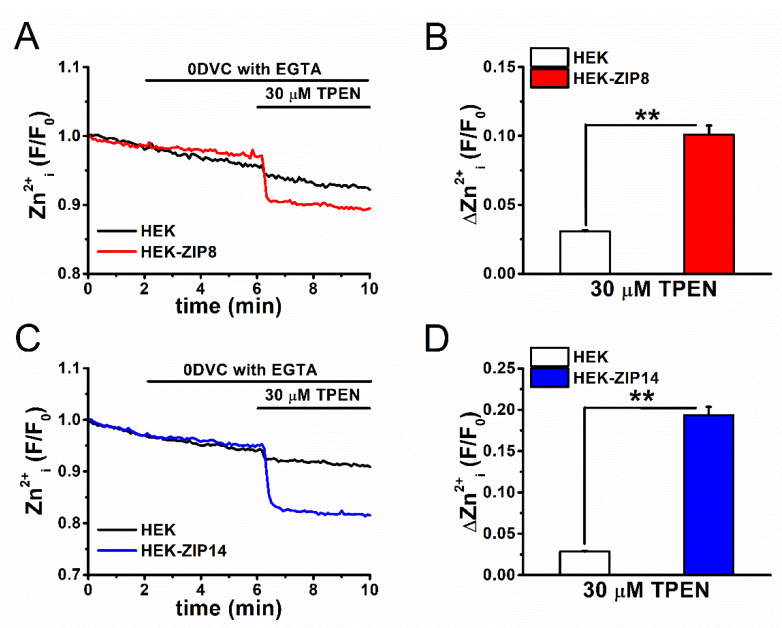
Finally, we confirmed that the heterologous expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 in HEK cells elevates basal [Zn2+]i. Control, ZIP8-, and ZIP14-expressing HEK cells were treated with 30 μM TPEN after the removal of extracellular Ca2+ and Zn2+ with EGTA (0DVC with EGTA), and the [Zn2+]i levels were monitored using FluoZin-3, as shown in Figure 7. TPEN, but not 0DVC, was found to induce relatively larger reduction in basal [Zn2+]i components in HEK-ZIP8 (Figure 7A,C) and HEK-ZIP14 cells (Figure 7B,D) as compared to the control. This demonstrates that active rapid Zn2+ influx through ZIP8 and ZIP14 was minimal within this recording range due to the negligible reduction by 0DVC. However, [Zn2+]i accumulation, followed by the overexpression of ZIP8 and ZIP14, was substantial in ZIP8- and ZIP14-expressing cells due to the significant reduction mediated by TPEN.
Figure 7.
The basal Zn2+ components in ZIP8- and ZIP14-expressing cells. TPEN-sensitive basal Zn2+ components assayed with FluoZin-3 were compared between HEK cells with and without expression of (A,B) ZIP8 and (C,D) ZIP14. Extracellular Ca2+ and Zn2+ was removed by 0DVC with EGTA and cells were treated with 30 μM TPEN. (B) Fluorescence signal was measured as Zn2+i (F/F0) and (D) the peak change by TPEN was plotted (mean ± SEM; B: n = 153 and n = 153 for HEK and HEK-ZIP8 cells, respectively, and three independent experiments each; ** p < 0.01; D: n = 153 and n = 153 for HEK and HEK-ZIP14 cells, respectively, and three independent experiments each; ** p < 0.01).
3. Discussion
In this study, we provide evidence that the transcription factor HIF-1α critically regulates the expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 in inflammatory FLSs and propose that transcriptionally upregulated Zn2+ carriers ZIP8, ZIP14, and TRPA1 can change [Zn2+]i levels in inflammation. Primary findings that are based on Fura-2/TPEN/Pyr assays identified a significant increase in the basal [Zn2+]i concentration in TRPA1-expressing HEK cells and inflammatory FLSs. More importantly, it is a novel finding that TNF-α and IL-1αupregulate ZIP8 and ZIP14 expression via NF-κB signaling and downstream HIF-1α. This overexpression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 resulted in the accumulation of basal [Zn2+]i, which may act as an endogenous agonist and activate TRPA1. Taken together, our observations suggest that inflammation upregulates the transcription of ZIP8 and ZIP14, as well as TRPA1, in FLSs; and these Zn2+ carriers could change basal [Zn2+]i in inflammatory cells.
In our previous study, we showed that Zn2+ is an endogenous TRPA1 agonist in inflammatory FLSs [26]. In addition, Zn2+ has been proposed to be an endogenous TRPA1 agonist when [Zn2+]i concentration is higher than the nanomolar levels [27,29]. In fact, the EC50 of [Zn2+]i that is required for the activation of TRPA1 in an inside-out patch configuration was reported to be 7.5 nM [27] and 50 nM [29], although the reason for this inconsistency is not clear. On the other hand, the present data show that inflammation significantly increased the basal [Zn2+]i concentration from 0.09 to 0.48 nM in FLSs. Therefore, [Zn2+]i that is close to the plasma membrane might show local increases in inflammatory FLSs and/or [Zn2+]i may co-activate TRPA1 with other endogenous agonists. Indeed, the intrinsic Ca2+ oscillations in inflammatory FLSs were partially inhibited by treatment with catalase, an H2O2 scavenger [26]. Additionally, the oscillatory elevation of [Ca2+]i in inflammatory FLSs could potentiate Zn2+-dependent activation of TRPA1, since [Ca2+]i [30,31] positively modulates TRPA1 activity.
Active TRPA1 potentially carries Zn2+ into inflammatory FLSs. In our experiments, an AITC-induced increase in [Zn2+]i was detected in FLSs with TRPA1, when 1 μM Zn2+ was added to the SBS (Figure 5D). On the other hand, the removal of external Zn2+ ([Zn2+]o) from the SBS reduced Zn2+ signals in TRPA1-expressing HEK cells (Figure 2D). These observations suggest that high expression levels of TRPA1 induce an inward flux of Zn2+, even when [Zn2+]o in SBS is less than 0.15 μM (Supplementary Figure S1). This mode of active transport would result in a higher basal [Zn2+]i concentration in TRPA1-expressing HEK cells (1.46 nM) when compared to control (0.03 nM). The treatment of mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons with 30 and 300 μM Zn2+ has been shown to induce TRPA1-mediated Zn2+ influx [29]. The total zinc concentration in synovial fluid is reported to be ~1.7 and ~2.6 μM in healthy subjects and patients with rheumatoid arthritis, respectively [32]. However, the concentration of free Zn2+ might be lower than 1 μM, due to the presence of metal-binding proteins in the synovial fluid. Nevertheless, TRPA1 functions as an active carrier of Zn2+ in inflammatory FLSs, since this channel is intrinsically activated in these cells (Figure 1A). The TRPA1-dependent Ca2+ response has been reported to be more sensitive to [Zn2+]o (>0.1 μM) in FLSs [26] when compared to that in mouse DRG (>5–30 μM) [27,29] and vagal pulmonary sensory (VPS) (>1 μM) [33] neurons. These reports collectively suggest that the oscillatory active TRPA1 channels act as carriers of small but sufficient amounts of Zn2+ for the facilitation of channel activity in FLSs, even when the [Zn2+]o concentration is low (~0.15 μM, Supplementary Figure S1). In contrast, 1–10 μM [Zn2+]o was sufficient for the facilitation in mouse DRG and VPS neurons, which was probably due to the low basal activity of TRPA1 in these cells. An alternative, and far more likely, scenario could be that human TRPA1 is more sensitive to [Zn2+]i and/or [Zn2+]o as compared to the murine analog of this channel (Matsubara and Muraki, unpublished data). It is notable that the control of [Zn2+]i is complex and multiple regulators affect the cellular Zn2+ pool. The upregulation of TRPA1 and/or inflammation itself can modify cellular redox, which is sensitive to Zn2+ pool. In fact, the expression of metallothioneins changes the balance between the binding and unbinding of Zn2+. Because these factors have a large capacity for Zn2+ buffering, TRPA1, ZIP8, and ZIP14 may play a minor role as [Zn2+]i determinants, even under inflammation. Further extensive analyses are required for an understanding of the physiological and pathophysiological roles of TRPA1, ZIP8, and ZIP14 as Zn2+ carriers,
In the present study, we estimated the basal [Zn2+]i concentration to be 1.46 and 0.03 nM in HEK cells with and without TRPA1, respectively; and 0.48 and 0.09 nM in FLSs with (inflammatory) and without TRPA1 (no inflammation), respectively, utilizing Fura-2, TPEN, and Pyr. Fura-2 showed the highest affinity for Zn2+ among the tested synthetic Zn2+ indicators (Kd-Zn: 2 nM) in spite of the disadvantages that are associated with sensitivity to a physiological concentration of Ca2+, and, therefore, it useful for the measurement of [Zn2+]i in sub-nanomolar concentrations. Moreover, the ratiometric readouts that were obtained from the Fura-2 assay enabled us to compare [Zn2+]i levels between different cells. The values that we estimated are in agreement with estimates in cells with physiological [Zn2+]i concentration in the picomolar to nanomolar range, using FluoZin-3 and ZnAF-2, both of which are highly selective for Zn2+ [34,35]. Moreover, biosensors with high affinity and selectivity to Zn2+, which were developed by Vinkenborg et al. [28], have yielded basal [Zn2+]i concentration estimates of 0.4 and 0.27 nM in pancreatic beta-cells and HEK cells, respectively. Therefore, the basal [Zn2+]i concentrations that have been reported in the present study are in overall agreement to earlier reports, suggesting that Fura-2/TPEN/Pyr are useful for estimating and comparing basal [Zn2+]i concentration values. However, the limitations of using Fura-2 were clear, since changes in [Ca2+]i were observed to affect the signal. Therefore, the development of synthetic ratiometric indicators with high affinity and selectivity for Zn2+ is crucial for monitoring the dynamic changes in physiological [Zn2+]i concentration.
Notably, the expression of ZIP8 and ZIP14 was found to be transcriptionally regulated by HIF-1α in FLSs under inflammatory conditions. In human lung epithelial cells, the overexpression of ZIP8 that is elicited by TNF-α has been shown to induce increase in [Zn2+]i, although the underlying mechanisms remain elusive [5]. On the other hand, the treatment of mouse hepatocytes with IL-1β caused an upregulation in ZIP14 expression via the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase and downstream activation of activator protein-1 [36]. The upregulation in ZIP8 and ZIP14 expression in inflammatory FLSs on transfection with a P65 expression vector, an active component of NF-κB, suggests the involvement of NF-κB signaling. Moreover, HIF-1α is critical for this regulation, as deduced from the observed upregulation in ZIP8 and ZIP14 on transfection with a HIF-1α expression vector and the attenuation of the former in the presence of the HIF inhibitor Echi. Inflammatory stimuli, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and lipopolysaccharides, which mediate NF-κB signaling, are known to increase HIF-1α levels at the gene and/or protein level [37,38,39]. In FLSs, TNF-α and IL-1α are both known to increase the expression of HIF-1α, but not HIF-2α, at the protein level [26]. Therefore, HIF-1α could act as a transcription factor of ZIP8 and ZIP14, and their overexpression that is induced by TNF-α and IL-1α results in an increase in basal [Zn2+]i in FLSs. In the present study, we did not identify any potential binding sites of HIF-1α on the promoters of ZIP8 and ZIP14. However, the transcription factor ATF4 potentially binds a region from -94 to -89 relative to the transcription start site (TSS) of the ZIP14 promoter for upregulation [10]. Moreover, NF-κB is known to bind four consensus sites (κB1-κB4), which correspond to a 100 bp region proximal to the TSS of the ZIP8 promoter, and the second binding site κB2 is critical for transcriptional activity [8]. NF-κB activated by TNF-α and IL-1α potentially interacts with κB2 and upregulates ZIP8 expression because κB2 is included in the promoter region of human ZIP8 in FLSs. Further investigation is required to elucidate the interaction between NF-κB and HIF-1α that underlies the upregulation of ZIP8 in inflammatory FLSs.
In the previous study, we showed that the activation of TRPA1 by AITC reduced the inflammatory production of IL-6 and IL-8 in FLSs [26]. In addition, the inhibition of basal activity of TRPA1 increased IL-8 production. Therefore, the activation of TRPA1 by Zn2+, which is transported by TRPA1 and ZIPs, may contribute to reducing the inflammatory response in FLSs. Coordinate transport of Zn2+ through TRPA1 and ZIPs is a potential feedback mechanism against inflammatory conditions via the activation of TRPA1 because it is well known that TRPA1 activation causes inflammatory pain. In addition, 0VDC with EGTA effectively reduced the basal Zn2+ in HEK cells with TRPA1 (Figure 2C,D), but not with ZIP8 and ZIP14 (Figure 7). It is possible that Zn2+ via TRPA1 is involved in Zn2+-dependent cellular processes within minutes and/or an hour. Nevertheless, the contribution of ZIP8 and ZIP14 as well as TRPA1 to the processes may be exclusive and redox signaling and Zn2+ buffering play dominant roles in cellular Zn2+ regulation [40].
In conclusion, inflammatory conditions transcriptionally upregulate ZIP8 and ZIP14, as well as TRPA1 expression in FLSs via NF-κB signaling and the downstream activation of HIF-1α. Therefore, these Zn2+ carriers could regulate basal [Zn2+]i levels in inflammatory FLSs.
4. Experimental Procedures
4.1. Reagents
The following drugs were used: allyl isothiocyanate (AITC; Kanto Chemical Co., Tokyo, Japan), ZnSO4 (Zn2+; Wako Pure Chemical Co., Osaka, Japan), HC-030031 (HC; Enzo Life Sciences, Farmingdale, NY, USA), A-967079 (A96; Sigma-Aldrich, Tokyo, Japan), zinc-pyrichione (Pyr; Sigma/Aldrich), echinomycin (Echi; Sigma/Aldrich), TNF-α (Wako Pure Chemical Co.), IL-1α (Wako Pure Chemical Co.), and N,N ‘,N’,N-tetrakis (2-pyridylmethyl) ethylenediamine (TPEN; Wako Pure Chemical Co.). Each drug was dissolved in the vehicle that was recommended by the manufacturer.
4.2. Cell Culture
Human FLSs were purchased from Cell Applications and cultured in Synoviocyte Growth Medium containing 10% growth supplement, 100 U/mL penicillin G (Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd.), as described previously [26]. The cultured cells were maintained at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. After FLSs acquired 70–80% confluence, the cells were reseeded once every 10 days until nine passages were complete. The cells that grew with a doubling time of 6–8 days after this stage were comprised of a homogenous population, in which induction of TRPA1 by cytokine treatment was found to be unaffected. For experiments, the reseeded cells were cultured for 16 days and then exposed to TNF-α and IL-1α. Human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK) cell lines were obtained from the Health Science Research Resources Bank (HSRRB) and maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Essential Medium (D-MEM, Sigma/Aldrich) that was supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS, SAFC Biosciences Inc, Tokyo, Japan), penicillin G (100 U/mL), and streptomycin (100 μg/mL).
4.3. Quantitative PCR
Real-time quantitative PCR was performed using SYBR Green on a Thermal Cycler Dice Real Time System (Takara Bio Inc., Kusatsu, Japan), as described previously [26]. The transcriptional quantification of gene products was carried out by normalization to that of β-ACTIN. Each cDNA sample was tested in duplicate or triplicate. The program that was used for quantitative PCR amplification included a 30 s activation of Ex Taq™ DNA polymerase at 95 °C, a 15 s denaturation step at 95 °C, a 60 s annealing and extension step at 60 °C (for 45 cycles), and a dissociation step (15 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 60 °C, and 15 s at 95 °C). Supplementary Table S1 shows the oligonucleotide sequences of primers specific for human TRPA1, ZNT1-8, ZIP1-14, and β-ACTIN.
4.4. Recombinant Expression of Wild and Mutant TRPA1, P65, HIF-1α, ZIP8, and ZIP14 in HEK Cells and FLSs
The partially confluent HEK cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1/neo(+) (pcDNA3.1, for [Ca2+]i and [Zn2+]i measurements) and pIRES2-AcGFP1 (for patch-clamp experiments) plasmids containing human wild and mutant TRPA1, pcDNA3.1-human ZIP8 plasmid DNA, and pcDNA3.1-human ZIP14 plasmid DNA using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Yokohama, Japan). The FLSs were similarly transfected with pCMV-human P65 plasmid DNA and pcDNA3.1/hyg(+)-human HIF-1α plasmid DNA using Lipofectamine 3000. The TRPA1 mutation was constructed by PCR using mutant oligonucleotide primers, in which an aspartic acid residue at 915 was changed to alanine (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). All of the experiments were performed within 48 h of transfection. Sequencing verified the construct.
4.5. Patch Clamp Electrophysiology
Whole-cell current recordings were performed, as described previously [41]. The resistance of the electrodes was 3–5 MΩ when filled with pipette solution. A Cs+-rich pipette solution contained (in mM) Cs-aspartate 110, CsCl 30, MgCl2 1, HEPES 10, EGTA 10, and Na2ATP 2 (adjusted to pH 7.2 with CsOH). The [Ca2+]i concentration was adjusted to a pCa value of 6.5 (0.3 μM Ca2+) by adding CaCl2 to the pipette solution to maintain TRPA1 currents. Membrane currents and voltage signals were digitized using an analogue-digital converter (PCI-6229, National Instruments Japan, Tokyo, Japan). The WinWCPV4.5 software was used for data acquisition and the analysis of whole-cell currents (developed by Dr. John Dempster, University of Strathclyde, UK). The liquid junction potential between the pipette and bath solutions (−10 mV) was corrected. A ramp voltage protocol from −110 to +90 mV for 100 ms was applied every 5 s from a holding potential of −10 mV. The leak current component was not subtracted from the recorded currents. A standard HEPES-buffered bathing solution (SBS (in mM): NaCl 137, KCl 5.9, CaCl2 2.2, MgCl2 1.2, glucose 14, HEPES 10 (adjusted to pH 7.4 with NaOH)) was used. All of the experiments were performed at 25 ± 1 °C.
4.6. Measurement of Ca2+ Fluorescence Ratio and Auto-Fluorescence Images of Cells
The changes in [Ca2+]i concentrations were monitored with Fura-2, as described previously [41]. The cells were loaded with 10 μM Fura-2-acetoxymethyl ester (Fura2-AM; Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc, Kumamoto, Japan) in SBS for 30 min. at room temperature. Fura-2 fluorescence signals were measured at 0.2 Hz in an ARGUS/HiSCA imaging system (Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu, Japan) that was operated using the Imaging Workbench software v6.0 (INDEC Medical Systems, Santa Clara, CA), and the fluorescence ratio (Ca2+i (F340/F380)) was calculated. For each analysis, the whole cell area was chosen as the region of interest to obtain the averaged values of fluorescence ratio. In the present study, we used a zero divalent cation (0DVC) bathing solution where both CaCl2 and MgCl2 were removed from SBS in the presence (Figure 4 and Figure 7) or absence (Figure 2 and Figure 3) of 1 mM EGTA. All of the experiments were performed at 25 ± 1 °C. For the recording of auto-fluorescence images, the cells were excited with light of 488 nm wavelength and the emitted fluorescence was collected at wavelengths longer than 505 nm in a confocal laser scanning microscope (LSM 510 META, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
4.7. Fluorescence-Based Measurement of Zn2+
The cells were incubated with 10 μM Fura-2-AM in SBS for 30 min. at room temperature. During the estimation of [Zn2+]i using Fura-2 (Figure 4), 1 mM EGTA was added to remove residual Ca2+ and Zn2+ in 0DVC. Fura-2 fluorescence signals were measured at 0.2 Hz using the Argus/HisCa imaging system that was driven by Imaging Workbench v6.0, and the corresponding fluorescence ratio (Zn2+i (F340/F380)) was calculated. In order to generate a mathematical relationship between the fluorescence intensity ratio and Zn2+ concentration, cells that were permeabilized with the Zn2+ ionophore Pyr were incubated with Zn2+ at a concentration range of 1–300 nM using the Zn2+-EGTA buffer. The change in ratio (ΔZn2+i (F340/F380)) normalized to that in the presence of TPEN was plotted against the corresponding Zn2+ concentration, and the generated data set was fitted to the following equation using the Origin J9.1 software (LightStone, Tokyo, Japan):
| ΔR = ΔRmax*Zn2+concentration/[Kd+Zn2+concentration] |
where ΔR is ΔZn2+i (F340/F380); and, Kd and ΔRmax are the dissociation constants of Fura-2 in the presence of Zn2+ and maximal ΔZn2+i (F340/F380), respectively. The change in [Zn2+]i was also measured using FluoZin-3. The cells were incubated with 10 μM FluoZin-3AM in SBS for 30 min. at room temperature. When the cells were excited with light of 488 nm wavelength, FluorZin-3 fluorescence signals that were emitted at wavelengths longer than 510 nm were collected at 0.2 Hz using the Argus/HisCa imaging system driven by Imaging Workbench v6.0, and the changes in the fluorescence intensity were calculated at time zero (Zn2+i (F/F0)). For each analysis, the whole cell area was chosen as the region of interest for averaging the fluorescence signals. For the quantitative measurement of changes in Zn2+ levels, we collected each cell on a single coverslip for analysis of HEK cells and FLSs (the total numbers (n) shown in figure legends), and then repeated the same experiment with other coverslips to reduce variation (the total number of independent experiments shown in figure legends).
4.8. Estimation of Zn2+ Concentration in SBS
The Zn2+ concentration in SBS was measured using a Metallo Assay Kit (Metallogenics Co., Ltd., Chiba, Japan), while following the manufacturer’ s protocol. The absorbance at 570 nm was determined to be between 0.153 and 3 μM Zn2+, and an absorbance-Zn2+ concentration relationship was constructed to confirm the concentration of Zn2+ in SBS.
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Origin J9.1 was used for data analysis and representation. The data reported are expressed as the mean ± SEM, where n indicates the total number of cells in independent experiments. The statistical significance between two groups and among multiple groups was examined using paired or unpaired Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA or Tukey-Kramer test, respectively. For all of the tests, the p-values below 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Dempster (University of Strathclyde, UK) for developing the electrophysiology software (WinWCPV4.5).
Abbreviations
| [Zn2+]i | intracellular free zinc |
| HIF-1α | hypoxia-induced factor 1α |
| TRPA1 | transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 |
| FLSs | human fibroblast-like synoviocytes |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL-1α | interleukin-1α |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| [Zn2+]e | extracellular free Zn2+ |
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Materials are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms22126349/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.M.; Data curation, N.H., M.M. and K.M.; Formal analysis, N.H.; Funding acquisition, N.H., H.S. and K.M.; Investigation, H.S.; Methodology, Y.M.; Project administration, K.M.; Resources, Y.M.; Writing—original draft, K.M.; Writing—review & editing, N.H., M.M., H.S. and Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research to K.M., N.H., and H.S. from Japanese Society of Promotion and Science (JSPS).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests in regards to this manuscript.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Rink L., Haase H. Zinc homeostasis and immunity. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ho L.H., Ruffin R.E., Murgia C., Li L., Krilis S.A., Zalewski P.D. Labile zinc and zinc transporter ZnT4 in mast cell granules: Role in regulation of caspase activation and NF-kappaB translocation. J. Immunol. 2004;172:7750–7760. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kabu K., Yamasaki S., Kamimura D., Ito Y., Hasegawa A., Sato E., Kitamura H., Nishida K., Hirano T. Zinc is required for Fc epsilon RI-mediated mast cell activation. J. Immunol. 2006;177:1296–1305. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Haase H., Ober-Blöbaum J.L., Engelhardt G., Hebel S., Heit A., Heine H., Rink L. Zinc Signals Are Essential for Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Signal Transduction in Monocytes. J. Immunol. 2008;181:6491–6502. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.9.6491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Besecker B., Bao S., Bohacova B., Papp A., Sadee W., Knoell D.L. The human zinc transporter SLC39A8 (Zip8) is critical in zinc-mediated cytoprotection in lung epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008;294:L1127–L1136. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00057.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yokoyama M., Koh J., Choi D. Brief exposure to zinc is toxic to cortical neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1986;71:351–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90646-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sensi S.L., Paoletti P., Bush A., Sekler I. Zinc in the physiology and pathology of the CNS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009;10:780–791. doi: 10.1038/nrn2734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liu M.J., Bao S., Galvez-Peralta M., Pyle C.J., Rudawsky A.C., Pavlovicz R.E., Killilea D.W., Li C., Nebert D.W., Wewers M.D., et al. ZIP8 regulates host defense through zinc-mediated inhibition of NF-kappaB. Cell Rep. 2013;3:386–400. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pyle C.J., Akhter S., Bao S., Dodd C.E., Schlesinger L.S., Knoell D.L. Zinc Modulates Endotoxin-Induced Human Macrophage Inflammation through ZIP8 Induction and C/EBPbeta Inhibition. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0169531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim M.-H., Aydemir T.B., Kim J., Cousins R.J. Hepatic ZIP14-mediated zinc transport is required for adaptation to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E5805–E5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704012114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bellomo E.A., Meur G., Rutter G.A. Glucose regulates free cytosolic Zn2+ concentration, Slc39 (ZiP), and metallothionein gene expression in primary pancreatic islet beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:25778–25789. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.246082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liuzzi J.P., Lichten L.A., Rivera S., Blanchard R.K., Aydemir T.B., Knutson M.D., Ganz T., Cousins R.J. Interleukin-6 regulates the zinc transporter Zip14 in liver and contributes to the hypozincemia of the acute-phase response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:6843–6848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502257102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jordt S.-E., Bautista D.M., Chuang H.-H., McKemy D.D., Zygmunt P.M., Högestätt E.D., Meng I.D., Julius D. Mustard oils and cannabinoids excite sensory nerve fibres through the TRP channel ANKTM1. Nature. 2004;427:260–265. doi: 10.1038/nature02282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.MacPherson L.J., Dubin A.E., Evans M.J., Marr F., Schultz P.G., Cravatt B.F., Patapoutian A. Noxious compounds activate TRPA1 ion channels through covalent modification of cysteines. Nature. 2007;445:541–545. doi: 10.1038/nature05544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Story G.M., Peier A.M., Reeve A.J., Eid S.R., Mosbacher J., Hricik T.R., Earley T.J., Hergarden A.C., Andersson D.A., Hwang S.W., et al. ANKTM1, a TRP-like Channel Expressed in Nociceptive Neurons, Is Activated by Cold Temperatures. Cell. 2003;112:819–829. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Suzuki H., Hatano N., Muraki Y., Itoh Y., Kimura S., Hayashi H., Onozaki K., Ohi Y., Haji A., Muraki K. The NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphenyleneiodonium activates the human TRPA1 nociceptor. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2014;307:C384–C394. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00182.2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Muraki K., Sekine T., Ando Y., Suzuki H., Hatano N., Hirata T., Muraki Y. An environmental pollutant, 9,10-phenanthrenequinone, activates human TRPA1 via critical cysteines 621 and 665. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2017;5:e00342. doi: 10.1002/prp2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Del Camino D., Murphy S., Heiry M., Barrett L.B., Earley T.J., Cook C.A., Petrus M.J., Zhao M., D’Amours M., Deering N., et al. TRPA1 Contributes to Cold Hypersensitivity. J. Neurosci. 2010;30:15165–15174. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2580-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fernandes E.S., Russell F.A., Spina D., McDougall J.J., Graepel R., Gentry C., Staniland A.A., Mountford D.M., Keeble J.E., Malcangio M., et al. A distinct role for transient receptor potential ankyrin 1, in addition to transient receptor potential vanilloid 1, in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia and Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced monarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:819–829. doi: 10.1002/art.30150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Karashima Y., Talavera K., Everaerts W., Janssens A., Kwan K.Y., Vennekens R., Nilius B., Voets T. TRPA1 acts as a cold sensor in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:1273–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808487106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kwan K.Y., Allchorne A.J., Vollrath M.A., Christensen A.P., Zhang D.-S., Woolf C.J., Corey D.P. TRPA1 Contributes to Cold, Mechanical, and Chemical Nociception but Is Not Essential for Hair-Cell Transduction. Neuron. 2006;50:277–289. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.03.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Obata K., Katsura H., Mizushima T., Yamanaka H., Kobayashi K., Dai Y., Fukuoka T., Tokunaga A., Tominaga M., Noguchi K. TRPA1 induced in sensory neurons contributes to cold hyperalgesia after inflammation and nerve injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2005;115:2393–2401. doi: 10.1172/JCI25437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bautista D.M., Jordt S.-E., Nikai T., Tsuruda P.R., Read A.J., Poblete J., Yamoah E.N., Basbaum A.I., Julius D. TRPA1 Mediates the Inflammatory Actions of Environmental Irritants and Proalgesic Agents. Cell. 2006;124:1269–1282. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mäki-Opas I., Hämäläinen M., Moilanen L.J., Haavikko R., Ahonen T.J., Alakurtti S., Moreira V.M., Muraki K., Yli-Kauhaluoma J., Moilanen E. Pyrazine-Fused Triterpenoids Block the TRPA1 Ion Channel in Vitro and Inhibit TRPA1-Mediated Acute Inflammation in Vivo. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019;10:2848–2857. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Moilanen L.J., Hamalainen M., Lehtimaki L., Nieminen R.M., Muraki K., Moilanen E. Pinosylvin Inhibits TRPA1-Induced Calcium Influx In Vitro and TRPA1-Mediated Acute Paw Inflammation In Vivo. Bas. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016;118:238–242. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hatano N., Itoh Y., Suzuki H., Muraki Y., Hayashi H., Onozaki K., Wood I.C., Beech D., Muraki K. Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α (HIF1α) Switches on Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin Repeat 1 (TRPA1) Gene Expression via a Hypoxia Response Element-like Motif to Modulate Cytokine Release. J. Biol. Chem. 2012;287:31962–31972. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Andersson D.A., Gentry C., Moss S., Bevan S. Clioquinol and pyrithione activate TRPA1 by increasing intracellular Zn2+ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:8374–8379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812675106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vinkenborg J.L., Nicolson T.J., Bellomo E., Koay M.S., Rutter G.A., Merkx M. Genetically encoded FRET sensors to monitor intracellular Zn2+ homeostasis. Nat. Methods. 2009;6:737–740. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hu H., Bandell M., Petrus M.J., Zhu M.X., Patapoutian A. Zinc activates damage-sensing TRPA1 ion channels. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009;5:183–190. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y.Y., Chang R.B., Waters H.N., McKemy D.D., Liman E.R. The Nociceptor Ion Channel TRPA1 Is Potentiated and Inactivated by Permeating Calcium Ions. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:32691–32703. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803568200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zurborg S., Yurgionas B., Jira J.A., Caspani O., Heppenstall P.A. Direct activation of the ion channel TRPA1 by Ca2+ Nat. Neurosci. 2007;10:277–279. doi: 10.1038/nn1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yazar M., Sarban S., Kocyigit A., Isikan U.E. Synovial Fluid and Plasma Selenium, Copper, Zinc, and Iron Concentrations in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2005;106:123–132. doi: 10.1385/BTER:106:2:123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gu Q., Lin R.-L. Heavy metals zinc, cadmium, and copper stimulate pulmonary sensory neurons via direct activation of TRPA1. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010;108:891–897. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01371.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Krężel A., Maret W. Zinc-buffering capacity of a eukaryotic cell at physiological pZn. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2006;11:1049–1062. doi: 10.1007/s00775-006-0150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Colvin R.A., Bush A., Volitakis I., Fontaine C.P., Thomas D., Kikuchi K., Holmes W.R. Insights into Zn2+ homeostasis in neurons from experimental and modeling studies. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2008;294:C726–C742. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00541.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lichten L.A., Liuzzi J.P., Cousins R.J. Interleukin-1beta contributes via nitric oxide to the upregulation and functional activity of the zinc transporter Zip14 (Slc39a14) in murine hepatocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009;296:G860–G867. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90676.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Frede S., Stockmann C., Freitag P., Fandrey J. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces HIF-1 activation in human monocytes via p44/42 MAPK and NF-kappaB. Biochem J. 2006;396:517–527. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Muz B., Khan M.N., Kiriakidis S., Paleolog E.M. The role of hypoxia and HIF-dependent signalling events in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009;11:201. doi: 10.1186/ar2568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhou J., Schmid T., Brune B. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha causes accumulation of a ubiquitinated form of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha through a nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2003;14:2216–2225. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-09-0598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Colvin R.A., Holmes W.R., Fontaine C.P., Maret W. Cytosolic zinc buffering and muffling: Their role in intracellular zinc homeostasis. Metallomics. 2010;2:306–317. doi: 10.1039/b926662c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Muraki K., Ohnishi K., Takezawa A., Suzuki H., Hatano N., Muraki Y., Hamzah N., Foster R., Waldmann H., Nussbaumer P., et al. Na+ entry through heteromeric TRPC4/C1 channels mediates (-)Englerin A-induced cytotoxicity in synovial sarcoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:16988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17303-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.