To the Editor: Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) is characterized by thrombosis and thrombocytopenia that occurs 5 to 30 days after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination and is associated with heparin-independent platelet factor 4 (PF4) antibodies.1-3 Mortality from VITT is approximately 30 to 60%.1-3 PF4 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) in the absence of heparin may be diagnostic; however, functional testing (e.g., serotonin release assay with added PF4 [PF4 SRA]) is recommended.1-4 Initial treatment includes nonheparin anticoagulation and high-dose intravenous immune globulin (IVIG). The treatment that should be used for patients with VITT that does not respond to initial treatment remains unclear.
Three patients with VITT who had positive results on PF4 SRA after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination had persistent thrombocytopenia and progressive thrombosis despite initial treatment. At presentation, the d-dimer level in each patient was above the upper limit of quantification of the assay used for measurement. None of the patients had coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19). Details of the treatment and responses are shown in Figure 1, and details of the presentations and apheresis are provided in the Supplementary Appendix, available with the full text of this letter at NEJM.org.
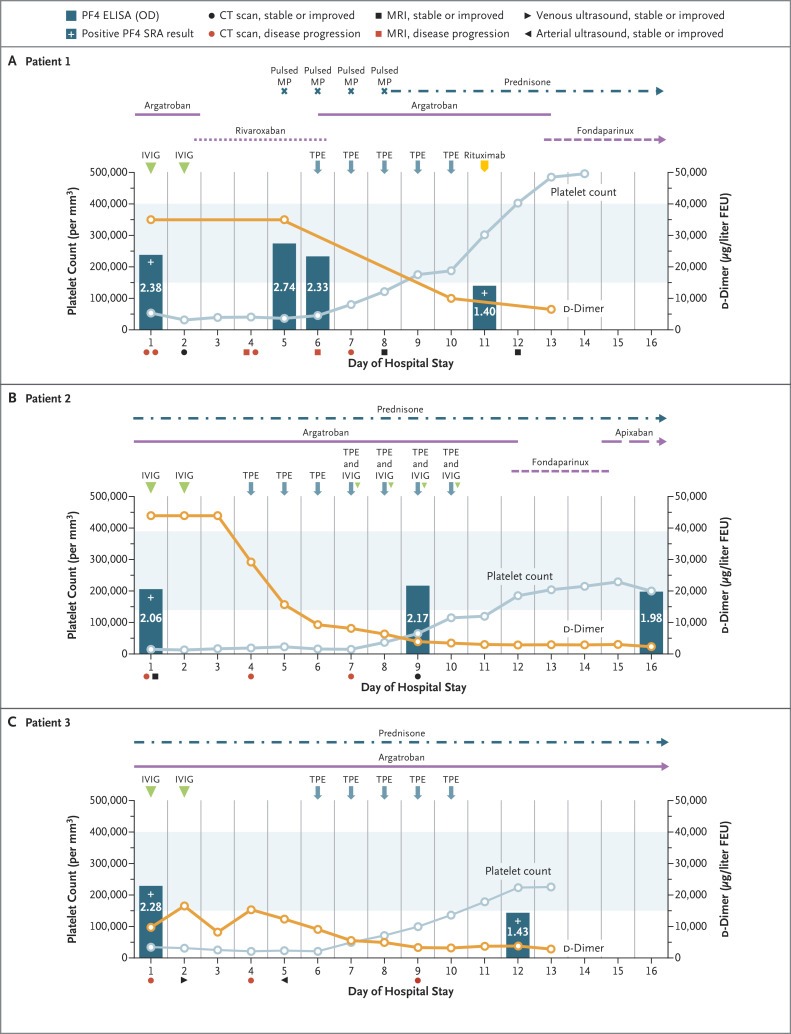
Figure 1. Clinical Course in Patients with Refractory VITT Treated with Therapeutic Plasma Exchange.
For all three patients, day 1 of the hospital stay was also the day on which suspected or confirmed VITT was diagnosed. Standard doses of anticoagulant were given to all three patients. Prednisone was given at a dose of 1 mg per kilogram of body weight. In each patient, the initial d-dimer level was above the upper limit of quantification of the assay used in the hospital to which she had been admitted; on day 2, Patient 3 was transferred to a hospital in which the laboratory used an assay with a higher upper limit of quantification. The d-dimer values have been converted to micrograms per liter fibrinogen equivalent units (FEU) for case comparison. The colors of the symbols below the x axis in each panel (indicating types of medical imaging performed) denote stable disease or improvement (black) or disease progression (red) relative to previous scans. Light blue shading indicates the normal range for platelet count. Details of the serial imaging are provided in the Supplementary Appendix. CT denotes computed tomography, ELISA enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, IVIG intravenous immune globulin, MP methylprednisolone, MRI magnetic resonance imaging, OD optical density, SRA serotonin release assay, and TPE therapeutic plasma exchange.
Patient 1, a previously healthy 45-year-old woman, was admitted 11 days after vaccination with a left renal infarct, bilateral adrenal hemorrhage, subsegmental pulmonary emboli, and right vertebral artery and left internal carotid artery thromboses. The platelet count was 53,000 per cubic millimeter, the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) 40.1 seconds, the international normalized ratio (INR) 1.3, the fibrinogen level 322 mg per deciliter, and the d-dimer level greater than 35,200 μg per liter fibrinogen equivalent units (FEU). The optical density on PF4 ELISA was 2.38.
Patient 2, a previously healthy 46-year-old woman, presented 10 days after vaccination with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis involving the transverse, sigmoid, and superior sagittal sinuses. The platelet count was 16,000 per cubic millimeter, the aPTT 31 seconds, the INR 1.3, the fibrinogen level 120 mg per deciliter, and the d-dimer level greater than 44,000 μg per liter FEU. The optical density on PF4 ELISA was 2.06.
Patient 3, a 48-year-old woman who had had breast cancer several years earlier, presented 16 days after vaccination with thrombosis of the left subclavian artery, thoracic and abdominal aorta, and right internal iliac artery. Arterial thrombi with ischemia and cyanosis was also present in the left leg. One dose of intravenous heparin was given. No recurrence of cancer was found. The platelet count was 37,000 per cubic millimeter, the aPTT 24.5 seconds, the INR 1.2, the fibrinogen level 100 mg per deciliter, and the d-dimer level greater than 9999 μg per liter FEU. The optical density on PF4 ELISA was 2.28.
Therapeutic plasma exchange was initiated (with full plasma for Patients 1 and 3 and half plasma and half albumin for Patient 2). Argatroban treatment was monitored closely before, during, and after the exchanges, and only minimal aPTT variation was found, with no attributable bleeding. Patients 1 and 2 recovered despite their severe presentation. Patient 1 received rituximab after the fifth therapeutic plasma exchange. The platelet count for Patient 2 did not improve until IVIG (0.5 g per kilogram of body weight) was given after therapeutic plasma exchanges 4 through 7. Patient 3 underwent above-knee amputation, but therapeutic plasma exchange most likely prevented more extensive resection. No further thromboses occurred.
VITT that is unresponsive (refractory) to initial treatment requires urgent additional intervention. Because VITT is IgG-mediated, antibody removal or neutralization is plausibly effective, although further study is needed, since therapeutic plasma exchange with the use of plasma as replacement fluid would not elevate IgG to inhibitory levels.4 We suggest consideration of therapeutic plasma exchange for thrombocytopenia and thrombosis that does not begin to abate after 5 days, continuing until platelet normalization. Earlier intervention could be considered.5 The usefulness of additional treatment with IVIG, glucocorticoids, and rituximab requires further study.
The anticoagulation regimen that should be used to treat VITT remains unsettled. Although acute-phase reactants may shorten the aPTT, levels in these three patients were mostly maintained during and after therapeutic plasma exchange without complications. Platelet normalization as a biomarker may not always be reliable2; combining an increase in platelet count with a decrease in d-dimer level may be more predictive of outcomes. The usefulness of serial PF4 ELISA results also requires evaluation.
VITT is a severe complication after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination. Up-front treatment remains anticoagulation and IVIG. Although further validation is required, we suggest that therapeutic plasma exchange may be effective for the treatment of refractory VITT.
Supplementary Appendix
Disclosure Forms
This letter was published on July 7, 2021, at NEJM.org.
Footnotes
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text of this letter at NEJM.org.
References
- 1.Greinacher A, Thiele T, Warkentin TE, Weisser K, Kyrle PA, Eichinger S. Thrombotic thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccination. N Engl J Med 2021;384:2092-2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schultz NH, Sørvoll IH, Michelsen AE, et al. Thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination. N Engl J Med 2021;384:2124-2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Scully M, Singh D, Lown R, et al. Pathologic antibodies to platelet factor 4 after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination. N Engl J Med 2021;384:2202-2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jones CG, Pechauer SM, Curtis BR, Bougie DW, Aster RH, Padmanabhan A. Normal plasma IgG inhibits HIT antibody-mediated platelet activation: implications for therapeutic plasma exchange. Blood 2018;131:703-706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pavord S, Lester W, Makris M, Scully M, Hunt B. Guidance from the Expert Haematology Panel (EHP) on Covid-19 vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (VITT). London: British Society for Haematology, May 28, 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.