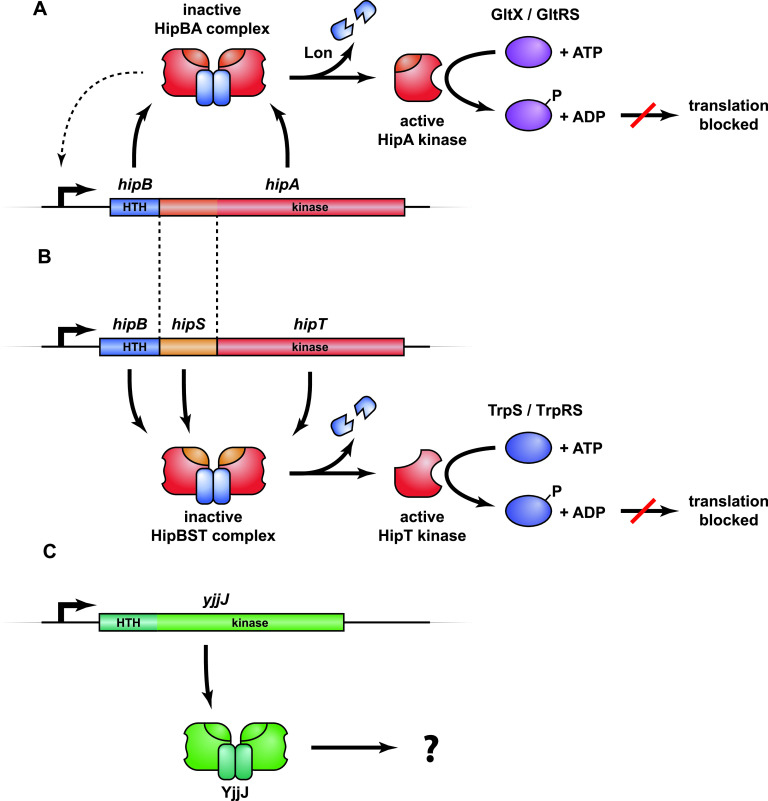
FIG 1.
Overview of the hipBA, hipBST, and yjjJ operons and their protein products. (A) hipBA encodes the antitoxin HipB (blue) and toxin kinase HipA (red/orange) that form an inactive HipB2HipA2 complex that can bind to operators in the promoter region via HTH DNA-binding domains in HipB and thereby autoregulate transcription (dashed line) (28). Upon HipB degradation by Lon protease (88) and activation of HipA, HipA phosphorylates and inhibits glutamine tRNA synthetase (GltX/GltRS), thereby halting translation and inducing the stringent response (51, 52, 54). (B) hipBST encodes three proteins, HipB (blue), HipS (orange), and HipT (red) that form an inactive HipBST complex (59). HipS is homologous to the N-subdomain-1 of HipA and functions as the antitoxin that neutralizes HipT (59). Like HipB of HipBA, HipB of HipBST has an HTH domain and augments the inhibition of HipT by HipS but does not function as an antitoxin on its own. Free HipT phosphorylates and inhibits tryptophan tRNA synthetase (TrpS) and thereby halts translation in a similar fashion as HipA. (C) yjjJ is a single cistron operon that encodes a HipA-homologous kinase YjjJ (green) that, when overproduced, inhibits cell growth (60). YjjJ, that we coin HipH, has an HTH-domain in its N terminus that may function to bind DNA.