Abstract
Vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease (VAERD) was previously observed in some preclinical models of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and MERS coronavirus vaccines. We used the SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mouse-adapted, passage 10, lethal challenge virus (MA10) mouse model of acute lung injury to evaluate the immune response and potential for immunopathology in animals vaccinated with research-grade mRNA-1273. Whole-inactivated virus or heat-denatured spike protein subunit vaccines with alum designed to elicit low-potency antibodies and Th2-skewed CD4+ T cells resulted in reduced viral titers and weight loss post challenge but more severe pathological changes in the lung compared to saline-immunized animals. In contrast, a protective dose of mRNA-1273 induced favorable humoral and cellular immune responses that protected from viral replication in the upper and lower respiratory tract upon challenge. A subprotective dose of mRNA-1273 reduced viral replication and limited histopathological manifestations compared to animals given saline. Overall, our findings demonstrate an immunological signature associated with antiviral protection without disease enhancement following vaccination with mRNA-1273.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, mRNA vaccine, mRNA-1273, protective immunity, vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease, type 2 responses, T cells, neutralizing antibodies
Graphical abstract
As vaccine-enhanced disease to respiratory viruses has been previously observed, a thorough safety evaluation of COVID-19 vaccines in preclinical animal models is essential. Here, DiPiazza and Leist et al. provide evidence for antiviral protection in the absence of lung disease following SARS-CoV-2 challenge in mice immunized with research-grade mRNA-1273.
Introduction
Since its discovery in late 2019, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 [COVID-19]) has resulted in more than 177 million infections and more than 3.8 million deaths worldwide as of June 17, 2021. Based on a strategy of using proline substitutions to stabilize viral glycoproteins (Sanders and Moore, 2021), stabilization of the prefusion conformation of the neutralization-sensitive viral spike (S) glycoprotein into a form known as S-2P (Pallesen et al., 2017) was key to the expedited development of many vaccines. Design and production of mRNA-lipid nanoparticle (mRNA-LNP) encoding transmembrane-anchored SARS-CoV-2 S-2P, mRNA-1273, was initiated immediately upon release of the first sequences of SARS-CoV-2. The mRNA-1273 vaccine protects from SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease in preclinical mouse (Corbett et al., 2020a) and non-human primate (NHP) (Corbett et al., 2020b) models, elicited neutralizing antibody and T cell responses in phase 1 clinical trials in adult and older adult populations (Anderson et al., 2020; Jackson et al., 2020), and was authorized for emergency use before the end of 2020.
Despite the unprecedented speed of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development and testing, specific safety questions required close attention. A primary safety concern is the induction of vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease (VAERD). VAERD is a modified or more severe presentation of disease, predominantly involving the lower respiratory tract, that results from infection by a pathogen after being vaccinated for the same pathogen (for more detail, see Munoz et al., 2021). Whole-inactivated viral vaccines developed in the 1960s against both respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and measles elicited VAERD when vaccinated children were subsequently naturally infected (Fulginiti et al., 1967; Kim et al., 1969; Nader et al., 1968; Polack et al., 2003; Ruckwardt et al., 2019). These adverse outcomes were associated with T helper (Th)2-skewed CD4+ T cells and the induction of poor-quality antibodies with little to no neutralizing activity. Animal models, where this immune profile is elicited after vaccination, recapitulate RSV and measles VAERD with hallmarks of increased inflammation and pulmonary eosinophilia after challenge that exceeds that in unvaccinated control animals (Graham et al., 1993). Although there has been no licensed prophylactic intervention for coronaviruses, there have been multiple findings of VAERD in preclinical studies of both Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-CoV and SARS-CoV vaccines in several species, using different vaccine platforms and antigenic targets (e.g., S and nucleocapsid [N]) formulated with and without alum adjuvant (Arvin et al., 2020; Graham, 2020; Haynes et al., 2020; Lambert et al., 2020; Peeples, 2020; Smatti et al., 2018; Zellweger et al., 2020). Although it is unclear whether animal models can reliably predict human VAERD, it is prudent to compare immune responses elicited by candidate vaccines to the detrimental immune responses known to result in VAERD in animal models, particularly at low doses that mimic waning immunity.
We assessed the immunological and safety signature of mRNA-1273 in challenge studies using the mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2, passage 10, lethal challenge virus (MA10) (Dinnon et al., 2020; Leist et al., 2020). BALB/c mice were immunized twice with whole-inactivated SARS-CoV-1 or SARS-CoV-2 virus, heat-denatured spike protein (S-2P), or mRNA-1273. Whole-inactivated virus and denatured S protein were formulated with alum to recapitulate conditions that resulted in VAERD in a prior preclinical coronavirus vaccine study (Bolles et al., 2011). These regimens consistently induced low to moderate concentrations of S-binding and neutralizing antibody and Th2-skewed S-reactive CD4+ T cells. After viral challenge, these mice were partially protected from weight loss and viral replication yet displayed enhanced pulmonary inflammation and eosinophil infiltration. In contrast, mRNA-1273 elicited potently neutralizing antibodies and a balanced or type-1-skewed response, particularly at the 1 μg dose, and mice were protected from viral replication and lung inflammation after viral challenge. Importantly, a subprotective mRNA dose of 0.1 μg was associated with reduced immunopathology after challenge compared to the control and Th2-skewing groups. These results demonstrate that mRNA-1273 elicits potent antiviral immunity and a favorable immune profile not associated with VAERD, even at subprotective doses.
Results
mRNA-1273 immunization elicits S-directed antibodies with high neutralizing potency compared to whole-inactivated virus and denatured S protein delivered with alum
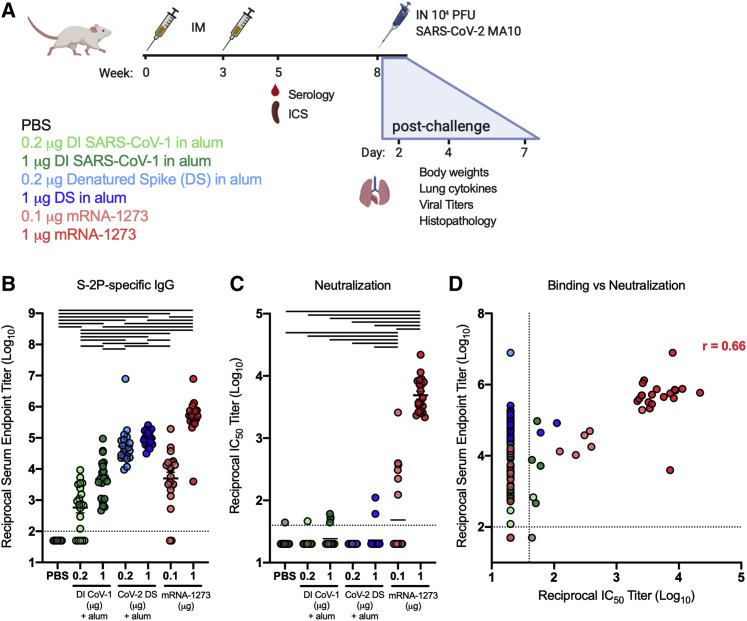
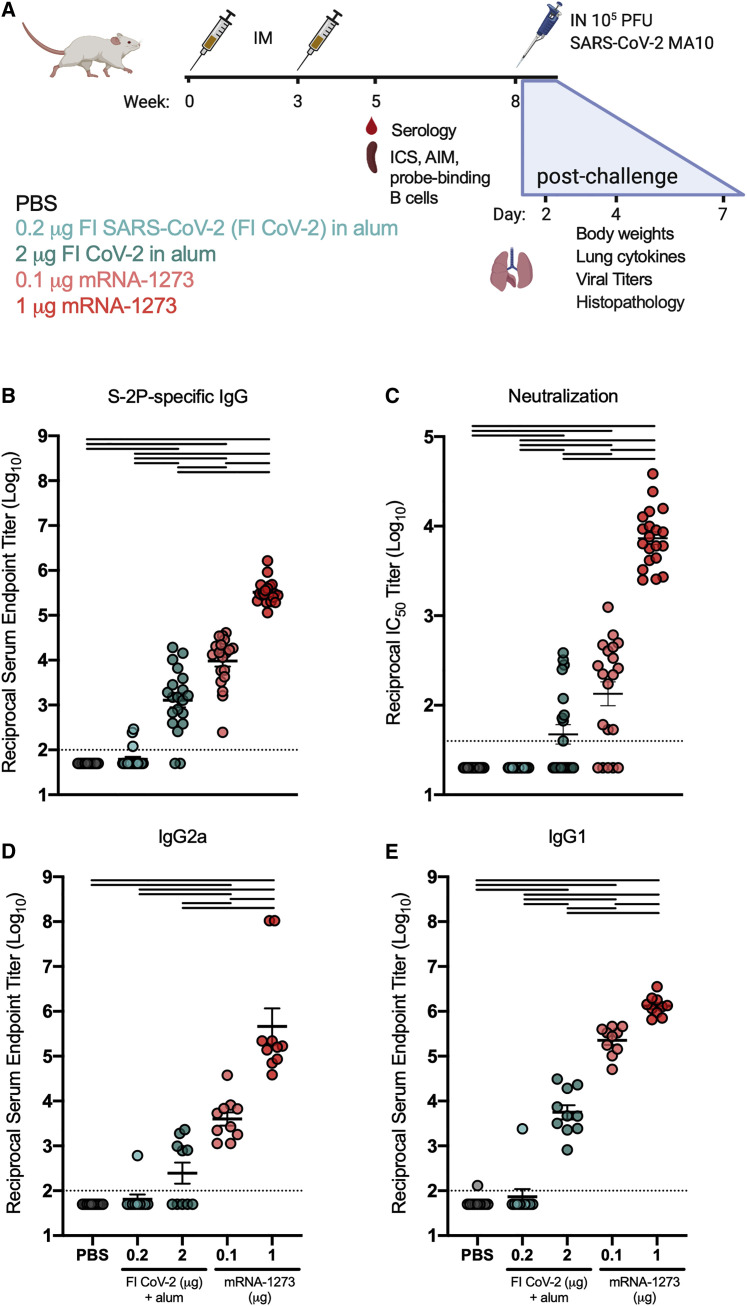
To assess the capacity of research-grade mRNA-1273 to elicit potentially adverse immune responses that could be associated with VAERD, we compared antibody and T cell responses generated from subprotective and protective doses of mRNA-1273 (0.1 and 1 μg, respectively) to those elicited by regimens previously associated with disease enhancement following infection. Due to the initial unavailability of whole-inactivated SARS-CoV-2, we elected to immunize mice with whole-inactivated SARS-CoV-1 virus or SARS-CoV-2 S protein that had been heat denatured to destroy the protein conformation. Both immunogens were delivered at doses of 0.2 or 1 μg, formulated with alum adjuvant (Figure 1 A) with the goal of inducing binding antibodies with little to no neutralizing activity (for disposition of animals in the study, see Table S1). Importantly, immunization with 0.2 μg of whole-inactivated SARS-CoV-1 in alum had previously resulted in enhanced disease following infection with mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-1 (Bolles et al., 2011). BALB/c mice were immunized twice 3 weeks apart with each vaccine or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) as a control, and humoral and cellular responses to S were assessed 2 weeks after the boost. We first quantified binding immunoglobulin G (IgG) to S-2P protein. Binding antibody was observed in all groups except the control group, with more than a three-log range between groups (Figure 1B). Cross-reactive antibody responses elicited by whole SARS-CoV-1 inactivated with both UV irradiation and formalin (double-inactivated SARS-CoV-1 or DI CoV-1) were lower than responses elicited by the homologous, denatured SARS-CoV-2 S protein (CoV-2 DS). The 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 dose elicited lower binding antibodies than both the 0.2 and 1 μg doses of CoV-2 DS, on par with binding antibodies induced by 1 μg of heterologous DI CoV-1. The 1 μg mRNA-1273 dose elicited higher antibody responses than either dose of CoV-2 DS, consistent with potent elicitation of antibodies previously described (Corbett et al., 2020a).
Figure 1.
mRNA-1273 potently elicits S-2P binding and neutralizing antibodies compared to inactivated SARS-CoV virus or denatured SARS-CoV-2 spike protein delivered in alum
(A) Experimental design aimed at eliciting immune responses that have historically been associated with vaccine-enhanced respiratory disease in BALB/c and to compare immunogenicity and efficacy with that of mRNA-1273. Type-2-skewing regimens (double-inactivated SARS-CoV virus, DI CoV-1, and denatured SARS-CoV-2 spike protein [CoV-2 DS]) were dosed at 0.2 or 1 μg. mRNA-1273 was given at 0.1 or 1 μg, established subprotective and protective doses, respectively. All mice were immunized intramuscularly (IM) at weeks 0 and 3. T cell (ICS) and serological readouts were obtained 2 weeks post-boost. 20 animals per group were challenged with 104 PFUs of SARS-CoV-2 MA10 (mouse-adapted, passage 10, lethal challenge virus), weight loss (10 animals per group through day 7), and viral titers (5 animals per group at days 2 and 4) in the lungs, and nasal turbinates were obtained after challenge. Data from study 1 are presented in Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and S1–S3 and Tables S1 and S2.
(B and C) S-2P-binding antibodies (B) neutralizing activity (C) against SARS-CoV-2 614G pseudovirus was assessed in sera obtained 2 weeks post-boost.
(D) Correlation between S-2P binding and SARS-CoV-2 614G pseudovirus neutralization. Correlation coefficient r = 0.66 for mRNA-1273 samples with measurable binding and neutralization. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between all experimental groups, with a black line between groups indicating adjusted p < 0.05. N = 20 animals per group; means of log-transformed data are shown. The limit of detection is indicated by a dotted line, and values below the limit of detection were assigned a value of half the limit of detection.
See also Table S1.
Neutralizing activity against a SARS-CoV-2 S 614G-pseudotyped virus was measured to assess neutralization of the predominant circulating virus. Mice immunized with 1 μg mRNA-1273 had a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) geometric mean titer (GMT) of 4,886. Neutralization was low or undetectable in other immunization groups, but notably, 6 of the 20 animals given 0.1 μg of mRNA-1273 had detectable neutralizing activity compared to only 3/20 and 2/20 animals immunized with 1 μg of DI CoV-1 or CoV-2 DS, respectively (Figure 1C). All but 1 of the 40 animals immunized at both doses of CoV-2 DS had binding antibody endpoint titers above 4 log10, and only 2 animals in those combined groups had detectable neutralizing activity. In contrast, only half (10/20) of the mice immunized with 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 had binding antibody endpoint titers above 4 log10, of which 6 had measurable neutralizing activity, a disparity in potency that is apparent when correlating binding to neutralizing activity (Figure 1D). Based on these results, mRNA-1273 elicited antibodies with higher average neutralizing potency than approaches aimed at Th2 skewing the S-directed response.
mRNA-1273 immunization elicits S-reactive antibody with a favorable IgG2a/IgG1 ratio and a distinct CD4+ T cell profile compared to Th2-skewing regimens
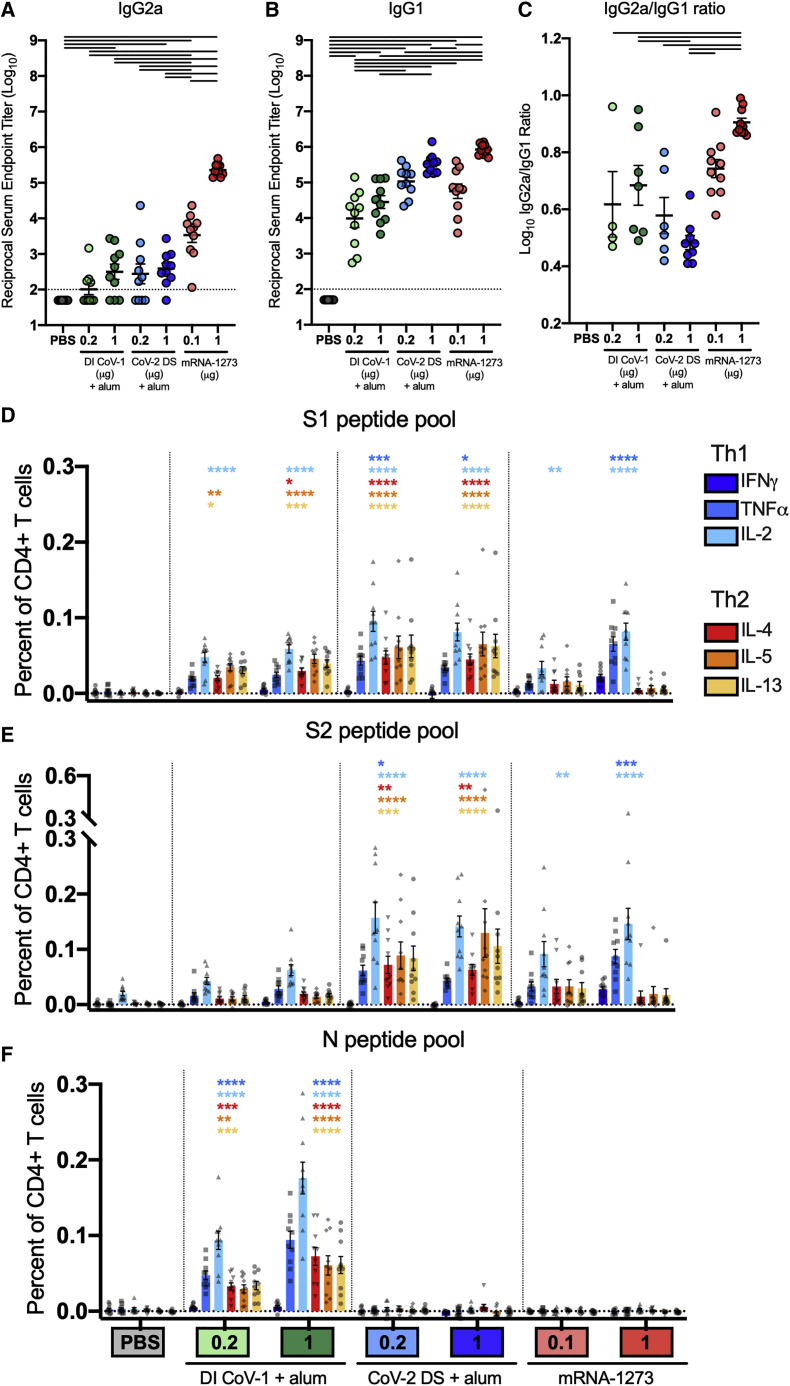
To gain insight into the induction of type 1 and type 2 immunity, we further assessed the IgG subclass of S-directed antibodies. In mice, although the type 1 cytokine interferon γ (IFNγ) promotes B cell secretion of IgG2a and inhibits IgG1, the type 2 cytokine interleukin-4 (IL-4) promotes IgG1 and inhibits the secretion of IgG2a antibodies (Coffman et al., 1993). As previously shown (Corbett et al., 2020a), mRNA-1273 elicited high titers of both S-binding IgG2a and IgG1 (Figures 2 A and 2B, respectively). mRNA-1273 given at the low dose of 0.1 μg elicited more S-binding IgG2a than seen in any group immunized with DI CoV-1 or CoV-2 DS (Figure 2A). In contrast, type-2-skewing regimens elicited IgG1 responses more similar to those elicited by 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 (Figure 2B), resulting in lower Ig2a/IgG1 ratios in mice that received either DI CoV-1 or CoV-2 DS compared to those that received 1 μg mRNA-1273 (Figure 2C). Taken together, serological assessment of S-directed antibodies confirmed the generation of a type 1 antiviral immune profile elicited by mRNA-1273 compared to vaccine approaches that elicit type-2-biased responses.
Figure 2.
mRNA-1273 elicits a type-1-associated serological and CD4+ Th cell profile compared to those elicited by type-2-skewing regimens
(A and B) S-2P-binding IgG2a and IgG1, respectively.
(C) Ratio of S-2P-binding IgG2a to IgG1. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between all experimental groups, with a black line between groups indicating adjusted p < 0.05. N = 10 mice per group; mean and SEM of log-transformed data (A and B) or mean and SEM (C) are shown. The limit of detection is indicated by a dotted line, and values below the limit of detection were assigned a value of half the limit of detection.
(D–F) At week 5, splenocytes (N = 10 mice per group) were isolated and stimulated in the presence of protein transport inhibitor (Thermo product 00-4980-03) and no peptides (DMSO only) or pools of overlapping peptides from the nucleocapsid (Pepmix JPT product PM-WCPV-NCAP) or spike (S1 and S2 peptide pools, 85% pure, JPT) proteins of SARS-CoV-2 (2 μg per mL each peptide). After 6 h, intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) was performed to quantify CD4+ T cells producing the cytokines IFNγ, TNFα, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in response to (D) S1 peptide pool, (E) S2 peptide pool, and (F) N peptide pool restimulation. Background cytokine expression in the no peptide condition was subtracted from that measured in the N, S1, and S2 peptide pools for each individual mouse. Error bars represent the SEM.
Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests to determine expression significantly different from the naive group for each cytokine. Significance is indicated above for each group (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). See also Figures S1 and S2.
We next assessed the CD4+ T cell cytokine profile of S-reactive cells in the spleen 2 weeks after the boost for all vaccine groups. We used intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) to measure the frequency of CD4+ T cells expressing three type 1 cytokines (IFNγ, tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNFα], and IL-2) and three type 2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) after in vitro restimulation with overlapping peptide pools spanning the S1 and S2 portions of the S protein (Figures 2D and 2E, respectively; gating strategy presented in Figure S1) or the SARS-CoV-2 N protein (Figure 2F). Although CD4+ Th cells were detectable in all immunization groups, the T cells of mice in the DI CoV-1 and CoV-2 DS groups exhibited a pattern of expression that included all three type 2 cytokines. As expected, only mice immunized with DI CoV-1 had responses to the N peptide pool (Figure 2F). Although IL-2 and TNFα expression exceeded background in some cases, most CD4+ T cells in the type-2-skewing immunization groups expressed one or more type 2 cytokines (cytokine co-expression profile following peptide pool restimulation shown in Figure S2A). In contrast, expression of type 2 cytokines was more limited in animals immunized with mRNA-1273. IFNγ expression was only found in mice that received 1 μg of mRNA-1273, and this was the only immunization group with strong induction of S-specific CD8+ T cell responses (Figure S2B).
mRNA-1273 immunization limits viral replication, morbidity, and pulmonary inflammation following mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 viral challenge
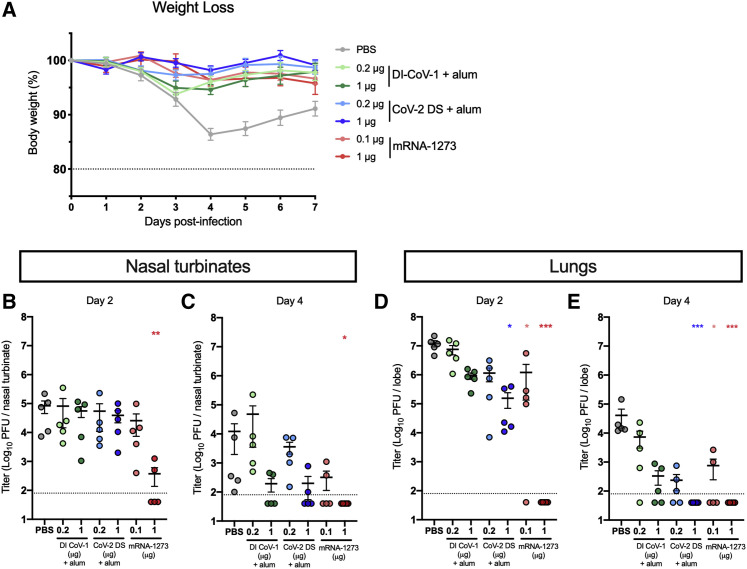
Twenty mice from each group were challenged with 104 plaque-forming units (PFUs) of mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 MA10 (MA10) 5 weeks after the boost immunization (Figure 1A; Table S1). The MA10 virus is capable of lethal disease in standard immunocompetent mice and recapitulates many aspects of COVID in humans (Leist et al., 2020). Weight loss was assessed in 10 mice per group until day 7 post-infection. Control animals had the greatest weight loss, which peaked at day 4 post-infection with an average peak of 14% loss of body weight. Modest but not significant weight loss occurred through day 3 in mice immunized with DI CoV-1, but they recovered more rapidly than control mice. There was no appreciable weight loss in groups immunized with either dose of CoV-2 DS or mRNA-1273 (Figure 3 A). Viral titers were measured in the nasal turbinates by plaque assay on day 2 (Figure 3B) and day 4 (Figure 3C) post-infection to assess protection in the upper airway. Low viral titers were detected in 2/5 mice in the 1 μg mRNA-1273 dose group 2 days after infection, and none had detectable virus in the nasal turbinates at day 4, as previously shown following vaccination with 1 μg of mRNA-1273 (Corbett et al., 2020a). In addition to protection in the nasal turbinates, 1 μg mRNA-1273 immunization completely prevented viral infection in the lungs at both day 2 (Figure 3D) and day 4 (Figure 3E) after challenge. Mice immunized with 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 or 1 μg CoV-2 DS also had reduced viral titer in the lungs at both time points post-challenge. In all, every vaccine tested offered some protection against either weight loss or virus titer post-challenge.
Figure 3.
mRNA-1273 protects from weight loss and viral replication after challenge with SARS-CoV-2 MA10
(A) The percent of starting weight (day 0) was calculated for animals weighed through day 7 post-infection. N = 10 mice per group; mean and SEM for each group is shown. The dotted line represents 80% of starting weight.
(B–E) Plaque-forming units (PFUs) of SARS-CoV-2 were measured from nasal turbinates on (B) day 2 and (C) day 4 post-infection and in clarified lung supernatants obtained on (D) day 2 or (E) day 4 post-infection in 5 mice per group. The dotted line indicates the limit of detection, and samples with no detectable virus are plotted at half the limit of detection.
Viral titer data were analyzed using a Kruskal-Wallis test of log-transformed data to identify groups significantly different than the PBS group (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
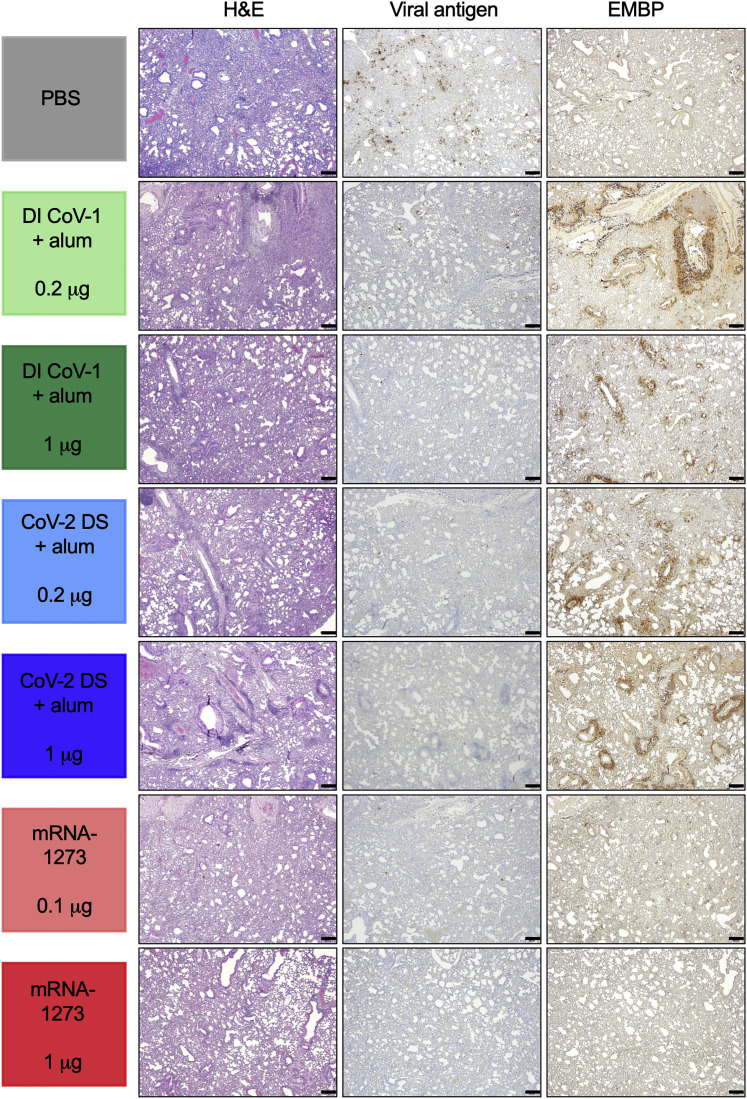
We examined lungs histologically on day 4 after challenge (for details and examples of scoring, see Figure S3; for scoring for each animal, see Table S2). Assessment of inflammation in sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) showed an inflammation and severity score in both groups of DI-CoV-immunized and the 0.2 μg CoV-2-DS-immunized mice that met or exceeded inflammation seen in control mice (Figure 4 ). Mononuclear and polymorphonuclear inflammation was moderate to severe in the PBS group, severe in the 0.2 μg DI CoV-1 group, moderately severe in the 1 μg DI CoV-1 and 0.2 μg CoV-2 DS groups, mildly to moderately severe in the 1 μg CoV-2 DS and 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 groups, and mild to minimally severe in the 1 μg mRNA group (rank by severity was 0.2 μg DI CoV-1 > 1 μg DI CoV-1 = 0.2 μg CoV-2 DS > PBS > 1 μg CoV-2 DS = 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 > 1 μg mRNA-1273). Type II pneumocyte hyperplasia was evident in all groups but mild in groups immunized with mRNA-1273. Immunohistochemistry for SARS-CoV-2 antigen revealed moderately abundant and diffusely distributed SARS-CoV-2 viral antigen throughout the alveolar interstitium in the PBS group, but sparse or rare infected cells were observed in most other groups, with minimal to absent SARS-CoV-2-antigen-positive cells in 1 μg mRNA-1273-immunized mice (Figure 4). These data are consistent with viral titer measured on day 4 (Figure 3E). Groups immunized with Th2-skewing regimens had abundant eosinophils, often in close association with and circumscribing airways and blood vessels. In contrast, eosinophils were sparsely abundant in control and mRNA-immunized mice (Figure 4). Thus, despite limited virus-induced weight loss and partial reduction of viral replication in lungs, Th2-skewing regimes exhibited histological hallmarks of VAERD.
Figure 4.
mRNA-1273 limits lung inflammation, viral antigen, and eosinophil recruitment after challenge with SARS-CoV-2 MA10
Inflammation was assessed 4 days after infection using H&E staining or immunohistochemistry (IHC) for nucleocapsid viral antigen or eosinophil major basic protein (EMBP) as indicated in the methods. Photomicrographs are 4×, and the scale bar indicated is 200 μm; a representative animal from each group is shown. Scoring for each animal and a summary for each group are presented in Table S2. See also Figure S3 and Table S2.
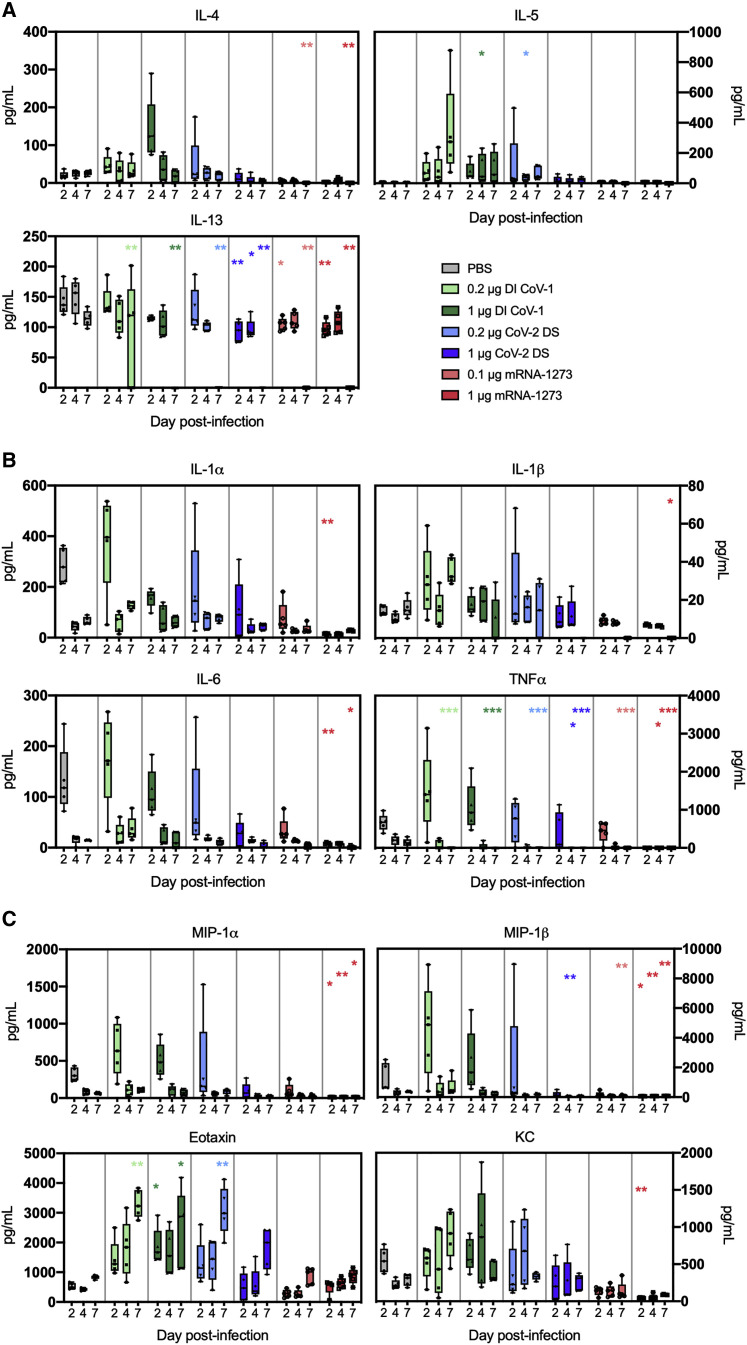
We evaluated lung cytokines to confirm the presence of a Th2 signature and increased association with pulmonary inflammation and eosinophilia elicited by the whole inactivated and denatured spike regimens and to assess protection from inflammation in mRNA-1273-immunized mice. Cytokines were measured in clarified lung supernatants obtained on days 2, 4, and 7 post-challenge using a Bioplex 23 multiplex assay. We first measured cytokines produced by Th2 cells: IL-4; IL-5; and IL-13 (Figure 5 A). Animals immunized with mRNA-1273 had lower concentrations of Th2-associated cytokines than animals in the PBS-immunized group. In contrast, animals immunized with whole-inactivated virus or denatured spike protein immunogens delivered in alum had elevated concentrations of IL-4 and IL-5 compared to the PBS group. We then evaluated the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα (Figure 5B). Although there was no statistical increase in proinflammatory cytokines in Th2-skewed immunization groups, with only five samples available per harvest day, there was a trend toward higher proinflammatory cytokine concentrations, particularly IL-1β and TNFα, in these groups, although concentrations of most were reduced compared to the PBS group and in animals immunized with mRNA-1273, particularly at the 1 μg dose. Finally, we assessed chemokines involved in the recruitment and activation of polymorphonuclear cells (acrophage inflammatory protein [MIP]-1α, MIP-1β, eotaxin, and CXCL1(KC); Figure 5C). There was a trend toward higher concentrations of MIP-1α and MIP-1β early in Th2-skewed groups, with lower expression in mRNA-1273-immunized mice than in the control group. mRNA-1273-immunized mice similarly did not have increased concentrations of CXCL1 or eotaxin, which were higher in most groups immunized with Th2-skewing regimens, consistent with eosinophil major basic protein (EMBP) staining (Figure 4) and with what was observed in earlier studies of DI-CoV1-enhanced disease following mouse-adapted SARS-CoV infection (Bolles et al., 2011). Overall cytokine concentrations in the lungs were consistent with the histopathological results and indicate an increase in inflammatory signatures and excess mononuclear and polymorphonuclear cell infiltration into the lungs of Th2-skewed immunization groups. Importantly, a distinct profile was observed in the 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 group despite a similar viral load. Although this dose was not sufficient to protect from viral replication, it resulted in histopathological protection and dampened inflammatory responses in the lung. Taken together, the elicitation of both protective and subprotective mRNA-1273-induced immunity resulted in reduced lung pathology without histologic evidence of VAERD.
Figure 5.
mRNA-1273 protects from lung inflammation post-MA10 challenge, while DI CoV-1 and CoV-2 DS vaccines lead to increased type 2 and inflammatory responses
(A) Concentrations of the type 2 cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in clarified lung supernatants on days 2, 4, and 7 post-infection for each group.
(B) Proinflammatory cytokine (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα) concentrations on days 2, 4, and 7 post-infection.
(C) Concentrations of the chemokines MIP-1α, MIP-1β, eotaxin, and KC in lung supernatants on days 2, 4, and 7 post-infection. N = 5 mice per group at each time point (15 total per group). Data are displayed as box and whisker plots, min to max with all points. Data were analyzed using a Kruskal-Wallis test comparing all groups to the PBS group at each time point (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
mRNA-1273 leads to protection following MA10 challenge that contrasts with enhancement observed following challenge of mice immunized with formalin-inactivated SARS-CoV-2 in alum
Following the results of the first study, we performed a second study in BALB/c mice to incorporate and compare immune responses to the newly available formalin-inactivated SARS-CoV-2 immunogen (FI CoV-2; made available by the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases [DMID], NIAID). The virus was inactivated in the media containing FBS, which challenged efforts to precisely quantitate viral antigen. Therefore, we selected 0.2 and 2 μg total, spanning a 10-fold dose range, and again compared responses to a control PBS group and groups immunized with 0.1 or 1 μg of mRNA-1273 (Figure 6 A; see Table S3 for disposition of study 2 animals). Both doses of FI CoV-2 elicited low concentrations of binding and neutralizing antibodies compared to the mRNA-1273 groups (Figures 6B and 6C, respectively). Again, although mRNA-1273 elicited both IgG2a and IgG1 subclasses of S-specific IgG, the response to 2 μg FI CoV-2 was dominated by IgG1, suggesting a Th2-biased immune response pattern (Figures 6D and 6E). Due to the low immunogenicity of the selected doses of FI CoV-2, we were unable to detect antigen-specific cytokine production by CD4+ T cells following stimulation with homologous peptide pools (S1, S2, and N) in both dose groups using ICS (Figure S4). Responses in mRNA-1273-immunized groups largely reflected the results of the first experiment, with a dose-dependent increase in type 1 profile and CD8+ T cell induction in only the 1 μg mRNA-1273 group (Figure S4).
Figure 6.
Serological responses to FI CoV-2 in alum and mRNA-1273
(A) Experimental design of study 2 comparing responses of mRNA-1273 (0.1 or 1 μg) to FI CoV-2 (0.2 or 2 μg). All mice were immunized at weeks 0 and 3. T cell and serological readouts were obtained 2 weeks post-boost from 10 animals per group. 20 animals per group were challenged with 105 PFUs of SARS-CoV-2 MA10 and weight loss (10 animals/group through day 7) and viral titers (5 animals per group at days 2 and 4) in the lungs, and nasal turbinates were obtained after challenge. Data from study 2 are presented in Figures 6, 7, and S4–S6 and Tables S3 and S4.
(B and C) S-2P-binding antibodies (B) and neutralizing activity (C) against SARS-CoV-2 614G pseudovirus were assessed in sera obtained 2 weeks post-boost.
(D and E) S-2P-specific (D) IgG2a and (E) IgG1 2 weeks post-boost. Statistics were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between all experimental groups, with a black line between groups indicating adjusted p < 0.05. N = 20 animals per group; mean and SEM of log-transformed data are shown. The limit of detection is indicated by a dotted line, and values below the limit of detection were assigned a value of half the limit of detection.
See also Figures S4–S6 and Tables S3 and S4.
We elected to challenge mice for the second study with an increased dose (10-fold) of 105 PFUs of MA10. There was less weight loss than seen in the first study, with no group showing sustained differences from the PBS control group (Figure S5A). Consistent with the first study, mice in the 1 μg mRNA-1273 dose group demonstrated near-complete inhibition of viral replication in the nasal turbinates (Figures S5B and S5C) and no detectable virus in the lungs (Figures S5D and S5E). Mice immunized with 0.1 μg of mRNA-1273 or 2 μg of FI CoV-2 had partial protection from viral replication in the upper and lower airway at some time points (Figures S5B–S5E). On day 4, lungs from all groups had a similar degree of inflammation with mononuclear and polymorphonuclear infiltration and diffuse type II pneumocyte hyperplasia, causing a reduction in alveolar air spaces across all study groups (Figure S5F). We believe this to be due to the high viral challenge dose used in this study. This was coincident with an overall higher presence of viral antigen, which was particularly abundant in the alveolar interstitium of control animals. The highest degree of EMBP staining, and abundant eosinophils adjacent to and surrounding blood vessels, was seen in the 0.2 μg FI CoV-2 with alum group (for individual animal scoring from study 2, see Table S4). Animals immunized with FI CoV-2 in alum experienced higher concentrations of Th2 cytokines and proinflammatory and chemotactic mediators (Figure S6). Although the high viral inoculum appeared to blunt some differences between groups, combined data from our second challenge study confirmed the finding of higher concentrations of inflammatory cytokines in mice given whole-inactivated virus in alum and reaffirmed a distinct immune signature in mRNA-1273 groups that was associated with antiviral protection.
mRNA-1273 vaccination elicits S-specific CD4+ Tfh and B cell responses
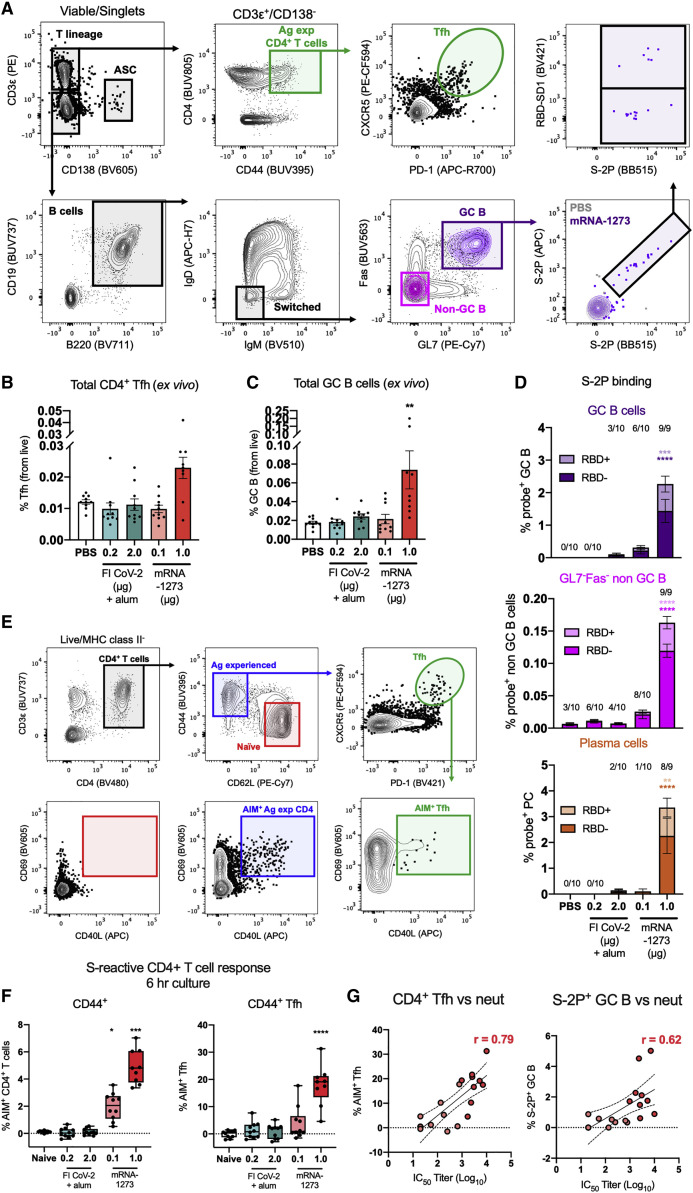
We further evaluated the induction of T and B cell responses in our second study. We were particularly interested in CD4+ T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, which are critical to the generation of germinal centers (GCs) and support the clonal selection and differentiation of antigen-specific memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells (Crotty, 2019). We developed a flow cytometry panel to quantify total Tfh (CXCR5+PD-1+) and GC B cell (GL7+Fas+) responses, as well as B cells capable of binding the prefusion-stabilized S protein and/or the neutralization-sensitive receptor binding domain (RBD) using tetramerized fluorochrome-conjugated capture probes (Figure 7 A; for gating and representative plots, see Figure S7A). 2 weeks after the boost, we found elevated total Tfh and GC B cell frequencies in the splenocytes from only the 1 μg mRNA-1273 dose group (Figures 7B and 7C, respectively). Mice that received 1 μg of mRNA-1273 also demonstrated significant induction of probe-binding, class-switched GC B cells, plasma cells (PCs) (identified as CD138+B220lo), and other B cells (GL7−Fas−; Figure 7D). Other vaccine groups had little to no detectable elicitation of S-reactive B cells. Among B cells that bound the stabilized S protein probe, approximately 20%–30% demonstrated specificity for the RBD based on co-capture of the RBD probe. This proportion is consistent with the proportion of S-directed B cells that bind RBD in SARS-CoV-2-experienced humans (Dan et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2020).
Figure 7.
mRNA-1273 elicits B cells targeting various epitopes on the spike glycoprotein and potently activates spike-specific CD4+ T cells, including follicular helper (Tfh) cells
(A) Gating strategy to quantify antigen-experienced (CD44+) CD4+ Tfh (CXCR5+ PD-1+) and germinal center (GC) B cells (GL7+ Fas+) in the spleen 2 weeks post-boost. Capture of full-length S-2P and receptor-binding domain (RBD) probes by IgD− IgM− B cells was also evaluated.
(B and C) Frequencies of total (B) Tfh and (C) GC B cells were quantified from 10 animals per group; mean and SEM are shown.
(D) Probe-binding GC B cells, non-GC (GL7−Fas−) B cells, and mature, class-switched plasma cells (CD138+ B220lo) were assessed. The numbers above each bar reflect the number of mice with measurable binding reactivity above 0.0%; mean and SEM are shown.
(E) Gating strategy to quantify AIM+ CD4+ T cells.
(F) Frequency of AIM+ CD44+ CD4+ T cells and Tfh cells following stimulation with S1 and S2 peptide pools (background subtracted). Data are displayed as box and whisker plots, min to max with all points.
(G) Correlations of % AIM+ CD4+ Tfh cells (r = 0.79) and % S-2P+ GC B cells (r = 0.62) to antibody neutralization titer (IC50) from mice immunized with mRNA-1273 (0.1 and 1 μg). N = 10 mice per group; data were analyzed using a Kruskal-Wallis test comparing all immunization to the PBS group (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
See also Figure S7.
To more fully capture the repertoire of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells elicited by vaccination, we employed a more inclusive, cytokine agnostic approach called activation-induced marker (AIM) assay, which can identify activated cells even if they do not express sufficient cytokine to be measured by traditional ICS methods (Figure 7E; Lee et al., 2021). Antigen-experienced (CD44+) T cells were assessed for the upregulation of activation markers CD69 and CD154 (CD40L) following stimulation with S1 and S2 peptide pools in a 6-h culture in vitro. CD4+ T cells from groups immunized with 0.1 μg or 1 μg of mRNA-1273 responded in a dose-dependent manner to S-derived peptides in higher frequencies than we measured using conventional ICS (Figure 7F; for representative staining, see Figure S7B). However, using this more sensitive method, we were still unable to detect T cell responses above background in groups immunized with FI CoV-2 at either dose. Further evaluation demonstrated strong induction of AIM+ CD4+ Tfh cells responding to spike peptides following immunization with 1 μg of mRNA-1273 (Figure 7F), with limited reactivity detected from all other groups. Both AIM+ Tfh and S-2P+ GC B cells correlated well with neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2, suggesting a well-coordinated cellular and serological response (Figure 7G). These data further support the activation of T cell responses that promote the generation of durable immune memory following mRNA-1273 immunization.
Discussion
Comprehensive evaluation of safety is a critical component of every human vaccine development program. Given the history of VAERD in preclinical evaluation of emerging coronavirus vaccines, animal models should be used to evaluate the potential for vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 to enhance disease following infection. Here, we show a clear distinction between the immune profile elicited by research-grade mRNA-1273 and vaccine regimens that result in enhanced inflammation following MA10 challenge in mice. mRNA-1273, even at a relatively modest dose of 1 μg, elicits high-potency neutralizing antibodies and primes T cell immunity toward effective antiviral T cell responses. In addition to increased virus-neutralizing activity, a higher prevalence of S-directed IgG2a antibodies may increase the potential for Fc-mediated effector functions, including direct killing (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity [ADCC]) and phagocytosis (antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis [ADCP]) of target cells due to increased activating FcγR (FcγRI, FcγRIII, and FcγRIV) engagement by innate immune cells relative to IgG1 (a more functionally restricted isotype in mice; Bruhns, 2012). Importantly, immunization with as little as 0.1 μg of mRNA-1273, a dose that minimally controlled viral replication, dampened lung inflammation after challenge. Conversely, mice immunized with whole-inactivated SARS viruses or denatured S with alum induced weak neutralizing activity and Th2-biased immune responses, including evidence of increased eosinophil and neutrophil infiltration of lung that are hallmark features of disease enhancement following challenge. We provide evidence for the absence of vaccine-enhanced illness by mRNA-1273 in comparison to regimens that elicit such a response, supporting a strong safety profile for mRNA vaccination against COVID-19.
Enhanced disease has long been associated with vaccines that elicit qualitative and quantitatively distinct immune responses, including Th2-biased T cells, and low or waning concentrations of antibodies, particularly if the antibodies have limited neutralization potency (Arvin et al., 2020; Graham, 2020). Using ICS, we determined that T cells elicited by inactivated virus and denatured protein were prone to express one or more of the prototypical Th2-associated cytokines, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. This was true for both S- and N-specific T cells elicited by heterologous DI CoV-1. IgG subclass determination for S-directed antibodies corroborated the ICS, with IL-4-regulated IgG1 prevailing over IFNγ-regulated IgG2a in the alum-containing immunization groups. In line with this profile, we observed no elicitation of S-directed CD8+ T cells by either of these protein-based vaccine regimens. Our data illustrate that suboptimal, pre-existing heterologous or homologous responses can upset a delicate balance and lead to cytokine deregulation and enhanced immunopathology following SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Although mRNA vaccines have previously been shown to strongly induce both IgG2a and IgG1 (Corbett et al., 2020a; Laczkó et al., 2020; Lederer et al., 2020), we consistently observed a dose response in the mRNA-1273 groups, with a higher proportion of T cells expressing Th2 cytokines and a lower IgG2a/IgG1 ratio in the 0.1 μg dose group. This is not surprising, given that antigen dose is a factor that can contribute to the differentiation of type 1 versus type 2 responses (Constant and Bottomly, 1997). Notably, 0.1 μg is a lower dose than tested for other mRNA COVID vaccines (Laczkó et al., 2020; Lederer et al., 2020; Vogel et al., 2020) and was intentionally selected as a subprotective dose that could serve as a surrogate of limited or waning immunity and allow breakthrough infections with active viral replication in the lung. Although immunity in this group was shifted away from a strong type-1-biased toward a more balanced immune response and S-specific CD8+ T cells were undetectable, mice in this group were protected from increased proinflammatory cytokine production and eosinophilic lung inflammation following challenge.
Cytokine expression by S-specific CD8+ T cells in the 1 μg mRNA-1273 group exhibited a typical IFNγ > TNFα > IL-2 hierarchy, but we noted that the hierarchy for Th1 cell cytokine expression was consistently IL-2 > TNFα > IFNγ in the 1 μg dose group, and there was a paucity of IFNγ-secreting CD4+ T cells in the 0.1 μg mRNA-1273 dose group. Other mRNA COVID-19 vaccines have more strongly elicited IFNγ in mouse models, but these studies used higher doses of mRNA (Laczkó et al., 2020; Lederer et al., 2020; Vogel et al., 2020). The elevated production of IFNγ by T cells in the 1 μg mRNA-1273 dose group may reflect a threshold needed to achieve increased IL-12-mediated polarization toward a “type 1” immune program by activated antigen presenting cells (APCs). It is likely that higher concentrations of IFNγ reinforced both CD4+ Th1 and CD8+ effector T cell responses and, in turn, promoted antigen processing and presentation by APC through expression of transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP), the beta catalytic subunits of the immunoproteasome, and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II molecules (de Araújo-Souza et al., 2015; Whitmire et al., 2005).
During natural SARS-CoV-2 infection, IFNγ does not appear to strongly dominate the S-specific Th1 CD4+ cell profile over IL-2 and TNFα, and SARS-CoV-2 may not polarize as strongly toward the type 1 signature as influenza (Braun et al., 2020; Law et al., 2021; Peng et al., 2020; Sekine et al., 2020). A similar pattern of cytokine expression is also observed following human vaccination with mRNA-1273 (Jackson et al., 2020) and a recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine (NVX-CoV2373; Keech et al., 2020). Whether this reflects immune modulation by SARS-CoV-2 or intrinsic properties of S-specific cells remains to be determined. Importantly, approaches that focus solely on IFNγ detection, particularly IFNγ ELISpot, could severely underestimate the SARS-CoV-2 T cell response following either vaccination or infection (Dan et al., 2016; Nakiboneka et al., 2019). We suspect that the IL-2+ IFNγ− CD4+ T cells detected 2 weeks post-boost following mRNA-1273 immunization in our study may reflect a primed but uncommitted subpopulation of memory cells with effector potential poised for differentiation into Th1 and Th2 cells depending on the cytokine microenvironment (Mosmann et al., 2009). It is conceivable that the added Th cell subset flexibility of such vaccine-induced memory cells may provide the benefit of supporting type 1 responses to control viral replication and type-2-associated functions to counteract excessive Th1-cell-mediated inflammatory tissue damage that may occur following severe cases of natural infection. Evidence for additional effector functions of IL-2+ IFNγ− cells (referred to as primed precursor Th or Thpp cells) include chemokine production for immune cell recruitment to lymphoid tissues (Mosmann et al., 2009; Yang and Mosmann, 2004).
Given the lack of strong Th1 cell polarization at the relatively low doses of mRNA used in our studies, we posited that ICS was not capturing all S-specific T cells. Using the AIM assay, we measured 10- to 20-fold more S-specific CD4+ T cells than were detected using the ICS and demonstrated a high frequency of S-specific Tfh cells, supporting the selection of high-affinity GC B cells and the generation of potently neutralizing antibody in the 1 μg mRNA-1273 group. Strong induction of Tfh cells is one feature that makes mRNA an attractive platform for vaccination (Pardi et al., 2018). A single immunization with mRNA encoding S demonstrated a superior capacity to induce GC responses compared to adjuvanted protein (Lederer et al., 2020). This could contribute to the observed efficacy of mRNA-1273 (NIAID, NIH and Moderna) and BNT162b2 (BioNTech and Pfizer) after a single immunization in phase 3 clinical trials.
In summary, our data demonstrate the absence of VAERD after MA10 challenge of mRNA-1273-vaccinated mice, even at an extremely low subprotective vaccine dose and under conditions where both whole-inactivated virus and denatured subunit protein immunization led to enhancement of lung immunopathology. mRNA-1273 elicits both B and T cell responses to the full-length S protein that contribute to effective antiviral immunity. It has demonstrated the ability to elicit potent and effective S-specific immunity in NHP (Corbett et al., 2020b) and humans (Anderson et al., 2020; Jackson et al., 2020; Widge et al., 2021) and demonstrated 94.1% efficacy in a phase 3 trial (Baden et al., 2021). Continued administration of mRNA-1273 under emergency use authorization is warranted based on its high efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19 and demonstration of clinical and preclinical safety.
Limitations of the study
The greatest limitation of our study is the imprecise ability to predict VAERD in humans using animal models. It is particularly difficult to interpret nuanced readouts, such as weight loss, and we relied on the combination of alterations in the lung cytokine milieu and histopathology after challenge for indications of enhancement. Together, these readouts corroborate a pattern of type 2-biasing and eosinophilia post-challenge for whole-inactivated and denatured vaccine regimens and protection from inflammation in mRNA-1273-vaccinated mice. Although animal models can reproduce RSV- and measles-driven VAERD (De Swart et al., 2002; Johnson and Graham, 1999; Johnson et al., 2003, 2004; Polack et al., 2003), it is difficult to implicate the same immunological mechanisms in humans. Despite several observations of vaccine-enhanced disease in animals for SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV, the lack of human coronavirus vaccine testing has left VAERD a major open question and something that should be prospectively evaluated in ongoing clinical trials across diverse vaccine platforms while the opportunity exists. This evaluation would need clear endpoints to identify and confirm infection events; the wide and complex spectrum of COVID in the human population adds a considerable challenge for discriminating enhanced symptomology and immune pathology. To date, across all platforms, including whole-inactivated viruses, there has been no evidence of VAERD in humans, but this should be followed carefully over time as immune responses wane in the presence of emerging variant viruses of concern. Dose reduction performed in these studies is a surrogate for waning immune responses but is not the same, and long-term monitoring is recommended. We relied on using the Th2-prone BALB/c and low doses of antigen that we anticipated could elicit low-potency antibodies and are encouraged both by the measures required to drive VAERD and the absence of inflammation seen in the mRNA-1273 groups. We anticipate the use of aged mice could further drive immune pathology and have ongoing studies to address mRNA-1273-mediated protection in that setting.
We are unable to parse the individual role of T cells and antibody to the VAERD seen in the whole inactivated virus and denatured S groups. T-cell-depletion studies would be needed to delineate their contribution to eosinophilic immune pathology and could help clarify the beneficial or possibly detrimental contribution of the T cell response following infection or vaccination (Chen and John Wherry, 2020; DiPiazza et al., 2021; Jarjour et al., 2021; Lipsitch et al., 2020). The apparent lack of induction of T cells by FI CoV-2 in our second study does not rule out a potential role for primed T cells following challenge; we were unable to address the T cell response post-challenge in these studies. Although antibodies to N are more frequently implicated in VAERD (Bolles et al., 2011; Deming et al., 2006; Yasui et al., 2008), enhanced immune pathology consistent with that which we observed for denatured S alone has been previously noted following S vaccination (Honda-Okubo et al., 2015). We note that antibodies to denatured S appear to be lower potency, but the sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 neutralization assays when S-specific antibody titers are low impedes our ability to effectively compare potency and determine how relative potency relates to disease outcome. The successes of passive transfer of antibody during early infection speak to a protective role for antibody (Chen et al., 2021; Weinreich et al., 2021), but selected antibodies are generally high potency. As viral mutations accumulate through adaptation and selection, the affinity, epitope specificity, and bioactivity of monoclonal countermeasures and polyclonal antibody responses to vaccination will need to be monitored. We believe that using conformationally correct, full-length S protein to elicit diverse T cell responses and potent neutralizing activity helps mitigate these risks. Combined, the high efficacy of mRNA-1273 and the preclinical data reported here provide some assurance that, even with variant strains that may be less susceptible to vaccine-induced neutralizing activity, protection against disease will be maintained.
STAR★Methods
Key resources table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 (Mouse BD Fc Block), Clone 2.4G2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#553142; RRID: AB_394657 |
| BD Optibuild BUV395 Rat Anti-Mouse CD44, Clone IM7 | BD Biosciences | Cat#740215; RRID: AB_2739963 |
| BD PharMingen PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD3 Molecular Complex, Clone 17A2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#555275; RRID: AB_395699 |
| BD Horizon BUV737 Rat Anti-Mouse CD19, Clone 1D3 | BD Biosciences | Cat#612781; RRID: AB_2870110 |
| BD Horizon BV711 Rat Anti-Mouse CD45R/B220, Clone RA3-6B2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#563892; RRID: AB_2738470 |
| BD Horizon BV605 Rat Anti-Mouse CD138, Clone 281-2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#563147; RRID: AB_2721029 |
| BD Optibuild BUV563 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD95, Clone Jo2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#741292; RRID: AB_2870823 |
| BD Optibuild BUV805 Rat Anti-Mouse CD4, Clone RM4-5 | BD Biosciences | Cat#741912; RRID: AB_2871226 |
| BD Horizon APC-R700 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1), Clone J43 | BD Biosciences | Cat#565815; RRID: AB_2739366 |
| BD PharMingen APC-H7 Rat Anti-Mouse IgD, Clone 11-26c.2a | BD Biosciences | Cat#565348; RRID: AB_2739201 |
| BD Horizon PE-CF594 Rat Anti-Mouse CD185 (CXCR5), Clone 2G8 | BD Biosciences | Cat#562856; RRID: AB_2737842 |
| BD Optibuild BUV737 Rat Anti-Mouse CD3 molecular complex, Clone 17A2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#741788; RRID: AB_2871136 |
| BD Horizon BV480 Rat Anti-Mouse CD4, Clone RM4-5 | BD Biosciences | Cat#565634; RRID: AB_2739312 |
| BD PharMingen PE Rat Anti-Mouse I-A/I-E, Clone M5/114.15.2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#557000; RRID: AB_396546 |
| BD Horizon BV421 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1), Clone J43 | BD Biosciences | Cat#562584; RRID: AB_2737668 |
| BD Horizon BV605 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD69, Clone H1.2F3 | BD Biosciences | Cat#563290; RRID: AB_2738120 |
| BD Horizon BUV805 Rat Anti-Mouse CD8α, Clone 53-6.7 | BD Biosciences | Cat#612898; RRID: AB_2870186 |
| BD Horizon BV605 Rat Anti-Mouse CD62L, Clone MEL-14 | BD Biosciences | Cat#563252; RRID: AB_2738098 |
| BD Horizon BV650 Rat Anti-Mouse IFN-γ, Clone XMG1.2 | BD Biosciences | Cat#563854; RRID: AB_2738451 |
| BD Horizon BV711 Rat Anti-Mouse TNFα, Clone MP6-XT22 | BD Biosciences | Cat#563944; RRID: AB_2738499 |
| BD Horizon BV421 Rat Anti-Mouse IL-2, Clone JES6-5H4 | BD Biosciences | Cat#562969; RRID: AB_2737923 |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse/human GL7 Antigen (T and B Activation Marker) Antibody | Biolegend | Cat#144620; RRID: AB_2800677 |
| Brilliant Violet 510 anti-mouse IgM Antibody, Clone RMM-1 | Biolegend | Cat#406531; RRID: AB_2650758 |
| APC anti-mouse CD154 Antibody, Clone MR1 | Biolegend | Cat#106510; RRID: AB_2561561 |
| PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD62L Antibody, Clone MEL-14 | Biolegend | Cat#104418; RRID: AB_313103 |
| Alexa FluorⓇ 488 anti-mouse IL-4 Antibody, Clone 11B11 | Biolegend | Cat#504109; RRID: AB_493320 |
| APC anti-mouse/human IL-5 Antibody, Clone TRFK5 | Biolegend | Cat#504306; RRID: AB_315330 |
| IL-13 Monoclonal Antibody (eBio13A), PE-Cyanine7, eBioscience | Invitrogen | Cat#25-7133-82; RRID: AB_2573530 |
| Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, HRP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# G-21040, RRID:AB_2536527 |
| SARS-CoV-2 S1_NTD-specific mAb S652-118 | Vaccine Research Center, NIH | N/A |
| Goat Anti-Mouse IgG1, Human ads-HRP antibody | SouthernBiotech | Cat# 1070-05, RRID:AB_2650509 |
| Goat Anti-Mouse IgG2a, Human ads-HRP antibody | SouthernBiotech | 1080-05, RRID:AB_2734756 |
| SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) nucleocapsid antibody | GeneTex | Cat# GTX135357, RRID:AB_2868464 |
| EMBP (S-16) antibody | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-33938, RRID:AB_2268679 |
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
| MA10 SARS-CoV-2 | Ralph Baric Lab | N/A |
| Biological samples | ||
| DI SARS-CoV-1 + alum | BEI resources | Cat# NR-3882 and NR-3883 |
| FI SARS-CoV-2 | DMID, NIAID | N/A |
| Research-grade mRNA-1273 | Moderna, Inc. | N/A |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 S-2P conjugated to Streptavidin-APC | Vaccine Research Center, NIH | N/A |
| Streptavidin Allophycocyanin (APC) (Invitrogen) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#S32362 |
| Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 S-2P conjugated to Streptavidin-BB515 | Vaccine Research Center, NIH | N/A |
| Streptavidin BB515 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 564453, RRID:AB_2869580 |
| Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 RBD-SD1 conjugated to Streptavidin BV421 | Vaccine Research Center, NIH | N/A |
| Streptavidin BV421 | BD Biosciences | Cat# 563259, RRID:AB_2869475 |
| BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer | BD Biosciences | Cat#566349 |
| eBioscience Protein Transport Inhibitor Cocktail (500X) | Invitrogen | Cat#00-4980-93 |
| PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike glycoprotein) | JPT | PM-WCPV-S |
| PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (NCAP) | JPT | PM-WCPV-NCAP |
| His-tagged SARS-CoV-2 S-2P (expressed from VRC7471_2019 nCoV S-2P-dFurin-F3CH2S_JSM) | Vaccine Research Center, NIH | N/A |
| KPL SureBlue TMB 1-component microwell peroxidase substrate | SureBlue | Cat#5120-0077 |
| 1N sulfuric acid | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#SA212-1 |
| Luciferase Cell Culture Lysis 5X Reagent | Promega | Cat#E1531 |
| FuGENE® 6 Transfection Reagent | Promega | Cat#E2692 |
| Bond Polymer Refine Detection | Leica Biosystems | Cat#DS9800 |
| Bond Dewax Solution | Leica Biosystems | Cat#AR9222 |
| Bond TM Epitope Retrieval 1 | Leica Biosystems | Cat#AR9961 |
| CAT Hematoxylin | Biocare Medical, Inc. | Cat#CATHE-MM |
| NovaUltra Eosin Solution | IHC World, LLC | Cat#IW-3100B |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| Luciferase Assay System | Promega | Cat#E1501 |
| Expifectamine 293 Transfection Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#A14525 |
| BD Cytofix/Cytoperm Fixation/Permeabilization Solution Kit | BD Biosciences | Cat#554714 |
| LIVE/DEAD Fixable Blue Dead Cell Stain Kit, for UV excitation | Invitrogen | Cat#L34962 |
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
| HEK293T/17 cell line | ATCC | Cat# CRL-11268, RRID:CVCL_1926 |
| 293T cell line stably overexpressing human ACE2 cell surface receptor | Michael Farzan and Huihui Mu, Scripps Research | N/A |
| HEK293T/17 SF cell line | ATCC | ACS-4500, RRID:CVCL_4V93 |
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
| BALB/cJ mouse | Jackson Laboratory | 000651; RRID: IMSR_JAX:000651 |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| VRC5601: pHR’ CMV Luc | Naldini et al. (1996) | N/A |
| VRC5602: pCMV ΔR8.2 | Naldini et al. (1996) | N/A |
| VRC9260: TMPRSS2 | Vaccine Research Center, NIH | N/A |
| VRC7480: Spike WH-Human_epi_402119 S_VRC8400 | Vaccine Research Center, NIH | N/A |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| FlowJo 10 software | FlowJo | N/A |
| Pestle software, version 2.0 | Joshua Nozzi and Mario Roederer | N/A |
| Spice software, version 6.0 | Joshua Nozzi and Mario Roederer | N/A |
| GraphPad Prism, version 8 | GraphPad Software | N/A |
| Bond RX v4 | Leica Biosystems | N/A |
| cellSens Dimension v1.9 | Olympus | N/A |
Resource availability
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be addressed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact Tracy Ruckwardt (truckwardt@nih.gov).
Materials availability
This study did not generate unique reagents.
Data and code availability
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
Experimental model and subject details
Mice
All experiments were conducted with age-matched (6–10 weeks) female BALB/cJ mice purchased from Jackson Laboratories (strain 000651). Mice were initially maintained under specific-pathogen-free conditions on standard rodent chow and water supplied ad libitum in the animal care facility at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). The protocol (19-799) was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Vaccine Research Center (VRC), NIAID, National Institutes of Health (NIH) and carried out in accordance with the recommendations and guidelines of the NIH Guide to the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Mice were housed in a facility fully accredited by the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International (AAALAC), and procedures were conducted in accordance with all relevant federal and National Institutes of Health guidelines and regulations. Upon transfer of the animals to the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, work was again carried out according to guidelines outlined by the AAALAC, and work performed with approved standard operating procedures and safety conditions for SARS-CoV-2 in BSL3 facilities designed to conform to the safety requirements recommended by Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories (BMBL), the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the NIH. The facility has been approved for use by the UNC Department of Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) and the CDC.
SARS-CoV-2 MA10 virus
SARS-CoV-2 MA10 was generated by serially passaging SARS-CoV-2 MA stock virus in the lungs of mice as previously described (Dinnon et al., 2020; Leist et al., 2020). A clonal isolate from P10 was plaque purified to obtain SARS-CoV-2 MA10. Viral stocks were propagated on Vero E6 cells in minimal essential medium (MEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone) and supplemented with penicillin and kanamycin (GIBCO). Virus plaques were visualized by neutral red staining for two to three days. All viral infections were conducted under biosafety level 3 (BSL-3) conditions at negative pressure, and personnel wore Tyvek suits connected to personal powered-air purifying respirators.
Cell lines
The simian kidney cell line Vero E6 (ATTC # CRL1586, female) was purchased from ATCC. Vero E6 cells used in plaque assays from nasal turbinates and lungs were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% Fetal Clone II and 1% antibiotic–antimycotic at 37 °C and 5% CO2. ACE2-expressing 293T cells (female, provided by M. Farzan, Scripps Research Institute) were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM glutamine and 1% penicillin–streptomycin at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Expi293 cells (female) were used for protein expression and maintained in the manufacturer’s suggested medium.
Method details
Protein production
Vectors encoding SARS-CoV-2 S-2P were generated as previously described (Wrapp et al., 2020). Proteins were expressed by transfection of plasmids into Expi293 cells using Expifectamine transfection reagent (ThermoFisher) in suspension at 37 °C for 4–5 days. Transfected cell culture supernatants were collected, buffer exchanged into 1 × PBS, and protein was purified using Strep-Tactin resin (IBA). For SARS-CoV-2 S-2P used for mouse inoculations, tags were cleaved with addition of HRV3C protease (ThermoFisher) (1% wt/wt) overnight at 4 °C. Size-exclusion chromatography using Superose 6 Increase column (GE Healthcare) yielded final purified protein. A mammalian codon-optimized plasmid encoding foldon inserted minifibritin previously described (Corbett et al., 2020a) was used to compete foldon-specific antibodies where indicated.
Immunogen preparation and immunizations
Products NR-3882 and NR-3883 were obtained from Biodefense and Emerging Infections Research Resources Repository (BEI Resources) and used for lower-dose (0.2 μg) and higher-dose (1 μg) DI CoV-1 immunization, respectively, in the rear hind legs of BALB/cJ mice. These products were originally intended for active immunization for SARS-CoV-1. A seed virus was prepared, and sucrose purified prior to double inactivation with both formaldehyde and UV irradiation, and the final product was formulated with alum at a final concentration of 5 or 10 μg/mL (NR-3882 and NR-3883, respectively). Formalin-inactivated SARS-CoV-2 was produced under contract with Battelle Biomedical Research Center (BBRC) and was kindly provided by DMID. Briefly, SARS-CoV-2 (isolate USA-WA1/2020, BEI resources NR-52352) grown on Vero E6 cells was harvested on day 2, and clarified supernatant was inactivated using formalin (37% formaldehyde, Fisher Scientific) at a concentration of 0.05% at 37°C for a minimum of 48 hours. Inactivation was confirmed using plaque assays, and protein quantitated using a Bradford assay testing kit. The material was formulated with Alhydrogel® adjuvant (InvivoGen catalog vac-alu-250) at a 1:1 ratio (v/v), and doses of 0.2 or 2 μg were injected into the rear hind limbs of BALB/c mice. Heat-denatured spike protein was produced by heating SARS-CoV-S-2P protein (Wrapp et al., 2020) for 10 minutes at 95°C. Denatured protein was formulated 1:1 (v/v) with Alhydrogel and doses of either 0.2 or 1 ug were injected into the rear hind limbs. Research-grade mRNA-1273, sequence-optimized mRNA encoding SARS-CoV-2 S-2P protein formulated in a lipid nanoparticle (LNP), was produced and purified at Moderna, Inc. as previously described (Corbett et al., 2020a). Mice were immunized in the rear hind limb with doses of either 0.1 or 1 μg of mRNA-1273.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Nunc Maxisorp ELISA plates (ThermoFisher) were coated with 100 ng of protein in 1X PBS at 4°C for 16 hr. After standard washes and blocks, plates were incubated with serial dilutions of sera for 1 hr at room temperature (RT). Where applicable, to block binding of foldon-specific antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 S-2P protein, sera dilutions were preincubated with 50 μg/mL of foldon protein for 1 hour at RT prior to adding to the plate. After washing, anti-mouse IgG, IgG1 or IgG2a–horseradish peroxidase conjugates (ThermoFisher) were used as secondary antibodies, and 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) (KPL) was used as the substrate to detect antibody responses. Endpoint titers were calculated as the dilution that emitted an optical density exceeding four times background from secondary antibody alone and extrapolated from a 4-parameter nonlinear fit curve using GraphPad Prism software.
Pseudovirus microneutralization assay
To produce SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses, a codon-optimized CMV/R-SARS-CoV-2 S (Wuhan-1, GenBank #: MN908947.3) plasmid was constructed. A single amino acid mutation was performed to change residue 614 to a glycine (G) to better reflect the more transmissible, predominant circulating strain of SARS-CoV-2. Pseudoviruses were produced by co-transfection of plasmids encoding a luciferase reporter, lentivirus backbone, and S genes into HEK293T/17 cells (ATCC), as previously described (Wang et al., 2015). A plasmid for expression of TMPRSS2 was also co-transfected (Böttcher et al., 2006). Pseudoneutralization assays were performed as previously described (Corbett et al., 2020a). Briefly, heat-inactivated (HI)-serum was mixed with pseudovirus, incubated, and then added to 293T-ACE2 cells. Three days later, cells were lysed, and luciferase activity (relative light units, RLU) was measured. Percent neutralization was calculated considering uninfected cells as 100% neutralization and cells transduced with pseudovirus as 0% neutralization. IC50 titers were determined based on 5-parameter nonlinear curve fit using GraphPad Prism software.
Intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry
Mononuclear single cell suspensions from whole mouse spleens were generated using a gentleMACS tissue dissociator (Miltenyi Biotec) followed by 70 μm filtration and density gradient centrifugation using Fico/Lite-LM medium (Atlanta Biologicals). Cells from each mouse were resuspended in R10 media (RPMI 1640 supplemented with Pen-Strep antibiotic, 10% HI-FBS, Glutamax, and HEPES) and incubated for 6 hr at 37°C with protein transport inhibitor cocktail (eBioscience) under four conditions: no peptide (DMSO only) stimulation, stimulation with two spike peptide pools (S1 and S2 peptide pools, 85% pure, JPT), and stimulation with a nucleocapsid peptide pool (N) (PepmixTM JPT product PM-WCPV-NCAP). Peptide pools were used at a final concentration of 2 μg/ml each peptide. Cells from each group were pooled for stimulation with cell stimulation cocktail (eBioscience) as a positive control. Following stimulation, cells were washed with PBS prior to staining with LIVE/DEAD Fixable Blue Dead Cell Stain (Invitrogen) for 20 min at RT. Cells were then washed in FC buffer (PBS supplemented with 2% HI-FBS and 0.05% NaN3) and resuspended in BD Fc Block (clone 2.4G2) for 5 min at RT prior to staining with a surface stain cocktail containing the following antibodies purchased from BD and Biolegend: I-A/I-E (M5/114.15.2) PE, CD8α (53-6.7) BUV805, CD44 (IM7) BUV395, CD62L (MEL-14) BV605, and CD4 (RM4-5) BV480 in brilliant stain buffer (BD). After 15 min at RT, cells were washed with FC buffer, then fixed and permeabilized using the BD Cytofix/Cytoperm fixation/permeabilization solution kit according to manufacturer instructions. Cells were washed in perm/wash solution and stained with Fc Block (5 min at RT), followed by intracellular staining (30 min at 4°C) using a cocktail of the following antibodies purchased from BD, Biolegend, or eBioscience: CD3 (17A2) BUV737, IFNγ (XMG1.2) BV650, TNFα (MP6-XT22) BV711, IL-2 (JES6-5H4) BV421, IL-4 (11B11) Alexa Fluor 488, IL-5 (TRFK5) APC, and IL-13 (eBio13A) PE-Cy7 in 1x perm/wash diluted with brilliant stain buffer. Finally, cells were washed in perm/wash solution and resuspended in 0.5% PFA-FC stain buffer prior to running on a Symphony A5 flow cytometer (BD). Analysis was performed using FlowJo software, version 10.6.2 according to the gating strategy outlined in Figure S1. Background cytokine expression in the no peptide condition was subtracted from that measured in the S1, S2, and N peptide pools for each individual mouse.
Antigen-specific CD4+ T cells, including Tfh cells were examined using an activation induced marker (AIM) assay. Splenocytes were resuspended in R10 media containing BD Fc Block and anti-CD154 (CD40L) antibody conjugated to APC (BD, clone: MR1) and incubated for 6 hr at 37°C under three conditions: no peptide (DMSO only) stimulation, and stimulation with the S1 and S2 peptide pools. Peptide pools were used at a final concentration of 2 μg/ml each peptide. Cells from each group were pooled for stimulation with cell stimulation cocktail (eBioscience) as a positive control. Following stimulation, cells were washed with PBS prior to staining with LIVE/DEAD Fixable Blue Dead Cell Stain (Invitrogen) for 20 min at RT. Cells were then washed in FC buffer (PBS supplemented with 2% HI-FBS and 0.05% NaN3) and resuspended in BD Fc Block (clone 2.4G2) for 5 min at RT prior to staining with a surface stain cocktail containing the following antibodies purchased from BD and Biolegend: CD3 (17A2) BUV737, CD4 (RM4-5) BV480, I-A/I-E (M5/114.15.2) PE, CD44 (IM7) BUV395, CD62L (MEL-14) PE-Cy7, CXCR5 (2G8) PE-CF594, PD-1 (J43) BV421, CD69 (H1.2F3) BV605. After 15 min at RT, cells were washed in FC stain buffer solution and resuspended in 0.5% PFA-FC stain buffer prior to running on a Symphony A5 flow cytometer (BD). Analysis was performed using FlowJo software, version 10.6.2 according to the gating strategy outlined in Figure 7A. Background cytokine expression in the no peptide condition (DMSO) was subtracted from that measured in the S1 and S2 peptide pools for each individual mouse, with representative upregulation of activation induced markers (CD69 and CD40L) shown in Figure S7B.
B cells and plasma cells were examined using a separate panel, which included molecular probes for identification of antigen-specific cells. Directly ex vivo, splenocytes were washed with PBS prior to staining with LIVE/DEAD Fixable Blue Dead Cell Stain (Invitrogen) for 20 min at RT. Cells were then washed in FC buffer (PBS supplemented with 2% HI-FBS and 0.05% NaN3) and resuspended in BD Fc Block (clone 2.4G2) for 5 min at RT prior to staining with a surface stain cocktail containing the following antibodies purchased from BD and Biolegend, and NIH Vaccine Research Center (VRC) generated B cell capture probes: CD3 (17A2) PE, CD19 (1D3) BUV737, B220 (RA3-6B2) BV711, CD138 (281-2) BV605, T and B cell activation marker (GL7) PE-Cy7, CD95/Fas (Jo2) BUV563, CD4 (RM4-5) BUV805, CD44 (IM7) BUV395, PD-1 (J43) APC-R700, CXCR5 (2G8) PE-CF594, IgD (11-26c.2a) APC-H7, IgM (RMM-1) BV510, S-2P probe APC, S-2P probe BB515, and RBD-SD1 probe BV421. After 15 min at RT, cells were washed in FC stain buffer solution and resuspended in 0.5% PFA-FC stain buffer prior to running on a Symphony A5 flow cytometer (BD). Analysis was performed using FlowJo software, version 10.6.2 according to the gating strategy outlined in Figure S7A.
SARS-CoV-2 MA10 infection and viral titer measurements
For virus challenge, mice were anesthetized (ketamine/xylazine) and infected intranasally with 104 (study 1) or 105 (study 2) PFU SARS-CoV-2 MA10 diluted in 50 μL PBS. Clinical signs of disease (weight loss) were monitored daily. Mice were euthanized by isoflurane overdose at days 2, 4, and 7 and samples for titer (caudal right lung lobe) and histopathological analyses (left lung lobe) were collected. Lung viral titers were determined using plaque assays. Briefly, right caudal lung lobes were homogenized in 1 mL PBS using glass beads and serial dilutions of the clarified lung homogenates were added to a monolayer of Vero E6 cells. After three days, plaques were visualized via staining with Neutral Red dye and counted. The left lung lobe was stored in 10% phosphate buffered formalin for seven days prior to removal from the BSL3 for processing.
Cytokine and chemokine analysis
BioPlex Pro mouse cytokine 23-plex assay (Bio-Rad) was utilized to analyze chemokines and cytokines in clarified lung supernatants according to manufacturer’s protocol. 50 μL of clarified lung samples were incubated with magnetic capture beads, washed, incubated with detection antibodies and streptavidin-PE. Cytokines were recorded on a MAGPIX machine (Luminex) and quantitated via comparison to a standard curve. Graphpad prism software was used for data analysis.
Lung Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
Lung samples from mice were processed per a standard protocol. Briefly, the tissues were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, processed with Leica ASP6025 tissue processor (Leica Microsystems), embedded in paraffin, and sectioned at 5 μm for histological analysis. Tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for routine histopathology. Sections were examined in a blinded manner by a board-certified veterinary pathologist using an Olympus BX51 light microscope, and photomicrographs were taken using an Olympus DP73 camera. For immunohistochemical (IHC) evaluation, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections (5 μm) were used to perform immunohistochemical staining using antibodies which identify SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid and eosinophils in tissue, respectively; for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid, a rabbit polyclonal SARS-CoV-2 (GeneTex, Irvine CA, GTX135357) with dilution of 1:2000 was used. For identification of tissue eosinophils, a goat polyclonal Eosinophil Major Basic Protein (EMBP; SantaCruz, Dallas TX, sc-33938) at a dilution of 1:500 was employed. Staining was carried out on the Bond RX (Leica Biosystems) platform according to manufacturer-supplied protocols. Briefly, 5 μm-thick sections were deparaffinized and rehydrated. Heat-induced epitope retrieval (HIER) was performed using Epitope Retrieval Solution 1, pH 6.0, heated to 100°C for 20 min. The specimen was then incubated with hydrogen peroxide to quench endogenous peroxidase activity prior to applying the primary antibody. Detection with DAB chromogen was completed using the Bond Polymer Refine Detection kit (Leica Biosystems CAT# DS9800). Slides were finally cleared through gradient alcohol and xylene washes prior to mounting and placing coverslips. Sections were examined by a board-certified veterinary pathologist using an Olympus BX51 light microscope and photomicrographs were taken using an Olympus DP73 camera.
Quantification and statistical analysis
Statistical Analysis
Serological responses, T and B cell readouts, and viral titer data were analyzed using Graphpad Prism using the methods outlined in each figure legend. Nonparametric methods were used when groups contained fewer than 10 mice per group.
Acknowledgments
These studies were supported by intramural funding from the Vaccine Research Center, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and NIH grant numbers U01 AI149644 (R.S.B.) and U54 CA260543 (R.S.B.). The following reagents were obtained through BEI Resources NIAID, NIH: SARS-CoV and formaldehyde- and UV-inactivated, purified, NR-3882 and NR-3883. The graphical abstract and some figure panels were created using https://biorender.com. We thank DMID, NIAID for the provision of formalin-inactivated SARS-CoV-2.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, A.T.D., S.R.L., K.M.M., B.S.G., and T.J.R.; data curation, A.T.D., S.R.L., E.P., L.A.C., and T.J.R.; formal analysis, A.T.D., S.R.L., and T.J.R.; funding acquisition, B.S.G.; investigation, A.T.D., S.R.L., O.M.A., J.I.M., A.W., M.M., B.M.N., K.W.B., A.S., K.H.D., R.J.L., S.B.-B., and T.J.R.; methodology, A.T.D., S.R.L., O.M.A., A.W., K.S.C., and T.J.R.; project administration, G.S.A.; resources, O.M.A., D.K.E., and A.C.; supervision, N.J.S., J.R.M., K.S.C., I.N.M., R.S.B., B.S.G., and T.J.R.; validation, A.T.D. and T.J.R.; visualization, A.T.D., S.R.L., and T.J.R.; writing – original draft, A.T.D. and T.J.R.; writing – review & editing, A.T.D., S.R.L., O.M.A., J.I.M., M.M., B.M.N., K.W.B., E.P., L.A.C., D.K.E., K.M.M., A.C., I.N.M., R.S.B., B.S.G., and T.J.R.
Declaration of interests
O.M.A., K.S.C., and B.S.G. are inventors on pending patent applications related to coronavirus vaccines. S.R.L. and R.S.B. have pending patents on recombinant viruses used in this study. A.T.D., D.K.E., and A.C. are current employees and shareholders of Moderna, Inc. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Published: July 2, 2021
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.018.
Supplemental information
References
- Anderson E.J., Rouphael N.G., Widge A.T., Jackson L.A., Roberts P.C., Makhene M., Chappell J.D., Denison M.R., Stevens L.J., Pruijssers A.J., et al. Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine in older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:2427–2438. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvin A.M., Fink K., Schmid M.A., Cathcart A., Spreafico R., Havenar-Daughton C., Lanzavecchia A., Corti D., Virgin H.W. A perspective on potential antibody-dependent enhancement of SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 2020;584:353–363. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2538-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baden L.R., El Sahly H.M., Essink B., Kotloff K., Frey S., Novak R., Diemert D., Spector S.A., Rouphael N., Creech C.B., et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:403–416. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolles M., Deming D., Long K., Agnihothram S., Whitmore A., Ferris M., Funkhouser W., Gralinski L., Totura A., Heise M., Baric R.S. A double-inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus vaccine provides incomplete protection in mice and induces increased eosinophilic proinflammatory pulmonary response upon challenge. J. Virol. 2011;85:12201–12215. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06048-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher E., Matrosovich T., Beyerle M., Klenk H.D., Garten W., Matrosovich M. Proteolytic activation of influenza viruses by serine proteases TMPRSS2 and HAT from human airway epithelium. J. Virol. 2006;80:9896–9898. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01118-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Loyal L., Frentsch M., Wendisch D., Georg P., Kurth F., Hippenstiel S., Dingeldey M., Kruse B., Fauchere F., et al. SARS-CoV-2-reactive T cells in healthy donors and patients with COVID-19. Nature. 2020;587:270–274. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhns P. Properties of mouse and human IgG receptors and their contribution to disease models. Blood. 2012;119:5640–5649. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-380121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Nirula A., Heller B., Gottlieb R.L., Boscia J., Morris J., Huhn G., Cardona J., Mocherla B., Stosor V., et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:229–237. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2029849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., John Wherry E. T cell responses in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020;20:529–536. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0402-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R.L., Lebman D.A., Rothman P. Mechanism and regulation of immunoglobulin isotype switching. Adv. Immunol. 1993;54:229–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constant S.L., Bottomly K. Induction of Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cell responses: the alternative approaches. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997;15:297–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett K.S., Edwards D.K., Leist S.R., Abiona O.M., Boyoglu-Barnum S., Gillespie R.A., Himansu S., Schäfer A., Ziwawo C.T., DiPiazza A.T., et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature. 2020;586:567–571. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2622-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett K.S., Flynn B., Foulds K.E., Francica J.R., Boyoglu-Barnum S., Werner A.P., Flach B., O’Connell S., Bock K.W., Minai M., et al. Evaluation of the mRNA-1273 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in nonhuman primates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:1544–1555. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotty S. T follicular helper cell biology: a decade of discovery and diseases. Immunity. 2019;50:1132–1148. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan J.M., Lindestam Arlehamn C.S., Weiskopf D., da Silva Antunes R., Havenar-Daughton C., Reiss S.M., Brigger M., Bothwell M., Sette A., Crotty S. A cytokine-independent approach to identify antigen-specific human germinal center T follicular helper cells and rare antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in blood. J. Immunol. 2016;197:983–993. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan J.M., Mateus J., Kato Y., Hastie K.M., Yu E.D., Faliti C.E., Grifoni A., Ramirez S.I., Haupt S., Frazier A., et al. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science. 2021;371:eabf4063. doi: 10.1126/science.abf4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Araújo-Souza P.S., Hanschke S.C., Viola J.P. Epigenetic control of interferon-gamma expression in CD8 T cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2015;2015:849573. doi: 10.1155/2015/849573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Swart R.L., Kuiken T., Timmerman H.H., van Amerongen G., Van Den Hoogen B.G., Vos H.W., Neijens H.J., Andeweg A.C., Osterhaus A.D. Immunization of macaques with formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) induces interleukin-13-associated hypersensitivity to subsequent RSV infection. J. Virol. 2002;76:11561–11569. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.22.11561-11569.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deming D., Sheahan T., Heise M., Yount B., Davis N., Sims A., Suthar M., Harkema J., Whitmore A., Pickles R., et al. Vaccine efficacy in senescent mice challenged with recombinant SARS-CoV bearing epidemic and zoonotic spike variants. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinnon K.H., 3rd, Leist S.R., Schäfer A., Edwards C.E., Martinez D.R., Montgomery S.A., West A., Yount B.L., Jr., Hou Y.J., Adams L.E., et al. A mouse-adapted model of SARS-CoV-2 to test COVID-19 countermeasures. Nature. 2020;586:560–566. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2708-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPiazza A.T., Graham B.S., Ruckwardt T.J. T cell immunity to SARS-CoV-2 following natural infection and vaccination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021;538:211–217. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulginiti V.A., Eller J.J., Downie A.W., Kempe C.H. Altered reactivity to measles virus. Atypical measles in children previously immunized with inactivated measles virus vaccines. JAMA. 1967;202:1075–1080. doi: 10.1001/jama.202.12.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham B.S. Rapid COVID-19 vaccine development. Science. 2020;368:945–946. doi: 10.1126/science.abb8923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham B.S., Henderson G.S., Tang Y.W., Lu X., Neuzil K.M., Colley D.G. Priming immunization determines T helper cytokine mRNA expression patterns in lungs of mice challenged with respiratory syncytial virus. J. Immunol. 1993;151:2032–2040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B.F., Corey L., Fernandes P., Gilbert P.B., Hotez P.J., Rao S., Santos M.R., Schuitemaker H., Watson M., Arvin A. Prospects for a safe COVID-19 vaccine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020;12:eabe0948. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abe0948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda-Okubo Y., Barnard D., Ong C.H., Peng B.H., Tseng C.T., Petrovsky N. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus vaccines formulated with delta inulin adjuvants provide enhanced protection while ameliorating lung eosinophilic immunopathology. J. Virol. 2015;89:2995–3007. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02980-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson L.A., Anderson E.J., Rouphael N.G., Roberts P.C., Makhene M., Coler R.N., McCullough M.P., Chappell J.D., Denison M.R., Stevens L.J., et al. mRNA-1273 Study Group An mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 - preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:1920–1931. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarjour N.N., Masopust D., Jameson S.C. T cell memory: understanding COVID-19. Immunity. 2021;54:14–18. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T.R., Graham B.S. Secreted respiratory syncytial virus G glycoprotein induces interleukin-5 (IL-5), IL-13, and eosinophilia by an IL-4-independent mechanism. J. Virol. 1999;73:8485–8495. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.10.8485-8495.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T.R., Parker R.A., Johnson J.E., Graham B.S. IL-13 is sufficient for respiratory syncytial virus G glycoprotein-induced eosinophilia after respiratory syncytial virus challenge. J. Immunol. 2003;170:2037–2045. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.4.2037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T.R., Teng M.N., Collins P.L., Graham B.S. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) G glycoprotein is not necessary for vaccine-enhanced disease induced by immunization with formalin-inactivated RSV. J. Virol. 2004;78:6024–6032. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.6024-6032.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keech C., Albert G., Cho I., Robertson A., Reed P., Neal S., Plested J.S., Zhu M., Cloney-Clark S., Zhou H., et al. Phase 1-2 trial of a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:2320–2332. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2026920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H.W., Canchola J.G., Brandt C.D., Pyles G., Chanock R.M., Jensen K., Parrott R.H. Respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants despite prior administration of antigenic inactivated vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969;89:422–434. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laczkó D., Hogan M.J., Toulmin S.A., Hicks P., Lederer K., Gaudette B.T., Castaño D., Amanat F., Muramatsu H., Oguin T.H., 3rd, et al. A single immunization with nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines elicits strong cellular and humoral immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 in mice. Immunity. 2020;53:724–732.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.07.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P.H., Ambrosino D.M., Andersen S.R., Baric R.S., Black S.B., Chen R.T., Dekker C.L., Didierlaurent A.M., Graham B.S., Martin S.D., et al. Consensus summary report for CEPI/BC March 12-13, 2020 meeting: assessment of risk of disease enhancement with COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine. 2020;38:4783–4791. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law J.C., Koh W.H., Budylowski P., Lin J., Yue F., Abe K.T., Rathod B., Girard M., Li Z., Rini J.M., et al. Systematic examination of antigen-specific recall T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 versus influenza virus reveals a distinct inflammatory profile. J. Immunol. 2021;206:37–50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2001067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer K., Castaño D., Gómez Atria D., Oguin T.H., 3rd, Wang S., Manzoni T.B., Muramatsu H., Hogan M.J., Amanat F., Cherubin P., et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines foster potent antigen-specific germinal center responses associated with neutralizing antibody generation. Immunity. 2020;53:1281–1295.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.11.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J.H., Hu J.K., Georgeson E., Nakao C., Groschel B., Dileepan T., Jenkins M.K., Seumois G., Vijayanand P., Schief W.R., Crotty S. Modulating the quantity of HIV Env-specific CD4 T cell help promotes rare B cell responses in germinal centers. J. Exp. Med. 2021;218:e20201254. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist S.R., Dinnon K.H., 3rd, Schäfer A., Tse L.V., Okuda K., Hou Y.J., West A., Edwards C.E., Sanders W., Fritch E.J., et al. A mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 induces acute lung injury and mortality in standard laboratory mice. Cell. 2020;183:1070–1085.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsitch M., Grad Y.H., Sette A., Crotty S. Cross-reactive memory T cells and herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020;20:709–713. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-00460-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T.R., Kobie J.J., Lee F.E., Quataert S.A. T helper cytokine patterns: defined subsets, random expression, and external modulation. Immunol. Res. 2009;45:173–184. doi: 10.1007/s12026-009-8098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz F.M., Cramer J.P., Dekker C.L., Dudley M.Z., Graham B.S., Gurwith M., Law B., Perlman S., Polack F.P., Spergel J.M., et al. Brighton Collaboration Vaccine-associated Enhanced Disease Working Group Vaccine-associated enhanced disease: case definition and guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine. 2021;39:3053–3066. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.01.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nader P.R., Horwitz M.S., Rousseau J. Atypical exanthem following exposure to natural measles: eleven cases in children previously inoculated with killed vaccine. J. Pediatr. 1968;72:22–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.12.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Blömer U., Gage F.H., Trono D., Verma I.M. Efficient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1996;93:11382–11388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.21.11382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakiboneka R., Mugaba S., Auma B.O., Kintu C., Lindan C., Nanteza M.B., Kaleebu P., Serwanga J. Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) negative CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells can produce immune mediators in response to viral antigens. Vaccine. 2019;37:113–122. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.11.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen J., Wang N., Corbett K.S., Wrapp D., Kirchdoerfer R.N., Turner H.L., Cottrell C.A., Becker M.M., Wang L., Shi W., et al. Immunogenicity and structures of a rationally designed prefusion MERS-CoV spike antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:E7348–E7357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707304114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi N., Hogan M.J., Naradikian M.S., Parkhouse K., Cain D.W., Jones L., Moody M.A., Verkerke H.P., Myles A., Willis E., et al. Nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines induce potent T follicular helper and germinal center B cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 2018;215:1571–1588. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples L. News feature: avoiding pitfalls in the pursuit of a COVID-19 vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:8218–8221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005456117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y., Mentzer A.J., Liu G., Yao X., Yin Z., Dong D., Dejnirattisai W., Rostron T., Supasa P., Liu C., et al. Oxford Immunology Network Covid-19 Response T cell Consortium. ISARIC4C Investigators Broad and strong memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells induced by SARS-CoV-2 in UK convalescent individuals following COVID-19. Nat. Immunol. 2020;21:1336–1345. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0782-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polack F.P., Hoffman S.J., Crujeiras G., Griffin D.E. A role for nonprotective complement-fixing antibodies with low avidity for measles virus in atypical measles. Nat. Med. 2003;9:1209–1213. doi: 10.1038/nm918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruckwardt T.J., Morabito K.M., Graham B.S. Immunological lessons from respiratory syncytial virus vaccine development. Immunity. 2019;51:429–442. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders R.W., Moore J.P. Virus vaccines: proteins prefer prolines. Cell Host Microbe. 2021;29:327–333. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine T., Perez-Potti A., Rivera-Ballesteros O., Strålin K., Gorin J.B., Olsson A., Llewellyn-Lacey S., Kamal H., Bogdanovic G., Muschiol S., et al. Karolinska COVID-19 Study Group Robust T cell immunity in convalescent individuals with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19. Cell. 2020;183:158–168.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smatti M.K., Al Thani A.A., Yassine H.M. Viral-induced enhanced disease illness. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:2991. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A.B., Kanevsky I., Che Y., Swanson K.A., Muik A., Vormehr M., Kranz L.M., Walzer K.C., Hein S., Güler A., et al. A prefusion SARS-CoV-2 spike RNA vaccine is highly immunogenic and prevents lung infection in non-human primates. bioRxiv. 2020 2020.2009.2008.280818. [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Shi W., Joyce M.G., Modjarrad K., Zhang Y., Leung K., Lees C.R., Zhou T., Yassine H.M., Kanekiyo M., et al. Evaluation of candidate vaccine approaches for MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:7712. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D.M., Sivapalasingam S., Norton T., Ali S., Gao H., Bhore R., Musser B.J., Soo Y., Rofail D., Im J., et al. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:238–251. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmire J.K., Tan J.T., Whitton J.L. Interferon-gamma acts directly on CD8+ T cells to increase their abundance during virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2005;201:1053–1059. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widge A.T., Rouphael N.G., Jackson L.A., Anderson E.J., Roberts P.C., Makhene M., Chappell J.D., Denison M.R., Stevens L.J., Pruijssers A.J., et al. Durability of responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:80–82. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2032195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrapp D., Wang N., Corbett K.S., Goldsmith J.A., Hsieh C.L., Abiona O., Graham B.S., McLellan J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 2020;367:1260–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Mosmann T. Synthesis of several chemokines but few cytokines by primed uncommitted precursor CD4 T cells suggests that these cells recruit other immune cells without exerting direct effector functions. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004;34:1617–1626. doi: 10.1002/eji.200424939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui F., Kai C., Kitabatake M., Inoue S., Yoneda M., Yokochi S., Kase R., Sekiguchi S., Morita K., Hishima T., et al. Prior immunization with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) nucleocapsid protein causes severe pneumonia in mice infected with SARS-CoV. J. Immunol. 2008;181:6337–6348. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.9.6337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger R.M., Wartel T.A., Marks F., Song M., Kim J.H. Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 and disease enhancement - knowns and unknowns. Expert Rev. Vaccines. 2020;19:691–698. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2020.1800463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou T., Teng I.T., Olia A.S., Cerutti G., Gorman J., Nazzari A., Shi W., Tsybovsky Y., Wang L., Wang S., et al. Structure-based design with tag-based purification and in-process biotinylation enable streamlined development of SARS-CoV-2 spike molecular probes. Cell Rep. 2020;33:108322. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.