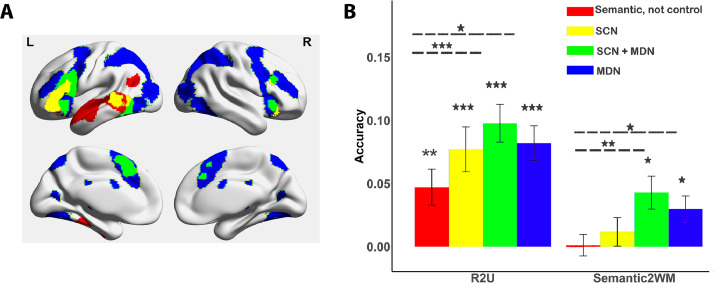
Fig. 4.
Decoding cognitive demand in large-scale brain networks; bars reflect average accuracy which is different from the conventional SVM classification and instead measures correlation (Fisher's z-transformed) between actual task demand (difficulty) and predicted task demand. A. Brain regions for each network. B. R2U: Cross-condition classification between semantic related and unrelated trials. Semantic2WM: Cross-task classification between semantic difficulty and WM load. Cross-task decoding was not significantly greater than chance level (0) in the ‘semantic, not control’ and SCN networks, and significantly higher than chance level in MDN+SCN regions and MDN (p = 0.012 and p = 0.018, respectively, with Bonferroni correction applied). All other decoding accuracy results are significantly higher than chance level in all networks (P < 0.001). Bonferroni correction was applied for each condition, separately; ***p < 0.001/4. **p < 0.01/4. *p < 0.05/4.