Abstract
Background
PTI1 (Pto-interacting 1) protein kinase belongs to the receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase (RLCK) group of receptor-like protein kinases (RLK), but lack extracellular and transmembrane domains. PTI1 was first identified in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and named SlPTI1, which has been reported to interact with bacterial effector Pto, a serine/threonine protein kinase involved in plant resistance to bacterial disease. Briefly, the host PTI1 specifically recognizes and interacts with the bacterial effector AvrPto, which triggers hypersensitive cell death to inhibit the pathogen growth in the local infection site. Previous studies have demonstrated that PTI1 is associated with oxidative stress and hypersensitivity.
Results
We identified 12 putative PTI1 genes from the genome of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) in this study. Gene replication analysis indicated that both segmental replication events played an important role in the expansion of PTI1 gene family in foxtail millet. The PTI1 family members of model plants, i.e. S. italica, Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), rice (Oryza sativa), maize (Zea mays), S. lycopersicum, and soybean (Glycine max), were classified into six major categories according to the phylogenetic analysis, among which the PTI1 family members in foxtail millet showed higher degree of homology with those of rice and maize. The analysis of a complete set of SiPTI1 genes/proteins including classification, chromosomal location, orthologous relationships and duplication. The tissue expression characteristics revealed that SiPTI1 genes are mainly expressed in stems and leaves. Experimental qRT-PCR results demonstrated that 12 SiPTI1 genes were induced by multiple stresses. Subcellular localization visualized that all of foxtail millet SiPTI1s were localized to the plasma membrane. Additionally, heterologous expression of SiPTI1–5 in yeast and E. coli enhanced their tolerance to salt stress.
Conclusions
Our results contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the roles of PTI1 protein kinases and will be useful in prioritizing particular PTI1 for future functional validation studies in foxtail millet.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12870-021-03077-4.
Keywords: Foxtail millet (Setaria italica), Pto-interacting 1 genes (PTI1s), Expression pattern, Functional identification, Salt stress
Background
PTI1 (Pto-interacting 1) protein kinase belongs to the receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase (RLCK) group of receptor-like protein kinases (RLK), but lack extracellular and transmembrane domains [1, 2]. In plants, PTI1 play an important role in plant defense against bacterial pathogens. It was first identified in tomato and was demonstrated to specifically recognize and interact with the AvrPto effector protein injected into the plant cells by the pathogenic bacteria, thereby triggering the downstream defense response [3].
PTI1 generally contains a kinase domain consisting of 250 to 300 amino acid residues [4], and possess characteristic domains of STKc_IRAK, Pkinase_Tyr, STYKc, and SPS1 [5, 6]. In recent years, PTI1 genes had been widely identified in many species such as tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) [3, 7], Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) [1, 8], maize (Zea mays) [9, 10], soybean (Glycine max) [11, 12], cucumber (Cucumis sativus) [13] and rice (Oryza sativa) [14].
PTI1 genes in different species and subtypes are involved in different processes. In Arabidopsis, PTI1–1, PTI1–2, PTI1–3, PTI1–4 and PTI1–5 were reported to interact with protein kinase OXIDATIVE SIGNAL INDUCIBLE1 (OXI1) and are phosphorylated by OXI1 in response to phosphatidic acid (PAs), H2O2, flg22, and xylanase [8, 15]. Moreover, PTI1–2/PTI1–4 responds to oxidative stress via OXI1-PTI1–2/PTI1–4 pathway [1, 8]. Abiotic stress activated PTI1–2 also enhances the expression of reactive oxygen species (ROS) stress-responsive genes [1]. OXI1-PTI1 is also involved in the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway, which in turn responds to oxidative and biotic stresses [8, 16]. AtPTI1–5 knockout greatly affects the growth of pollen tubes resulting in male gametophyte sterility [15]. Tomato SlPTI1 interacts with and is activated by Pto, which regulates downstream signal transduction upon pathogen invasion [3, 17]. There are four members of the PTI1s in maize, which ZmPTI1a is involved in pollen propagation [9]. The ZmPTI1a hetero-overexpressed Arabidopsis lines showed enhanced salt stress tolerance, with higher fresh and dry weight compared to wild type plants [10]. Overexpressing cucumber CsPTI1-L in tobacco could enhance salt tolerance via up-regulation of multiple resistance-related genes [13]. Overexpression of OsPTI1 increases rice resistance to fungal invasion [14].
Foxtail millet (Setaria italica) was domesticated in neolithic China approximately 8700 years ago and has been regarded as an important dietary staple food in China for millennia [18, 19]. It possesses attractive qualities, such as small diploid genome (~ 510 Mb) [20], lower repetitive DNA, short life cycle, and C4 photosynthesis [21, 22]. These characteristics promote it as a model crop for exploring basic biology processes, such as plant architecture, physiology and genome evolution [23, 24]. At the same time, the stresses and barren tolerance characteristics of foxtail millet make them reduced the dependence on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and insecticides [25]. And millet cultivation could decrease the over-reliance on the major cereals that are limited in number worldwide [23]. Especially during the hard time of COVID-19 pandemic around the world, the strategic roles of foxtail millet in stabilizing grain production, ensuring the global economy and people’s livelihood are attracted more and more attentions worldwide [26, 27]. Analysis of stress resistance mechanisms and quality traits of foxtail millet are important for the development of modern foxtail millet germplasms or cultivars. With the rapid development of molecular biology, the whole genome of foxtail millet has been sequenced and published, which enables better understanding of the stress response and molecular regulatory mechanisms of this crop plant [28, 29].
PTI1 gene family of foxtail millet is not yet been identified. In our previous transcriptome analysis of salt stress in foxtail millet, a stress induced gene of Seita.5G023100.1 with unknown function were identified [30]. JGI/NCBI BLAST sequence analysis showed that it was a putative PTI1 protein kinase. Considering that PTI1 proteins participate in a variety of stress defense responses in several plant species such as tomato [3, 7], Arabidopsis [1, 8], maize [9, 10], and no PTI1 was identified in foxtail millet up to now. The systematic analysis of PTI1 gene family was carried out in this study, and 12 PTI1 genes were identified. Their chromosomal locations and protein structures were predicted and analyzed. The expression patterns of 12 SiPTI1 genes were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Our results showed that most SiPTI1 genes were differentially expressed in response to salt stress and oxidative stress. A key gene SiPTI1–5 that may be associated with salt stress was selected for further studies. Overexpression of SiPTI1–5 in yeast and Escherichia coli (E. coli) enhance their tolerance to salt stress.
These results could deepen our understanding of the characteristics and functions of PTI1 genes in foxtail millet, and also assist to identifies potential abiotic stress-responsive genes for improving foxtail millet and other crop species. In addition, this study is the first systematic report on the PTI1 gene family in plants, which will also provide reference for the subsequent systematic study on the function of PTI1 genes in foxtail millet. At the same time, it also provides reference for the study of PTI1 genes family in other species.
Results
SiPTI1s identification and annotation in foxtail millet
Our transcriptome analysis of salt stress in foxtail millet revealed an over-expressed gene (Seita.5G023100.1) with unknown function [30]. JGI/NCBI BLAST sequence analysis showed that it was a putative PTI1 protein kinase. In view of the fact that PTI1 proteins participate in a variety of stress defense responses and no PTI1 was previously identified in foxtail millet, we decided to further analyze the PTI1 gene family in foxtail millet to identify those responsive to salt stress and explore their application in crop improvement.
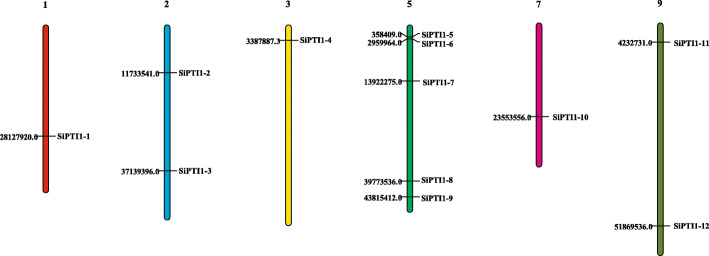
In this study, a total of 12 putative PTI1 genes were identified in foxtail millet via genome-wide analysis (Table 1, Additional file 1). The genes were named SiPTI1–1 to SiPTI1–12 according to their location on the chromosome. Foxtail millet has 9 chromosomes, ranging from 35.9 Mb (chromosome 6) to 58.9 Mb (chromosome 9). The physical map positions of the 12 SiPTI1 genes in the 9 chromosomes of foxtail millet are presented in Fig. 1. The specific location of each SiPTI1 gene on the chromosome was provided in the Additional file 4. However, the distribution of SiPTI1s on chromosomes was uneven, with five genes located on chromosome 5 (SiPTI1–5, SiPTI1–6, SiPTI1–7, SiPTI1–8, and SiPTI1–9) and only one gene located on chromosome 1, chromosome 3 and chromosome 7, respectively. Interestingly, chromosome 9 is the longest, but only two SiPTI1s are located on it (SiPTI1–11 and SiPTI1–12). Therefore, there was no positive correlation between the chromosome length and the number of PTI1 genes.
Table 1.
The identification of PTI1 members in Setaria italica
| Gene name | Gene ID | Protein length (aa) |
MW (Da) | pI | Prediction of protein Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiPTI1–1 | Seita.1G201600.1 | 364 | 39,048 | 8.43 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–2 | Seita.2G116400.1 | 369 | 40,816.1 | 6.44 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–3 | Seita.2G271300.1 | 366 | 40,364.7 | 6.84 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–4 | Seita.3G053500.1 | 362 | 39,229.4 | 7.89 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–5 | Seita.5G023100.1 | 727 | 80,955.8 | 8.38 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–6 | Seita.5G030900.1 | 428 | 46,446.6 | 9.15 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–7 | Seita.5G154400.1 | 426 | 46,095.4 | 9.26 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–8 | Seita.5G358000.1 | 395 | 43,452 | 6.01 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–9 | Seita.5G415300.1 | 387 | 42,967.9 | 7.8 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–10 | Seita.7G147800.1 | 388 | 42,733.1 | 7.38 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–11 | Seita.9G072200.1 | 364 | 39,016 | 8.43 | plasmamembrane |
| SiPTI1–12 | Seita.9G478500.1 | 366 | 38,980.2 | 8.84 | plasmamembrane |
Fig. 1.
Distribution of 12 SiPTI1 genes onto the nine foxtail millet chromosomes. Localization of the foxtail millet PTI1 genes on the foxtail millet chromosomes. Chromosomal distances are given in bp
Their domains were further confirmed by the three databases of SMART, NCBI CDD and Pfam. Gene classification and detailed annotation are listed in Table 1. The predicted SiPTI1s protein sequences ranged from 362 amino acids (SiPTI1–4) to 727 amino acids (SiPTI1–5), and the corresponding molecular weights varied from 38.9802 to 80.9558 kDa. The predict pI varied from 6.01 to 9.26. Little differed among the 12 SiPTI1 proteins except SiPTI1–5, generally, the length of PTI1 protein kinase was about 300–400 amino acids, while SiPTI1–5 encodes 727 amino acids, and the highest molecular weight was about 81 kDa.
Phylogenetic analysis of SiPTI1s with PTI1s of other plant species
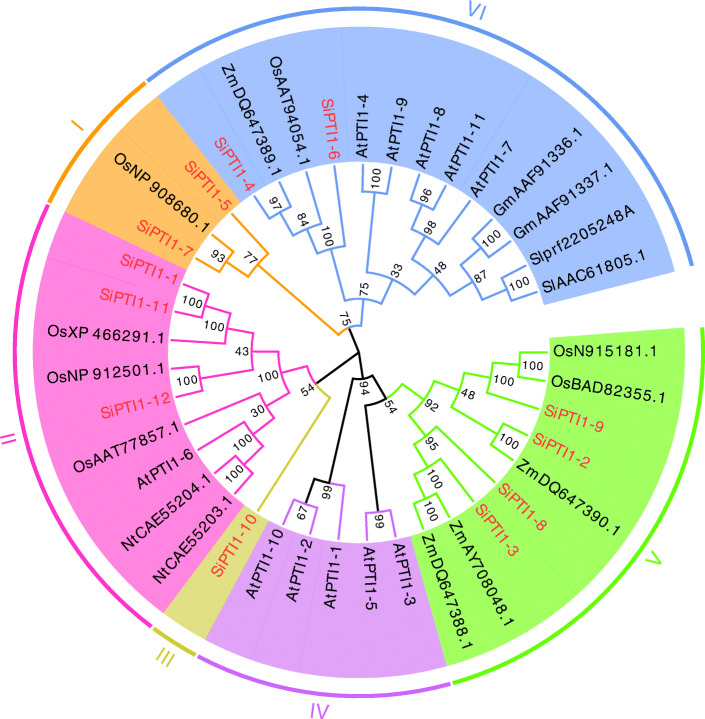
The PTI1 genes have been identified in many plant species in the recent years. Based on the publicly available information and the degree of relatedness, we chose PTI1 genes from A. thaliana (At), O. sativa (Os), tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) (Nt), Z. mays (Zm), S. lycopersicum (Sl), and G. max (Gm) to construct the phylogenetic trees with the PTI1 genes of S. italica (Si). As shown in (Fig. 2, Additional file 2), the phylogenetic analysis suggested that all PTI1 genes could be grouped into six classes and each SiPTI1 protein sequence was highly similar to their homologues in other plant species. Since a good number of the internal branches were observed to have high bootstrap values. The phylogenetic tree also revealed that the majority of foxtail millet SiPTI1 families distribution predominates with species bias, they are more closely related to those in grass species (rice and maize), in contrast, they are relatively distant relatives of the dicotyledonous Arabidopsis.
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic of the PTI1 proteins in different species. Phylogenetic analysis was based on 45 PTI1 protein sequences. Species abbreviations are as follows. At: A. thaliana; Os: O. sativa; Zm: Z. mays; Sl: S. lycopersicum; Gm: G. max; Nt: N. tabacum. Multiple sequence alignments of PTI1 amino-acid sequences were performed using ClustalX, and the phylogenetic was constructed using MEGA7 by the maximum likelihood method and 1000 bootstrap replicates. The tree was divided into six phylogenetic subgroups, designated I-VI. Letters outside of the tree indicate the defined groups
Gene structure, motif patterns analysis of PTI1 genes in foxtail millet
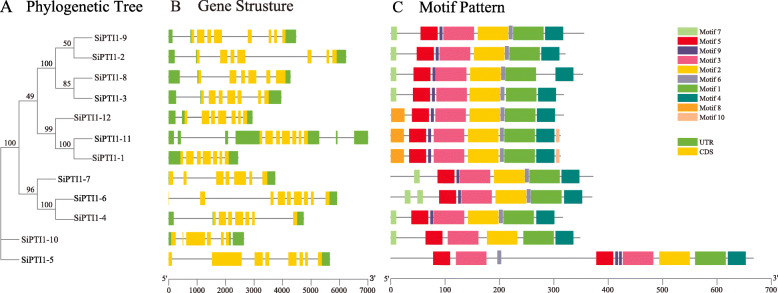
To explore the structural diversity of SiPTI1s, the distribution of exon-intron structure was analyzed and mapped in the phylogenetic tree. As shown in Fig. 3B, two PTI1 genes (SiPTI1–9 and SiPTI1–5) contained seven introns, SiPTI1–8 and SiPTI1–10 had five introns and SiPTI1–6 had eight introns. The rest of SiPTI1 genes had six introns. Exon-intron structural analysis indicated that members of some PTI1 subfamilies have similar exon-intron structures. Similar results were also found in maize [31] and other studies.
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic relationships, gene structure and architecture of conserved protein motifs in PTI1 genes from foxtail millet. The phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the full-length sequences of foxtail millet PTI1 proteins using MEGA7 software (A). Exon-intron structure of foxtail millet PTI1 genes. Green boxes indicate untranslated 5′- and 3′-regions; yellow boxes indicate exons; black lines indicate introns (B). The motif composition of foxtail millet PTI1 proteins. The motifs, numbers 1–10, are displayed in different colored boxes (C). The sequence information for each motif is provided in Additional file 2. The length of protein can be estimated using the scale at the bottom
The motif patterns among SiPTI1s were investigated (Fig. 3 C and Additional file 3). A total of 10 motifs were discovered and 5 of them were found to be highly conserved. In addition, all of SiPTI1s contained motifs 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. Except for SiPTI1–10, all of other SiPTI1s contain motifs 6 and 9. Furthermore, motif 8 was found in three of the SiPTI1s members (SiPTI1–1, SiPTI1–11 and SiPTI1–12), while motif 10 was only presented in two members (SiPTI1–1, SiPTI1–11). Interestingly, the motif distribution of SiPTI1–5 was different from other members of the family, in that motifs 3, 5, 9 appear twice each. Despite the difference of motif types between groups, members within the same group such as SiPTI1–9 and SiPTI1–2, SiPTI1–8 and SiPTI1–3, SiPTI1–11 and SiPTI1–1 tend to exhibit similar motif patterns (Fig. 3 A and C), which indicate functional similarity between them. Amino acid sequence analyses showed that the SiPTI1s contain the representative kinase domains, such as STKC_IRAK, Pkinase_Tyr, STYKc, and SPS1 (data not shown). As known that the catalytic domain of serine/threonine kinases contains 11 subdomains [31, 32], the pileup analysis also showed that the 12 SiPTI1 kinases also contained the conserved 11 subdomains like known PTI1 gene of SlPTI1 in tomato (Supplementary Fig. 2). In addition, when compared the SiPTI1s sequence of foxtail millet with the PTI1 sequences of maize and rice, we found that the catalytic domain of serine/threonine kinases also contains 11 subdomains, which were consistent with the results of SiPTI1s and SlPTI1 sequence analysis (Supplementary Fig. 3).
Cis-acting elements and subcellular localization of PTI1 genes in foxtail millet
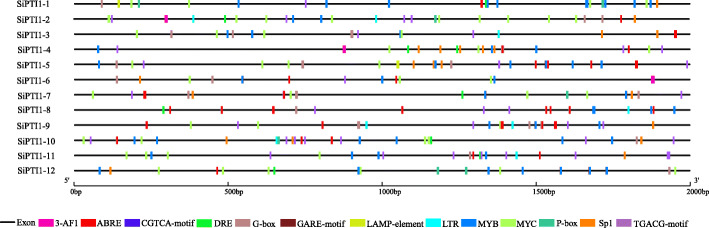
Cis-elements analysis showed that all SiPTI1 genes promoter contained MYB, MYC and ABA-responsive (ABRE) elements. In addition, excepted for SiPTI1–12, both CGTCA-motif and TGACG-motif cis-elements were present in foxtail millet PTI1 genes family (Fig. 4 and Additional file 5). In addition, 50% of the members had a low-temperature responsive element (LTR), and 75% contained a dehydration responsive element (DRE) (Fig. 4 and Additional file 5). Furthermore, SiPTI1s contained a large number of cis-elements regulatory elements involved in light response, such as Sp1, G-box, and AF-box. Gibberellin-responsive elements such as P-box and GARE-motif were also presented (Fig. 4 and Additional file 5).
Fig. 4.
Cis-elements prediction in the 2.0 kb promoter region upstream from the start codon of SiPTI1s. The relative positions of cis-elements in each SiPTI1 gene are marked by different-colored boxes
Using five publicly available subcellular localization prediction tools we found that all of the SiPTI1s were predicted to localize in the plasma membrane (Table 1). To investigate the potential role of SiPTI1–5 a vital salt tolerance-related gene of PTI1 family in the foxtail millet, we examined the subcellular localization of SiPTI1–5 fused to GFP and GFP alone (as a control) in onion epidermal cells. When observed by confocal microscopy, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) fluorescence of SiPTI1–5-GFP was distributed on the plasma membrane in the onion cells (Fig. 5), which indicated that SiPTI1–5 was localized in the plasma membrane.
Fig. 5.
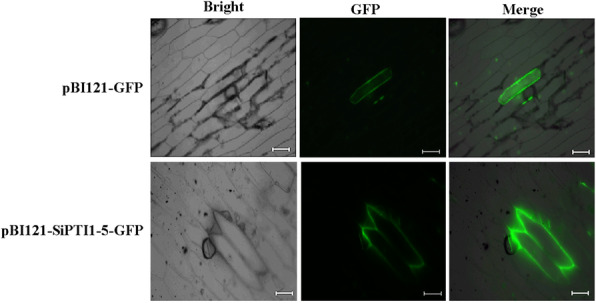
Subcellular localization of SiPTI1–5 protein. Fluorescent microscopic images of GFP and SiPTI1–5-GFP fusion protein in the onion epidermal cells (Bar = 100 μm)
Duplication and divergence rates of the SiPTI1 genes
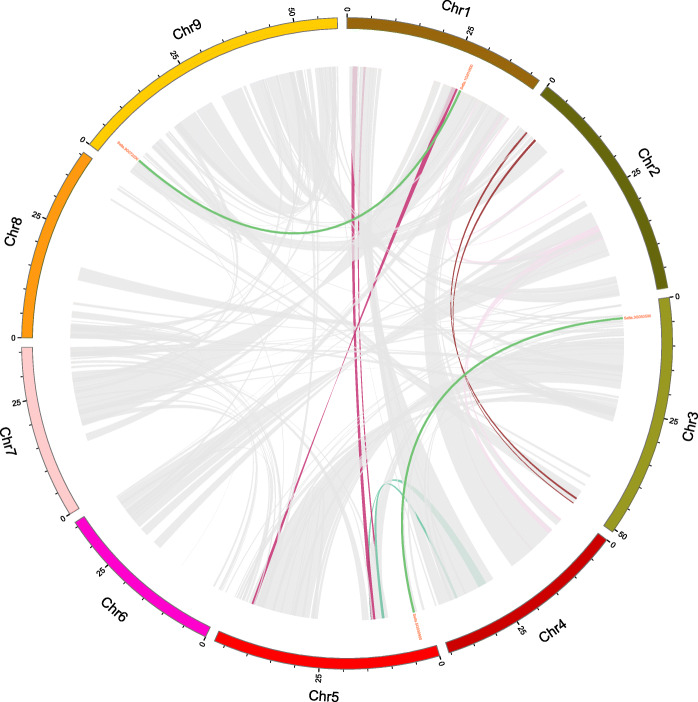
Gene duplications, including segmental and tandem duplication, have long been considered as one of the main forces in the evolution and expansion of a gene family [33]. In addition, two pairs of segmentally duplicated genes were found within the SiPTI1s family (SiPTI1–4/SiPTI1–6 and SiPTI1–1/SiPTI1–11) (Fig. 6 and Additional file 6). To further unveil the relationship between duplication events and natural selection, the Ka and Ks values of SiPTI1s in duplicated gene pairs were calculated, and the results of Ka/Ks values were found to be less than 1, suggesting that SiPTI1 family has gone through purifying selection after gene duplications.
Fig. 6.
Schematic representations for the chromosomal distribution and interchromosomal relationships of foxtail millet PTI1 genes. Gray or other color lines indicate all synteny blocks in the foxtail millet genome, and the dark green lines indicate duplicated PTI1 gene pairs and the end of the line shows the ID number of the corresponding gene. The chromosome number is indicated at the bottom of each chromosome
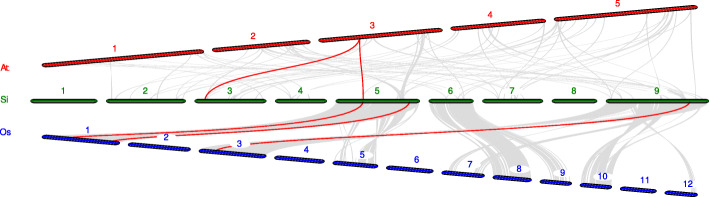
To further infer the phylogenetic mechanisms of foxtail millet PTI1 family, we constructed two comparative syntenic maps of foxtail millet associated with two representative species, including dicots (Arabidopsis) and monocots (rice) (Fig. 7 and Additional file 7). A total of 2 SiPTI1 genes showed syntenic relationship with those in Arabidopsis. Moreover, we found that SiPTI1–4 and SiPTI1–7 present the same collinear gene (AT3G17410), three genes in rice had a colinear relationship with foxtail millet SiPTI1s (SiPTI1–9/Os01t0899000, SiPTI1–7/Os01t0323100, SiPTI1–12/Os03t0226300). In addition, compared to the Arabidopsis, the PTI1s gene of foxtail millet had more colinearity with the rice PTI1 genes, and the colinearity between genomes was more abundant.
Fig. 7.
Synteny analysis of PTI1 genes between foxtail millet and two representative plant species. Gray lines in the background indicate the collinear blocks within foxtail millet and other plant genomes, while the red lines highlight the syntenic PTI1 gene pairs. The species names with ‘At’, ‘Os’, ‘Si’ indicate Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa and Setaria italica, respectively
Expression patterns of SiPTI1
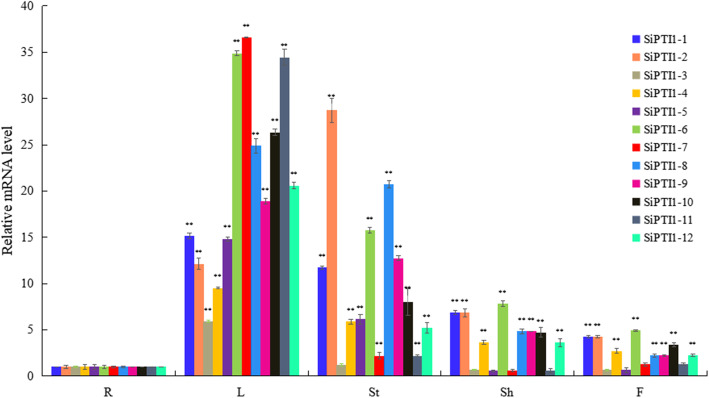
To investigate the tissue-specific expressions of the 12 SiPTI1 genes in foxtail millet, total RNA from roots, stems, leaves, sheaths and flowers were prepared and analyzed by qRT-PCR. As shown in Fig. 8 and additional file 9, the expressions of these SiPTI1 genes were highest in the stems and leaves, followed by the expressions in the sheaths and flowers, and lowest in the roots. Except of SiPTI1–3, SiPTI1–7, and SiPTI1–11, the expression levels of SiPTI1s family members in stems were more than five-fold higher than those in roots, and the expression levels of all SiPTI1 family members in leaves were also more than five-fold higher than that in roots. These results suggested that SiPTI1 genes may perform an important function in the stems and leaves.
Fig. 8.
Expression profile analysis of SiPTI1 genes in different foxtail millet tissues. Expression analysis of SiPTI1s by qRT-PCR. R, Roots; St, Stems; L, Leaves; Sh, Sheathes and F, Flowers. The values are the average of three biological repeats ± SD (standard deviation). Asterisks above bars denote a statistically significant difference by Duncan’s multi-range tests (*0.01 < P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)
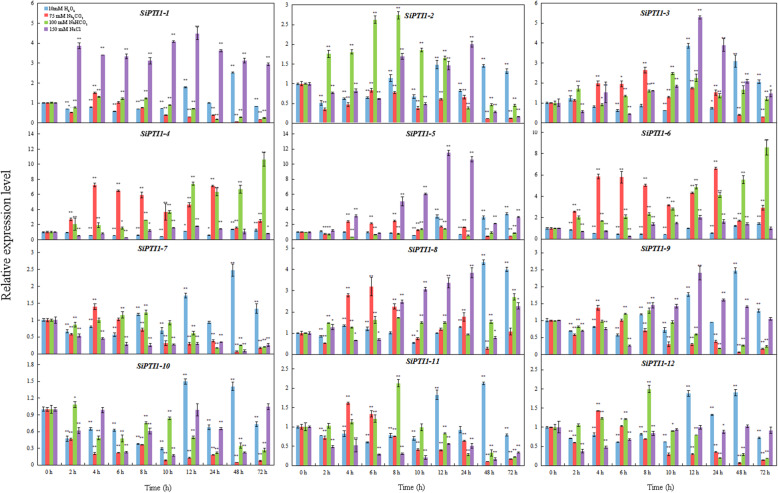
To further confirm whether the expression of SiPTI1 genes were influenced by different abiotic stresses, we used qRT-PCR to monitor the expression patterns of the 12 SiPTI1 genes in plants grown under different treatments namely salinity stress induced by treatment with NaCl, NaHCO3, Na2CO3, and oxidative stress induced by H2O2. As shown in Fig. 9 and Additional file 9, the expressions of most of the SiPTI1 genes were responsive to abiotic stress treatment. The expression patterns of SiPTI1 genes under NaCl-stress could classified into three categories. Firstly, fluctuation change, including SiPTI1–2, SiPTI1–4, SiPTI1–6 and SiPTI1–10. The second, up-regulation expression trend, such as SiPTI1–1, SiPTI1–3, SiPTI1–5, SiPTI1–8 and SiPTI1–9. Among them, the highest expression induced by NaCl was SIPTI1–5. In addition, the expression of SiPTI1–5 reached peak when salt-stress treatment arrived at 12 h, which was about eleven-fold compare with control. The last one, down-regulation expression, including SiPTI1–7, SiPTI1–11 and SiPTI1–12. Besides, under H2O2 treatment, most of SiPTI1s were induced at 12 h (Fig. 9). Under Na2CO3 treatment, most of SiPTI1s were induced at 4 h and 6 h, and then down-regulated after 8 h. Moreover, except of the up-regulated SiPTI1–4, SiPTI1–6 and SiPTI1–8, other SiPTI1s were not significantly induced and/or down-regulated under Na2CO3 treatment, such as SiPTI1–1 and SiPTI1–10 (Fig. 9). In addition, under NaHCO3 stress, SiPTI1–4 and SiPTI1–6 were significantly induced (Fig. 9). Importantly, SiPTI1–3 and SiPTI1–5 were all up-regulated under the various stress conditions. Among them, SiPTI1–5 was significantly induced up to 11.5-fold change under NaCl stress (Fig. 9).
Fig. 9.
Expression profiles of SiPTI1 genes in response to various abiotic stress treatments. The values are the average of three biological repeats ± SD (standard deviation). Asterisks above bars denote a statistically significant difference by Duncan’s multi-range tests (*0.01 < P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)
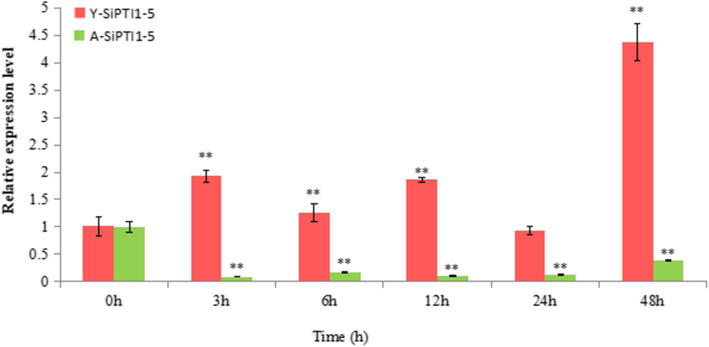
In order to further evaluate the role of the SiPTI1–5 in salt stress, the expression of SiPTI1–5 gene was compared in ‘Yugu1’, salt-tolerant variety, and ‘AN04’, a salt-sensitive variety under salt (NaCl) treatment. The results showed that the expression of SiPTI1–5 gene was up-regulated in ‘Yugu 1’, but down-regulated in ‘AN04’ (Fig. 10 and Additional file 9).
Fig. 10.
Expression pattern analysis of SiPTI1–5 genes in different varieties of foxtail millet to salt stress treatments. Two-week-old seedlings of foxtail millet (‘Yugu1’, salt-tolerant variety, and ‘AN04’, a salt-sensitive variety are shown in red and green, respectively) leaves were treated with 150 mM NaCl. Transcription levels were analyzed via qRT-PCR and the expression of Y-SiPTI1–5 (Represents the expression characteristics of SiPTI1–5 in ‘Yugu1’)/A-SiPTI1–5 (Represents the expression characteristics of SiPTI1–5 in ‘AN04’), respectively, The values are the average of three biological repeats ± SD (standard deviation). Asterisks above bars denote a statistically significant difference by Duncan’s multi-range tests (*0.01 < P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)
Overexpression of SiPTI1–5 in yeast conferred tolerance to salinity
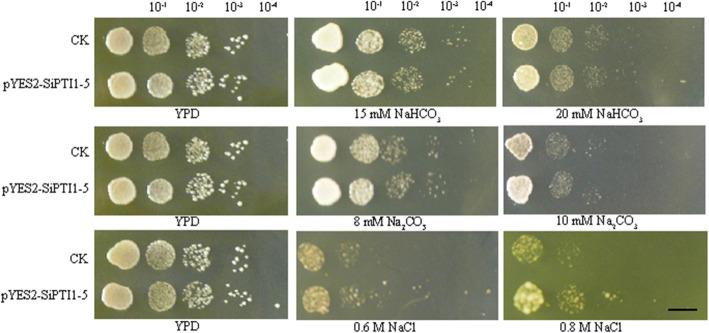
In the YPD medium without salt stress, there was almost no difference between control yeast strain (transformed with pYES2) and SiPTI1–5-expressing yeast strain (transformed with pYES2-SiPTI1–5) (Fig. 11). When exposed to Na2CO3 (8 mM, 10 mM) and NaHCO3 (15 mM, 20 mM) treatment, control strain and SiPTI1–5-expressing yeast strain had no difference in plaque growth at different concentrations, indicating that the SiPTI1–5 does not confer tolerance to Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 stress in yeast, which is in agreement with the expression patterns of SiPT1–5 in response to Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 (Fig. 11). There had shown no growth differences of control and SiPTI1–5-expressing yeast under 12 mM Na2CO3 and 25 mM NaHCO3 (data were not shown). Under NaCl stress, when NaCl concentration increased to 0.6 M, the SiPTI1–5-expressing yeast strain, grew better than the control strain (Fig. 11). In summary, the SiPTI1–5 genes may be involved in response to salt stress induced by NaCl.
Fig. 11.
Assay for salt stress tolerance of SiPTI1–5 transformed yeast. The pYES2-SiPTI1–5 fusion vectors were transformed into Invsc I yeast cells. The transformants were cultivated on YPD plates with NaHCO3, Na2CO3 and NaCl for two or three days. The 10− 1, 10− 2, 10− 3 and 10− 4 represent the dilution fold. Bar = 1 cm, transformant with empty vector pYES2 was used as a control (CK)
Overexpression of SiPTI1–5 in E. coli conferred tolerance to salinity stress
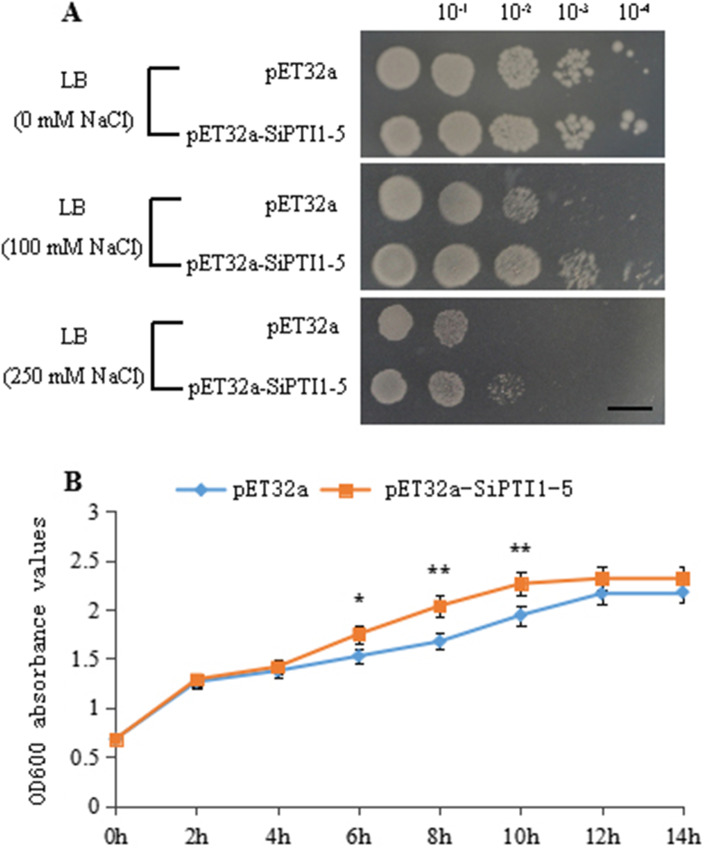
In order to test the relationship between SiPTI1–5 protein kinase and salt stress, the in vitro salt tolerance test was performed on control and SiPTI1–5-expressing strains (Fig. 12A). There are no significant differences in colony number between transformed E. coli harboring SiPTI1–5 and the control under normal conditions, indicating that overexpression of SiPTI1–5 did not affect the growth of E. coli recombinants in non-stress conditions. However, when grown on Luria-Bertani (LB) plates supplemented with 100 mM NaCl or higher, the number of transformed cells grew better than that of the control. Similar results were obtained in liquid LB with 250 mM NaCl, the growth rate of the SiPTI1–5-overexpressing strain was higher than that of the control strain, and it priorly arrived the logarithmic growth phase, indicating that the strain containing the pET32a-SiPTI1–5 recombinant plasmid had a certain salt-resistant ability compared with control (Fig. 12B).
Fig. 12.
Assay for salt stress tolerance of SiPTI1–5 transformed. The pET32a-SiPTI1–5 fusion vectors were transformed into E. coli (BL21) cells. The transformants were cultivated on LB plates with 0, 100 and 250 mM NaCl for 24 h. The 10− 1, 10− 2, 10− 3 and 10− 4 represent the dilution fold. Bar = 1 cm (A). Growth curves of pET32a-SiPTI1–5 plasmids containing BL21 strains in LB liquid medium with 250 mmol/L of NaCl. Transformant with empty vector pET32a was used as a control (B)
These results demonstrated that overexpression of SiPTI1–5 in E. coli was significantly enhanced tolerance to salt stress.
Discussion
Phylogenetic analysis revealed that SiPTI1 genes were conserved in gramineous plant species
In this study, a total of 12 members of PTI1 genes family were identified from foxtail millet. All the family members have the similar molecular wight and structure characteristics except SiPTI1–5. Most of PTI1s from various plant species contain about 300–400 amino acids (aa), while SiPTI1–5 contains 727 amino acids, and its molecular weight is about 81 kDa. Previous reports showed that most of the PTI1s were composed of 300–400 aa with a molecular weight of about 40 kDa, such as GmPTI1 (366 aa) of soybean [12], SlPTI1 (370 aa) of tomato [3], OsPTI1 (368 aa) of rice [14], and CsPTI1-L (362 aa) of cucumber [13]. Whether the larger SiPTI1–5 has specific function needs to be further investigated.
The phylogenetic analysis indicated that each SiPTI1 protein sequence was similar to their homologues from gramineous rice and maize. This implied that the orthologues proteins would share similar functions from a common ancestor [34]. It revealed the species bias in the distribution of the majority of foxtail millet SiPTI1 genes in gramineous species, when compared to their homologues in dicot species. These were consistent with the present understanding of plant evolutionary history [35]. As a rational systematic approach, such phylogeny-based function prediction has been applied for prediction of stress-responsive proteins in other plant species such as rice [36] and maize [37].
New insights into the biological function of foxtail millet PTI1 genes could be inferred by combining gene expression, phylogenetic and synteny analysis, as well as comparison with the function of known PTI1 genes in model plant species. For example, SiPTI1–5 exhibited the highest homology with its orthologs in rice OsNP_908680 (OsPTI1b) that mediates the hypersensitive response (HR), indicating that SiPTI1–5 may share similar functions in foxtail millet. SiPTI1–3 showed high degree of similarity with ZmPTI1b and ZmPTI1a, which implied that it probably be involved in flower development and defense stress [31, 38]. In addition, the multiple sequence alignment of PTI1 protein sequences implied that PTI1 were conserved among tomato, rice, maize, and foxtail millet. Especially, the kinase catalytic domain is highly conserved (Supplementary Fig. 2 and Supplementary Fig. 3).
We experimentally confirmed the predicted plasma membrane subcellular localization of SiPTI1–5 (Fig. 5). Interestingly, SiPTI1s lack predicted transmembrane structure or signal peptide. So, we speculated that its plasma membrane localization is due to interaction with the plasma membrane proteins [39]. Previous studies reported that rice OsPTI1a localizes to the plasma membrane through N-terminal palmitoylation and plays a role in immune responses via forming a complex at the plasma membrane [39]. As the phylogenetic tree branch shows that the SiPTI1 gene family members of the foxtail millet had a closely relationship with the rice and maize, it is speculated that the mechanisms of action of foxtail millet SiPTI1s may be similar to rice and maize.
The expression patterns of SiPTI1s under abiotic stresses
While essential for the growth and development of plants, excessive concentration of inorganic salts in the soil causes significant damage to the plants [40, 41], ranging from ion poisoning [42, 43], osmotic stress [44, 45], to oxidative stress [46, 47]. Salt stress is a prominent source of abiotic stress [48, 49] globally as over 20% of arable land and more than 40% of irrigated land [50, 51] worldwide considered to have some degree of excess salinity [52, 53]. Therefore, it is particularly important to study the salt tolerance mechanisms of plants, especially for agronomic crops.
In this study, qRT-PCR analysis revealed the expression characteristics of SiPTI1 genes under diverse salinity treatments (150 mM NaCl, 100 mM NaHCO3, and 75 mM Na2CO3) (Fig. 9). Among twelve SiPTI1 genes, the expression of SiPTI1–5 was obviously induced under various treatments for 12 h. It is well known that salt stress is usually accompanied by excessive accumulation of ROS, including H2O2, that causes oxidative damage to proteins, DNA and lipids [54]. ROS are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation [55], cell defense [56], and signal transduction [54, 57]. Therefore, oxidative stress is important for the study of the mechanisms of salt tolerance. Interestingly, the expression of SiPTI1–5 was induced by NaCl and H2O2, indicating that SiPTI1–5 participates in salt stress response through regulation ROS dynamic balance. It is well known that, the serine/threonine protein kinase OXI1, mediated oxidative stress signaling. Previous research report that AtPTI1–2 could been activated by OXI1 in response to PA, H2O2, and flagellin [13]. In addition, AtPTI1–4 signals via OXI1 and MPK6 signaling cascades functioned in oxidative stress [8]. Moreover, the PTI1 genes also were induced by other stresses. For example, GmPTI1 expression was induced by salicylic acid and wounding [12], ZmPTI1–1 was dramatically induced by abscisic acid (ABA) and mannitol [58], and the CsPTI1-L of cucumber expression was induced when cucumber plants were challenged with the fungal pathogen Sphaerotheca fuliginea or with salt treatment [13]. It is well known that promoters could regulate temporal and spatial expression of gene, and cis-elements in promoters are crucial for gene function regulation by interacting with trans-acting factors. In this study, the promoters of SiPTI1 family members were analyzed, and a large number of cis-elements related to stress response (e.g., MYB, MYC, ABRE, and DRE) were found. Meanwhile, the qRT-PCR results of the SiPTI1 family members indicated that they could be induced by various salinity and oxidative stresses, which were well correlated with previous reports. Furthermore, the expressions of SiPTI1–5 in ‘Yugu1’ and ‘AN04’ under salinity were analyzed (Fig. 10), which implied that the SiPTI1–5 were positively correlated with salt stress response.
SiPTI1–5 gene is involved in salt tolerance
The PTI1 gene was identified in tomatoes firstly, which was involved in a Pto-mediated signaling pathway, acting as a member downstream of Pto in a phosphorylation cascade during plant-pathogen interaction [3]. Besides, different members of PTI1 family have been reported to function in stress response in Arabidopsis [1, 8], soybean [12] and cucumber [13]. The PTI1 gene in monocotyledonous maize [31], wheat [39, 59], and rice [39, 59] were involved in flower development and stress response, respectively. It has been reported that over-expression of PTI1-like gene ZmPTI1 in Arabidopsis enhanced the salt resistance [38], and over-expression of ZmPTI1–1 significantly enhanced the drought tolerance of Arabidopsis [58]. In addition, over-expression CsPTI1-L of cucumber positive regulated the responses of pathogen-defense and salt-stress [13]. In the current study, our results revealed that over-expression of SiPTI1–5 genes in yeast and E. coli. Strains increased their salinity tolerances. Taken together with its stress induction, we speculated that SiPTI1–5 genes would play important roles in foxtail millet in response to salinity and oxidative responses. However, the detailed salinity-responsive mechanism in the phosphorylation cascade needs to be further confirmed.
Conclusion
A total of 12 putative SiPTI1 genes were identified in foxtail millet using genome-wide analysis. The chromosomal distribution, intron-exon structures, motifs, duplication and divergence rates, cis-acting elements and subcellular localizations of the resulting proteins were analyzed. Synteny analysis and phylogenetic comparison of PTI1 genes from several different plant species provided valuable clues about the evolutionary characteristics of foxtail millet SiPTI1 genes. SiPTI1 genes play important roles in foxtail millet growth and development, and the expression patterns showed that they are induced by various developmental and environmental cues. The phylogenetic and gene expression analysis shed some lights on the functional analysis of SiPTI1 genes, suggesting a role for SiPTI1–5 may be involved in salt tolerance. Heterologous expression of SiPTI1–5 in yeast and E. coli enhanced tolerance to salt stress in this study. These results provide a valuable resource for better understanding of the biological roles of individual SiPTI1 genes in foxtail millet.
Methods
Plant materials and growth conditions
The seeds of “Yugu1” and “AN04” were kindly provided by Professor Diao Xianmin, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing.
For organ expression analysis of SiPTI1 genes, the seeds of “Yugu1” were soaked in water and germinated at 28 °C for two days, and then the seeds were sowed in the field and the seedlings were cultured. At florescence, the samples were collected from roots, sixth internode, the seventh leaf and its sheath, as well as flowers, respectively.
For stress-responsive analysis of SiPTI1 genes, three-week-old seedlings cultured in Hoagland solution were exposed to various salinity treatments (150 mM NaCl, 75 mM Na2CO3, and 100 mM NaHCO3), as well as 10 mM H2O2 for 0 h, 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 10 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. Besides, for the comparation of the SiPTI1–5 gene expression in “Yugu1” (salt-tolerant variety) and “AN04” (salt-sensitive variety), two-week old seedlings from two varieties were cultured and treated with 150 mM NaCl for 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h. After treatments, the five young leaves were collected for qRT-PCR analysis.
In these experiments, collections from five plants were pooled in each sample, and the samples were frozen immediately in liquid nitrogen and then stored at − 80 °C for further analysis. For each sample, three biological replications were performed for qRT-PCR analysis.
Total RNA isolation, cDNA synthesis and quantitative real-time PCR
The total RNA of foxtail millet was extracted by TransZol Up (TRANS), and the specific experimental steps were described in the instructions. RNA integrity has been confirmed by electrophoresis with 1% agarose gels. The expression characteristics of SiPTI1s in foxtail millet under different stress treatments were detected by qRT-PCR. For each plant sample, 1 μg of total RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA in a 20 μl reaction system using a PrimeScriptTM 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (TaKaRa). The primers used for qRT-PCR analysis were designed from a non-conserved region by Primer-BLAST (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/) [34]. SiActin gene (AF288226.1) was used as reference gene for qRT-PCR analysis [34]. The primers used in these experiments are listed in the Additional file 8. Fold change was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method [44]. Each experiment was repeated for three times. The data were shown as means ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed on SPSS 17.0. The statistical significance was determined using an analysis of variance (ANOVA), and significant differences (P < 0.05) between the values were determined using Duncan’s multiple range test [44].
Bioinformatic analysis of the SiPTI1 family in foxtail millet
A Hidden Markov Model (HMM) was established by indexing the PTI1 family sequence of Rice, Arabidopsis, and Maize, and HMM profile was prepared using HMMER suite [60]. The HMM profile was then searched against the foxtail millet proteome data under default E value cut-off of 0.01 [61]. The sequences of SiPTI1s (coding sequences (CDS), Protein and Gene) were all downloaded from Phytozome (JGI) (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html), and demonstrate in Additional file 1, whereas, Arabidopsis and maize PTI1 sequences (CDS, Protein and Gene) were deposited from Ensembl (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html). Each putative PTI1 gene sequence was checked against three databases: SMART (https://www.omicsclass.com/article/681), NCBI CDD (https://www.omicsclass.com/article/310), and Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/databas) to confirm the presence of the PTI1 domain. The predicted genes were further validated by PCR amplification and sequencing, 12 PTI1 genes models were finally identified in the foxtail millet genome after comprehensive curation, for nomenclature, the prefix ‘Si’ for S. italica was used, followed by ‘PTI1’, which were designated from SiPTI1–1 through SiPTI1–12 on the basis of their chromosomal location. Length of sequences, molecular weights, isoelectric points of identified PTI1 proteins were obtained using tools from ExPasy website (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/). In addition subcellular locations were predicted using five publicly available tools: http://abi.inf.uni-tuebingen.de/Services/YLoc/webloc.cgi, https://rostlab.org/services/loctree3/, http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/, http://genome.unmc.edu/ngLOC/index.html, and http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/ according to Suo et al. [62].
Phylogenetic analysis of PTI1 genes
To further investigate the evolutionary relationships of the PTI1 proteins in various plants species, the phylogenetic trees of the PTI1 was constructed. Multiple sequence alignment of PTI1 protein sequences were conducted with the ClustalX 1.81 program using the default multiple alignment parameters. The unrooted phylogenetic tree were constructed using MEGA7.0 software with a maximum likelihood method using sequences from S. italica (Si), S. lycopersicum (Sl), N. tabacum, (Nt), A. thaliana (At), O. sativa (Os), and Z. mays (Zm) [31], the PTI1 protein sequences used to construct phylogenetic tree but does not include SiPTI1s were acquired from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and the corresponding protein sequences of list in Additional file 2. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1000 replicates [63, 64].
Homologous alignment of PTI1 protein sequences
The sequences alignment analysis of PTI1s from foxtail millet, tomato, rice and maize. Was conducted using DNAMAN_6.0.
Chromosomal location, gene structure analysis, promoter analysis and estimation of genomic distribution and gene duplication
All SiPTI1 genes were mapped to the nine foxtail millet chromosomes according to their ascending order of physical position (bp), from the short arm telomere to the long arm telomere, and were visualized using MapChart [65]. The exon-intron structures of the SiPTI1 genes were determined by comparing the CDS with their corresponding genomic sequences using the Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS) (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) [66]. The MEME online program (http://meme.nbcr.net/meme/ intro.html) for protein sequence analysis was used to identify conserved motifs in the identified foxtail millet PTI1 proteins [67]. The optimized parameters were employed are the following: the number of repetitions: any, the maximum number of motifs: 15, and the optimum width of each motif: between 6 and 100 residues [34, 68]. The cis-regulatory elements were identified using Plantcare (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) database. All SiPTI1 genes were mapped to foxtail millet chromosomes based on physical location information from the database of foxtail millet genome using Circos [69]. Multiple Collinearity Scan toolkit (MCScanX) adopted to analyze the gene duplication events, with the default parameters [33, 70]. To exhibit the synteny relationship of the orthologous PTI1 genes obtained from foxtail millet and other selected species, the syntenic analysis maps were constructed using the Dual Systeny Plotter software (https://github.com/CJ-Chen/TBtools) [71]. Non-synonymous (ka) and synonymous (ks) substitution of each duplicated PTI1 genes were calculated using KaKs_Calculator 2.0 [72, 73]. Substitution rate of the PTI1 genes Ks and Ka were estimated according to previously-described criteria [34, 74] Ks and Ka substitution rates were calculated using the CODEML program and confirmed with the GEvo tool (https://genomevolution.org/CoGe/SynMap.pl). The time (million years ago, MYA) of duplication and divergence time (T) was calculated using a synonymous mutation rate of λ substitutions per synonymous site per year as T = Ks/2λ (λ = 6.5 × 10–9) [33].
Subcellular localization of SiPTI1–5
The recombinant plasmid pBI121-SiPTI1–5-GFP was generated by amplifying the coding sequence of SiPTI1–5 without the termination codon, and then inserting the sequence into the XbaI/SalI restriction site of pBI121-GFP. Onion epidermal cells were bombarded with the constructs pBI121-GFP and pBI121-SiPTI1–5-GFP, and used a particle gun-mediated system PDS-1000/He (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). GFP signals were observed with a confocal laser scanning microscopy (LSM 510, Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH, Jena, Germany) [75].
Assay for salinity tolerance of E. coli transformants
The recombinant plasmid pET32a-SiPTI1–5 was generated by amplifying the coding sequence of SiPTI1–5 without the termination codon, and then inserting the sequence into the SacI/XhoI restriction site of pET32a. Then pET32a empty vector (as control) and pET32a-SiPTI1–5 recombinant plasmid were transformed into E. coli host strain BL21 (DE3), respectively. The expression of SiPTI1–5 in the recombinant cells was confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis (Supplementary Fig. 1). Transformed E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells carrying pET32a-SiPTI1–5 or pET-32a were grown overnight in LB liquid medium (contained 100 μg/ml ampicillin), respectively, which culture condition was 37 °C, 180 rpm. For salinity resistance analysis, the bacterial cultures were diluted 50-fold using liquid LB, and incubated for 2–3 h at 37 °C until OD600 = 0.5–0.6 [75]. Isopropylthio-β-D-galactoside (IPTG) was added to the cultures and make it final concentration was 0.5 mM for induction of expression of the inserted gene.
Spot assay was applied for salinity resistance analysis of SiPTI 1–5 transformed E. coli [75]. After 4 h (25 °C) IPTG induction, the concentration of E. coli was adjusted to OD600 0.6 using LB liquid medium (contained 100 μg/ml ampicillin) [75]. In order to measure the response to salinity, the samples were diluted by 10− 1, 10− 2, 10− 3, and 10− 4 folds with LB medium contained ampicillin. Three microliters of each diluted sample were plated on LB agar plates, LB agar plates supplemented with 0, 100, 250 mM NaCl, respectively. After incubation for 12 h on LB agar plates at 37 °C [75]. The bacterial colony growth under salt stress was recorded with Canon digital camera.
For salt resistance detection of SiPTI 1–5 transformed E. coli in liquid culture media, the bacteria were cultured for 14 h at 25 °C in liquid LB after IPTG induction. The absorbance value at OD600 was measured every 2 h and the data were recorded until OD600 reached to approximately two. The experiments were repeated for three times.
Assay for salt-stress tolerance of yeast transformants
The sequence of SiPTI1–5 was amplified and cloned into the KpnI/XhoI sites of pYES2 to construct the expression vector pYES2-SiPTI1–5, which was then transformed into yeast host strain INVSc 1. The pYES2 empty vector was used as the control. Fresh cultures of control and pYES2-SiPTI1–5 strains were prepared and adjusted to OD600 of 0.6 in YPD medium. This culture was successively diluted to 10− 1, 10− 2, 10− 3, 10− 4 times, spotted on YPD (No salinity) or YPD medium supplemented with Na2CO3 (8 mM, 10 mM, and 12 mM), NaHCO3 (15 mM, 20 mM, and 25 mM), or NaCl (0.6 M, 0.8 M, and 1 M) and incubate at 28 °C for 2 days to observe and photograph the phenotype with Canon digital camera. All experiments were repeated independently for three times.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. The sequences of PTI1 genes in foxtail millet.
Additional file 2. The PTI1 proteins used to construct phylogenetic but does not include SiPTI1s.
Additional file 3. Detailed characteristics of the motifs in the SiPTI1 proteins.
Additional file 4. The specific location of each SiPTI1 gene on the chromosomes.
Additional file 5. Characteristics of the promoter region of SiPTI1 genes.
Additional file 6. Segmentally and tandemly duplicated SiPTI1 gene pairs.
Additional file 7. One-to-one orthologous relationships between foxtail millet and other two plant species.
Additional file 8. Sequences of the primers used in this study.
Additional file 9. The relative expression value of SiPTI1s.
Additional file 10: Supplementary Fig. 1. SiPTI1–5 fusion protein identification by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. M: marker, 1: pET32a (0 h), 2: pET32a-SiPTI1–5 (0 h), 3: pET32a-SiPTI1–5T604A (0 h), 4: pET32a-SiPTI1–5K452N (0 h), 5: pET32a (4 h), 6: pET32a-SiPTI1–5 (4 h), 7: pET32a-SiPTI1–5T604A (4 h), 8: pET32a-SiPTI1–5K452N (4 h).
Additional file 11: Supplementary Fig. 2. Sequence homology of SiPTI1s. The sequences alignment of PTI1s from foxtail millet and tomato.. The 11 canonical subdomains conserved in serine/threonine kinases are indicated with Roman numerals. Invariant residues common to the majority of protein kinases are marked with black dots. The highly conserved lysine residue in subdomain II which is required for activity in SlPTI1 and most protein kinases is boxed.
Additional file 12: Supplementary Fig. 3. Sequence homology of PTI1s. The sequences alignment of PTI1s from foxtail millet, rice and maize. The 11 canonical subdomains conserved in serine/threonine kinases are indicated with Roman numerals. Invariant residues common to the majority of protein kinases are marked with black dots. The highly conserved lysine residue in subdomain II which is required for activity in most protein kinases is boxed.
Acknowledgments
None.
Abbreviations
- RLK
Receptor-like protein kinases
- PTI1
Pto-interacting 1
- CDS
Coding sequence
- ORF
Open reading frame
- qRT-PCR
Quantitative real-time PCR
- UTR
Untranslated region
- ABA
Abscisic Acid
- MeJA
Methyl Jasmonate
- PEG
Polyethylene Glycol
- SA
Salicylic acid
- IPTG
Isopropylthio-β-D-galactoside
- LB
Luria-Bertani
- OXI1
Oxidative signal-inducible 1
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- MAPK
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
Authors’ contributions
YG-HF, WL and SJD designed the study and supervised the experiments. YG-HF, ZL, QGW, YL and ML performed the experiments. YG-HF, JWP analyzed the data, YG-HF wrote the manuscript. WL, SJD, JWP, MF and SY reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2020MC110), the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. ZD2019C003), National Key Research & Development Program of China (2019YFD1002701–04). The funders had no role in study design, data collection, analysis and interpretation, and manuscript writing.
Availability of data and materials
All relevant data of this article are available within the manuscript and its additional files. The sequences of SiPTI1s (coding sequences (CDS), Protein and Gene) were all downloaded from Phytozome (JGI) (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html), and demonstrated in Additional file 1, whereas, Arabidopsis and maize PTI1 sequences (CDS, Protein and Gene) were deposited from Ensembl (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html). The PTI1 protein sequences used to construct phylogenetic tree but does not include SiPTI1s were acquired from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and the corresponding protein sequences of list in Additional file 2.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Shaojun Dai, Email: daishaojun@hotmail.com.
Wei Liu, Email: wheiliu@163.com.
References
- 1.Anthony RG, Khan S, Costa J, Pais MS, Bögre L. The Arabidopsis protein kinase PTI1-2 is activated by convergent phosphatidic acid and oxidative stress signaling pathways downstream of PDK1 and OXI1. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(49):37536–37546. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607341200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shiu SH, Bleecker AB. Expansion of the receptor-like kinase/Pelle gene family and receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003;132(2):530–543. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhou JM, Loh YT, Bressan RA, Martin GB. The tomato gene Pti1 encodes a serine/threonine kinase that is phosphorylated by Pto and is involved in the hypersensitive response. Cell. 1995;83(6):925–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hanks SK, Hunter T. The eukaryotic protein kinase superfamily: (catalytic) domain structure and classification. FASEB J. 1995;9(8):576–596. doi: 10.1006/excr.1995.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Oh MH, Wang X, Kota U, Goshe MB, Clouse SD, Huber SC. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the BRI1 receptor kinase emerges as a component of brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(2):658–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810249106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Peck SC. Analysis of protein phosphorylation: methods and strategies for studying kinases and substrates. Plant J. 2006;45(4):512–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Garcia AV, Al-Yousif M, Hirt H. Role of AGC kinases in plant growth and stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(19):3259–3267. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1093-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Forzani C, Carreri A, de la Fuente van Bentem S, Lecourieux D, Lecourieux F, Hirt H. The Arabidopsis protein kinase Pto-interacting 1-4 is a common target of the oxidative signal-inducible 1 and mitogen-activated protein kinases. FEBS J. 2011;278(7):1126–1136. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sessa G, D'ascenzo M, Martin GB. The major site of the Pti1 kinase phosphorylated by the pto kinase is located in the activation domain and is required for Pto-Pti1 physical interaction. Eur J Biochem. 2010;267(1):171–178. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.00979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zou HW, Tian XH, Ma GH, Zhao MM, Li ZX. ZmPto, a maize Pto-like gene, significantly affects salt resistance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Aust J Crop Sci. 2012;6(5):952–956. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Staswick P. Two expressed soybean genes with high sequence identity to tomato Pti1 kinase lack autophosphorylation activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;383(2):233–237. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.2080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tian AG, Luo GZ, Wang YJ, Zhang JS, Gai JY, Chen SY. Isolation and characterization of a Pti1 homologue from soybean. J Exp Bot. 2004;55(396):535–537. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Oh SK, Jang HA, Lee SS, Cho HS, Lee DH, Choi D, Kwon SY. Cucumber Pti1-L is a cytoplasmic protein kinase involved in defense responses and salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol. 2014;171(10):817–822. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Matsui H, Fujiwara M, Hamada S, Shimamoto K, Nomura Y, Nakagami H, Takahashi A, Hirochika H. Plasma membrane localization is essential for Oryza sativa Pto-interacting protein 1a-mediated negative regulation of immune signaling in rice. Plant Physiol. 2014;166(1):327–336. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.243873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liao HZ, Zhu MM, Cui HH, Du XY, Yu T, Chen LQ, Ye D, Zhang XQ. MARIS plays important roles in Arabidopsis pollen tube and root hair growth. J Integr Plant Biol. 2016;58(11):927–940. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yoshioka H, Numata N, Nakajima K, Katou S, Kawakita K, Rowland O, Jones JD, Doke N. Nicotiana benthamiana gp91phox homologs NbrbohA and NbrbohB participate in H2O2 accumulation and resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell. 2003;15(3):706–718. doi: 10.1105/tpc.008680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bogdanove AJ, Martin GB. AvrPto-dependent Pto-interacting proteins and AvrPto-interacting proteins in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(16):8836–8840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.8836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Liu JM, Xu ZS, Lu PP, Li WW, Chen M, Guo CH, Ma YZ. Genome-wide investigation and expression analyses of the pentatricopeptide repeat protein gene family in foxtail millet. BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):840. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3184-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Xiong L, Zhu JK. Regulation of abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2003;133(1):29–36. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.025395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lata C, Gupta S, Prasad M. Foxtail millet: a model crop for genetic and genomic studies in bioenergy grasses. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2013;33(3):328–343. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2012.716809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brutnell TP, Wang L, Swartwood K, Goldschmidt A, Jackson D, Zhu XG, Kellogg E, Eck JV. Setaria viridis: a model for C4 photosynthesis. Plant Cell. 2010;22(8):2537–2544. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.075309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pan JW, Li Z, Wang QG, Garrell AK, Liu M, Guan YA, Zhou WQ, Liu W. Comparative proteomic investigation of drought responses in foxtail millet. BMC Plant Biol. 2018;18(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1533-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li PH, Brutnell TP. Setaria viridis and Setaria italica, model genetic systems for the Panicoid grasses. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(9):3031–3037. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang PF, Wang HL, Wang YM, Ren FS, Liu W. Analysis of bHLH genes from foxtail millet (Setaria italica) and their potential relevance to drought stress. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Muthamilarasan M, Prasad M. Advances in Setaria genomics for genetic improvement of cereals and bioenergy grasses. Theor Appl Genet. 2015;128(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/s00122-014-2399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Doust AN, Kellogg EA, Devos KM, Bennetzen JL. Foxtail millet: a sequence-driven grass model system. Plant Physiol. 2009;149(1):137–141. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.129627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Muthamilarasan M, Prasad M. Small millets for enduring food security amidst pandemics. Trends Plant Sci. 2021;26(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2020.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fang XM, Dong KJ, Wang XQ, Liu TP, He JH, Ren RY, Zhang L, Liu R, Liu XY, Li M, Huang MZ, Zhang ZS, Yang TY. A high density genetic map and QTL for agronomic and yield traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv) BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2628-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Peng RH, Zhang BH. Foxtail millet: a new model for C4 plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2021;26(3):199–201. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2020.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pan JW, Li Z, Dai SJ, Ding HF, Wang Q, Li XB, Ding GH, Wang PF, Guan YA, Liu W. Integrative analyses of transcriptomics and metabolomics upon seed germination of foxtail millet in response to salinity. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):13660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70520-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Herrmann MM, Pinto S, Kluth J, Wienand U, Lorbiecke R. The PTI1-like kinase ZmPti1a from maize (Zea mays L.) co-localizes with callose at the plasma membrane of pollen and facilitates a competitive advantage to the male gametophyte. BMC Plant Biol. 2006;6(1):22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-6-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hanks SK, Quinn AM. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lynch M, Conery JS. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science. 2000;290(5494):1151–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5494.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li WW, Chen M, Wang E, Hu L, Hawkesford MJ, Zhong L, Chen Z, Xu ZS, Li LC, Zhou YB, Guo CH, Ma YZ. Genome-wide analysis of autophagy-associated genes in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) and characterization of the function of SiATG8a in conferring tolerance to nitrogen starvation in rice. BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):797. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3113-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kellogg EA. Evolutionary history of the grasses. Plant Physiol. 2001;125(3):1198–1205. doi: 10.1104/pp.125.3.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nghi KN, Tondelli A, Valè G, Tagliani A, Marè C, Perata P, Pucciariello C. Dissection of coleoptile elongation in japonica rice under submergence through integrated genome-wide association mapping and transcriptional analyses. Plant Cell Environ. 2019;42(6):1832–1846. doi: 10.1111/pce.13540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Li YX, Wei KF. Comparative functional genomics analysis of cytochrome P450 gene superfamily in wheat and maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2020;20(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2288-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zou HW, Wu ZY, Zhang XH, Wang YQ, Huang CL. Over-expression of ZmPti1, a homologue to Pti1, increases salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Afr J Biotechnol. 2010;9(5):656–662. doi: 10.5897/AJB09.1660. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Matsui H, Takahashi A, Hirochika H. Rice immune regulator, OsPti1a, is specifically phosphorylated at the plasma membrane. Plant Signal Behav. 2015;10(3):e991569. doi: 10.4161/15592324.2014.991569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhang YX, Zhang Y, Yu JJ, Zhang H, Wang LY, Wang SN, Guo SY, Miao YC, Chen SX, Li Y, Dai SJ. NaCl-responsive ROS scavenging and energy supply in alkaligrass callus revealed from proteomic analysis. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):990. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6325-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yu JJ, Chen SX, Wang T, Sun GR, Dai SJ. Comparative proteomic analysis of Puccinellia tenuiflora leaves under Na2CO3 stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(1):1740–1762. doi: 10.3390/ijms14011740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Maathuis FJ, Ahmad I, Patishtan J. Regulation of Na+ fluxes in plants. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:467. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu J, Gao H, Wang X, Zheng Q, Wang C, Wang X, Wang Q. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on plant growth, osmotic regulation and ion homeostasis of salt-stressed canola. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 2014;16(2):440–450. doi: 10.1111/plb.12052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li JP, Yuan F, Liu YL, Zhang MJ, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Wang BS, Chen M. Exogenous melatonin enhances salt secretion from salt glands by up regulating the expression of ion transporter and vesicle transport genes in Limonium bicolor. BMC Plant Biol. 2020;20(1):493. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02703-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Greenway H, Munns RA. Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. Ann Rev Plant Physiol. 1980;31(4):149–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pp.31.060180.001053. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Luo Z, Kong XQ, Dai JL, Dong HZ. Soil plus foliar nitrogen application increases cotton growth and salinity tolerance. J Plant Nutr. 2015;38(3):443–455. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2014.912324. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang YX, Sun GR, Suo B, Chen G, Wang JB, Yan Y. Effects of Na2CO3 and NaCl stresses on the antioxidant enzymes of chloroplasts and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of leaves of Puccinellia tenuiflora (Turcz.) scribn.Et Merr. Acta Physiol Plant. 2008;30(2):143–150. doi: 10.1007/s11738-007-0102-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhao Q, Zhang H, Wang T, Chen SX, Dai SJ. Proteomics-based investigation of salt-responsive mechanisms in plant roots. J Proteome. 2013;82:230–253. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang H, Han B, Wang T, Chen SX, Li HY, Zhang YX, Dai SJ. Mechanisms of plant salt response: insights from proteomics. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(1):49–67. doi: 10.1021/pr200861w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Corwin DL, Lesch SM. Apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements in agriculture. Comput Electron Agr. 2005;46(1–3):11–43. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2004.11.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yin ZP, Zhang H, Zhao Q, Yoo MJ, Zhu N, Yu JL, Yu JJ, Guo SY, Miao YC, Chen SX, Qin Z, Dai SJ. Physiological and comparative proteomic analyses of saline-alkali NaHCO3-responses in leaves of halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflora. Plant Soil. 2019;437(1–2):137–158. doi: 10.1007/s11104-019-03955-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gomez L, Alvarez A, D'Ambrosio S, Zalazar G, Aravena R. Use of isotopes techniques to reveal the origin of water salinity in an arid region of Central-Western Argentina. Sci Total Environ. 2020;755(Pt 2):142576. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dalton FN, Maggio A, Piccinni G. Effect of root temperature on plant response functions for tomato: comparison of static and dynamic salinity stress indices. Plant Soil. 1997;192(2):307–319. doi: 10.1023/A:1004263505595. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yu JJ, Jin X, Sun XM, Gao TX, Chen XM, She YM, Jiang TB, Chen SX, Dai SJ. Hydrogen peroxide response in leaves of poplar (Populus simonii × Populus nigra) Revealed from Physiological and Proteomic Analyses. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2085. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Suo JW, Zhang H, Zhao Q, Zhang N, Zhang YX, Li Y, Song BH, Yu JJ, Cao JG, Wang T, Luo J, Guo LH, Ma J, Zhang XM, She YM, Peng LW, Ma W, Guo SY, Miao YC, Chen SX, Qin Z, Dai SJ. Na2CO3-responsive photosynthetic and ROS scavenging mechanisms in chloroplasts of alkaligrass revealed by phosphoproteomics. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. 2019;871046(3):271–288. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Uchida A, Jagendorf AT, Hibino T, Takabe T, Takabe T. Effects of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide on both salt and heat stress tolerance in rice. Plant Sci. 2002;163(3):515–523. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00159-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mittler R. ROS are good. Trends Plant Sci. 2017;22(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Li ZL, Bian MD, Wu ZY, Zhang XH, Yang Q, Huang CL. Isolation and drought-tolerant function analysis of ZmPti1-1, a homologue to Pti1, from maize (Zea mays L.) Afr J Biotechnol. 2011;10(27):5327–5336. doi: 10.1242/dev.00611. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Takahashi A, Agrawal GK, Yamazaki M, Onosato K, Miyao A, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K, Hirochika H. Rice Pti1a negatively regulates RAR1-dependent defense responses. Plant Cell. 2007;19(9):2940–2951. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.047142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Eddy SR. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 1998;14(9):755–763. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Muthamilarasan M, Bonthala VS, Mishra AK, Khandelwal R, Khan Y, Roy R, Prasad M. C2H2 type of zinc finger transcription factors in foxtail millet define response to abiotic stresses. Funct Integr Genomics. 2014;14(3):531–543. doi: 10.1007/s10142-014-0383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Suo JW, Zhao Q, Zhang ZX, Chen SX, Cao JG, Liu GJ, Wei X, Wang T, Yang CP, Dai SJ. Cytological and proteomic analyses of osmunda cinnamomea germinating spores reveal characteristics of fern spore germination and rhizoid tip growth. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015;14(9):2510–2534. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.047225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. 1985;39(4):783–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Voorrips RE. MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered. 2002;93(1):77–78. doi: 10.1093/jhered/93.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Guo AY, Zhu QH, Chen X, Luo JC. GSDS: a gene structure display server. Hereditas. 2007;29(8):1023–1026. doi: 10.1360/yc-007-1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS. MEME suite: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Web Server issue):W202–W208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Li DH, Liu P, Yu JY, Wang LH, Dossa K, Zhang Y, Zhou R, Wei X, Zhang X. Genome-wide analysis of WRKY gene family in the sesame genome and identification of the WRKY genes involved in responses to abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 2017;17(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1099-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009;19(9):1639–1645. doi: 10.1101/gr.092759.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wang YP, Tang HB, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li JP, Wang XY, Lee TH, Jin HZ, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yang ZF, Gu SL, Wang XF, Li WJ, Tang ZX, Xu CW. Molecular evolution of the CPP-like gene family in plants: insights from comparative genomics of Arabidopsis and Rice. J Mol Evol. 2008;67(3):266–277. doi: 10.1007/s00239-008-9143-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhang Z, Li J, Zhao XQ, Wang J, Wong GK, Yu J. KaKs_Calculator: calculating Ka and Ks through model selection and model averaging. Genom Proteom Bioinf. 2006;4(4):259–263. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(07)60007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T. Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J. 1994;6(2):271–282. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.6020271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Chen Z, Chen M, Xu ZS, Li LC, Chen XP, Ma YZ. Characteristics and expression patterns of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene superfamily of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) PloS One. 2014;9(7):e101136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Wang MZ, Li P, Li C, Pan YL, Jiang XY, Zhu DY, Zhao Q, Yu JQ. SiLEA14, a novel atypical LEA protein, confers abiotic stress resistance in foxtail millet. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0290-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. The sequences of PTI1 genes in foxtail millet.
Additional file 2. The PTI1 proteins used to construct phylogenetic but does not include SiPTI1s.
Additional file 3. Detailed characteristics of the motifs in the SiPTI1 proteins.
Additional file 4. The specific location of each SiPTI1 gene on the chromosomes.
Additional file 5. Characteristics of the promoter region of SiPTI1 genes.
Additional file 6. Segmentally and tandemly duplicated SiPTI1 gene pairs.
Additional file 7. One-to-one orthologous relationships between foxtail millet and other two plant species.
Additional file 8. Sequences of the primers used in this study.
Additional file 9. The relative expression value of SiPTI1s.
Additional file 10: Supplementary Fig. 1. SiPTI1–5 fusion protein identification by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. M: marker, 1: pET32a (0 h), 2: pET32a-SiPTI1–5 (0 h), 3: pET32a-SiPTI1–5T604A (0 h), 4: pET32a-SiPTI1–5K452N (0 h), 5: pET32a (4 h), 6: pET32a-SiPTI1–5 (4 h), 7: pET32a-SiPTI1–5T604A (4 h), 8: pET32a-SiPTI1–5K452N (4 h).
Additional file 11: Supplementary Fig. 2. Sequence homology of SiPTI1s. The sequences alignment of PTI1s from foxtail millet and tomato.. The 11 canonical subdomains conserved in serine/threonine kinases are indicated with Roman numerals. Invariant residues common to the majority of protein kinases are marked with black dots. The highly conserved lysine residue in subdomain II which is required for activity in SlPTI1 and most protein kinases is boxed.
Additional file 12: Supplementary Fig. 3. Sequence homology of PTI1s. The sequences alignment of PTI1s from foxtail millet, rice and maize. The 11 canonical subdomains conserved in serine/threonine kinases are indicated with Roman numerals. Invariant residues common to the majority of protein kinases are marked with black dots. The highly conserved lysine residue in subdomain II which is required for activity in most protein kinases is boxed.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data of this article are available within the manuscript and its additional files. The sequences of SiPTI1s (coding sequences (CDS), Protein and Gene) were all downloaded from Phytozome (JGI) (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html), and demonstrated in Additional file 1, whereas, Arabidopsis and maize PTI1 sequences (CDS, Protein and Gene) were deposited from Ensembl (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html). The PTI1 protein sequences used to construct phylogenetic tree but does not include SiPTI1s were acquired from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and the corresponding protein sequences of list in Additional file 2.