FIG 2.
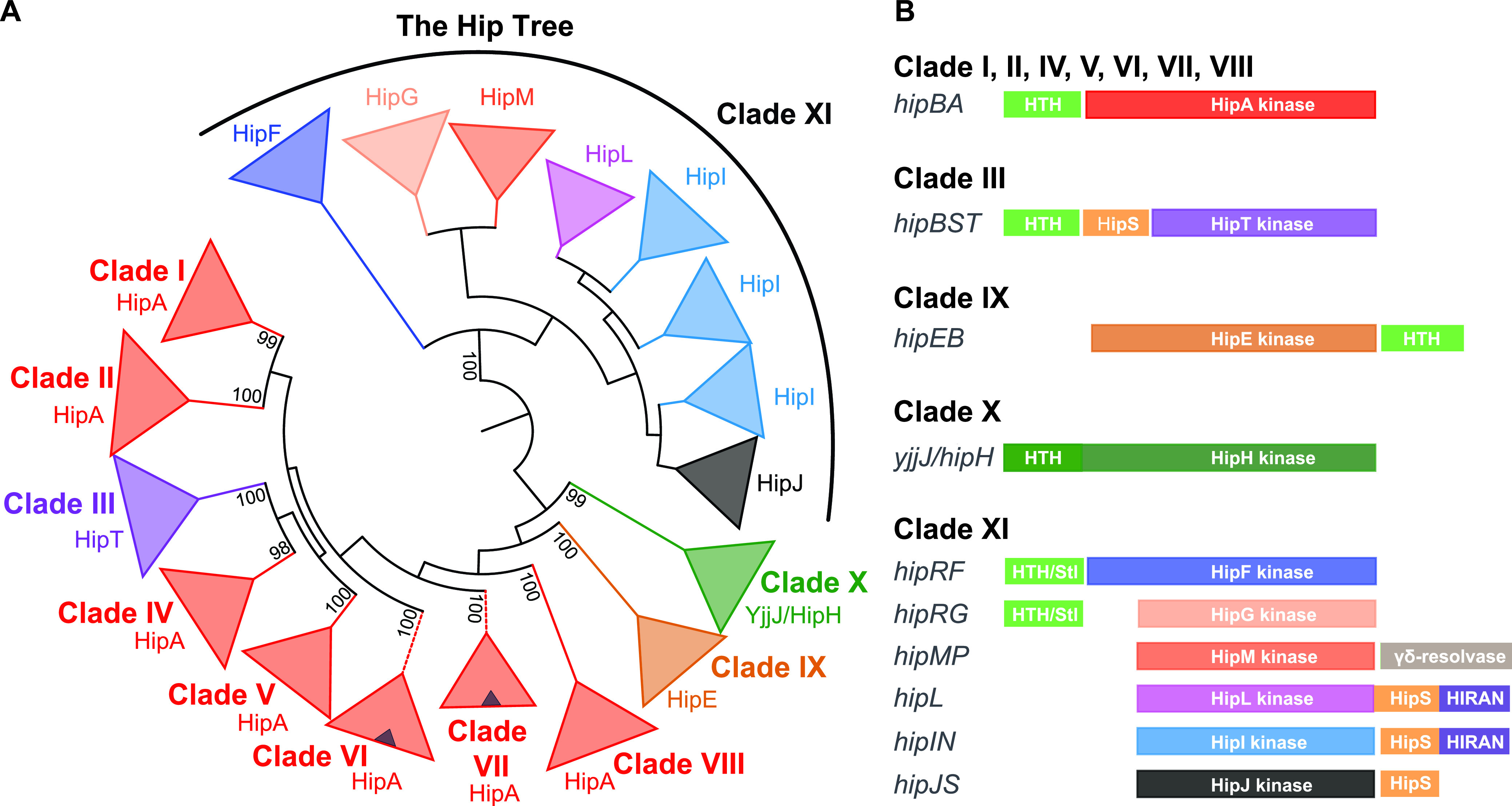
Phylogeny and genetic contexts of HipA-homologous kinases. (A) Simplified phylogenetic tree covering 1,239 HipA-homologous kinases (the “Hip Tree”) (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material for details). The Hip Tree was divided into 11 main clades I to XI. The coloring of the Hip Tree reflects the genetic contexts that encode the kinases such that each color corresponds to a distinct kinase family encoded by a distinct type of TA module. All main clades are monophyletic except clade XI that consists of six different kinase families. Small blue triangles within the red triangles of main clades VI and VII symbolize subclades of kinases encoded by TA modules with a reversed gene order relative to hipBA—that is—with the gene order hipAB. The Hip Tree was visualized by iTOL (82). (B) Genetic organizations of the TA modules encoding the 1,239 HipA-homologous kinases. The various types of genetic organization were obtained by manual inspection of the genes upstream and downstream of the kinase genes listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material. The coloring of the Hip kinases in panel B follows the coloring of the clades in panel A. Putative antitoxins with helix-turn-helix (HTH) domains are colored light green. Stl/HTH, putative antitoxins containing HTH domain and a domain with structural similarity to the “polyamorous” repressor Stl encoded by Staphylococcus aureus; HipS, HipS-like; HIRAN, HIP116 Rad5p N-terminal domain.
