Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the caring scenarios that result in severe depression in caregivers caring for dementia patients.
Patients and Methods
A cross-sectional study with 1111 dementia patients and their caregivers in Taiwan from October 2015 to January 2020 was conducted. Gender, age, type of dementia, clinical dementia rating, walking ability, mood symptoms, behavioral symptoms, and psychological symptoms were the variables from the dementia patients. Age, relation to the patient, employment, type of primary care, frequency of care, mood symptoms, and the score from the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale were the variables from the caregivers. A comprehensive viewpoint of both dementia patients and their caregivers was evaluated by the Apriori algorithm to find the attributes resulting in different caregiving depressions.
Results
Forty-seven rules were found with 18 rules of mild depressive symptomatology, 17 rules of moderate depressive symptomatology, and 12 rules of severe depressive symptomatology. A total of 7 general rules were summarized to be the severe depressive symptomatology. The results showed that an unemployed or retired caregiver with the mood symptoms such as helplessness, anger, emotional liability, or anxiety who took care of AD patients or AD patients with a moderate severity would have severe depression. Increased care frequencies (≥6 days per week) and multiple mood problems from caregivers result in severe depression. The composition of adult children, patients’ aggression, and caregivers’ helplessness as well as the combinations of male patients aged 75–84 years with the caregiver’s mood of helplessness or nervousness and hopelessness were highly associated with severe depression.
Conclusion
For those caring for AD patients, severe depression was associated with the combination of different parameters to constitute each of these seven scenarios. Unlike previous studies which often evaluated one or two variables related to caregiver’s depression, this study provided a more comprehensive viewpoint that enabled the collaborative team to efficiently identify and manage different scenarios by summarizing the rules of caregivers with severe depression from a systematic viewpoint.
Keywords: patient with dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, caregiver, caregiver’s mood, depressive symptomatology, Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale, caring scenario, Apriori algorithm
Introduction
Due to global aging, the number of people with dementia is doubling every 20 years. The costs of dementia to society are very large and have been estimated to exceed 1 trillion US dollars globally in 2020.1 Over 50% of dementia caregivers experience health problems as a consequence of their caring responsibilities.1 In Taiwan, the population of dementia has exceeded 270 thousand in the end of 2017. Due to the increased aging population, the number of people with dementia in Taiwan is on track with international numbers, and is projected to reach 0.32 million and 0.6 million by 2030 and 2050, respectively.2 In 1992, the percentage of the population over the age of 65 years was 6.8% but the number became 14.1% in 2018. With an 8.04% prevalence of all-cause dementia in older Taiwanese in 2014 based on a nationwide cross-sectional survey, the number of persons living with dementia (PLWD) in 2018 was estimated to be 250,000.3
Previous studies have reported that nearly 80% of PLWD were cared for by family members in Western countries, and this phenomenon was similar in Taiwan.4–6 Family caregivers played an important role in caring for patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but the caregiving load often brought the problems in their mental and physical health.7 For dementia caregivers, the prevalence of caregivers’ depression ranged from 30%-83%.8–11
Several factors have been reported to be highly correlated with the caregiver’s depression, including female gender,12 spousal relationship,13,14 living with the patient,12,15,16 caregiver’s relatively poor health status,15,16 higher caregiver’s distress,15–17 and more behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD).18–20 However, no studies have been found to explore the comprehensive viewpoints of dementia patients and caregivers by combining multiple variables attributing to caregivers’ depression in PLWD. Clissett et al21 pointed out that person-centered care would be an ideal approach to care for PLWD from a long-term perspective. In order to have a holistic healthcare, both the individual and the care team for PLWD should be evaluated. Therefore, the relationships between PLWD and caregivers should be combined together to provide comprehensive person-centered care.
The purpose of this study was to assess severe depression in caregivers caring for PLWD. We encompassed variables such as type of dementia, age of caregiver and PLWD, type of primary care, caregiver’s mood, caregiver’s employment, dementia severity, frequency of care, and BPSD by applying the Apriori algorithm to identify possible combinations of attributes that could result in severe caregiver’s depression through a comprehensive viewpoint of both people with dementia and their caregivers.
Patients and Methods
A total of 1629 registered dementia patients in the database of a medical center in Taiwan from October 2015 to January 2020 was used. By removing incomplete data sets containing missing information from one or more columns, 518 data sets were removed and the effective number of PLWD and their caregivers was 1111. In this study, the most recent diagnosis and interview data were used to record the conditions of dementia patients and their caregivers in a timely basis. The clinical trial approval certificate was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Changhua Christian Hospital in Changhua County, Taiwan with the protocol number of CCH IRB 160615. This study used a retrospective study design such that the informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board of Changhua Christian Hospital. The recorded data used in this study had the highest confidentiality and compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The variables assessed for PLWD included gender, age, type of dementia, clinical dementia rating (CDR), walking ability, mood symptoms, behavioral symptoms, and psychological symptoms as shown in Table 1, while the variables assessed for caregivers consisted of age, relation to the patient, employment, type of primary care, frequency of care, mood symptoms, and the score from the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) as shown in Table 2.
Table 1.
Demographic Variables for PLWD
| Variables | Frequency | Percentage | Data Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 413 | 37.2 | 1 |
| Female | 698 | 62.8 | 0 | |
| Age | <65 years old | 55 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 65–74 years old | 166 | 14.9 | 2 | |
| 75–84 years old | 498 | 44.8 | 3 | |
| ≥85 years old | 392 | 35.3 | 4 | |
| Type of dementia | Alzheimer’s disease | 576 | 51.8 | 1 |
| Vascular dementia | 242 | 21.8 | 2 | |
| Mixed dementia | 50 | 4.5 | 3 | |
| Lewy body Disease | 28 | 2.5 | 4 | |
| Parkinson’s disease | 51 | 4.6 | 5 | |
| Alcohol related dementia | 2 | 0.2 | 6 | |
| Frontotemporal dementia | 20 | 1.8 | 7 | |
| Others | 142 | 12.8 | 8 | |
| CDR | Very mild dementia | 401 | 36.1 | 0 |
| Mild dementia | 451 | 40.6 | 1 | |
| Moderate dementia | 184 | 16.6 | 2 | |
| Severe dementia | 75 | 6.8 | 3 | |
| Walking ability | Independent | 676 | 60.8 | 0 |
| Walker or cane | 304 | 27.4 | 1 | |
| Wheelchair | 121 | 10.9 | 2 | |
| Bedridden | 10 | 0.9 | 3 | |
| Mood symptoms (multiple choice) | Pathological crying or laughing | 42 | 3.8 | 1: with the symptom; and 0: without the symptom |
| Phobia | 7 | 0.6 | ||
| Dysthymia | 198 | 17.8 | ||
| Depression | 135 | 12.2 | ||
| Anxiety | 79 | 7.1 | ||
| Worry | 58 | 5.2 | ||
| Anger | 189 | 17.0 | ||
| Irritability | 116 | 10.4 | ||
| Emotional Liability | 116 | 10.4 | ||
| Apathy | 46 | 4.1 | ||
| Behavioral symptoms (multiple choice) | Agitation | 39 | 3.5 | |
| Screaming | 0 | 0 | ||
| Curse | 32 | 2.9 | ||
| Akathisia | 30 | 2.7 | ||
| Wandering | 15 | 1.4 | ||
| Pacing | 0 | 0 | ||
| Nighttime behavior | 80 | 7.2 | ||
| Akinesia | 50 | 4.5 | ||
| Shadowing | 10 | 0.9 | ||
| Aggression (verbal/body) | 49 | 4.4 | ||
| Aberrant motor behavior (stereotype) | 22 | 2.0 | ||
| Disinhibition | 0 | 0 | ||
| Psychological symptoms (multiple choice) | Delusion | 223 | 20.1 | |
| Hallucination | 142 | 12.8 | ||
| Misidentification | 74 | 6.7 | ||
Abbreviation: CDR, clinical dementia rating.
Table 2.
Demographic Variables for Caregivers
| Variables | Frequency | Percentage | Data Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <50 years old | 274 | 24.7 | 1 |
| 50–59 years old | 391 | 35.2 | 2 | |
| 60–69 years old | 218 | 19.6 | 3 | |
| ≥70 years old | 228 | 20.5 | 4 | |
| Relation to the patient | Spouse | 290 | 26.1 | 1 |
| Partner | 3 | 0.3 | 2 | |
| Child | 619 | 55.7 | 3 | |
| Brothers/sisters | 8 | 0.7 | 4 | |
| Other relatives | 191 | 17.2 | 5 | |
| Employment | Unemployed or retired | 512 | 46.1 | 0 |
| Employed | 599 | 53.9 | 1 | |
| Type of primary care | Sole caregiver | 351 | 31.6 | 1 |
| Shared caregiving by a caregiver and a foreign worker/household | 411 | 37.0 | 2 | |
| Shared caregiving by different relatives | 22 | 2.0 | 3 | |
| Caregiving by a foreign worker | 153 | 13.8 | 4 | |
| Other | 174 | 15.6 | 5 | |
| Frequency of care | 1–2 days per week | 105 | 9.5 | 1 |
| 3–5 days per week | 110 | 9.9 | 2 | |
| ≥6 days per week | 896 | 80.6 | 3 | |
| Caregiver’s mood (multiple choice) | Helplessness | 964 | 86.8 | 1: with the mood; and 0: without the mood |
| Loneliness | 1074 | 96.7 | ||
| Anxiety | 963 | 86.7 | ||
| Frustration | 1015 | 91.4 | ||
| Nervousness | 895 | 80.6 | ||
| Anger | 901 | 81.1 | ||
| Sadness | 1066 | 95.9 | ||
| Emotional liability | 1032 | 92.9 | ||
| Troublesome | 920 | 82.8 | ||
| Hopelessness | 966 | 86.9 | ||
| Caregiver’s depression | No depressive symptomatology | 758 | 68.2 | 1: applied to a particular depression; and 0: otherwise |
| Mild depressive symptomatology | 145 | 13.1 | ||
| Moderate depressive symptomatology | 128 | 11.5 | ||
| Severe depressive symptomatology | 80 | 7.2 | ||
The presence of BPSD was assessed by psychologists or trained nursing case managers of the collaborative team members in this medical center. All of the BPSD in the neuropsychiatric inventory were used, such as delusion, hallucination, anxiety, irritability, agitation, aggression, aberrant motor activity, and disinhibition. Please refer to Table 1 for the detailed information of mood, behavioral and psychological symptoms.22 Other abnormal behaviors including wandering, pathological crying or laughing, cursing others, akathisia, and akinesia were also evaluated by nursing case managers. New case managers received standardized training in the first month in order to collect data correctly and learn how to form an individualized care plan. Caregiver’s depression was evaluated by the CES-D.23 Both the Chinese Health Questionnaire (CHQ-12) and the Brief Symptom Rating Scale (BSRS-5), which are short, self-administered screening tools for general mental health, were applied to assess the caregiver’s mood.24,25 When caregivers felt worried and nervous, easily felt angry, felt low or sad, or felt that it was difficult to catch up with others, the terms of nervousness, anger, sadness, or frustration are defined in Table 2, respectively. In addition, when caregivers had the feeling of unable to get along with families and friends, loss of confidence or a feeling of helplessness, tension or anxious, discourage or troublesome about family, and hopeless in life were defined as loneliness, helplessness, anxiety, troublesome, and hopelessness, respectively.24 In contrast, somatic symptoms including feeling paresthesia, palpitation, chest tightness, or insomnia in the CHQ-1224 were not used in this study because those symptoms were difficult to distinguish from other diseases. Moreover, if a caregiver had rapid, exaggerated changes in the mood assessed by the collaborative team members, emotional liability was chosen.
A two-point scale was applied in PLWD’s mood symptoms and BPSD and the caregiver’s mood (1 if the symptom/mood was applied; 0 if not). Additionally, caregiver’s depression, as assessed by the CES-D, was classified into four categories based on numerical scores from 0 to 60: no depressive symptomatology (0 point), mild depressive symptomatology (1–15 points), moderate depressive symptomatology (16–23 points), and severe depressive symptomatology (24–60 points). The stratification was based on a previous report to reveal the standard cut-offs of CES-D of ≥16 and ≥24 for “possible depression” and “probable depression”, respectively.26 A value of 1 was given to a particular category of a caregiver’s depression, while a value of zero was assigned to the other three categories.
Most of PLWD in Table 1 were female (62.8%) with Alzheimer’s disease (51.8%), aged 75 years or older (80.1%), and had mild dementia (CDR=1, 40.6%). The majority of the patients could either walk independently (60.8%) or use a walker or cane (27.4%). The age of the caregivers was distributed across four age groups, and children (55.7%) and spouses (26.1%) were the major forces to care PLWD. Sole caregiver (31.6%) and shared caregiving by a caregiver and a foreign worker/household (37.0%) were the two major types of primary care. Frequency of care ≥6 days per week was the most (80.6%). Additionally, caregiver’s depression mainly fell into the category of no depressive symptomatology (68.2%).
The aim of the study was to find the associations among PLWD, caregivers, and the caregiver’s depression levels. In other words, this study intended to find attribute combinations (scenarios) resulting in the severe depressive symptomatology for each caregiver. Association rules using “If antecedent, then consequent” to generate rules enables the decision makers to identify statistical correlations among a group of attributes.27,28 The Apriori algorithm, which has been applied in dementia-related studies, was employed in this study to find statistical associations between any of the attributes by satisfying both minimum support and confidence threshold values along with lift >1.6,7,29–33
The definitions of support, confidence, and lift are depicted as below.6,29,32,33 The support of A ⇒ B calculates the percentage of transactions containing both A and B in the database depicted in Equation (1):
 |
(1) |
The confidence of A ⇒ B evaluates the accuracy of the rule by computing the percentage of transactions containing A and also containing B simultaneously in the database depicted in Equation (2):
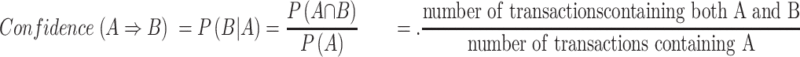 |
(2) |
Lift defined in Equation (3) is to evaluate the relationship between A and B. A lift value of one indicates A and B are independent such that no rules will be found. When a lift value is larger than one, A and B are dependent and correlated positively.
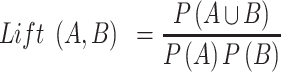 |
(3) |
The IBM SPSS modeler 14.1 was the software package to perform the Apriori algorithm. Tables 1 and 2 provide the notations in terms of numerical values for PLWD and caregivers, respectively. The input variables for antecedents included gender, age, type of dementia, CDR, walking ability, mood symptoms (10 types), behavioral symptoms (11 types), and psychological symptoms (3 types) from PLWD as well as age, relation to the patient, employment, type of primary care, frequency of care, and caregiver’s mood (10 types) from caregivers. Caregiver’s depression (4 types) was the input variables for the consequent. Due to the heterogeneous data, the minimum support and minimum confidence were set to 2% and 80%, respectively, along with a lift >1.
Results
In the beginning, 390 rules were found by the Apriori algorithm. However, those rules which belonged to no depressive symptomatology (CES-D=0) and did not provide useful information to identify caregivers with severe depression. Therefore, the 758 data sets containing CES-D=0 were removed. That is, there were 353 data sets left containing CES-D=1, CES-D=2, and CES-D=3. The Apriori algorithm was performed again with support of 2%, confidence of 80%, and lift >1. In doing so, 47 rules were found, with 18 rules of mild depressive symptomatology, 17 rules of moderate depressive symptomatology, and 12 rules of severe depressive symptomatology. The rules of mild depressive symptomatology and moderate depressive symptomatology are summarized in the Appendix. Table 3 lists the detailed information of the severe depressive symptomatology including antecedents, number of the cases in the database, support, confidence, and lift.
Table 3.
Twelve Rules with CES-D=3
| Rule no. | Antecedent | No. of the Cases in the Database | Support (%) | Confidence (%) | Lift |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Relation to the patient: Child Behavioral symptoms of PLWD: Aggression Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness |
8 | 2.27 | 87.50 | 3.86 |
| 2 | CDR of PLWD: Moderate dementia Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety |
8 | 2.27 | 87.50 | 3.86 |
| 3 | Age of PLWD: 75–84 years Gender of PLWD: Male Caregiver’s mood: Nervousness Caregiver’s mood: Hopelessness |
8 | 2.27 | 87.50 | 3.86 |
| 4 | Age of PLWD: 75–84 years Type of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease Age of Caregiver: 50–59 years Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness |
8 | 2.27 | 87.50 | 3.86 |
| 5 | Type of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease Caregiver’s employment: Unemployed or retired Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety Caregiver’s mood: Emotional liability |
8 | 2.27 | 87.50 | 3.86 |
| 6 | Type of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease Type of primary care: Sole caregiver Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety Caregiver’s mood: Anger Caregiver’s mood: Emotional liability |
8 | 2.27 | 87.50 | 3.86 |
| 7 | Type of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease Walking ability of PLWD: Independent Type of primary care: Sole caregiver Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety Caregiver’s mood: Anger Caregiver’s mood: Emotional liability |
8 | 2.27 | 87.50 | 3.86 |
| 8 | CDR of PLWD: Moderate dementia Caregiver’s employment: Unemployed or retired Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness |
10 | 2.83 | 80.00 | 3.53 |
| 9 | Age of PLWD: 75–84 years Type of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety |
10 | 2.83 | 80.00 | 3.53 |
| 10 | Type of dementia: Alzheimer’s disease Caregiver’s employment: Unemployed or retired Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety Caregiver’s mood: Anger Caregiver’s mood: Emotional liability |
10 | 2.83 | 80.00 | 3.53 |
| 11 | Frequency of care: ≥6 days per week Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety Caregiver’s mood: Hopelessness |
10 | 2.83 | 80.00 | 3.53 |
| 12 | Walking ability of PLWD: Independent Frequency of care: ≥6 days per week Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety Caregiver’s mood: Hopelessness |
10 | 2.83 | 80.00 | 3.53 |
Abbreviations: CDR, clinical dementia rating; PLWD, persons living with dementia.
The rules summarized in Table 3 can be interpreted as follows. For instance, in the first rule, a caregiver would have severe depression when the patient cared by his or her child had a behavioral symptom of aggression and the caregiver felt helpless. The second rule expressed that the caregiver would experience severe depression when the caregiver cared the patient with moderate dementia and felt helpless and anxious. That is, when the terms in antecedent in Table 3 were incurred simultaneously, the depressive symptomatology would be severe. These twelve rules in Table 3 can be further summarized into seven general rules with similarities as shown in Table 4. These general rules were composed of different patient-caregiver parameters, including age, gender, type of dementia, dementia severity, relation with patients, frequency of care, and caregiver’s mood.
Table 4.
Seven General Rules Based on 12 Rules with CES-D=3
| General Rule | Original rule | Antecedent | Consequent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | Type of dementia: AD Type of primary care: Sole caregiver Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety, Anger, and Emotional liability |
CES-D=3 |
| 7 | Type of dementia: AD Walking ability of PLWD: Independent Type of primary care: Sole caregiver Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety, Anger, and Emotional liability |
||
| 2 | 4 | Type of dementia: AD Age of PLWD: 75–84 years Age of caregiver: 50–59 years Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness |
CES-D=3 |
| 9 | Type of dementia: AD Age of PLWD: 75–84 years Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness and Anxiety |
||
| 3 | 5 | Type of dementia: AD Caregiver’s employment: Unemployed or retired Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness, Anxiety, and Emotional liability |
CES-D=3 |
| 10 | Type of dementia: AD Caregiver’s employment: Unemployed or retired Caregiver’s mood: Anxiety, Anger, and Emotional liability |
||
| 4 | 2 | CDR of PLWD: Moderate dementia Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness and Anxiety |
CES-D=3 |
| 8 | CDR of PLWD: Moderate dementia Caregiver’s employment: Unemployed or retired Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness |
||
| 5 | 11 | Frequency of care: ≥6 days per week Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness, Anxiety, and Hopelessness |
CES-D=3 |
| 12 | Walking ability of PLWD: Independent Frequency of care: ≥6 days per week Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness, Anxiety, and Hopelessness |
||
| 6 | 1 | Relation to the patient: Child Behavioral symptoms of PLWD: Aggression Caregiver’s mood: Helplessness |
CES-D=3 |
| 7 | 3 | Age of PLWD: 75–84 years Gender of PLWD: Male Caregiver’s mood: Nervousness and Hopelessness |
CES-D=3 |
Abbreviations: CDR, clinical dementia rating; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; PLWD, persons living with dementia.
The first general rule containing the original 6th and 7th rules showed that AD patients cared by a sole caregiver who felt anxiety, anger, and emotional liability was highly correlated with severe depression. In addition to the above scenario, if AD patients could walk independently, the odds of severe depression in the caregiver was also high. The second general rule containing the original 4th and 9th rules indicated that the caregiver who felt helpless in caring AD patients aged 75–84 years had higher odds of severe depression. The third general rule expressed that the odds of caregiver’s depression was increased when the caregiver was unemployed or retired with some mood problems such as helplessness, anger, emotional liability, or anxiety developed in caring AD patients. The fourth general rule depicted that unemployed or retired caregivers caring for PLWD with moderate severity as well as experiencing some mood states (helplessness and anxiety) were associated with severe depression. The fifth general rule showed that increased care frequencies (≥6 days per week) in caregivers who experienced multiple mood problems (helplessness, hopelessness, and anxiety) were highly correlated with severe depression. Additionally, independent walking ability added the odds of severe depression. The composition of adult children, patients’ aggression, and caregivers’ helplessness was associated with severe depression in the sixth general rule. Finally, severe depression in the caregiver was highly associated with the combinations of male PLWD aged 75–84 years and the caregiver’s mood (helplessness or nervousness and hopelessness).
Discussion
The study found that caregivers experienced severe depression with the following scenarios. AD patients were cared by a caregiver solely who had mood symptoms of anxiety, anger, and emotional liability. AD patients aged 75–84 years were cared by a caregiver who felt helpless. An unemployed or retired caregiver with the mood symptoms such as helplessness, anger, emotional liability, or anxiety took care of AD patients or PLWD with CDR=2. Increased care frequencies (≥6 days per week) and multiple mood problems (helplessness, hopelessness, and anxiety) from caregivers result in severe depression scores. The composition of adult children, patients’ aggression, and caregivers’ helplessness as well as the combinations of male patients aged 75–84 years and the caregiver’s mood (helplessness or nervousness and hopelessness) were highly associated with severe depression.
Previous studies such as Cheng34 and Schulz and Williamson35 reported that more social support for caregivers were related to less depression. Etters et al36 pointed out caregiver’s gender, relationship to the patient, and personal characteristics were the factors that might influence the impact of the caregiving experience. In a Korean community study, cohabited family caregiver with dementia patients was significantly associated with depression, and the significance remained high especially in male caregivers in a low-income family and female caregivers in a high-income family.37 However, caregiver’s gender was not an important factor related to depression in our study.
Cheng34 identified that neuropsychiatric symptoms were the most predictive variable of caregivers’ depression regardless of types of dementia. Black and Almeida38 and Pinquart and Sorensen39 summarized that associations between the BPSD and negative outcomes for caregivers of AD patients included the increased caregiver’s burden, stress, or depressive symptoms. However, few studies focused on the psychological state or even mood disturbance of caregivers related to depression. The mood impact may precede the development of depression. Bowen et al40 found that not only low or high moods but also mood instability were highly correlated with depression. Helplessness, anger, and emotional liability may be a proxy of depression. Therefore, more attention is needed for the mood change in caregivers.
The studies regarding the dementia severity and caregiver’s depression are inconsistent. For instance, Omranifard et al41 reported that the dementia severity was highly related to caregiver’s depression but no significant association between patients’ dementia severity and their caregivers’ depression scores was found statistically.42 In our study, the fourth general rule indicated that unemployed or retired caregivers in caring PLWD with moderate severity as well as experiencing some mood states (helplessness and anxiety) were associated with severe depression. This implied that caregivers with emotional problems in caring PLWD with a moderate severity may be prone to having severe depression.
Increased care frequencies (≥6 days per week) in caregivers who experienced multiple mood problems (helplessness, hopelessness, and anxiety) were highly correlated with severe depression. Additionally, PLWD’s independent walking ability added the odds of severe depression. In contrast to our findings, Covinsky et al13 found that more dependency in activities of daily living increased the risk of caregiver depression by 1.55-fold. In our study, it was possible that these patients wandered around without purposes to result in an increased caregiving burden, which in turn led to more depressive symptomatology.16
Determining specific BPSD that increases caregivers’ depression may decrease the caregiving burden and can prevent the development of depression in caregivers. BPSDs include many varieties of patient behaviors, and aggression has been one of the most frequently cited symptoms associated with caregiver’s depression.20 Other BPSDs, such as patient’s depression, psychosis, and agitation, were also reported in multiple studies.20 For each individual BPSD, agitation/aggression, anxiety, nighttime behavior disturbances, irritability/lability, and hallucinations were the five leading symptoms significantly associated with caregiver’s depression.10 However, no symptom was found as having a negative impact on caregiver’s depression consistently. In our study, adult children experiencing helplessness in tackling the aggression in PLWD had more odds of severe depression. Similar to our study, Choi et al18 reported that agitation alone was not correlated with caregiver’s depression, multiple symptom clusters had a positive correlation with caregiver’s depression.
Female caregivers had more depressive symptoms than male caregivers.12,38 In a cohort of 335 dyads of wife-husband couples, the caregiving burden scale was higher among female than male caregivers statistically though depression between male and female caregivers was not statistically significant.43 In a systematic review including 22 studies, the physical and mental health of family caregivers on gender differences were inconsistent.44 In our study, if a caregiver felt nervous and hopeless in caring male PLWD aged 75–84 years, the possibility of severe depression in caregivers should be highlighted.
Clissett et al21 have suggested person-centered care as the ideal approach to care for PLWD because the person-centered approach is to identify the interconnected relationships between PLWD and their caregivers and to respect personhood as a respected and valued social being despite cognitive impairment.45 The value of our study was to group together different scenarios leading to caregiver’s depression systematically that enables a collaborative care team to provide more efficient care for AD patients as well as PLWD.
The strength of this study was that it provided a comprehensive viewpoint to combine a wide variety of variables into consideration. The Apriori algorithm was employed to combine various variables and to identify the association between particular conditions and severe caregiver depression. In doing so, the collaborative team can understand the care needs more efficiently and lessen the severity of the caregiving depression. Unlike previous studies which often evaluated one or two variables related to caregiver’s depression such as Cheng,34 De Fazio et al46 and Jang et al,37 our study can provide a more comprehensive scenario to reduce caregiver’s depression from a systematic viewpoint.
There are several limitations in our study. First, it was a cross-sectional study; thus, we could not reach conclusions regarding the causality. Second, though our study had a relatively large sample size, it would be recommended to have a much larger sample size in order to have more generalized findings. Third, our study was carried out in a medical center, and these results may not be generalized to other settings such as primary care or residential care.
Conclusion
This study identified associations between PLWD and their caregivers by combining various variables in order to find attributes resulting in severe depression scores of caregivers from a comprehensive viewpoint. This study showed that caregiver’s severe depression was associated with seven general rules by the combination of different parameters to constitute each particular scenario. Unlike previous studies which often evaluated one or two variables related to caregiver’s depression, our study provided a more comprehensive viewpoint that enabled the collaborative team to efficiently identify and manage different scenarios for reducing the caregiver’s depression from a systematic viewpoint.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Alzheimer’s Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2020 Design, Dignity, Dementia: Dementia-Related Design and the Built Environment, Volume I. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wu Y-T, Lee H-Y, Norton S, et al. Prevalence studies of dementia in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e66252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066252 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sun Y, Lee H-J, Yang S-C, et al. A nationwide survey of mild cognitive impairment and dementia, including very mild dementia, in Taiwan. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fuh JL, Wang SJ, Liu HC, et al. The caregiving burden scale among Chinese caregivers of Alzheimer patients. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1999;10(3):186–191. doi: 10.1159/000017118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Haley WE. The family caregiver’s role in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1997;48(5 Suppl 6):S25–29. doi: 10.1212/wnl.48.5_suppl_6.25s [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yan GJ, Wang WF, Jhang KM, et al. Association between patients with dementia and high caregiving burden for caregivers from a medical center in Taiwan. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2019;12:55–65. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S187676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen YA, Chang CC, Wang WF, et al. Association between caregivers’ burden and neuropsychiatric symptoms in female patients with Alzheimer’s disease with varying dementia severity. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2021;14:929–940. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S298196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Buckwalter KC, Gerdner L, Kohout F, et al. A nursing intervention to decrease depression in family caregivers of persons with dementia. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 1999;13(2):80–88. doi: 10.1016/s0883-9417(99)80024-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Clark PC. Effects of individual and family hardiness on caregiver depression and fatigue. Res Nurs Health. 2002;25(1):37–48. doi: 10.1002/nur.10014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Huang SS, Lee MC, Liao YC, et al. Caregiver burden associated with behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) in Taiwanese elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012;55(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2011.04.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schulz R, McGinnis KA, Zhang S, et al. Dementia patient suffering and caregiver depression. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2008;22(2):170–176. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0b013e31816653cc [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mahoney R, Regan C, Katona C, et al. Anxiety and depression in family caregivers of people with Alzheimer disease: the LASER-AD study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2005;13(9):795–801. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajgp.13.9.795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Covinsky KE, Newcomer R, Fox P, et al. Patient and caregiver characteristics associated with depression in caregivers of patients with dementia. J Gen Intern Med. 2003;18(12):1006–1014. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2003.30103.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zivin K, Christakis NA. The emotional toll of spousal morbidity and mortality. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15(9):772–779. doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e318050c9ae [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Beeson R, Horton-Deutsch S, Farran C, et al. Loneliness and depression in caregivers of persons with Alzheimer’s disease or related disorders. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2000;21(8):779–806. doi: 10.1080/016128400750044279 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Clyburn LD, Stones MJ, Hadjistavropoulos T, et al. Predicting caregiver burden and depression in Alzheimer’s disease. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2000;55(1):S2–13. doi: 10.1093/geronb/55.1.s2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Takahashi M, Tanaka K, Miyaoka H. Depression and associated factors of informal caregivers versus professional caregivers of demented patients. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005;59(4):473–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2005.01401.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Choi SSW, Budhathoki C, Gitlin LN. Impact of three dementia-related behaviors on caregiver depression: the role of rejection of care, aggression, and agitation. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019;34(7):966–973. doi: 10.1002/gps.5097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huang SS, Liao YC, Wang WF. Association between caregiver depression and individual behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in Taiwanese patients. Asia Pac Psychiatry. 2015;7(3):251–259. doi: 10.1111/appy.12175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ornstein K, Gaugler JE. The problem with “problem behaviors”: a systematic review of the association between individual patient behavioral and psychological symptoms and caregiver depression and burden within the dementia patient-caregiver dyad. Int Psychogeriatr. 2012;24(10):1536–1552. doi: 10.1017/S1041610212000737 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Clissett P, Porock D, Harwood RH, Gladman JR. The challenges of achieving person-centred care in acute hospitals: a qualitative study of people with dementia and their families. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013;50(11):1495–1503. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2013.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, et al. The neuropsychiatric inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology. 1994;44(12):2308–2314. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.12.2308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lewinsohn PM, Seeley JR, Roberts RE, et al. Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) as a screening instrument for depression among community-residing older adults. Psychol Aging. 1997;2(2):277–287. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.12.2.277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chong MY, Wilkinson G. Validation of 30- and 12-item versions of the Chinese Health Questionnaire (CHQ) in patients admitted for general health screening. Psychol Med. 1989;19(2):495–505. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700012526 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen HC, Wu CH, Lee YJ, et al. Validity of the five-item brief symptom rating scale among subjects admitted for general health screening. J Formos Med Assoc. 2005;104(11):824–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in general population. Appl Psyc Meas. 1977;1(3):385–401. doi: 10.1177/014662167700100306 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Han J, Kamber M. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. 2nd ed. New York: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Larose DT. Discovering Knowledge in Data: An Introduction to Data Mining. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jhang KM, Chang MC, Lo TY, et al. Using the Apriori algorithm to classify the care needs of patients with different types of dementia. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2019;13:1899–1912. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S223816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chen WJ, Wang WF, Liu YH, et al. Using Apriori algorithm to explore the influence of pressure from patients with dementia on caregivers from a medical center in Taiwan. J Qual. 2019;26(6):395–418. doi: 10.6220/joq.201912_26(6).0004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lin YS, Wang WF, Liu YH, et al. The study of care targets combination in women with Alzheimer’s disease: a case study in a medical center in central Taiwan. J Qual. 2020;20(1):1–25. doi: 10.6220/joq.202002_27(1).0001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jhang KM, Wang WF, Chang HF, et al. Care needs of community-residing male patients with vascular cognitive impairment. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020;16:2613–2621. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S277303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jhang KM, Wang WF, Chang HF, et al. Characteristics predicting the high caregiver burden in patients with vascular cognitive impairment: using the Apriori algorithm to delineate the caring scenario. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2021;14:1335–1351. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S297204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cheng ST. Dementia caregiver burden: a research update and critical analysis. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2017;19(9):64. doi: 10.1007/s11920-017-0818-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schulz R, Williamson GM. A 2-year longitudinal study of depression among Alzheimer’s caregivers. Psychol Aging. 1991;6(4):569–578. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.6.4.569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Etters L, Goodall D, Harrison BE. Caregiver burden among dementia patient caregivers: a review of the literature. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008;20(8):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00342.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jang SI, Bae HC, Shin J, et al. Depression in the family of patients with dementia in Korea. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2016;31(6):481–491. doi: 10.1177/1533317515628048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Black W, Almeida OP. A systematic review of the association between the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia and burden of care. Int Psychogeriatr. 2004;16(3):295–315. doi: 10.1017/s1041610204000468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pinquart M, Sorensen S. Associations of stressors and uplifts of caregiving with caregiver burden and depressive mood: a meta-analysis. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2003;58(2):112–128. doi: 10.1093/geronb/58.2.p112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bowen R, Peters E, Marwaha S, et al. Moods in clinical depression are more unstable than severe normal sadness. Front Psychiatry. 2017;8:56. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Omranifard V, Haghighizadeh E, Akouchekian S. Depression in main caregivers of dementia patients: prevalence and predictors. Adv Biomed Res. 2018;7:34. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.225924 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Alfakhri AS, Alshudukhi AW, Alqahtani AA, et al. Depression among caregivers of patients with dementia. Inquiry. 2018;55:46958017750432. doi: 10.1177/0046958017750432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Poysti MM, Laakkonen ML, Strandberg T, et al. Gender differences in dementia spousal caregiving. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;2012:162960. doi: 10.1155/2012/162960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xiong C, Biscardi M, Astell A, et al. Sex and gender differences in caregiving burden experienced by family caregivers of persons with dementia: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2020;15(4):e0231848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hanley J. Dawn Brooker and Isabelle Latham, Person-Centred Dementia Care: Making Services Better with the VIPS Framework. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishing; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 46.De Fazio P, Ciambrone P, Cerminara G, et al. Depressive symptoms in caregivers of patients with dementia: demographic variables and burden. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:1085–1090. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S74439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


