Glucagon signaling governs REV-ERBα stability to modulate hepatic glucose production in a model of lung cancer cachexia.
Abstract
Lung adenocarcinoma is associated with cachexia, which manifests as an inflammatory response that causes wasting of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. We previously reported that lung tumor–bearing (TB) mice exhibit alterations in inflammatory and hormonal signaling that deregulate circadian pathways governing glucose and lipid metabolism in the liver. Here, we define the molecular mechanism of how de novo glucose production in the liver is enhanced in a model of lung adenocarcinoma. We found that elevation of serum glucagon levels stimulates cyclic adenosine monophosphate production and activates hepatic protein kinase A (PKA) signaling in TB mice. In turn, we found that PKA targets and destabilizes the circadian protein REV-ERBα, a negative transcriptional regulator of gluconeogenic genes, resulting in heightened de novo glucose production. Together, we identified that glucagon-activated PKA signaling regulates REV-ERBα stability to control hepatic glucose production in a model of lung cancer–associated cachexia.
INTRODUCTION
The circadian clock is a network of tissue-specific pacemakers that govern physiological, endocrine, and metabolic processes (1, 2). The clock impinges on several facets of metabolism such as glucose production and consumption (3, 4), lipid metabolism (5–7), availability of amino acids (8, 9), and nucleotides (9, 10), which are rhythmic over the day/night cycle. Circadian control of metabolism is critical in maintaining homeostasis of the organism (11–13); however, the clock also serves as an adaptive mechanism to environmental alterations and stressors. For instance, peripheral circadian pacemakers can be rewired by restricted feeding rhythms (14–18), prolonged fasting (19, 20), caloric restriction (21–23), high-fat diet (10, 16, 24, 25), and pathological conditions such as cancer (26, 27). These data suggest a fundamental importance of the circadian clock in governing metabolic rhythms to maintain organismal homeostasis, in addition to a clock-dependent role in metabolic adaptation to nutritional challenge and environmental perturbation.
The mechanism of how the circadian clock adjusts to environmental perturbation has been characterized in dietary and nutritional challenge paradigms (14, 16, 19, 25), but little is known about how the clock is involved in metabolic adaption to disease states. Late-stage tumor burden is associated with cachexia in specific cancer types and is linked with marked inflammation that causes breakdown of adipose and muscle tissues, which results in severe weight loss due to tissue wasting (28, 29). Unlike adipose and muscle tissue, the liver maintains its mass and even increases its metabolic rate under cachexic conditions (30). Disrupted insulin signaling and elevated glucose levels have been reported in patients with cancer (31, 32), as one of the features of cachexia is activated gluconeogenesis (29, 33). Historical studies point to a potential cancer-associated type of Cori cycle where tumor-secreted lactate can fuel hepatic glucose production (31, 34). We and others previously demonstrated that mouse models of lung (27) and breast cancer (26), which are prone to cancer-associated cachexia (CAC), exhibited alterations in systemic inflammation that led to deregulation in circadian metabolic rhythms in peripheral tissues such as the liver. We further identified that lung adenocarcinoma tumor–bearing (TB) mice displayed disruptions in insulin/glucose signaling pathways that resulted in elevated fasting glucose levels (27), although the detailed molecular mechanism underpinning these metabolic alterations remain unknown.
Gluconeogenesis, or the de novo production of glucose from lactate, glycerol, or certain amino acids, is especially important during periods of prolonged fasting or nutritional deprivation, as a mechanism to sustain blood glucose levels (35, 36). Gluconeogenesis is initiated through glucagon (GC) signaling and downstream stimulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) release that activates protein kinase A (PKA)–dependent phosphorylation of cAMP response element–binding protein (CREB), resulting in an up-regulation of gluconeogenic targets, Pck1 and glucose 6-phosphatase (G6pc) (35, 37, 38). Furthermore, the circadian clock has been reported to regulate hepatic gluconeogenesis, although different putative proteins have been proposed. The circadian repressors, cryptochromes 1 and 2 (CRY1 and CRY2), have been reported to block the GC-mediated release of cAMP, which results in the repression of the PKA/CREB axis (39). Glucocorticoids also promote gluconeogenesis through CRY-mediated repression of the glucocorticoid receptor (40, 41), and several clock proteins regulate nuclear receptors to control circadian metabolic gene expression programs (42). In addition, the circadian repressor NR1D1 or REV-ERB alpha (REV-ERBα), a known heme sensor that integrates circadian and metabolic rhythms (43), has been reported to primarily control not only hepatic lipid metabolism but also gluconeogenic gene expression (6, 7, 44, 45). REV-ERBα is known to repress the expression of Pck1 and G6pc and thereby suppress hepatic glucose production (44), and disruption of hepatic REV-ERB is also reported to impinge on insulin signaling, carbohydrate metabolism, and fasting glucose levels (6). Collectively, these findings implicate the circadian clock in the direct regulation of hormonal signaling that governs hepatic gluconeogenesis. However, the molecular mechanism of how the circadian clock integrates endocrine signaling to transcriptionally regulate gluconeogenic genes and modulate hepatic glucose production remains undefined.
We previously reported that KrasLSL-G12D/+;p53fl/fl lung TB mice exhibited early-stage CAC, which significantly activated circadian expression of Pck1 in the liver (27), the rate-limiting enzyme that controls gluconeogenesis. To define the molecular mechanism of how the circadian clock controls gluconeogenesis, our findings now demonstrate that GC, through the cAMP/PKA signaling axis, degrades REV-ERBα in a proteasome-dependent manner. Loss of REV-ERBα alleviates the transcriptional repression of the gluconeogenic gene Pck1, which results in elevated glucose production both in primary hepatocytes (PH) ex vivo and in vivo through pyruvate tolerance tests (PTT). In addition, use of stable isotope tracing by mass spectrometry demonstrates that hepatocytes from lung TB mice produce significantly more glucose, which is suppressed upon reexpression of REV-ERBα. Our results point to a previously unidentified molecular mechanism to define how the metabolic sensor REV-ERBα integrates hormonal signaling and carbohydrate metabolism to control hepatic glucose production in CAC.
RESULTS
Hepatic REV-ERBα protein is destabilized in a model of lung adenocarcinoma
The KrasLSL-G12D/+;p53fl/fl genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) of lung adenocarcinoma replicates human non–small cell lung cancer and exhibits CAC (46–48). Using this GEMM, viral Cre recombinase administered via intratracheal delivery induces the genetic rearrangement of the Lox-stop-Lox cassette to activate oncogenic Kras and knock out the tumor suppressor p53. We used this GEMM and induced lung tumors, which developed uniformly with 100% penetrance at 3 months post intratracheal delivery of adenoviral Cre. Control wild-type (WT) littermates received an equivalent virus titer of the FlpO recombinase and did not develop any lung tumors (Fig. 1A). Lung TB mice exhibited significant weight loss by 3 months of age post infection compared to WT mice (Fig. 1A). Consistent with the development of cachexia, lung TB mice displayed a loss of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle as determined by fat mass and lean mass measurements (Fig. 1A), similar to previous reports (27, 49). No metastatic lesions were observed in the liver, in agreement with our previous findings (27).
Fig. 1. Expression of the circadian protein REV-ERBα and its metabolic target Pck1 in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma.
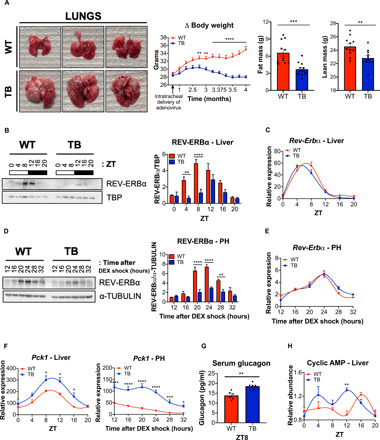
(A) Representative images of WT and TB lung tissue from mice euthanized 4 months post intratracheal delivery of adenovirus expressing FlpO or Cre recombinase, respectively. Body weight and fat and lean mass measurements are shown in the right (n = 11 mice per genotype). Photo credit: A.V., S.K.C., and M.G. (UCI). (B) Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα and TATA box–binding protein (TBP), used as a normalization control, from liver nuclear fractions isolated at the indicated ZT. Histogram indicates quantification of REV-ERBα/TBP signals over the circadian cycle (three independent experiments). (C) Circadian gene expression of Rev-erbα in liver (n = 5 independent mice per genotype and time point). (D) Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα and α-TUBULIN in isolated PH at the indicated times (hours) after synchronization with dexamethasone (DEX). Histograms represent quantification of REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (three independent experiments). (E) Circadian gene expression of Rev-erbα in PH at the indicated times (hours) after synchronization with DEX (three independent experiments). (F) Circadian gene expression of Pck1 in liver and PH at the indicated times (hours) after synchronization with DEX. (G) Serum GC levels as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (n = 6 mice per genotype). (H) Levels of cAMP as determined by metabolomics analysis in liver (n = 5 independent mice per genotype and time point). Data represent the means ± SEM with P value cutoff indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 as determined by multiple t test.
To define the effect of lung adenocarcinoma on the liver, we performed a circadian experiment where mice were euthanized every 4 hours at the indicated Zeitgeber times (ZT): 0, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20. Circadian proteins expression was examined in nuclear and cytosolic fractions of WT and TB mouse livers (fig. S1A). The circadian protein REV-ERBα was significantly reduced in both nuclear and cytosolic fractions from livers of TB mice at ZT4 and ZT8, compared to WT liver (Fig. 1B and fig. S1, B and C). In contrast, we did not observe any differences in the circadian oscillation of Rev-erbα gene expression (Fig. 1C), potentially suggesting a posttranslational mechanism for REV-ERBα regulation. Unlike the notable loss of REV-ERBα protein levels, we did not observe a loss of other core clock components such as Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (ARNTL) or BMAL1 and CRY1 (fig. S1B). We used an ex vivo approach to confirm these observations, and PH were isolated from livers of WT and TB mice and treated with dexamethasone (DEX) to synchronize the circadian clock. Consistent with our in vivo findings, REV-ERBα expression was also reduced in synchronized PH isolated from livers of TB mice after 20, 24, and 28 hours of DEX shock (Fig. 1D and fig. S2A) with no differences in Rev-erbα gene expression between both genotypes (Fig. 1E). Considering the known repressive function of REV-ERBα, the expression of core clock and metabolic target genes was examined. Gene expression of Bmal1 and Cry1 and their protein levels were elevated in PH isolated from livers of TB mice (fig. S2, A and B), as they are known targets of the transcriptional repressor REV-ERBα (43). Similarly, increased gene expression of Pck1, which encodes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPCK), and G6pc, rate-limiting enzymes of the gluconeogenesis pathway (50), was observed from liver tissue and PH isolated from livers of TB mice (Fig. 1F and fig. S2B). Increased Pck1 gene expression in PH is in accordance with our previous findings showing that lung TB mice displayed elevated fasting serum glucose levels (27), suggesting enhanced hepatic gluconeogenesis in lung TB mice.
Insulin and GC are the two most important hormones regulating hepatic gluconeogenesis, and we previously showed that impaired insulin secretion occurs in a time-dependent manner in lung TB mice (27). To corroborate these findings, we measured GC levels in the serum of WT and lung TB mice and found a significant elevation of GC in TB mice at ZT8 (Fig. 1G). GC levels are increased during fasting and decrease after refeeding (51). Consistent with these findings, serum GC levels are elevated in fasted WT mice and decrease upon feeding at ZT16; however, this dynamic endocrine response in GC levels is ablated in TB mice (fig. S2C). GC signals through its receptor on the surface of hepatocytes to activate heterotrimeric G proteins, and the Gs alpha subunit activates the adenylyl cyclases to stimulate production of cAMP (52). Using mass spectrometry–based metabolomics analysis, we measured cAMP levels in livers isolated from WT and TB mice over the circadian cycle. cAMP peaked at ZT16 in livers from WT mice, while cAMP levels were significantly shifted and peaked in abundance at ZT12 in livers isolated from TB mice (Fig. 1H). Together, these data suggest that activation of the GC signaling pathway in the livers of TB mice likely impinges on cAMP release to potentially control gluconeogenesis.
The circadian protein REV-ERBα is a target of the PKA signaling pathway
To investigate the link between GC signaling and clock-dependent control of gluconeogenesis, we examined a potential cross-talk between REV-ERBα and hormonal control of glucose metabolism. Increased cAMP is known to activate PKA and the downstream transcription factor CREB (37, 38). Given the changes in GC and cAMP levels we observed in TB mice, we investigated the pattern of PKA-dependent CREB activation by phosphorylation on its target residue, serine-133 (S133). CREB phosphorylation is rhythmic and peaks at ZT16, ZT20, and ZT0 in the livers of WT mice (Fig. 2A and fig. S2D), which is in accordance with the peak in cAMP observed at ZT16 (Fig. 1H). Conversely, the pattern of CREB phosphorylation was shifted in livers of TB mice where a clear activation was detected at ZT8 and ZT12 (Fig. 2A and fig. S2D), consistent with an earlier peak in cAMP levels in liver of TB mice (Fig. 1H). Similar to in vivo findings, a phase advance of pCREB-Ser133 was observed in PH isolated from livers of TB mice versus WT (Fig. 2B and fig. S2E).
Fig. 2. Activation of CREB and gluconeogenic target genes in the livers of lung TB mice.
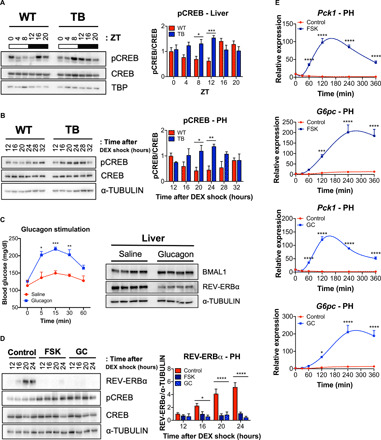
(A) Western blot analysis for phospho-CREB S133 (pCREB), total CREB, and TBP from liver nuclear fractions isolated from WT and TB mice at the indicated ZT. Histogram displays quantification of pCREB/total CREB over the circadian cycle (three independent experiments). (B) Western blot analysis for pCREB, total CREB, and α-TUBULIN in isolated PH at the indicated times (hours) after synchronization with DEX. Histogram displays quantification of pCREB/total CREB over the circadian cycle (three independent experiments). (C) Blood glucose levels (milligram per deciliter) measured at 0, 5, 15, 30, and 60 min after saline or GC (2 mg/kg body weight) administration via intraperitoneal injection at ZT7 in fasted WT mice. Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα, BMAL1, and α-TUBULIN in liver nuclear fractions at ZT9 (n = 4 independent mice per group). (D) Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα, pCREB, total CREB, and α-TUBULIN in WT PH treated with FSK (10 μM) or GC (0.1 μM) for 2 hours at the indicated times (hours) 12 hours after synchronization with DEX. Histograms show quantification of REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (three independent experiments). (E) Gene expression of Pck1 and G6pc in WT PH treated with FSK or GC at the indicated times (minutes) immediately after synchronization with DEX (three independent experiments). Data represent the means ± SEM with P value cutoff indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 as determined by multiple t test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (with more than two groups).
Intriguingly, activation of CREB (Fig. 2A) is antiphasic with REV-ERBα protein abundance in WT livers (Fig. 1B). However, CREB activation (Fig. 2A) is phase advanced and coincides with the down-regulation of REV-ERBα protein levels in livers of TB mice (Fig. 1B). These data suggest that the GC/PKA signaling axis may impinge on REV-ERBα stability. To investigate this, we injected WT mice with saline or GC and analyzed hepatic protein abundance of REV-ERBα and BMAL1. Notably, a net reduction in REV-ERBα protein was observed in the livers of GC-stimulated mice, while no decrease in BMAL1 was detected, and these mice displayed the expected increase in blood glucose levels (Fig. 2C). Similarly, we treated synchronized PH with GC or forskolin (FSK), an adenylyl cyclase activator, to stimulate the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. Notably, both FSK and GC induced significant down-regulation of REV-ERBα protein in DEX-synchronized PH when treated for 2 hours (Fig. 2D and fig. S3A), while no major decrease was observed in other circadian proteins such as BMAL1 and CRY1 (fig. S3B). We did not observe any differences in the gene expression of Bmal1 and Cry1 at 2 hours; however, gene expression was increased at later time points (fig. S3C). REV-ERBα represses gluconeogenesis and CREB is known to stimulate glucose production by binding to the CREB response elements (CRE) in the Pck1 and G6pc promoters (37, 38). FSK and GC treatment induced strong activation of Pck1 and G6pc gene expression in PH (Fig. 2E).
To dissect the mechanism of REV-ERBα protein destabilization by pharmacological PKA activation, we used an in vitro cell culture system using the nontumorigenic mouse hepatocyte cell line AML12 (alpha mouse liver 12), derived from livers of transgenic mice overexpressing a hepatocyte mitogen. In AML12 cells, REV-ERBα consistently peaked 2 to 4 hours after DEX treatment (Fig. 3A). Next, AML12 cells were treated with FSK and GC to determine the impact of cAMP and downstream PKA signaling on REV-ERBα stability. REV-ERBα protein abundance was strongly reduced in the presence of FSK and GC 2 to 4 hours after DEX treatment, corresponding with activation of CREB (Fig. 3A and fig. S4, A and B). Also, consistent with down-regulation of REV-ERBα protein levels, FSK treatment of AML12 cells significantly elevated gene expression of Pck1, G6pc, Bmal1, and Cry1, direct targets of REV-ERBα (Fig. 3B and fig. S4C). Similar trends in gene expression were observed with GC treatment of AML12 cells (Fig. 3B and fig. S4C). FSK and GC stimulate the production of cAMP via activation of the adenylyl cyclases. To confirm that the observed effects are specific to cAMP signaling, we used dibutyryl-cAMP (dbcAMP), a cell-permeable cAMP analog, and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Both dbcAMP and IBMX led to a significant reduction in REV-ERBα protein levels (Fig. 3C and fig. S5, A and B). Moreover, AML12 cells were treated with a cell-permeable PKA peptide inhibitor, PKI 14-22 amide (PKI), to directly block PKA-dependent kinase activity. PKI promoted a significant accumulation of REV-ERBα at 2 to 4 hours after DEX treatment, when the protein reaches its zenith (Fig. 3D and fig. S5C). Together, these data demonstrate that the stability of the circadian protein REV-ERBα is regulated by cAMP and downstream PKA signaling.
Fig. 3. The cAMP and PKA signaling pathway destabilizes hepatic REV-ERBα and targets it for proteosomal degradation.
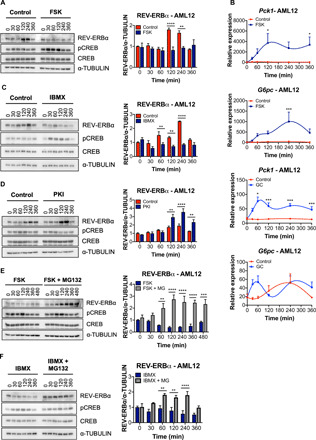
(A) Western blot analysis of REV-ERBα, pCREB, total CREB, and α-TUBULIN in AML12 cells treated with FSK for the indicated time in serum-free media containing DEX (40 ng/ml). Histograms display quantification of REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (three independent experiments). (B) Expression of Pck1 and G6pc genes in AML12 cells treated with FSK or GC at the indicated times in serum-free media containing DEX (40 ng/ml) (three independent experiments). (C) Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα, pCREB, total CREB, and α-TUBULIN in AML12 cells treated with IBMX (200 μM) for the indicated time in serum-free media containing DEX (40 ng/ml). Histogram illustrates quantification of REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (three independent experiments). (D) Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα, pCREB, total CREB, and α-TUBULIN in AML12 cells treated with PKI (20 μM) for the indicated times in serum-free media containing DEX (40 ng/ml). Histogram shows quantification of REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (three independent experiments). (E) Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα, pCREB, total CREB, and α-TUBULIN in AML12 cells treated with FSK (10 μM) and MG132 (20 μM) for the indicated time in serum-free media containing DEX (40 ng/ml). Histogram represents quantification of REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (three independent experiments). (F) Western blot analysis for REV-ERBα, pCREB, total CREB, and α-TUBULIN in AML12 cells treated with IBMX (200 μM) and MG132 (20 μM) for the indicated times in serum-free media containing DEX (40 ng/ml). Histogram displays quantification of REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (three independent experiments). Data represent the means ± SEM with P value cutoff indicated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 as determined by multiple t test.
PKA targets serine residues on REV-ERBα to regulate protein stability
Our data support the hypothesis that activated PKA signaling promotes the degradation of REV-ERBα protein. To confirm that PKA-dependent signaling is responsible for REV-ERBα destabilization through proteasomal degradation, AML12 cells were treated with FSK, dbcAMP, GC, or IBMX with the addition of the proteasome inhibitor MG132. Degradation of REV-ERBα induced by the cAMP and PKA pathway activators was blocked in the presence of MG132 (Fig. 3, E and F, and fig. S6, A to D). We also performed the opposing experiment using a cycloheximide (CHX) chase to block new protein translation and identified that REV-ERBα is more rapidly degraded in the presence of FSK and GC versus PKI (fig. S6E). These data indicate that REV-ERBα protein stability is targeted by the PKA signaling pathway for proteasomal degradation.
To identify PKA-dependent phosphorylation sites on REV-ERBα, we used the Scansite (https://scansite4.mit.edu) and NetPhos programs (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk). Based on the PKA consensus motif, residue conservation among multiple species, and surface accessibility to the kinase, we selected S28, S160, and S281 as putative phosphorylation sites for further analysis. These three serine residues are well conserved among various species of vertebrates and might reflect their evolutionary importance in regulating REV-ERBα stability (Fig. 4A). Also, these sites are not located in the ligand-binding domain (Fig. 4A) and therefore are unlikely to perturb heme binding. S28, S160, and S281 were mutated to the non-phosphorylatable alanine by site-directed mutagenesis. The single mutation of each of these sites did not rescue REV-ERBα from degradation using IBMX, although a minor stabilization in protein level was observed with REV-ERBα S160A (Fig. 4B and fig. S7A). These findings are consistent with the fact that S160 was identified using Scansite as the strongest PKA phosphorylation motif within REV-ERBα. The double mutants, REV-ERBα S28A + S160A and REV-ERBα S28A + S281A, almost fully rescued REV-ERBα from PKA-dependent degradation, while REV-ERBα S160A + S281A prevented degradation by PKA activation (Fig. 4B and fig. S7A). These data suggest that all three sites are substrates for PKA, with S160 and S281 potentially being the two most important sites. Based on these findings, we created the non-degradable triple mutant, REV-ERBα S28A + S160A + S281A, which is fully stabilized in the presence of pharmacological PKA activation using IBMX (Fig. 4B and fig. S7A). In addition, the nondegradable triple mutant displayed an increased protein stability compared to WT using a CHX chase experiment (Fig. 4C and fig. S7B). To further pinpoint the direct contribution of these serine residues on REV-ERBα stability, we compared the S160A + S281A double mutant to the S28A + S160A + S281A triple mutant using a CHX chase experiment and identified that all three serine residues of the triple mutant contribute to the increased stability of REV-ERBα (Fig. 4C and fig. S7B). These data indicate that PKA targets REV-ERBα stability through three different conserved serine residues within the protein.
Fig. 4. Identification of PKA-dependent REV-ERBα phosphorylation sites.
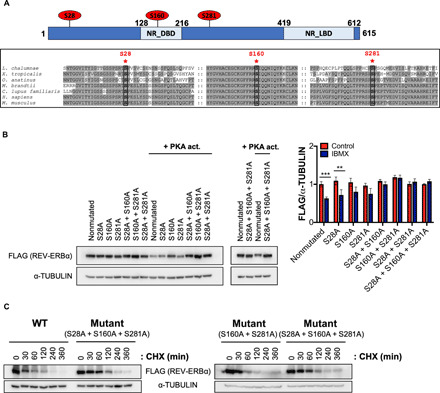
(A) Location and sequence conservation surrounding S28, S160, and S281 residues of REV-ERBα in vertebrates (Latimeria chalumnae, Xenopus tropicalis, Ornithorhynchus anatinus, Myotis brandtii, Canis lupus familiaris, Homo sapiens, and Mus musculus) using BoxShade (EMBnet). The nuclear receptor DNA binding domain (NR_DBD) and ligand-binding domain (NR_LBD) of REV-ERBα are indicated. (B) Western blot analysis of FLAG-tagged WT REV-ERBα or REV-ERBα single, double, or triple mutants in HEK293 cells treated with IBMX (1 mM) for 2 hours. Histogram displays quantification of FLAG-tagged REV-ERBα/α-TUBULIN (two independent experiments). (C) Western blot analysis of FLAG-tagged WT REV-ERBα or REV-ERBα double (S160A + S281A) or triple (S28A + S160A + S281A) mutants in AML12 cells treated with CHX (20 μg/ml) for 6 hours (two independent experiments). Data represent the means ± SEM with P value cutoff indicated as **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 as determined by multiple t test.
REV-ERBα controls Pck1 expression through promoter regulation
We identified a significant up-regulation of Pck1 gene expression in the livers of TB mice and PH isolated from these animals (Fig. 1F), yet the precise transcriptional regulatory mechanism of how REV-ERBα controls Pck1 expression needed further validation. To determine the binding pattern of REV-ERBα to the Pck1 promoter, we analyzed published chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) data (45). REV-ERBα binds to the proximal promoter of Pck1 in a region containing a strong and unique consensus hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α) recognition motif (Fig. 5A). In addition, the REV-ERBα cistrome in liver has been shown to overlap with HNF4α motifs (53, 54), where REV-ERBα tethers to the liver-specific transcription factor to regulate metabolic genes. This is in contrast to the direct occupancy of REV-ERBα at clock gene promoters through the RevDR2 response element (43). The protein level of HNF4α and its gene expression in the livers of WT and TB mice remained unchanged (fig. S7C), suggesting that Pck1 gene expression could be linked to the stability of the transcriptional repressor REV-ERBα.
Fig. 5. Transcriptional regulation by REV-ERBα of the Pck1 promoter.
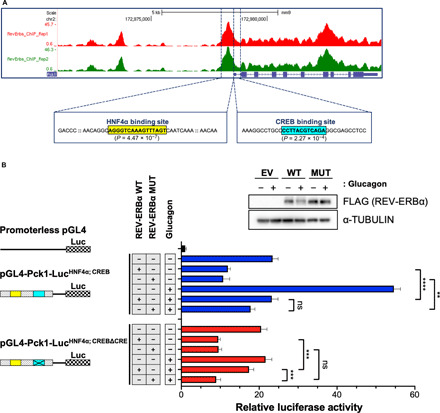
(A) Recruitment of REV-ERBα on the Pck1 promoter based on published ChIP-seq data (45). Binding sites of HNF4α and CREB in the proximal promoter region of Pck1 are indicated. (B) Luciferase assays were performed using WT PH that are ectopically expressed with the Pck1 luciferase reporter containing either WT (pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREB) or a six-nucleotide deletion of the CRE (pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREBΔCRE) and WT or the non-degradable REV-ERBα triple mutant (MUT). Transfected PH were treated the next day with either vehicle or GC (0.1 μM) for 8 hours before cells were harvested and luciferase assays performed. Quantification of relative luciferase activity is shown as a histogram (three independent experiments). Western blot analysis of FLAG-tagged WT REV-ERBα or MUT REV-ERBα in transfected PH used in the luciferase assays. Data represent the means ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA. ns, not significant.
To define the REV-ERBα–dependent regulation of Pck1 in a functional transcriptional assay, we constructed the Pck1-luciferase construct containing the proximal promoter region that harbors both the HNF4α and the CREB binding sites, pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREB. This CREB binding site was rated as the strongest CRE regulatory element, P value (2.27 × 10−4), according to the genome-wide position weight matrix scanner (https://ccg.epfl.ch//pwmscan/), and has been previously reported as a robust regulatory motif in the Pck1 proximal promoter (55, 56). Ectopic expression of WT and the REV-ERBα triple mutant repressed Pck1 gene transcription in isolated PH, and this repression was maintained when cells were treated with GC (Fig. 5B). One major limitation of this pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREB construct is its inability to discriminate between GC-stimulated CREB-dependent transcriptional activity versus REV-ERBα gene regulation through HNF4α binding of the Pck1 promoter. Therefore, to isolate these two opposing transcriptional regulatory axes, we mutated the consensus CRE. This is especially relevant given the strong induction of Pck1-dependent luciferase activity upon GC treatment, which is activated by CREB (Fig. 5B). We deleted the six central nucleotides of the consensus CREB recognition motif in the Pck1 promoter (pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREBΔCRE), consistent with previous reports that these central nucleotides within the CRE are critical for CREB binding to DNA (37, 38, 57). Using this pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREBΔCRE luciferase reporter, we observed an expected REV-ERBα–mediated repression of Pck1-driven luciferase activity (Fig. 5B). In contrast, upon GC treatment, a derepression of Pck1 gene transcription was observed with WT REV-ERBα, suggesting degradation of the transcriptional repressor (Fig. 5B). Conversely, the REV-ERBα phosphomutant was resistant to GC-dependent degradation and therefore significantly repressed Pck1 luciferase activity through the HNF4α regulatory motif (Fig. 5B). As a control, we confirmed the expected GC-mediated turnover of WT REV-ERBα, while the REV-ERBα mutant is stable in the presence of GC (Fig. 5B and fig. S7D). Collectively, these data suggest that degradation of REV-ERBα alleviates the transcriptional repression on Pck1 gene expression.
Degradation of hepatic REV-ERBα alleviates repression of gluconeogenesis to enhance de novo glucose production
Our data indicate that REV-ERBα represses Pck1 gene expression and this transcriptional inhibition is alleviated when REV-ERBα is degraded through the cAMP/PKA signaling axis. These data suggest that down-regulation of REV-ERBα protein in the livers of lung TB mice could derepress gluconeogenesis and subsequently enhance de novo glucose production. To test this hypothesis ex vivo and provide a physiological context for our findings, we performed a glucose production assay in synchronized PH isolated from livers of WT and lung TB mice. PH derived from livers of lung TB mice produced significantly more glucose than their WT counterparts after 120, 240, and 480 min, in the presence of gluconeogenic substrates lactate and pyruvate (Fig. 6A). In addition, we isolated PH from WT and TB mice and ectopically expressed REV-ERBα to determine its direct role in glucose production. Consistent with Fig. 6A, de novo glucose production was elevated from PH isolated from TB mice versus WT, and glucose levels were significantly suppressed upon ectopic expression of REV-ERBα, specifically in hepatocytes from TB mice (Fig. 6B). As a control, levels of REV-ERBα are quantified by Western blot analysis in PH isolated from WT and TB mice (Fig. 6C). To confirm this finding in vivo, a PTT was performed to quantify de novo glucose production, as an indicator of active gluconeogenesis. Overnight fasted WT and TB mice were administered pyruvate intraperitoneally and their blood glucose was measured over time. Lung TB mice had the largest fold change in blood glucose produced 1 hour post injection of pyruvate (Fig. 6D), which is indicative of active gluconeogenesis. When this PTT was performed using 2-month post-intratracheal viral delivery old mice, where REV-ERBα protein was not decreased in the liver (fig. S7E), no difference was observed in blood glucose levels (fig. S7F). These data demonstrate that lung TB mice have an enhanced rate of de novo glucose production through gluconeogenesis both in vivo and from PH isolated ex vivo.
Fig. 6. Glucose production and stable isotope tracing in WT and TB isolated PH.
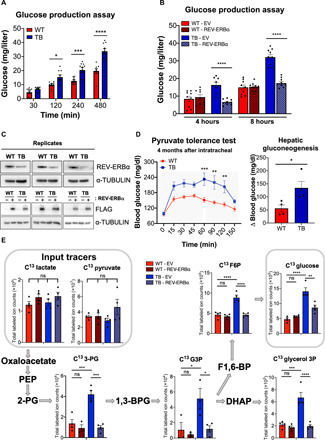
(A) Glucose production assays from DEX-synchronized PH (three independent experiments). Glucose concentration was measured in glucose-free buffer supplemented with pyruvate (2 mM) and lactate (20 mM) 12 hours after synchronization. (B) Glucose production assays from PH that are ectopically expressed with WT REV-ERBα (three independent experiments). Glucose concentration was measured in glucose-free buffer supplemented with pyruvate (2 mM) and lactate (20 mM) at 4 and 8 hours. (C) Top: Western blot analysis of endogenous REV-ERBα in PH used in the glucose production assays in Fig. 6A (three independent experiments). Bottom: Western blot analysis of FLAG-tagged REV-ERBα in transfected PH used in the glucose production assays in Fig. 6B (three independent experiments). (D) PTT in overnight-fasted mice, 4 months post intratracheal viral delivery (n = 5 mice per genotype). Sodium pyruvate (2 g/kg body weight) was administered by intraperitoneal injection. Fold increase in hepatic gluconeogenesis (from 0 to 60 min) after pyruvate injection (n = 5 mice per genotype), based on PTT data. (E) Labeled pyruvate, lactate, gluconeogenic intermediates, glycerol 3-phosphate (glycerol 3P), and glucose extracted from PH transfected with WT REV-ERBα and measured by LC–MS. Serum and glucose-free media were supplemented with 20 mM 13C lactate and 2 mM 13C pyruvate, and metabolites were extracted from cells after 8 hours incubation with the input tracers. Data represent the means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA (B and E), multiple t test (A and C), or unpaired Student’s t test (D). 3-PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate.
Lung adenocarcinomas are known to be highly glycolytic and metabolize glucose through aerobic glycolysis, or the Warburg effect, resulting in secretion of large amounts of lactate as a glycolytic by-product (58). Lactate has not only been shown to be the primary carbon source to fuel the tricarboxylic acid cycle in GEMMs of lung cancer (59, 60) but lactate is also converted to pyruvate to drive gluconeogenesis following pyruvate carboxylation to oxaloacetate (59, 60). We previously demonstrated that lung TB mice have elevated expression of lactate dehydrogenases (LDH) that interconvert lactate and pyruvate (27). Therefore, to trace the metabolic fate of lactate and pyruvate, PH isolated from WT and lung TB mice were incubated with uniformly labeled 13C (U-13C) lactate and U-13C pyruvate stable isotopes followed by targeted metabolomics analysis. The total abundance of U-13C lactate and pyruvate was similar between all samples (Fig. 6E). Incubation of U-13C lactate and pyruvate resulted in labeling of several gluconeogenic intermediates including 3-phosphoglycerate, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, and fructose 6-phosphate. PH isolated from TB mice had increased labeling of the gluconeogenic intermediates and glucose, which was dampened upon ectopic expression of REV-ERBα (Fig. 6E). Unexpectedly, we also observed elevated labeling of glycerol 3-phosphate in hepatocytes isolated from TB mice (Fig. 6E). This finding further supports the usage of lactate and pyruvate in a parallel pathway called glyceroneogenesis, which is used to synthesize triglycerides, and this pathway shares common enzymes with gluconeogenesis, including PEPCK (61). Using metabolic fate mapping through stable isotope tracing, our data indicate that gluconeogenesis is elevated in hepatocytes isolated from lung TB mice versus WT, and that REV-ERBα is a critical regulator of hepatic glucose production in a model of CAC.
DISCUSSION
Our findings define a previously unknown molecular mechanism for how the circadian protein REV-ERBα integrates hormonal signaling with the downstream modulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis (Fig. 7). Our model illustrates that GC signaling, mediated through the cAMP/PKA axis, is responsible for the proteasome-mediated degradation of REV-ERBα protein. Loss of REV-ERBα alleviates the transcriptional repression of gluconeogenic gene expression. Using a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma that undergoes CAC, we show that loss of hepatic REV-ERBα and activation of the gluconeogenic program enhance de novo glucose production in isolated PH from lung TB mice. In addition, using stable isotope metabolic tracing, we demonstrate that lactate and pyruvate are used as gluconeogenic substrates to produce increased glucose in hepatocytes from TB mice, which is suppressed by REV-ERBα. Together, our data demonstrate that the circadian protein REV-ERBα is an important point of convergence that integrates GC-mediated signaling with the direct control of glucose production from the liver. These findings suggest that elevated hepatic glucose production could be beneficial to support tumor metabolism, and further studies are required to address this.
Fig. 7. Model for REV-ERBα–dependent regulation of gluconeogenesis.
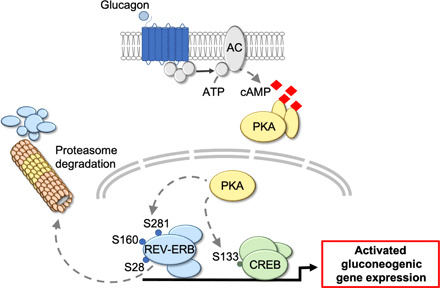
GC signaling activates the cAMP/PKA axis that targets REV-ERBα, on serine residues S28, S160, and S281, for proteasome-mediated degradation. Turnover of REV-ERBα protein alleviates the transcriptional repression of gluconeogenic target genes and results in elevated hepatic glucose production.
The circadian protein REV-ERBα is a nuclear hormone receptor that regulates rhythmic metabolic pathways in the liver (6, 7, 45, 62, 63). Rev-erbα−/− mice exhibit disrupted lipid metabolism and elevated fasting hyperglycemia (7, 44). Similarly, the Rev-erbα/β double knockout has been shown to modulate insulin signaling and systemic glucose levels (6, 45). Specifically, REV-ERBα is reported to repress the expression of gluconeogenic target genes Pck1 and G6pc (44), and the expression of Pck1 and the gluconeogenic pathway are known to be circadian. Yet, the upstream REV-ERB–dependent regulatory mechanism that governs rhythmic gluconeogenesis to control hepatic glucose production remained undefined. Our data now suggest that REV-ERBα stability is regulated by GC-activated PKA signaling, and degradation of the transcriptional repressor REV-ERBα activates gluconeogenic gene expression. In line with published ChIP-seq data (53), we now show through functional luciferase assays that REV-ERBα controls Pck1 expression through the HNF4α binding motif, located within the proximal promoter region of Pck1. Our data do not exclude a role for CREB in regulating Pck1 expression and the gluconeogenic program, but rather, we suggest a cooperative transcriptional regulatory function of REV-ERBα with the CREB pathway. Further experiments are required to define the precise cross-talk and timing of the PKA-dependent phosphorylation of REV-ERBα and CREB that dictate control of gluconeogenesis.
The opposing insulin and GC signaling pathways are a critical endocrine axis that control carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in the fed versus fasted states (64, 65). Given that nutritional deprivation activates GC-dependent signaling and downstream activation of glucose production (64, 65), these fasting-dependent endocrine and metabolic features mirror the biological consequences of CAC. Therefore, we believe that our findings regarding cachexia-induced activation of gluconeogenesis parallel fasting paradigms in terms of the role of the circadian clock. Consistent with our findings, fasting results in a marked down-regulation of REV-ERBα protein abundance in liver and muscle that is linked with the activation of fasting-sensing transcriptional pathways, such as CREB (19, 20). These data suggest that REV-ERBα could be the upstream regulatory node of the circadian clock that is coordinately controlled during nutritional deprivation and CAC. However, inherent downstream differences likely exist between fasting and CAC-dependent activation of gluconeogenesis based on substrate utilization for glucose production. For instance, glycogen stores are immediately liberated through glycogenolysis to regulate blood glucose levels during the initial stages of short-term fasting, which is subsequently followed by activation of gluconeogenesis (66). In our model of CAC, lung TB mice have depleted short-term energy storage depots (27) and instead rely primarily on gluconeogenesis for glucose production. Furthermore, our data indicate that lung TB mice use tumor-derived lactate, which is converted into pyruvate, as a substrate for hepatic glucose production based on PTT data and stable isotope tracing experiments (Fig. 6, C and D). To further support this concept, lung TB mice exhibit elevated expression of LDH and pyruvate in the liver (27), suggesting that tumor-derived lactate can readily be converted into pyruvate to fuel hepatic gluconeogenesis. Collectively, our findings indicate a potential parallel biological response between nutritional deprivation and CAC that impinges on GC-mediated activation of gluconeogenesis through the cAMP/PKA signaling axis to control REV-ERBα stability. However, further studies are needed to dissect the inherent differences between these metabolic adaptation responses that likely converge on substrate preference and utilization for hepatic glucose production.
Moreover, REV-ERBα is a dynamically regulated protein as evidenced by the different sites of phosphorylation that have been demonstrated to dictate its transcriptional activity and stability under fed versus fasted states. For example, the insulin axis through GSK3β has been reported to phosphorylate REV-ERBα at serine residues S55 and S59 to stabilize the protein (67). Also, untargeted mapping of the circadian phosphoproteome in the liver has revealed additional sites of rhythmic phosphorylation on REV-ERBα, including a known CDK1 site (68, 69). Our findings now demonstrate that PKA targets REV-ERBα to control its stability and regulate downstream gluconeogenic gene expression, and these results broaden the known mode of action of PKA (70, 71). Given this dynamic posttranslational regulation, these findings suggest that REV-ERBα may play an integral role in rewiring circadian metabolic rhythms. To support this hypothesis, our findings using a model of cachexia and recent published data looking at the fed/fasted state (72) place REV-ERBα as a central player in the adaptation response to metabolic perturbation, suggesting that this circadian protein could be a sensor for changes in metabolic homeostasis. Overall, these findings suggest that several signaling pathways and downstream kinases likely impinge on REV-ERBα to regulate its transcriptional activity, and further studies are required to delineate these pathways under various conditions of nutritional challenge and metabolic stress.
In addition, the circadian clock has also been reported to modulate gluconeogenesis through CRY-dependent inhibition of cAMP signaling and the CREB transcriptional pathway (39). Yet, published findings on the effects of fasting on the circadian clock reveal that CRY1 expression is actually markedly decreased in the liver (19, 23), where gluconeogenesis is actually activated. Therefore, an alternative model may support a role for the CRY proteins in fine-tuning gluconeogenesis exclusively during the day/night transition, while more severe insults such as fasting, starvation, and CAC may cause a robust rewiring of transcription that is dependent on REV-ERBα and its control of rhythmic metabolic pathways in the liver. Together, these data suggest that multiple pathways may regulate gluconeogenesis, and further studies are required to tease out the precise control of the circadian clock under nutritional challenge paradigms such as fasting, caloric restriction, time-restricted feeding, and starvation.
Our findings indicate that lung TB mice produce more hepatic glucose through gluconeogenesis (Fig. 6). These results are especially interesting in the context of tissue-tissue communication that is likely coordinated through the circadian clock, and specifically, it is of importance to dissect how these communication cues are altered in disease state. Mapping the metabolic fate of liver-derived glucose in GEMMs of cancer is imperative to determine whether this fuel source is shunted to the tumor to satisfy the heightened metabolic demand of rapidly proliferating cancer cells. In addition, the contribution of other peripheral tissues could be of interest to further characterize the extent of the tumor macroenvironment and how it is influenced by systemic metabolism. Although GC action is mainly liver specific, GC receptors are also expressed in human adipose tissue and can stimulate lipolysis through the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway, resulting in increased whole-body energy expenditure (73, 74). Also, REV-ERBα represses the gene expression of uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) (75). Therefore, loss of REV-ERBα could alleviate Ucp1 transcriptional repression to uncouple mitochondrial respiration, leading to elevated lipid mobilization and energy expenditure. Activated lipolysis and changes in mitochondrial respiration are hallmark features of cachexia (76), suggesting that REV-ERBα may play a role in cachexia-dependent changes in adipose tissue architecture and metabolism. Finally, determining whether cancer cachexia underpins activation of gluconeogenesis will be important to dissect in different GEMMs of cancer that undergo CAC, including pancreatic, gastric, and colorectal cancers. In summary, our findings define a molecular mechanism for GC-mediated activation of the cAMP/PKA axis that impinges on REV-ERBα as a central player in regulating gluconeogenesis and hepatic glucose production in a mouse model of cancer cachexia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animal housing and experimental procedures
KrasLSL-G12D/+;p53fl/fl mice have been previously described (46, 47, 77, 78). All experiments were performed in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines at the University of California, Irvine. Animals were housed in a standard 12-hour light/dark paradigm and fed ad libitum. For viral infection, ad5-CMV:FlpO or ad5-CMV:Cre (University of Iowa, Viral Vector Core) were used at a titer of 3 × 107 plaque-forming units and administered by intratracheal delivery. Mice were euthanized between 3.5 and 4 months post infection for tissue collection.
Construction of plasmids and site-directed mutagenesis
The proximal Pck1 promoter was amplified from mouse liver genomic DNA (The Jackson Laboratory) and cloned into pGL4.10[luc2] vector using restriction enzymes Sac I and Xho I to create the luciferase reporter Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREB, containing the consensus DNA binding motifs of HNF4α and CREB. Site-directed mutagenesis of Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREB was performed to delete the six central nucleotides of the CREB binding motif, the CRE to create Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREBΔCRE. Also, serine residues S28, S160, and S281 were mutated to alanine by site-directed mutagenesis. Primer sequences used for Pck1 promoter amplification, deletion of the CRE sequence, and generation of the REV-ERBα point mutants are listed in table S1.
Pyruvate tolerance test
WT and lung TB mice were overnight fasted for 12 hours. Blood samples were collected via tail tip excision and measured using a glucometer before the start of the experiment to measure basal glucose levels and at 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, and 150 min following administration of sodium pyruvate (2 g/kg body weight) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) by intraperitoneal injection.
Isolation of PH
KrasLSL-G12D/+;p53fl/fl mice at 3 to 3.5 months post infection were used for PH isolation. Mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital, and hepatocytes were isolated by collagenase perfusion as previously described, with slight modifications (79). Briefly, livers were perfused through the inferior vena cava with Ca2+-free Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer (115 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCI, 1 mM KH2PO4, 2.5 mM MgSO4, and 25 mM sodium HEPES) containing 0.5 mM EGTA for 5 min. Subsequently, livers were perfused with EGTA-free and Mg2+-free Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer (115 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCI, 1 mM KH2PO4, 25 mM sodium HEPES, and 1 mM CaCl2) containing collagenase (0.1 mg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) for 15 min. Hepatocytes were released from liver by mechanical disassociation in EGTA-free Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer (115 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCI, 1 mM KH2PO4, 25 mM sodium HEPES, 2.5 mM MgSO4, and 2 mM CaCl2) containing 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and filtered through a 70-μm nylon cell strainer. Viable hepatocytes were purified by centrifugation at 40g for 2 min. Viability of isolated PH was measured by trypan blue exclusion and viability was routinely determined to be over 90%.
PH glucose production assay
PH were isolated from WT and lung TB mice, cultured in low-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s media (DMEM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Indianapolis, IN) for 24 hours, and synchronized with 100 nM DEX in glucose-free DMEM-F12 media (Biowest, Riverside, MO) for 1 hour. For ectopic expression of REV-ERBα, PH isolated from livers of WT and TB mice were transfected using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Indianapolis, IN) and synchronized with DEX 24 hours later. After synchronization, PH were incubated 12 hours in DMEM-F12 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Then, cells were washed thoroughly with Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer (115 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCI, 1 mM KH2PO4, 25 mM sodium HEPES, 2.5 mM MgSO4, and 2 mM CaCl2) and incubated in Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer supplemented with 1% BSA, 20 mM lactate, and 2 mM pyruvate at 37°C. The media were removed at the indicated times and centrifuged at 15,000g for 10 min to remove debris. The glucose content of the supernatant was measured with the Glucose (HK) Assay Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Cell lysates were lysed and REV-ERBα protein level was determined by Western blotting.
Cell culture
AML12 cells were cultured in DMEM-F12 media (Corning, Corning, NY) supplemented with 10% FBS, insulin (10 μg/ml), transferrin (5.5 μg/ml), selenium (5 ng/ml), and DEX (40 ng/ml), supplemented with penicillin and streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells were cultured in high-glucose DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. Isolated PH were resuspended in low-glucose DMEM media supplemented with 10% FBS and cultured on tissue culture dishes coated with rat tail collagen (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 4 hours. For circadian analysis, isolated PH were incubated for 24 hours with glucose-free DMEM-F12 media containing 10% FBS. Subsequently, hepatocytes were changed to serum-free DMEM-F12 media containing 100 nM DEX for 1 hour to synchronize the circadian clock. Media were replaced with fresh serum-free DMEM-F12 media and incubated for 12 hours. Cells were harvested every 4 hours for circadian analysis. The third-generation lentivirus packaging system was used for overexpression of REV-ERBα in AML-12 cells. For lentivirus production, HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding lentiviral packaging (pRSV-Rev and pMDLg/pRRE), lentiviral envelope (pMD2.G), and the transfer vector containing our sequence of interest [pLenti-Rev-erbα WT, pLenti-Rev-erbα double mutant (S160A + S281A), or pLenti-Rev-erbα triple mutant (S28A + S160A + S281A)]. Lentivirus-containing media were harvested 48 hours after transfection and used for AML-12 infection.
Gene expression analysis
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Indianapolis, IN), according to manufacturer recommendations. Equal amounts of total RNA were reverse transcribed to complementary DNA (cDNA) using Maxima H Minus cDNA Synthesis Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Indianapolis, IN) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. cDNA was used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction using the PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Gene expression was normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA. Primer sequences used for gene expression analysis are listed in table S2.
Sample preparation for Western blotting
Livers were homogenized in ice-cold radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer [50 mM tris (pH 8), 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 15 mM MgCl2, and 1% NP-40] containing proteases and phosphatases inhibitors (1× cOmplete EDTA free cocktail tablet, 0.5 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 20 mM NaF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM Na4P2O7, and 100 μM C3H7Na2O6P) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Samples were nutated for 20 min at 4°C and sonicated briefly. Cell lines and PH were washed with 1× phosphate-buffered saline, harvested in RIPA lysis buffer, rocked, and briefly sonicated. Samples were centrifugated at top speed for 10 min at 4°C and the supernatant was collected. Protein concentrations were measured using Bradford reagent and a Varioskan LUX multimode microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Indianapolis, IN). Ten to fifty micrograms of lysate was resolved on SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels. Antibodies used for Western blots were REV-ERBα, phospho-CREB, total CREB (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), BMAL1, TATA box–binding protein (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), CRY1 (Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, TX), and α-TUBULIN (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO).
Nuclear fractionation
Nuclear fractionation in mouse liver was performed according to a previously published protocol, with slight modifications (80). Briefly, mouse liver was resuspended and homogenized in STM buffer [250 mM sucrose, 50 mM tris-HCl (pH 7.4), and 5 mM MgCl2, containing proteases and phosphatases inhibitors]. The homogenate was incubated on ice for 30 min, vortexed, and centrifuged at 800g for 15 min. The pellet contains nuclei and debris, and the supernatant comprises the cytosol. The pellet was washed 2× in STM buffer, resuspended in NET buffer [20 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 M NaCl, 0.2 mM EDTA, 20% glycerol, and 1% Triton X-100, containing proteases and phosphatases inhibitors], incubated on ice for 30 min, briefly sonicated, and centrifuged at 9000g for 30 min. The resultant supernatant is the final nuclear fraction. The supernatant from the homogenate was washed 2× in STM buffer, centrifuged at 11,000g for 10 min, and the resultant supernatant was collected and constitutes the final cytosolic fraction.
Luciferase reporter assays
PH isolated from livers of WT mice were transfected with p3XFLAG-CMV-7.1 plasmid containing either WT or REV-ERBα triple phosphomutant using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Indianapolis, IN), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. LacZ was ectopically expressed with pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREB or pGL4-Pck1-LucHNF4α; CREBΔCRE. Transfected PH were treated with or without GC (0.1 μM) for 8 hours and subsequently harvested with luciferase lysis buffer [25 mM tris (pH 7.8), 2 mM EDTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 10% glycerol, and 1% Triton X-100] after 24 hours. Cell lysates were mixed with luciferase reaction buffer [20 mM tris (pH 7.8), 1.07 mM MgCl2, 2.7 mM MgSO4, 0.1 mM EDTA, 33.3 mM DTT, 470 μM beetle luciferin, 530 μM ATP, and 270 μM coenzyme A], and luminescence was detected with Varioskan LUX multimode microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Indianapolis, IN). β-Galactosidase measurements were performed at 450 nm and used for normalization of luciferase light units.
Metabolite extraction for metabolomics
Metabolites were extracted from 1 million isolated PH cultured in a 6-well plate. Nine hundred microliters of ice-cold 80% MeOH (extraction solvent) containing 0.5% formic acid was added to each well and the plate was gently nutated for 10 s. NH4HCO3 [15% (w/v); 80 μl for 900 μl of a 80% MeOH solution] was added to every well to neutralize pH. Plates were placed in −80°C for 1 hour. Cells were scraped and the entire content of the well was transferred to an Eppendorf tube. The well was rinsed with a small amount of ice-cold 80% MeOH and the remaining cells were added to the tube. Samples were vortexed for 10 s and centrifuged at 16,000g for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant was transferred to a new tube (first extraction), and 100 μl of extraction solvent was added to resuspend the pellet, followed by vortexing and centrifugation at 16,000g for 5 min at 4°C. The resulting supernatant that represents the second extraction was combined with the first extraction. The extract was dried down with nitrogen to concentrate metabolites 10 times. The samples were centrifuged at 16,000g for 10 min at 4°C, and 30 μl of supernatant was transferred to vials for mass spectrometry analysis.
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry metabolomics analysis
Metabolite abundance and labeling was measured by quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometer (Q Exactive Plus Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer, Thermo Fisher Scientific), operating in a negative ion mode via electrospray ionization and used to scan from mass/charge ratio 70 to 830 and 140,000 resolution. Liquid chromatography (LC) separation was on an Xbridge BEH Amide column (2.1 mm by 150 mm, 2.5-μm particle size, 130-Å pore size; Waters) at 25°C using a gradient of solvent A (5% acetonitrile in water with 20 mM ammonium acetate and 20 mM ammonium hydroxide) and solvent B (100% acetonitrile). Flow rate was 350 μl/min. The LC gradient was as follows: 0 min, 75% B; 3 min, 75% B; 4 min, 50% B; 5 min, 10% B; 7 min, 10% B; 7.5 min, 75% B; and 11 min, 75% B. The injection volume of the sample was 3 μl. Data were analyzed using the MAVEN software, and natural isotope correction was performed with the AccuCor R code (https://github.com/XiaoyangSu/AccuCor).
Acknowledgments
Human and mouse REV-ERBα expression plasmids were a gift from the lab of M. Lazar (University of Pennsylvania). Also, the pGL4-Basic luciferase plasmid used for construction of the Pck1 reporter was a gift from the lab of P. Kaiser (University of California, Irvine). We thank J. ten Hoeve and T. G. Graeber (UCLA Metabolomics Center) for the helpful discussions. Funding: A.V. was supported by the Hitachi-Nomura postdoctoral fellowship awarded through the Department of Biological Chemistry at the University of California, Irvine. Financial support for the S.M. laboratory is provided through the NIH (K22CA212045 and R01CA244519), the Concern Foundation, the V Foundation for Cancer Research, the Cancer Research Coordinating Committee, and shared resources supported through the Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center (P30CA062203) at the University of California, Irvine. Author contributions: A.V. and S.M. conceived the research and designed the experiments. A.V. performed intratracheal delivery of adenovirus in mice, in vivo experiments, molecular studies in vitro, and metabolite extraction. S.K.C. performed PH isolation, ex vivo studies with this PH model system, glucose production assays, and in vitro studies. M.O.G. and B.M.F. provided assistance with in vitro experiments. C.J. and H.B. performed LC-MS data acquisition and analysis. A.V., S.K.C., and S.M. performed data analysis and wrote the manuscript, with input from all coauthors. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Data and materials availability: All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper and/or the Supplementary Materials. Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the authors.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/7/26/eabf3885/DC1
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Verlande A., Masri S., Circadian clocks and cancer: Timekeeping governs cellular metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 30, 445–458 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Partch C. L., Green C. B., Takahashi J. S., Molecular architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Trends Cell Biol. 24, 90–99 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rudic R. D., McNamara P., Curtis A.-M., Boston R. C., Panda S., Hogenesch J. B., FitzGerald G. A., BMAL1 and CLOCK, two essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in glucose homeostasis. PLOS Biol. 2, e377 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dyar K. A., Ciciliot S., Wright L. E., Biensø R. S., Tagliazucchi G. M., Patel V. R., Forcato M., Paz M. I. P., Gudiksen A., Solagna F., Albiero M., Moretti I., Eckel-Mahan K. L., Baldi P., Sassone-Corsi P., Rizzuto R., Bicciato S., Pilegaard H., Blaauw B., Schiaffino S., Muscle insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism are controlled by the intrinsic muscle clock. Mol. Metab. 3, 29–41 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aviram R., Manella G., Kopelman N., Neufeld-Cohen A., Zwighaft Z., Elimelech M., Adamovich Y., Golik M., Wang C., Han X., Asher G., Lipidomics analyses reveal temporal and spatial lipid organization and uncover daily oscillations in intracellular organelles. Mol. Cell 62, 636–648 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cho H., Zhao X., Hatori M., Yu R. T., Barish G. D., Lam M. T., Chong L.-W., DiTacchio L., Atkins A. R., Glass C. K., Liddle C., Auwerx J., Downes M., Panda S., Evans R. M., Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and REV-ERB-β. Nature 485, 123–127 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Feng D., Liu T., Sun Z., Bugge A., Mullican S. E., Alenghat T., Liu X. S., Lazar M. A., A circadian rhythm orchestrated by histone deacetylase 3 controls hepatic lipid metabolism. Science 331, 1315–1319 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Krishnaiah S. Y., Wu G., Altman B. J., Growe J., Rhoades S. D., Coldren F., Venkataraman A., Olarerin-George A. O., Francey L. J., Mukherjee S., Girish S., Selby C. P., Cal S., Er U., Sianati B., Sengupta A., Anafi R. C., Kavakli I. H., Sancar A., Baur J. A., Dang C. V., Hogenesch J. B., Weljie A. M., Clock regulation of metabolites reveals coupling between transcription and metabolism. Cell Metab. 25, 961–974.e4 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Eckel-Mahan K. L., Patel V. R., Mohney R. P., Vignola K. S., Baldi P., Sassone-Corsi P., Coordination of the transcriptome and metabolome by the circadian clock. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109, 5541–5546 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dyar K. A., Lutter D., Artati A., Ceglia N. J., Liu Y., Armenta D., Jastroch M., Schneider S., de Mateo S., Cervantes M., Abbondante S., Tognini P., Orozco-Solis R., Kinouchi K., Wang C., Swerdloff R., Nadeef S., Masri S., Magistretti P., Orlando V., Borrelli E., Uhlenhaut N. H., Baldi P., Adamski J., Tschöp M. H., Eckel-Mahan K., Sassone-Corsi P., Atlas of circadian metabolism reveals system-wide coordination and communication between clocks. Cell 174, 1571–1585.e11 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bass J., Lazar M. A., Circadian time signatures of fitness and disease. Science 354, 994–999 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guan D., Xiong Y., Trinh T. M., Xiao Y., Hu W., Jiang C., Dierickx P., Jang C., Rabinowitz J. D., Lazar M. A., The hepatocyte clock and feeding control chronophysiology of multiple liver cell types. Science 369, 1388–1394 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Masri S., Sassone-Corsi P., The emerging link between cancer, metabolism, and circadian rhythms. Nat. Med. 24, 1795–1803 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chaix A., Zarrinpar A., Miu P., Panda S., Time-restricted feeding is a preventative and therapeutic intervention against diverse nutritional challenges. Cell Metab. 20, 991–1005 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chaix A., Lin T., Le H. D., Chang M. W., Panda S., Time-restricted feeding prevents obesity and metabolic syndrome in mice lacking a circadian clock. Cell Metab. 29, 303–319.e4 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hatori M., Vollmers C., Zarrinpar A., DiTacchio L., Bushong E. A., Gill S., Leblanc M., Chaix A., Joens M., Fitzpatrick J. A. J., Ellisman M. H., Panda S., Time-restricted feeding without reducing caloric intake prevents metabolic diseases in mice fed a high-fat diet. Cell Metab. 15, 848–860 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stokkan K. A., Yamazaki S., Tei H., Sakaki Y., Menaker M., Entrainment of the circadian clock in the liver by feeding. Science 291, 490–493 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Damiola F., Le Minh N., Preitner N., Kornmann B., Fleury-Olela F., Schibler U., Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes Dev. 14, 2950–2961 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kinouchi K., Magnan C., Ceglia N., Liu Y., Cervantes M., Pastore N., Huynh T., Ballabio A., Baldi P., Masri S., Sassone-Corsi P., Fasting imparts a switch to alternative daily pathways in liver and muscle. Cell Rep. 25, 3299–3314.e6 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kondratov R. V., Kondratova A. A., Gorbacheva V. Y., Vykhovanets O. V., Antoch M. P., Early aging and age-related pathologies in mice deficient in BMAL1, the core componentof the circadian clock. Genes Dev. 20, 1868–1873 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sato S., Solanas G., Peixoto F. O., Bee L., Symeonidi A., Schmidt M. S., Brenner C., Masri S., Benitah S. A., Sassone-Corsi P., Circadian reprogramming in the liver identifies metabolic pathways of aging. Cell 170, 664–677.e11 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Salzer M. C., Lafzi A., Berenguer-Llergo A., Youssif C., Castellanos A., Solanas G., Peixoto F. O., Stephan-Otto Attolini C., Prats N., Aguilera M., Martín-Caballero J., Heyn H., Benitah S. A., Identity noise and adipogenic traits characterize dermal fibroblast aging. Cell 175, 1575–1590.e22 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Patel S. A., Velingkaar N., Makwana K., Chaudhari A., Kondratov R., Calorie restriction regulates circadian clock gene expression through BMAL1 dependent and independent mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 6, 25970 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kohsaka A., Laposky A. D., Ramsey K. M., Estrada C., Joshu C., Kobayashi Y., Turek F. W., Bass J., High-fat diet disrupts behavioral and molecular circadian rhythms in mice. Cell Metab. 6, 414–421 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Eckel-Mahan K. L., Patel V. R., de Mateo S., Orozco-Solis R., Ceglia N. J., Sahar S., Dilag-Penilla S. A., Dyar K. A., Baldi P., Sassone-Corsi P., Reprogramming of the circadian clock by nutritional challenge. Cell 155, 1464–1478 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hojo H., Enya S., Arai M., Suzuki Y., Nojiri T., Kangawa K., Koyama S., Kawaoka S., Remote reprogramming of hepatic circadian transcriptome by breast cancer. Oncotarget 8, 34128–34140 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Masri S., Papagiannakopoulos T., Kinouchi K., Liu Y., Cervantes M., Baldi P., Jacks T., Sassone-Corsi P., Lung adenocarcinoma distally rewires hepatic circadian homeostasis. Cell 165, 896–909 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Al-Zhoughbi W., Huang J., Paramasivan G. S., Till H., Pichler M., Guertl-Lackner B., Hoefler G., Tumor macroenvironment and metabolism. Semin. Oncol. 41, 281–295 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Baracos V. E., Martin L., Korc M., Guttridge D. C., Fearon K. C. H., Cancer-associated cachexia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 4, 17105 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Porporato P. E., Understanding cachexia as a cancer metabolism syndrome. Oncogenesis 5, e200 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Holroyde C. P., Skutches C. L., Boden G., Reichard G. A., Glucose metabolism in cachectic patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 44, 5910–5913 (1984). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Edén E., Edström S., Bennegård K., Scherstén T., Lundholm K., Glucose flux in relation to energy expenditure in malnourished patients with and without cancer during periods of fasting and feeding. Cancer Res. 44, 1718–1724 (1984). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rohm M., Zeigerer A., Machado J., Herzig S., Energy metabolism in cachexia. EMBO Rep. 20, e47258 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shearer J. D., Buzby G. P., Mullen J. L., Miller E., Caldwell M. D., Alteration in pyruvate metabolism in the liver of tumor-bearing rats. Cancer Res. 44, 4443–4446 (1984). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu Y., Dentin R., Chen D., Hedrick S., Ravnskjaer K., Schenk S., Milne J., Meyers D. J., Cole P., Iii J. Y., Olefsky J., Guarente L., Montminy M., A fasting inducible switch modulates gluconeogenesis via activator/coactivator exchange. Nature 456, 269–273 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rodgers J. T., Lerin C., Haas W., Gygi S. P., Spiegelman B. M., Puigserver P., Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1α and SIRT1. Nature 434, 113–118 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W. III, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R., A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature 337, 749–752 (1989). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R., Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell 59, 675–680 (1989). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang E. E., Liu Y., Dentin R., Pongsawakul P. Y., Liu A. C., Hirota T., Nusinow D. A., Sun X., Landais S., Kodama Y., Brenner D. A., Montminy M., Kay S. A., Cryptochrome mediates circadian regulation of cAMP signaling and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Nat. Med. 16, 1152–1156 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lamia K. A., Papp S. J., Yu R. T., Barish G. D., Uhlenhaut N. H., Jonker J. W., Downes M., Evans R. M., Cryptochromes mediate rhythmic repression of the glucocorticoid receptor. Nature 480, 552–556 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.So A. Y.-L., Bernal T. U., Pillsbury M. L., Yamamoto K. R., Feldman B. J., Glucocorticoid regulation of the circadian clock modulates glucose homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106, 17582–17587 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kriebs A., Jordan S. D., Soto E., Henriksson E., Sandate C. R., Vaughan M. E., Chan A. B., Duglan D., Papp S. J., Huber A.-L., Afetian M. E., Yu R. T., Zhao X., Downes M., Evans R. M., Lamia K. A., Circadian repressors CRY1 and CRY2 broadly interact with nuclear receptors and modulate transcriptional activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, 8776–8781 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Preitner N., Damiola F., Lopez-Molina L., Zakany J., Duboule D., Albrecht U., Schibler U., The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBα controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell 110, 251–260 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yin L., Wu N., Curtin J. C., Qatanani M., Szwergold N. R., Reid R. A., Waitt G. M., Parks D. J., Pearce K. H., Wisely G. B., Lazar M. A., Rev-erbα, a heme sensor that coordinates metabolic and circadian pathways. Science 318, 1786–1789 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bugge A., Feng D., Everett L. J., Briggs E. R., Mullican S. E., Wang F., Jager J., Lazar M. A., Rev-erbα and Rev-erbβ coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic function. Genes Dev. 26, 657–667 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jackson E. L., Willis N., Mercer K., Bronson R. T., Crowley D., Montoya R., Jacks T., Tuveson D. A., Analysis of lung tumor initiation and progression using conditional expression of oncogenic K-ras. Genes Dev. 15, 3243–3248 (2001). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jackson E. L., Olive K. P., Tuveson D. A., Bronson R., Crowley D., Brown M., Jacks T., The differential effects of mutant p53 alleles on advanced murine lung cancer. Cancer Res. 65, 10280–10288 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Papagiannakopoulos T., Bauer M. R., Davidson S. M., Heimann M., Subbaraj L., Bhutkar A., Bartlebaugh J., Vander Heiden M. G., Jacks T., Circadian rhythm disruption promotes lung tumorigenesis. Cell Metab. 24, 324–331 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fearon K., Strasser F., Anker S. D., Bosaeus I., Bruera E., Fainsinger R. L., Jatoi A., Loprinzi C., MacDonald N., Mantovani G., Davis M., Muscaritoli M., Ottery F., Radbruch L., Ravasco P., Walsh D., Wilcock A., Kaasa S., Baracos V. E., Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: An international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 12, 489–495 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rognstad R., Rate-limiting steps in metabolic pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 254, 1875–1878 (1979). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tse T. F., Clutter W. E., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E., Mechanisms of postprandial glucose counterregulation in man. Physiologic roles of glucagon and epinephrine vis-a-vis insulin in the prevention of hypoglycemia late after glucose ingestion. J. Clin. Invest. 72, 278–286 (1983). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jelinek L. J., Lok S., Rosenberg G. B., Smith R. A., Grant F. J., Biggs S., Bensch P. A., Kuijper J. L., Sheppard P. O., Sprecher C. A., Expression cloning and signaling properties of the rat glucagon receptor. Science 259, 1614–1616 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhang Y., Fang B., Emmett M. J., Damle M., Sun Z., Feng D., Armour S. M., Remsberg J. R., Jager J., Soccio R. E., Steger D. J., Lazar M. A., Discrete functions of nuclear receptor Rev-erbα couple metabolism to the clock. Science 348, 1488–1492 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhang Y., Fang B., Damle M., Guan D., Li Z., Kim Y. H., Gannon M., Lazar M. A., HNF6 and Rev-erbα integrate hepatic lipid metabolism by overlapping and distinct transcriptional mechanisms. Genes Dev. 30, 1636–1644 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bokar J. A., Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Kaetzel D. M., Hanson R. W., Nilson J. H., Characterization of the cAMP responsive elements from the genes for the alpha-subunit of glycoprotein hormones and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Conserved features of nuclear protein binding between tissues and species. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 19740–19747 (1988). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Quinn P. G., Wong T. W., Magnuson M. A., Shabb J. B., Granner D. K., Identification of basal and cyclic AMP regulatory elements in the promoter of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8, 3467–3475 (1988). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H. III, Montminy M. R., Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature 334, 494–498 (1988). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hensley C. T., Faubert B., Yuan Q., Lev-Cohain N., Jin E., Kim J., Jiang L., Ko B., Skelton R., Loudat L., Wodzak M., Klimko C., McMillan E., Butt Y., Ni M., Oliver D., Torrealba J., Malloy C. R., Kernstine K., Lenkinski R. E., DeBerardinis R. J., Metabolic heterogeneity in human lung tumors. Cell 164, 681–694 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Faubert B., Li K. Y., Cai L., Hensley C. T., Kim J., Zacharias L. G., Yang C., Do Q. N., Doucette S., Burguete D., Li H., Huet G., Yuan Q., Wigal T., Butt Y., Ni M., Torrealba J., Oliver D., Lenkinski R. E., Malloy C. R., Wachsmann J. W., Young J. D., Kernstine K., DeBerardinis R. J., Lactate metabolism in human lung tumors. Cell 171, 358–371.e9 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hui S., Ghergurovich J. M., Morscher R. J., Jang C., Teng X., Lu W., Esparza L. A., Reya T., Zhan L., Guo J. Y., White E., Rabinowitz J. D., Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate. Nature 551, 115–118 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kalhan S. C., Mahajan S., Burkett E., Reshef L., Hanson R. W., Glyceroneogenesis and the source of glycerol for hepatic triacylglycerol synthesis in humans. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 12928–12931 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Le Martelot G., Claudel T., Gatfield D., Schaad O., Kornmann B., Sasso L., Moschetta A., Schibler U., REV-ERBα participates in circadian SREBP signaling and bile acid homeostasis. PLOS Biol. 7, e1000181 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Raspé E., Duez H., Mansén A., Fontaine C., Fiévet C., Fruchart J.-C., Vennström B., Staels B., Identification of Rev-erbα as a physiological repressor of apoC-III gene transcription. J. Lipid Res. 43, 2172–2179 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Longuet C., Sinclair E. M., Maida A., Baggio L. L., Maziarz M., Charron M. J., Drucker D. J., The glucagon receptor is required for the adaptive metabolic response to fasting. Cell Metab. 8, 359–371 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ramnanan C. J., Edgerton D. S., Kraft G., Cherrington A. D., Physiologic action of glucagon on liver glucose metabolism. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 13, 118–125 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Roach P., Glycogen and its metabolism. Curr. Mol. Med. 2, 101–120 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Yin L., Wang J., Klein P. S., Lazar M. A., Nuclear receptor Rev-erbα is a critical lithium-sensitive component of the circadian clock. Science 311, 1002–1005 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Robles M. S., Humphrey S. J., Mann M., Phosphorylation is a central mechanism for circadian control of metabolism and physiology. Cell Metab. 25, 118–127 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wang J., Mauvoisin D., Martin E., Atger F., Galindo A. N., Dayon L., Sizzano F., Palini A., Kussmann M., Waridel P., Quadroni M., Dulić V., Naef F., Gachon F., Nuclear proteomics uncovers diurnal regulatory landscapes in mouse liver. Cell Metab. 25, 102–117 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Berthet J., Rall T., Sutherland E., The relationship of epinephrine and glucagon to liver phosphorylase. IV. Effect of epinephrine and glucagon on the reactivation of phosphorylase in liver homogenates. J. Biol. Chem. 224, 463–475 (1957). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Petersen M. C., Vatner D. F., Shulman G. I., Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 13, 572–587 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Hunter A. L., Pelekanou C. E., Adamson A., Downton P., Barron N. J., Cornfield T., Poolman T. M., Humphreys N., Cunningham P. S., Hodson L., Loudon A. S. I., Iqbal M., Bechtold D. A., Ray D. W., Nuclear receptor REVERBα is a state-dependent regulator of liver energy metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. , 25869–25879 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mérida E., Delgado E., Valverde I., Molina L. M., Villanueva-Peñacarrillo M. L., Valverde I., Presence of glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36)amide receptors in solubilized membranes of human adipose tissue. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 77, 1654–1657 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Slavin B., Ong J., Kern P., Hormonal regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase activity and mRNA levels in isolated rat adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 35, 1535–1541 (1994). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gerhart-Hines Z., Feng D., Emmett M. J., Everett L. J., Loro E., Briggs E. R., Bugge A., Hou C., Ferrara C., Seale P., Pryma D. A., Khurana T. S., Lazar M. A., The nuclear receptor Rev-erbα controls circadian thermogenic plasticity. Nature 503, 410–413 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Argilés J. M., Busquets S., Stemmler B., López-Soriano F. J., Cancer cachexia: Understanding the molecular basis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 754–762 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Johnson L., Mercer K., Greenbaum D., Bronson R. T., Crowley D., Tuveson D. A., Jacks T., Somatic activation of the K-ras oncogene causes early onset lung cancer in mice. Nature 410, 1111–1116 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.DuPage M., Dooley A. L., Jacks T., Conditional mouse lung cancer models using adenoviral or lentiviral delivery of Cre recombinase. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1064–1072 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Chun S. K., Lee S., Flores-Toro J., U R. Y., Yang M.-J., Go K. L., Biel T. G., Miney C. E., Louis S. P., Law B. K., Law M. E., Thomas E. M., Behrns K. E., Leeuwenburgh C., Kim J.-S., Loss of sirtuin 1 and mitofusin 2 contributes to enhanced ischemia/reperfusion injury in aged livers. Aging Cell 17, e12761 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Dimauro I., Pearson T., Caporossi D., Jackson M. J., A simple protocol for the subcellular fractionation of skeletal muscle cells and tissue. BMC. Res. Notes 5, 513 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/7/26/eabf3885/DC1


