Abstract
Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD) is a tickborne hemorrhagic disease affecting primates along the Western Ghats mountain range in India. Our retrospective study indicated that >3,314 monkey deaths attributed to KFD were reported in KFD-endemic states in India during 1957–2020. These data can help guide surveillance to protect animal and human health.
Keywords: Kyasanur Forest disease, vector-borne infections, tickborne diseases, monkey, deaths, sentinel species, meningitis/encephalitis, viruses, primates, India
Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD) is a highly infectious tickborne disease affecting humans and monkeys. The etiologic agent of this disease is the Kyasanur Forest disease virus (KFDV), a flavivirus. Since its discovery in 1957 in Karnataka State, India, KFD has expanded to 5 states along the western coastline in India (1) and ≈10,000 reported cases of KFD in humans, averaging 400–500 cases annually (2). After an incubation period of 3–8 days, primary clinical symptoms include fever, myalgia, and gastrointestinal and bleeding problems. In a small subset of patients, a second phase of the disease can include neurologic manifestations and fever. If the disease is detected early, symptomatic supportive care can improve recovery from the disease. Case-fatality rates range from 3% to 15% (1,3). The primary vectors of KFDV are Haemaphysalis spinigera and H. turturis ticks, which are endemic to southern India and transmit the virus to monkeys and humans (4). Larvae and nymphs of these ticks feed on monkeys when the monkeys are ground foraging, providing routes of infection and spread. In addition, KFDV can be transmitted transovarially in these ticks (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
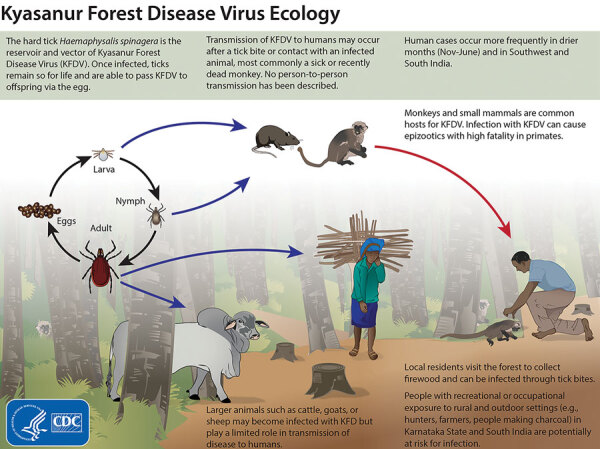
Ecology of Kyasanur Forest disease virus. Reproduced from https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/kyasanur/resources/virus-ecology.html.
Macaca radiata and Semnopithecus entellus are 2 monkey species in the KFD-endemic region frequently associated with KFD; these monkeys can succumb to the virus quickly (3). For monkeys, KFDV causes nonspecific and degenerative changes in abdominal organs, hemorrhage, and encephalitis. Experimentally infected monkeys have diarrhea, bradycardia, and hypotension and ultimately die (5). Monkey migration might expand KFDV geographic distribution, in which infected ticks are carried across state borders through connected natural areas (1,3,4). Although reporting of monkey deaths from KFD during the past 60 years has been unsystematic and inconsistent, the data provide valuable information. We summarize reports of monkey deaths connected with KFD in India and evaluate the utility of reporting KFD occurrence in monkeys for human disease surveillance.
The Study
We conducted a retrospective review of scientific literature through Web of Science, PubMed Central, and Google Scholar and included data from Pro-MED Mail, newspapers, and government reports issued during 1957–2020. The search keywords included KFD, KFDV, monkey fever, Kyasanur Forest disease, and mankan kayla (a local term in Karnataka, India). We used 55 peer-reviewed journal articles, 109 Pro-MED Mail reports, 1 report by the Karnataka State government, and 1 newspaper report to generate estimates. We created a database from all information sources; our final dataset (Table 1) contains the most updated information for all years from the available data.
Table 1. Monkey deaths attributed to Kyasanur Forest disease in the southwestern states of India, 1957–2020*.
| Year | Total no. monkey deaths | No. monkey deaths, state of occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| 1957 Jan–Sep | 105 | 105, KN |
| 1957–1958 Oct–Sep | 92 | 92, KN |
| 1958–1959 | 290 | 290, KN |
| 1959–1960 | 187 | 187, KN |
| 1960–1961 | 80 | 80, KN |
| 1961–1962 | 114 | 114, KN |
| 1962–1963 | 147 | 147, KN |
| 1963–1964 | 144 | 144, KN |
| 1964–1965 | 109 | 109, KN |
| 1965–1966 | 191 | 191, KN |
| 1967–1968 | 126 | 126, KN |
| 1968–1969 | 138 | 138, KN |
| 1969–1970 | 135 | 135, KN |
| 1970–1971 | 88 | 88, KN |
| 1971–1972 | 75 | 75, KN |
| 1972–1973 | 101 | 101, KN |
| 1973–1974 | 83 | 83, KN |
| 1975–1981 | No data | No data |
| 1982–1983 | >35 | <35, KN |
| 1983–1997 | No data | No data |
| 1998 | Dead monkeys reported | No figure reported† for KN |
| 1999 | No data | No data |
| 2000 | Several dead monkeys reported | No figure reported for KN |
| 2001–2002 | No data | No data |
| 2003 | 132 | 132, KN |
| 2004 | 86 | 86, KN |
| 2005 | 53 | 53, KN |
| 2006 | 61 | 61, KN |
| 2007 | 19 | 19, KN |
| 2008 | 23 | 23, KN |
| 2009 | 86 | 86, KN |
| 2010 | 28 | 28, KN |
| 2011 | >35 | <35, KN |
| 2012 | >64 | 39-64, KN; No figure reported for TN |
| 2013 | 50 | 50, KN |
| 2014 | >131 | 31, KN; <100, KL |
| 2015 | 60 | 42, KN; 18, KL |
| 2016 | 72 | 3, MH; 69, GA |
| 2017 | >81 | <51, KL; <10, GA |
| 2018 | >76 | <76, KN; No figure reported for KL or MH |
| 2019 | >15 | 15, KN; No figure reported for KL |
| 2020 | >2 | 2, KN; No figure reported for KL |
*GA, Goa; KL, Kerala; KN, Karnataka; MH, Maharashtra; TN, Tamil Nadu. †No figure reported indicates that monkey deaths were reported in a state but an exact number was not provided.
Information on monkey deaths caused by KFD is limited, particularly for species-specific deaths. Our review of all data sources indicates that >3,314 monkey deaths associated with KFD were reported during 1957–2020 (Table 1). However, only a subset of deaths were tested for KFDV. During this period, 760 monkeys underwent necropsy, and 334 were laboratory-confirmed to have KFDV infection (Appendix). Of the reported monkey deaths, a total of 1,676 deaths occurred in S. entellus monkeys and 400 deaths occurred in M. radiata monkeys; species were not reported for the remaining 1,238 deaths.
We found an early report of KFD in monkeys outside of Karnataka in Tamil Nadu state in 2012, which could be linked to an outbreak of human cases at the Bandipur Tiger Reserve in 2012. Monkeys from Karnataka might have entered Tamil Nadu carrying the virus or infected ticks. Subsequently, KFD in monkeys was reported in Kerala state in 2014 and Goa and Maharashtra states in 2016. Substantial overlap occurred between reported monkey deaths and human cases of KFD (Figure 2). We identified the drivers behind KFD transmission and geographic expansion based on the literature (Table 2).
Figure 2.
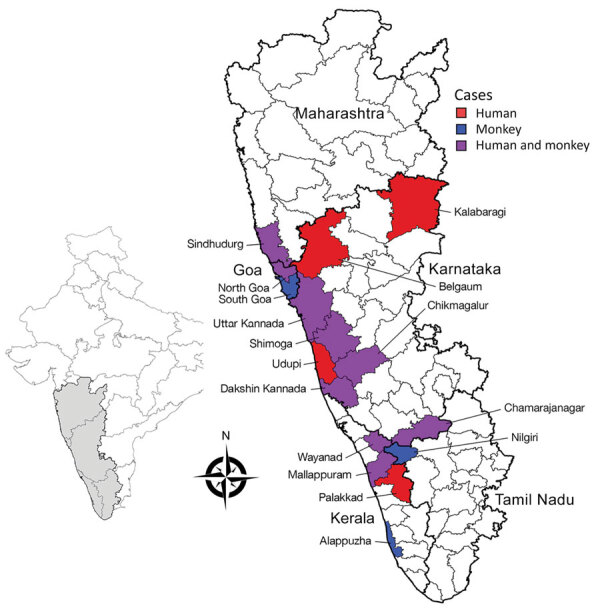
Hotspot areas for human cases and monkey deaths attributable to Kyasanur Forest disease, India,1957–2020. Inset map shows the region in context of the Indian subcontinent.
Table 2. Information about potential drivers of Kyasanur Forest Disease transmission based on review of available literature.
| Drivers | Source of information (reference) |
|---|---|
| Large-scale deforestation for various reasons (e.g., paddy fields and plantations) |
Ajesh et al., 2017 (1); Pattnaik, 2006 (3) |
| Human encroachment into forested areas |
Pattnaik, 2006 (3); Murhekar et al., 2015 (6) |
| Humidity in paddy fields ideal for tick survival |
Pattnaik, 2006 (3) |
| Vector ticks can survive in various kinds of biotypes |
Sadanandane et al., 2018 (4) |
| Number of small mammalian animals that act as reservoirs for the virus and for the vector tick |
Pattnaik, 2006 (3) |
| Movement of monkeys into new areas |
Chakraborty et al., 2019 (2); Pattnaik, 2006 (3) |
| Cattle may act as amplifying hosts for Kyasanur Forest disease virus and help in maintenance and propagation of the tick vector (handling of cows might also be a risk factor) | Chakraborty et al., 2019 (2) |
Higher mortality rates occurred among S. entellus monkeys (81% of 1,159 deaths) than among M. radiata monkeys during 1957–1964 (7). Most monkey deaths were reported in evergreen and semievergreen forests in the Western Ghats (8). We found no other information associating the frequency of monkey deaths to habitat.
The abundance of these primate species in the area of interest is difficult to determine because of limited studies with inconsistent sampling methods. In Karnataka, higher encounter rates with M. radiata monkeys were reported in wet evergreen forests and human-inhabited areas (9). M. radiata monkeys were encountered mainly in the Western Ghats and the Southern Plateau, whereas S. entellus monkeys were abundant in the Western Ghats and Northern Plains. Based on a 2001 Environmenta Information System bulletin (10), the national population of M. radiata monkeys in India was ≈150,000 and that of S. entellus monkeys was ≈300,000. Both species have suffered population decline because of habitat loss, translocation, and hunting, and minimal efforts have been undertaken to conserve these species (9,11).
Conclusions
Our study highlights the need for consistent surveillance of monkey deaths. Monkey deaths caused by KFDV are harbingers of human cases (1,3,4), making these animals potential sentinels for KFD (6). Therefore, determining these primate species’ relative susceptibility to KFDV to evaluate the potential to use monkey deaths for surveillance is essential. In laboratory experiments, higher mortality rates have been reported in S. entellus than M. radiata monkeys (12). Patil et al. (13) experimentally infected M. radiata monkeys with KFDV and found that only 20% of these primates had onset of severe clinical signs, but all exhibited viral shedding and a humoral immune response. Thus, other factors might contribute to KFD mortality rates under natural conditions, and M. radiata monkeys might be less susceptible to KFD than previously thought. KFDV infection can often be subclinical in nature, explaining why fewer deaths have been observed for M. radiata than S. entellus monkeys. By shedding the virus through body secretions, M. radiata monkeys might aid in expanding KFDV into new areas. This phenomenon underscores the need for conducting serum or fecal surveillance of primates to determine KFDV epidemiology and transmission.
Most human cases of KFD are typically reported during December–May, the same period during which monkey deaths generally occur. Local public health authorities often undertake precautionary measures on the basis of monkey deaths, including spraying acaricide around areas with monkey carcasses and vaccination of persons within a 5-km radius (6,14). The importance of animals as sentinels of infectious diseases, environmental hazards, and acts of bioterrorism is well documented (15). Because monkey deaths are used as sentinels for KFD, establishing year-round surveillance systems that consistently report KFD-related monkey deaths by date, location, and species is essential to better understand the epidemiology of the disease and design appropriate public health measures.
One limitation of our review is the inconsistency and gaps in the availability of reported monkey deaths caused by KFD. Few studies report monkey mortality data or provide specific monkey deaths by location, year, and species, so assessing whether mortality rates have changed over time is difficult. Another limitation is the incomplete data on testing and diagnoses of monkey carcasses for KFDV because of challenges such as distance to the testing site and delays in discovery.
Further research is needed to develop serosurveys specific to KFDV among monkeys, determine species-specific vulnerability to KFDV, and assess whether KFDV can spread through routes other than tick transmission. Testing capacity in KFD-endemic states should be strengthened to conduct timely monkey necropsies, providing more information on the prevalence of KFD in these sentinel animals, to elucidate the epidemiology of KFDV and protect monkey and human health.
Information related to Kyasanur Forest disease and deaths among nonhuman primates.
Acknowledgments
Funding for this study was obtained through the University of Illinois Campus Research Board and was supported by the Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service of the US Department of Agriculture (project no. ILLU 875-952).
Biography
Ms. Chakraborty is a doctoral candidate in the Program in Ecology Evolution and Conservation Biology at the University of Illinois, Urbana–Champaign. Her research interests include the ecology and epidemiology of vectorborne diseases and One Health approaches in disease surveillance and prevention.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Chakraborty S, Sander WE, Allan BF, Andrade FCD. Retrospective study of Kyasanur Forest disease and deaths among nonhuman primates, India, 1957–2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Jul [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2707.210463
References
- 1.Ajesh K, Nagaraja BK, Sreejith K. Kyasanur forest disease virus breaking the endemic barrier: An investigation into ecological effects on disease emergence and future outlook. Zoonoses Public Health. 2017;64:e73–80. 10.1111/zph.12349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chakraborty S, Andrade FCD, Ghosh S, Uelmen J, Ruiz MO. Historical expansion of Kyasanur Forest disease in India from 1957 to 2017: a retrospective analysis. Geohealth. 2019;3:44–55. 10.1029/2018GH000164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pattnaik P. Kyasanur forest disease: an epidemiological view in India. Rev Med Virol. 2006;16:151–65. 10.1002/rmv.495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sadanandane C, Gokhale MD, Elango A, Yadav P, Mourya DT, Jambulingam P. Prevalence and spatial distribution of Ixodid tick populations in the forest fringes of Western Ghats reported with human cases of Kyasanur forest disease and monkey deaths in South India. Exp Appl Acarol. 2018;75:135–42. 10.1007/s10493-018-0223-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pavri K. Clinical, clinicopathologic, and hematologic features of Kyasanur Forest disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11(Suppl 4):S854–9. 10.1093/clinids/11.Supplement_4.S854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Murhekar MV, Kasabi GS, Mehendale SM, Mourya DT, Yadav PD, Tandale BV. On the transmission pattern of Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD) in India. Infect Dis Poverty. 2015;4:37. 10.1186/s40249-015-0066-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goverdhan MK, Rajagopalan PK, Narasimha Murthy DP, Upadhyaya S, Boshell-M J, Trapido H, et al. Epizootiology of Kyasanur Forest Disease in wild monkeys of Shimoga district, Mysore State (1957-1964). Indian J Med Res. 1974;62:497–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mehla R, Kumar SR, Yadav P, Barde PV, Yergolkar PN, Erickson BR, et al. Recent ancestry of Kyasanur Forest disease virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1431–7. 10.3201/eid1509.080759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kumara HN, Singh M, Kumar S, Sinha A. Distribution, abundance, group size and demography of dark-bellied bonnet macaque Macaca radiata in Karnataka, South India. Curr Sci. 2010;99:663–7. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sinha A. The bonnet macaque revisited: ecology, demography and behavior. Environmental Information System bulletin. Wildlife and Protected Areas. 2001;1:32–41. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kumara HN, Kumar S, Singh M. Of how much concern are the ‘least concern’ species? Distribution and conservation status of bonnet macaques, rhesus macaques and Hanuman langurs in Karnataka, India. Primates. 2010;51:37–42. 10.1007/s10329-009-0168-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Technical Information Bulletin—Indian Council on Medical Research. Kyasanur Forest disease 1957–1964. Poona (India): Virus Research Centre.; 1964. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Patil DR, Yadav PD, Shete A, Chaubal G, Mohandas S, Sahay RR, et al. Study of Kyasanur forest disease viremia, antibody kinetics, and virus infection in target organs of Macaca radiata. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12561. 10.1038/s41598-020-67599-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kasabi GS, Murhekar MV, Sandhya VK, Raghunandan R, Kiran SK, Channabasappa GH, et al. Coverage and effectiveness of Kyasanur forest disease (KFD) vaccine in Karnataka, South India, 2005-10. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2025. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Neo JPS, Tan BH. The use of animals as a surveillance tool for monitoring environmental health hazards, human health hazards and bioterrorism. Vet Microbiol. 2017;203:40–8. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.02.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Information related to Kyasanur Forest disease and deaths among nonhuman primates.


