Abstract
The transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) is a key molecule for SARS-CoV-2 invading human host cells. To provide insights into SARS-CoV-2 infection of various human tissues and understand the potential mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 infection, we investigated TMPRSS2 expression in various normal human tissues and SARS-CoV-2-infected human tissues. Using publicly available datasets, we performed computational analyses of TMPRSS2 expression levels in 30 normal human tissues, and compared them between males and females and between younger (ages ≤ 49 years) and older (ages > 49 years) populations in these tissues. We found that TMPRSS2 expression levels were the highest in the prostate, stomach, pancreas, lungs, small intestine, and salivary gland. The TMPRSS2 protein had relatively high expression levels in the parathyroid gland, stomach, small intestine, pancreas, kidneys, seminal vesicle, epididymis, and prostate. However, TMPRSS2 expression levels were not significantly different between females and males or between younger and older populations in these tissues. The pathways enriched in TMPRSS2-upregulated pan-tissue were mainly involved in immune, metabolism, cell growth and proliferation, stromal signatures, and cancer and other diseases. Many cytokine genes displayed positive expression correlations with TMPRSS2 in pan-tissue, including TNF-α, IL-1, IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-8, IL-12, IL-18, IFN-α, MCP-1, G-CSF, and IP-10. We further analyzed TMPRSS2 expression levels in nasopharyngeal swabs from SARS-CoV-2-infected patients. TMPRSS2 expression levels showed no significant difference between males and females or between younger and older patients. However, they were significantly lower in SARS-CoV-2-infected than in healthy individuals and patients with other viral acute respiratory illnesses. Interestingly, TMPRSS2 expression levels were positively correlated with the enrichment levels of four immune signatures (B cells, CD8+ T cells, NK cells, and interferon response) in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients but likely to be negatively correlated with them in the normal lung tissue. Our data may provide insights into the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, Transmembrane serine protease 2, Immune signatures, Gene expression profiles, Pathway and gene ontology, Gene co-expression network
1. Background
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection has lasted for more than one year and caused more than 183 million cases and 3.9 million deaths as of July 5, 2021 [1]. The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) are two key molecules for SARS-CoV-2 invading human host cells [2]. SARS-CoV-2 uses ACE2 as its entry receptor and engages TMPRSS2 for S protein priming [[3], [4], [5]]. Thus, some studies have proposed to use ACE2 and/or TMPRSS2 inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 infection [6,7]. Our previous study showed that ACE2 is expressed in various human tissues besides the lungs [8]. This fact indicates that SARS-CoV-2 may infect other tissues aside from the lungs. This was evidenced by a plenty of clinical data [9]. Likewise, TMPRSS2 is expressed in various human tissues [10]. Because androgens play a role in regulating TMPRSS2 [11], some studies have connected that to the higher risk and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection in males than in females [12].
In this study, we analyzed the TMPRSS2 expression in 30 normal human tissues and compared TMPRSS2 expression levels between males and females and between younger population and older population. Besides, we investigated the correlation between TMPRSS2 and immune signatures in multiple normal tissues of different genders and ages groups. We identified pathways, gene ontology, and gene co-expression networks associated with TMPRSS2 expression in pan-tissue. Furthermore, we explored the expression of TMPRSS2 in COVID-19 patients.
2. Methods
2.1. Datasets
We downloaded the data of RNA-Seq gene expression profiles (TPM normalized) in 30 human normal tissues from GTEx (https://www.gtexportal.org/home/datasets) [13]. The 30 tissues included adipose tissue, adrenal gland, bladder, blood vessel, blood, brain, breast, cervix uteri, colon, esophagus, fallopian tube, heart, kidney, liver, lung, muscle, nerve, ovary, pancreas, pituitary, prostate, salivary gland, skin, small intestine, spleen, stomach, testis, thyroid, uterus, vagina. We log2-transformed all gene expression values before further analyses. In addition, we downloaded two datasets (GSE152075 and GSE156063) of gene expression profiles in SARS-CoV-2-infected human nasopharyngeal swabs from the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). A summary of these datasets is presented in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2. Evaluation of the enrichment levels of immune signatures in tissue
We evaluated the enrichment levels of four immune signatures in tissue. The four immune signatures included B cells, CD8+ T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and interferon response. The enrichment level of an immune signature in a sample was defined as the mean expression value of all marker genes of the immune signature. The marker genes of the four immune signatures are listed in Supplementary Table S2.
2.3. Gene-set enrichment analysis
We first identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the high-TMPRSS2-expression-level (upper third) and low-TMPRSS2-expression-level (bottom third) pan-tissue, based on Student's t tests with a threshold of false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 and fold change (FC) of mean expression levels > 2. Based on the DEGs, we identified KEGG [14] pathways highly enriched in both groups of pan-tissue by GSEA [15] with a threshold of FDR < 0.05. Furthermore, we identified gene modules representing gene ontology (GO) highly enriched in both groups of pan-tissue by WGCNA [16].
2.4. Statistical analysis
In comparisons of TMPRSS2 expression levels between two-classes of samples, we used Student's t tests (two-tailed). In evaluation of correlations between TMPRSS2 expression levels and immune signatures' enrichment levels and between expression correlations between two genes, we used the Pearson's correlation coefficient (r). We employed FDR to adjust P values in multiple tests. The FDR was calculated by the Benjamini and Hochberg method [17].
3. Results
3.1. TMPRSS2 expression in various human tissues
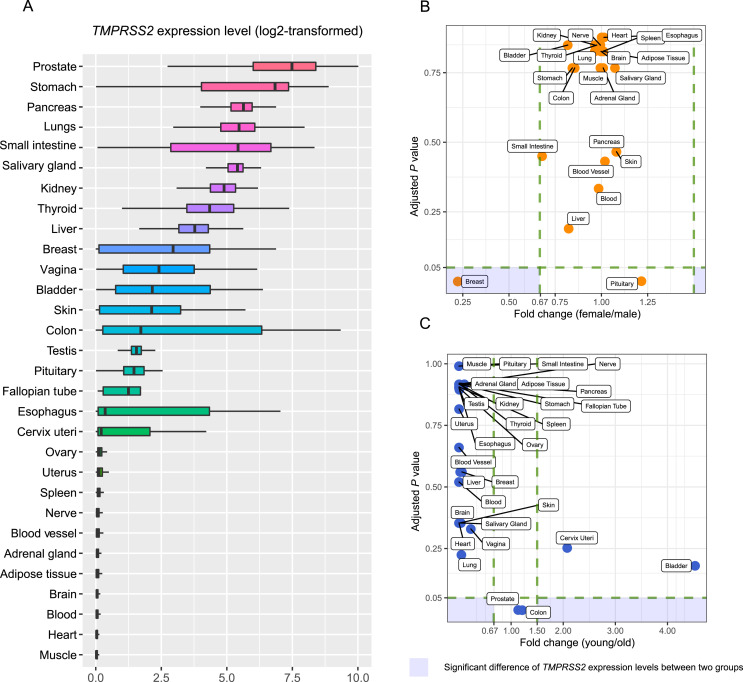
Among the 30 normal human tissues, the prostate, stomach, pancreas, lungs, small intestine, and salivary gland had the highest TMPRSS2 expression levels, while muscle, heart, blood, brain, adipose tissue, adrenal gland, blood vessel, nerve, spleen, uterus, and ovary showed the lowest TMPRSS2 expression levels (Fig. 1 A). These results indicate that TMPRSS2 is expressed in multiple human tissues, especially in the lungs, prostate, and the digestive system. This is consistent with the observation that SARS-CoV-2 infection may induce damage in multiple organs [9]. We further compared the expression levels of TMPRSS2 between females and males in 22 individual human tissues and between younger (ages ≤ 49 years) and older (ages > 49 years) cohorts in 30 individual human tissues (Fig. 1C). Interestingly, TMPRSS2 expression levels were not significantly different between females and males in any of the 22 individual tissues with a threshold of FDR < 0.05 and FC > 1.5 (Fig. 1B). Besides, TMPRSS2 expression levels were not significantly different between younger and older cohorts in any of the 30 individual tissues (Fig. 1C).
Fig. 1.
TMPRSS2 expression in various human tissues. (A) Comparison of TMPRSS2 expression levels across 30 human tissues in GTEx [13]. Comparison of TMPRSS2 expression levels between males and females (B) and between older (ages > 49 years) and younger (ages ≤ 49 years) (C) in individual human tissues in GTEx. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used in (B) and (C). The adjusted P value was calculated by the Benjamini and Hochberg method [17]. TMPRSS2: Transmembrane serine protease 2; GTEx: Genotype-Tissue Expression.
The Human Protein Atlas (HPA) database (http://www.proteinatlas.org/) showed that the TMPRSS2 protein had relatively high expression levels in the parathyroid gland, stomach, pancreas, kidneys, epididymis, and prostate. The HPA database also showed that the parathyroid gland, gastrointestinal tract (stomach, duodenum, small intestine, and rectum), kidney, pancreas, and male tissues (epididymis, prostate, and seminal vesicle) had high expression levels of both TMPRSS2 gene and protein. Previous studies have shown that ACE2 has high expression levels in male tissues (testis and seminal vesicle) [8]. Taken together, these data indicate that SARS-CoV-2 infection may affect male reproductive functions.
3.2. Correlations between TMPRSS2 expression and immune signatures
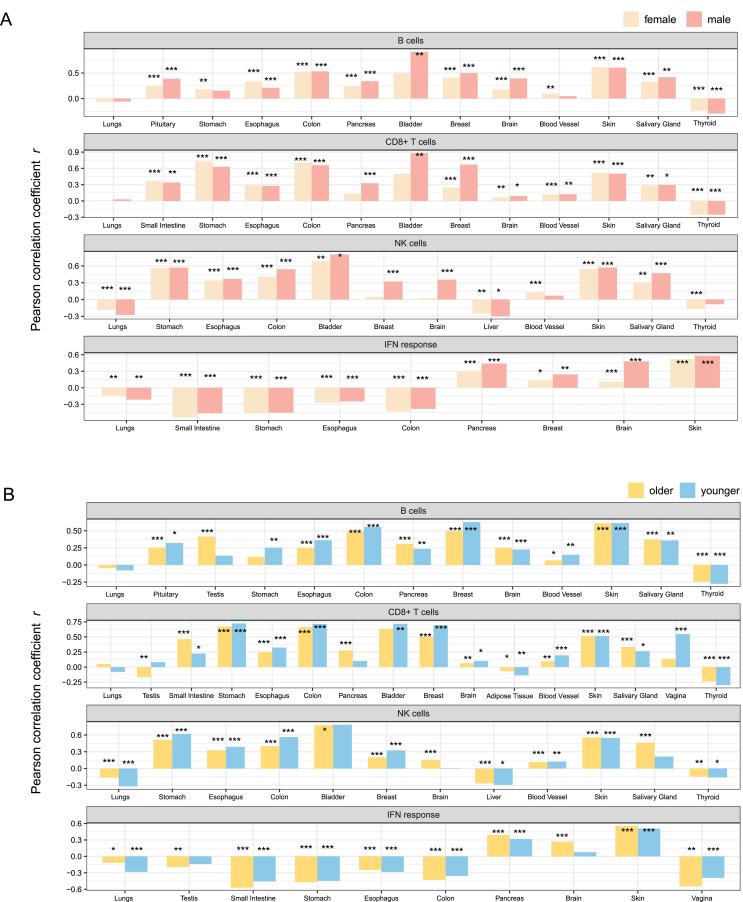
In the pituitary, esophagus, colon, pancreas, breast, brain, skin, salivary gland, and thyroid, TMPRSS2 expression levels were positively correlated with the enrichment levels of B cells (FDR < 0.05, 0.18 ≤ r ≤ 0.91) in both males and females (Fig. 2 A). In the stomach and blood vessel, the significant correlation between TMPRSS2 expression levels and B cell enrichment levels were only observed in females (0.10 ≤ r ≤ 0.19). Similarly, in the small intestine, stomach, esophagus, breast, brain, blood vessel, salivary gland, skin, and colon, CD8+ T cell enrichment levels had positive correlations with TMPRSS2 expression levels in both males and females (0.06 ≤ r ≤ 0.73) (Fig. 2A). However, TMPRSS2 expression showed significant positive correlations with the CD8+ T cell signature solely in the male bladder (r = 0.33) and pancreas (r = 0.88). In the esophagus, bladder, colon, stomach, blood vessel, salivary gland, and skin, TMPRSS2 showed positive expression correlations with the enrichment levels of NK cells in both males and females (0.30 ≤ r ≤ 0.80). Besides, TMPRSS2 expression was positively correlated with the NK cell signature in the female blood vessel (r = 0.13), male breast (r = 0.32), and male brain (r = 0.36). However, in the lungs and liver, TMPRSS2 expression levels were negatively correlated with NK cell enrichment levels in both males and females (−0.30 ≤ r ≤ −0.17). For the interferon response signature, TMPRSS2 showed positive correlations with it in the pancreas, breast, brain, and skin (0.11 ≤ r ≤ 0.58), while negative correlations in the lungs, colon, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine (−0.54 ≤ r ≤ −0.15) in both males and females.
Fig. 2.
Association between TMPRSS2 expression and immune signatures in various human tissues. Correlation between TMPRSS2 expression levels and immune signature enrichment levels in various human tissues in males and females (A) and in older (ages > 49 years) and younger (ages ≤ 49 years) populations (B). Pearson correlation coefficients (r) and P values are shown in (A, B). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. NK: natural killer.
We further analyzed the correlations between TMPRSS2 expression and immune signatures in younger and older cohorts, respectively (Fig. 2B). For B cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells, their enrichment levels were likely to be positively correlated with TMPRSS2 expression levels in individual tissues in both younger and older cohorts. However, the enrichment levels of NK cells were negatively correlated with TMPRSS2 expression levels in the liver, lungs, and thyroid in both younger and older cohorts (−0.32 ≤ r ≤ −0.14). For the interferon response signature, TMPRSS2 showed positive correlations with it in the pancreas and skin (0.32 ≤ r ≤ 0.55) and negative correlations in the colon, esophagus, lungs, vagina, small intestine, and stomach (−0.57 ≤ r ≤ −0.12).
3.3. Pathways and GO associated with TMPRSS2 expression
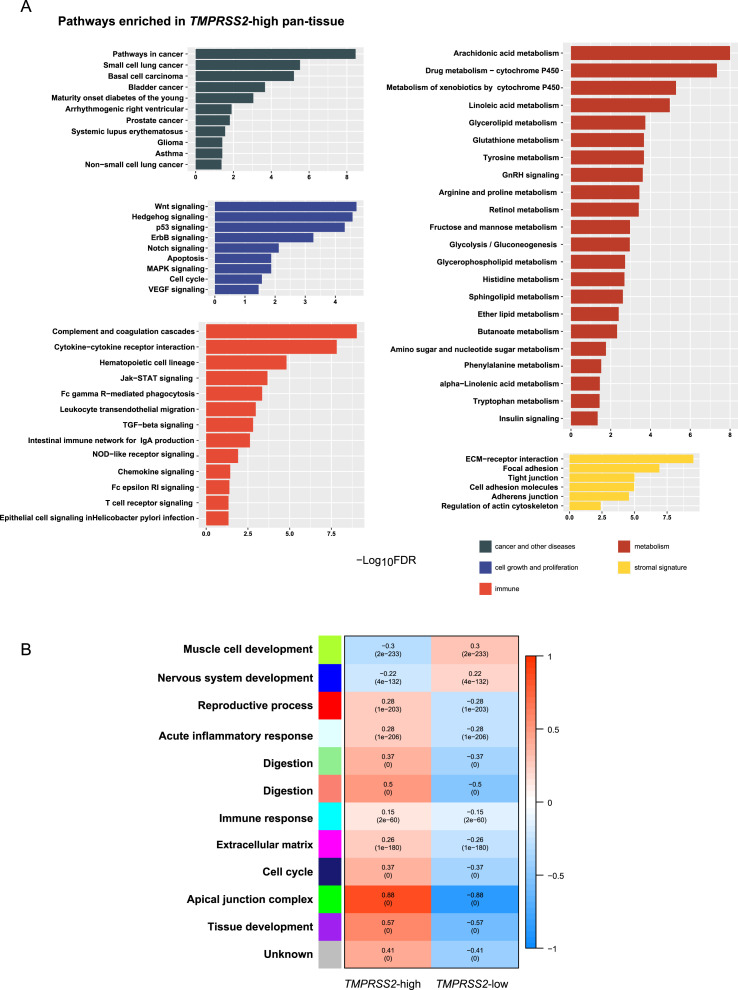
Using the gene set enrichment analysis tool GSEA [15], we identified a number of pathways highly enriched in the high-TMPRSS2-expression-level pan-tissue. These pathways were mainly associated with immune, cell growth and proliferation, cancer and other diseases, metabolism, and stromal signatures (Fig. 3 A). The immune-related pathways included the complement and coagulation cascades, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, hematopoietic cell lineage, Jak-STAT signaling, Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis, leukocyte transendothelial migration, TGF-β signaling, intestinal immune network for IgA production, NOD-like receptor signaling, chemokine signaling, Fc epsilon RI signaling, T cell receptor signaling, and Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection. The pathways associated with cell growth and proliferation included Wnt, Hedgehog, p53, ErbB, Notch, MAPK, VEGF signaling, apoptosis, and cell cycle. The pathways associated with cancer and other diseases included pathways in cancer, small cell lung cancer, basal cell carcinoma, bladder cancer, maturity onset diabetes of the young, arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, prostate cancer, systemic lupus erythematosus, glioma, asthma, and non-small cell lung cancer. The metabolism-related pathways included arachidonic acid metabolism, drug metabolism-cytochrome P450, linoleic acid metabolism, glycerolipid metabolism, glutathione metabolism, tyrosine metabolism, GnRH signaling, arginine and proline metabolism, retinol metabolism, fructose and mannose metabolism, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, glycerophospholipid metabolism, histidine metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, ether lipid metabolism, butanoate metabolism, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism, alpha-linolenic acid metabolism, tryptophan metabolism, and insulin signaling pathways. The pathways related to stromal signature involved ECM-receptor interaction, focal adhesion, tight junction, cell adhesion molecules, adherens junction, and regulation of actin cytoskeleton.
Fig. 3.
Pathways and gene ontology associated with TMPRSS2 expression in pan-tissue. (A) The KEGG pathways enriched in TMPRSS2-high pan-tissue which were identified by GSEA [15]. (B) 12 gene modules and their representative gene ontology differentially enriched between TMPRSS2-high and TMPRSS2-low pan-tissue, which were identified by WGCNA [16]. The P values are shown in parenthesis.
WGCNA [16] identified 12 gene modules differentially enriched between the high- and low-TMPRSS2-expression-level pan-tissue (Fig. 3B). Among the 12 gene modules, 10 were highly enriched in the high-TMPRSS2-expression-level pan-tissue (indicated in cyan, green, light cyan, light green, magenta, midnight blue, purple, red, and salmon, respectively). The representative GO terms for these gene modules were immune response, apical junction complex, acute inflammatory response, digestion, extracellular matrix, cell cycle, tissue development, reproductive process, and digestion, respectively (Fig. 3B). In contrast, two gene modules were highly enriched in the low-TMPRSS2-expression-level pan-tissue (indicated in blue and green yellow, respectively). Their representative GO terms were nervous system development and muscle cell development, respectively. Again, these results indicate that TMPRSS2 expression has a positive association with immune signatures.
3.4. Gene co-expression networks of TMPRSS2
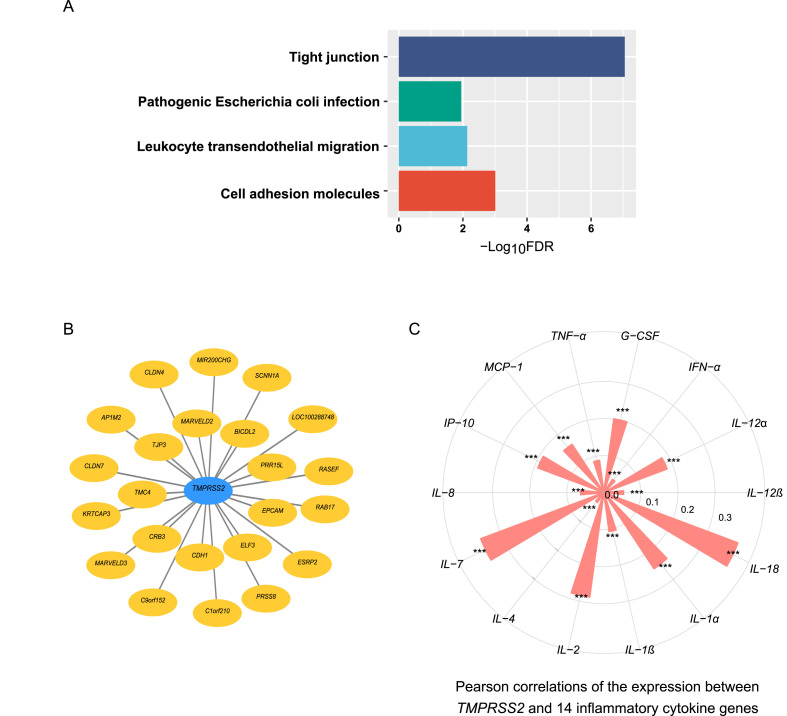
We identified 86 genes having strong positive expression correlations with TMPRSS2 in pan-tissue (r > 0.7). GSEA [15] identified four KEGG pathways significantly associated with the 86 genes (FDR < 0.05). The four pathways included tight junction, cell adhesion molecules, leukocyte transendothelial migration, and pathogenic Escherichia coli infection (Fig. 4 A). Again, these results suggest that TMPRSS2 upregulation is associated with increased immune and stromal signatures in tissue. Fig. 4B shows 23 genes with the strongest positive expression correlations with TMPRSS2 in pan-tissue (r > 0.8). In addition, we found that many genes encoding cytokines [18,19] had significantly positive expression correlations with TMPRSS2 in pan-tissue (FDR < 0.05). These cytokines included TNF-α, IL-1, IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-8, IL-12, IL-18, IFN-α, MCP-1, G-CSF, and IP-10 (Fig. 4C).
Fig. 4.
Genes having significant expression correlation with TMPRSS2 in pan-tissue. (A) Four KEGG pathways associated with 86 genes having strong expression correlations with TMPRSS2 (Pearson correlation coefficient (r) > 0.7). (B) 23 genes having the strongest positive expression correlations with TMPRSS2 (r > 0.8). (C) Positive expression correlation between TMPRSS2 and 14 genes encoding inflammatory cytokines. Pearson correlation coefficients (r) and P values are shown. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
3.5. TMPRSS2 expression in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients
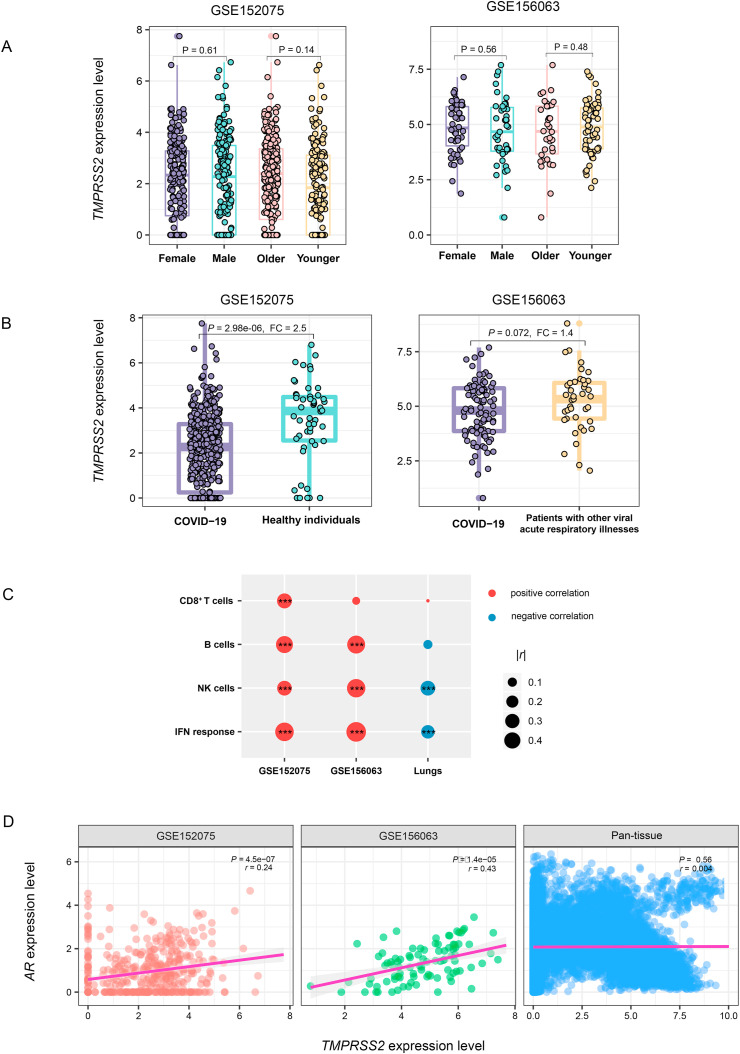
We further analyzed the expression levels of TMPRSS2 in nasopharyngeal swabs from SARS-CoV-2-infected patients. Likewise, TMPRSS2 expression levels had no significant difference between males and females or between younger (ages ≤ 49 years) and older (ages > 49 years) people (Fig. 5 A). However, TMPRSS2 expression levels were significantly lower in SARS-CoV-2-infected than in healthy individuals in GSE152075 (P = 2.98 × 106, FC = 2.5) (Fig. 5B). Moreover, compared to patients with other viral acute respiratory illnesses, SARS-CoV-2-infected patients had significantly lower expression levels of TMPRSS2 in GSE156063 (P = 0.072, FC = 1.4). Interestingly, TMPRSS2 expression levels were positively correlated with the enrichment levels of the four immune signatures (B cells, CD8+ T cells, NK cells, and interferon response) in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients but likely to be negatively correlated with them in the normal lung tissue (Fig. 5C).
Fig. 5.
TMPRSS2 expression in SARS-CoV-2-infected human tissues. (A) Comparisons of TMPRSS2 expression levels between males and females and between older (ages > 49 years) and younger (ages ≤ 49 years) in SARS-CoV-2-infected human tissues. (B) Comparisons of TMPRSS2 expression levels between SARS-CoV-2-infected and normal and other-viruses-infected human tissues. Two-tailed Student's t-test P values are indicated in (A, B). FC: fold change. (C) Pearson correlation between TMPRSS2 expression levels and immune signature enrichment levels in SARS-CoV-2-infected human tissues. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (D) Expression correlation between TMPRSS2 and androgen receptor gene AR in SARS-CoV-2-infected human tissues and in normal human pan-tissue. Pearson correlation coefficients (r) and P values are shown.
Besides, we explored the expression correlation between TMPRSS2 and androgen receptor gene AR in normal human pan-tissue and SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. We found that the expression correlation between TMPRSS2 and AR was not significant in pan-tissue (P = 0.56, r = 0.004), while it was significant in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients (GSE152075: P = 4.48 × 107, r = 0.24; GSE156063: P = 1.43 × 105, r = 0.43) (Fig. 5D). These results indicate a higher risk for males versus females to develop into severe illness with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
4. Discussion
For the first time, we analyzed the expression of TMPRSS2 in a wide variety of normal human tissues. We found that the lungs and gastrointestinal tissues had the highest TMPRSS2 expression levels. It indicates that the lungs and gastrointestinal tissues are likely to have higher risk infected with SARS-CoV-2. Indeed, clinical data have shown that pneumonia and gastrointestinal disorders are the most common manifestations in COVID-19 patients [20]. Similar to ACE2 [8], TMPRSS2 showed no significant expression difference between males and females and between younger and older people in individual normal human tissues. Interestingly, the expression levels of TMPRSS2 were negatively correlated with the enrichment levels of innate and adaptive immune response signatures (NK and CD8+ T cells) in the lungs. It indicates that increased TMPRSS2 expression correlates with reduced immune response in the lungs. This could favor the invasion of SARS-CoV-2 for the lungs. In contrast, the expression levels of TMPRSS2 showed positive correlations with the enrichment levels of NK and CD8+ T cells in most other tissues. It suggests that high TMPRSS2 expression correlates with high immune responses in most tissues.
We found that SARS-CoV-2-infected people have lower expression levels of TMPRSS2 than healthy individuals and the people with other viral acute respiratory illnesses. Moreover, TMPRSS2 expression levels were positively correlated with the enrichment levels of immune signatures in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients. Collectively, these data indicate that SARS-CoV-2-infected patients have weaker immune responses than the people with other viral acute respiratory illnesses. It could partially explain why SARS-CoV-2 infection is more contagious and more likely to result to severe outcomes than most other respiratory viruses. On the other hand, the expression levels of interferon and interleukin, the major members of cytokine storm [18], were negatively correlated with TMPRSS2 expression levels in the lungs. It implies that cytokine storm is more likely to occur in SARS-CoV-2-infected people than in the people with other viral acute respiratory illnesses.
Similar to normal human tissues, TMPRSS2 showed no significant expression difference between males and females and between younger and older people within SARS-CoV-2-infected people. Moreover, the androgen receptor gene AR has a significant positive expression correlation with TMPRSS2 in SARS-CoV-2-infected tissues. It indicates that males have a higher risk to develop into severe illness relative to females with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Moreover, similar to ACE2, both TMPRSS2 gene and protein are highly expressed in male tissues. It suggests that male reproductive system is susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection [21].
This study has several limitations. First, the correlations between TMPRSS2 and other variables, such as immune signatures, are not necessarily causal relationships. Second, the correlations between TMPRSS2 and other variables need to be validated by experiments. Finally, because mRNA expression pattern of TMPRSS2 is not necessarily consistent with its protein expression pattern, the validation of the mRNA-based findings at protein level is worth further investigation.
5. Conclusions
TMPRSS2 is expressed in various human tissues. The lungs and gastrointestinal tissues have the highest TMPRSS2 expression levels. TMPRSS2 expression levels are negatively correlated with the enrichment levels of innate and adaptive immune response signatures in the lungs. TMPRSS2 expression levels are significantly lower in SARS-CoV-2-infected people than in healthy individuals and the people with other viral acute respiratory illnesses. AR and TMPRSS2 has a significant positive expression correlation in SARS-CoV-2-infected tissues. Both TMPRSS2 gene and protein are highly expressed in male tissues. They suggest that males have a higher risk to develop into severe illness relative to females with SARS-CoV-2 infection and that male reproductive system is susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our data provide insights into SARS-CoV-2 infection of various human tissues and the potential mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Funding
This work was supported by the China Pharmaceutical University (grant number 3150120001 to XW).
Availability of data and materials
The GTEx and GEO gene expression profiling datasets for human normal tissues were downloaded from the UCSC Xena project (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/) and the Gene Expression Omnibus (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), respectively.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was waived since we used only publicly available data and materials in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Wenxiu Cao: Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Qiushi Feng: Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Visualization. Xiaosheng Wang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109583.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.COVID-19 Dashboard Johns hopkins university. 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
- 2.Li W., Moore M.J., Vasilieva N., Sui J., Wong S.K., Berne M.A., Somasundaran M., Sullivan J.L., Luzuriaga K., Greenough T.C., Choe H., Farzan M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003;426:450–454. doi: 10.1038/nature02145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Glowacka I., Bertram S., Müller M.A., Allen P., Soilleux E., Pfefferle S., Steffen I., Tsegaye T.S., He Y., Gnirss K., Niemeyer D., Schneider H., Drosten C., Pöhlmann S. Evidence that TMPRSS2 activates the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein for membrane fusion and reduces viral control by the humoral immune response. J. Virol. 2011;85:4122–4134. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02232-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Matsuyama S., Nagata N., Shirato K., Kawase M., Takeda M., Taguchi F. Efficient activation of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein by the transmembrane protease TMPRSS2. J. Virol. 2010;84:12658–12664. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01542-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shulla A., Heald-Sargent T., Subramanya G., Zhao J., Perlman S., Gallagher T. A transmembrane serine protease is linked to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor and activates virus entry. J. Virol. 2011;85:873–882. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02062-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Krüger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.-H., Nitsche A., Müller M.A., Drosten C., Pöhlmann S. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. e278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rahman N., Basharat Z., Yousuf M., Castaldo G., Rastrelli L., Khan H. Virtual screening of natural products against type II transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2), the priming agent of coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Molecules. 2020;25 doi: 10.3390/molecules25102271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li M.Y., Li L., Zhang Y., Wang X.S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9:45. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet (London, England) 2020;395:497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vaarala M.H., Porvari K.S., Kellokumpu S., Kyllönen A.P., Vihko P.T. Expression of transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2 in mouse and human tissues. J. Pathol. 2001;193:134–140. doi: 10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH743>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lin B., Ferguson C., White J.T., Wang S., Vessella R., True L.D., Hood L., Nelson P.S. Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membrane-bound serine protease TMPRSS2. Cancer Res. 1999;59:4180–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Stopsack K.H., Mucci L.A., Antonarakis E.S., Nelson P.S., Kantoff P.W. TMPRSS2 and COVID-19: serendipity or opportunity for intervention? Canc. Discov. 2020;10:779–782. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lonsdale J., Thomas J., Salvatore M., Phillips R., Lo E., Shad S., Hasz R., Walters G., Garcia F., Young N., Foster B., Moser M., Karasik E., Gillard B., Ramsey K., Sullivan S., Bridge J., Magazine H., Syron J., Fleming J., Siminoff L., Traino H., Mosavel M., Barker L., Jewell S., Rohrer D., Maxim D., Filkins D., Harbach P., Cortadillo E., Berghuis B., Turner L., Hudson E., Feenstra K., Sobin L., Robb J., Branton P., Korzeniewski G., Shive C., Tabor D., Qi L., Groch K., Nampally S., Buia S., Zimmerman A., Smith A., Burges R., Robinson K., Valentino K., Bradbury D., Cosentino M., Diaz-Mayoral N., Kennedy M., Engel T., Williams P., Erickson K., Ardlie K., Winckler W., Getz G., DeLuca D., MacArthur D., Kellis M., Thomson A., Young T., Gelfand E., Donovan M., Meng Y., Grant G., Mash D., Marcus Y., Basile M., Liu J., Zhu J., Tu Z., Cox N.J., Nicolae D.L., Gamazon E.R., Im H.K., Konkashbaev A., Pritchard J., Stevens M., Flutre T., Wen X., Dermitzakis E.T., Lappalainen T., Guigo R., Monlong J., Sammeth M., Koller D., Battle A., Mostafavi S., McCarthy M., Rivas M., Maller J., Rusyn I., Nobel A., Wright F., Shabalin A., Feolo M., Sharopova N., Sturcke A., Paschal J., Anderson J.M., Wilder E.L., Derr L.K., Green E.D., Struewing J.P., Temple G., Volpi S., Boyer J.T., Thomson E.J., Guyer M.S., Ng C., Abdallah A., Colantuoni D., Insel T.R., Koester S.E., Little A.R., Bender P.K., Lehner T., Yao Y., Compton C.C., Vaught J.B., Sawyer S., Lockhart N.C., Demchok J., Moore H.F. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013;45:580–585. doi: 10.1038/ng.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kanehisa M., Furumichi M., Tanabe M., Sato Y., Morishima K. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D353–d361. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V.K., Mukherjee S., Ebert B.L., Gillette M.A., Paulovich A., Pomeroy S.L., Golub T.R., Lander E.S., Mesirov J.P. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Langfelder P., Horvath S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinf. 2008;9:559. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B: Methodological. 1995;57:289–300. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Costela-Ruiz V.J., Illescas-Montes R., Puerta-Puerta J.M., Ruiz C., Melguizo-Rodríguez L. SARS-CoV-2 infection: the role of cytokines in COVID-19 disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020;54:62–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hu B., Huang S., Yin L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021;93:250–256. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Smyk W., Janik M.K., Portincasa P., Milkiewicz P., Lammert F., Krawczyk M. COVID-19: focus on the lungs but do not forget the gastrointestinal tract. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2020;50 doi: 10.1111/eci.13276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tian Y., Zhou L.Q. Evaluating the impact of COVID-19 on male reproduction. Reproduction. 2021;161:R37–r44. doi: 10.1530/REP-20-0523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The GTEx and GEO gene expression profiling datasets for human normal tissues were downloaded from the UCSC Xena project (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/) and the Gene Expression Omnibus (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), respectively.