We read with interest the response by Lee et al.1 to our previous letter2 on the effectiveness of the varicella vaccine in Korea. However, we have found that Lee et al.1 misrepresented our simulation analysis and its results presented in our previous letter.2 In addition, we have found that in their response, the authors were misleading to suggest that an age-shift phenomenon among varicella cases in Korea has occurred with an increasing annual incident rate of varicella after the introduction of the one-dose varicella national immunization program (NIP) in 2005. In this letter, we explicate and defend our simulation analysis that was a key basis for our position that the effectiveness of varicella vaccines in the authors' previous case-control study3 may have been considerably underestimated. Also, we contend that an age-shift phenomenon among varicella cases has occurred with a decreasing annual incidence rate of varicella in Korea, as consistent with the cases in the United States,4 and the one-dose varicella NIP program has been effective in containing varicella in Korea.
In our previous letter, we pointed out a possible bias in selecting the control group for the authors' case-control study,3 which likely resulted in a significant underestimation of the effectiveness of varicella vaccines (e.g., 12% vs. 65-90%). Our simulation in our previous letter was intended to examine how the crude effectiveness of varicella vaccines in the authors' case-control study would have changed if an alternative population-based control group with three different vaccination rates (90-97% vs. 78%) had been used as the control group in the authors' case-control study. It was not intended to ignore the nature of age-matching in the case-control study, although there was little difference in the crude and age-adjusted odds ratios.
Lee et al.1 argued that we misunderstood the age distribution of their study subjects, “heavily concentrated near an average of 5.7 years old”1 at the time of their study in 2013. With respect, we cannot agree with the authors. We fully understood the age distribution of their study subjects and considered that in our simulation analysis. That's why in our simulation analysis, we tested not only 95% and 97%, but also 90% as the most conservative estimate of the national varicella vaccination rate around the authors' case-control study period. We deemed that the national varicella vaccination rate in Korea would be at least 90% in 2007 when most subjects of the authors' study in 2013 were not born or yet eligible for varicella vaccination (12–15 months old). It was based on the result in one nationwide case-control study5 that had been conducted during 2007–2008 in 212 children (mean age: 5.2 years old; range from 1 year to 14 years). The vaccination rate for varicella vaccines in the case-control study during 2006–2007 was already above 90% (94% in the case group and 97% in the control group), which was considerably greater than 78% reported in the authors' case-control study in 2013.3 In terms of the age distribution of study subjects, the case-control study5 and the authors' case-control study were similar to each other. Thus, we stand by the results of our simulation analysis in our previous letter, supporting the possibility of a significant underestimation of the effectiveness of varicella vaccines in the authors' case-control study.
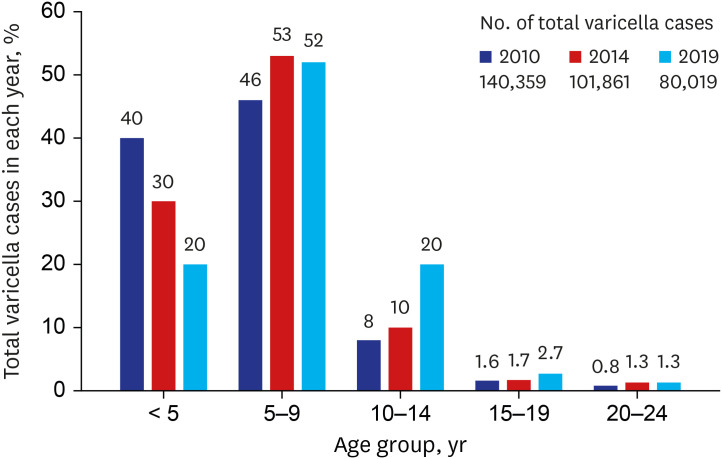
On the other hand, the authors1 said in their response that “…it is identified in common for both data that the age peak in the incidence rate has shifted from 4 or 5 to 6 years old, although the incidence rate of varicella with the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) data decreased contrary to an increasing trend with the National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System (NNDSS) data. The lack of age-shifting phenomenon strongly suggests that the varicella vaccination program has not been effective in preventing varicella in Korea.” Although the authors' statements about age-shift phenomenon looks contradictory to each other (“shifted…lack of age-shifting”), it seems like the authors argued for an age-shift phenomenon with an increasing incidence rate of varicella in Korea after the varicella NIP program. We disagree with the authors on this issue due to the following reasons. The authors' position is largely based on the NNDSS data; however, the data include several critical weaknesses (e.g., a substantial underreporting of incident varicella until recent years) to be used for monitoring the trend in the incidence rate of varicella in Korea as we mentioned in our previous letter and the authors partially acknowledged in their response. In addition, Choi et al.6 has reported an age-shift phenomenon with a decreasing age-standardized incidence rate of varicella in Korea during 2003–2015, using the NHIS data. Our analysis using the more recent NHIS data during 2010-2019 (Fig. 1) also shows an age-shift phenomenon with a decreasing trend in the annual total number of varicella cases in Korea. The age-group composition of varicella cases has continued to change during 2010–2019: for example, the proportion of varicella cases aged < 5 years has decreased twofold, while the proportion of varicella cases aged 10–14 years has increased more than twofold. More importantly, this change has occurred with a consistent and significant reduction (43%) in the total number of varicella cases over the years. In their response, the authors stated a possibility of over-reported varicella cases in the NHIS data. However, in our view, it cannot explain a significant decrease trend in the incidence rate of varicella over time in the NHIS data unless the possibility of over-reported varicella cases in the NHIS data, if any, has increased over time as well. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no evidence for supporting the possibility in the literature. In the United States, the median age of varicella cases among vaccinated children increased by three years during 1995–2005 after their national one-dose varicella NIP program and during the period, varicella cases have consistently and significantly decreased.4 Thus, we think that a similar pattern of age shift phenomenon has been indeed observed in Korea after the varicella NIP as in the United States.
Fig. 1. Change in age-group composition of varicella cases in Korea during 2010-2019 with a significant reduction in the annual total number of varicella cases. Three-year (2010, 2014, and 2019) data from the Korea National Health Insurance Service were used. The proportion of the 25+ years old group in each year was very small (≤ 0.5%) and not presented here for simplicity.
We agree with the authors that most of varicella incident cases during recent years in Korea are breakthrough cases given the high coverage of varicella vaccination after the one-dose NIP program. In a recent longitudinal study with the 2011 birth cohort in Korea,7 the incident rate of breakthrough varicella was estimated to be 23.6 per 1,000 person-years. It is generally comparable to those (21.7–28.3 per 1,000 person-years) reported in other studies8,9 from the United States in which one-dose Oka-strain vaccines were administered. More studies with recent birth cohorts in Korea are warranted to examine whether the incident rate of breakthrough varicella has further decreased during recent years. And future epidemiological and cost-effectiveness studies are urgently needed to discuss and determine a two-dose varicella NIP program in Korea.10
Footnotes
Disclosure: Shin JH, Lee JE and Ko SB have no potential conflicts of interest. Choi B is an employee of GC Pharma, a pharmaceutical company in South Korea. However, the aim of the submitted manuscript as a correspondence is to discuss methodological issues in epidemiological research on the effectiveness of the varicella vaccine in Korea. The submitted manuscript does not discuss any specific product of GC Pharma.
- Conceptualization: Choi B.
- Data curation: Choi B.
- Formal analysis: Choi B.
- Investigation: Choi B, Shi JH, Lee JE, Koh SB.
- Writing - original draft: Choi B.
- Writing - review & editing: Lee JE, Koh SB, Shin JH.
References
- 1.Lee YH, Choe YJ, Cho SI, Park HK, Bang JH, Lee JK. The author's response: effects of one-dose varicella vaccination on disease severity in children during outbreaks in Seoul, Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(28):e266. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Choi B, Shin JH, Lee JE, Koh S. Letter to the editor: epidemiological comments on the effectiveness of the varicella vaccine in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(28):e265. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee YH, Choe YJ, Cho SI, Kang CR, Bang JH, Oh MD, et al. Effectiveness of varicella vaccination program in preventing laboratory-confirmed cases in children in Seoul, Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016;31(12):1897–1901. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.12.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Guris D, Jumaan AO, Mascola L, Watson BM, Zhang JX, Chaves SS, et al. Changing varicella epidemiology in active surveillance sites--United States, 1995-2005. J Infect Dis. 2008;197(Suppl 2):S71–S75. doi: 10.1086/522156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee YH, Choe YJ, Cho SI, Bang JH, Oh MD, Lee JK. Increasing varicella incidence rates among children in the Republic of Korea: an age-period-cohort analysis. Epidemiol Infect. 2019;147:e245. doi: 10.1017/S0950268819001389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Choi JK, Park SH, Park S, Choi SM, Kim SH, Lee DG, et al. Trends in varicella and herpes zoster epidemiology before and after the implementation of universal one-dose varicella vaccination over one decade in South Korea, 2003-2015. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(11):2554–2560. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1603985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Choi EH. Effectiveness of Varicella Immunization in Korea. Cheongju, Korea: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Black S, Ray P, Shinefield H, Saddier P, Nikas A. Lack of association between age at varicella vaccination and risk of breakthrough varicella, within the Northern California Kaiser Permanente Medical Care Program. J Infect Dis. 2008;197(Suppl 2):S139–S142. doi: 10.1086/522124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Clements DA, Moreira SP, Coplan PM, Bland CL, Walter EB. Postlicensure study of varicella vaccine effectiveness in a day-care setting. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999;18(12):1047–1050. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199912000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Suh J, Lee T, Choi JK, Lee J, Park SH. The impact of two-dose varicella vaccination on varicella and herpes zoster incidence in South Korea using a mathematical model with changing population demographics. Vaccine. 2021;39(18):2575–2583. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]