Fig. 1.
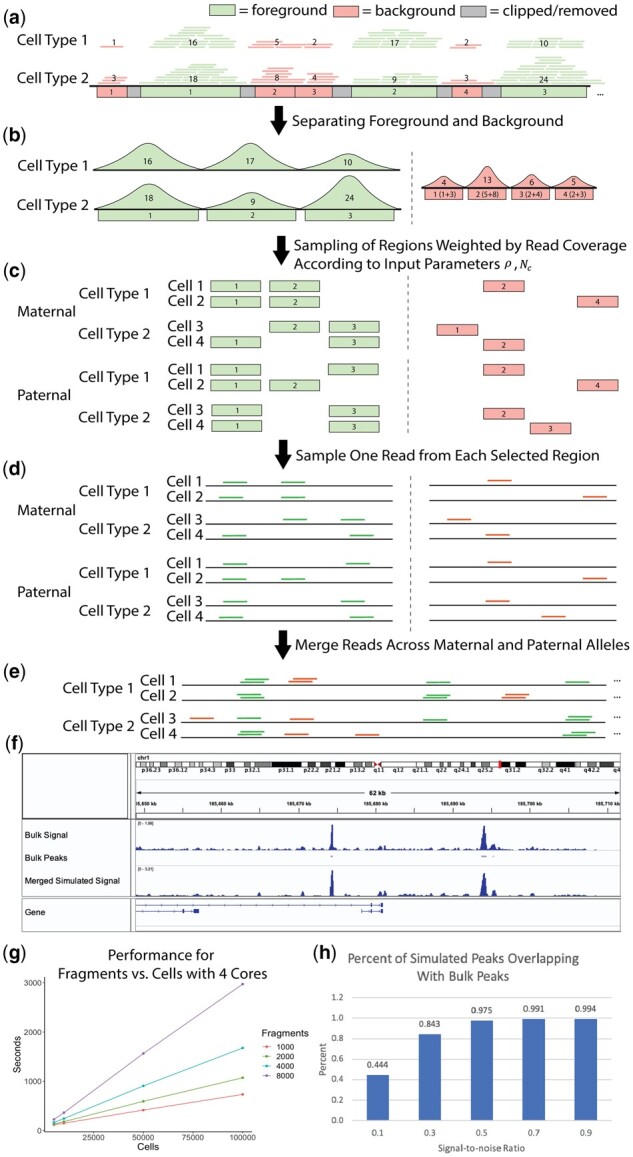
(a) Bulk-tissue ATAC-seq reads are partitioned into foreground and background based on overlap with merged peaks. The number in each region indicates the read coverage. (b) The cell-type-specific foreground reads are separated, and a unified background is created by combining background reads across all cell lines. (c) The regions are sampled without replacement, with the read coverage as weights for the foreground and background, for paternal and maternal alleles. (d) Reads are sampled from the selected regions using a uniform distribution. (e) All sampled reads are combined to form reads covering a cell. (f) chr1 visualization of bulk and simulated () CLP cells is shown in the Integrative Genome Browser. (g) Performance for region number versus cell number is shown for four cores. (h) Percentage of peaks from simulated CLP cells that overlap with CLP bulk peaks is shown, demonstrating the relationship between the signal-to-noise ratio and the cell-type specificity of the simulation
