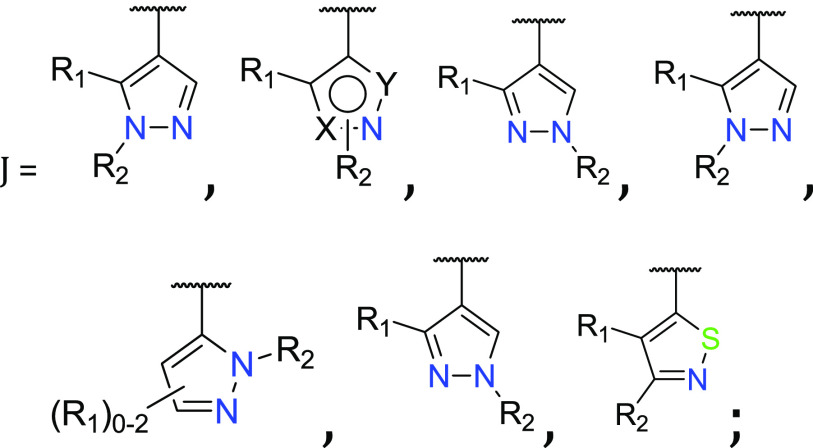
Important Compound Classes
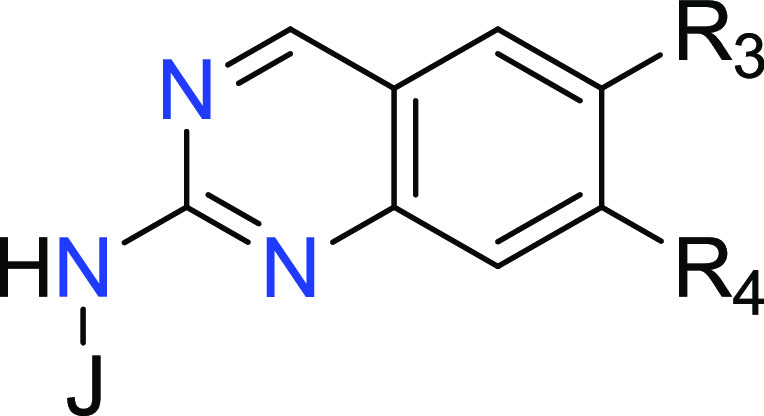
Title
N-Heteroaryl Quinazoline-2-amine Derivatives as LRRK2 Inhibitors, Pharmaceutical Compositions and Uses Thereof
Patent Publication Number
WO 2021/080929 A1
Publication Date
April 29, 2021
Priority Application
US 62/926,033
Priority Date
October 25, 2019
Inventors
Keylor, M. H.; Ardolino, M. J.; Chau, R. W.; Fuller, P. H.; Gulati, A.; Johnson, R. E.; Kattar, S. D.; Margrey, K. A.; Morriello, G. J.; Neelamkavil, S. F.; Yan, X.; Yu, E. C.; Zarate Saef, C. C.
Assignee Company
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., USA
Disease Area
Parkinson’s disease
Biological Target
Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2)
Summary
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease caused by progressive loss of midbrain dopaminergic neurons leading to abnormal motor symptoms such as bradykinesia, rigidity, and resting tremor. Many PD patents show a variety of nonmotor symptoms including cognitive dysfunction, emotional changes and sleep disruption. The combined motor and nonmotor symptoms of PD severely impact patient quality of life.
While most PD cases are idiopathic, there are several genetic determinants such as mutations in SNCA, Parkin, PINK1, DJ-1, and LRRK2. Linkage analysis studies have demonstrated that multiple missense mutations in the Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene lead to an autosomal late onset form of PD. LRRK2 is a 286 kDa cytoplasmic protein containing kinase and GTPase domains as well as multiple protein–protein interaction domains.
In vitro biochemical studies have demonstrated that LRRK2 proteins harboring the PD associated proteins generally confer increased kinase activity and decreased GTP hydrolysis compared to the wild type protein, thereby suggesting that small molecule LRRK2 kinase inhibitors may be able to block aberrant LRRK2-depedent signaling in PD. LRRK2 expression is highest in the same brain regions that are affected by PD. LRRK2 is found in Lewy bodies, a pathological hallmark of PD as well as other neurodegenerative diseases such as Lewy body dementia.
The present application describes a series of novel N-heteroaryl quinazolin-2-amine derivatives as LRRK2 inhibitors for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Further, the application discloses compounds and their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
R3 = CH3, CF3, OCH3, Cl, CN, and cyclopropyl; and
R4 = (C3-C6)cycloalkyl, piperidinyl, pyrrolidinyl, spiropentanyl, spirohexanyl, azaspiroheptanyl, azabicycloheptanyl, azabicyclooctanyl, and azabicyclononanyl, said cycloalkyl, piperidinyl, pyrrolidinyl, spiropentanyl, spirohexanyl, azaspiroheptanyl, azabicycloheptanyl, azabicyclooctanyl, and azabicyclononanyl optionally substituted with 1–3 groups of Rb.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The LRRK2 Km ATP LanthaScreen assay was performed using a GST20 tagged truncated human mutant G2019S LRRK2 in the presence of the fluorescein-labeled peptide substrate LRRKtide. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit LRRK2. The LRRK2 pIC50 are shown in the following Table.
Biological Data
The Table below
shows representative
compounds were tested for LRRK2 inhibition. The biological data obtained
from testing representative examples are listed in the following Table.
Claims
Total claims: 19
Compound claims: 15
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 2
Use of compound claims: 1
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Pischedda F.; Piccoli G.. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 297.
-
2.
Usmani A.; Shavarebi F.; Hiniker A.. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 41, e00660.
-
3.
Trinh D.; Israwi A. R.; Arathoon L. R.; Gleave J. A.; Nash J. E.. J. Neurochem. 2021, 156, 715.
-
4.
Schneider S. A.; Hizli B.; Alcalay R. N.. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1378.
-
5.
Taylor M.; Alessi D. R.. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 63, 102.
-
6.
Poewe W.; Seppi K.; Marini K.; Mahlknecht P.. Neuropharmacology 2020, 171, 108085.
The author declares no competing financial interest.