Abstract
The sacrum is a triangular shaped bone made up of five fused vertebral bodies. It is composed of bone, cartilage, marrow elements as well as notochord remnants and is a common site for both benign and malignant (primary and secondary) tumors. Familiarity with the imaging features and clinical presentations of sacral bone tumors could be helpful in narrowing the differential diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are the preferred imaging modalities for evaluating sacral masses. This pictorial review will highlight imaging features of common sacral tumors with pathologic correlation. Additionally, this article will review some critical principles and helpful tips to successfully biopsy these lesions.
Keywords: chondrosarcoma, chordoma, giant cell tumor, metastasis, osteosarcoma, sacrum
Introduction
The sacrum is composed of bone, cartilage, marrow elements as well as notochord remnants. 1 Sacral tumors can arise from any one of these components. Since the sacrum contains hematopoietic bone marrow, it is a common site of metastases, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, or plasmacytoma. In fact, metastases are the most common tumors of the sacrum ( Fig. 1 ). Primary malignant sacral tumors are less common and include chordoma, chondrosarcoma, osteosarcoma, and Ewing sarcoma. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) are the preferred imaging modalities for evaluating sacral masses. In this pictorial review, we will briefly describe the anatomy, imaging, and pathological features of common and unique sacral tumors and techniques to safely obtain a diagnostic biopsy specimen.
Fig. 1.
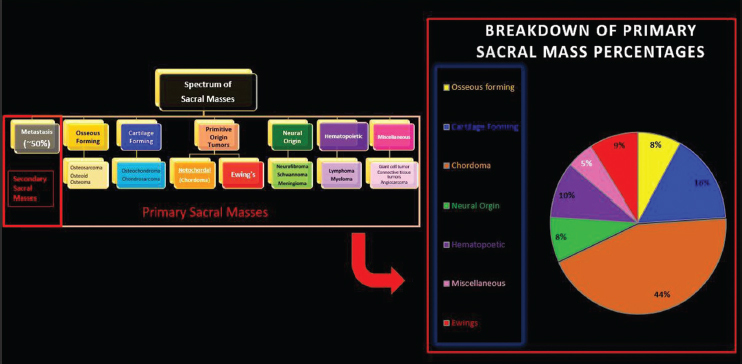
Pie chart showing the relative incidence of various types of sacral masses.
Sacral Anatomy
The sacrum is a triangular-shaped structure composed of five fused vertebral bodies (S1–S5). The sacrum has a critical role in stabilizing the posterior portion of the pelvic ring. At its wider superior aspect, the sacrum forms the lumbosacral joint with the fifth lumbar vertebra above it. The sacrum narrows to a point at its inferior margin, where it forms the sacrococcygeal joint with the much smaller coccyx (tail bone) ( Fig. 2A ). On each lateral margin, the sacrum articulates with the iliac bone at the sacroiliac (SI) joints. The SI joint is stabilized by several ligaments ( Fig. 2A ). The sciatic nerve, superior and inferior gluteal neurovascular bundles, posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and internal pudendal vessels traverse the sciatic notch to enter/exit the pelvis ( Fig. 2B ).
Fig. 2.
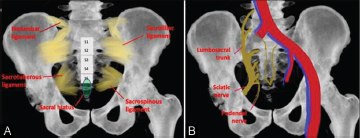
( A and B ) Illustration of the sacrum showing the stabilizing ligaments (A), and vessels and nerves (B).
Research Ethics Standards Compliance
This article was completed under an Institutional Review Board (IRB) approved protocol. The IRB number was 2004777. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Benign Tumors
Giant Cell Tumor
Age and Sex
Between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Giant cell tumors (GCTs) are twice as common in women. 2
Incidence
About 3 to 7% of all GCTs occur in the spine and most GCTs of the spine occur in the sacrum. 3 GCTs make up approximately 2 to 5% of primary sacral tumor. 4
Location in the Sacrum
Sacral GCTs are frequently eccentric and abut or extend across the SI joint ( Fig. 3A ). 5
Fig. 3.
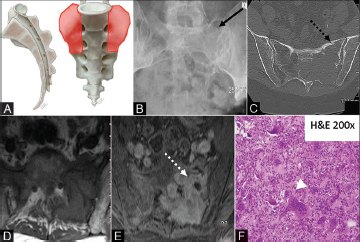
( A–F ) Illustration (A) showing the characteristic location for sacral giant cell tumor (orange shaded areas), most commonly arising eccentrically and frequently traversing the sacroiliac joint. Radiograph of the pelvis (B) demonstrating a lytic lucent lesion in the left hemisacrum (solid black arrow). Axial CT of the pelvis (C) demonstrates a lytic mass (dashed black arrow) with associated cortical thinning and pathologic fracture. Axial T1 nonenhanced image (D) shows a hypointense mass in the left sacrum with moderate postcontrast enhancement (E) (dashed white arrow). The photomicrograph (F) demonstrates a sheet of benign neoplastic mononuclear cells with indistinct cell border, scant eosinophilic cytoplasm, round to ovoid nuclei, admixed with numerous multinucleated osteoclast-like giant cells (white arrowhead). CT, computed tomography.
Presentation
Nonspecific, pain, and neurologic deficits. Malignant transformation is reported in less than 2% of patients. 3 6
Imaging
GCTs are purely lytic destructive lesions without dystrophic calcification or matrix mineralization. CT often demonstrates a soft-tissue attenuation mass with a narrow zone of transition and nonsclerotic margin which may remodel bone or extend through the cortex into the soft tissue. On MRI, GCTs are frequently heterogeneous because of the presence of necrosis (T1 hypointense signal), hemorrhage (hyperintense signal on T1- and T2-weighted sequences or fluid–fluid levels), fibrosis (T1 and T2 hypointense), or cystic spaces (T2 hyperintense). Contrast-enhanced (CE) MRI is often non-specific ( Fig. 3B–E ).
Additional Features
GCTs are generally very aggressive locally in the sacrum, despite their benign pathology. GCTs may have fluid–fluid levels as they can coexist with secondary aneurysmal bone cysts. 7
Pathology
Microscopic features include numerous multinucleated osteoclast-like giant cells scattered among several mononuclear cells that have round to ovoid nuclei, scant eosinophilic cytoplasm, and indistinct cell borders ( Fig. 3F ). The nuclei of the mononuclear cells and the multinucleated giant cells are morphologically similar. 7
Nerve Sheath Tumor (Schwannoma and Neurofibroma)
Age and Sex
Most commonly diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 40 years. No sex predilection. 8
Incidence
They commonly occur in the spine, accounting for 6 to 30% of spinal lesions. In the spine, nerve sheath tumors may be intradural extramedullary, extradural, or both. 9 10 Neurogenic tumors account for 8% of primary sacral tumors. 4
Location in the Sacrum
Nerve sheath tumors do not arise from the osseous sacrum, but instead, arise from the neurogenic tissue within the sacral canal or neural foramina ( Fig. 4A ). 11 12
Fig. 4.
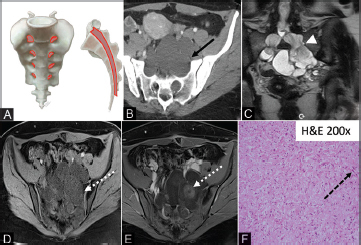
( A–F ) Illustration (A) showing the characteristic location of nerve sheath tumors. Intradural/extramedullary and/or extradural mass can arise from the lumbar nerve roots and extend along the course of the nerve through the neural foramina. Axial CT image (B) shows bilateral symmetric cystic masses (solid black arrow) extending through the enlarged neural foramen. Coronal T2 MRI (D) showing dumbbell configuration of nerve roots as they traverse the neural foramen (white arrowhead). The multiseptated T1 hypointense mass (D) demonstrates area of solid enhancement (E) (dashed white arrow). The photomicrograph (F) shows a benign neurofibroma featuring a diffuse proliferation of loosely arranged bland spindle cells with wavy elongated nuclei (dashed black arrow) and associated with shredded-carrot-like collagen fibers. CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Presentation
The most common signs and symptoms are pain and radiculopathy due to compression of the affected nerve root.
Imaging
The slow growth of these tumors causes remodeling and widening of the sacral neural foramina by exerting mass effect on the foramina, best seen on CT ( Fig. 4B ). The tumors are generally solitary lesions with intradural and extradural components. The presence of more than one nerve sheath tumor or tumor extension along the length of a nerve (a plexiform neurofibroma) should prompt investigation for syndromic association including neurofibromatosis or schwannomatosis. On MRI, the masses are most commonly intradural and extramedullary, T2 hyperintense, and often contain enhancing solid components ( Fig. 4C–E ). A peripheral nerve sheath tumor containing both intra- and extradural components is often recognized by a “dumbbell sign” as it courses through the neural foramina, with relative expansion of the mass on both sides of the neural foramina. The “target sign” (central T2 intermediate or hypodensity surrounded by T2 hyperintensity) is commonly seen with peripheral nerve sheath tumors, due to a combination of fibrous and collagenous tissues (T2 intermediate/hypointense) surrounded by myxoid tissue (T2 hyperintense). On positron emission tomography (PET)/CT, nerve sheath tumors may demonstrate fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) avidity, with significantly more uptake seen in nerve sheath tumors that have undergone malignant degeneration. 13
Pathology
Microscopic features include diffuse proliferation of loosely arranged bland spindle cells with elongated wavy nuclei ( Fig. 4F ) associated with shredded-carrot-like collagen bundles. 3 7
Malignant Tumors
Chordoma
Age and Sex
Usually diagnosed in the 5th decade with men being twice as commonly affected as women. 14 15
Incidence
Chordomas are relatively rare tumors that account for 2 to 4% of all primary malignant bone tumors. 7 Chordomas make up approximately 44% of primary sacral tumors. 4 Approximately 50 to 60% of chordomas occur in the sacrococcygeal region and it is the most common primary malignant sacral tumor. 7 14
Location in the Sacrum
This tumor arises from intraosseous notochordal remnants. Most of the chordomas present as a midline mass involving the lower sacral segment ( Fig. 5A ).
Fig. 5.
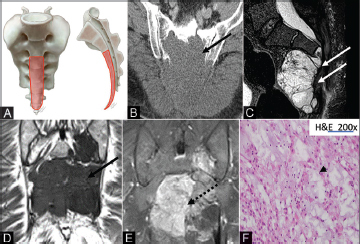
( A–F ) Illustration (A) showing the characteristic locations of chordomas. Chordomas arise in the lower sacral segments in the midline (orange shaded areas). Axial CT image (B) demonstrates lytic erosion through the sacrum (solid black arrow). Sagittal T2 images (C) demonstrate a heterogeneous hyperintense soft tissue mass arising from the S3 sacral body in midline (solid white arrows). Numerous characteristic T2 hypointense septa are seen with characteristic erosion of the lower sacrum and coccyx. Unenhanced coronal T1 image (D) shows a hypointense mass in the lower sacrum (solid black arrows) with avid postcontrast (E) enhancement (dashed black arrow). The photomicrograph (F) depicts large epithelioid cells some featuring physaliphorous cells with intracytoplasmic bubbly vacuoles (black arrowhead) embedded in a myxoid stroma. CT, computed tomography.
Presentation
Chordomas are slow-growing tumors that are commonly discovered from pain associated with large masses.
Imaging
CT images often show large destructive lesions centered in the midline with an associated soft-tissue mass ( Fig. 5B ). Calcification is present in 50 to 70% of patients. 7 On MRI, the mass appears heterogeneously hyperintense on T2-weighted images ( Fig. 5C ) due to the high water content of the myxoid matrix with numerous characteristic hypointense septa. Hemosiderin from previous hemorrhage may be seen as T2 hypointensity. 16 Enhancement is variable and is typically moderate to intense ( Figs. 5D and E ). 18F-FDG uptake in chordomas on PET/CT is either low or intermediate. 17 18
Pathology
Microscopic features of a conventional chordoma include proliferation of large epithelioid cells, some with clear intracytoplasmic bubbly vacuoles known as physaliphorous cells ( Fig. 5F ). The stroma is frequently mucinous to myxoid. 3
Chondrosarcoma
Age and Sex
The mean age of patients with chondrosarcoma is 45 years. 7 19 20 Males are affected two to four times more frequently than females. 7
Incidence
Chondrosarcomas are more common than osteosarcomas in the spine. Chondrosarcomas account for 7 to 12% of malignant primary tumors of the sacrum 7 ; approximately 10% of all chondrosarcomas are found in the spine. 7
Location in the Sacrum
Often eccentric in location and occurs in the upper segments ( Fig. 6 A).
Fig. 6.
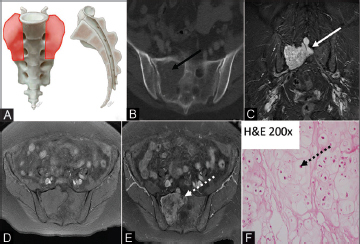
( A–F ) Illustration (A) showing the characteristic location for chondrosarcoma (orange shaded areas). Sacral chondrosarcoma is typically located eccentrically in the upper portion of the sacrum. Axial CT image (B) with an eccentrically located lytic lesion in the right hemisacrum. There is a subtle calcified chondroid matrix (solid black arrow). Coronal T2 MRI (C) showing a hyperintense mass invading through the neural foramina and extending into the epidural space (solid white arrow). The axial nonenhanced T1 image (D) demonstrates an iso/hypointense mass with heterogeneous enhancement (dashed white arrow) on the postcontrast images (E). The photomicrograph (F) shows an infiltrative proliferation of malignant chondrocytes featuring enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei with prominent nucleoli (dashed black arrow). CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Presentation
Pain.
Imaging
Radiographs and CT images reveal large lytic lesions with characteristic chondroid matrix-ring and arc calcification. 7 21 Calcifications are manifested as areas of signal void on all pulse sequences at MRI. On MRI the noncalcified portion is hyperintense on T2-weighted images and hypo- to isointense to skeletal muscle on T1-weighted images. CE MRI typically shows peripheral and septal enhancement (rings and arches) corresponding to vascular septations between cartilaginous lobules ( Fig. 6B–E ). 3 22
Pathology
Microscopically, chondrosarcoma features an infiltrative growth pattern, replacing the existing bone marrow with large malignant chondrocytes demonstrating increased cellularity, enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei, and large nucleoli ( Fig. 6F ). 7
Ewing’s Sarcoma
Age and Sex
Most lesions occur in patients between 10 and 30 years old, more commonly in males than females. 19 In addition, 95% of all Ewing’s sarcoma cases are diagnosed before the age of 30.
Incidence
About, 3 to 10% of all primary Ewing’s sarcomas and primitive neuroectodermal tumors occur in the spine. 3 Approximately 9% of all primary sacral tumors are Ewing’s sarcoma. 4 23
Location in the Sacrum
The sacral ala is the most common site in the sacrum ( Fig. 7A ). 19 24
Fig. 7.
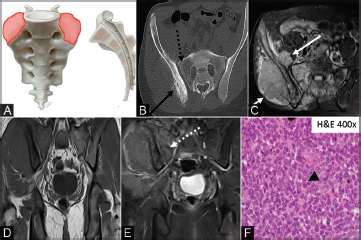
( A–F ) Illustration (A) showing the characteristic location of sacral Ewing’s (orange shaded areas). Ewing’s generally originates within the sacral ala, often with extension across the sacroiliac joint. On the axial CT image (B), there is a mixed sclerotic/lucent osseous lesion (dashed black arrow) in the right sacrum with aggressive sunburst periosteal reaction (solid black arrow). Axial T2 MRI (C) demonstrates a large hyperintense soft tissue mass that extends through both inner and outer tables of the ilium and sacrum (solid white arrow). Coronal nonenhanced T1 MRI (D) shows a hypointense mass which demonstrates enhancement (dashed white arrow) on the coronal postcontrast images (E). The photomicrograph (F) demonstrates a diffuse sheet of uniform malignant small round cells with finely dispersed chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli, and scant cytoplasm (black arrowhead). CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Presentation
Pain and neurological changes, including loss of bowel and bladder function.
Imaging
Radiographs and CT images may demonstrate a destructive osteolytic lesion, frequently with a dominant extraosseous soft-tissue component. An aggressive periosteal reaction may be seen. Diffuse sclerosis is seen in 70% of cases. 12 25 The MRI appearance is nonspecific with a T2 hyperintense destructive soft-tissue mass with heterogeneous contrast enhancement ( Fig. 7B–E ).
Pathology
Microscopically, the tumor consists of uniform malignant small round blue cells with finely dispersed chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli, and scant cytoplasm ( Fig. 7F ). The neoplastic cells typically grow in sheets, nests, or cords, sometimes with palisading and Homer-Wright rosettes. 25
Osteosarcoma
Age and Sex
Patients present at an older age than those with appendicular tumors with most lesions in the fourth decade of life, compared with the second for appendicular lesions. Males are more affected than the females.
Incidence
Osteosarcoma is the most common primary malignant bone tumor, but uncommon in the axial skeleton with less than 3% found in the spine. 26 27
Location in the Sacrum
The lumbosacral spine is the most common site (60–70% of the patients). 7 In the sacrum it is eccentrically located ( Fig. 8A ).
Fig. 8.
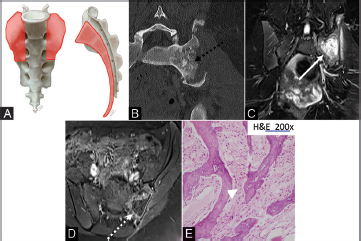
( A–E ) Illustration (A) showing the characteristic location of sacral osteosarcomas (orange shaded areas), which nearly always involve the sacral ala and body. Axial CT (B) image shows a large destructive lytic lesion centered within the left hemisacrum and obliterates the left SI joint to extend into the left ilium. Amorphous osteoid matrix deposition is seen (dashed black arrow). Coronal T2 MRI (C) shows a hyperintense mass (solid white arrow). Postcontrast T1 image (D) shows minimal peripheral enhancement (dashed white arrow). Photomicrograph (E) depicts irregular neoplastic woven bones lacking osteoblastic rimming (white arrowhead), which are produced by the malignant neoplastic polygonal, oval, and spindle osteosarcoma cells in the background. CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Presentation
Palpable mass, with 80% presenting with neurological deficits. 28 Some osteosarcomas arise from malignant degeneration of Paget’s disease and commonly affect the pelvis and sacrum.
Imaging
Radiographs and CT images demonstrate a predominantly osteoblastic permeative lesion with cortical breakthrough and soft-tissue extension ( Fig. 8B ). CT is useful to identify osteoid matrix mineralization. The MRI of nonmineralized areas is nonspecific; the lesions are hypointense on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2-weighted images with heterogeneous contrast enhancement. The ossified portion is dark, isointense to cortical bone, on all sequences ( Fig. 8 B–D ).
Pathology
Microscopic features include irregular neoplastic woven bones lacking osteoblastic rimming ( Fig. 8E ), which are produced by the malignant neoplastic polygonal, oval, and spindle osteosarcoma cells in the background. 17
Multiple Myeloma and Plasmacytoma
Age and Sex
Most patients are 60 years of age at presentation, with a male predominance (2:1). 19
Incidence
Multiple myeloma accounts for 45% of vertebral tumors. 3 Plasmacytoma (solitary lesion) often precedes the development of multicentric disease. The axial skeleton is the most common site of multiple myeloma.
Imaging
On CT the lesions appear as punched-out lytic areas—narrow zone of transition with a nonsclerotic margin. On MRIs, plasmacytomas and myeloma lesions are hypointense on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2-weighted images. Diffuse bone marrow infiltration may precede focal involvement in some cases of multiple myeloma ( Fig. 9A–C ). 29
Fig. 9.
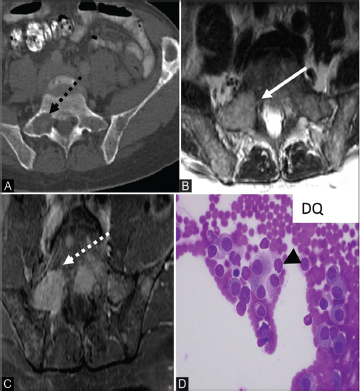
( A–D ) Axial CT in a patient with multiple myeloma (A) demonstrates a punched out lytic lesion within the right sacrum (dashed black arrow) and left iliac bones. Axial T2 MRI (B) shows a hyperintense well-defined marrow replacing lesion (solid white arrow) in the right sacrum. Axial postcontrast (C) T1 image shows a well-defined enhancing lesion (dashed white arrow). The photomicrograph (D) depicts abnormal proliferation of malignant plasmacytic cells with enlarged “clock-face” eccentric nuclei, and basophilic cytoplasm as well as perinuclear hof (black arrowhead). CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Pathology
Multiple myeloma exhibits a monoclonal proliferation of malignant plasma cells of the bone marrow. The plasma cells have eccentric nuclei with characteristic “clock-face” chromatin without nucleoli ( Fig. 9D ). 30
Lymphoma
Age and Sex
Primary lymphoma of the sacrum has a peak incidence during the second and third decades of life, affecting more males than females at a ratio of 2:1. 5
Incidence
Primary bone lymphoma involves a single bone with no evidence of disseminated disease. 31 It is extremely rare, accounting for only 1% of cases of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 31
Imaging
A permeative lytic lesion is most often seen, with minimal cortical destruction. On CT, the abnormality may be very subtle. MRI demonstrates replacement of the bone marrow, on T1- and T2-weighted imaging, which enhanced after contrast administration at the sites of disease.
Pathology
The tumor is often composed of sheets of large cells of lymphoid lineage. There are areas of hemorrhage and necrosis. Tumor cells have brisk mitotic activity with many apoptotic bodies ( Fig. 10C ). Immunohistochemistry shows the tumor cells to be strongly positive for CD-45, CD-20, and CD-19 and negative for CD-3, CD-5, CD-99, and cytokeratin. 32
Fig. 10.
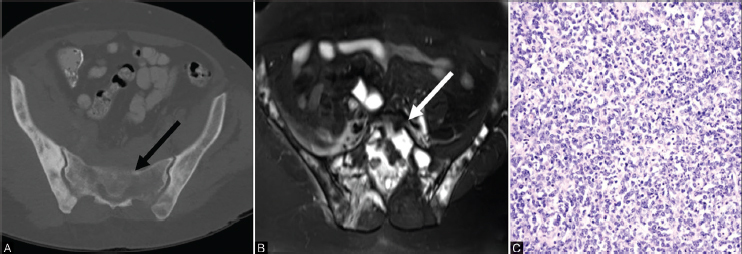
( A–C ) Axial CT image in a patient with lymphoma (A) shows a mixed lytic and sclerotic lesion in the sacrum (solid black arrow) and both iliac bones. T2 MRI image (B) demonstrates heterogeneous hyperintensity throughout the sacrum (solid white arrow), and mixed signal within the iliac bones bilaterally. Photomicrograph (C) depicts a diffuse proliferation of dis-cohesive malignant lymphocytes with enlarged round to lobulated nuclei with multiple prominent nucleoli, and minimal cytoplasm. CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Metastasis
Metastases from lung, breast, prostate, kidney, head, and neck; melanoma; and gastrointestinal cancers are the most common malignant sacral tumors. 5 33 Metastases are usually osteolytic ( Fig. 11A , B ), except in prostate and breast cancers, where they are frequently osteoblastic.
Fig. 11.
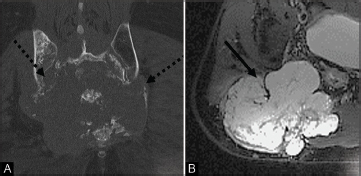
Coronal CT image (a) in a patient with metastasis, shows bone destruction and soft tissue mass extending to the sacroiliac joints bilaterally (dashed black arrows). Axial MRI T2 image (b) demonstrates an expansile T2 hyperintense mass (solid black arrow).
Lesions usually present with pathological fracture. History of primary tumor and multiple bone lesions raises the concern for metastatic bone disease.
Sclerotic metastases typically display low signal intensity on all MRI sequences. Kidney and thyroid metastases may have expansile appearance, and both may be hypervascular.
Tips to Perform Biopsy of Sacral Masses
Always use coaxial techniques—preserves access and allows for multiple samples.
For extremely lytic lesions, a soft tissue core biopsy needle can be used through the outer coaxial cannula. If this does not work, aspiration though the coaxial needle may yield positive samples.
Avoid crossing joint lines—minimizes risk of tumor seeding.
Biopsy of nerve sheath tumors—consider increased sedation, as these biopsies are more painful.
Identify and target most hyperenhancing or hypermetabolic portion of mass.
When hematological malignancies are suspected, obtain additional samples for flow cytometry.
Plan biopsy tract:
Shortest route which avoids vascular and neural structures.
Avoid violating more than 1 compartment—tumor seeding in >1 compartment can result in expanded resection, which can ultimately affect patient’s mobility.
Discuss the biopsy tract with the surgeon to ensure inclusion of the tract in the resection.
Conclusion
Sacral tumors are rare, with the majority being metastases. Majority of the primary sacral tumors are malignant. Most tumors present with nonspecific symptoms and a high degree of clinical suspicion along with high-quality imaging is required for the diagnosis. Sacral tumors are usually missed on radiographs. MRI and CT have complementary roles in imaging the sacrum and are vital for preoperative/biopsy planning and assessing the effect of the masses on the surrounding structures. The educational objectives for this review are to highlight key clinical, radiological, and pathological features of various sacral masses and provide a concise yet comprehensive roadmap to approach these lesions ( Table 1 ).
Table 1. Approach to sacral masses.
| Tumor | ML | EC | US | LS | Solitary | Multiple | Matrix | Remodeling | Soft tissue mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: EC, eccentric; LS, lower sacrum; ML, midline; US, upper sacrum. | |||||||||
| GCT | − | + | + | − | + + | − | − | − | +/− |
| NF | = | − | + | + | + | + | − | + + + | + + |
| Chordoma | + + + | − | − | + + + | + + | − | − | − | + + + |
| Chondrosarcoma | − | + + + | + + | − | + + | − | + + +Arcs and rings-Cartilage | − | +/− |
| Osteosarcoma | − | + | + | − | + | − | + + +0sseous | − | +/− |
| Metastasis | + | + | + | + | + | + + + | − | − | +/− |
| Myeloma | + | + | + | + | + | + + + | − | − | +/− |
Acknowledgments
None.
Footnotes
Conflicts of InterestFinancial Support and Sponsorship There are no conflicts of interest.
Nil.
References
- 1.Thornton E, Krajewski K M, O’Regan K N, Giardino A A, Jagannathan J P, Ramaiya N.Imaging features of primary and secondary malignant tumours of the sacrum Br J Radiol 201285(1011)279–286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Junming M, Cheng Y, Dong C et al. Giant cell tumor of the cervical spine: a series of 22 cases and outcomes. Spine. 2008;33(03):280–288. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318162454f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Llauger J, Palmer J, Amores S, Bagué S, Camins A. Primary tumors of the sacrum: diagnostic imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;174(02):417–424. doi: 10.2214/ajr.174.2.1740417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Varga P P, Bors I, Lazary A. Sacral tumors and management. Orthop Clin North Am. 2009;40(01):105–123, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.ocl.2008.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Disler D G, Miklic D. Imaging findings in tumors of the sacrum. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999;173(06):1699–1706. doi: 10.2214/ajr.173.6.10584822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Verma M, Yarlagadda B, Hendrani A, Bhat A P, Kumar S. Simplified rapid protocol for assessing the thoracic aortic dimensions and pathology with noncontrast MR angiography. Int J Angiol. 2019;28(02):130–136. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Murphey M D, Andrews C L, Flemming D J, Temple H T, Smith W S, Smirniotopoulos J G. From the archives of the AFIP. Primary tumors of the spine: radiologic pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1996;16(05):1131–1158. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.16.5.8888395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Diggs-Andrews K A, Brown J A, Gianino S M, Rubin J B, Wozniak D F, Gutmann D H. Sex is a major determinant of neuronal dysfunction in neurofibromatosis type 1. Ann Neurol. 2014;75(02):309–316. doi: 10.1002/ana.24093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chew S, Barboriak D P, Palmer W Eet al. Radiologic-pathologic conferences of the Massachusetts General-Hospital sacral neurofibroma AJR 19921596001503033 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schuchardt P A, Yasin J T, Davis R M, Tewari S O, Bhat A P. The role of an IVC filter retrieval clinic-A single center retrospective analysis. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2019;29(04):391–396. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_258_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Celli P, Trillò G, Ferrante L. Spinal extradural schwannoma. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(04):447–456. doi: 10.3171/spi.2005.2.4.0447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kabeel K, Marjara J, Bhat R, Gaballah A H, Abdelaziz A, Bhat A P. Spontaneous hemorrhage of an adrenal myelolipoma treated with transarterial embolization: a case report. Radiol Case Rep. 2020;15(07):961–965. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2020.04.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Broski S M, Johnson G B, Howe B M et al. Evaluation of (18)F-FDG PET and MRI in differentiating benign and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Skeletal Radiol. 2016;45(08):1097–1105. doi: 10.1007/s00256-016-2394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Diel J, Ortiz O, Losada R A, Price D B, Hayt M W, Katz D S. The sacrum: pathologic spectrum, multimodality imaging, and subspecialty approach. Radiographics. 2001;21(01):83–104. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.21.1.g01ja0883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schuchardt P, Yasin J, Davis R M, Thimmappa N, Bhat A P. Pelvic trauma. Contemp Diagnostic Radiol. 2019;42:1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sung M S, Lee G K, Kang H S et al. Sacrococcygeal chordoma: MR imaging in 30 patients. Skeletal Radiol. 2005;34(02):87–94. doi: 10.1007/s00256-004-0840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Park S-A, Kim H S. F-18 FDG PET/CT evaluation of sacrococcygeal chordoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2008;33(12):906–908. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e31818c4e88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bhat A, Layfield L J, Tewari S O, Gaballah A H, Davis R, Wu Z. Solitary fibrous tumor of the ischioanal fossa-a multidisciplinary approach to management with radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiol Case Rep. 2018;13(02):468–474. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.01.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rodallec M H, Feydy A, Larousserie F et al. Diagnostic imaging of solitary tumors of the spine: what to do and say. Radiographics. 2008;28(04):1019–1041. doi: 10.1148/rg.284075156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bhat A P, Pimpalwar A, Dyke Ii P C. Ultrasonography and X-ray guided drain placement to evacuate a pneumopericardium/pneumomediastinum in a 1-day-old infant. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2019;29(01):94–97. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_447_18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bhat A P, Davis R M, Bryan W D. A rare case of bleeding duodenal varices from superior mesenteric vein obstruction -treated with transhepatic recanalization and stent placement. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2019;29(03):313–317. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_21_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sreenivasan N, Kalyanpur A, Bhat A, Sridhar P, Singh J. CT diagnosis of cecal diverticulitis. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2006;16:451–452. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bhat P, Sridhar P, Sreenivasan N, Kalyanpur A. Ct diagnosis of epiploic appendagitis-a case report. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2006;16:447–449. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bhat A P, Schuchardt P A, Bhat R, Davis R M, Singh S. Metastatic appendiceal cancer treated with Yttrium 90 radioembolization and systemic chemotherapy: a case report. World J Radiol. 2019;11(09):116–125. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i9.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shirley S K, Gilula L A, Siegal G P, Foulkes M A, Kissane J M, Askin F B. Roentgenographic-pathologic correlation of diffuse sclerosis in Ewing sarcoma of bone. Skeletal Radiol. 1984;12(02):69–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00360810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Green R, Saifuddin A, Cannon S. Pictorial review: imaging of primary osteosarcoma of the spine. Clin Radiol. 1996;51(05):325–329. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(96)80108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Senne J, Davis R, Yasin J, Brimmo O, Evenski A, Bhat A P. Computed tomography guided radio-frequency ablation of osteoid osteomas in atypical locations. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2019;29(03):253–257. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_259_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barwick K W, Huvos A G, Smith J. Primary osteogenic sarcoma of the vertebral column: a clinicopathologic correlation of ten patients. Cancer. 1980;46(03):595–604. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800801)46:3<595::aid-cncr2820460328>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Navarro S M, Matcuk G R, Patel D B et al. Musculoskeletal imaging findings of hematologic malignancies. Radiographics. 2017;37(03):881–900. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lasocki A, Gaillard F, Harrison S J. Multiple myeloma of the spine. Neuroradiol J. 2017;30(03):259–268. doi: 10.1177/1971400917699426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Becker S, Babisch J, Venbrocks R, Katenkamp D, Wurdinger S.Primary non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the spine Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1998117(6-7)399–401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu J K, Kan P, Schmidt M H. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as a sacral tumor. Report of two cases. Neurosurg Focus. 2003;15(02):E10. doi: 10.3171/foc.2003.15.2.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Quraishi N A, Giannoulis K E, Edwards K L, Boszczyk B M. Management of metastatic sacral tumours. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(10):1984–1993. doi: 10.1007/s00586-012-2394-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


