Significance
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) and trichothiodystrophy (TTD), which may arise from mutations in the same genes, are distinct clinical entities with opposite skin cancer predisposition. Whereas XP is characterized by cutaneous photosensitivity and cancer proneness frequently associated with neurodegeneration, TTD shows hair anomalies, physical and mental retardation, and, in 50% of cases, cutaneous photosensitivity but no skin cancer despite the accumulation of unrepaired ultraviolet-induced DNA lesions. This study identifies a TTD-specific transcription deregulation of PTGIS (prostaglandin I2 synthase) that results in reduced levels of prostaglandin I2. Reduced PTGIS is found in all TTD but not in XP patients, thus representing a biomarker for this disorder.
Keywords: NER-defective disorders, TFIIH transcription, PTGIS
Abstract
The cancer-free photosensitive trichothiodystrophy (PS-TTD) and the cancer-prone xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) are rare monogenic disorders that can arise from mutations in the same genes, namely ERCC2/XPD or ERCC3/XPB. Both XPD and XPB proteins belong to the 10-subunit complex transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) that plays a key role in transcription and nucleotide excision repair, the DNA repair pathway devoted to the removal of ultraviolet-induced DNA lesions. Compelling evidence suggests that mutations affecting the DNA repair activity of TFIIH are responsible for the pathological features of XP, whereas those also impairing transcription give rise to TTD. By adopting a relatives-based whole transcriptome sequencing approach followed by specific gene expression profiling in primary fibroblasts from a large cohort of TTD or XP cases with mutations in ERCC2/XPD gene, we identify the expression alterations specific for TTD primary dermal fibroblasts. While most of these transcription deregulations do not impact on the protein level, very low amounts of prostaglandin I2 synthase (PTGIS) are found in TTD cells. PTGIS catalyzes the last step of prostaglandin I2 synthesis, a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Its reduction characterizes all TTD cases so far investigated, both the PS-TTD with mutations in TFIIH coding genes as well as the nonphotosensitive (NPS)-TTD. A severe impairment of TFIIH and RNA polymerase II recruitment on the PTGIS promoter is found in TTD but not in XP cells. Thus, PTGIS represents a biomarker that combines all PS- and NPS-TTD cases and distinguishes them from XP.
The transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) is a 10-subunits complex involved in basal transcription, gene expression regulation, and nucleotide excision repair (NER), the pathway capable of removing the bulky DNA adducts induced by ultraviolet (UV) light, environmental mutagens, and chemotherapeutic agents (1–5). Mutations in either ERCC2/XPD (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man [OMIM]: 126340) or ERCC3/XPB (OMIM: 133510) genes encoding the two largest subunits of TFIIH account for distinct clinical entities, including xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) and the photosensitive form of trichothiodystrophy (PS-TTD). Differently, mutations in the GTF2H5/TTDA (OMIM: 608780) gene, which encodes the smallest polypeptide of TFIIH, only give rise to PS-TTD.
Both XP and PS-TTD are rare recessive hereditary disorders. While XP is characterized by high skin cancer predisposition and progressive neurological degeneration (6), PS-TTD is a disease with multisystem developmental defects whose major hallmark is sulfur-deficient brittle hair caused by reduced levels of cysteine-rich matrix proteins. TTD hair has characteristic alternating dark and light transverse “tiger tail” bands on polarized microscopy (7). This microscopic examination of cut hair is commonly used for confirmation of the diagnosis of TTD with defects in different genes. TTD patients exhibit other features of varying clinical severity, which include ichthyotic skin, nail dysplasia, physical and mental retardation, decreased fertility, proneness to infections, and signs of premature aging (6, 8, 9). Cutaneous photosensitivity is observed in both XP and PS-TTD patients and is associated with an altered cellular response to UV light caused by NER defects. Differently from XP, PS-TTD patients do not develop premalignant skin lesions and cutaneous tumors, with the only exception being a mild 44-y-old case mutated in the GTF2H5/TTDA gene (10).
To elucidate how mutations in the same gene may result in distinct clinical entities and opposed skin cancer predisposition, it has been suggested that XP pathological features are associated with mutations that mainly affect the DNA repair activity of TFIIH, whereas those typical of PS-TTD also impair transcription (11, 12). Indeed, persistence of NER proteins at the site of damage and accumulation of unrepaired DNA lesions impairs more XP than PS-TTD cells (13, 14). Moreover, several lines of evidence support the relevance of transcriptional alterations in the TTD pathological phenotype, including the observations that TTD-specific mutations interfere with the basal transcription activity of TFIIH in vitro (15) and impair its stability in vivo, thus explaining the reduced TFIIH levels in PS-TTD (16, 17). Studies in the PS-TTD mouse model or in patient cells demonstrated the reduced expression of several genes in terminally differentiated cells (18–25). Furthermore, the recent finding that among the causative genes for nonphotosensitive (NPS)-TTD, which share most of PS-TTD clinical features except skin photosensitivity, GTF2E2 encodes the β-subunit of the basal transcription factor TFIIE, while CARS1 and TARS1 are implicated in transcript translation, supports the notion that gene expression alterations are at the basis of TTD phenotypes (26–28).
With the aim to identify transcription deregulations accounting for PS-TTD clinical features and their diversity from XP, we performed whole transcriptome sequencing in cells isolated from PS-TTD family members. Widening the analysis to a large cohort of PS-TTD and XP patients, we identified TTD-specific transcriptional marks that were further investigated at the protein level. PS-TTD but not XP fibroblasts synthetize reduced levels of prostaglandin I2 synthase (PTGIS), the enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), to prostaglandin I2 (PGI2). This transcriptional defect is caused by an almost absent recruitment of TFIIH and RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) protein complexes on PTGIS promoter and affects not only PS- but also NPS-TTD, indicating an involvement of PTGIS reduction in TTD etiopathogenesis.
Results
Transcriptional Signature of TTD Skin Fibroblasts Cultured under Basal Condition or after UV Irradiation.
To define TTD-specific transcriptional signatures, we compared RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)–based transcriptomic maps of primary dermal fibroblasts from a PS-TTD female patient (TTD7PV) with that of her healthy mother. This strategy was designed to reduce the variability caused by different genetic backgrounds. Most cases of PS-TTD are mutated in the ERCC2/XPD gene and are hereafter indicated as PS-TTD/XP-D. The TTD7PV patient is affected by a severe form of the disorder and is compound heterozygous for one of the most frequent PS-TTD alterations in XPD, the Arg722Trp substitution, and for the complex alteration Leu461Val;Val716-Arg730del (29, 30). RNAs were collected from early-passage fibroblasts cultured under basal condition or at 2 h after UV irradiation and processed for RNA-seq (31). Interstrains (TTD7PV versus TTD7PVmother) and intrastrain (basal condition versus UV irradiated) transcriptome comparisons were performed to identify TTD-specific transcription deregulations as well as the normal or PS-TTD transcriptional response to UV irradiation. Differentially expressed genes were identified using the CuffDiff software with a cutoff of log2FC (fold change) < −1 and > +1 for the under- and overexpressed transcripts, respectively, and FDR-adjusted P < 0.05. We identified 718 and 730 transcriptionally deregulated genes in PS-TTD/XP-D compared to control fibroblasts in basal condition (SI Appendix, Table S1) and upon UV irradiation (SI Appendix, Table S2), respectively. Relevant of note, in TTD cells, the majority of the identified genes are down-regulated, consistent with the reduced levels of TFIIH in these cells (Fig. 1 A and B). Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) functional annotation clustering analysis revealed that in PS-TTD cells cultured under basal condition, the transcriptionally altered genes are mainly implicated in “developmental processes,” “cell adhesion and cell communication,” “inflammatory and wound healing response,” and “regulation of cell proliferation” (SI Appendix, Fig. S1A). Upon UV irradiation, the differentially expressed genes are involved in “cell signaling response,” “chondrocyte differentiation,” “platelet degranulation,” and “extracellular matrix organization” (SI Appendix, Fig. S1B).
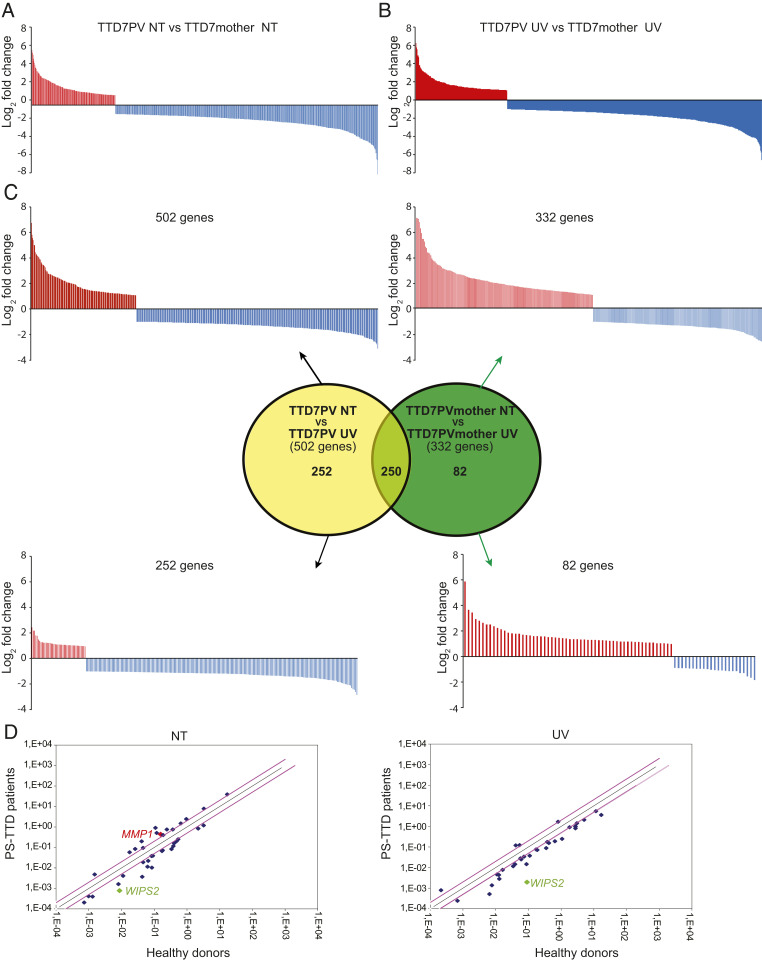
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the genes differentially expressed in TTD7PV skin fibroblasts compared to those from the healthy TTD7PVmother. (A and B) In total, 718 and 730 genes are differentially expressed in TTD7PV fibroblasts cultured under basal condition (A) or 2 h after 10 J/m2 UV irradiation (B), respectively. Red and blue bars indicate the up- and down-regulated genes, respectively. (C) Venn diagram and schematic representation of the transcript coding genes whose expression is modified following UV irradiation in TTD7PVmother (green, 332 genes) or TTD7PV (yellow, 502 genes) fibroblasts. The expression of 250 genes is commonly modified in TTD and control cells in response to UV light, whereas the transcriptional alteration of 82 and 252 genes occurs specifically in the control and patient fibroblasts, respectively. Red and blue bars indicate the up- and down-regulated genes, respectively. (D) Scatter plots in logarithmic scale representing the comparison of the 174 messenger RNA levels [log2(−ΔCt)] found in the TTD patient RNA pool versus healthy parent RNA pool from fibroblasts cultured in basal condition (Left) and upon UV irradiation (Right). Only values with a log2 fold change higher than ±|2| are indicated (gene names and fold change values, SI Appendix, Table S12). The previously identified deregulated gene (MMP1) in TTD cells and the most down-regulated gene found in this study (WISP2) have been pinpointed. The black line indicates fold changes of 1 (=no deregulation), whereas the pink lines correspond to log2 fold changes ±|2|.
By deeply investigating the RNA-seq and computational data, we found that normal human dermal fibroblasts respond to UV irradiation by modifying the expression profile of 332 genes, equally distributed between up- and down-regulated ones (Fig. 1C). The majority of the overexpressed genes encode proteins implicated in “transcriptional regulation” and “DNA-binding proteins” gene ontology (GO) categories, pointing to a transcriptional-mediated response to UV irradiation in human skin fibroblasts (SI Appendix, Table S3). Differently, irradiated PS-TTD cells modulate the expression of 502 genes, the majority of which are once more down-regulated (Fig. 1C and SI Appendix, Table S4). Among the 502 genes, 250 are in common with the normal cellular response to UV irradiation, whereas 252 occur specifically in patient fibroblasts. Moreover, after UV irradiation, PS-TTD fibroblasts fail to regulate the expression of 82 genes, the majority of which should be up-regulated (SI Appendix, Table S5). Functional annotation clustering of the GO categories revealed that the 82 genes encode proteins involved in “developmental processes.” It is conceivable that some of these gene expression alterations might account for the multisystemic nature and the developmental defects of TTD pathological phenotype.
Identification of the TTD-Specific Gene Expression Profile.
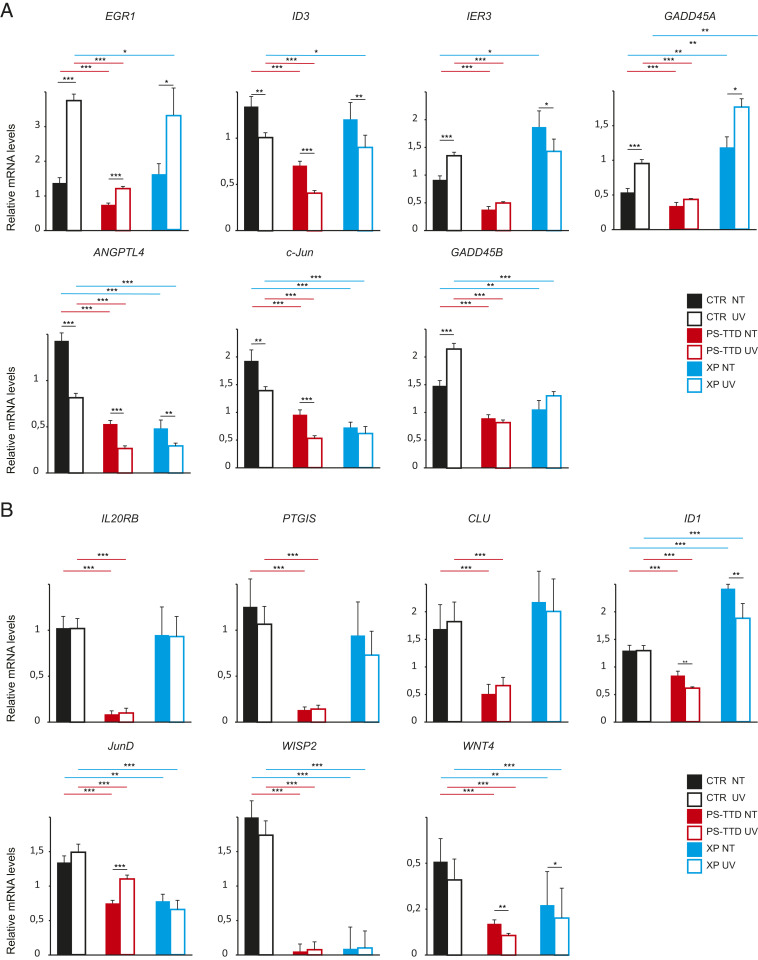
In the attempt to identify transcriptional deregulations that might account for TTD clinical features, we selected the 174 genes that according to Integrative Genomic Viewer showed the highest deregulation in all TTD7PV sample replicates in comparison with the control TTD7PVmother replicates (SI Appendix, Table S6). The expression level of the 174 genes was then investigated by RT-PCR with RealTime ready Custom Panel in RNA pools obtained by mixing equal amounts of total RNAs isolated from skin fibroblasts of either four PS-TTD/XP-D patients (TTD7PV, TTD12PV, TTD15PV, and TTD23PV) or four PS-TTD parents (TTD12-15PVmother, TTD12-15PVfather, TTD7PVmother, and TTD7PVfather). The selected patients are all severely affected and are compound heterozygous for the most frequent XPD alterations associated with TTD, namely, the Arg112His and the Arg722Trp amino acid changes (SI Appendix, Table S7). By comparing the expression levels of the 174 genes in RNA pools from PS-TTD or control fibroblasts cultured under basal condition or after UV irradiation (SI Appendix, Tables S8–S11), we identified 61 genes with an FC higher than ±|2| (Fig. 1D), among which WISP2 represents the most deregulated one in PS-TTD/XP-D with a FC of −11,726 and −45,203 in basal condition and upon UV exposure, respectively. Consistent with our previous observations, the matrix metalloprotease 1 (MMP-1) is included in the list of the most deregulated genes. We recently addressed the relevance and the impact of MMP-1 transcription deregulations on the skin of PS-TTD patients (25); therefore, no further investigations have been performed on this gene in the present study. For the remaining 60 genes, we established real-time RT-PCR analysis in single patient fibroblasts from seven PS-TTD cases, representative of different types and combinations of mutated XPD alleles (SI Appendix, Table S7). The expression levels observed in PS-TTD cells were compared with those identified in fibroblasts from the corresponding healthy parents analyzed in parallel. By increasing the size of the patient and control cohorts, we could reduce to 14 the list of genes differentially expressed in all PS-TTD/XP-D cells strains (Fig. 2 and SI Appendix, Figs. S2 and S3 and Table S12). In particular, the expression of ANGPTL4, c-Jun, EGR1, IER3, GADD45A, GADD45B, and ID3 in control fibroblasts appears modulated by UV irradiation, while in PS-TTD cells, it is reduced both in basal condition and after UV irradiation (Fig. 2A and SI Appendix, Fig. S2). The transcription deregulation does not involve other UV-responsive genes, as attested by the proper up-regulation of the early responsive c-Fos gene in PS-TTD/XP-D cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S4) (32). Moreover, the expression of IL20RB, PTGIS, CLU, ID1, JunD, WISP2, and WNT4, which are not modulated by UV exposure, is strongly reduced in PS-TTD (Fig. 2B and SI Appendix, Fig. S3).
Fig. 2.
Gene expression deregulation in XP-D cells. (A and B) Transcription profile of the UV-responsive genes EGR1, ID3, c-Jun, IER3, ANGPTL4, GADD45B, and GADD45A (A) and the UV-unresponsive genes IL20RB, PTGIS, JunD, CLU, WISP2, WNT4, and ID1 (B). Graphs indicate the mean values of the transcript levels analyzed by real-time RT-PCR in single-strain fibroblasts from healthy control (CTR; namely, TTD12PV-15PV parents, TTD11PV parents, and TTD7PV parents; black bars), TTD/XP-D (namely, TTD12PV, TTD15PV, TTD11PV, TTD7PV, TTD23PV, TTD20PV, and TTD8PV; red bars), and XP/XP-D (XP15PV, XP-16PV, XP17PV, XP49BR, and XP1BR; blue bars) individuals. Fibroblasts were cultured under basal condition (not treated [NT]; solid bars) or after UV irradiation (UV; empty bars). The single-strain values normalized to the expression of the GAPDH housekeeping gene are indicated in SI Appendix, Figs. S2 and S3. The reported values represent the means of at least two independent experiments, whose samples have been analyzed in triplicate (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; Student’s t test; only the significant differences are shown). Bars indicate the SEs.
With the aim to define whether these gene expression deregulations also impair XP/XP-D cells, we extended the real-time RT-PCR analysis to single patient fibroblasts isolated from five XP patients also mutated in the ERCC2/XPD gene and homozygous or combined heterozygous for the Arg683Gln or Arg683Trp substitutions (SI Appendix, Table S7), the most frequent XPD alterations associated to XP (33). Among the deregulated genes, ID3, EGR1, IER3, IL20RB, PTGIS, and CLU are more distinctive of the PS-TTD phenotype, with the exception of XP16PV cells showing an expression profile similar to TTD cells. In contrast, ANGPTL4, c-Jun, GADD45B, JunD, WISP2, and WNT4 are transcriptionally deregulated both in TTD and XP cells. Moreover, GADD45A and ID1 appear to be up-regulated in XP cells, thus behaving in an opposite way compared to PS-TTD (Fig. 2 and SI Appendix, Figs. S2 and S3).
Reduced Levels of PTGIS Characterize PS-TTD/XP-D Primary Dermal Fibroblasts.
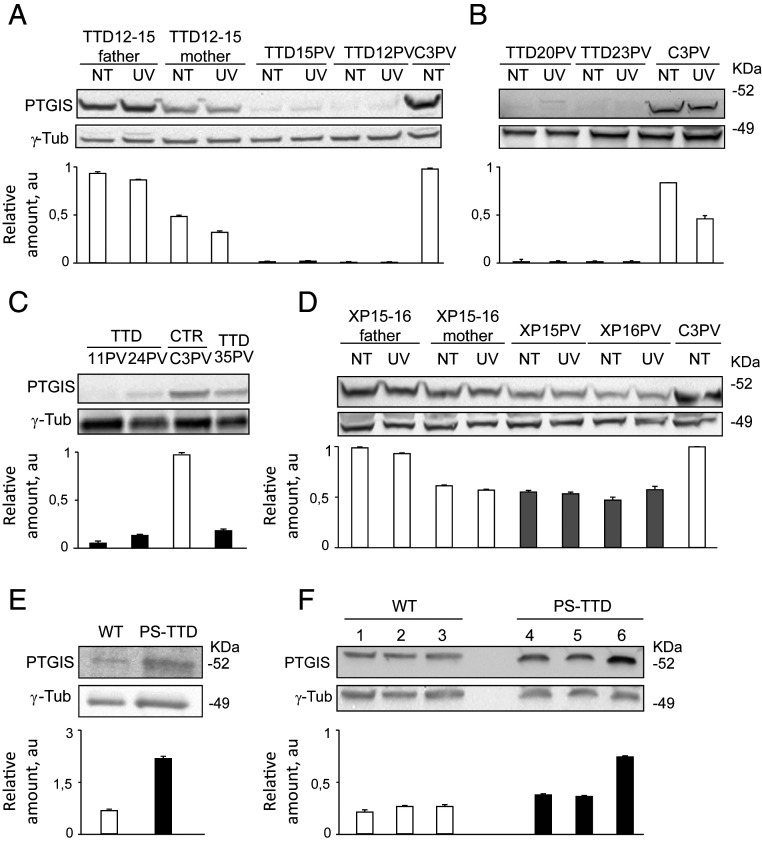
We next searched whether the PS-TTD/XP-D gene expression deregulations impact the amount of the corresponding encoded proteins, thus contributing to the typical TTD clinical features. Western blot analysis of whole-cell extracts isolated from several XP-D patients (either TTD or XP) and healthy individuals was carried out (Fig. 3 and SI Appendix, Fig. S5). While the immunoblots with anti-WNT4, -IL20RB, and -ID3 did not reveal any detectable protein band, likely because of their low expression levels (SI Appendix, Table S12) and/or extracellular secretion, the amount of ANGPTL4 protein in control, TTD, and XP fibroblasts appears abundant and constant among the different samples (SI Appendix, Fig. S5) despite the strong transcriptional reduction in all XP-D cells (Fig. 2). An interindividual variability of WISP2, ID1, CLU, EGR1, c-Jun, JunD, and GADD45A protein amounts is observed among the different samples, and the differences do not correlate with the transcript levels or patient phenotypes. Therefore, most of the severe transcription deregulations affecting PS-TTD fibroblasts seem to be compensated by protein synthesis and/or protein stability (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). However, we found a drastic reduction of PTGIS protein in all the PS-TTD/XP-D fibroblasts cultured under basal condition as well as after UV irradiation (Fig. 3). In comparison to healthy individuals, either family members or genetically unrelated donors, PTGIS is strongly reduced in TTD/XP-D fibroblasts irrespective of whether the patients are homozygotes or compound heterozygotes for ERCC2/XPD mutations (Fig. 3 A–C and SI Appendix). A strong PTGIS reduction is also observed in thermo-sensitive TTD cells (TTD1RO) cultured at either 37 °C or 41 °C, the latter being a condition that further increases the instability of the TFIIH complex in these patients (SI Appendix, Fig. S6) (17, 34). Differently, only a very mild reduction of PTGIS protein level is observed in XP/XP-D fibroblasts (Fig. 3D), indicating that PTGIS defect correlates with TTD rather than XP clinical features.
Fig. 3.
PTGIS protein amount in XP-D human and mouse cell/tissues. (A–D) Immunoblot analysis of PTGIS in total protein extracts from (A) healthy human control (C3PV and TTD12-15PV parents; black empty bars) and TTD/XP-D (TTD12PV and TTD15PV; black solid bars) primary skin fibroblasts cultured under basal condition (NT) and 2 h after UV irradiation; (B) healthy control (C3PV; black empty bar), TTD/XP-D (TTD20PV and TTD23PV; black bars) primary skin fibroblasts cultured under basal condition (NT) and 2 h after UV irradiation; (C) healthy control (C3PV; black empty bar) and TTD/XP-D (TTD11PV, TTD24PV, and TTD35PV; black solid bars) primary skin fibroblasts; and (D) healthy controls (C3PV, mother and father of XP15-16PV siblings; black empty bars) and XP/XP-D (XP15PV and XP16PV; gray bars) fibroblasts cultured in basal condition (NT) and 2 h after UV irradiation. The signals were quantified and normalized to the γ-tubulin amount. (E and F) Immunoblot analysis of PTGIS in total protein extracts from (E) wild-type (WT; white bars) and PS-TTD/XP-D (black bars) MEF; (F) WT (black empty bars) and TTD/XP-D (black solid bars) mouse skin. γ-tubulin was used as the loading control. The diagram below each blot represents the mean values of at least three independent experiments. Bars indicate SEs. Arbitrary unit, au.
Next, we extended the gene expression profile and immunoblot analysis on mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) isolated from the PS-TTD mouse model homozygous for the XPDR722W allele (35). The TTD mouse resembles many of the human syndrome clinical features (such as brittle hair, UV sensitivity, growth delay, reduced fertility, and short lifespan), but contrary to humans, it was reported to develop skin cancer after UV irradiation (36). Interestingly, most of the transcription deregulations found in PS-TTD/XP-D patient fibroblasts are also retained in MEFs from the PS-TTD mouse model (SI Appendix, Fig. S7), including the reduced PTGIS expression. Thus, the altered expression of this set of genes correlates with PS-TTD clinical features. However, despite the marked transcriptional defect, no PTGIS protein reduction is observed in MEFs or in any other TTD mouse tissues, not even in the skin (Fig. 3 E and F), indicating that PTGIS protein reduction is specific of PS-TTD/XP-D human patients. Conversely, the presence of PTGIS protein correlates with the feature of XP patients or TTD mouse model to develop skin cancer in response to UV irradiation.
Reduced PTGIS Levels as a Biomarker for Both PS- and NPS-TTD.
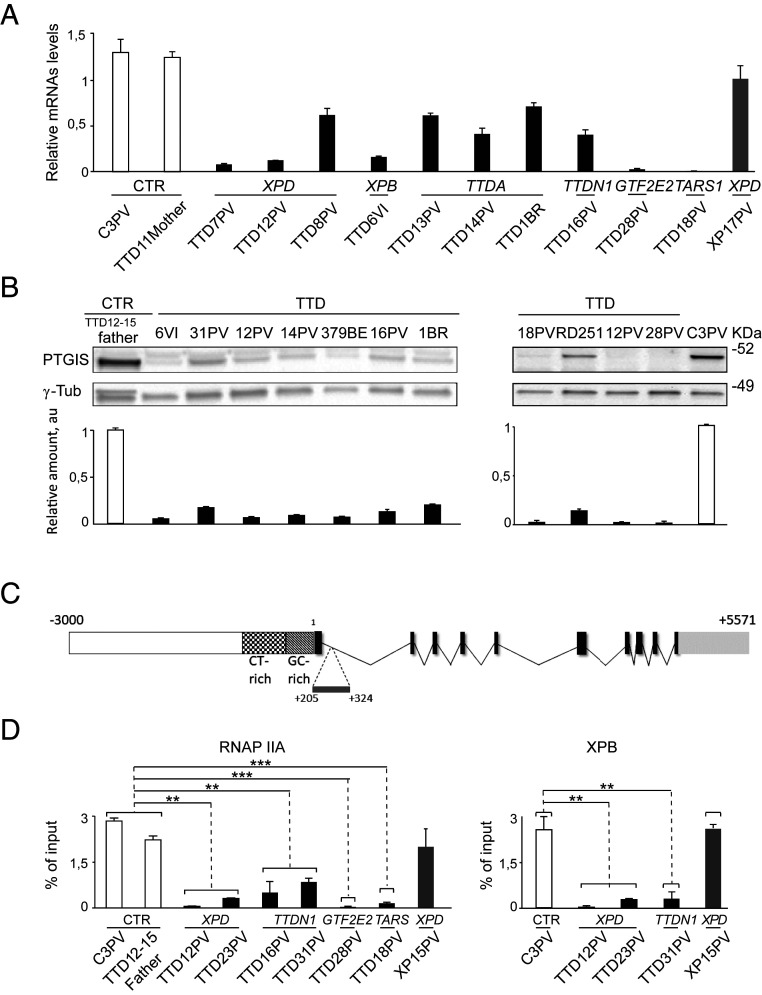
To understand to what extent PTGIS reduction contributes to TTD clinical features, the PTGIS expression level by real-time RT-PCR and immunoblot analysis were extended to other PS-TTD cases with mutations in either ERCC3/XPB or TTDA genes as well as to NPS-TTD cases with mutations in MPLKIP/TTDN1, GTF2E2, CARS1, or TARS1 genes (Fig. 4). A significant reduction of both transcript and protein levels was found in all TTD primary dermal fibroblasts analyzed, irrespective of the causative gene or the type of mutations causing the TTD phenotype (Fig. 4 A and B).
Fig. 4.
PTGIS deregulation in PS-TTD and NPS-TTD. (A) Graphs indicate the mean values of the transcript levels analyzed by real-time RT-PCR in single-strain fibroblasts from healthy controls (CTR; white bars), TTD (PS-TTD/XP-D, PS-TTD/XP-B, PS-TTD/TTD-A, NPS-TTD/MPLKIP, NPS-TTD/GTF2E2, and NPS-TTD/TARS1; black bars), and XP-XP-D (gray bar). The single-strain values were normalized to the expression of the GAPDH housekeeping gene. The reported values represent the means of at least two independent experiments, whose samples have been analyzed in triplicate. Bars indicate the SEs. (B) Immunoblot analysis of PTGIS in total protein extracts from healthy control (TTD12-15PV father and C3PV; white bar), PS-TTD (TTD6VI/XP-B, TTD12PV/XP-D, TTD14PV/TTD-A, TTD1BR/TTD-A, and TTD28PV/TTD-A; black bars), and NPS-TTD (TTD16PV/MPLKIP, TTD31PV/MPLKIP, TTD379BE/GTF2E2, TTD18PV/TARS1, and RD251/CARS1; black bars) skin fibroblasts. The signals were quantified and normalized to the γ-tubulin amount. The diagrams below represent the mean values of at least three independent experiments. Bars indicate SEs. (C) Schematic organization of the genomic fragment included between nucleotides −3,000 + 5,571 of PTGIS gene (GenBank accession number NG_007940.1). The spotted and tessellated boxes are the CT-rich and GC-rich regions of PTGIS promoter, respectively. Introns are shrunk to a minimal length. Exons are indicated with solid black boxes. The light gray box indicates the 3′ untranscribed region. Horizontal broken lines delimitate the position of the fragment amplified by quantitative ChIP assays (amplicon location: I +205/+324). (D) RNAP IIA and TFIIH (XPB) occupancy on the proximal intron of PTGIS promoter in healthy (white bars), PS- and NPS-TTD (black bars), and XP/XP-D (gray bar) primary dermal fibroblasts. The values are the mean of at least two independent experiments (**P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001; Student’s t test).
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis has been then carried out to investigate the dynamic of TFIIH and the hypophosphorylated form of RNAP II (RNAP IIA) on PTGIS promoter. Both factors are essential elements of the transcription preinitiation complex (PIC) that assembles on active gene promoters. Antibodies directed against RNAP IIA or XPB subunit of the TFIIH complex were used to immunoprecipitate the chromatin of primary dermal fibroblasts from TTD or XP patients or healthy individuals. PCR amplification of the coimmunoprecipitated genomic DNA fragment spanning the 5′ region of PTGIS transcript allowed for the detection of the transcription machinery occupancy on this gene (Fig. 4C). Compared to control cells, very low levels of RNAP IIA and TFIIH were observed in all TTD samples analyzed independently of the causative gene (Fig. 4D). In XP/XP-D cells, the PIC recruitment on PTGIS promoter was less severely affected. These findings indicate that TTD- more than the XP-specific alterations impact the recruitment of the transcription apparatus on PTGIS promoter, thus leading to PTGIS transcriptional impairment and, in turn, to reduced protein amounts in both PS-TTD and NPS-TTD primary dermal fibroblasts.
Discussion
Compelling evidence suggests that TTD cells are characterized by transcriptional impairments that may ascribe for various clinical features in patients, including hypoplasia of adipose tissue (21), developmental and neurological defects (22, 24), and joint and bone alterations (23, 25). The identification of a gene expression signature specific for TTD represents a useful tool both for the identification of the molecular faults responsible for TTD clinical features and to facilitate patient diagnosis.
In the present study, we identify the transcription alterations specific for TTD skin fibroblasts by first comparing the whole transcriptome from a single ERCC2/XPD-defective TTD patient with that of the corresponding healthy mother and thereafter by expanding the gene expression analysis to a large cohort of PS-TTD and XP patients carrying differently mutated ERCC2/XPD alleles. The advantage of comparing patients and healthy parents’ gene expression profiles is directed to reduce the expression variability caused by different genetic backgrounds.
Overall, 14 distinct genes have been found to be consistently deregulated in patient cells. Besides GADD45A and ID1 that show an opposite transcription deregulation in PS-TTD and XP cells, EGR1, IER3, ID3, IL20RB, PTGIS, and CLU are down-regulated in TTD, while ANGPTL4, GADD45B, c-Jun, WNT4, WISP2, and JunD are deregulated in all XP-D cases. As TFIIH was shown to activate the expression of specific subsets of target genes through the phosphorylation of defined transcription activators or repressors (19, 21, 23, 25, 37, 38), it is tempting to speculate that the gene deregulations occurring both in TTD and XP cells are caused by TFIIH malfunctioning independently on the type of XPD alterations. In contrast, TTD-specific transcription deregulations are likely ascribed to the reduced levels of TFIIH, which are known to characterize TTD cells (16, 17).
When analyzed at the protein level, most of the transcription deregulations characterizing TTD fibroblasts do not end up in protein amount alterations, indicating that human cells have the means to compensate for the drastic consequences of transcription deficiency. This does not hold true for PTGIS, whose protein content is drastically reduced in all the TTD fibroblasts so far analyzed, both PS-TTD (with mutations in ERCC2/XPD, ERCC3/XPB, or GTF2H5/TTDA genes) and NPS-TTD (with mutations in MPLKIP/TTDN1, GTF2E2, CARS1, or TARS1 genes). The finding that PTGIS impairment always occurs at transcriptional level, even in CARS1- and TARS1-defective cells whose gene products are not known to be directly involved in transcriptional processes, suggests that PTGIS reduction is not the result of TFIIH malfunctioning but rather represents a TTD-specific dysfunction that is strictly associated with the TTD clinical framework. Alternatively, PTGIS transcriptional failure may represent a TTD common defect that derives from distinct mechanistic alterations, each related to the mutated causative gene.
PTGIS is a protein of 500 amino acids that contains a heme-binding site in position 441 and a single transmembrane domain in its most N-terminal 20 amino acids. PTGIS is bound to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, where it catalyzes the conversion of PGH2 to the lipid mediator PGI2 (39). Low levels of PTGIS and, in turn, reduced PGI2 amounts likely contribute to the multisystemic nature of TTD clinical features. Indeed, PGI2 is considered a potent endogenous vasodilator that acts by relaxing smooth muscle, preventing platelet aggregations, and dissolving the existing platelet aggregates (40). Several studies have shown genetic variations affecting PGI2 levels in human blood and urine (41, 42). In particular, reduced levels of PGI2 have been reported to be a risk factor for high blood pressure, systolic hypertension, and myocardial and cerebral infarction in the over 50 population (43–45). Whereas the risk of cardiovascular diseases has been rarely reported in TTD patients, likely because of their very short average life (46), cerebral infarction has been described in these patients (7).
Recently, it has been shown that PGI2 regulates the innate and adaptive immune system by modulating the function of dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, endothelial cells, and eosinophils. Moreover, it was demonstrated to have an immune-modulatory effect on B and T cells (ref. 40 and references therein). Considering that TTD patients suffer from severe and recurrent infections, particularly at the level of the respiratory tract (8, 9), associated with hypogammaglobulinemia and neutropenia (47), it is conceivable that reduced levels of PTGIS may contribute to an altered immune response in these individuals.
In contrast, overproduction of PGI2 appears to sustain cancer progression. Coculturing experiments demonstrated that PGI2-expressing cells or even a stable analog of PGI2 (carbaprostacyclin) can reduce apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells and sustain tumor cell survival (48). It has been demonstrated that under hypoxic conditions, the expression of PTGIS is induced in human lung fibroblasts and cancer cell lines, an event that is paralleled by a translocation of PTGIS protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus (49). The restriction of oxygen (hypoxia) and nutrients are events that occur in the tumor-surrounding area and lead to the activation of the hypoxia-signaling pathway and the hypoxia-inducible factors. Indeed, an overproduction of PGI2 has been observed in cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts (CAFs) that surround the human colorectal cancer cells but not in the fibroblasts from normal colonic tissue. By activating the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PARP)δ-mediated transcription, PGI2 leads to increased levels of the proangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in CAF fibroblasts that, in turn, contributes to the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) and tumor growth (49, 50). In addition, various pharmacological and experimental animal studies attest to the relevance of cyclooxygenase (COX)-derived prostaglandins in the progression of nonmelanoma skin tumors, such as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and basal cell carcinoma. Indeed, depletion of the upstream and key enzyme COX-2 in the prostaglandin biosynthetic pathway makes the mouse skin resistant to SCC (ref. 6 and reference therein). Taking into account that TTD patients do not develop skin cancer despite the accumulation of unrepaired DNA damage (9), it is tempting to speculate that the reduced amount of PGI2 may be insufficient to exert the proinflammatory and anti-apoptotic function in TTD patient tissues. This event combined with other factors, including the extracellular matrix (ECM) alterations previously demonstrated, may counteract the tumor growth in TTD (23, 25). Differently from humans, we found that the PTGIS transcription deregulation in the TTD mouse model is compensated at the protein level (Fig. 3 E and F), in agreement with the ability of these mice to develop skin cancer after UV irradiation. This notion may help explain the yet unsolved discrepancy in UV-induced skin cancer susceptibility between patients and the TTD mouse (36).
Finally, recent evidence suggests that various prostaglandins play a role in regulating hair growth. In particular, PGE2 protects from radiation-induced hair loss in mice, PGD2 inhibits hair growth, and an analog of PGF2α is routinely used to enhance the growth of human eyelashes (ref. 51 and references therein). So far, there is no clear evidence that PGI2 also regulates the hair follicle, thus failing to link it with the brittle and fragile hair in TTD. Considering that the TTD mouse model resembles many of the developmental and neurological abnormalities of the human TTDs, including the hair defect and the signs of premature aging, it is reasonable to assume that PTGIS does not contribute to these pathological features. Indeed, differently from the prostaglandin PGE2, PGI2 does not seem to play a relevant role during neurodevelopment (52). Nevertheless, we cannot exclude the fact that in specific tissue/cell types and in a specific time frame of development, the mouse PTGIS protein stability does not compensate for the gene transcriptional impairment, thus contributing to the neuroectoderm-derived developmental defects of TTD.
Prostaglandins are also lipid mediators that promote the differentiation of adipocyte precursor cells to adipose cells. These proteins are important transcription factors in the activation of the early phase of adipogenesis differentiation (53, 54). According to its role in adipocyte metabolism, it is tempting to speculate that PTGIS deregulation may also contribute to the atrophy of subcutaneous fat frequently described in TTD (55).
Besides supporting the hypothesis that transcriptional defects make a major contribution to the TTD phenotype while DNA repair defects represent the major abnormality in XP, these findings demonstrate a specific transcription deregulation that results in reduced synthesis and secretion of PTGIS amounts in TTD patients. PTGIS reduction represents an easily accessible gold standard biomarker that combines the PS- and NPS-TTD cases so far investigated. In addition, the present study opens the possibility for promising therapeutic prospects. Indeed, PGI2 analogs have been successfully used for therapy in pulmonary arterial hypertension, peripheral occlusive disease, and vascular complication of diabetes mellitus (40).
Materials and Methods
Patient fibroblast strains used in this study are listed in SI Appendix, Table S7. Normal primary fibroblasts were from a genetically unrelated healthy donor (C3PV) and eight phenotypically normal PS-TTD/XP-D or XP/XP-D parents (mother and father of the patients TTD7PV, TTD11PV, TTD12-15PV, and XP15-16PV). RNAs for sequencing and RNA-seq processing were prepared as detailed in SI Appendix, Materials and Methods. Gene expression analysis was performed by RealTime ready Custom Panels (Roche) and quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Immunoblot and ChIP assay experiments were performed according to standard protocols. Full details are provided in SI Appendix, Materials and Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Grants 17710 and 21737 to D.O.), the Project International de cooperation scientique- Centre National pour la Recherche Scientifique (Grant 6824 to E.C.), and the Flagship project Epigen Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche-Ministero dell'Istruzione Università e Ricerca (to G.B.). We are grateful to the clinicians, patients, and patient families for their support in our research studies.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.2024502118/-/DCSupplemental.
Data Availability
The data discussed in this publication have been deposited in ArrayExpress https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/ (accession no. E-MTAB-10567).
References
- 1.Marteijn J. A., Lans H., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H. J., Understanding nucleotide excision repair and its roles in cancer and ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 465–481 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Compe E., Egly J. M., Nucleotide excision repair and transcriptional regulation: TFIIH and beyond. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 85, 265–290 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rimel J. K., Taatjes D. J., The essential and multifunctional TFIIH complex. Protein Sci. 27, 1018–1037 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kusakabe M., et al., Mechanism and regulation of DNA damage recognition in nucleotide excision repair. Genes Environ. 41, 2–6 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tiwari V., D. M. Wilson, III, DNA damage and associated DNA repair defects in disease and premature aging. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 105, 237–257 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lehmann A. R., McGibbon D., Stefanini M., Xeroderma pigmentosum. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 6, 70 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Faghri S., Tamura D., Kraemer K. H., Digiovanna J. J., Trichothiodystrophy: A systematic review of 112 published cases characterises a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations. J. Med. Genet. 45, 609–621 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stefanini M., Botta E., Lanzafame M., Orioli D., Trichothiodystrophy: From basic mechanisms to clinical implications. DNA Repair (Amst.) 9, 2–10 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Orioli D., Stefanini M., “Trichothiodystrophy” in DNA Repair Disorders—Clinical and Molecular Aspects, Nishigori C., Sugasawa K., Eds. (Springer-Japan, 2019), pp. 133–159. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Takeichi T., et al., Trichothiodystrophy, complementation group A complicated with squamous cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 32, e75–e77 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yan C., et al., Transcription preinitiation complex structure and dynamics provide insight into genetic diseases. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 26, 397–406 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Compe E., Genes C. M., Braun C., Coin F., Egly J. M., TFIIE orchestrates the recruitment of the TFIIH kinase module at promoter before release during transcription. Nat. Commun. 10, 2084–14 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Riou L., et al., Differential repair of the two major UV-induced photolesions in trichothiodystrophy fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 64, 889–894 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Boyle J., et al., Persistence of repair proteins at unrepaired DNA damage distinguishes diseases with ERCC2 (XPD) mutations: Cancer-prone xeroderma pigmentosum vs. non-cancer-prone trichothiodystrophy. Hum. Mutat. 29, 1194–1208 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dubaele S., et al., Basal transcription defect discriminates between xeroderma pigmentosum and trichothiodystrophy in XPD patients. Mol. Cell 11, 1635–1646 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vermeulen W., et al., Sublimiting concentration of TFIIH transcription/DNA repair factor causes TTD-A trichothiodystrophy disorder. Nat. Genet. 26, 307–313 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Botta E., et al., Reduced level of the repair/transcription factor TFIIH in trichothiodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 2919–2928 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Viprakasit V., et al., Mutations in the general transcription factor TFIIH result in beta-thalassaemia in individuals with trichothiodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 2797–2802 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Keriel A., Stary A., Sarasin A., Rochette-Egly C., Egly J. M., XPD mutations prevent TFIIH-dependent transactivation by nuclear receptors and phosphorylation of RARalpha. Cell 109, 125–135 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Backendorf C., et al., Repair characteristics and differentiation propensity of long-term cultures of epidermal keratinocytes derived from normal and NER-deficient mice. DNA Repair (Amst.) 4, 1325–1336 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Compe E., et al., Dysregulation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor target genes by XPD mutations. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 6065–6076 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Compe E., et al., Neurological defects in trichothiodystrophy reveal a coactivator function of TFIIH. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1414–1422 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Orioli D., et al., XPD mutations in trichothiodystrophy hamper collagen VI expression and reveal a role of TFIIH in transcription derepression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22, 1061–1073 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Traboulsi H., Davoli S., Catez P., Egly J. M., Compe E., Dynamic partnership between TFIIH, PGC-1α and SIRT1 is impaired in trichothiodystrophy. PLoS Genet. 10, e1004732 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Arseni L., et al., TFIIH-dependent MMP-1 overexpression in trichothiodystrophy leads to extracellular matrix alterations in patient skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 1499–1504 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kuschal C., et al., GTF2E2 mutations destabilize the general transcription factor complex TFIIE in individuals with DNA repair-proficient trichothiodystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 98, 627–642 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Theil A. F., et al., Trichothiodystrophy causative TFIIEβ mutation affects transcription in highly differentiated tissue. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26, 4689–4698 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Theil A. F., et al., Bi-allelic TARS mutations are associated with brittle hair phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 105, 434–440 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fassihi H., et al., Deep phenotyping of 89 xeroderma pigmentosum patients reveals unexpected heterogeneity dependent on the precise molecular defect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, E1236–E1245 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ferri D., Orioli D., Botta E., Heterogeneity and overlaps in nucleotide excision repair disorders. Clin. Genet. 97, 12–24 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Orioli D., Gene expression profiles in TTD patient and control. ArrayExpress. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-10567/. Deposited 31 May 2021.
- 32.Blattner C., et al., UV-Induced stabilization of c-fos and other short-lived mRNAs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 3616–3625 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lehmann A. R., The xeroderma pigmentosum group D (XPD) gene: One gene, two functions, three diseases. Genes Dev. 15, 15–23 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Vermeulen W., et al., A temperature-sensitive disorder in basal transcription and DNA repair in humans. Nat. Genet. 27, 299–303 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.de Boer J., et al., A mouse model for the basal transcription/DNA repair syndrome trichothiodystrophy. Mol. Cell 1, 981–990 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.de Boer J., et al., Mouse model for the DNA repair/basal transcription disorder trichothiodystrophy reveals cancer predisposition. Cancer Res. 59, 3489–3494 (1999). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Drané P., Compe E., Catez P., Chymkowitch P., Egly J. M., Selective regulation of vitamin D receptor-responsive genes by TFIIH. Mol. Cell 16, 187–197 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chen D., et al., Activation of estrogen receptor alpha by S118 phosphorylation involves a ligand-dependent interaction with TFIIH and participation of CDK7. Mol. Cell 6, 127–137 (2000). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vane J. R., Botting R. M., Pharmacodynamic profile of prostacyclin. Am. J. Cardiol. 75, 3A–10A (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dorris S. L., Peebles R. S. Jr, PGI2 as a regulator of inflammatory diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2012, 926968–926969 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cho S.-A., et al., Analysis of genetic polymorphism and biochemical characterization of a functionally decreased variant in prostacyclin synthase gene (CYP8A1) in humans. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 569, 10–18 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yi X., Ming B., Wang C., Chen H., Ma C., Variants in COX-2, PTGIS, and TBXAS1 are associated with carotid artery or intracranial arterial stenosis and neurologic deterioration in ischemic stroke patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 26, 1128–1135 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nakayama T., Soma M., Rahmutula D., Izumi Y., Kanmatsuse K., Nonsense mutation of prostacyclin synthase gene in a family. Lancet 349, 1887–1888 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Iwai N., et al., Human prostacyclin synthase gene and hypertension: The suita study. Circulation 100, 2231–2236 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nakayama T., et al., Splicing mutation of the prostacyclin synthase gene in a family associated with hypertension. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 297, 1135–1139 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Toelle S. P., Valsangiacomo E., Boltshauser E., Trichothiodystrophy with severe cardiac and neurological involvement in two sisters. Eur. J. Pediatr. 160, 728–731 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Randall G., et al., Mortality-associated immunological abnormalities in trichothiodystrophy: Correlation of reduced levels of immunoglobulin and neutrophils with poor patient survival. Br. J. Haematol. 185, 752–754 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cutler N. S., et al., Stromal production of prostacyclin confers an antiapoptotic effect to colonic epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 63, 1748–1751 (2003). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang J., et al., VEGF expression is augmented by hypoxia-induced PGIS in human fibroblasts. Int. J. Oncol. 43, 746–754 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gupta R. A., et al., Prostacyclin-mediated activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta in colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 13275–13280 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Xu X.-G., Chen H.-D., Prostanoids and hair follicles: Implications for therapy of hair disorders. Acta Derm. Venereol. 98, 318–323 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Andreasson K., Emerging roles of PGE2 receptors in models of neurological disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 91, 104–112 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Michaud A., et al., Expression of genes related to prostaglandin synthesis or signaling in human subcutaneous and omental adipose tissue: Depot differences and modulation by adipogenesis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 451620 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Moseti D., Regassa A., Kim W.-K., Molecular regulation of adipogenesis and potential anti-adipogenic bioactive molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 124 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lambert W. C., Gagna C. E., Lambert M. W., Trichothiodystrophy: Photosensitive, TTD-P, TTD, tay syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 685, 106–110 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data discussed in this publication have been deposited in ArrayExpress https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/ (accession no. E-MTAB-10567).