Abstract
In a large regional observational cohort study of adult (≥ 18 years), outpatients with COVID-19, prevalence, characteristics, and outcome of patients with rash and/or chilblain-like lesions (CLL), compared with population without cutaneous features, were studied. In total, 28,957 outpatients were included; the prevalence of rash and CCL were 9.5% and 3.7%, respectively. Presence of rash was significantly associated with presence of asthenia, shivers or myalgia, respiratory and gastro-intestinal symptoms, and anosmia/ageusia. The presence of CCL was associated with chest pain, chest oppression, nausea/vomiting, and anosmia/ageusia. Patients with CCL were significantly less prone to an unfavourable outcome (hospitalization or death).
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10096-021-04305-3.
Keywords: Rash, Chilblain-like lesion, COVID19, Risk factors, Hospitalization
Introduction
The most described clinical manifestation during the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is respiratory tract infection, but SARS-CoV-2 could reach nearly every organ. Some reports and small clinical cohort series described a wide spectrum of mucocutaneous manifestations [1–3]. However, most cutaneous descriptions are from hospitalized patients, despite more than 80% of patients not requiring hospitalization and being managed as outpatients [4]. Chilblain-like lesions (CLL) and rashes are the most frequently reported cutaneous manifestations [2, 3, 5].
CLL are similar in morphology to chilblains, located mostly on the feet, with acrocyanosis and erythematous–oedematous lesions, or in some cases, bullous and necrotic lesions [6].
In most patients, a coppery red background, haemorrhagic dots, and non-blanching vessels could indicate the presence of inflammatory cells and hemosiderin in the dermis and vascular damage [7–9].
The aim of our study was to describe the prevalence of rash and/or CLL among a large population of COVID-19 outpatients, the characteristics of patients presenting these symptoms, and to evaluate whether they were associated with unfavourable outcome.
Method
This study is part of a large cohort study, including all adult (≥ 18 years) patients that were managed from 9th of March until 20th of August 2020 initially as outpatients in Covidom, a telesurveillance solution for home-monitoring of patients with COVID-19 in greater Paris area [4], who answered a standardized medical questionnaire.
We identified all patients reporting rash and/or CLL and compared them to patients without these cutaneous signs.
The study and data collection were approved by the Scientific and ethical committee of APHP (IRB00011591). All patients accepted the use of their anonymized data for research purpose.
Several data were collected, such as age, gender, date of first symptoms and of inclusion in Covidom; weight, height, comorbidities, symptoms, and diagnosis confirmation by a molecular test (RT-PCR), from 3 self-reported medical questionnaires (at day of registration, day 14 of symptoms, and day 30 of symptoms). Outcome was collected through 3 means to be exhaustive: from patients’ questionnaire, data reported by the regional control centre, and the hospital regional database.
Unfavourable outcome was defined as hospitalization or death within 1 month after symptom onset.
Characteristics of patients were described with frequencies and percentages for qualitative variables and means and standard deviation as appropriate for quantitative variables.
To evaluate epidemiological and clinical characteristics associated with cutaneous features, uni- and multivariate logistic regression models were performed.
Then, we evaluated whether rash and CLL were independently associated with unfavourable outcome using multivariate logistic regression models adjusted on all available potential confounding factors (sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and absence of PCR testing). To avoid collinearity, we considered together two sets of highly correlated symptoms (anosmia/ageusia, and general symptoms).
Alpha risk was set at 5% for all analyses.
Results
During this period, 45,870 outpatients were followed by the Covidom solution (Fig. 1), and 28,957 were included in our study, among which the rate of negative PCR was 18.0% (n = 5205). Indeed, patients with negative PCR but high clinical suspicion of COVID-19 could be included in Covidom and in our study.
Fig. 1.
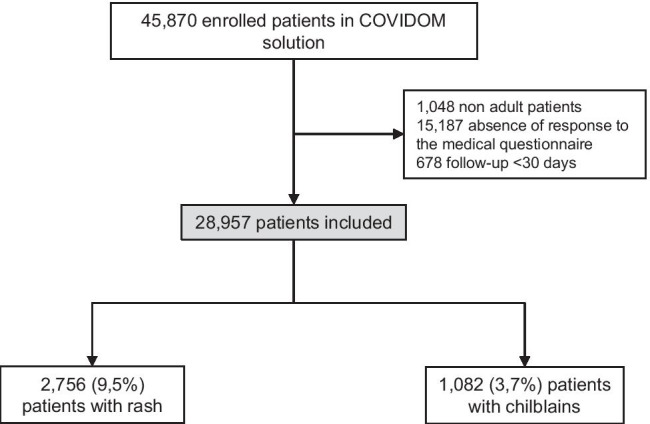
Flow chart
Mean age was 43.1 ± 14.0 years, and sex ratio (M/F) was 0.58 (Supplementary Table 1).
Main comorbidities, general symptoms, and specific COVID-19 symptoms are also presented in Supplementary Table 1.
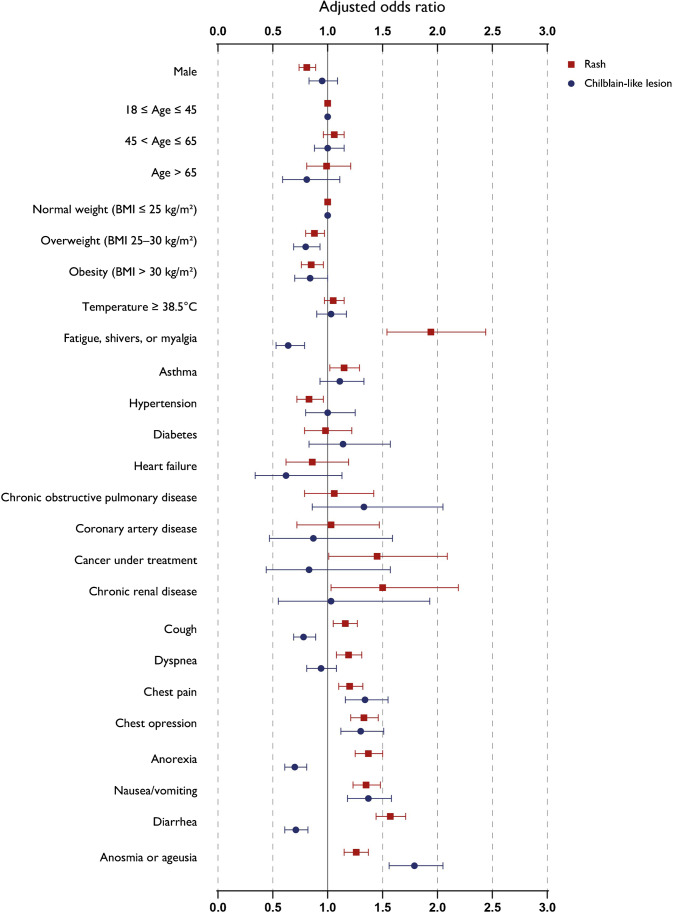
The prevalence of rash was 9.5% (2756/28957). In multivariate analysis (Fig. 2), factors associated with the presence of rash included asthma (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.15; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.02–1.29). Presence of rash was significantly associated positively with the following: general symptoms (asthenia, shivers, or myalgia) (aOR = 1.94; 95%CI 1.54–2.44), respiratory symptoms (dyspnea [aOR = 1.19; 95%CI 1.08–1.31], cough [aOR = 1.16; 95%CI 1.05–1.27], chest pain [aOR = 1.20; 95%CI 1.10–1.32], and chest oppression [aOR = 1.33; 95%CI 1.21–1.46]), and gastro-intestinal symptoms (anorexia [aOR = 1.37; 95%CI 1.25–1.50], nausea/vomiting [aOR = 1.35; 95%CI 1.23–1.48], diarrhoea [aOR = 1.57; 95%CI 1.44–1.71), and anosmia or ageusia [aOR = 1.26; 95%CI 1.15–1.37]). It was negatively associated with male gender (aOR = 0.80; 95%CI 0.73–0.88), overweight (BMI 25–30 kg/m2) (aOR = 0.88; 95%CI 0.80–097), and high-blood pressure (aOR = 0.83; 95%CI 0.72–0.96).
Fig. 2.
Selected adjusted odd ratios and confidence intervals from multivariate analysis of characteristics associated with rash or chilblain-like lesions among outpatients with COVID19
The prevalence of CLL was 3.7% (1082/28957). In multivariate analysis (Fig. 2), factors associated with the presence of CLL were chest pain (aOR = 1.34; 95%CI 1.16–1.55), chest oppression (aOR = 1.30; 95%CI 1.12–1.51), nausea/vomiting (aOR = 1.37; 95%CI 1.18–1.58), and anosmia/ageusia (aOR = 1.79; 95%CI 1.56–2.05). It was negatively associated with asthenia, shivers, or myalgia (aOR = 0.64; 95%CI 0.53–0.79); cough (aOR = 0.78; 95%CI 0.69–0.89); anorexia (aOR = 0.70; 95%CI 0.61–0.81); and diarrhoea (aOR = 0.71; 95%CI 0.61–0.82).
Finally, only 239 (0.8%) patients presented both rash and CLL.
Overall, 1119 (3.9%) patients experienced an unfavourable outcome with 1112 hospitalizations and 7 deaths. In the multivariate analysis, rash was not significantly associated with unfavourable outcome (aOR = 0.97; 95%CI 0.78–1.20; p = 0.758). On the opposite, patients with CLL were significantly less prone to an unfavourable outcome (aOR = 0.64; 95%CI 0.43–0.97; p = 0.0366).
Discussion
Skin manifestations are part of the clinical features of COVID-19. These lesions may be under-estimated because of the lack of systematic dermatologic expertise during the pandemic. Consequently, prevalence of cutaneous manifestation during COVID-19 remains unknown, with wide variations ranging from 0.2 to 68% when systematically checked [2, 5, 10–13]. Some authors suggested to classify cutaneous manifestations in COVID‐19 into two major forms according to their pathomechanisms: viral exanthems (e.g. rash) and vasculopathy‐related skin lesions, such as CLL [14]. Our cohort is the largest of outpatients with COVID-19, and the prevalence of rash and CLL were about 10% and 4% in this population, respectively.
In a recent review of cutaneous manifestations in SARS-CoV-2 infection, rashes were the most frequent manifestations [2]. However, rashes included several clinical presentations, as macular and maculopapular exanthemas, urticarial rashes, vesicular eruption, or purpuric lesions. In our study, we were unable to distinguish the types of rashes as this information was patient-reported and not based on a thorough physical examination.
Among hospitalized patients, rashes could not always be discriminated from drug-induced reactions [15]. Nevertheless, in our outpatient cohort, this hypothesis seems less likely because most patients did not receive any specific treatments.
CLL are pink-to-violaceous purpuric lesions [16], which may not be immediately related to COVID-19 [1]. Several studies reported association between CLL and negative PCR results [14, 16, 17]. Their pathogenesis in COVID-19 remains poorly understood, but could be due to a viral-induced type I interferonopathy [14, 16].
Yet, CLL could be a potential marker of the recovery phase and/or the reflect of the immune system response [18]. The majority of COVID-19 patients presenting with CCL concerned mild forms of the disease [19] and were generally young and without comorbidity [14].
Finally, CLL occurring during COVID-19 should be differentiated from vaccine-induced CLL [20].
Thus, the association between dermatological manifestations in COVID-19 and the prognosis of the disease remains unknown. Despite rashes and CLL being both cutaneous manifestations linked with COVID-19, they are two different clinical entities with different physiopathology. Indeed, rashes are probably the result of an aberrant immune response and consequently could predispose to systemic manifestation, while CLL are probably mostly local manifestations [3]. Furthermore, patients with both signs were rare in our cohort.
Moreover, in literature, they seem to be associated with opposite prognoses. In a study, severity defined as hospital admission, pneumonia, transfer to Intensive care unit, or death was found in more than half of hospitalized patients with rashes and only 5% of patients with CLL [2]. In our study, the presence of CLL was associated with less hospitalization, though presence of rashes was not significantly associated with unfavourable outcome.
Despite the fact that the Covidom cohort is the largest cohort of patients with COVID-19 in community setting, some limits are raised by the self-reporting method which could lead to some inclusion or declarative bias (i.e. the responders could be more at risk to have a rash or CLL than non-responders), the absence of systematic molecular diagnosis, and the absence of temporality which prevents any analyses on the delay of apparition and possible unfavourable outcome. At last, as several symptoms were frequently present to be included in COVIDOM in case of negative PCR results, anosmia/agueusia could have been overrepresented in the included population.
This is the largest cohort of community setting outpatients with cutaneous signs during COVID-19 infection. Rash and CCL were infrequent and occurred especially among young female patients without comorbidities. CLL were associated with a decreased risk of hospitalization.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients for granting permission to publish this information. We thank Alexandre Falzon, Guillaume Fayolle, Fanny Laporte, Amélie Tortel, and all the Nouveal-e-Santé team for their help in the web application and regional centre surveillance interface development. We also thank Laurent De bastard, Alexandre Grenier, Julien Hody, Thomas Penn, and the Paris region URPS (Union régionale des professionnels de santé) for their help in the development and spreading of the Covidom solution. We thank Clara DURAN for her help in writing the manuscript. None of the contributors were compensated for this work.
AP-HP / Universities / Inserm COVID-19 research collaboration members
Writing committee: Hélène Mascitti1, Luc Jaulmes2, Alexandre Bleibtreu3, Agnès Dechartres4, Xavier Lescure5, Youri Yordanov6, Patrick Jourdain7, and Aurélien Dinh1.
1Infectious Disease Department, University Hospital R. Poincaré, APHP, Paris Saclay University, Garches, France.
2Centre de Pharmaco-épidémiologie (Cephepi), Pitié Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, France.
3Infectious Disease Department, University Hospital Pitié Salpétrière, APHP, Paris University, Paris, France.
4Clinical Research Department, University Hospital Pitié Salpétrière, APHP, Paris University, Paris, France.
5Infectious Disease Department, University Hospital Bichat, APHP, Paris University, Paris, France.
6Emergency Department, University Hospital Saint Antoine, APHP, Paris University, Paris, France.
7Cardiology Department, University Hospital Kremlin Bicêtre, APHP, Paris Saclay University, Garches, France.
Data-sciences committee: Apra Caroline (AC), Jaulmes Luc (JL), Mensch Arthur (MA).
AC is affiliated with the Sorbonne Université, AP-HP, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Service de Neurochirurgie, Paris, France.
JL is affiliated with Centre de Pharmaco-épidémiologie (Cephepi), Pitié Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, France.
MA is affiliated with Ecole Normale Supérieure, PSL University, CNRS, Départment de Mathématiques et Applications, 75,005 Paris, France.
Scientific committee: Aime-Eusebi Amélie, Apra Caroline, Bleibtreu Alexandre, Debuc Erwan, Dechartres Agnes, Deconinck Laurène, Dinh Aurélien, Jourdain Patrick, Katlama Christine, Lebel Josselin, Lescure François-Xavier, Yordanov Youri.
Covidom regional center steering committee: Artigou Yves, Banzet Amélie, Boucheron Elodie, Boudier Christiane, Buzenac Edouard, Chapron Marie-Claire, Chekaoui Dalhia, De Bastard Laurent, Debuc Erwan, Dinh Aurélien, Grenier Alexandre, Haas Pierre-Etienne, Hody Julien, Jarraya Michèle, Jourdain Patrick, Lacaille Louis, Le Guern Aurélie, Leclert Jeremy, Male Fanny, Marchand-Arvier Jerôme, Martin-Blondet Emmanuel, Nassour Apolinne, Ourahou Oussama, Penn Thomas, Ribardiere Ambre, Robin Nicolas, Rouge Camille, Schmidt Nicolas, Villie Pascaline.
Author contribution
HM, LJ, ADe, YY, and ADi conceptualized the study. HM, LJ, ADe, YY, and ADi collected analysed and interpreted the data. LH conducted the statistical analysis. HM, LJ, and Adi wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript and approved the final version. ADi had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Funding
This study received a funding by the Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique 2020 of the French Ministry of Health, by a research fund by APHP-Fondation de France. The Covidom platform received a funding from EIT Health specific COVID-19 fund.
Availability of data and material
The datasets analysed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study and data collection were approved by the Scientific and ethical committee of APHP (IRB00011591).
Consent to participate
All patients accepted the use of their anonymized data for research purpose.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Aurélien Dinh, Email: aurelien.dinh@aphp.fr.
on behalf of the AP-HP/Universities/INSERM COVID-19 research collaboration:
Caroline Apra, Arthur Mensch, Amélie Aime-Eusebi, Erwan Debuc, Agnes Dechartres, Laurène Deconinck, Christine Katlama, Josselin Lebel, François-Xavier Lescure, Yves Artigou, Amélie Banzet, Elodie Boucheron, Christiane Boudier, Edouard Buzenac, Marie-Claire Chapron, Dalhia Chekaoui, Laurent De Bastard, Alexandre Grenier, Pierre-Etienne Haas, Julien Hody, Michèle Jarraya, Louis Lacaille, Aurélie Le Guern, Jeremy Leclert, Fanny Male, Jerôme Marchand-Arvier, Emmanuel Martin-Blondet, Apolinne Nassour, Oussama Ourahou, Thomas Penn, Ambre Ribardiere, Nicolas Robin, Camille Rouge, Nicolas Schmidt, and Pascaline Villie
References
- 1.Herman A, Peeters C, Verroken A, Tromme I, Tennstedt D, Marot L et al (2020) Evaluation of chilblains as a manifestation of the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Dermatol 1(156):998. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/2767774 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.Matar S, Oulès B, Sohier P, Chosidow O, Beylot‐Barry M, Dupin N et al (2020) Cutaneous manifestations in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection (COVID‐19): a French experience and a systematic review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 20. 10.1111/jdv.16775. Ahead of print. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jdv.16775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.Mascitti H, Bonsang B, Dinh A, Assan F, Perronne V, Leblanc T et al (2020) Clinical cutaneous features of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 hospitalized for pneumonia: a cross-sectional study. Open Forum Infect Dis 7. 10.1093/ofid/ofaa394. https://academic.oup.com/ofid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofaa394/5929650 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Yordanov Y, Dechartres A, Lescure X, Apra C, Villie P, Marchand-Arvier J et al (2020) Covidom, a telesurveillance solution for home monitoring of patients with Covid-19. (Preprint). J Med Internet Res. 10.2196/20748. http://preprints.jmir.org/preprint/20748/accepted [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Tammaro A, Adebanjo GAR, Parisella FR, Pezzuto A, Rello J (2020) Cutaneous manifestations in COVID‐19: the experiences of Barcelona and Rome. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34. 10.1111/jdv.16530https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jdv.16530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Bassi A, Russo T, Argenziano G, Mazzatenta C, Venturini E, Neri I, et al. Chilblain-Like lesions during COVID-19 pandemic: the state of the art. Life. 2021;11:23. doi: 10.3390/life11010023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Piccolo V, Bassi A, Argenziano G, Mazzatenta C, Guglielmo A, Patrizi A, et al. Dermoscopy of chilblain-like lesions during the COVID-19 outbreak: a multicenter study on 10 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Piccolo V, Bassi A. Acral findings during the COVID-19 outbreak: chilblain-like lesions should be preferred to acroischemic lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:e231. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Piccolo V, Bassi A, Russo T, Mazzatenta C, Baraldi M, Argenziano G, et al. Chilblain-like lesions and COVID-19: second wave, second outbreak. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;2(35):e316–8. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mungmunpuntipantip R, Wiwanitkit V (2020) COVID‐19 and cutaneous manifestations. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34. 10.1111/jdv.16483. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jdv.16483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Guarneri C, Venanzi Rullo E, Gallizzi R, Ceccarelli M, Cannavò SP, Nunnari G (2020) Diversity of clinical appearance of cutaneous manifestations in the course of COVID‐19. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34. 10.1111/jdv.16669. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jdv.16669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Duong TA, Velter C, Rybojad M, Comte C, Bagot M, Sulimovic L et al (2020) Did Whatsapp ® reveal a new cutaneous COVID‐19 manifestation? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34. 10.1111/jdv.16534. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jdv.16534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Skayem C, Cassius C, Ben Kahla M, Fiani C, Frumholtz L, Mrad M et al (2020) Teledermatology for COVID‐19 cutaneous lesions: substitute or supplement? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34. 10.1111/jdv.16630. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jdv.16630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Suchonwanit P, Leerunyakul K, Kositkuljorn C. Diagnostic and prognostic values of cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13650. doi: 10.1111/dth.13650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Suchonwanit P, Leerunyakul K, Kositkuljorn C (2020) Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: lessons learned from current evidence. 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.094. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0190962220307106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Hubiche T, Cardot-Leccia N, Le Duff F, Seitz-Polski B, Giordana P, Chiaverini C et al (2020) Clinical, laboratory, and interferon-alpha response characteristics of patients with chilblain-like lesions during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Dermatol. 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.4324. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/2773121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Piccolo V, Neri I, Manunza F, Mazzatenta C, Bassi A. Chilblain-like lesions during the COVID-19 pandemic: should we really worry? Int J Dermatol. 2020 doi: 10.1111/ijd.14993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Piccolo V, Neri I, Filippeschi C, Oranges T, Argenziano G, Battarra VC et al (2020) Chilblain‐like lesions during COVID‐19 epidemic: a preliminary study on 63 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34. 10.1111/jdv.16526. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jdv.16526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Galván Casas C, Català A, Carretero Hernández G, Rodríguez-Jiménez P, Fernández-Nieto D, Rodríguez-Villa Lario A, et al. Classification of the cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: a rapid prospective nationwide consensus study in Spain with 375 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:71–7. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Piccolo V, Bassi A, Argenziano G, Mazzatenta C, Cutrone M, Neri I et al (2021) BNT162b2 mRNA COVID‐19 vaccine‐induced chilblain‐like lesions reinforces the hypothesis of their relationship with SARS‐CoV‐2. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol jdv.17320. 10.1111/jdv.17320. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33914966 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analysed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.