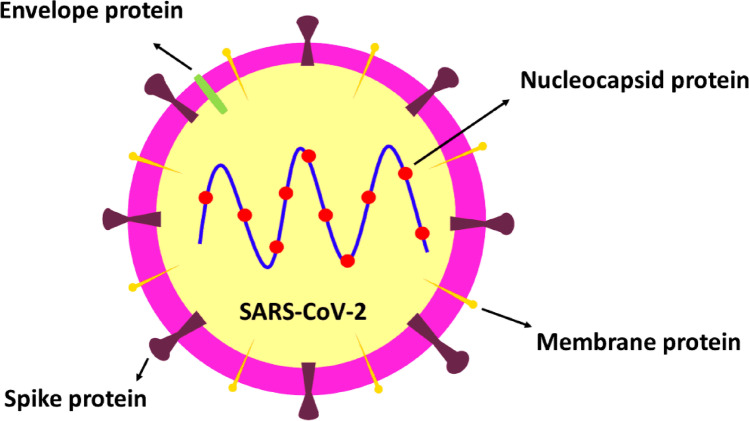
One and a half year has passed since the outbreak of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Nowadays information on SARS-CoV-2 and its receptors are increasing. It’s been showed that O-acetylated sialic acids (SAs) can interact with viral spike glycoprotein for the primary attachment of virus and its penetration into the host cells [1]. Most beta coronaviruses recognize 9-O-acetyl-SAs but it has changed to 4-O-acetyl-SA through the evolution of Coronaviruses [1]. Its viral ligand, the hemagglutinin esterase (HE) gene was transmitted to a beta coronavirus lineage A through horizontal gene adaption from a 9-O-acetyl-SA–specific HEF, as in influenza C [1, 2]. Adaption of HE occurs via cross-species transmission and HE evolution [1]. This fact demonstrates viral evolutionary compatibility to host glycans. Thus, studying emerging viruses like SARS-CoV-2 may result in better recognition of viral evolution process. For instance, as mentioned above, HE gene transfer is discovered in the beta coronaviruses, which choose 9-di-O-Ac-SAs. A more interesting example of such events happens in the murine CoVs, with attachment to two various subtypes of the canonical 9-O-Ac-SA (type I) and unique 4-O-Ac-SA (type II) [3]. But noticeably it must be mentioned that same as SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV genome has no HE gene [4]. Incorrectly a recent published article in the journal of stem cell reviews and reports states that SARS-CoV-2 has HE and hemagglutinin protein [5], also the authors has illustrated viral hemagglutinin glycoprotein on viral envelope. This is in contrast to previous studies which experimentally showed that SARS-CoV-2 lacks HE gene and glycoprotein. According to data from different full genome sequencing studies using next generation sequencing (NGS) and phylogenic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 virus has no HE gene and consequently HE glycoprotein [4]. Therefore this virus lacks HE gene and cannot carry HE protein (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Kim C-H. SARS-CoV-2 evolutionary adaptation toward host entry and recognition of receptor O-Acetyl sialylation in virus–host interaction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020;21(12):4549. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kienzle TE, Abraham S, Hogue B, Brian DA. Structure and orientation of expressed bovine coronavirus hemagglutinin-esterase protein. Journal of Virology. 1990;64(4):1834–1838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1834-1838.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Langereis MA, Van Vliet AL, Boot W, De Groot RJ. Attachment of mouse hepatitis virus to O-acetylated sialic acid is mediated by hemagglutinin-esterase and not by the spike protein. Journal of Virology. 2010;84(17):8970–8974. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00566-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chan JF-W, Kok K-H, Zhu Z, Chu H, To KK-W, Yuan S, et al. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerging Microbes & Infections. 2020;9(1):221–36. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bagheri, H. S., Karimipour, M., Heidarzadeh, M., Rajabi, H., Sokullu, E., & Rahbarghazi, R. (2021). Does the global outbreak of COVID-19 or other viral diseases threaten the stem cell reservoir inside the body? Stem Cell Reviews and Reports, 17, 214–230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]