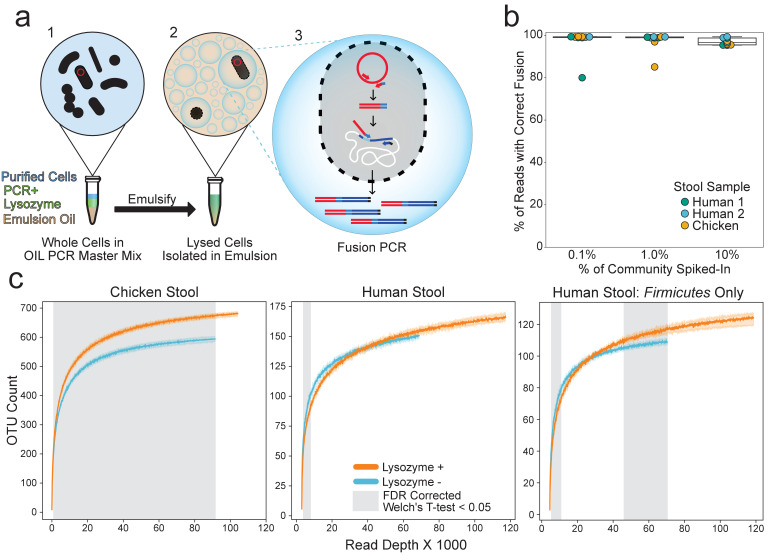
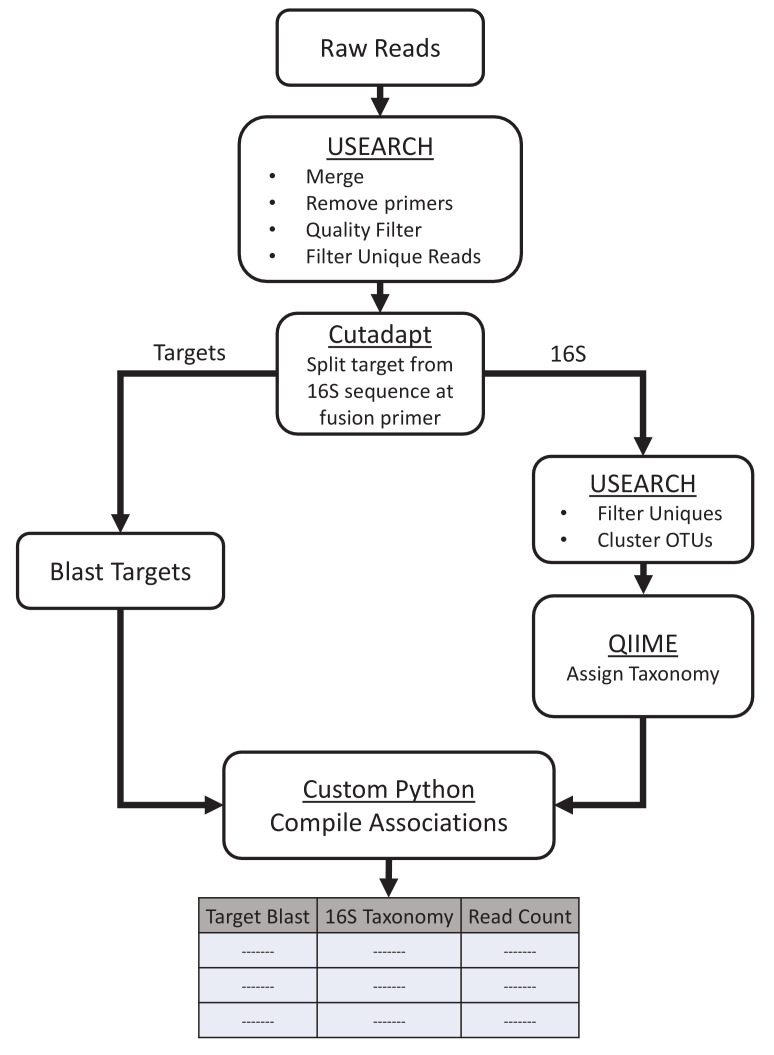
Figure 1. OIL-PCR can specifically link plasmid-encoded genes with their hosts.
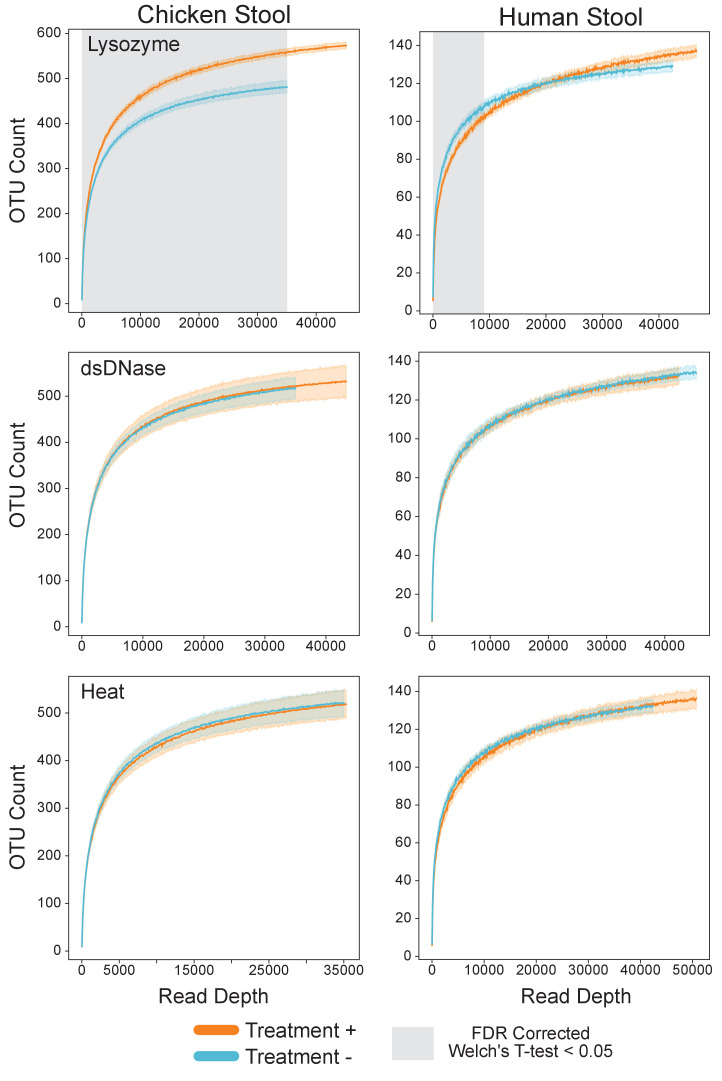
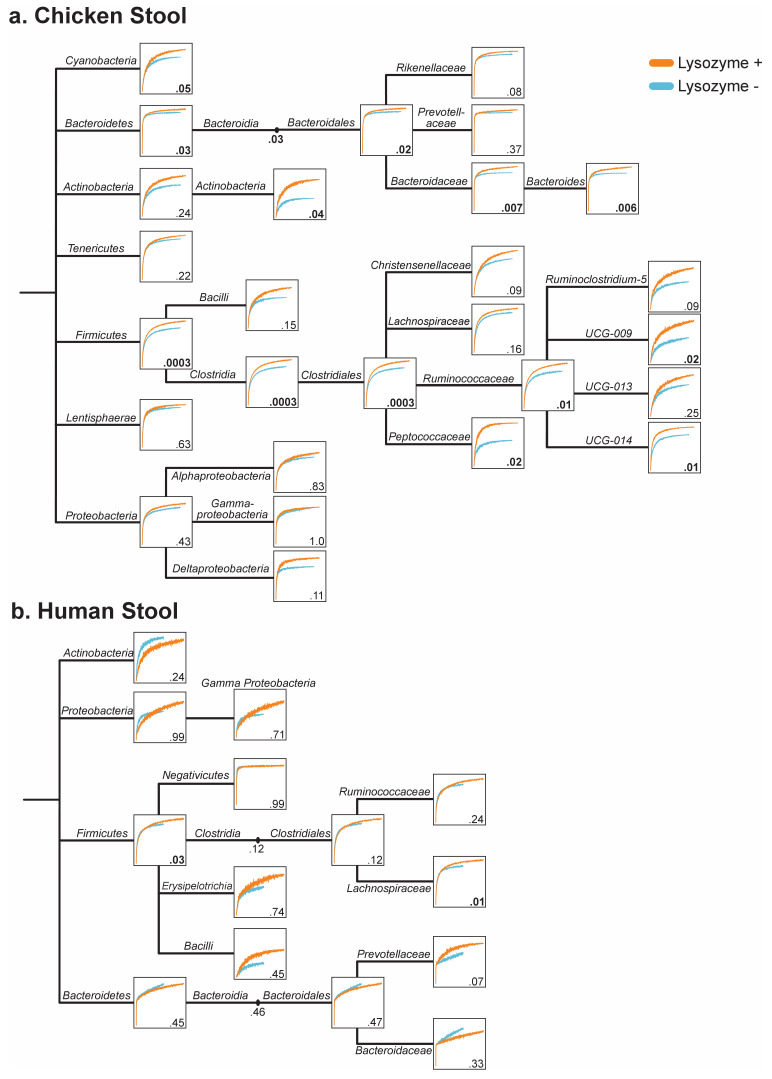
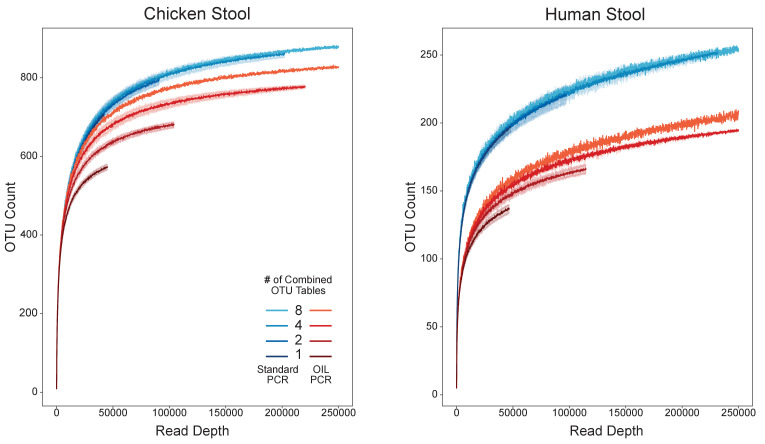
(a) Depiction of the OIL-PCR method. (1) Nycodenz-purified cells are mixed with PCR master mix, lysozyme, and emulsion oil and shaken to create an emulsion. (2) Cells are lysed within the emulsion. (3) Fusion PCR is performed in droplets containing cells harboring the targeted gene. Fused amplicons between the gene of interest and the 16S rRNA gene are the product. (b) A boxplot showing the percent of Illumina reads containing correct fusion products, namely the fusion of plasmid-borne cmR and the 16S rRNA gene of E. coli MG1655. OIL-PCR was performed on two individuals’ and one chicken’s gut microbiome sample in triplicate, spiked with varying concentrations of E. coli. (c) Rarefaction analysis of chicken (left) or human gut microbiome sample (middle) with (orange) and without (blue) lysozyme treatment. At right is the rarefaction analysis performed on Firmicutes only in the human stool sample. Grayed regions in the plot represent areas where the curves, each composed of four technical replicates, are significantly different (p<0.05) from one another, according to an FDR-corrected Welch’s t-test.
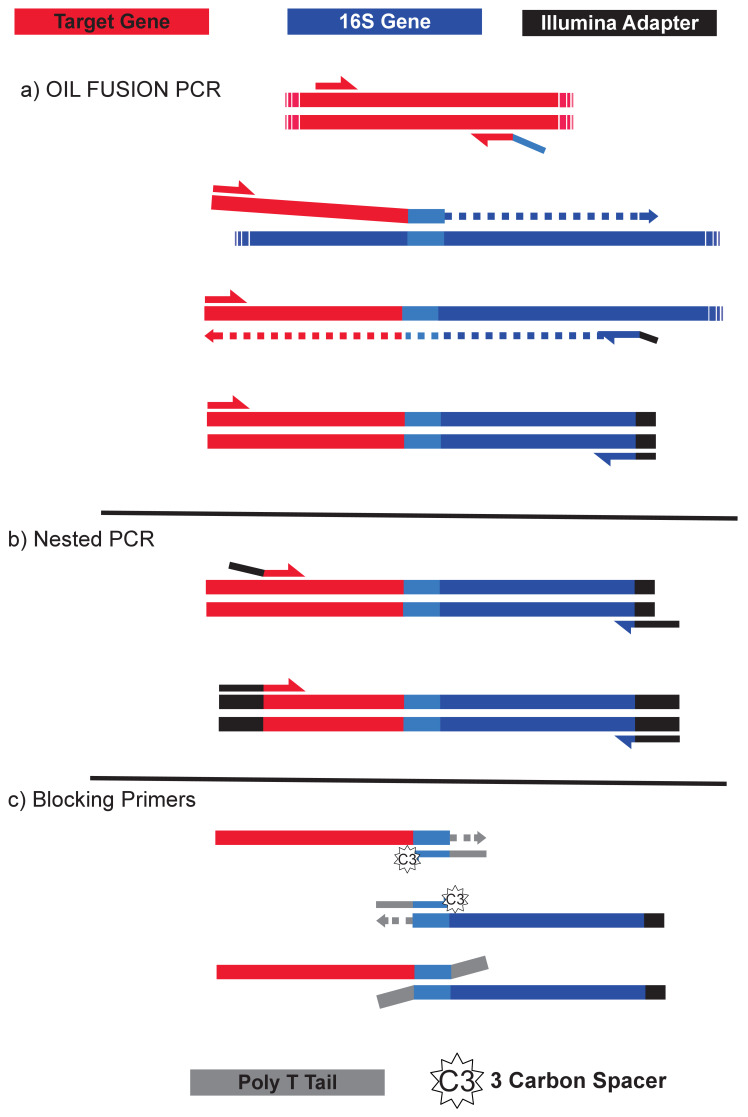
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Depiction of the fusion PCR.
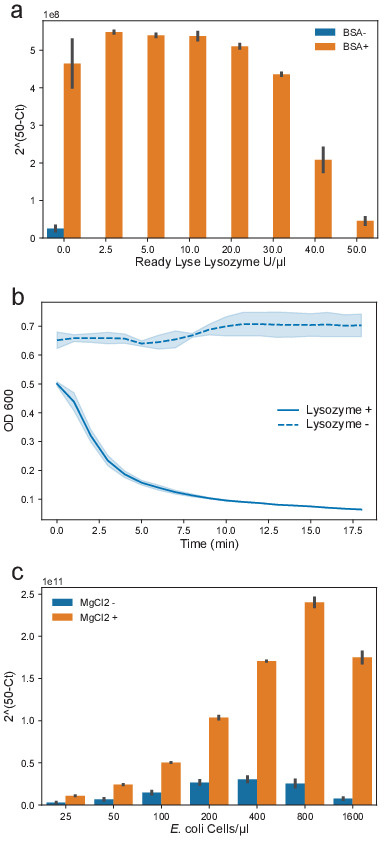
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. BSA and excess MgCl2 improve the efficiency of OIL-PCR and Ready Lyse Lysozyme remains active in OIL-PCR master mix.