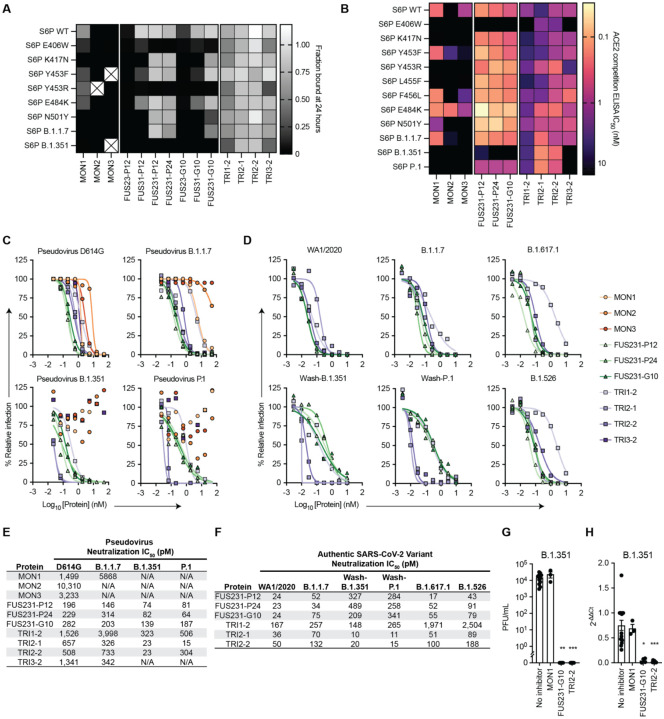
Fig. 4. Multivalency enhances both the breadth and potency of neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 variants by minibinders.
(A) Dissociation of minibinder constructs from S6P variants after 24 hours was measured via competition with untagged TRI2–1 using AlphaLISA (mean, n = 3 replicates from a single experiment). Cells containing an X indicate insufficient signal in the no competitor condition to quantify the fraction of protein bound. (B) Competition of minibinder constructs with ACE2 for S6P measured via ELISA (mean, n = 2). (C) Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus variants by minibinder constructs (mean, n = 2). (D) Neutralization of authentic SARS-CoV-2 by minibinder constructs (mean, n = 2). (E) Table summarizing neutralization potencies of multivalent minibinder constructs against SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus variants. N/A indicates an IC50 value above the tested concentration range and an IC50 greater than 50,000 pM. (F) Table summarizing neutralization potencies of multivalent minibinder constructs against authentic SARS-CoV-2 variants. (G) Neutralization of B.1.351 SARS-CoV-2 variant by minibinder constructs (0.3 μM) in human kidney organoids (n = 3 to 12: Kruskal-Wallis test: ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001). (H) Relative gene expression of SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein (SARS-CoV2-E) in kidney organoids post viral infection with and without multivalent mini binders (0.3 μM) (n = 3 to 15: Kruskal-Wallis test: * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001).