Abstract
This an interesting case of an asymptomatic 60-year-old postmenopausal patient with an incidental pelvic mass mimicking a pelvic malignancy on imaging. Biopsy revealed findings consistent with polypoid endometriosis. After discontinuation of hormone replacement therapy, the mass showed decrease in size on follow-up imaging. Polypoid endometriosis is a rare but distinct variant of endometriosis with histopathologic features akin to an endometrial polyp. Clinical and imaging features of polypoid endometriosis differ from classic endometriosis. While classic endometriosis predominates in premenopausal women, polypoid endometriosis more commonly affects peri- to postmenopausal women and is associated with the exposure to Tamoxifen or hormone replacement therapy. Imaging features that aid in the differential diagnosis of polypoid endometriosis are a T2 hyperintense polypoid mass with signal characteristics similar to uterine endometrium, a T2 hypointense peripheral rim, contrast enhancement pattern mirroring the enhancement of the uterine endometrium, and lack of diffusion restriction. Radiologists should be familiar with polypoid endometriosis because this clinically and morphologically distinct variant may mimic malignant neoplasms on imaging.
History
A 60-year-old postmenopausal woman was referred to a tertiary cancer center for further work-up of a pelvic mass that was discovered incidentally on pelvic ultrasound performed during a routine gynecological examination.
The patient’s past surgical history was notable for a remote supracervical hysterectomy for symptomatic leiomyomata and resection of benign breast cysts. Her past medical history was unremarkable. Of note, the patient had been on continuous hormonal replacement therapy (Premarin, unconjugated estrogen) for the past ten years. Her routine health screening examinations (i.e., mammography and pap smear) were normal. She reported no symptoms of vaginal bleeding, discharge, hematuria, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits or weight loss.
A bimanual pelvic examination revealed an anteriorly displaced cervical remnant and a palpable pelvic mass in the cul-de-sac posterior to the cervical remnant. A digital rectal examination revealed a firm mass abutting the anterior and lateral rectal wall; the mass was situated approximately 6 cm superior to the anal verge. Laboratory work-up and tumor markers including CA-125 were all within normal limits. Further work-up included MRI of pelvis and flexible proctosigmoidoscopy (see selected images).
Imaging Findings
Axial T2-weighted image from MRI of pelvis showed a lobulated heterogeneous high T2 signal intensity mass that was centered in the cul-de-sac. It was inseparable from the cervical remnant anteriorly and anterior wall of the rectum posteriorly, and possibly involving the rectum (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
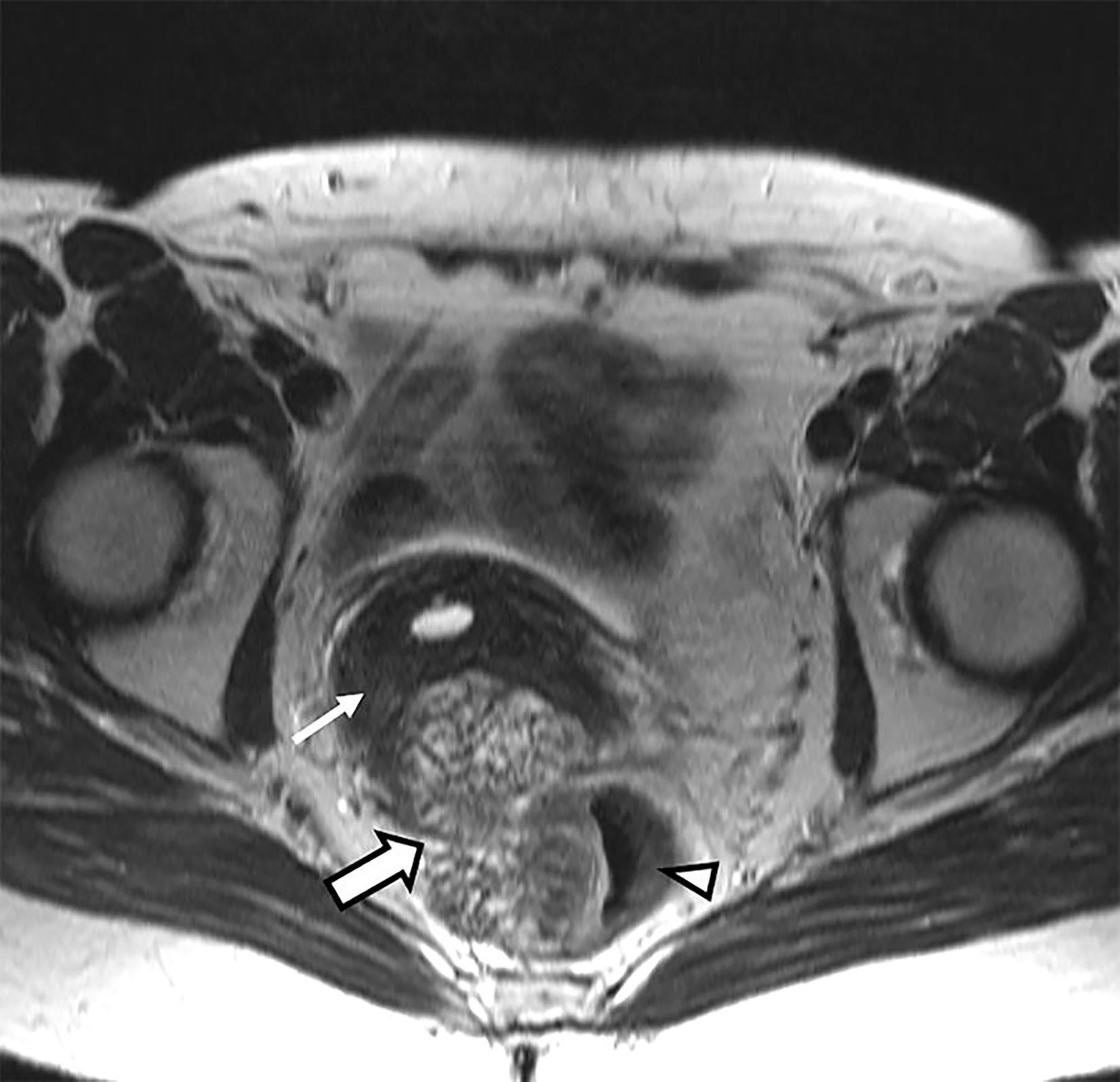
Axial T2-weighted image without fat saturation at the level of the cervix. A lobulated, heterogeneously T2-hyperintense mass (thick arrow) is shown to be centered in the cul-de-sac and inseparable from the cervical remnant (thin arrow) and anterior rectum (arrow head); the latter seems to be invaded by the mass
Coronal T2-weighted image depicted the craniocaudal extent of the mass and demonstrated a low T2 signal intensity rim along its periphery (Fig. 2). The mass was relatively hyperintense on both high b-value axial DWI (Fig. 3) and the corresponding ADC map (Fig. 4). The mean ADC value was 1.4 × 10−3 mm2/s, indicating absent restricted diffusion. The subtraction image from post-contrast axial fat-suppressed T1-weighted imaging (Fig. 5) showed mild heterogeneous enhancement within the mass.
Fig. 2.
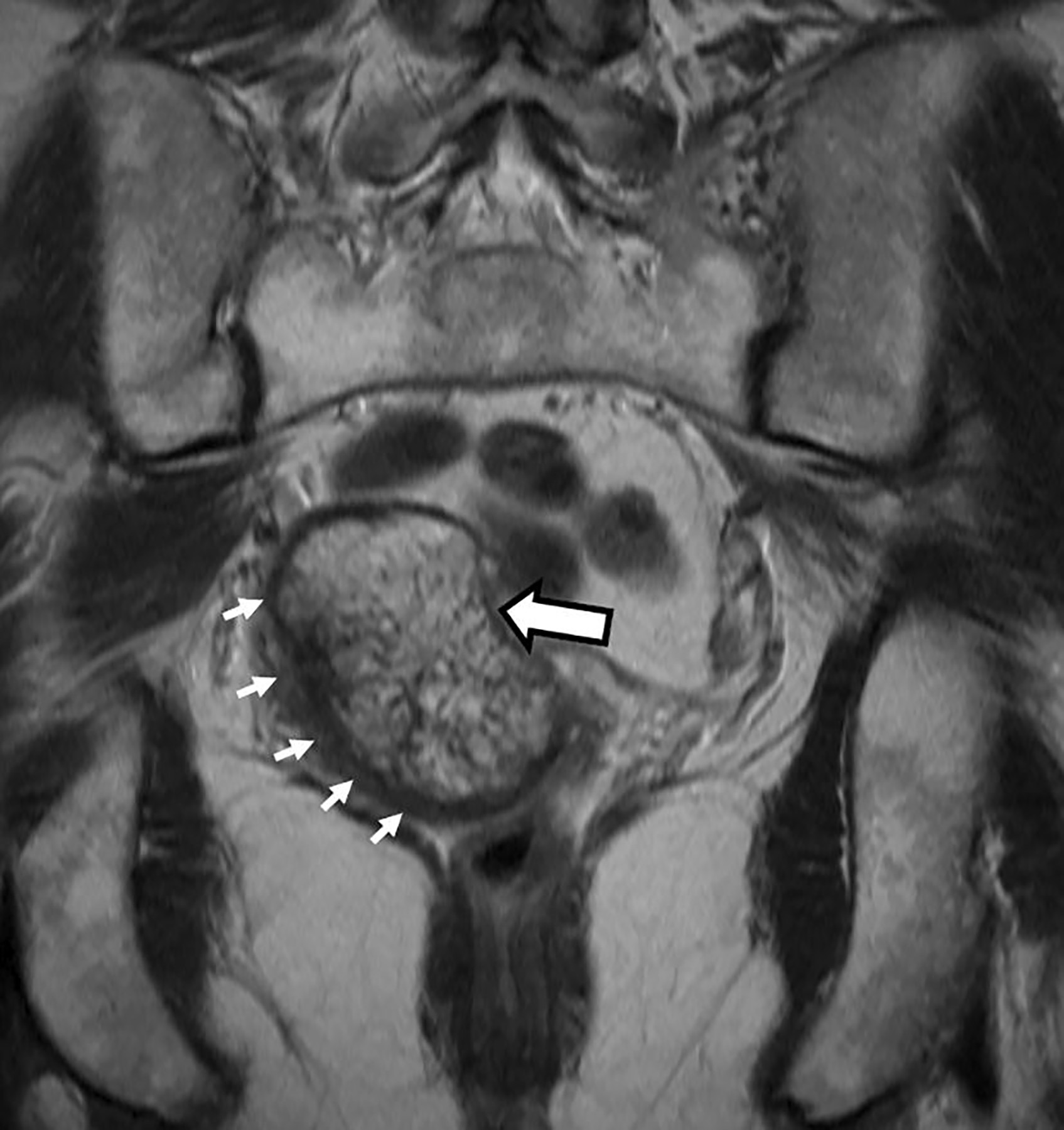
Coronal T2 weighted images. Heterogeneously T2-hyperintense mass (thick arrow) with a T2-hypointense peripheral rim (thin short arrows)
Fig. 3.
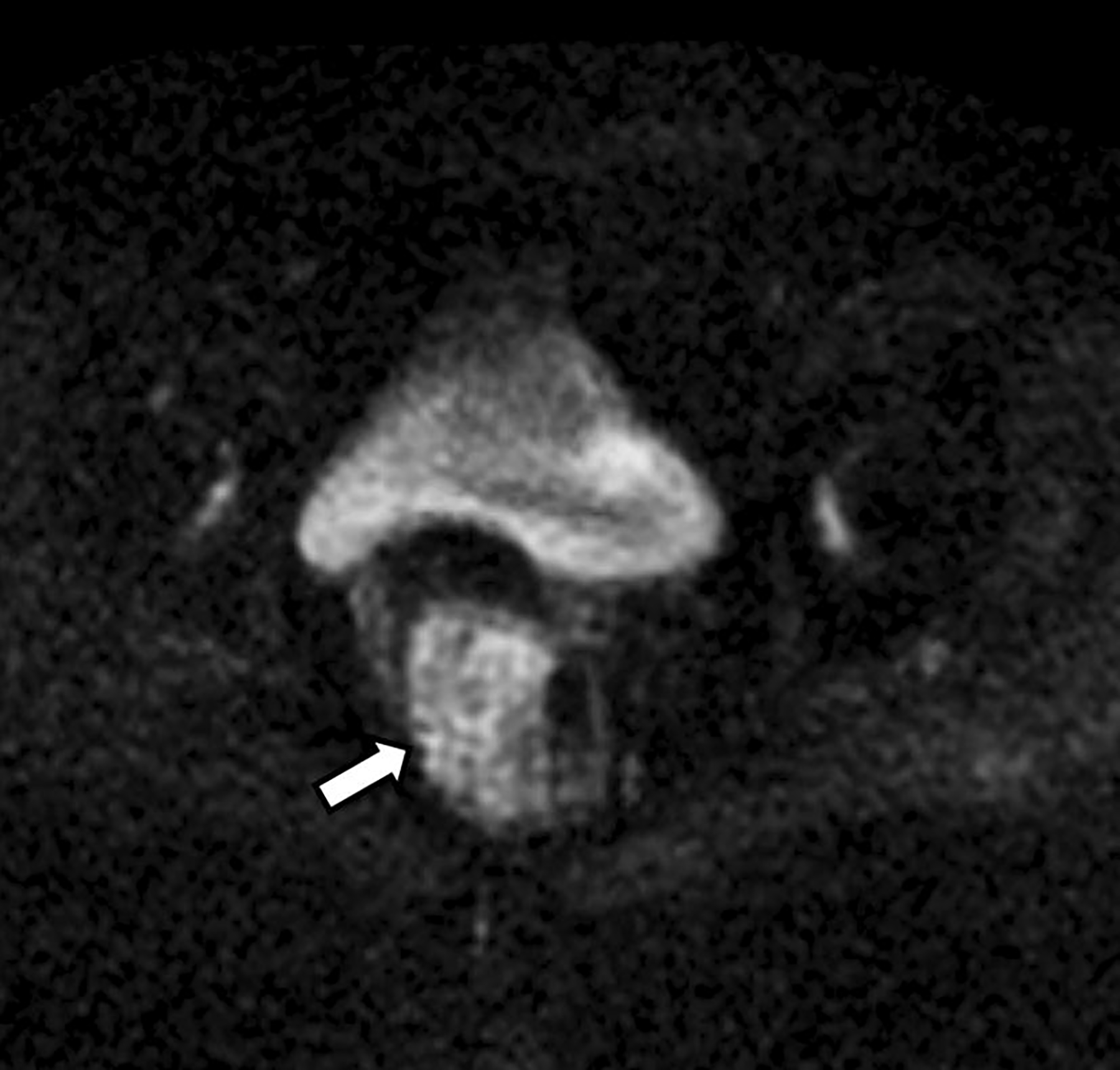
High b-value (b = 800 s/mm2) axial diffusion weighted image. The mass (arrow) is hyperintense on DWI
Fig. 4.
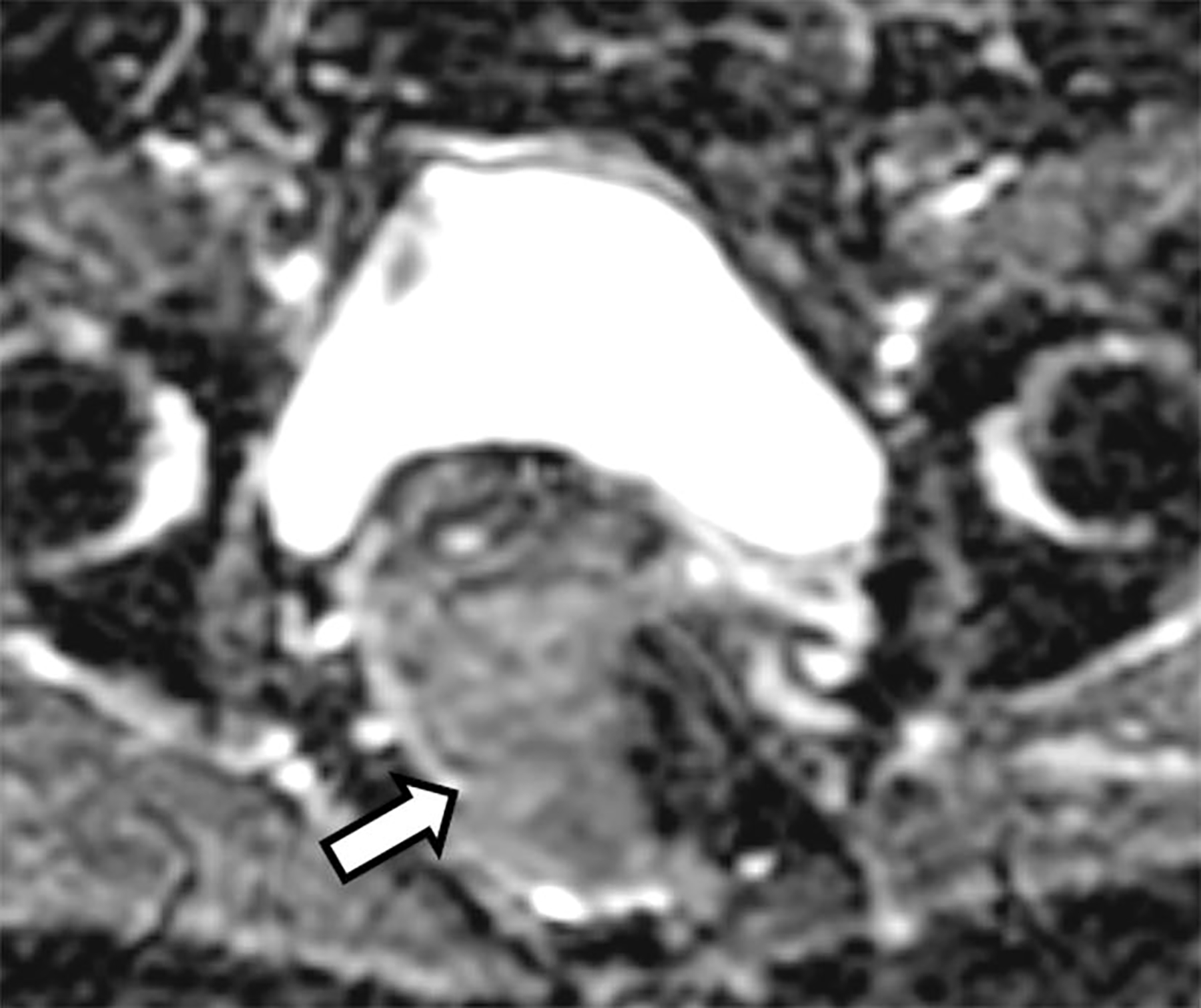
Axial apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map. The mass (arrow) is relatively hyperintense with a mean value of 1.4 × 10−3 mm2/s (measurement not shown)
Fig. 5.
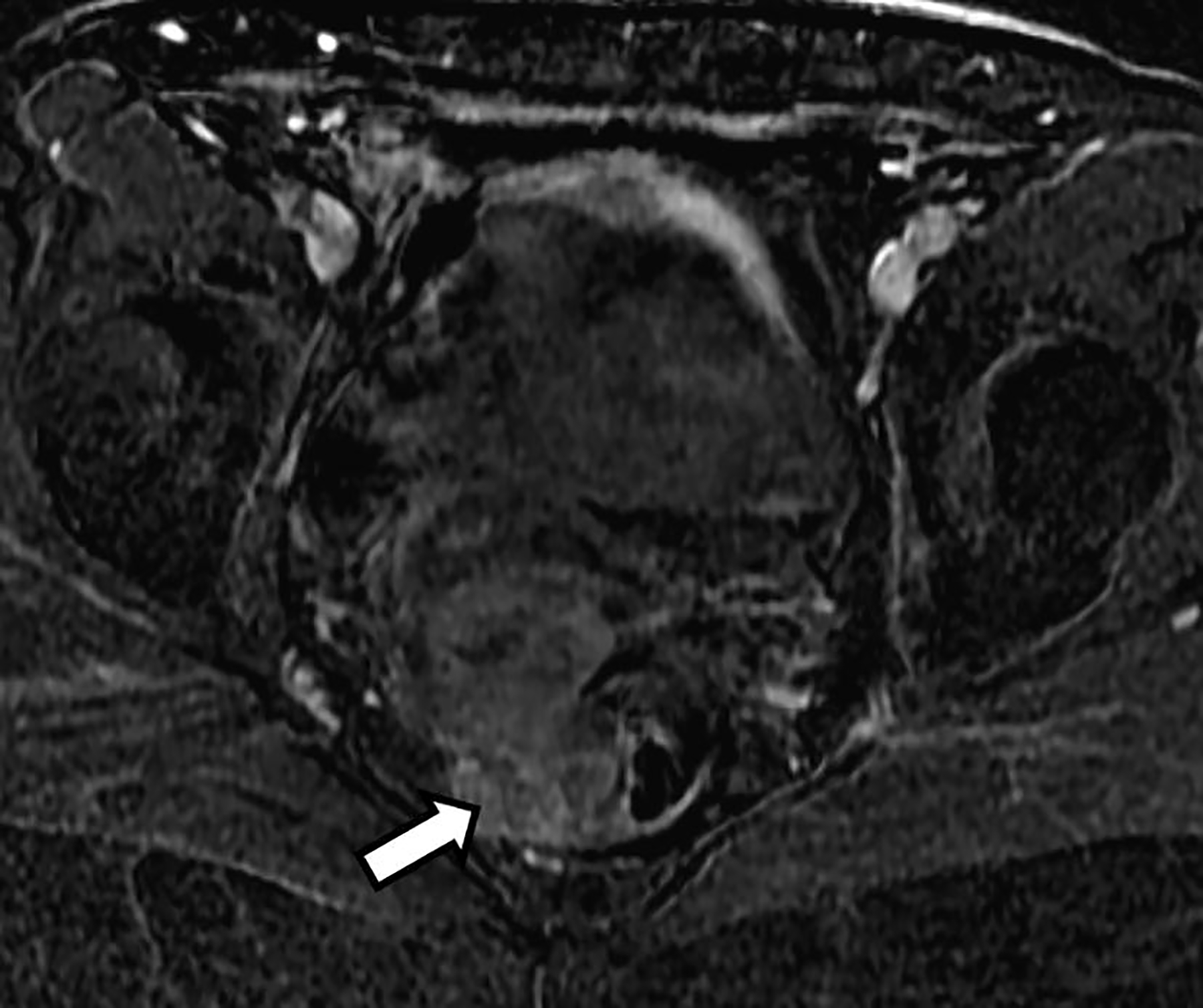
Subtraction image from the axial post contrast 3D T1-weighted fat-suppressed image with fat saturation shows mild heterogeneous contrast enhancement of the mass (arrow)
Flexible proctosigmoidoscopy showed the polypoid mass indenting the rectum. The rectal mucosa appeared relatively normal, indicating that the mass was unlikely to be of primary rectal origin (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
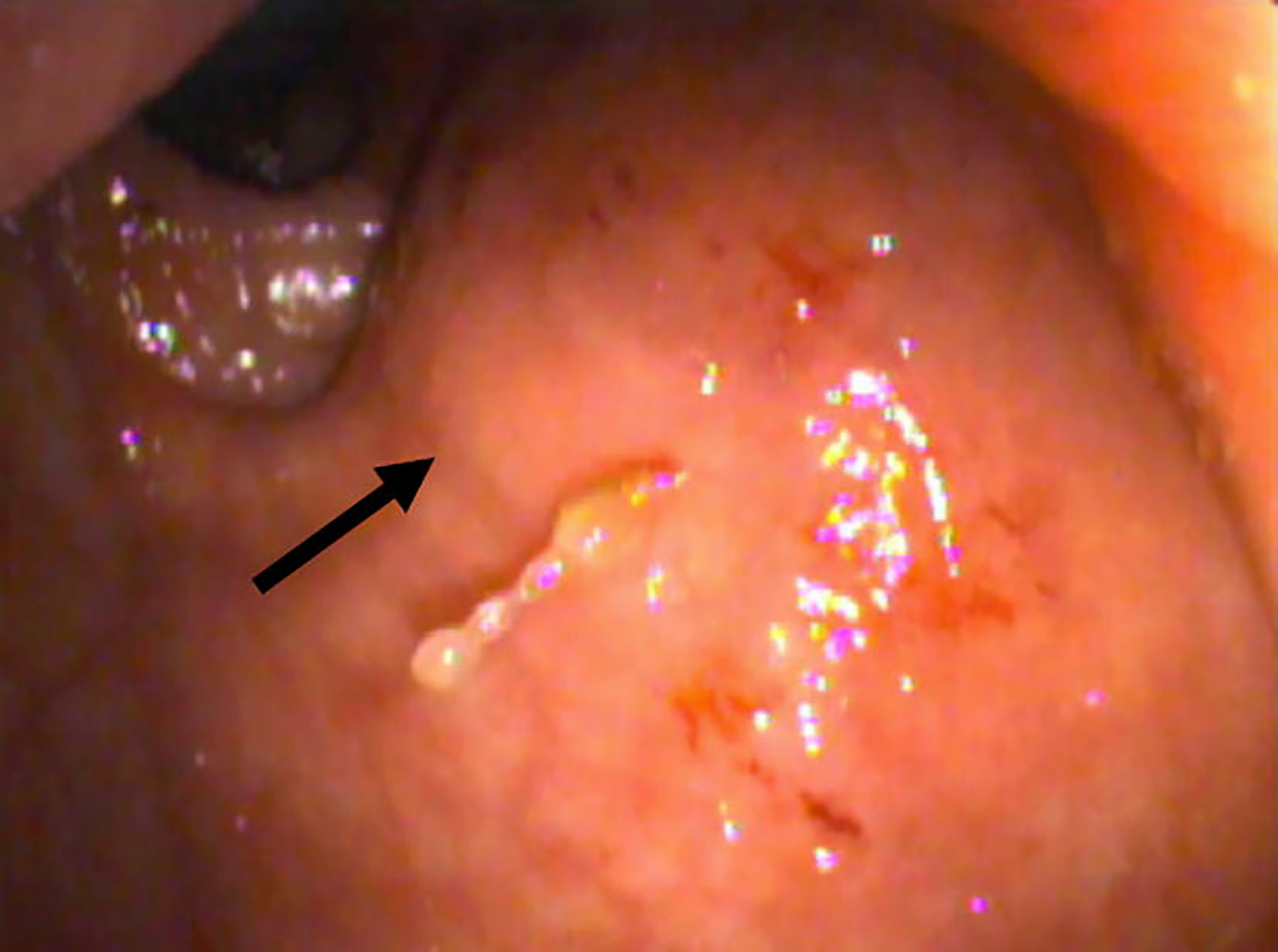
Photograph from flexible proctosigmoidoscopy taken at the level of the mid-rectum shows a round mass indenting the rectum (thick arrow) with relatively normal appearing mucosa
On a 2-[fluorine 18]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG) PET/CT performed for further work-up, the mass demonstrated mild FDG avidity (maximal standard uptake value (SUVmax) of 3.3, liver background mean SUV 2.1) (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7.
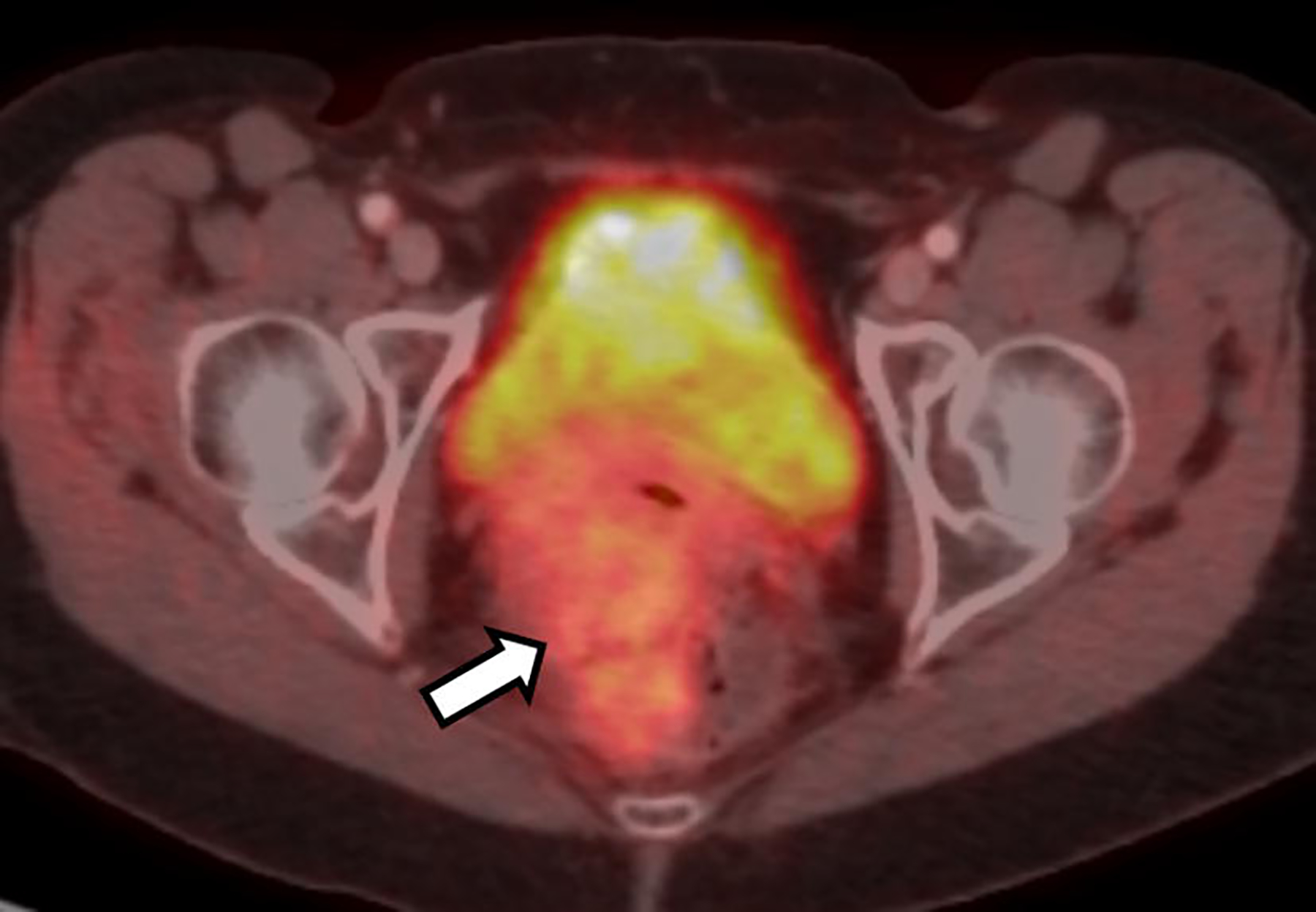
Axial fused FDG-PET/CT image demonstrated mildly increased radiotracer uptake (arrow) in the mass with a maximal SUV of 3.3 (measurement not shown). Note the normal intense radiotracer activity in the partially imaged bladder which corresponds to the excreted radiotracer
Discussion
An asymptomatic 60-year old postmenopausal patient presented with a polypoid pelvic mass that was discovered incidentally at the time of pelvic ultrasound. The mass was centered in the cul-de-sac abutting the cervix anteriorly and rectum posteriorly. It did not clearly originate from either of these organs. The primary diagnostic considerations were malignancy arising from the cervical remnant, endometriosis-associated malignancy (e.g., endometrioid or clear cell carcinoma) or rectal tumor (e.g., mucinous rectal adenocarcinoma or gastrointestinal stroma tumor).
The polypoid mass demonstrated the following key imaging findings: high signal intensity on T2-weighted images, a peripheral low T2 signal intensity rim, lack of diffusion restriction and mild enhancement following intravenous contrast administration. Ascites, peritoneal implants and lymphadenopathy were notably absent. The mass showed mildly increased FDG uptake on FDG-PET/CT.
After the initial inconclusive biopsy during colonoscopy, the mass was biopsied transvaginally, and the histopathology was notable for polypoid fragments of endometrioid glands with squamous metaplasia in a background of endometrial stroma, consistent with polypoid endometriosis (Fig. 8 and 9). The stroma demonstrated positive immunoreactivity for CD10, a known marker of normal endometrial stroma [1].
Fig. 8.
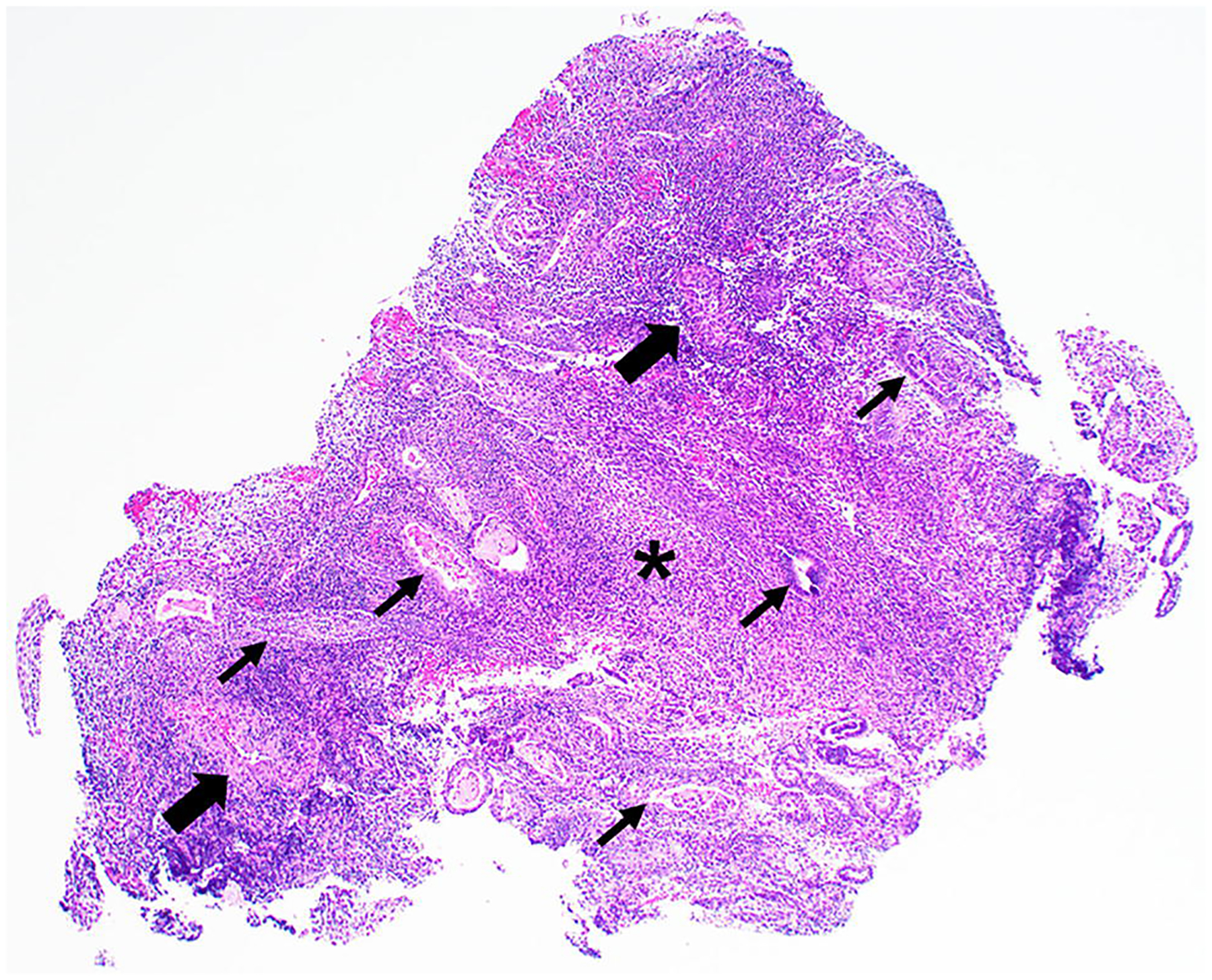
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) image of the transvaginal biopsy specimen at 20× magnification shows a polypoid fragment of endometrial stroma (*) and glands (thin arrows) with thick-walled vessels (thick arrows), resembling an endometrial polyp
Fig. 9.
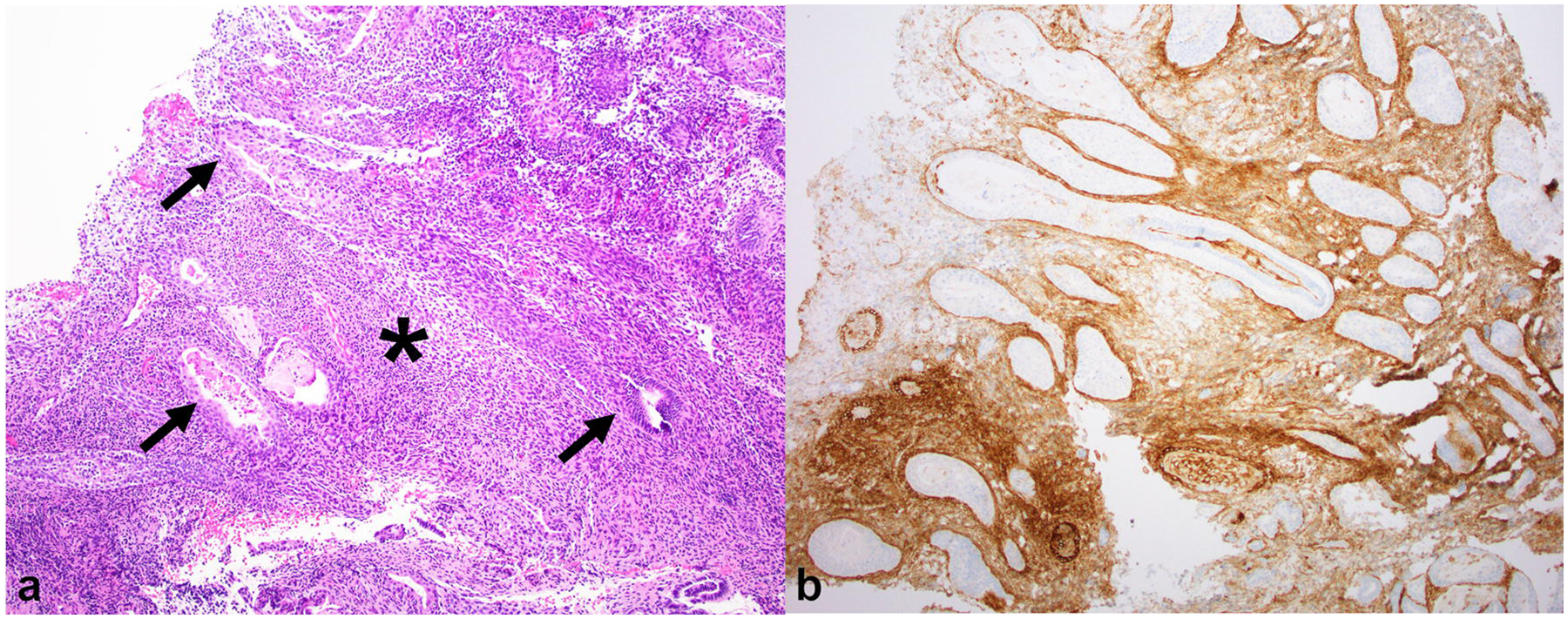
(a) Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) image of the same biopsy specimen as above at 40× magnification shows simple tubular endometrial glands (thin arrows) lined by columnar cells embedded in stroma with ovoid spindle cells (*) resembling proliferative phase endometrium. (b) On CD10 immunohistochemistry, the stroma stains positive, confirming endometrial-type stroma, while the endometrial glands are negative. The unstained glands are irregularly dispersed with focal back-to-back crowding
Given the benign findings at biopsy and the risk of complications that may result from pelvic surgery, the patient and her care team opted for the discontinuation of hormone replacement therapy and active surveillance with imaging. Three months after hormone replacement therapy was stopped, the follow-up MRI showed mild decrease in the size of the pelvic mass (Fig. 10).
Fig. 10.
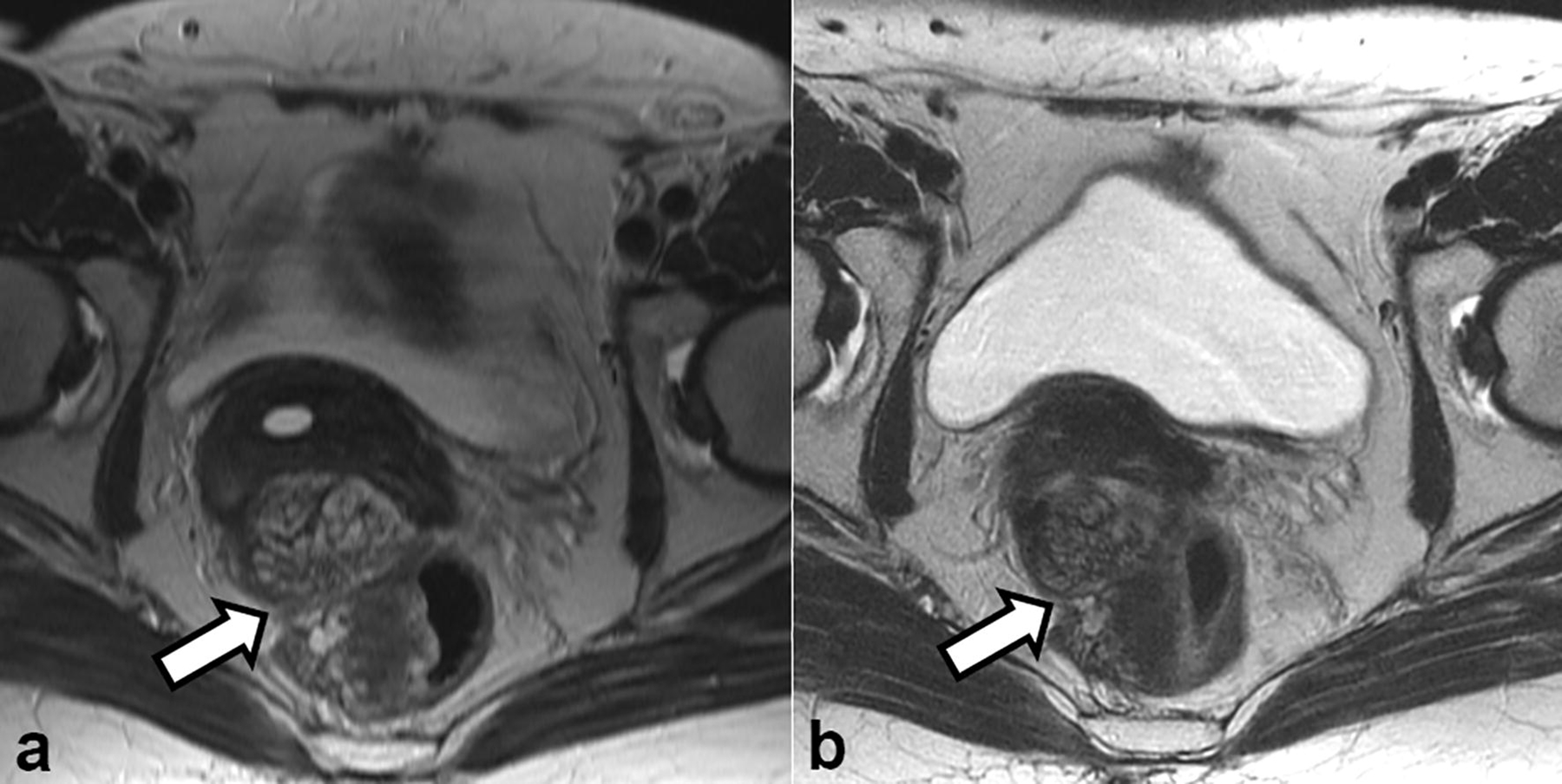
Axial T2-weighted images obtained (a) at initial presentation and (b) 3 months after the discontinuation of hormone replacement therapy showed a slight decrease in the size of the pelvic mass (arrow in a and b)
Polypoid endometriosis is an uncommon distinct variant of endometriosis. The term was first proposed by Mostoufizadeh and Scully in 1980 [2]. The authors described “ectopic endometriotic tissue with histology features similar to those of endometrial polyp.” They suggested that polypoid endometriosis presents as “large, often multiple, polypoid masses stimulating malignant tumors” and resembles endometrial polyp at histopathology.
The literature on polypoid endometriosis is limited to small case series and case reports, with most publications focusing on histopathologic rather than imaging features. In one of the largest case series to date, Parker et al. reported on 24 patients with polypoid endometriosis and described the key clinical and histopathologic features that help to distinguish polypoid variant from classic from of endometriosis [3]. The authors noticed that patients with polypoid endometriosis were older (typically peri- or postmenopausal in age) compared with patients with classic endometriosis which usually presents before menopause. Furthermore, nearly 50% of the patients with polypoid endometriosis were on hormonal treatment (either unopposed estrogen or mixed estrogen-progestin therapy) at the time of diagnosis. The ovaries, colon and its mesentery, uterine serosa and vaginal mucosa were among the most common locations affected by polypoid endometriosis. In contrast, the cervix, fallopian tubes, ureters and bladder serosa were among the less commonly involved sites. On histopathology, the lesions appeared as benign endometriotic glands (with variable degrees of atypical features) embedded in a benign endometrial stroma “resembling that of an inactive or proliferative endometrium” [3].
In this present case, an important clue to the correct diagnosis is provided by patient’s history, i.e., the information about hormone replacement therapy with an unconjugated estrogen. Similar to classic endometriosis, the polypoid variant relates to estrogenic stimulation, e.g., hormone replacement therapy or Tamoxifen use [4–8]. Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). It is widely used in the adjuvant setting in women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer because it has been shown to reduce recurrence risk and mortality [9,10]. While the primary therapeutic effect of Tamoxifen is derived from its antiestrogenic effects in the breast tissue, it acts as a moderate estrogen agonist on the endometrium and bone [11,12]. Tamoxifen-induced endometrial changes may range from cystic endometrial atrophy, endometrial hyperplasia and polyps to endometrial carcinoma [13].
In addition to the abovementioned clinical clue, several imaging features may also help to narrow the differential diagnosis. First, the polypoid mass was relatively T2-hyperintense and had a characteristic T2-hypointense peripheral rim, a feature that has been described in the literature and thought to represent a rim of fibrotic tissue [14–16]. Furthermore, the mass had relatively high signal intensity on both high b-value DWI and ADC map, indicating the absence of high cellularity. Lack of diffusion restriction in polypoid endometriosis was described previously by several case reports [15–19]. While not applicable in this case due to supracervical hysterectomy, an additional imaging feature that may suggest the correct diagnosis is the similarity in T2-signal characteristics and the pattern of contrast enhancement between polypoid endometriosis and the endometrium [15,16].
Imaging findings on FDG-PET/CT were non-specific. The mass showed very mild FDG uptake, which was slightly higher than the reference background liver uptake. The radiotracer uptake on FDG-PET/CT is not diagnostic of malignancy and may also be seen at sites of infection or inflammation as a result of increased glycolytic activity of inflammatory cells. Furthermore, several prior reports noted that increased FDG uptake may be observed in classic endometriosis, with SUV values ranging from 3.52 to 5.44 [20–22]. The FDG uptake in endometriosis is thought to be related to inflammation [23].
Concurrent classic endometriosis was absent in our patient, but two forms of endometriosis often co-exist in the same patient. Hence, it is useful to review patient’s clinical history for prior diagnosis of endometriosis and to evaluate MR images for imaging stigmata of endometriosis. Imaging findings of endometriosis may include endometrioma(s), “T1 bright spots” (that are best seen on fat-saturated T1-weighted images and correspond to hemorrhagic endometriotic deposits), and fibrotic changes/scarring in typical locations such as the cul-de-sac, vesicouterine pouch, rectovaginal septum, and uterosacral ligaments.
Beyond to the above considerations, there were several aspects of the patient’s clinical history and laboratory data that helped to narrow the diagnosis. Our patient was completely asymptomatic. While this observation does not exclude malignancy, it is remarkable given the location of the mass and, taken together with imaging findings, may raise the possibility of a benign etiology. Furthermore, all tested serum tumor markers were within normal limits [16,15,24,25]. Based on the location of the mass, differential possibilities included mucinous rectal carcinoma and rectal gastrointestinal stroma tumor (GIST). Although the signal characteristics (T2 and DWI/ADC hyperintensity), relatively low level of enhancement and minimal uptake on FDG PET/CT are frequent with mucinous rectal carcinoma, the finding of intact mucosa at flexible sigmoidoscopy ruled this entity out as a possibility [26,27]. Rectal GIST arises from the non-epithelial mesenchymal component of the bowel wall and can present with intact mucosa. The eccentric location and T2 signal characteristics of the mass would be consistent with rectal GIST. When large, GISTs are commonly more heterogeneous in appearance as a result of cystic, necrotic and hemorrhagic changes [28]. Furthermore, GISTs are more commonly round to ovoid in shape and most patients are symptomatic if the tumor has reached a size similar to that observed in our patient [29]. Lastly, endometriosis-associated malignancy (EAM) can arise from ovarian and extraovarian endometriotic deposits, although the latter is less common. Interestingly, Modesitt et al. [30] reported on 115 patients with EAM and found that extraovarian EAM was more common in postmenopausal women and in women receiving hormone replacement therapy, as was the case in our patient. However, unlike our patient, extraovarian EAM is often encountered in patients with known endometriosis and may occur at unusual postsurgical sites [31]. On imaging, extraovarian EAM displays heterogeneous T1 and T2 signal characteristics with areas of hemorrhage and demonstrates restricted diffusion, both of which were absent in our patient [31].
While polypoid endometriosis is rare, this entity is important to recognize because it is a benign mimic of malignancy. Oncologic imagers should be familiar with polypoid endometriosis and consider this rare entity in peri- or postmenopausal women being treated with Tamoxifen, a drug that is currently widely used in patients with breast cancer.
The definitive diagnosis of polypoid endometriosis requires histopathology. Nevertheless, there are several imaging features that can aid in narrowing the differential possibilities. These are:
T2 signal characteristics and contrast enhancement pattern of the mass that mirror those of the endometrium
Peripheral T2 hypointense rim surrounding the masses
Lack of diffusion restriction
Lack of ancillary features suggestive of malignancy (e.g., lymphadenopathy and peritoneal implants)
+/− presence of imaging stigmata of endometriosis
In summary, polypoid endometriosis is a rare distinct mass-like variant of endometriosis that mimics malignancy and poses a diagnostic challenge both clinically and radiologically. Common locations include the ovaries, uterine serosa, vagina, large bowel, and, occasionally, the cervix. Knowledge of several important clinical and imaging features including older age (peri- or postmenopausal age group), association with hormonal treatment, MR signal characteristics mirroring endometrium, T2 hypointense peripheral rim and high signal on DWI/ADC may help in narrowing the differential diagnosis.
Acknowledgements
We thank Joanne Chin for her editorial support on this manuscript.
Funding:
This work was supported in part through the NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA008748.This research received no funding.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This Author Accepted Manuscript is a PDF file of an unedited peer-reviewed manuscript that has been accepted for publication but has not been copyedited or corrected. The official version of record that is published in the journal is kept up to date and so may therefore differ from this version.
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Sumathi VP, McCluggage WG (2002) CD10 is useful in demonstrating endometrial stroma at ectopic sites and in confirming a diagnosis of endometriosis. Journal of clinical pathology 55 (5):391–392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mostoufizadeh M, Scully RE (1980) Malignant tumors arising in endometriosis. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology 23 (3):951–963 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Parker RL, Dadmanesh F, Young RH, Clement PB (2004) Polypoid endometriosis: a clinicopathologic analysis of 24 cases and a review of the literature. The American journal of surgical pathology 28 (3):285–297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Choi IH, Jin SY, Jeen YM, Lee JJ, Kim DW (2015) Tamoxifen-associated polypoid endometriosis mimicking an ovarian neoplasm. Obstetrics & gynecology science 58 (4):327–330. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2015.58.4.327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kraft JK, Hughes T (2006) Polypoid endometriosis and other benign gynaecological complications associated with Tamoxifen therapy-a case to illustrate features on magnetic resonance imaging. Clinical radiology 61 (2):198–201. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2005.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chang CK, Chen P, Leu FJ, Lou SM (2003) Florid polypoid endometriosis exacerbated by tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol 102 (5 Pt 2):1127–1130 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schlesinger C, Silverberg SG (1999) Tamoxifen-associated polyps (basalomas) arising in multiple endometriotic foci: A case report and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol 73 (2):305–311. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1998.5305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yamamoto A, Usami T, Kondo E, Kato K, Motoyama TJICCJ (2016) Huge polypoid endometriosis: report of a case and review of the literature. 5 (1):31–35. doi: 10.1007/s13691-015-0220-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee ES, Han W, Kim MK, Kim J, Yoo TK, Lee MH, Lee KH, Kim TY, Moon HG, Im SA, Noh DY, Lee ES (2016) Factors associated with late recurrence after completion of 5-year adjuvant tamoxifen in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. BMC cancer 16:430. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2423-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ferno M, Baldetorp B, Bendahl PO, Borg A, Ewers SB, Olsson H, Ryden S, Sigurdsson H, Killander D (1995) Recurrence-free survival in breast cancer improved by adjuvant tamoxifen--especially for progesterone receptor positive tumors with a high proliferation. Breast cancer research and treatment 36 (1):23–34 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Powles TJ, Hickish T, Kanis JA, Tidy A, Ashley S (1996) Effect of tamoxifen on bone mineral density measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in healthy premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 14 (1):78–84. doi: 10.1200/jco.1996.14.1.78 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gielen SC, Santegoets LA, Hanifi-Moghaddam P, Burger CW, Blok LJ (2008) Signaling by estrogens and tamoxifen in the human endometrium. The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 109 (3–5):219–223. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2008.03.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hann LE, Giess CS, Bach AM, Tao Y, Baum HJ, Barakat RR (1997) Endometrial thickness in tamoxifen-treated patients: correlation with clinical and pathologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168 (3):657–661. doi: 10.2214/ajr.168.3.9057510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ozaki K, Gabata T, Tanaka M, Matsui O, Suzuki M, Kawashima H, Minami M, Zen Y (2008) Polypoid endometriosis: An uncommon and distinctive variant of endometriosis. European Journal of Radiology Extra 65 (3):97–100. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrex.2008.01.004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Takeuchi M, Matsuzaki K, Furumoto H, Nishitani H (2008) Case report: A case of polypoid endometriosis: MR pathological correlation. The British journal of radiology 81 (964):e118–119. doi: 10.1259/bjr/23847518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kozawa E, Inoue K, Iwasa N, Fujiwara K, Yasuda M, Tanaka J, Kimura F (2012) MR imaging of polypoid endometriosis of the ovary. Magn Reson Med Sci 11 (3):201–204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee NK KB, Choi KU, Song YJ, Suh DS, Kim KH (2018) Polypoid endometriosis of the ovary mimicking advanced ovarian carcinoma with extensive peritoneal metastases. Int J Clin Exp Med (11):4279–4284 [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tham WP, Busmanis I, Tan WC, Kwek JW (2016) Polypoid endometriosis of post vaginal fornix: utility of MRI imaging of pelvis with diffusion weighted imaging for diagnosis. The Medical journal of Malaysia 71 (3):144–146 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Takeuchi M, Matsuzaki K, Bando Y, Nishimura M, Yoneda A, Harada M (2016) A case of polypoid endometriosis with malignant transformation. Abdominal radiology (New York) 41 (9):1699–1702. doi: 10.1007/s00261-016-0696-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jeffry L, Kerrou K, Camatte S, Metzger U, Lelievre L, Talbot JN, Lecuru F (2004) Endometriosis with FDG uptake on PET. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology 117 (2):236–239. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2004.04.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ge J, Zuo C, Guan Y, Zhang X (2015) Increased 18F-FDG uptake of widespread endometriosis mimicking ovarian malignancy. Clinical nuclear medicine 40 (2):186–188. doi: 10.1097/rlu.0000000000000657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Setubal A, Maia S, Lowenthal C, Sidiropoulou Z (2011) FDG-PET value in deep endometriosis. Gynecological Surgery 8 (3):305–309. doi: 10.1007/s10397-010-0652-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Risum S, Hogdall C, Loft A, Berthelsen AK, Hogdall E, Nedergaard L, Lundvall L, Engelholm SA (2007) The diagnostic value of PET/CT for primary ovarian cancer--a prospective study. Gynecol Oncol 105 (1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.11.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kim JY, Song TJ, Choi HK, Shim JY (2015) Multifocal Polypoid Endometriosis Mimicking Malignancy in a Young Woman with a History of Hormonal Treatment. J Pathol Transl Med 49 (5):418–420. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2015.05.12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Moss EL, Hollingworth J, Reynolds TM (2005) The role of CA125 in clinical practice. Journal of clinical pathology 58 (3):308–312. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2004.018077 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jhaveri KS, Hosseini-Nik H (2015) MRI of Rectal Cancer: An Overview and Update on Recent Advances. AJR Am J Roentgenol 205 (1):W42–55. doi: 10.2214/ajr.14.14201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Berger KL, Nicholson SA, Dehdashti F, Siegel BA (2000) FDG PET evaluation of mucinous neoplasms: correlation of FDG uptake with histopathologic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174 (4):1005–1008. doi: 10.2214/ajr.174.4.1741005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jiang ZX, Zhang SJ, Peng WJ, Yu BH (2013) Rectal gastrointestinal stromal tumors: imaging features with clinical and pathological correlation. World J Gastroenterol 19 (20):3108–3116. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Scola D, Bahoura L, Copelan A, Shirkhoda A, Sokhandon F (2017) Getting the GIST: a pictorial review of the various patterns of presentation of gastrointestinal stromal tumors on imaging. Abdominal radiology (New York) 42 (5):1350–1364. doi: 10.1007/s00261-016-1025-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Modesitt SC, Tortolero-Luna G, Robinson JB, Gershenson DM, Wolf JK (2002) Ovarian and extraovarian endometriosis-associated cancer. Obstet Gynecol 100 (4):788–795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McDermott S, Oei TN, Iyer VR, Lee SI (2012) MR Imaging of Malignancies Arising in Endometriomas and Extraovarian Endometriosis. RadioGraphics 32 (3):845–863. doi: 10.1148/rg.323115736 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


