Correction to: Communications Biology 10.1038/s42003-021-02145-7, published online 10 June 2021.
The original version of this Article contained an error in Fig. 2, in which the y axis was titled, “Change from 1600 (%)”. The correct y axis title is “Change from 1600 (0–1 scale)”. The correct version of Fig. 2 is:
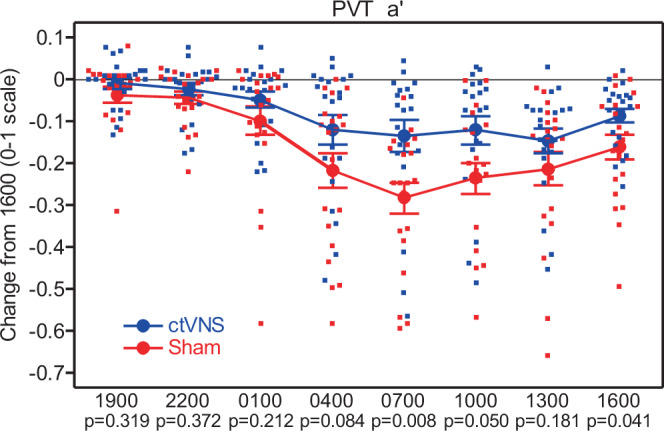
which replaces the previous incorrect version:

The original version of this Article also contained an error in Fig. 3, in which the y axis was titled, “Change from 1600 (%)”. The correct y axis title is “Change from 1600 (1–7 scale)”. The correct version of Fig. 3 is:

which replaces the previous incorrect version:
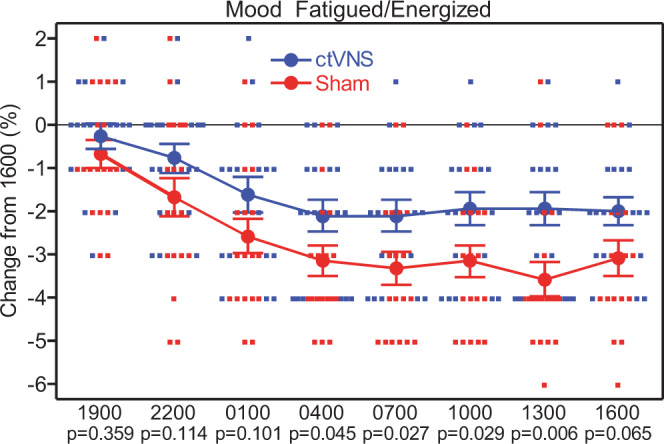
Both errors have now been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the Article.


