Abstract
Inflammation is a risk factor for the onset and progression of schizophrenia, and dietary factors are related to chronic inflammation. We investigated whether the dietary inflammatory index (DII) is associated with schizophrenia in the Korean population. Of the 256 subjects who responded to the questionnaire, 184 subjects (117 controls; 67 individuals with schizophrenia) were included in this case-control study. A semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire was used to evaluate the dietary intakes of the study participants. The energy-adjusted DII (E-DII) was used to assess the inflammatory potential of the participants’ diets. Dietary intakes of vitamin C, niacin, and folate were significantly reduced in the patients with schizophrenia. The patients with schizophrenia had higher E-DII scores than the controls (p = 0.011). E-DII was positively associated with schizophrenia (odds ratio = 1.254, p = 0.010). The additional analysis confirmed that E-DII was significantly associated with schizophrenia, especially in the third tertile group of E-DII scores (odds ratio = 2.731, p = 0.016). Our findings suggest that patients with schizophrenia have more pro-inflammatory diets.
Keywords: dietary inflammation, folate, niacin, schizophrenia, vitamin C
1. Introduction
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that affects approximately 20 million people worldwide [1]. A substantial proportion of patients with schizophrenia do not receive appropriate care due to socioeconomic barriers, especially in low- and middle-income countries [2]. Symptoms of this devastating disease can be classified as positive (hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, and disorganized behavior), negative (affective flattening, avolition, diminished interest, and social withdrawal), and cognitive symptoms [3]. Although the etiology of schizophrenia is unclear, studies have found that altering dopamine levels and their functions contributes to the onset of schizophrenia and its pathophysiological changes [4]. Many studies have also identified roles for the dysregulation of other neurotransmitters (e.g., serotonin, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and acetylcholine) in the etiology of schizophrenia [5,6].
Anti-psychotic medications acting on dopamine D2 receptor and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) 2A receptor are first-line treatments for patients with schizophrenia [7]. Chronic use of these anti-psychotic medications is often associated with adverse effects on components of metabolic syndrome, including abdominal obesity, atherogenic dyslipidemia (high triglyceride and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations), hypertension, insulin resistance, and glucose intolerance. Weight gain, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome are also reportedly associated with the use of anti-psychotic medications [8,9]. Patients with schizophrenia require long-term treatment, and many adverse effects of chronic anti-psychotic treatment are related to diet and nutrition. Therefore, a healthy diet and exercise are essential in reducing the incidences of adverse effects of anti-psychotic medications. In [10], patients with schizophrenia had poor dietary habits, including excessive intakes of full-fat creams and carbonated drinks, as well as low intakes of milk and dairy products, vegetables, and fruits. These patients also had lower dietary pattern scores [10].
Inflammation is a protective response against external damage and pathogens. However, chronic or exaggerated inflammatory responses are detrimental to health [11]. Elevated maternal levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-8 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, increase the risk of schizophrenia in the offspring [12,13]. Increased levels of inflammatory cytokines have also been observed in patients with schizophrenia. Studies regarding humans and animals have identified chronic inflammation as a risk factor for schizophrenia [14,15,16,17].
Dietary factors play an important role in regulating the inflammatory response [18,19]. The dietary inflammatory characteristics may signify the presence of chronic inflammation in the body. The dietary inflammatory index (DII) is a population-based index derived from the literature, which was developed to evaluate dietary inflammatory potential. Elevated DII scores have robust validity in indicating an increased inflammatory response, as evidenced by increased inflammatory biomarkers, such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), IL-1 beta, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-alpha [20]. DII has been used to estimate dietary inflammation in various diseases, including colorectal cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome [21,22,23,24]. Studies have also been conducted regarding the use of DII in mental illnesses, specifically in patients with depression [25,26]. Few studies have evaluated dietary inflammation in patients with schizophrenia. Two recent studies conducted in Bahrain and the UK showed increased DII and energy-adjusted DII (E-DII) scores in patients with schizophrenia [19,27]. To our knowledge, dietary inflammation in schizophrenia has not been investigated in the Korean population. Understanding the relationship between dietary inflammation and schizophrenia in the Korean population will help to formulate dietary guidelines that can reduce schizophrenia risk and symptom severity.
Here, we investigated the association between dietary inflammation and schizophrenia in the Korean population. The findings of the current study may help to suggest dietary guidelines for schizophrenia subjects, considering the aspect of dietary inflammation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
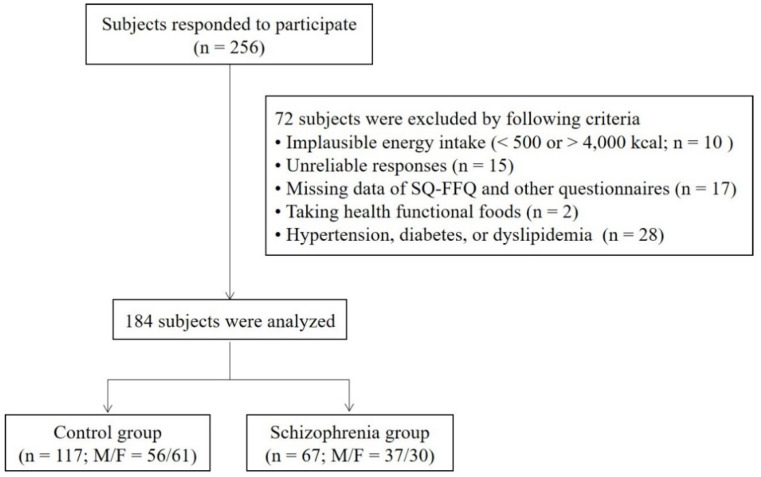
The study participants were recruited from the community or community mental health centers in Gwangju, Korea, by posting advertisements. A subset of the registered participants were identical to the cohort discussed in our previous report [28]. We collected data concerning the participants’ general characteristics, including age, sex, presence of metabolic diseases, smoking status, alcohol consumption, changes in body weight over the past six months, and physical activity. Alcohol consumption and smoking status were classified as “yes” if the subject responded that they drink alcohol and smoke every day, respectively. Physical activity was determined by asking about the frequency of moderate exercise (more than 30 min a day). Height and body weight were measured by the examiner. The body mass index (BMI; kg/m2) was calculated based on height (m) and body weight (kg). The Asia-Pacific BMI classification was used to categorize participants into underweight (below 18.5 kg/m2), normal (18.5 to 22.9 kg/m2), overweight (23.0 to 24.9 kg/m2), and obese (over 25.0 kg/m2) groups. The study questionnaire was completed by 256 people, and 72 subjects (30 control subjects and 42 patients with schizophrenia) were excluded according to the exclusion criteria summarized in Table 1. A total of 184 participants were included in this study (117 controls; 67 individuals with schizophrenia). Participants in the control group did not have any personal or family histories of psychiatric diseases and were not using psychotropic drugs. Schizophrenia was diagnosed in accordance with criteria described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. All participants were aged 18 to 60 years. None had any current or past histories of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or dyslipidemia. We excluded participants with serious medical diseases or pregnancy. Based on the responses to the questionnaires, including the semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire (SQ-FFQ), we also excluded participants with an implausible energy intake (<500 kcal or >4000 kcal), unreliable responses, and those who consumed health functional foods. The flow of study participants is shown in Figure 1. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Chonnam National University (1040198-150114-HR-003-03). All subjects who participated in this study provided written informed consent. The study was carried out in accordance with the latest version of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Table 1.
Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria for study participants.
| Control | Schizophrenia | |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria |
|
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
|
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for study participants. SQ-FFQ, semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire.
2.2. Dietary Assessment
The dietary intakes of participants were evaluated using the SQ-FFQ, which had questions concerning 76 food items in the following categories: (1) rice and other grains; (2) fishes and meats; (3) vegetables; (4) oil and sugar; (5) milk and dairy products; (6) fruits; and (7) tea and beverages. The SQ-FFQ included colored photographs of three portion sizes of 17 food items from all food groups. The participants were asked to report the frequencies and portion sizes of 76 food items consumed during the past month. The frequency was reported as never or seldom; once per month; two or three times per month; once or twice per week; three or four times per week; five or six times per week; once per day; twice per day; and three times per day. The portion sizes were classified as small, medium, and large. Computer-Aided Nutritional Analysis Program version 5.0 (Korean Nutrition Society, Seoul, Korea) was used to analyze the dietary intakes of energy and nutrients.
2.3. DII Score
In the present study, dietary inflammation was predicted based on the DII calculation previously published [20]. The process of creating the overall DII score for an individual was as follows. We calculated the z-score to compare the DII scores of participants in relation to scores from the global database. The z-score was calculated by subtracting the global daily mean nutrient intake from the nutrient intakes of our participants, then dividing the result by the standard deviation (SD) of the mean. A percentile score was calculated for this value to reduce the effect of a “right-skewed” data distribution. The percentile score of each nutrient was converted to a centered percentile through multiplication by 2 and subtraction of 1. Each nutrient’s centered percentile value was multiplied by its overall inflammatory effect score. The DII score of each participant was calculated by summing the DII scores of individual nutrients. To obtain an E-DII score, the dietary intake was converted to intake per 1000 kcal energy intake. A higher DII score indicated a pro-inflammatory dietary potential, while a lower DII score indicated an anti-inflammatory dietary potential.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
We analyzed differences in general characteristics, dietary intake, and E-DII scores between participants with and without schizophrenia. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov and Shapiro–Wilk tests were used to assess whether variables were normally distributed. Continuous variables were analyzed using Student’s t-test (if the variables were normally distributed) or the Mann–Whitney U test (if the variables were not normally distributed). Categorical variables were analyzed using the chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test. P-values for the statistical differences in dietary intakes between groups were corrected using the analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model with the nutrients as dependent variables and age, sex, and BMI as covariates. ANCOVA-corrected p-value was presented as corrected P. Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the association between E-DII and schizophrenia using an unadjusted model and a model adjusted for age, sex, and BMI. Participants were classified into three groups based on the tertiles (T) of E-DII scores: T1: E-DII < −0.8767; T2: −0.8767E-DII < 1.0105; and T3: E-DII 1.0105. The association between E-DII and schizophrenia was analyzed using logistic regression analysis based on the tertiles of E-DII. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS version 24 (IBM SPSS Statistics, Armonk, NY, USA). Data were expressed as mean SD for continuous variables. Statistically significant differences were defined as p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Study Participants
The general characteristics of the study participants are described in Table 2. Participants with and without schizophrenia had a similar age, sex distribution, height, alcohol use, smoking status, and level of physical activity. However, body weight, BMI, and frequency of obesity were significantly higher in the participants with schizophrenia than in the controls (Table 2).
Table 2.
Participant characteristics.
| Control | Schizophrenia | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 30.17 ± 8.12 | 32.72 ± 10.78 | 0.358 |
| Sex (n, %) | 0.337 | ||
| Male | 56 (47.9) | 37 (55.2) | |
| Female | 61 (52.1) | 30 (44.8) | |
| Height (cm) | 167.15 ± 8.52 | 166.61 ± 9.02 | 0.697 |
| Body weight (kg) | 62.54 ± 14.20 | 69.26 ± 15.75 | 0.004 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.19 ± 3.65 | 24.97 ± 5.44 | 0.001 |
| Obesity (n, %) | 0.046 | ||
| Underweight | 14 (12.0) | 5 (7.5) | |
| Normal | 63 (53.8) | 25 (37.3) | |
| Overweight | 15 (12.8) | 12 (17.9) | |
| Obese | 25 (21.4) | 25 (37.3) | |
| Alcohol (n, %) | 0.059 | ||
| Yes | 7 (6.0) | 0 (0) | |
| Sometimes | 20 (17.1) | 8 (11.9) | |
| No | 90 (76.9) | 59 (88.1) | |
| Smoking (n, %) | 0.445 | ||
| Yes | 17 (14.5) | 12 (17.9) | |
| Sometimes | 3 (2.6) | 0 (0) | |
| No | 97 (82.9) | 55 (82.1) | |
| Physical activity (n, %) | 0.061 | ||
| Yes | 24 (20.5) | 22 (32.8) | |
| Sometimes | 37 (31.6) | 24 (35.8) | |
| No | 56 (47.9) | 21 (31.3) |
Data are expressed as mean SD.
3.2. Comparison of Dietary Intakes between Controls and Patients with Schizophrenia
Total energy intakes were similar between the control and schizophrenia groups (1667.43 ± 607.30 kcal and 1787.42 ± 754.05 kcal, respectively). The energy-adjusted dietary intakes of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are presented in Table 3. The only statistically significant difference between groups was a reduced dietary intake of arachidonic acid, an n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), in the schizophrenia group, compared with the control group (corrected p = 0.016). The dietary intakes of vitamins and minerals are shown in Table 4. In comparison with participants in the control group, participants in the schizophrenia group had lower dietary intakes of vitamin C (corrected p = 0.030), vitamin K (corrected p = 0.007), niacin (corrected p = 0.003), folate (corrected p = 0.042), calcium from vegetables (corrected p = 0.021), and phosphorous (corrected p = 0.035).
Table 3.
Dietary intakes of energy and energy-adjusted dietary intakes (per 1000 kcal) of carbohydrate, protein, and fats.
| Control | Schizophrenia | p | Corrected P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) | 1667.43 ± 607.30 | 1787.42 ± 754.05 | 0.345 | 0.442 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 166.98 ± 19.40 | 172.71 ± 24.98 | 0.112 | 0.078 |
| Fiber (g) | 13.09 ± 4.56 | 12.22 ± 6.84 | 0.020 | 0.204 |
| Protein (g) | 35.76 ± 6.32 | 33.68 ± 8.07 | 0.055 | 0.076 |
| Protein, vegetable (g) | 20.31 ± 3.46 | 19.35 ± 4.67 | 0.145 | 0.118 |
| Protein, animal (g) | 15.45 ± 6.19 | 14.15 ± 7.79 | 0.244 | 0.252 |
| Fat (g) | 21.69 ± 6.55 | 20.01 ± 8.48 | 0.167 | 0.097 |
| Fat, vegetable (g) | 10.60 ± 3.68 | 9.69 ± 4.33 | 0.131 | 0.257 |
| Fat, animal (g) | 15.45 ± 6.19 | 14.15 ± 7.79 | 0.244 | 0.252 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 154.07 ± 64.13 | 139.73 ± 73.84 | 0.173 | 0.422 |
| Saturated fat (g) | 5.06 ± 2.34 | 5.35 ± 3.66 | 0.878 | 0.645 |
| MUFAs (g) | 5.26 ± 2.38 | 5.27 ± 3.35 | 0.549 | 0.902 |
| PUFAs (g) | 3.44 ± 1.64 | 3.20 ± 2.10 | 0.156 | 0.377 |
| n-6 PUFAs 1 (g) | 2.94 ± 1.42 | 2.61 ± 1.68 | 0.059 | 0.143 |
| Linoleic acid (g) | 2.84 ± 1.40 | 2.51 ± 1.63 | 0.050 | 0.131 |
| AA (g) | 0.0081 ± 0.0063 | 0.0058 ± 0.0064 | 0.001 | 0.016 |
| n-3 PUFAs 2 (g) | 0.44 ± 0.24 | 0.43 ± 0.33 | 0.225 | 0.872 |
| EPA+DHA (g) | 0.17 ± 0.14 | 0.15 ± 0.15 | 0.108 | 0.156 |
Data are expressed as mean SD. 1 Sum of AA, LA, 20:2(n-6), DGLA, and 22:5(n-6). 2 Sum of ALA, DHA, DPA, EPA, and ETA. AA, arachidonic acid; ALA, α-linolenic acid; DGLA, dihomo-γ-linolenic acid; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; DPA, docosapentaenoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; ETA, eicosatetraenoic acid; LA, linoleic acid; MUFAs, monounsaturated fatty acids; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Table 4.
Energy-adjusted dietary intakes (per 1000 kcal) of vitamins and minerals.
| Control | Schizophrenia | p | Corrected P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A (μg RAE) | 339.75 ± 180.00 | 289.10 ± 188.83 | 0.024 | 0.161 |
| Vitamin D (μg) | 1.62 ± 0.84 | 1.78 ± 1.28 | 0.377 | 0.174 |
| Vitamin E (mg α-TE) | 6.16 ± 2.24 | 5.49 ± 2.24 | 0.036 | 0.090 |
| Vitamin K (μg) | 114.91 ± 73.51 | 85.82 ± 68.33 | 0.002 | 0.007 |
| Vitamin B1 (mg) | 0.75 ± 0.18 | 0.71 ± 0.19 | 0.037 | 0.129 |
| Vitamin B2 (mg) | 0.63 ± 0.19 | 0.61 ± 0.23 | 0.503 | 0.616 |
| Niacin (mg NE) | 7.53 ± 1.58 | 6.77 ± 2.07 | 0.010 | 0.003 |
| Vitamin B5 (mg) | 3.01 ± 0.42 | 2.98 ± 0.54 | 0.713 | 0.990 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.80 ± 0.17 | 0.74 ± 0.24 | 0.013 | 0.077 |
| Vitamin B7 (mg) | 10.61 ± 5.09 | 10.07 ± 4.55 | 0.475 | 0.956 |
| Folate (μg DFE) | 298.24 ± 100.92 | 264.16 ± 105.29 | 0.014 | 0.042 |
| Vitamin B12 (μg) | 3.45 ± 1.60 | 3.53 ± 3.18 | 0.222 | 0.526 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 59.76 ± 28.91 | 49.37 ± 31.38 | 0.008 | 0.030 |
| Calcium (mg) | 261.47 ± 93.46 | 245.19 ± 122.45 | 0.089 | 0.436 |
| Calcium, vegetable (mg) | 137.17 ± 56.38 | 117.31 ± 60.45 | 0.013 | 0.021 |
| Calcium, animal (mg) | 122.21 ± 63.91 | 112.90 ± 76.77 | 0.207 | 0.789 |
| Chloride (mg) | 172.66 ± 102.63 | 167.06 ± 115.22 | 0.628 | 0.870 |
| Iron (mg) | 7.12 ± 1.47 | 6.61 ± 1.89 | 0.011 | 0.066 |
| Iron, vegetable (mg) | 5.56 ± 1.35 | 5.21 ± 1.61 | 0.122 | 0.109 |
| Iron, animal (mg) | 1.56 ± 0.65 | 1.40 ± 0.74 | 0.055 | 0.257 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 41.71 ± 19.91 | 42.96 ± 27.96 | 0.626 | 0.672 |
| Phosphorous (mg) | 569.24 ± 102.46 | 532.23 ± 130.37 | 0.048 | 0.035 |
| Potassium (mg) | 1557.45 ± 451.39 | 1448.75 ± 525.94 | 0.085 | 0.144 |
| Selenium (μg) | 51.00 ± 9.20 | 49.23 ± 11.50 | 0.283 | 0.357 |
| Sodium (mg) | 1815.54 ± 707.05 | 1809.80 ± 943.05 | 0.582 | 0.833 |
| Zinc (mg) | 5.43 ± 0.85 | 5.13 ± 0.96 | 0.033 | 0.061 |
Data are expressed as mean SD. DFE, dietary folate equivalents; NE, niacin equivalents; RAE, retinol activity equivalents; TE, tocopherol equivalents.
3.3. Association between E-DII Score and Schizophrenia
E-DII scores, a measure of the dietary inflammatory potential, were higher in the participants with schizophrenia than in the controls (p = 0.011), indicating a pro-inflammatory dietary intake in the patients with schizophrenia (Table 5). Importantly, participants with higher E-DII scores had significantly increased odds of schizophrenia in unadjusted analyses (odds ratio = 1.228, p = 0.012) and in analyses adjusted for age, sex, and BMI (odds ratio = 1.254, p = 0.010; Table 6). Additional analysis, according to the tertiles of E-DII, also confirmed the positive association between E-DII and schizophrenia, showing an increased odds ratio for schizophrenia in the unadjusted model (odds ratio = 2.471, p = 0.019) and in model adjusted for age, sex, and BMI (odds ratio = 2.731, p = 0.016), especially in the third tertile group of E-DII, compared with tertile 1 (Table 7).
Table 5.
Energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index (DII) scores of control and schizophrenia subjects.
| Control | Schizophrenia | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy-adjusted DII | −0.25 ± 1.91 | 0.56 ± 2.13 | 0.011 |
Data are expressed as mean SD.
Table 6.
Odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) for schizophrenia by energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index (DII) scores.
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy-adjusted DII scores | 1.228 (1.046–1.441) p = 0.012 |
1.254 (1.055–1.490) p = 0.010 |
Associations were explored by logistic regression analysis. Model 1: unadjusted; Model 2: adjusted for age (1-year increment), sex, and body mass index (1 kg/m2 increment).
Table 7.
Odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) for schizophrenia according to the tertiles of energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index (E-DII) scores.
| Energy-Adjusted DII Scores | Tertile 1 | Tertile 2 | Tertile 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Reference | 0.824 (0.366–1.854) p = 0.639 |
2.471 (1.159–5.269) p = 0.019 |
| Model 2 | Reference | 0.868 (0.369–2.043) p = 0.746 |
2.731 (1.210–6.165) p = 0.016 |
Associations were explored by logistic regression analysis. Model 1: unadjusted; Model 2: adjusted for age, sex, and body mass index. Tertile ranges of energy-adjusted DII: T1 (E-DII < −0.8767), T2 (−0.8767 E-DII < 1.0105), and T3 (E-DII 1.0105).
4. Discussion
Our results suggest that pro-inflammatory potentials of diets are associated with schizophrenia. Of the nutrients analyzed, vitamin C, niacin, and folate were especially less consumed in the schizophrenia population. From these findings, encouraging the consumption of anti-inflammatory nutrients may be considered when preparing a dietary guideline for patients with schizophrenia to reduce dietary inflammation and subsequently improve their systemic inflammatory state and related abnormalities.
In comparison with the controls, the participants with schizophrenia in our study had higher body weights, BMIs, and a higher frequency of obesity. The increased body weight and BMI may be attributed to the metabolic effects of anti-psychotic medications [5]. Second-generation anti-psychotic drugs are involved in the pharmacological mechanisms of blocking the dopamine D2 receptor to control psychotic symptoms, and antagonizing the serotonin 5-HT receptor to reduce extrapyramidal side effects liability [5,29,30]. Weight gain and metabolic disorders can occur with the use of second-generation anti-psychotic drugs in patients with schizophrenia. Dopamine is also involved in diet and nutrition. Blocking dopamine D2 receptors on sensory neurons in the lateral hypothalamus increases hunger [31]. When dopamine D2 receptors are blocked, feeding behavior is not properly regulated: this causes overeating and weight gain [32]. In addition, the antagonistic effects of anti-psychotic medications on 5-HT2c, histaminergic (H1), and muscarinic (M3) receptors lead to increased appetite and body weight [33]. Significant increases in BMI have been reported in inpatients with schizophrenia [34]. Female patients with schizophrenia have a higher body fat percentage than do female controls [10]. Abdominal obesity is observed more frequently in patients with a history of multiple episodes of schizophrenia than in controls, as well as in patients with a first episode of schizophrenia [35].
Dietary factors, including omega-3 fatty acids, can affect schizophrenia development and symptom severity [36]. Patients with schizophrenia have increased caloric intakes due to the consumption of high-density foods and low energy expenditures [37]. In addition, patients with schizophrenia have inadequate intakes of several vitamins [28,38]. Supplementation with vitamin B12 and folate improves the negative symptoms of schizophrenia [39]. Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency were observed in patients with schizophrenia [38], and vitamin D intake is negatively associated with the risk of schizophrenia [40]. We previously reported significantly lower dietary intakes of proteins, n-3 PUFAs, vitamin K, vitamin C, niacin, and folate in male patients with schizophrenia, compared with male controls [28]. A previous study found reduced intakes of milk, dairy products, vegetables, and fruits in patients with schizophrenia, compared with the general population [10]. Patients with schizophrenia also had increased intakes of full-fat creams and carbonated drinks, as well as lower dietary habit scores, compared with the general population [10].
Inflammation has been suggested as a potential etiological factor in schizophrenia [41,42]. Increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and microglial activation accelerate schizophrenia’s onset and worsen schizophrenia’s symptom severity [16,17,43,44]. Currently, the most widely accepted hypotheses regarding the etiology of schizophrenia are the “inflammation and two-hit hypothesis” and “inflammation and neural diathesis-stress hypothesis” [45,46]. Excessive inflammation induces the stress response and neurodegeneration, which is a neuronal aging process. Stress response secondary to inflammation sensitizes and primes the microglial cells, thereby increasing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Patients with schizophrenia have higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines than do healthy controls [47,48]. In addition, positron emission tomography studies of receptors (PK11195 and DAA1106) have demonstrated that the activation of microglial receptors is associated with neuronal damage in patients with recent-onset schizophrenia [43,49]. Another study showed that higher proportions of microglial cells were bound to the DAA1106 receptor in patients with longer disease duration and worse positive symptoms [50]. Therefore, the evidence thus far implicates inflammation in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia [17,44].
Dietary factors also affect the inflammatory response [18]. Dietary imbalance and dietary inflammation contribute to metabolic alterations related to obesity and metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia. We used the DII to assess dietary inflammatory potential in participants with and without schizophrenia. The DII is a valid indicator of dietary inflammation. Many studies have investigated the associations of DII scores with inflammatory markers. A cross-sectional study (HEalthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescents) showed that higher DII scores were associated with increased inflammatory biomarkers, including TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-2, and interferon-gamma [51]. Similar results were observed in two studies involving the Korean population [52,53]. These studies showed that increased DII scores were associated with higher hs-CRP levels. Numerous studies have shown that the DII is a qualified estimating tool of dietary inflammation, which plays an important role in the systemic inflammatory response. Only two previous studies (from Bahrain and the UK) have evaluated dietary inflammation in patients with schizophrenia [19,27]: dietary inflammation, measured using the DII and E-DII, was significantly increased in patients with schizophrenia in both of these studies. The increased dietary inflammation in patients with schizophrenia in these studies is consistent with the results of our study involving the Korean population. To our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate dietary inflammation using the DII in Korean patients with schizophrenia. As there are no criteria for comparisons between studies, the E-DII scores in the present study cannot be directly compared to other studies. Nevertheless, the data on dietary intake and E-DII scores in the Korean population are significant because they reflect the unique dietary characteristics of the Korean population, with high levels of consumption of various grains, plant foods, and fermented foods [54]. Dietary intakes of vitamin C, niacin, and folate were significantly lower in patients with schizophrenia than in healthy controls. These nutrients have anti-inflammatory properties [20], and their reduced intakes may contribute to the increased dietary inflammation scores in Korean patients with schizophrenia. Our results emphasize the importance of adequate intakes of vitamin C, niacin, and folate in patients with schizophrenia.
Although several studies have been conducted regarding the dietary inflammatory potential in patients with mental disorders and depression [25,26,55], this is the first report of dietary inflammation measured with DII in Korean patients with schizophrenia. Despite its originality, our study had some limitations. First, this study had a modest sample size, and we did not match the cases and controls at a 1:1 ratio. Thus, selection bias may have influenced our results. Second, we could not study the effects of dietary inflammation on the development of schizophrenia because we enrolled patients who had already been diagnosed with schizophrenia. Third, because this was an observational study, we could not identify a causative role for a pro-inflammatory diet in the onset of schizophrenia. Fourth, it is possible that FFQ, the most common dietary assessment tool, under- or over-estimated the individuals’ dietary intakes. Finally, we did not consider psychotic symptoms or anti-psychotics in the present analyses. Further studies, including illness duration, formal scales for psychotic symptoms, or the amounts and types of anti-psychotics, would provide a better understanding of the relation between DII and schizophrenia.
The diets of patients with schizophrenia are generally pro-inflammatory, as evidenced by the higher E-DII scores of the patients with schizophrenia than of the controls. Dietary inflammation was associated with schizophrenia. To reduce dietary inflammation, patients with schizophrenia should be encouraged to maintain adequate dietary intakes of vitamin C, niacin, and folate. These results have implications for developing dietary recommendations for patients with schizophrenia, considering dietary inflammation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J.Y. and S.-W.K.; formal analysis, H.Y.C., S.J.Y. and S.-W.K.; investigation, H.Y.C., S.J.Y. and S.-W.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Y.C.; writing—review and editing, S.J.Y. and S.-W.K.; funding acquisition, S.J.Y. and S.-W.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by research grants from Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2017R1A2B4010830 (S.-W.K.) and NRF-2020R1F1A1065326 (S.J.Y.)) and Seoul Women’s University (2021-0133) (S.J.Y.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Chonnam National University (protocol code 1040198-150114-HR-003-03, approved on 22 January 2015).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lora A., Kohn R., Levav I., McBain R., Morris J., Saxena S. Service availability and utilization and treatment gap for schizophrenic disorders: A survey in 50 low- and middle-income countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012;90:47–54B. doi: 10.2471/BLT.11.089284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McCutcheon R.A., Reis Marques T., Howes O.D. Schizophrenia-An Overview. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77:201–210. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McCutcheon R.A., Abi-Dargham A., Howes O.D. Schizophrenia, Dopamine and the Striatum: From Biology to Symptoms. Trends Neurosci. 2019;42:205–220. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yang A.C., Tsai S.J. New Targets for Schizophrenia Treatment beyond the Dopamine Hypothesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18:1689. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McCutcheon R.A., Krystal J.H., Howes O.D. Dopamine and glutamate in schizophrenia: Biology, symptoms and treatment. World Psychiatry. 2020;19:15–33. doi: 10.1002/wps.20693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ijaz S., Bolea B., Davies S., Savović J., Richards A., Sullivan S., Moran P. Antipsychotic polypharmacy and metabolic syndrome in schizophrenia: A review of systematic reviews. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18:275. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1848-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kahn R.S., Sommer I.E., Murray R.M., Meyer-Lindenberg A., Weinberger D.R., Cannon T.D., O’Donovan M., Correll C.U., Kane J.M., van Os J., et al. Schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2015;1:15067. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stepnicki P., Kondej M., Kaczor A.A. Current Concepts and Treatments of Schizophrenia. Molecules. 2018;23:2087. doi: 10.3390/molecules23082087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Amani R. Is dietary pattern of schizophrenia patients different from healthy subjects? BMC Psychiatry. 2007;7:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-7-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sochocka M., Diniz B.S., Leszek J. Inflammatory Response in the CNS: Friend or Foe? Mol. Neurobiol. 2017;54:8071–8089. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0297-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brown A.S., Hooton J., Schaefer C.A., Zhang H., Petkova E., Babulas V., Perrin M., Gorman J.M., Susser E.S. Elevated maternal interleukin-8 levels and risk of schizophrenia in adult offspring. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2004;161:889–895. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.5.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Buka S.L., Tsuang M.T., Torrey E.F., Klebanoff M.A., Wagner R.L., Yolken R.H. Maternal cytokine levels during pregnancy and adult psychosis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2001;15:411–420. doi: 10.1006/brbi.2001.0644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Azizi E., Zavaran Hosseini A., Soudi S., Noorbala A.A. Alteration of Serum Levels of Cytokines in Schizophrenic Patients before and after Treatment with Risperidone. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;18:262–268. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v18i3.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Francesconi L.P., Victorino A.T., Salah I.A., Cordova V.H.S., Dias da Rosa E., Oliveira L., Jacobus R.V.M., Belmonte-de-Abreu P.S., Ceresér K.M. Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory biomarkers in schizophrenia and influence of simvastatin on the interleukin-6. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019;34:84–88. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hartwig F.P., Borges M.C., Horta B.L., Bowden J., Davey Smith G. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Risk of Schizophrenia: A 2-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1226–1233. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lesh T.A., Careaga M., Rose D.R., McAllister A.K., Van de Water J., Carter C.S., Ashwood P. Cytokine alterations in first-episode schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: Relationships to brain structure and symptoms. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018;15:165. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1197-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Galland L. Diet and inflammation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2010;25:634–640. doi: 10.1177/0884533610385703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Firth J., Stubbs B., Teasdale S.B., Ward P.B., Veronese N., Shivappa N., Hebert J.R., Berk M., Yung A.R., Sarris J. Diet as a hot topic in psychiatry: A population-scale study of nutritional intake and inflammatory potential in severe mental illness. World Psychiatry. 2018;17:365–367. doi: 10.1002/wps.20571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shivappa N., Steck S.E., Hurley T.G., Hussey J.R., Hebert J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014;17:1689–1696. doi: 10.1017/S1368980013002115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cho Y.A., Lee J., Oh J.H., Shin A., Kim J. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Case-Control Study in Korea. Nutrients. 2016;8:469. doi: 10.3390/nu8080469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Abulimiti A., Zhang X., Shivappa N., Hébert J.R., Fang Y.J., Huang C.Y., Feng X.L., Chen Y.M., Zhang C.X. The Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Positively Associated with Colorectal Cancer Risk in a Chinese Case-Control Study. Nutrients. 2020;12:232. doi: 10.3390/nu12010232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim H.Y., Lee J., Kim J. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Metabolic Syndrome in the General Korean Population. Nutrients. 2018;10:648. doi: 10.3390/nu10050648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Khan I., Kwon M., Shivappa N., Hebert J.R., Kim M.K. Positive Association of Dietary Inflammatory Index with Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease: Findings from a Korean Population-Based Prospective Study. Nutrients. 2020;12:588. doi: 10.3390/nu12020588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jorgensen D., White G.E., Sekikawa A., Gianaros P. Higher dietary inflammation is associated with increased odds of depression independent of Framingham Risk Score in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr. Res. 2018;54:23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sánchez-Villegas A., Ruíz-Canela M., de la Fuente-Arrillaga C., Gea A., Shivappa N., Hébert J.R., Martínez-González M.A. Dietary inflammatory index, cardiometabolic conditions and depression in the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015;114:1471–1479. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515003074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jahrami H., Faris M.A., Ghazzawi H.A., Saif Z., Habib L., Shivappa N., Hébert J.R. Increased Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Associated with Schizophrenia: Results of a Case-Control Study from Bahrain. Nutrients. 2019;11:1867. doi: 10.3390/nu11081867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim E.J., Lim S.Y., Lee H.J., Lee J.Y., Choi S., Kim S.Y., Kim J.M., Shin I.S., Yoon J.S., Yang S.J., et al. Low dietary intake of n-3 fatty acids, niacin, folate, and vitamin C in Korean patients with schizophrenia and the development of dietary guidelines for schizophrenia. Nutr. Res. 2017;45:10–18. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li P., Snyder G.L., Vanover K.E. Dopamine Targeting Drugs for the Treatment of Schizophrenia: Past, Present and Future. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016;16:3385–3403. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160608084834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tandon R., Nasrallah H.A., Keshavan M.S. Schizophrenia, “just the facts” 5. Treatment and prevention. Past, present, and future. Schizophr. Res. 2010;122:1–23. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yonemochi N., Ardianto C., Yang L., Yamamoto S., Ueda D., Kamei J., Waddington J.L., Ikeda H. Dopaminergic mechanisms in the lateral hypothalamus regulate feeding behavior in association with neuropeptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019;519:547–552. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Singh M. Mood, food, and obesity. Front. Psychol. 2014;5:925. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miron I.C., Baroană V.C., Popescu F., Ionică F. Pharmacological mechanisms underlying the association of antipsychotics with metabolic disorders. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2014;40:12–17. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.40.01.02. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Song M.S., Hahm W., Park S.Y., Hong K.H., Paik I.H. Obesity and Psychopathology of Inpatients with Schizophrenia. J. Korean Neuropsychiatrc Assoc. 2015;54:172–180. doi: 10.4306/jknpa.2015.54.2.172. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vancampfort D., Wampers M., Mitchell A.J., Correll C.U., De Herdt A., Probst M., De Hert M. A meta-analysis of cardio-metabolic abnormalities in drug naive, first-episode and multi-episode patients with schizophrenia versus general population controls. World Psychiatry. 2013;12:240–250. doi: 10.1002/wps.20069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Amminger G.P., Schäfer M.R., Schlögelhofer M., Klier C.M., McGorry P.D. Longer-term outcome in the prevention of psychotic disorders by the Vienna omega-3 study. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:7934. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Manu P., Dima L., Shulman M., Vancampfort D., De Hert M., Correll C.U. Weight gain and obesity in schizophrenia: Epidemiology, pathobiology, and management. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2015;132:97–108. doi: 10.1111/acps.12445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cieslak K., Feingold J., Antonius D., Walsh-Messinger J., Dracxler R., Rosedale M., Aujero N., Keefe D., Goetz D., Goetz R., et al. Low vitamin D levels predict clinical features of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2014;159:543–545. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.08.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Roffman J.L., Lamberti J.S., Achtyes E., Macklin E.A., Galendez G.C., Raeke L.H., Silverstein N.J., Smoller J.W., Hill M., Goff D.C. Randomized multicenter investigation of folate plus vitamin B12 supplementation in schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:481–489. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhu D.M., Liu Y., Zhang A.G., Chu Z.X., Wu Q., Li H., Ge J.F., Dong Y., Zhu P. High levels of vitamin D in relation to reduced risk of schizophrenia with elevated C-reactive protein. Psychiatry Res. 2015;228:565–570. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.05.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Miller B.J., Herzig K.H., Jokelainen J., Karhu T., Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S., Järvelin M.R., Veijola J., Viinamäki H., Tanskanen P., Jääskeläinen E., et al. Inflammation, hippocampal volume, and cognition in schizophrenia: Results from the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021;271:609–622. doi: 10.1007/s00406-020-01134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Muller N. Inflammation in Schizophrenia: Pathogenetic Aspects and Therapeutic Considerations. Schizophr. Bull. 2018;44:973–982. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sby024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.van Berckel B.N., Bossong M.G., Boellaard R., Kloet R., Schuitemaker A., Caspers E., Luurtsema G., Windhorst A.D., Cahn W., Lammertsma A.A., et al. Microglia activation in recent-onset schizophrenia: A quantitative (R)-[11C]PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Biol. Psychiatry. 2008;64:820–822. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.04.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Laskaris L.E., Di Biase M.A., Everall I., Chana G., Christopoulos A., Skafidas E., Cropley V.L., Pantelis C. Microglial activation and progressive brain changes in schizophrenia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016;173:666–680. doi: 10.1111/bph.13364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Feigenson K.A., Kusnecov A.W., Silverstein S.M. Inflammation and the two-hit hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014;38:72–93. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Howes O.D., McCutcheon R. Inflammation and the neural diathesis-stress hypothesis of schizophrenia: A reconceptualization. Transl. Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1024. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Goldsmith D.R., Rapaport M.H., Miller B.J. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: Comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol. Psychiatry. 2016;21:1696–1709. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.He X., Ma Q., Fan Y., Zhao B., Wang W., Zhu F., Ma X., Zhou L. The Role of Cytokines in Predicting the Efficacy of Acute Stage Treatment in Patients with Schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020;16:191–199. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S218483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Doorduin J., de Vries E.F., Willemsen A.T., de Groot J.C., Dierckx R.A., Klein H.C. Neuroinflammation in schizophrenia-related psychosis: A PET study. J. Nucl. Med. 2009;50:1801–1807. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.066647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Takano A., Arakawa R., Ito H., Tateno A., Takahashi H., Matsumoto R., Okubo Y., Suhara T. Peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A PET study with [11C]DAA1106. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13:943–950. doi: 10.1017/S1461145710000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shivappa N., Hebert J.R., Marcos A., Diaz L.E., Gomez S., Nova E., Michels N., Arouca A., González-Gil E., Frederic G., et al. Association between dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory markers in the HELENA study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017;61:1600707. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shin D., Lee K.W., Brann L., Shivappa N., Hebert J.R. Dietary inflammatory index is positively associated with serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in a Korean adult population. Nutrition. 2019;63–64:155–161. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Na W., Kim M., Sohn C. Dietary inflammatory index and its relationship with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in Korean: Data from the health examinee cohort. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2018;62:83–88. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.17-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Song Y., Joung H. A traditional Korean dietary pattern and metabolic syndrome abnormalities. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012;22:456–462. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2010.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Haghighatdoost F., Feizi A., Esmaillzadeh A., Feinle-Bisset C., Keshteli A.H., Afshar H., Adibi P. Association between the dietary inflammatory index and common mental health disorders profile scores. Clin. Nutr. 2019;38:1643–1650. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.