Abstract
COVID-19 is a particularly aggressive disease for the elderly as 86% of deaths related to COVID-19 occur in people over 65 years of age. Despite the urgent need for a preventive treatment, there are currently no serious leads, other than the vaccination. The aim of this retrospective case-control study is to find a pharmacological preventive treatment of COVID-19 in elderly patients. One-hundred-seventy-nine patients had been in contact with other COVID-19 patients at home or in hospital, of whom 89 had tested RT-PCR-positive (COVID-pos) for the virus and 90 had tested RT-PCR-negative (COVID-neg). Treatments within 15 days prior to RT-PCR (including antihypertensive drugs, antipsychotics, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), oral antidiabetics (OADs), corticosteroids, immunosuppressants), comorbidities, symptoms, laboratory values, and clinical outcome were all collected. COVID-pos patients more frequently had a history of diabetes (P = .016) and alcoholism (P = .023), a lower leukocyte count (P = .014) and a higher mortality rate — 29.2% versus 14.4% — (P = .014) when compared to COVID-neg patients. Patients on PPIs were 2.3 times less likely (odds ratio [OR] = 0.4381, 95% confidence interval [CI] [0.2331, 0.8175], P = .0053) to develop COVID-19 infection, compared to those not on PPIs. No other treatment decreased or increased this risk. COVID-pos patients on antipsychotics (P = .0013) and OADs (P = .0153), particularly metformin (P = .0237), were less likely to die. Thus, patients on treatment with PPI were less likely to develop COVID-19 infection, and those on antipsychotics or metformin had a lower risk of mortality. However, prospective studies, including clinical trials, are needed to confirm or not these findings.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s11357-021-00397-z.
Keywords: COVID-19, Prevention, Elderly, Geriatrics, Proton pump inhibitors, Antipsychotics, Metformin
Introduction
In November 2019, Wuhan city in China became the centre of an outbreak of pneumonia due to a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). This disease was named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in February 2020 by the World Health Organization (WHO) [36]. COVID-19 is far more dangerous for people aged over 60, with a death rate of 3.6% between 60 and 69 years, 8.0% between 70 and 79 years and 14.8% after 80 years — and, according to Italian statistics, over 20% after 90 years — compared to 2.3% in the general population [11, 29]. According to WHO, in Europe, before the beginning of vaccination, 86% of deaths related to COVID-19 have occurred in people over 65 years of age [33]; the median age of death for 147,623 Europeans was 81 years (range: 0–109) [33]. Furthermore, 96% of deaths occurred in patients with at least one underlying condition: cardiovascular disease (83%), diabetes (61%), renal disease (25%), lung disease (22%) neurological disease including dementia (19%), and obesity (12%) [33]. Chinese data have confirmed that most of the elderly patients who died had multiple comorbidities, and in particular cardiovascular disease (10.5% mortality), diabetes (7.3%), chronic respiratory disease (6.3%) and hypertension (6%) [29]. In the USA, obesity appears to be an additional risk factor to other co-morbidities [26]. COVID-19 is therefore an eminently geriatric disease, i.e., it most strongly affects the elderly with multiple comorbidities [24].
The first articles on a therapeutic vaccine trial have been published, and vaccination has begun at the end of 2020. One of the vaccines developed at Oxford University consists of a replication-deficient chimpanzee adenoviral vector containing the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 [31]. The second one developed by BioNTech is a nucleoside-modified RNA vaccine that encodes a prefusion stabilized spike protein [25], and the third one from Moderna is also an RNA vaccine [2]. Despite the excellent results described in these papers, with an efficacy rate of more than 95% for RNA vaccines, the first failures of RNA vaccination are beginning to be described, notably due to variants of SARS-CoV-2 [13]. Vaccine adaptation to SARS-CoV-2 variants will therefore be necessary.
Treatments commonly used in the elderly may have a protective effect against COVID-19. Thus, angiotensin 2 AT1 receptor antagonist (angiotensin II receptor blockers [ARBs]) could be of interest to treat or prevent COVID-19 [30]. COVID-19 uses ACE2 as a receptor, a modulator of the activity of different angiotensins (I, II and A). The COVID-19–ACE2 interaction increases the activity of angiotensin and thus increases the activity of the AT1 receptor, which results in increased pulmonary vascular permeability and therefore contributes to lung injury. Thus, ARBs could be a protector against lung injury due to SARS-CoV-2, by inhibiting AT1 receptor [12]. Another avenue of potentially preventive or curative drugs is lysosome-targeted drugs, such as antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs), and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) [15, 35]. Coronavirus transduction in the cell requires acidification of the endosome or extracellular medium [27]. PPIs could inhibit the acidic microenvironment around the cell and in the lysosome, and prevent the SARS-CoV-2 from entering the cell.
In order to look for a treatment that could prevent the development of COVID-19 in elderly patients, we studied the treatments that elderly hospitalized patients were taking before they were tested for COVID-19.
Methods
Study design and patients
This was a retrospective case–control study. Elderly patients were considered for the study if they underwent nasopharyngeal swab testing for SARS-CoV-2 between 2 March and 8 April 2020 at Robertsau Geriatric Hospital (University Hospital of Strasbourg [HUS]), Strasbourg, France, including geriatric internal medicine units, follow-up care and rehabilitation units, and long-term care units. Indications for testing were suspicion of COVID-19 because of symptoms consistent with a viral infection including viral pneumonitis, contact with COVID-19-infected persons, or presence of COVID-19 cases in a hospital unit. The demographic, clinical, biological, and imaging data were retrieved from the professional medical software of the HUS: “DX-care”. No patients were excluded as the patient records were all up to date.
We investigated which treatments taken regularly in the 15 days prior to the first swab could have a preventive effect on the disease by analysing the risk associated with each drug. We also looked at the effect of these treatments taken beforehand on survival. If a treatment with an effect on survival was found, we checked whether this treatment was also taken after the first RT-PCR. Patient survival was analysed up to April 17, 2020.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine and University Hospitals of Strasbourg) under number CE-2020–68. Patients were kept informed of our clinical research activity regarding their clinical records via a display in each of the medical units and via an information note given to them upon their arrival.
Data collection
A manual chart review of randomly selected patients was performed by five investigators (CW, BS, CMH, CD, and FB). Basic demographic and clinical data were extracted, including: medical history and comorbidities, treatment within 15 days prior to SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR, viral symptoms (cough, fever, dyspnoea, asthenia, or diarrhoea), geriatric syndromes (pain, falls, confusion), pulmonary auscultation, temperature, pulse, blood pressure, weight, height, oxygen saturation (with or without oxygen therapy), clinical outcome (recovery or death), number of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCRs done for the diagnosis, basic blood results and lung CT scan. Lung CT scan was considered as COVID-19-positive when it demonstrated bilateral or unilateral ground glass opacities or consolidation [3]. Different treatment of elderly people, including ARBs, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, diuretics, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, statins, drugs for Alzheimer’s disease (including rivastigmine, donepezil, galantamine and memantine), drugs for Parkinson’s disease (levodopa and dopaminergic agonists), antidepressants (serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tetracyclic, tricyclic), antipsychotics (risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, clozapine, haloperidol), anxiolytics (benzodiazepine, zopiclone, zolpidem), anti-epileptics, antibiotics, L-thyroxin, NSAIDs, PPIs, paracetamol, antiplatelet therapies, anticoagulants, oral antidiabetics (OADs) — including metformin and Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, insulin, corticosteroids (oral or inhaled), immunosuppressants, and potassium, were compared between SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR-positive (COVID-pos) and RT-PCR-negative patients (COVID-neg).
SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR
SARS-CoV2 RNA was extracted from nasopharyngeal swabs using the eMAG®/eSTREAM® system (bioMérieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France), then amplified on the LightCycler® 480 Instrument II (Roche Diagnostics, France). Quantitative real-time RT-PCR used two targets on the RdRp gene amplified in duplex [32]. The primers and probes were: Flo2 and Flo4: CoV_IP2-12669Fw ATGAGCTTAGTCCTGTTG and CoV_IP2-12759Rv CTCCCTTTGTTGT with the CoV_IP2-12696Probe ( +) AGATGTCTTGTGCTGCCGGTA [5']Hex [3']BHQ-1; CoV_IP4-14059Fw GGTAACTGGGTATGATTTCG and CoV_IP4-14146Rv CTGGTCAAGGTTAATATATAGG with probe CoV_IP4-14084Probe ( +) TCATACAAAACCACGCCAGG [5 '] Fam [3'] BHQ-1. They were developed by the national reference centre of respiratory viruses at the Institut Pasteur (Paris, France). A standard range of CoV_IP RNA transcript was used for relative quantification. The RT-PCR is specific for SARS-CoV2 and assay sensitivity is around 10 copies/reaction.
Statistical analysis
The Statistical Package for Social Sciences software (SPSS ver. 22.0.0.0) was used for demographic and clinical data. Differences in these data were assessed using parametric t-tests and for categorical measures χ2 tests were applied. For each test statistic, a probability value of < 0.05 was regarded as significant.
For exhibiting treatment effect on the probability to have positive RT-PCR, Logistic regression models were used, estimated with Bayesian techniques (McMC, Markov chains and Monte Carlo integration in R statistical software) with the prior assumption that the probabilities of positive RT-PCR in the absence of treatment and in the presence of treatment were of the order of 0.50. The same kind of model was used with aim to study the treatment impact on mortality adjusting on RT-PCR status.
For posterior summaries, median and symmetric 95% credible intervals were retrieved, and the posterior probability for a parameter to be negative (or positive) was use as a similar quantity than the frequentist P-value.
Results
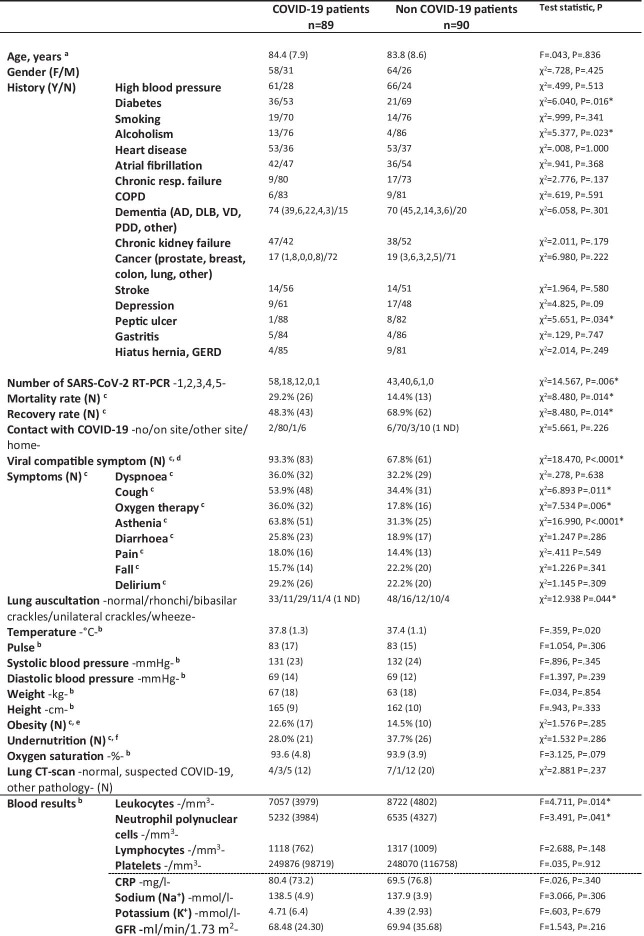
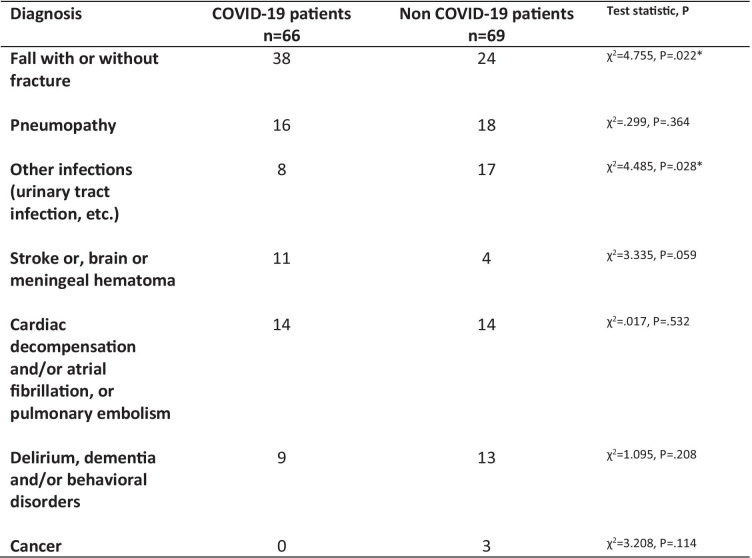
By 8 April 2020, 179 patients were suspected of SARS-CoV-2 infection at the Geriatric Hospital of the University Hospital of Strasbourg, France, 45 patients (25.1%) living in the community and 134 hospitalized (74.9%). Among them, 89 were RT-PCR-positive (COVID-pos) and 90 were RT-PCR-negative (COVID-neg). Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes of COVID-pos and COVID-neg patients are shown in Table 1, the initial reasons for hospitalization of the 134 patients were detailed in Table 2. The mean age of the 179 patients was 84.06 years (SD 8.20), and all but two were older than 60 years. Most patients were women (N = 122; 68%). Most patients had contact with COVID-19 at the Geriatric hospital site (89.9% for COVID-pos, 77.8% for COVID-neg). COVID-pos patients more frequently had a history of diabetes (P = 0.016) and alcoholism (P = 0.023), a higher frequency of viral compatible symptoms — particularly cough and asthenia — (P < 0.0001), a lower leukocyte count (P = 0.014) and a higher mortality rate (29.2%) when compared to COVID-neg patients (14.4%) (P = 0.014). The median length of stay at the hospital site was 8 weeks (SD 82 weeks; minimum = 2 weeks, maximum = 658 weeks). The median time from hospital entry to SARS-CoV-2 testing was 27 days (SD 567 days; min = 0 day, max = 576 days). One hundred and twenty-seven patients (70.9%) had already been hospitalized for more than 8 days by the time they were tested. The median length of follow-up after first SARS-CoV-2 testing was 25 days (SD 7.46; min = 9 days, max = 39 days).
Table 1.
Clinical and demographic characteristics of COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 elderly patients
a Age at time of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR. Mean (standard deviation)
b Mean (standard deviation)
c Percentage
d Hyperthermia above 38 °C and/or cough and/or dyspnoea and/or asthenia and/or diarrhoea
e Body mass index > 30 kg/m2
f Body mass index < 21 kg/m2
AD, Alzheimer’s disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRP, C-reactive protein; CT-scan, computed tomography scanner; DLB, dementia with Lewy bodies; F, female; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; M, male; N, no; n, number; PDD, Parkinson’s disease dementia; VD, vascular dementia; Y, yes
Table 2.
Causes of Hospital admission among the 135 patients hospitalized in acute Geriatric Medicine or Geriatric Rehabilitation service. There are 189 reasons for admission, as many patients had two (N = 46) or even three causes (N = 4) for their hospitalization
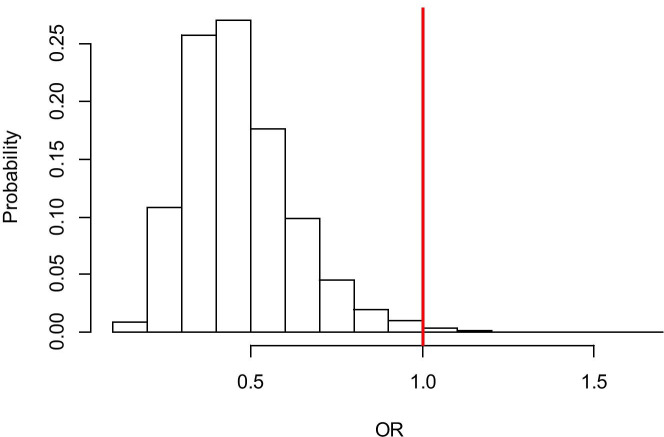
Elderly patients on PPIs were 2.3 times less likely (odds ratio [OR] = 0.4381, 95% confidence interval [CI] [0.2331, 0.8175], P = 0.0053) to develop COVID-19 infection, compared to those with no PPIs (Fig. 1 and Table 3). Forty COVID-neg patients were on PPIs versus 23 COVID-pos patients. The types of PPIs taken by the COVID-neg patients were as follows: pantoprazole (N = 16), lansoprazole (N = 11), esomeprazole (N = 8), omeprazole (N = 4), and rabeprazole (N = 1). PPIs taken by the COVID-pos patients were as follows: pantoprazole (N = 15), esomeprazole (N = 6), lansoprazole (N = 1), and omeprazole (N = 1). The median and mean doses for COVID-neg patients were 1.0 (SD 0.31; min = 0.5, max = 2.0) and 0.83 (SD = 0.31), respectively, and for COVID-pos patients were 0.5 (SD 0.25, min = 0.5, max = 1.0) and 0.71 (SD 0.25), respectively (P = 0.37). No other treatment decreased or increased the risk of COVID-19.
Fig. 1.
Probability of COVID-19 in elderly patients on proton pump inhibitors
Table 3.
Probability of COVID-19 with or without each of the treatments. The columns indicate the frequency of treatment in the sample, the odds-ratio -OR- (multiplication of the risk of COVID-19 when the patient has the treatment, as an a posteriori median and its 95% credibility interval), the estimated frequency of COVID-19 without treatment (median and 95% CI), the estimated frequency of COVID-19 with treatment (median and 95% CI) and the probability that the difference between the two frequencies (“with” and “without”) is positive
| Treatment frequency (%) | OR | Probability of COVID-19 without treatment | Probability of COVID-19 with treatment | P (with > without) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 2.5% | 97.5% | 50% | 2.5% | 97.5% | 50% | 2.5% | 97.5% | |||
| ARBs | 15.08 | 1.3246 | 0.5813 | 2.9804 | 48.75 | 40.78 | 56.6 | 55.59 | 36.77 | 72.95 | .7514 |
| ACE inhibitors | 21.79 | 1.6003 | 0.7931 | 3.3015 | 47.27 | 38.98 | 55.49 | 58.88 | 43.37 | 73.18 | .9029 |
| Diuretics | 45.81 | 1.2192 | 0.6869 | 2.1713 | 47.34 | 37.79 | 57.32 | 52.38 | 41.66 | 62.95 | .7453 |
| CCB | 22.35 | 0.782 | 0.3870 | 1.5718 | 51.09 | 42.85 | 59.34 | 45.04 | 30.42 | 60.15 | .2527 |
| Beta-blockers | 40.78 | 1.2799 | 0.7085 | 2.3135 | 47.3 | 37.85 | 56.44 | 53.42 | 41.99 | 64.4 | .7909 |
| Other antihypertensives | 6.15 | 0.8291 | 0.2319 | 2.7007 | 50.04 | 42.55 | 57.65 | 45.14 | 19.86 | 72.32 | .3771 |
| Statins | 16.76 | 0.8723 | 0.3942 | 1.9177 | 50.36 | 42.3 | 58.21 | 46.82 | 29.98 | 64.35 | .3607 |
| AD drugs | 3.35 | 0.9992 | 0.1939 | 5.1687 | 49.73 | 42.26 | 57.11 | 49.84 | 16.34 | 83.47 | .4995 |
| PD drugs | 7.26 | 1.1984 | 0.3790 | 3.745 | 49.42 | 41.96 | 56.84 | 53.96 | 27.65 | 77.8 | .6224 |
| Antidepressants | 18.44 | 1.0936 | 0.5162 | 2.3259 | 49.35 | 41.32 | 57.38 | 51.51 | 34.82 | 67.86 | .5907 |
| Antipsychotics | 15.64 | 0.8583 | 0.3800 | 1.9028 | 50.33 | 42.5 | 58.19 | 46.53 | 29 | 64.52 | .3558 |
| Anxiolytics | 32.4 | 1.2479 | 0.6685 | 2.3451 | 47.84 | 39.25 | 56.73 | 53.39 | 40.51 | 65.93 | .7537 |
| Antiepileptics | 7.26 | 0.8517 | 0.2641 | 2.6427 | 49.99 | 42.36 | 57.57 | 45.99 | 21.34 | 71.8 | .3897 |
| Antibiotics | 9.5 | 1.1494 | 0.4277 | 3.1204 | 49.44 | 41.91 | 56.99 | 52.97 | 30.14 | 74.82 | .6070 |
| L-Thyroxin | 17.88 | 1.0114 | 0.4717 | 2.1574 | 49.63 | 41.77 | 57.78 | 50.01 | 33.07 | 66.63 | .5131 |
| PPIs | 35.2 | 0.4381 | 0.2331 | 0.8175 | 56.78 | 47.6 | 65.45 | 36.58 | 25.5 | 48.75 | .0053* |
| Paracetamol | 33.52 | 1.5143 | 0.8160 | 2.8415 | 46.33 | 37.35 | 55.19 | 56.56 | 44.16 | 68.64 | .9083 |
| NSAIDs | 1.12 | 7.3082 | 0.4612 | 275.3777 | 49.36 | 42.02 | 56.74 | 87.53 | 31.4 | 99.63 | .9155 |
| APT | 27.93 | 1.4209 | 0.7354 | 2.7624 | 47.23 | 38.92 | 55.85 | 55.98 | 42.17 | 69.28 | .8523 |
| Anticoagulant | 42.46 | 0.8537 | 0.4746 | 1.5198 | 51.46 | 41.96 | 60.94 | 47.41 | 36.64 | 58.37 | .2981 |
| Insulin | 12.29 | 2.3754 | 0.9676 | 6.4591 | 47.26 | 39.61 | 54.99 | 68.06 | 47.71 | 84.39 | .9711 |
| OADs | 11.73 | 1.7402 | 0.7002 | 4.5356 | 48.13 | 40.64 | 55.84 | 61.67 | 40.60 | 80.04 | 0.8808 |
| Metformin | 8.94 | 2.3428 | 0.8298 | 7.3697 | 47.90 | 40.22 | 55.52 | 68.34 | 44.15 | 86.89 | 0.9451 |
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 3.91 | 2.5046 | 0.5412 | 15.0748 | 48.95 | 41.50 | 56.30 | 70.62 | 34.94 | 93.43 | 0.8802 |
| Corticosteroids | 5.59 | 0.6605 | 0.1735 | 2.3329 | 50.22 | 42.84 | 57.72 | 40.23 | 15.12 | 69.78 | .2617 |
| Immunosuppressants | 1.12 | 7.379 | 0.4876 | 269.8301 | 49.65 | 42.34 | 57.08 | 87.85 | 32.52 | 99.62 | .9185 |
| Potassium | 25.14 | 0.759 | 0.3840 | 1.4731 | 51.44 | 43.07 | 59.61 | 44.51 | 30.8 | 58.88 | .2074 |
| Others | 64.8 | 0.7022 | 0.3781 | 1.2963 | 55.47 | 43.05 | 67.17 | 46.61 | 37.49 | 55.72 | .1301 |
AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ACE, angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors; APT, antiplatelet therapy; ARBs, angiotensin II receptor blockers; CCB, calcium channel blockers; DDP-4 inhibitors, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors; NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; OADs, oral antidiabetic drugs; PD, Parkinson’s disease; PPIs, proton pump inhibitors
The risk of death was lower for COVID-19 patients on antipsychotics (P = 0.0013) and OADs (P = 0.0153), particularly for metformin (P = 0.0237) (supplementary Table S1). It should be noted that no deaths occurred in patients on antipsychotic drugs and only one death occurred in patients on OADs. The types of antipsychotics taken by the 12 COVID-pos patients on antipsychotic drugs were as follows: risperidone (N = 5), clozapine (N = 3), olanzapine (N = 2), alimemazine (N = 1), haloperidol (N = 1). The patient on alimemazine and one patient on olanzapine had these treatments in the 15 days prior to RT-PCR but had their treatment stopped during the COVID-19 infection. All other patients continued their antipsychotic medication during COVID-19 infection. The types of OADs taken by 12 COVID-pos patients on OADs drugs were as follows: metformin (N = 10, mean dose = 1310 mg, min = 500 mg, max = 2500 mg), vildagliptin (N = 3; associated with metformin in one case) and sitagliptin (N = 2, associated with metformin in both cases). Two patients with metformin, including one with sitagliptin, had their treatment stopped during the COVID-19 infection.
Discussion
This case–control study aimed to look for treatments that could have a preventive effect on the appearance of COVID-19 in a geriatric population, using data from the main Geriatric hospital of Strasbourg, in the Grand Est region, one of the epicentres of the COVID-19 pandemic in France.
We show for the first time that PPIs could have a preventative effect on COVID-19 infection. Indeed, in our study, patients on PPIs had a 2.3-fold reduction in the risk of COVID-19. We did not find that any of the other drugs could have a preventive effect on COVID-19. PPIs are among the most prescribed medications for the elderly. Indeed, more than 30% of people over the age of 80 were reported to take them [14], as was the case in this study where 35.2% were taking PPIs. PPIs are prescribed for acid-related disorders such as peptic ulcer disease and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD). In our study, out of 63 patients taking PPIs, 31 had a clear indication for this treatment, whereas for the remainder we were unable to ascertain the reason for the prescription, though most of them were also taking antiplatelets or anticoagulants. These drugs are associated with acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding [16], and PPIs are effective in treating ulcers. Clinical guidelines generally recommend a PPI treatment duration of less than 8 to 12 weeks. Although usually considered safe, these drugs have been associated with increased risks of side effects such as bone fractures, kidney disease, microscopic colitis, and hypomagnesaemia [14]. Furthermore, the long-term use of PPIs was recently reported to be associated with an increased mortality risk [4], and an increased dementia risk [9]. PPIs decrease intracellular pH and increase the extracellular pH via inhibition of vacuolar H+-ATPases (V-ATPases) in a covalent interaction [20]. V-ATPases play a critical role in the maintenance of a neutral intracellular pH in all cells, and an acidic extracellular pH by actively excreting protons either through ion exchange mechanisms or by segregating H + within cytoplasmic organelles that are subsequently expelled [28]. SARS-CoV-1 and most likely SARS-CoV-2, like other coronaviruses and other enveloped viruses, enter target cells by inducing fusion between viral and cellular membranes. This is mediated by a viral fusion protein named spike of S protein [27]. The S protein transduction in the cell requires acidification of the endosome or extracellular medium [27]. Therefore, blocking these receptors inhibits the acidic microenvironment around the cell and in the lysosome, and could prevent the virus from entering the cell. However, an online study in the USA using a marketing website has found an increased risk of positive COVID-19 test among people taking PPIs [1]. In addition to the fact that this study did not focus on geriatric patients, it also had many biases: it only involved people with digestive complaints, who were able to fill in a questionnaire on the internet, which presumably may have oversampled COVID-19 patients (home quarantine, health concerns). Furthermore, there was no medical control of the data entered. The authors of the article assumed that some of the responses may have been dishonest.
Recent studies have demonstrated a higher risk of mortality for COVID-19 patients taking PPIs [19]. The hypothesis explaining a greater severity under PPI would be that PPIs facilitate bacterial superinfections, due to a decrease in gastric acidity [21].
For this study, we were in quasi-experimental conditions and able to detect COVID-19 infection live since most patients who developed COVID-19 developed it on site, directly inside the geriatric hospital (89.9%). These are therefore nosocomial infections: presumably through transmission by other patients, through transmission by the paramedical team (nurse, care assistant) or medical team, or, before the introduction of containment measures in France on 17 March 2020, by the families or relatives of the patients. From that date onwards, all visits to the hospital, including those of patients’ families, were prohibited. This nosocomial contamination is likely also related to the low use of masks upstream of the contagion, at the beginning of the pandemic in France as there were insufficient stocks [18], as well as to the lack of mass testing capability in France [23], and more generally to the inexperience and denial of the French population in the face of such a pandemic in its early stages.
The two co-morbidities that were significantly more common than the others in our COVID-pos patients were diabetes and chronic alcoholism. Both diseases decrease immune capacity and promote infections [8, 22], which is entirely consistent given the context. The mortality rate in our study was particularly high: in our geriatric hospital, COVID-19 has doubled the patient mortality rate. First, the mortality rate for COVID-neg patients, which was 14.4% (over the month and a half of the study) was close to the mortality rate in the follow-up and rehabilitation units of the HUS geriatric hospital in 2017, which was 10% (unpublished data). COVID-pos patients had a mortality rate of 29.2%, which was equivalent to the data in residential institutions for dependent elderly people (EHPAD or retirement homes) in France where the mortality rate described is 25 to 33% (unpublished data). In the same way in Italy and in China, the mortality rate is reported to have reached 34.5% in elderly people [6].
We have demonstrated also that metformin seem to diminish the mortality of elderly patients with COVID-19. Recent research analysed the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 proteins and human proteins [10]. It appears that SARS-CoV-2 proteins probably interact with the mTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1) pathway [10]. Metformin is an indirect inhibitor of mTORC1, and thus could explain the potential interest of metformin against COVID-19 [10]. A recent retrospective electronic health record data analysis of more than 25,000 patients was also in favour of a protective effect of metformin, with a reduction of mortality ([OR] = 0.33, 95% [CI] [0.13, 0.84], P = 0.0210) [7]. Antipsychotics also decreased COVID-pos patient mortality: none of the 12 COVID-pos patients on antipsychotics died. As early as 1975, the first findings of the antiviral properties of antipsychotics were reported, first clinically, with the massive decrease of recurrences of genital herpes infections under chlorpromazine, and then biologically [5]. Thus, phenothiazine and thiothixene compounds inhibit the replication of HSV 1 and 2, tick-borne encephalitis virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and measles virus [17]. Haloperidol increases cell survival in the context of retroviral infection [34]. In the same way, it has been demonstrated that the metabolites of clozapine, a so-called atypical antipsychotic, inhibit the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. The discovery of these two types of therapeutic classes (OADs and antipsychotics) should encourage us to test some of these drugs in therapeutic trials. We have therefore started a trial called COVID-Aging (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04359953), dedicated solely to the elderly.
This study has methodological limitations. First, it was retrospective. Nevertheless, the fact that all data were accessible on professional medical software made it possible to better guarantee the completeness of the data. The second limitation concerns the use of RT-PCR: its sensitivity is most likely excellent, but the timing and depth of swabbing are limitations of this technique. To overcome this, the swabs were repeated in the COVID-neg group and when possible, a chest CT scan was performed. In only one case among 20 in the COVID-neg group was the CT scan consistent with COVID-19 infection.
Here, we have shown for the first time that some specific treatments frequently used in the elderly in a geriatric context could have a preventive or curative effect. On the preventive side, PPIs seem to reduce the risk of infection with COVID-19 in a highly contagious context. Therefore, it seems important to keep patients on PPIs, including those taking them for no obvious reason, awaiting further studies in this area. However, PPIs have no curative interest in our study, and they increase the risk of death if the treatment is left during the disease according to a retrospective Korean study [19]. On the curative side, metformin and antipsychotics seem to have beneficial effects on patient survival. In the latter case, it is obviously necessary for therapeutic trials to be carried out, and this must be done quickly in view of the major mortality rate in the elderly. Our finding regarding PPIs needs to be confirmed by prospective studies.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
We do thank all the patients and their families involved in the study, and all the staff of the Robertsau Geriatric Hospital in contact with patients, including interns, medical students, nurses, physiotherapists, psychologists, nurses’ aides, housekeepers, as well as the hospital’s support teams.
Author contribution
Literature search: FB, BS, AB, TV, SFK; Figure: FB, ES; Tables: FB, ES; Study design: FB, ES; data collection: CW, FB, BS, CMH, CD; Data interpretation: FB, AB, BS, ES; Writing: FB, ES; Revision of the final manuscript: CW, MM, TV, BS, CD, CMH, DM, NB, SFK, LC, ES, DI, CJ, AB, CS, FW, AM, CM, PK, GK.
Data and materials availability
After publication, the data will be made available to others on reasonable requests to the corresponding author. A proposal with detailed description of study objectives and statistical analysis plan will be needed for evaluation of the reasonability of requests. Additional materials might also be required during the process of evaluation. Deidentified participant data will be provided after approval from the corresponding author.
Code availability
R statistical software and SPSS ver. 22.0.0.0.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics committee “Faculté de Médecine de Strasbourg” number CE-2020–68.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Almario CV, Chey WD, Spiegel BMR. Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:1707–1715. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baden LR, et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;384:403–416. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Caruso D et al. Chest CT features of COVID-19 in Rome, Italy. Radiology. 2020; 201237. 10.1148/radiol.2020201237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Cetin H et al. Increased risk of death associated with the use of proton pump inhibitors in dementia patients and controls – a pharmacoepidemiological claims data analysis. Eur J Neurol. 2020. 10.1111/ene.14252 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Chang TW. Letter: suppression of herpetic recurrence by chlorpromazine. N Engl J Med. 1975;293:153–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen T, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of older patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China (2019): a single-centered, retrospective study. J Gerontol Ser A. 2020 doi: 10.1093/gerona/glaa089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crouse AB, Grimes T, Li P, Might M, Ovalle F, Shalev A. Metformin use is associated with reduced mortality in a diverse population with COVID-19 and diabetes. Front Endocrinol. 2021; 11. 10.3389/fendo.2020.600439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Geerlings SE, Hoepelman AI. Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999;26:259–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1999.tb01397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gomm W, et al. Association of proton pump inhibitors with risk of dementia: a pharmacoepidemiological claims data analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73:410–416. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.4791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gordon DE, et al. A SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interaction map reveals drug targets and potential drug-repurposing. BioRxiv. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Grasselli G, et al. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region Italy. JAMA. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gurwitz D. Angiotensin receptor blockers as tentative SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics. Drug Dev Res. 2020 doi: 10.1002/ddr.21656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hacisuleyman E, et al. Vaccine breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 variants. N Engl J Med. 2021 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hálfdánarson ÓÖ, et al. Proton-pump inhibitors among adults: a nationwide drug-utilization study. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2018;11:1756284818777943. doi: 10.1177/1756284818777943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Homolak J, Kodvanj I. Widely available lysosome targeting agents should be considered as a potential therapy for COVID-19. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Hreinsson JP, Palsdóttir S, Bjornsson ES. The association of drugs with severity and specific causes of acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50:408–413. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jones-Brando LV, Buthod JL, Holland LE, Yolken RH, Torrey EF. Metabolites of the antipsychotic agent clozapine inhibit the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Schizophr Res. 1997;25:63–70. doi: 10.1016/s0920-9964(97)00007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Klompas M. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): protecting hospitals from the invisible. Ann Intern Med. 2020 doi: 10.7326/m20-0751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee SW, et al. Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching. Gut. 2020 doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee YY, et al. Proton pump inhibitors enhance the effects of cytotoxic agents in chemoresistant epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:35040–35050. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Luxenburger H, et al. Treatment with proton pump inhibitors increases the risk of secondary infections and ARDS in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: coincidence or underestimated risk factor? J Intern Med. 2020 doi: 10.1111/joim.1312110.1111/joim.13121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mehta AJ, Yeligar SM, Elon L, Brown LA, Guidot DM. Alcoholism causes alveolar macrophage zinc deficiency and immune dysfunction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188:716–723. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201301-0061OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Moatti J-P. The French response to COVID-19: intrinsic difficulties at the interface of science, public health, and policy. Lancet Public Health. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Nikolich-Zugich J, Knox KS, Rios CT, Natt B, Bhattacharya D, Fain MJ. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: what we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes. GeroScience. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00186-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Polack FP, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, Consortium atNC-R Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Simmons G, Reeves JD, Rennekamp AJ, Amberg SM, Piefer AJ, Bates P. Characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) spike glycoprotein-mediated viral entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:4240–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0306446101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Spugnini EP, et al. Lansoprazole as a rescue agent in chemoresistant tumors: a phase I/II study in companion animals with spontaneously occurring tumors. J Transl Med. 2011;9:221. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Team TNCPERE Vital surveillances: the epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 Novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19)—China, 2020 China. CDC Wkly. 2020;2:113–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Vaduganathan M, Vardeny O, Michel T, McMurray JJV, Pfeffer MA, Solomon SD. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with Covid-19. 2020. N Engl J Med. 10.1056/NEJMsr2005760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Voysey M, et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.WHO (2020a) https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/real-time-rt-pcr-assays-for-the-detection-of-sars-cov-2-institut-pasteur-paris.pdf?sfvrsn=3662fcb6_2. Accessed 6 July 2021.
- 33.WHO E (2020b) COVID-19 weekly surveillance report, data of the week of 23–29 nov 2021 https://www.eurowhoint/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19/previous-weekly-surveillance-reports/previous-weekly-surveillance-reports-2020/data-for-the-week-of-23-29-november-2020-epi-week-48. Accessed April, 2021
- 34.Wunderlich V, Fey F, Sydow G. Antiviral effect of haloperidol on Rauscher murine leukemia virus. Archiv fur Geschwulstforschung. 1980;50:758–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang N, Shen H-M. Targeting the endocytic pathway and autophagy process as a novel therapeutic strategy in COVID-19. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16:1724–1731. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhu N, et al. (2020) A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China. N Engl J Med. 2019;382:727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
After publication, the data will be made available to others on reasonable requests to the corresponding author. A proposal with detailed description of study objectives and statistical analysis plan will be needed for evaluation of the reasonability of requests. Additional materials might also be required during the process of evaluation. Deidentified participant data will be provided after approval from the corresponding author.
R statistical software and SPSS ver. 22.0.0.0.