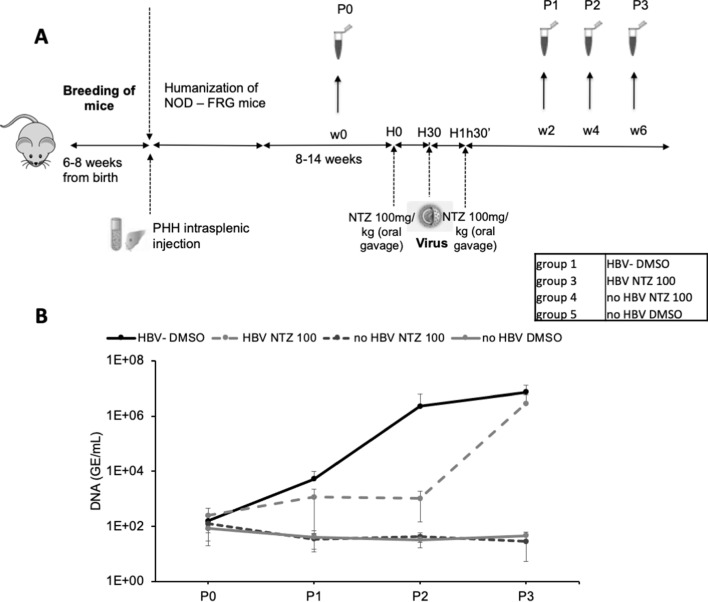
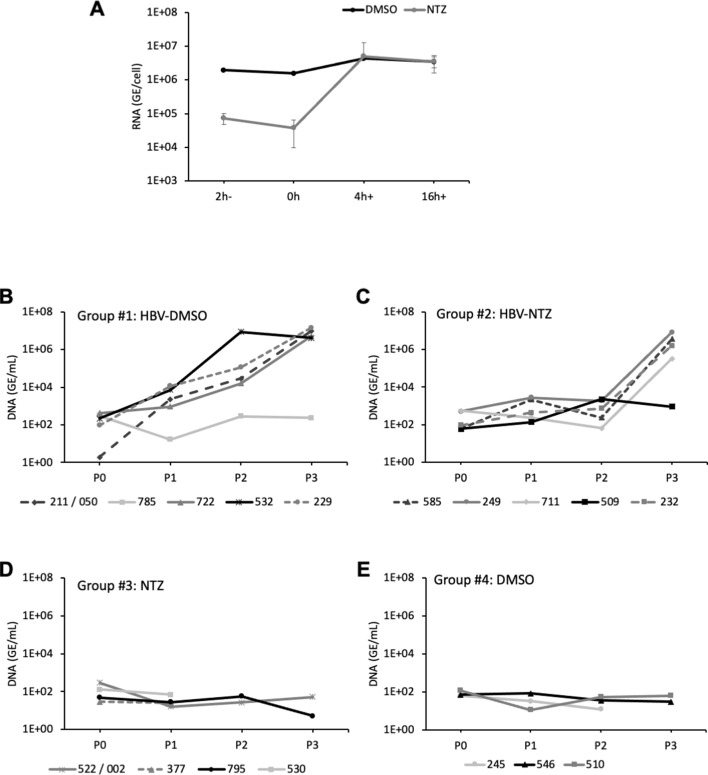
Figure 9. In vivo assessment of ERp57 inhibition.
(A) 4- to 8-week-old NOD-FRG mice were engrafted with primary human hepatocytes (PHH). After approximately 2–3 months, the animals displaying human serum albumin (HSA) levels >15 mg/ml were randomly split into four different groups (N = 3 to N = 5 animals, see Table in the inset) that were infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) (108 genome equivalent (GE)/mouse), using the displayed nitazoxanide (NTZ) treatment schedule. (B) At different time points post-infection, blood samples (50 µl) were collected and the viremia in sera was monitored by quantitative PCR (qPCR) (GE/ml of serum). The graphs show the results of viremia (means ± SD) of HBV. See results of individual mice in Figure 9—figure supplement 1.