Abstract
γδ T cells are situated at barrier sites and guard the body from infection and damage. However, little is known about their roles outside of host defense in nonbarrier tissues. Here, we characterize a highly enriched tissue-resident population of γδ T cells in adipose tissue that regulate age-dependent regulatory T cell (Treg) expansion and control core body temperature in response to environmental fluctuations. Mechanistically, innate PLZF+ γδ T cells produced tumor necrosis factor and interleukin (IL) 17 A and determined PDGFRα+ and Pdpn+ stromal-cell production of IL-33 in adipose tissue. Mice lacking γδ T cells or IL-17A exhibited decreases in both ST2+ Treg cells and IL-33 abundance in visceral adipose tissue. Remarkably, these mice also lacked the ability to regulate core body temperature at thermoneutrality and after cold challenge. Together, these findings uncover important physiological roles for resident γδ T cells in adipose tissue immune homeostasis and body-temperature control.
Adipose tissue contains a unique immunological compartment that is important for physiologic responses to fasting and feeding, regulation of body weight, and thermogenesis. In adipose tissue, compared with lymphoid organs, approximately 80–90% of the immune system is innate. Much of what is known about the adipose tissue immune system suggests that its major roles are not focused on fighting infection. Instead, obesity studies have revealed that perturbations in immune cells or signaling molecules can either protect against or contribute to inflammation and insulin sensitivity. Although it is less understood, the resident innate immune compartment of adipose tissue also probably has important functions in the absence of obesity.
Beyond innate myeloid cells, a substantial component of adipose tissue comprises innate lymphocytes such as type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, mucosal-associated invariant T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and γδ T cells1,2. In the lean state, ILC2s and iNKT cells are critical for maintaining an anti-inflammatory environment through secretion of type 2 cytokines that support the function and survival of eosinophils, alternatively activated macrophages, and Treg cells3–6. Moreover, under other conditions including cold challenge, ILC2s and iNKT cells can induce thermogenic programs in adipose tissue7,8. In contrast, in obesity, NK8,9 cells and mucosal-associated invariant T cells10–12 secrete proinflammatory cytokines that impair glucose handling by adipocytes, hepatocytes, and muscle cells, and interfere with insulin production and insulin signaling. Despite recent advances in the understanding of adipose innate lymphocytes, the roles of γδ T cells in this dynamic organ remain largely unknown.
Foxp3+ Treg cells are a key adaptive cell type in adipose tissue. Treg cells are low in number in adipose tissue in mice until 20 weeks of age, after which they greatly expand and compose 40–80% of the CD4+ T cell population9–12. Adipose Treg cells have enhanced expression of genes, such as Il10, Gata3, Pparg, and Ilrl1, that define their adipose and anti-inflammatory phenotype9,10,13,14. Furthermore, they express high amounts of the IL-33 receptor ST2 (also known as IL-1R4), and IL-33 is critical for their local expansion and transcriptional stability11,15. We previously described a critical role of iNKT-cell-derived IL-2 in maintaining Treg cell numbers and boosting their function in adipose tissue3. In addition, ILC2s have been shown to play a role in Treg cell homeostasis via inducible T cell co-stimulator–ligand interactions after IL-33 administration, and Treg cells from mice deficient in inducible T cell co-stimulator ligand do not expand after IL-33 treatment16. Although these studies have provided mechanistic insights into the regulation of Treg homeostasis, the basis for the marked increase in Treg cell numbers with age is unknown.
IL-33 is an important factor in nonshivering thermogenesis, a metabolic adaptation to cold temperatures17,18. Adaptive thermogenesis is mediated largely by uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), which uncouples oxidative phosphorylation from ATP synthesis, thereby generating heat. IL-33 is critical for body-temperature regulation in newborns18, and adult mice deficient in IL-33 cannot induce UCP1 and consequently exhibit defects in thermogenesis8,19. In adipose tissue, the main source of IL-33 is debated and has been ascribed to a number of different stromal cell types including mesenchymal Cadherin-11+ (Cdh11) cells, podoplanin+ (Pdpn+) fibroblasts, or CD31+ endothelial cells15,16,20,21. Importantly, the mechanisms that regulate the endogenous expression of IL-33 in adipose tissue remain elusive.
Here, we describe an unexpected role of a canonical IL-17A-producing adipose-resident γδ T cell population that is required for age-dependent increases in Treg cells and the maintenance of body temperature and thermogenic tenor.
Results
γδ T cells are enriched and resident in adipose tissue.
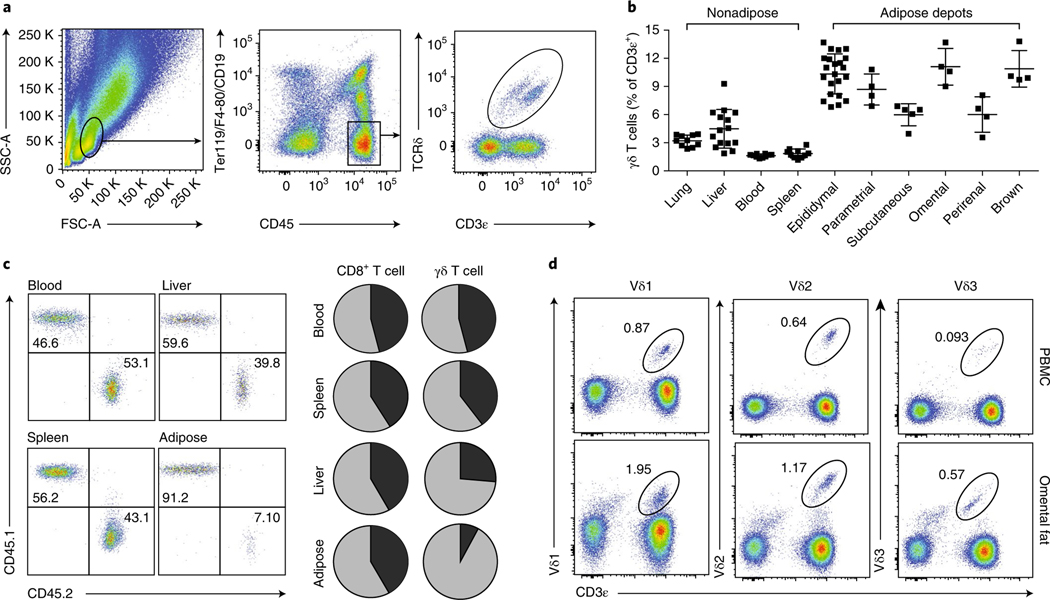
We profiled visceral adipose tissue through flow cytometry and found that γδ T cells were highly enriched in adipose tissue compared with other organs (Fig. 1a,b). γδ T cells were more abundant across several adipose depots than in peripheral sites including the lung, liver, blood, and spleen (Fig. 1b). To determine whether the enriched population of γδ T cells in visceral adipose tissue was constantly replenished from the periphery or whether these cells represented a tissue-resident population, we performed parabiosis experiments on congenic CD45.1 and CD45.2 mice (Fig. 1c). Whereas CD8+ T cells reached near-complete chimerism for the blood, spleen, liver, and adipose tissue, γδ T cells showed full recirculation only in the blood and spleen, whereas the liver and, more strikingly, the adipose tissue showed less chimerism (Fig. 1c). In adipose tissue, >90% of γδ T cells were endogenous to the host mice, thus indicating a resident or long-dwelling phenotype. Importantly, γδ T cells, identified by their Vδ chain usage, were also found in human omental adipose tissue (Fig. 1d). In human omentum, compared with peripheral blood, Vδ1, Vδ2, and Vδ3 subsets accounted for higher percentages of CD45+ lymphocytes. Thus, γδ T cells are enriched and resident in mouse and human adipose tissues.
Fig. 1 |. γδ T cells are enriched and resident in adipose tissue.
a, Representative flow cytometry plots of γδ T cells from the epididymal WAT stromal vascular fraction (eWAT SVF). K denotes thousand. b, Frequency of γδ T cells across various adipose tissue depots as a percentage of CD3ε+ T cells in male eWAT (n ≥ 4 mice per group). Each symbol represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate the mean. c, Flow cytometry of lymphocytes in the blood, liver, spleen, and adipose tissue of CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ congenic C57BL/6 parabiotic pairs joined at 6 weeks of age and analyzed 2 weeks later (left); and frequency pie charts of CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ CD8+ and γδ T cells (right). d, Frequency of Vδ1+, Vδ2+, and Vδ3+ γδ T cells (% of CD45+PI− cells) in peripheral blood (PBMCs) or from matched omental fat from patients before bariatric surgery. Data are representative of three experiments (a,b,d; mean ± s.e.m. in b) or one experiment (c).
PLZF discriminates two γδ T cell populations.
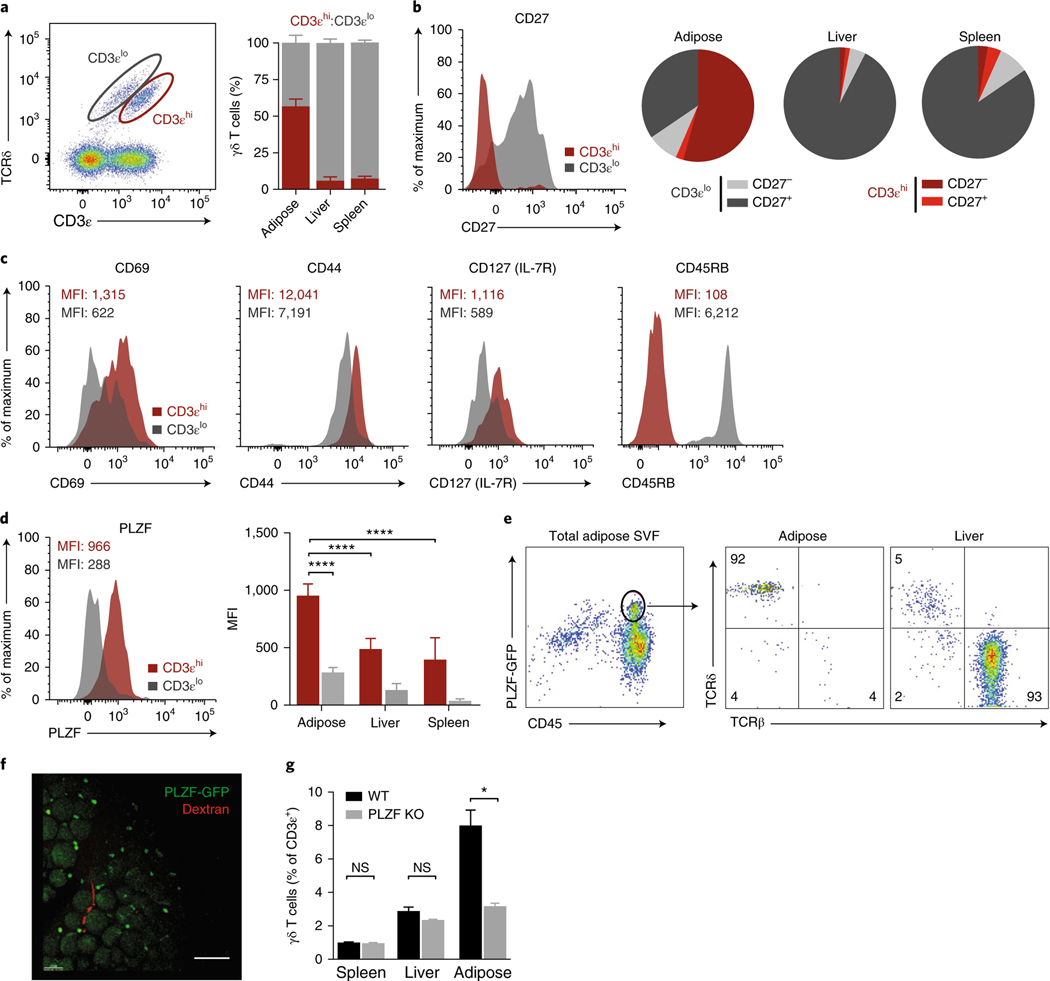
When profiling γδ T cells in adipose tissue, we found that they could be separated into two distinct populations on the basis of CD3ε intensity22 (Fig. 2a). CD3εhi γδ T cells were more abundant than CD3εlo cells in adipose tissue, making up to two-thirds of the total γδ T cell pool, whereas other organs such as the liver and spleen had few CD3εhi cells (Fig. 2a). CD27, a member of the TNFR superfamily and a costimulatory molecule, demarcates functionally distinct γδ subsets in mice23. We found that adipose γδ T cells were largely CD27−, corresponding to the CD3εhi subset, whereas in the spleen and liver, γδ T cells were largely CD3εloCD27+ (Fig. 2b). Additional phenotyping indicated that the enriched population of CD3εhiCD27− γδ T cells was CD69hi CD44hiCD127+CD45RB− (Fig. 2c).
Fig. 2 |. PLZF discriminates two γδ T cell populations.
a, Representative flow cytometry and frequency quantification of CD3εhi and CD3εlo γδ T cells from eWAT SVF across adipose, liver, and spleen (n = 5 mice). b, CD27 expression by CD3εhi and CD3εlo γδ T cells (left) and subset quantification from adipose, liver, and spleen (right) (n = 5 mice). c, Representative histograms of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD69, CD44, CD127, and CD45RB expression by CD3εhi and CD3εlo γδ T cells. d, Representative histogram of PLZF expression by CD3εhi and CD3εlo γδ T cells (left) and MFI quantification across adipose, liver, and spleen (right) (n = 5 mice). e, Representative flow cytometry and quantification of TCRβ+ versus TCRδ+ cells of PLZF+CD45+ cells from eWAT SVF. f, Immunofluorescence microscopy of whole-mount adipose tissue from Zbtb16GFP mice (green) injected with dextran (red). Scale bar, 100 μm. g, Frequency of γδ T cells from wild-type (WT) and Zbtb16−/− mice (n = 5). KO, knockout. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Data are representative of three experiments (a–e; mean ± s.e.m. in a,d) or two experiments (f,g; mean ± s.e.m. in g).
The BTB-POZ transcription factor PLZF, encoded by Zbtb16, imparts innate-like qualities to lymphocytes. PLZF is expressed on certain γδ T cells from other organs24,25, iNKT cells26, and human mucosal-associated invariant T cells27. We analyzed PLZF expression in adipose γδ T cells through flow cytometry and found that CD3εhi γδ T cells, compared with CD3εlo cells, highly expressed PLZF (Fig. 2d). PLZF expression was significantly higher in CD3εhi γδ T cells in the adipose tissue than in the liver and spleen (Fig. 2d). Furthermore, using Zbtb16GFP mice, we found that almost all the PLZF signal (>92% of PLZF+ cells) from adipose CD45+ cells was attributable to γδ T cells, whereas in the liver, most of the PLZF+CD45+ lymphocytes were TCRβ+ cells (Fig. 2e). Whole-mount staining of adipose tissue from Zbtb16GFP mice further confirmed the presence of PLZF+ cells and revealed them to be interspersed among adipocytes (Fig. 2f). PLZF-deficient (Luxoid) mice showed a two-thirds decrease in the frequency of adipose γδ T cells, corresponding to the relative frequency of PLZF+CD3εhi γδ T cells in adipose tissue (Fig. 2g). γδ T cell frequencies in other organs were unaffected by the loss of PLZF, because fewer PLZF+CD3εhi γδ T cells were present (Fig. 2g), thus highlighting the requirement of PLZF for the CD27− γδ T cell population resident in adipose tissue.
γδ T cells are important for adipose Treg accumulation.
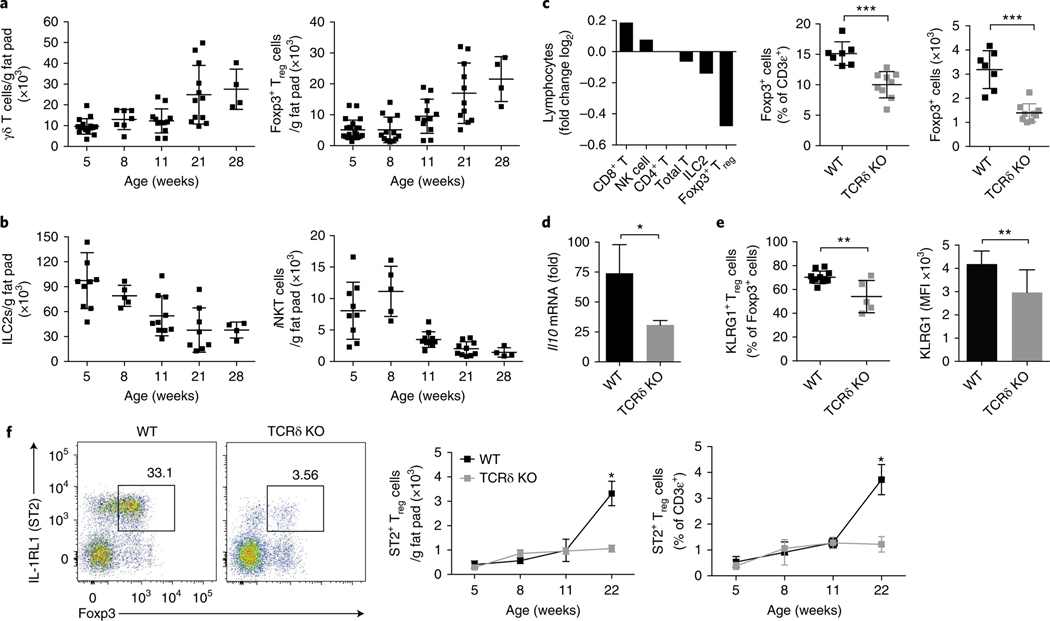
Next, we quantified the numbers of γδ T cells to determine changes in their frequency in adipose tissue over time. Interestingly, γδ T cells displayed accumulation kinetics similar to those of Foxp3+ Treg cells in adipose tissue (Fig. 3a). In contrast, both ILC2s and iNKT cells, two populations previously shown to influence adipose Treg numbers, decreased at the time of Treg expansion (Fig. 3b). Beyond Treg cells and γδ T cells, no other quantified lymphocyte population increased with age (Supplementary Fig. 1). Treg cells are well known to expand in adipose tissue with age, but a unifying mechanism explaining their temporal accumulation remains unknown. Thus, we wondered whether γδ T cells might play a role in adipose Treg homeostasis. To test this possibility, we profiled wild-type mice and mice deficient in T cell receptor (TCR) delta (Tcrd−/−). We found that the frequency of Treg cells was significantly lower in Tcrd−/− mice than in their wild-type counterparts at 20 weeks of age (Fig. 3c). A characteristic feature of adipose Treg cells is their high expression of IL-10 and the receptor proteins KLRG1 and ST2 (ref. 10). Treg cells sorted from Tcrd−/− adipose tissue expressed significantly less Il10 (Fig. 3d) and surface KLRG1 than did those sorted from wild-type adipose tissue (Fig. 3e). Finally, we found a striking defect in ST2+ Treg cell accumulation in Tcrd−/− mice compared with their wild-type littermates at 22 weeks of age, at the time of physiologic Treg cell expansion (Fig. 3f). Together these results reveal a concomitant increase in γδ T cells and Treg cells with age and a requirement of γδ T cells for visceral adipose Treg accumulation.
Fig. 3 |. γδ T cells are important for adipose Treg accumulation.
a,b, Numbers per gram eWAT of γδ T and Foxp3+ Treg cells (a) and ILC2s and iNKT cells (b) at 5, 8, 11, 21, and 28 weeks of age (n ≥ 4 mice per time point). c, Ratio (log2 normalized fold change) of CD8+ T, NK, CD4+ T, ILC2s, and Treg cell numbers from Tcrd−/− mice compared with WT mice (left) at 16 weeks of age (n = 10 mice). Frequency and numbers of Foxp3+ Treg cells in eWAT between WT and Tcrd−/− mice (right) at 16 weeks (n = 4 mice per group). d, Quantitative real-time PCR for Il10 expression normalized to Tbp from sorted CD25+CD4+ Treg cells from WT and Tcrd−/− mice at 16 weeks (n = 5 mice). e, Frequency (left) and MFI (right) of cell-surface KLRG1 expression on eWAT Foxp3+ Treg cells from mice 16 weeks of age (n = 5 mice). f, Representative flow cytometry of ST2+Foxp3+ Treg cells from eWAT (left) and cell numbers from WT and Tcrd−/− littermate (right) mice (n = 5) at 5, 8, 11, and 22 weeks of age. Each symbol represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate the mean. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (Two-tailed Student’s t test in c–e; one-way ANOVA in f). Data are representative of three experiments (a,b,f; mean ± s.e.m. in a,b,f) or two experiments (c–e; mean ± s.e.m. in c–e).
PLZF+ γδ T cells are innate IL-17A-producing cells.
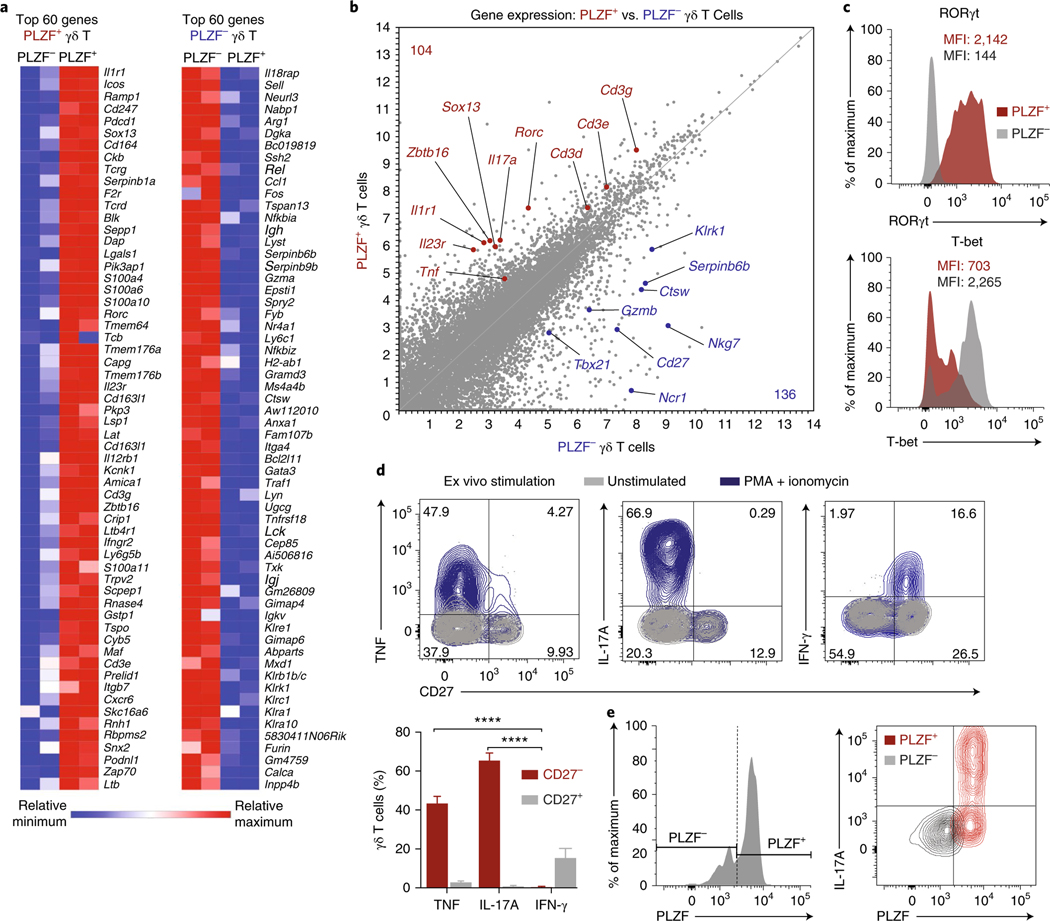
γδ T cells are generally recognized as innate-like lymphocytes that induce inflammation in response to pathogens and cellular stress. They rapidly secrete inflammatory cytokines such as TNF, IFN-γ, and IL-17, as well as chemokines that recruit key phagocytes to injured or infected tissues28. To understand how γδ T cells modulate Treg numbers in adipose tissue, we sought to further characterize their transcriptional phenotype and function. PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cells were sorted from adipose tissue from Zbtb16GFP mice and subjected to RNA sequencing and gene-expression analysis. Differential expression analysis revealed 247 and 205 genes that were significantly upregulated in adipose PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cells, respectively, of which the top 60 genes are shown (Fig. 4a). In accordance with the sorting strategy, Zbtb16 was among the most differentially expressed genes (Fig. 4a,b). Notably, transcripts of genes including Sox13, Rorc, Il1r1, and Il23r were significantly higher in PLZF+ γδ T cells than their PLZF− counterparts (Fig. 4a,b). Moreover, the high transcript levels of Tcrg, Tcrd, Cd3e, and Cd3g in PLZF+ γδ T cells reaffirmed the flow cytometry data distinguishing the CD3εhi versus CD3εlo γδ subsets (Fig. 4a). In contrast, the PLZF− γδ T cells showed significantly higher expression of genes characteristic of NK cells, including Ncr1, Nkg7, Klrk1, Gzmb, and Gzma (Fig. 4a,b). The high expression of these genes, together with the overexpression of genes encoding the transcription factor T-bet (Tbx21) as well as CD27 (Cd27), highlight their type 1 helper T cell– and NK-like transcriptional phenotype (Fig. 4b). Finally, we validated the protein expression of the receptor RORγt and of T-bet in γδ T cells and found them to be discretely expressed by PLZF+ and PLZF− subsets, respectively (Fig. 4c).
Fig. 4 |. PLZF+ γδ T cells are innate-IL17A− producing cells.
a, Heat map of the top 60 genes differentially expressed (false-discovery-rate-adjusted P value < 0.01) between PLZF+ (left) and PLZF− (right) γδ T cells. b, Scatter plot of gene transcripts differentially expressed by PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cells from 14-week-old male mice. c, Flow cytometry of RORγt (top) and T-bet (bottom) expression in PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cells from eWAT SVF. d, Representative intracellular cytokine staining (top) and quantification (bottom) on gated γδ T cells from eWAT SVF for TNF, IL-17A, and IFN-γ after 4-h stimulation with PMA and ionomycin (n = 4 mice). e, Representative intracellular IL-17A staining of gated PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cells from eWAT SVF after 4-h treatment with PMA and ionomycin (n = 5 mice). Small horizontal lines indicate the mean. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA in d). Data are representative of two experiments (c–e; mean ± s.e.m. in d).
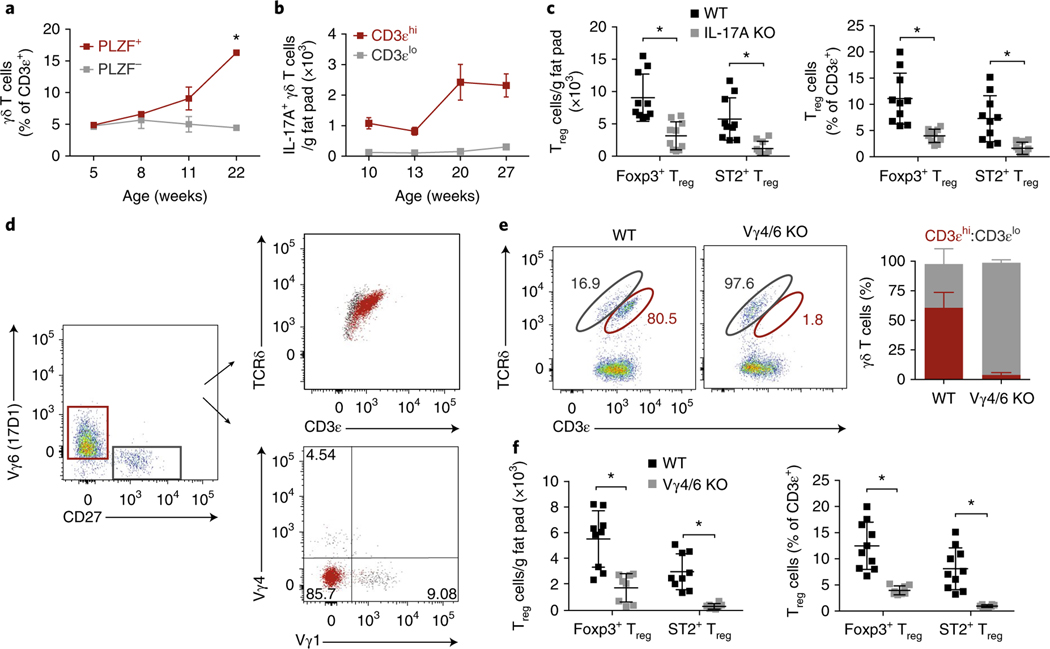
Transcriptional analysis revealed that PLZF+ γδ T cells expressed Il17a, whereas PLZF− γδ T cells expressed Ifng. Because CD27 is useful to demarcate IL-17A-producing (CD27−) versus IFN-γ-producing (CD27+) γδ T cells, we used CD27 as a marker for functional analysis. After stimulation, PLZF+ γδ T cells produced exclusively IL-17A and TNF, whereas PLZF− γδ T cells produced exclusively IFN-γ, results consistent with their gene expression (Fig. 4d,e). Together, our transcriptional, phenotypic, and functional characterizations highlight PLZF+ γδ T cells as innate IL-17A-producing cells and reveal an effector program distinct from that of the NK-like PLZF− γδ T cells in adipose tissue.
ST2+ Treg numbers depend on PLZF+ γδ T cells and IL-17A.
To parse the relative contributions of the two γδ T cell populations to the observed Treg phenotype, we determined the kinetics of accumulation of the two subsets over time (Fig. 5a). Flow cytometry analysis of visceral fat pads showed that IL-17A-producing PLZF+ γδ T cells, but not PLZF− γδ T cells, expanded with age (Fig. 5a). Importantly, profiling γδ T cells from Il17aGFP mice showed that the cell numbers significantly increased in adipose tissue with age (Fig. 5b). We next asked whether IL-17A might be important for the observed Treg cell accumulation. We found that IL-17A-deficient (Il17a−/−) mice, compared with wild-type mice, had significantly lower numbers and frequencies of total Foxp3+ Treg cells and did not accumulate ST2+ Treg cells in adipose tissue at 20 weeks of age (Fig. 5c). The iNKT and ILC2 numbers were not different between wild-type and Il17a−/− mice (Supplementary Fig. 2). Our data thus suggest that IL-17A is a key factor in the homeostatic expansion of Treg cells in visceral adipose tissue.
Fig. 5 |. ST2+ Treg numbers depend on PLZF+ γδ T cells and IL-17A.
a, Frequency of PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cells from eWAT at 5, 8, 11, and 22 weeks of age (n = 5 mice per time point). b, Numbers of GFP+ CD3εhi and CD3εlo γδ T cells from eWAT of Il17aGFP male mice at 10, 13, 20, and 27 weeks of age (n = 5 mice per time point). c, Numbers and frequency of ST2+ and total Treg cells from eWAT of 16-week-old males from WT and Il17a−/− mice (n = 5 mice, pooled). d, Representative flow cytometry of γδ T cells stained with anti-CD27, 17D1, anti-Vγ1, and anti-Vγ4 to characterize TCR usage. e, Representative flow cytometry plots of γδ T cells from WT and Vg4/6−/− eWAT (left) and quantification of CD3εhi and CD3εlo γδ frequencies (right) (n = 5 mice). f, Numbers and frequency of ST2+ and total Treg cells from eWAT of 16-week-old WT and Vg4/6−/− male mice (n ≥ 4). Each symbol represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate the mean. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA in a,c,f). Data are pooled across two experiments (mean ± s.e.m. in a–c,f) or representative of two experiments (d,e; mean ± s.e.m. in e).
γδ T cells with specific V-gene rearrangements leave the thymus in concerted waves during neonatal development and seed tissues29. The innate-IL17A-producing subset is largely dominated by Vγ6+ TCRs, although other IL-17A-producing Vγ4+ cells can arise later. Because some PLZF+ γδ T cells have been reported to bear the canonical Vγ6+ TCR chain, we stained γδ T cells from adipose tissue with antibodies to determine TCR usage30. In adipose tissue from mice at 20 weeks of age, most CD3εhiPLZF+CD27− γδ T cells were Vγ6+, whereas CD3εloPLZF−CD27+ γδ T cells expressed Vγ1+ and Vγ4+ TCR chains and composed a smaller fraction of the total adipose γδ T cells (Fig. 5d).
To deplete most of the PLZF+ γδ T cells, we characterized adipose tissue from Vγ4- and Vγ6-deficient (Vg4/6−/−) mice. We confirmed that the Vg4/6−/− mice had severely low numbers of PLZF+CD3εhi γδ T cells in adipose tissue, whereas PLZF–CD3εlo γδ T cells were still present (Fig. 5e). Next, we analyzed 20-week-old Vg4/6−/− mice and found that they, like Il17a−/− and Tcrd−/− mice, displayed significantly fewer total adipose Foxp3+ and ST2+ Treg cells than did wild-type mice (Fig. 5f). When profiling other immune populations, we observed similar frequencies of ILC2s, but unexpectedly, the number of iNKT cells was significantly lower in Vg4/6−/− mice than in wild-type mice, thus suggesting that cross-talk may exist between PLZF+ γδ T cells and iNKT cells in adipose tissue (Supplementary Fig. 2). Interestingly, the low frequencies of ST2+ Treg cells were not observed in the spleen and lung in Il17a−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice (Supplementary Fig. 2). In summary, these data uncover an important role of both IL-17A and PLZF+ γδ T cells in age-dependent increases in adipose tissue Treg cell numbers.
TNF and IL-17A induce IL-33 in adipose stromal cells.
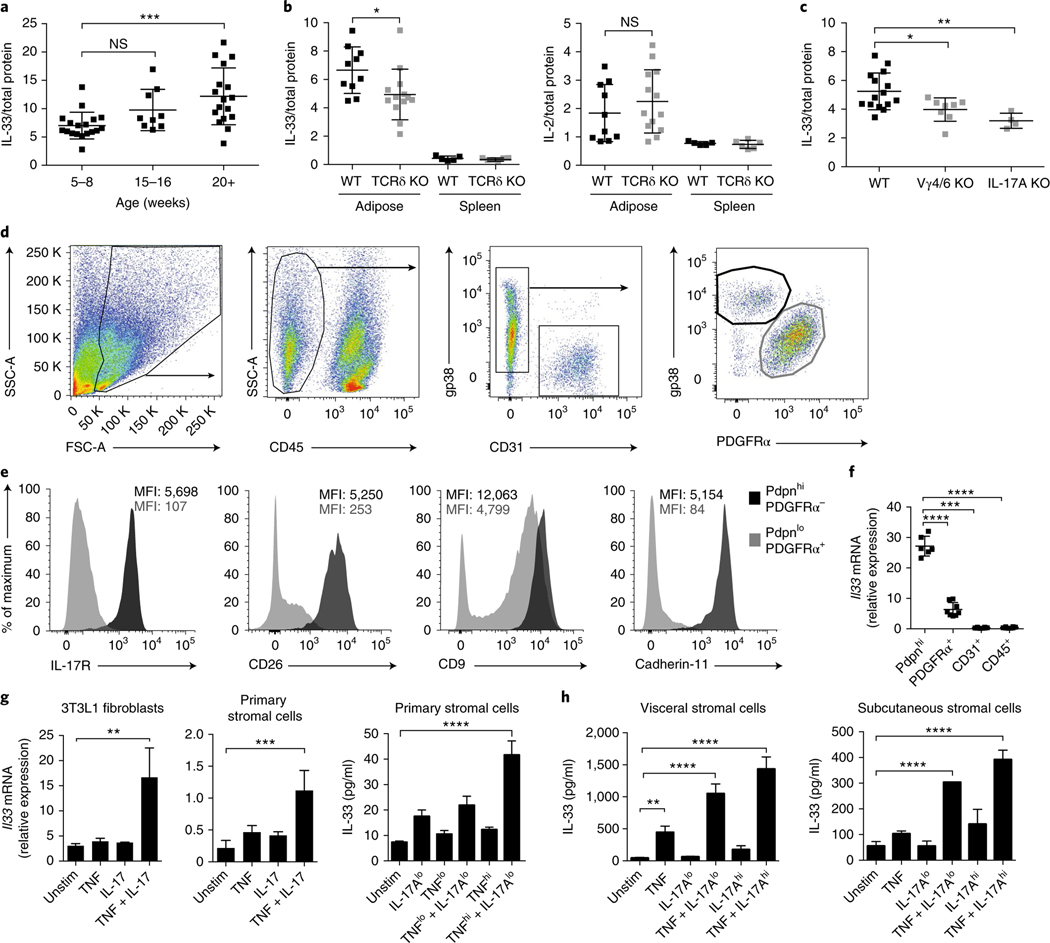
IL-33, a member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, is an important regulator of adipose ILC2 and Treg cell homeostasis because both cell types express the cognate receptor, ST2 (refs 11,15,31–34). Adipose Treg cells have high expression of ST2, and engagement of the ST2 receptor by IL-33 results in Treg proliferation11,15. We found that IL-33 protein increased with age in visceral adipose tissue, in a manner concomitant with Treg and PLZF+ γδ T cell accumulation (Fig. 6a). Because of the significantly lower Treg numbers in Tcrd−/−, Il17a−/−, and Vg4/6−/− mice compared with wild-type mice, we asked whether γδ T cells might affect IL-33 in adipose tissue. Indeed, 20-week-old Tcrd−/− mice, compared with wild-type mice, showed significantly less in IL-33 protein in the adipose tissue but not the spleen (Fig. 6b). IL-2, a critical cytokine for Treg maintenance in other peripheral organs, did not differ between wild-type and Tcrd−/− mice (Fig. 6b). IL-33 protein in adipose tissue was clearly less abundant in Il17a−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice than in wild-type mice (Fig. 6c). Interestingly, Il17a−/− mice had significantly less IL-33 protein and fewer ST2+ Treg cell numbers in visceral adipose tissue even at 11 weeks of age, thus suggesting that this phenotype manifests earlier in Il17a−/− mice than in wild-type mice (Supplementary Fig. 2). Together, these results suggest that IL-17A-producing PLZF+ γδ T cells are necessary for age-induced increases IL-33 protein in visceral adipose tissue.
Fig. 6 |. TNF and IL-17A induce IL-33 in adipose stromal cells.
a, IL-33 protein from SVF eWAT lysates of WT male mice 5–8, 15–16, and 20+ weeks of age, determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; n = 4 mice per time point) and normalized to total SVF protein. b, IL-33 (left) and IL-2 (right) protein from SVF eWAT and splenic lysates of 14-week-old WT and Tcrd−/− male mice (n ≥ 3, pooled). c, IL-33 protein from SVF eWAT lysates of 16-week-old WT, Vg4/6−/−, and Il17a−/− male mice (n ≥ 4), normalized to total SVF protein. d, Representative flow cytometry plots for stromal cell subsets in the eWAT SVF in male WT mice. e, Cell-surface IL-17R, CD26, CD9, and Cdh11 MFI of CD45−PdpnhiPDGFRα− and CD45−PdpnloPDGFRα+ stromal cells. f, Quantitative real-time PCR for Il33 mRNA normalized to Tbp mRNA from sorted Pdpnhi, PDGFRα+, CD31+, and CD45+ cells from WT mice (n = 6). g, 3T3L1 or primary adipose stromal cells derived from eWAT SVF were unstimulated (unstim) or stimulated with TNFlo (0.1 ng/mL), TNF (1 ng/mL), IL-17Alo (0.1 ng/mL), IL-17A (1 ng/mL), or TNF (1 ng/mL) + IL-17A (1 ng/mL) for 18 h. Il33 transcript levels were measured with quantitative real-time PCR (left), and protein levels were measured with ELISA (right). h, Primary human stromal cells derived from visceral (Lonza) and subcutaneous (ATCC) adipose tissues were unstimulated (unstim) or stimulated with TNFlo (0.1 ng/mL), TNF (1 ng/mL), IL-17Alo (0.1 ng/mL), IL-17A (1 ng/mL), or TNF (1 ng/mL) + IL-17A (1 ng/mL) for 18 h. Cell lysates were collected, and IL-33 protein was measured with ELISA. In plots, each symbol represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate the mean. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA in a–c,f–h). Data are pooled across three experiments (a–c; mean ± s.e.m.) or representative of two experiments (d–h; mean ± s.e.m. in f–h).
To assess the contribution of IL-17A-producing PLZF+ γδ T cells to IL-33 concentrations, we sought to identify the IL-33-expressing cell type and, importantly, test whether it would respond to IL-17A. Flow cytometry of the adipose stromal compartment identified a substantial population of CD31+ endothelial cells, as well as Pdpn+ (gp38+) stromal cells, among the nonhematopoietic (CD45−) pool (Fig. 6d). These Pdpn+ cells could further be segregated according to their expression of the surface marker platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha (PDGFRα) (Fig. 6d) as well as CD26, CD9, and Cdh11 (Fig. 6e). Staining for IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) to determine the subset that would respond to IL-17A identified Pdpn+CD26+PDGFRα–Cdh11+ stromal cells as the dominant IL-17R-expressing population in adipose tissue (Fig. 6e).
Intriguingly, when we quantified Il33 mRNA from sorted stromal cells, we found that Pdpn+PDGFRα− cells, as compared with other cells in adipose tissue, highly expressed Il33 (Fig. 6f). Our data highlight Pdpn+CD26+PDGFRα−Cdh11+ stromal cells as the main IL-33- and IL-17R-expressing cell type in visceral adipose tissue.
In addition to amplifying inflammation, IL-17A plays important homeostatic and antimicrobial roles at mucosal sites35. However, its effects on adipose tissue stromal cells (fibroblasts and adipocytes), as well as other resident immune cells, are less appreciated36. Because Il17a−/− mice exhibited severely low Treg cell numbers and IL-33 protein, we asked whether IL-17A might be sufficient to induce IL-33 expression in adipose stromal cells. Using 3T3L1 preadipocytes and fresh primary adipose stromal cells, we found that IL-17A stimulated increases in Il33 mRNA and IL-33 protein, but the presence of both TNF and IL-17A synergistically induced high expression of IL-33 (Fig. 6g). Moreover, this stimulation was specific to the combination of TNF and IL-17A, because neither IFN-γ nor IL-1β increased IL-33 to the same extent (Supplementary Fig. 3).
We next injected purified recombinant TNF and IL-17A into mice and found that, after injection, Il33 mRNA increased in adipose tissue (Supplementary Fig. 3). Mechanistically, TNF and IL-17A expanded IL-33-expressing Pdpn+ stromal cells and upregulated Il33 mRNA within the PDGFRα+ population (Supplementary Fig. 3). Although Pdpn+ stromal cells expressed the highest amounts of IL-33 at steady state, in vivo, both Pdpn+ and PDGFRα+ stromal subsets appeared to contribute to endogenous IL-33 expression in visceral adipose tissue and to be affected by TNF and IL-17A.
To assess why mice deficient in γδ T cells or IL-17A exhibited low IL-33 expression in adipose tissue, we quantified the numbers and IL-33 expression of stromal populations from wild-type, Tcrd−/−, Vg4/6−/−, and Il17a−/− mice. We found that both the Pdpn+ and PDGFRα+ stromal-subset numbers were markedly low in Tcrd−/−, Vg4/6−/−, and Il17a−/− mice, whereas IL-33 expression within stromal cells showed no significant differences (Supplementary Fig. 4). Our data suggest that in γδ-deficient and IL-17A-deficient animals, the low IL-33 expression is largely a result of low numbers of IL-33-expressing or IL-33-producing Pdpn+ and PDGFRα+ cells, respectively, but is less dependent on lower Il33 mRNA within stromal populations.
Recent reports have demonstrated IL-33 expression in human adipocytes and endothelial cells37,38 and have indicated that human omental Treg cells express ST2 (ref. 11). We asked whether this newly defined IL-17A–TNF–IL-33 axis might exist in human adipose tissue. In human primary preadipocytes from both visceral and subcutaneous adipose depots, stimulation with TNF and IL-17A greatly enhanced expression of IL-33 (Fig. 6h). Together, our results indicate that TNF and IL-17A produced by PLZF+ γδ T cells promote IL-33 within the stromal compartment in adipose tissue.
γδ T cells and IL-17A regulate body temperature.
Beyond its role in adipose immune regulation, IL-33 is important in thermogenesis, the metabolic adaptation to cold temperatures17,18. When we extended our analysis to brown adipose tissue (BAT) and inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT), depots important for increasing body temperature, we found that IL-33 protein was significantly less abundant in the BAT in Tcrd−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice than in wild-type mice (Supplementary Fig. 5). Although the protein levels were not different in iWAT, Il33 mRNA was less abundant in Tcrd−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice than in wild-type mice (Supplementary Fig. 5), thus raising the possibility that mice lacking γδ T cells might exhibit defects in body-temperature regulation.
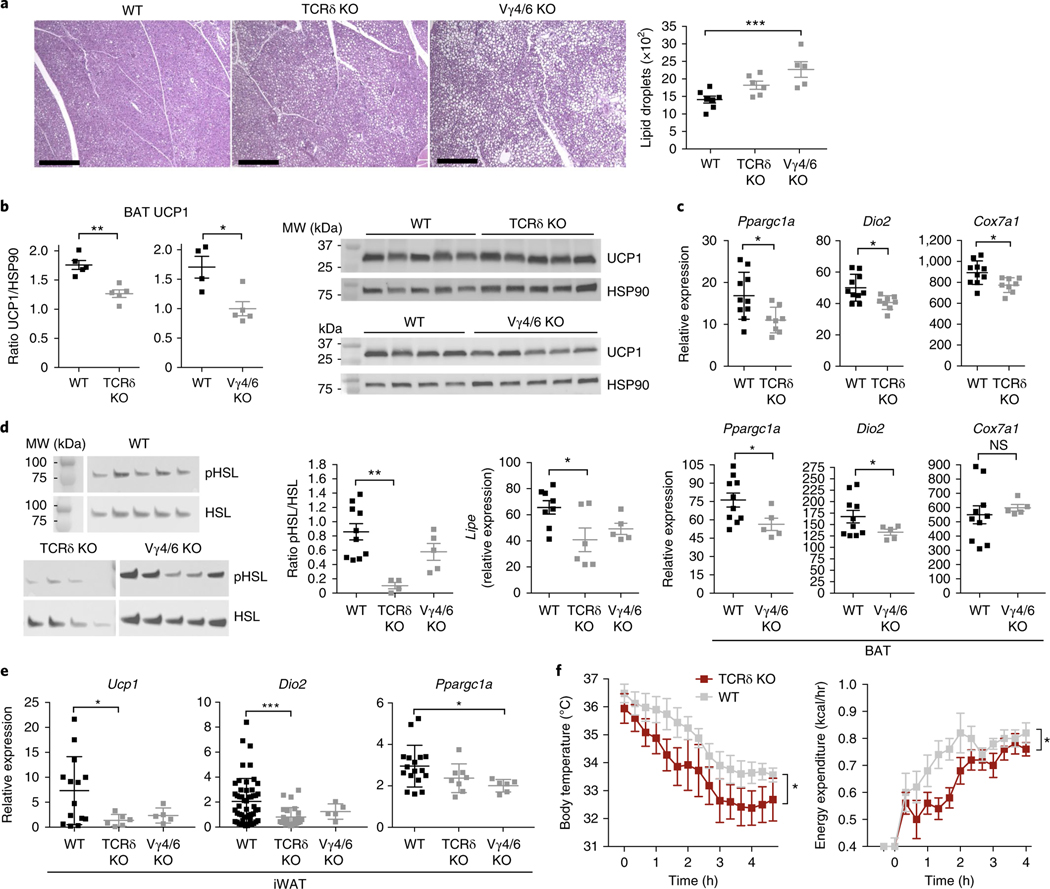
In support of this possibility, histological sections of BAT from cold-challenged mice showed that Tcrd−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice, compared with their wild-type littermates, contained more lipids in brown adipocytes (Fig. 7a). Importantly, Tcrd−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice, compared with wild-type mice, had less UCP1 protein in BAT, and lower expression of thermogenic genes, including Ppargc1a, Dio2, and Cox7a1, after cold challenge (Fig. 7b,c). Notably, when we evaluated iWAT after cold challenge, we found that Tcrd−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice, compared with wild-type mice, were unable to burn lipids, as evidenced by gross anatomy (Supplementary Fig. 5), and had lower expression and activation of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), a critical lipolytic enzyme (Fig. 7d). Like the BAT, the iWAT depot from Tcrd−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice, compared with wild-type mice, after cold challenge showed lower expression of thermogenic genes (Fig. 7e), thus suggesting that mice deficient in γδ T cells are unable to upregulate adaptive thermogenesis in BAT and iWAT.
Fig. 7 |. γδ T cells are important for adaptive thermogenesis after cold.
a, Representative histology of hematoxylin- and eosin-stained BAT and lipid-droplet quantification from WT, Tcrd−/−, and Vg4/6−/− mice after 6 h at 4 °C. Scale bars, 500 μm. b, Immunoblot analysis and densitometry quantification of UCP1 and HSP90 loading control in BAT of WT, Tcrd−/−, and Vg4/6−/− mice after 6 h at 4 °C (n = 5 mice). MW, molecular weight. c, Quantitative real-time PCR of thermogenesis genes from WT and Tcrd−/− BAT (top), and WT and Vg4/6−/− BAT (bottom) after 6 h at 4 °C (n ≥ 5 mice). d, Immunoblot analysis of phospo-HSL (pHSL) and HSL and quantitative real-time PCR of Lipe (also known as Hsl) from iWAT of WT, Tcrd−/−, and Vg4/6−/− mice after 6 h at 4 °C (n ≥ 5 mice). e, Quantitative real-time PCR of thermogenesis genes from WT, Tcrd−/−, and Vg4/6−/− iWAT after 6 h at 4 °C (n ≥ 5 mice). f, Body temperature (left) and energy expenditure (right) in WT and Tcrd−/− male mice from 30 °C to 4 °C (n = 5 per group). Each symbol represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate the mean. Gene expression normalized to Tbp. Immunoblots have been cropped to show relevant proteins. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (metabolic variable adjusted for differences in body composition by analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) in g; one-way ANOVA in a,e,f; two-tailed Student’s t test in b,c). Data are representative of two experiments (a–f; mean ± s.e.m. in a–g).
To determine whether these local adipose defects had physiological consequences, we measured body temperature and energy expenditure through indirect calorimetry. The body temperature of Tcrd−/− mice, compared with that of wild-type mice, decreased significantly more rapidly in the cold, and the knockout mice correspondingly were unable to increase energy expenditure (Fig. 7f). Of note, when challenged with the β-adrenergic agonist CL-316 243, which maximally activates BAT thermogenesis, Tcrd−/− mice did not show a defect in their ability to expend energy as heat, thereby suggesting that β-adrenergic signaling is downstream of γδ T cell control (Supplementary Fig. 5). Thus, mice deficient in γδ T cells are unable to engage nonshivering thermogenesis in response to cold, in part because of an inability to upregulate factors important for turning on the thermogenic program in BAT and iWAT.
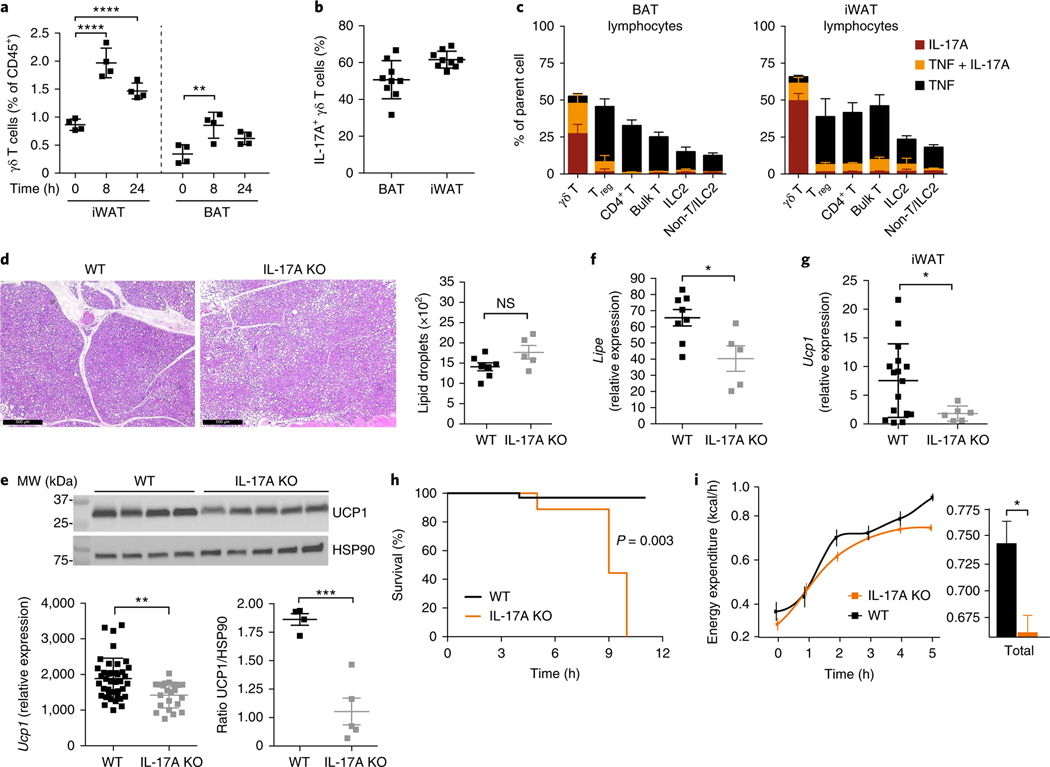
To better understand how γδ T cells promote thermogenic responses, we quantified the frequencies and cytokine profiles of γδ T cells in BAT and iWAT after cold challenge. We found that 8 h after cold challenge, γδ T cells significantly increased in frequency in both BAT and iWAT and remained elevated at 24 h (Fig. 8a). Despite their increased frequency, the number of γδ T cells did not change, thus suggesting a decline in other immune populations with cold (Supplementary Fig. 6). When γδ T cells were stimulated with the phorbol ester PMA and ionomycin, more than 40% produced IL-17A in BAT and iWAT (Fig. 8b). In contrast, other immune populations produced little IL-17A, thus highlighting the role of γδ T cells as the dominant source of IL-17A in both depots (Fig. 8c). γδ T cells thus make up a larger percentage of immune cells after cold challenge and are a major source of IL-17A in situ.
Fig. 8 |. IL-17A promotes thermogenic responses in brown and inguinal adipose tissue.
a, Frequency of γδ T cells of CD45+ cells in BAT and iWAT 0, 8, and 24 h at 4 °C (n = 4 mice). b, Frequency of IL-17A-producing γδ T cells from BAT and iWAT after 5-h stimulation with PMA and ionomycin (n = 10 mice). c, Frequency of immune cells from BAT and iWAT that produce TNF, IL-17A, or TNF + IL-17A after 4-h stimulation with PMA and ionomycin at 4 °C (n = 5 mice). d, Representative histology of hematoxylin- and eosin-stained BAT and lipid-droplet quantification from WT and Il17a−/− mice after 6 h at 4 °C. Scale bars, 500 μm. e, Quantitative real-time PCR of Ucp1 (left) and immunoblot analysis of UCP1 and HSP90 loading control (right) in BAT tissue obtained from WT and Il17a−/− mice (n ≥ 5) after 6 h at 4 °C. f, Quantitative real-time PCR of Lipe (also known as Hsl) from WT and Il17a−/− iWAT after 6 h at 4 °C (n ≥ 5 mice). g, Quantitative real-time PCR of Ucp1 from WT and Il17a−/− iWAT after 6 h at 4 °C (n ≥ 5 mice). h, WT and Il17a−/− mice were gradually shifted from 30 °C to 4 °C at a continuous rate and monitored for survival. Mice (n = 5) were rescued when body temperature dropped to <28 °C. i, Energy expenditure measured between WT and Il17a−/− male mice (n = 5). Each symbol represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate the mean. Gene expression was normalized to that of Tbp. Immunoblots have been cropped to show relevant proteins. NS, not significant (P > 0.05); *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (metabolic variable adjusted for differences in body composition by ANCOVA in h,i; one-way ANOVA in a; Two-tailed Student’s t test in d–g; log-rank Mantel–Cox test in h). Data are representative of two experiments (a–g; mean ± s.e.m. in a–g).
Because γδ T cells produce IL-17A in BAT and iWAT, we hypothesized that IL-17A might be an important regulator of the thermogenic phenotype observed. Indeed, like Tcrd−/− and Vg4/6−/− mice, Il17a−/− mice exhibited more lipid droplets in BAT than did wild-type mice (Fig. 8d) and did not upregulate BAT UCP1 (Fig. 8e) after cold exposure. Moreover, defects in lipolysis were observed in the iWAT in Il17a−/− mice (Fig. 8f), and a similar inability of Il17a−/− mice to upregulate Ucp1 in iWAT was measured (Fig. 8g). Il17a−/− mice, compared with wild-type mice, showed lower expression of other thermogenic genes in both BAT and iWAT (Supplementary Fig. 6). Strikingly, when WT and Il17a−/− mice were placed in metabolic cages for indirect calorimetry assessment, all of the Il17a−/− mice had to be rescued from death 5–12 h after cold challenge, because of their inability to increase energy expenditure (Fig. 8h,l). This inability was evidenced by the lack of increase in body temperature 5 h after cold challenge (Supplementary Fig. 6). Interestingly, Il17a−/− mice also showed abnormal circadian control of body temperature and the respiratory exchange ratio (Supplementary Fig. 6). Together, these data support a critical role for IL-17A in body-temperature regulation.
To understand the mechanism underlying thermogenic control by γδ T cells and IL-17A, we first quantified the gene expression of thermogenic enzymes and receptors (Supplementary Fig. 7). Interestingly, Adrb3 mRNA decreased across all genotypes in iWAT at thermoneutrality and after cold. Expression of Lipe and Pnpla2, two key genes for lipolysis, also significantly decreased, thus suggesting that mice lacking γδ T cells or IL-17A were relatively less sensitive to catecholamine stimulation for lipolysis induction. Second, stimulation with TNF and IL-17A synergistically upregulated thermogenic genes including Ucp1, Dio2, Cidea, and Il33 in brown adipocyte cultures (Supplementary Fig. 8). Stimulation with IL-33 itself did not induce the same increases in gene expression, thus suggesting that TNF and IL-17A can induce a thermogenic program in BAT independently of IL-33 (Supplementary Fig. 8). In iWAT, TNF and IL-17A injections in vivo were sufficient to induce Ucp1, Ppargc1a, and Dio2 in sorted Pdpn+ stromal cells but not PDGFRα+ cells (Supplementary Fig. 8). Finally, in BAT and iWAT in wild-type, Tcrd−/− and Vγ4/6−/− mice, we quantified immune cells known to be important for thermogenic responses (Supplementary Fig. 8). There were no differences observed in the ILC2, eosinophil, iNKT, and Treg frequencies between wild-type and Tcrd−/− mice in both depots, thus suggesting that the thermogenic defects seen in γδ T cell–deficient mice were independent of other immune populations. Together, our data suggest that γδ T cells promote thermogenic responses directly through the cytokines that they produce, namely TNF and IL-17A, and indirectly through maintenance of catecholamine sensitivity.
Discussion
The role of γδ T cells as guardians against pathogens at barrier sites has been well documented. However, the physiological roles of γδ T cells at steady state and in nonbarrier tissues are less appreciated. We uncovered a new biological axis in which PLZF+ IL-17A-producing γδ T cells cross-talk with adipose stromal cells and consequently regulate IL-33 abundance and exert downstream effects on Treg cell accumulation and thermoregulation. Post-translational processing tightly controls the levels of IL-33 (ref. 39), but the upstream mechanisms that control its transcription have been less studied. In addition, the main cell type that produces IL-33 in mouse adipose tissue had been a matter of debate. Our studies reveal Pdpn+ and PDGFRα+ cells to be IL-17A-responsive stromal cells in visceral adipose tissue. Moreover, TNF and IL-17A synergistically increase the cell numbers and Il33 expression, respectively, of Pdpn+ and PDGFRα+ cells, thereby modulating IL-33 abundance in situ. These findings highlight an important homeostatic role of IL-17A in adipose tissue, a function independent of its antimicrobial role.
Such effects mediated by γδ T cells are also intriguing given the previously defined roles of iNKT cells that also regulate Treg cell homeostasis3,7. We suggest that, whereas iNKT cells play a key role in regulating Treg numbers and function in young mice via IL-2, PLZF+ γδ T cells play a key role in adult mice via IL-33 when iNKT cell numbers decline. Despite their important roles as regulators of type 2 immunity in young mice, ILC2s and iNKT cells decrease with age, while a new wave of immune cells composed of γδ T cells and Treg cells expand. This temporal regulation of adipose lymphocytes may ensure redundancy in the molecular pathways that maintain healthy adipose tissue, as is critical for local and systemic metabolic homeostasis.
In addition, we discovered that γδ T cells and the cytokine IL-17A are critical regulators of thermogenesis, a distinctive function of adipose tissue. Deficiencies in γδ T cells and IL-17A dramatically affect the ability of mice to survive after cold challenge and robustly induce UCP1-dependent thermogenic responses. Remarkably, iNKT cells and PLZF+ γδ T cells in adipose tissue regulate thermogenesis through FGF-21 and IL-17A, respectively3,7. These roles of iNKT cells and γδ T cells in regulating both Treg cells and thermogenesis through complementary mechanisms underscores the remarkable importance of these innate T cell populations in adipose tissue. Our work opens a new dimension in adipose biology, whereby the dynamic cross-talk between innate lymphocytes and tissue-specific stromal cells dictates local immune composition and systemic energy expenditure.
Methods
Mice.
C57BL/6 J (WT), Il17a−/−, Tcrd−/−, and Il17aGFP mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory. Littermates were bred and maintained in specific-pathogen-free animal facilities at Brigham and Women’s Center for Comparative Medicine. In almost all experiments, male mice of specified ages were used. PLZF reporter mice (Zbtb16GFP mice) and Zbtb16−/− were generated in the laboratory of D. Sant’Angelo as previously described3,40. Vgamma4/6−/− (Vg4/6−/−) mice were a kind gift from R. O’Brien30. All studies were executed by following the relevant ethical regulations detailed in animal-use protocols. All animal work and protocols were approved by, and were in compliance with the guidelines of, the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
Parabiosis.
Parabiosis studies were conducted as previously described41. CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ mice were first anesthetized with ketamine (100 mg/kg body weight) and xylazine (10 mg/kg body weight). After mice were shaved, a linear incision was made from the scapulae to the lower abdomen on opposing sides of each member of the pair. Mice were placed side by side, and skin edges were sewn together. Each pair was housed singly, with food placed on the floor of the cage for the first week during recovery. Parabiotic mice were kept together for 2–3 weeks. Chimerism in the blood and tissues was defined for gated lymphocytes or lymphocyte subsets as the percentage of CD45.1+ cells over the percentage of CD45.1+ cells plus CD45.2+ cells in CD45.2+ mice, and as the percentage of CD45.2+ cells over the percentage of CD45.2+ cells plus CD45.1+ cells in CD45.1+ mice.
Comprehensive Lab Animal Monitoring System.
Indirect calorimetry experiments were performed with a Comprehensive Lab Animal Monitoring System (CLAMS, Columbus Instruments) essentially as previously described42. Mice were surgically implanted with intraperitoneal wireless temperature transmitters. After recovery, mice were housed in the CLAMS and maintained at thermoneutrality for 3 d. To observe the response to adrenergic agonist versus the effects of injection alone, we first injected mice housed at thermoneutrality with a control solution of sterile saline (200 μl) and monitored them for 3 h. The animals were then injected (1 mg/kg) with the selective β3-adrenergic receptor agonist CL316,243 (Sigma) and monitored as indicated. For the 4 °C cold challenge, mice were gradually shifted from 30 °C to 4 °C at a continuous rate over 3 h. For each experimental condition, metabolic variables were adjusted for differences in body composition by ANCOVA in the R programming language with a custom package for indirect calorimetry experiments (CalR).
Tissue digestion.
Adipose tissue was carefully excised, minced, and digested with 1 mg/mL collagenase type 2 (Worthington LS004188) in RPMI (Life Technologies) for 25 min at 37 °C, with shaking. Cells were passed through a 70-μm cell strainer, washed, and centrifuged for 5 min at 300 g to pellet the stromal-vascular fraction (SVF) from floating mature adipocytes. For the preparation of single-cell suspensions of the liver, the organ was perfused via the portal vein with 10 mL PBS and mashed through a 70-μm cell strainer. Liver samples underwent enrichment for lymphocytes by centrifugation with a Percoll gradient. Spleens were strained through a 70-μm cell strainer and spun. Pellets from all tissues were subjected to red blood cell lysis and subsequently resuspended in flow cytometry buffer (2% FBS and 0.02% NaN3 in phenol-free DMEM) for further staining.
Flow cytometry and cell sorting.
Single-cell suspensions were incubated with Fc-receptor-blocking antibody (14–0161-82; eBioscience) before being stained on ice. Dead cells were excluded with a live/dead Zombie Aqua stain (BioLegend). For intracellular transcription-factor staining, cells were fixed and permeabilized with eBioscience Transcription Factor Fix/Perm Buffer. Mouse antibodies were as follows. Anti-CD45 (30-F11), anti-CD45.1 (A20), anti-CD45.2 (104), anti-CD27 (LG.3A10), anti-CD69 (FN50), anti-CD44 (BJ18), anti-CD127 (A019D5), anti-CD4 (RM4–5), anti-CD8α (53–6.7), anti-TCRβ (H57–597), anti-KLRG1 (2F1/KLRG1), anti-pdpn (8.1.1), anti-CD26 (H194–112FC), and anti-CD31 (390) were purchased from BioLegend. Anti-Ter119 (TER-119), anti-F4/80 (BM8), anti-CD19 (ID3), anti-γδ TCR (GL3), anti-CD3e (500A2), anti-PLZF (Mags.21F7), anti-Foxp3 (FJK-16s), anti-ST2 (RMST2–2), anti-T-bet (4B10), anti-RORγt (B2D), anti-TNF (MP6-XT22), anti-IL-17A (17B7), anti-IFN-γ (XMB1.2), anti-PDGFRα (APA5), anti-IL-17RA (PAJ-17R), and streptavidin-APC (Cat 17–4317-82) were purchased from eBioscience. To stain for Vγ6+ cells, we used GL3 (anti-TCRγδ) and 17D1 (anti-Vγ5 Vδ1) antibodies as previously described30. Anti-Vγ4 (UC3–10A6) was purchased from BD Pharmingen. Biotinylated anti-Cad11 was generated in house. Mouse PBS-57-loaded CD1d tetramers were from the NIH tetramer facility. Human antibodies were as follows. Anti-TCR Vδ1 (REA173) and anti-TCR Vδ2 (123R3) were purchased from Miltenyi Biotec. Anti-CD3 (UCHT1) was purchased from BioLegend. Anti-TCR Vδ3 was custom made in Labpan (Europe). After being stained, cells were passed through a 70-μm filter, and data were acquired on a BD FACSAria Fusion, BD Fortessa, or BD Canto II analyzer with FACSDiva software. Spherotech AccuCount fluorescent particles were added for cell quantification before analysis on the flow cytometers. Cell doublets were excluded by comparison of the side-scatter width to the forward-scatter area. For analysis of γδ T cells, a ‘dump gate’ with Ter119, CD19, and F4/80 was used for elimination of nonspecific staining.
PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cells were sorted directly from freshly digested adipose tissue from PLZFGFP mice. Fibroblast subsets were sorted according to the gating scheme outlined in Fig. 6d. Cell sorting was performed on a BD FACSAria Fusion sorter with a 70-μm nozzle. The cell purity was routinely >98%. For RNA analyses, sorted cells were lysed in either TRIzol (Qiagen) or RLT lysis buffer (Qiagen) with 1% β-mercaptoethanol (2-ME, Sigma).
Immunofluorescence.
For detection of GFP, epididymal adipose tissue was harvested into 0.02% sodium azide and 5% normal mouse serum in PBS (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories). Adipose tissue mounted on glass slides with Aqua Poly/Mount (Polysciences), and coverslips was imaged with a confocal microscope (Leica TCS SP5).
In vitro stimulations.
Adipose tissue was digested as described above, and bulk SVF was stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, 50 ng/mL) and ionomycin (1 μg/mL) for 6 h in complete RPMI medium (RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS (Gemini), HEPES (Invitrogen), l-glutamine, penicillin/streptomycin, and 2-ME). Brefeldin A (1:1,000, eBioscience) was added for the last 5 h. Cells were washed twice in 2% FBS in DMEM, surface stained, and fixed and permeabilized with eBioscience Transcription Factor Fix/Perm Buffer to assay cytokine production by γδ T cells.
Primary stromal cells from mouse and human adipose tissue were generated by digesting adipose tissue and expanding bulk cells in six-well plates in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS (Gemini), 2 mM l-glutamine, 50 μM 2-ME, and antibiotics (penicillin and streptomycin). After 3–5 d, nonadherent cells were washed off, and stromal cells were trypsinized. Stromal cells were plated on day 1 at a density of 5 × 104 cells per well in 24-well plates in 10% FBS-containing medium. Human cells were serum starved on day 2 by being switched to 1% FBS-containing medium. Cells were left unstimulated or were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of TNF (Peprotech), IL-17A (Peprotech), or a combination of the two, for 18 h. Cells were then washed in PBS, and cell lysates were harvested for protein analysis.
Immunoblotting.
Whole adipose tissues were homogenized in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, protease-inhibitor cocktail (Roche), 500 U/mL benzonase nuclease (Novagen), 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM Na3VO4, and 10 mM NaF). Samples were clarified by centrifugation for 15 min at 16,100 g. The protein concentration was measured with a BCA protein assay kit (Pierce). 20–50 μg of protein was loaded on 4–20% Mini Protean TGX gradient gels (Bio-Rad). Protein was transferred to 0.2 μm PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad). Membranes were blocked in Tris-buffered saline plus 0.1% Tween 20 (TBS-T) containing 5% BSA or 5% milk for 1 h at 25 °C, then incubated overnight with primary antibodies at 4 °C. Primary antibodies were diluted 1:1,000 in 5% BSA or 5% milk in TBS-T. The primary antibodies used were against UCP1 (Abcam, 10983) and HSP90 (Cell Signaling, 4877, C45G5). Membranes were washed with TBS-T and incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (Jackson Immunoresearch; anti-rabbit 111–035-144 and anti-mouse 115–035-003) for 1 h at 25 °C. HRP was activated with Bio-Rad Clarity Western ECL Substrate (Bio-Rad) and visualized with a chemiluminscence detection system (Bio-Rad Chemidoc). The densitometry of blots was analyzed in ImageJ.
ELISA.
Processed adipose SVF lysates or stromal cell cultures were diluted 1:2 in reagent diluent (1% BSA in PBS), and IL-33 protein concentrations were quantified with a Mouse/Rat IL-33 Quantikine ELISA kit (M3300, R&D Systems). Adipose SVF lysates were similarly analyzed for IL-2 with a Ready-SET-Go! ELISA kit (eBioscience).
RT–PCR analyses.
Tissues were snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until use. Inguinal, epididymal, and brown adipose tissue depots were homogenized in TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies, 15596026) and mixed with chloroform at a ratio of 5:1. After samples were spun, the upper aqueous phase was mixed with the same volume of 70% EtOH, and RNA was isolated with RNeasy Mini Kits (Qiagen, 74104). cDNA was prepared through Quantitect RT–PCR (Qiagen, 205311), and PCR was performed with Brilliant III SYBRGreen (Agilent, 600882) on a Stratagene Mx3000 instrument. The primers used were as follows: Tbp (forward, 5′-CTACCGTGAATCTTGGCTGTAAAC-3′; reverse, 5′-AATCAACGCAGTTGTCCGTGGC-3′), Il10 (forward, 5′-AATAAGCTCCAAGACCAAGG-3′; reverse, 5′-CAGACTCAATACACACTG-3′), Il33 (forward, 5′-ATGGGAAGAAGCTGATGGTG-3′; reverse, 5′-CCGAGGACTTTTTGTGAAGG-3′), Ucp1 (forward, 5′-GGCCTCTACGACTCAGTCCA-3′; reverse, 5′-TAAGCCGGCTGAGATCTTGT-3′), Ppargc1a (forward, 5′-AGCCGTGACCACTGACAACGAG-3′; reverse, 5′-GCTGCATGGTTCTGAGTGCTAAG-3′), Dio2 (forward, 5′-TGCCACCTTCTTGACTTTGC-3′; reverse, 5′-GGTTCCGGTGCTTCTTAACC-3′), Cox7a1 (forward, 5′-AAA CCGTGTGGCAGAGAAGCAG-3′; reverse, 5′-CCCAAGCAGTATAAGCAGTAGGC-3′), Adrb3 (forward, 5′-AACTGAAACAGCAGACAGGGAC-3′; reverse, 5′-CCCCCATGTACACCCTAGTT-3′), Th (forward, 5′-CCAAGGTTCATTGGACGGC-3′; reverse, 5′-CTCTCCTCGAATACCACAGC-3′), Lipe (forward, 5′-GCTCATCTCCTATGACCTACGG-3′; reverse, 5′-TCCGTGGATGTGAACAACCAGG-3′), and Pnpla2 (forward, 5′-GGAACCAAAGGACCTGATGACC-3′; reverse, 5′-ACATCAGGCAGCCACTCCAACA-3′).
Histology.
For whole-fat-tissue staining, 5 mm2 of BAT was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS overnight, washed in PBS, and stored in 70% ethanol. Samples were processed and embedded in paraffin and stained with H&E by the Dana Farber Rodent Histopathology Core. For lipid-droplet quantification, histological sections of BAT were placed under a microscope, and images were acquired under 100× magnification. These images in TIFF format were analyzed in the automated Fiji-based Open Source software package Adiposoft. Under 0.485 μm per pixel, a minimum diameter of 20 μm and a maximum diameter of 100 μm were set for the calculation of adipocyte area.
RNA sequencing.
RNA was isolated from 800–1,000 cells from sorted γδ T cell populations from Zbtb16GFP mice as described. 5 μl of total RNA was placed in wells of a 96-well plate, and RNA sequencing libraries were prepared at Broad Technology Labs at the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT via the Illumina SmartSeq2 platform. Samples were sequenced on a NextSeq500 instrument with 75-bp paired-end reads to an average depth of 9 million pairs of reads per sample by the Broad Genomics Platform. Reads were mapped to the mouse genome (mm10) with HISAT43 (0.1.6-beta release). Bam files were sorted and indexed in SAMtools44 (1.2 release). Assembly, quantification, and normalization were performed in CuffLinks45 (1.2 release) according to the Tuxedo pipeline46. A merged transcriptome constructed from all samples was used as a reference annotation for quantification (by CuffQuant) and normalization (by CuffNorm) stages. Differentially expressed genes between PLZF+ and PLZF− γδ T cell subsets were identified in CuffDiff47 (false-discovery rate and adjusted P value <0.1). Genes with calculated FPKM values (according to CuffDiff’s pooled dispersion measure) lower than 26 in both subsets were removed from the analysis to avoid low noisy measurements. For heat maps, values lower than 1 were replaced by 1, and then the data were log2 transformed.
Human tissue.
Omental adipose tissue was obtained from patients undergoing weight-loss surgery, with the approval of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Institutional Review Board. The tissue was processed similarly to mouse adipose tissue. Matched peripheral blood was also collected for analysis. Informed consent was obtained from all patients, and samples were collected in accordance with BWH ethical regulations. Cultured stromal cell fibroblast lines were generated from visceral preadipocytes (Lonza, PT-5005) and subcutaneous preadipocytes (ATCC, PLS-210–010), and grown in T-75 cm2 flasks in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS (Gemini), 2 mM L-glutamine, 50 μM 2-ME, and antibiotics (penicillin and streptomycin).
Statistics.
Independent experiments were repeated at least two to three times, and the data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined with two-tailed Student’s t test, one-way ANOVA, or two-way ANOVA as indicated. A P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant, and significance is presented as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, or ****P < 0.0001. No exclusion of data points or mice was used. Pilot studies were used for estimation of the sample size required to ensure adequate power. GraphPad Prism 6 was used for all statistical analyses.
Reporting Summary.
Further information on experimental design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary.
Data availability.
RNA-seq expression data have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus database under accession number GSE103742. The data that support the findings of this study are additionally available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank A.T. Chicoine, flow cytometry core manager at the Human Immunology Center at BWH, for flow cytometry sorting. We thank D. Sant’Angelo (Rutgers Cancer Institute) for providing Zbtb16−/− mice and R. O’Brien (National Jewish Health) for providing Vg4/6−/−- mice. Supported by NIH grant R01 AI11304603 (to M.B.B.) and by NIH grant R01AI134861, ERC Starting Grant 679173 (to L.L.), the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (1013667), an Australian Research Council Future Fellowship (FT140100278 for A.P.U.) and a National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia Senior Principal Research Fellowship (1117766 for D.I.G.).
Footnotes
Competing interests
M.B.B. is a consultant to Roche.
Additional information
Supplementary information is available for this paper at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0094-2.
Methods
Methods, including statements of data availability and any associated accession codes and references, are available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0094-2.
References
- 1.Brestoff JR & Artis D. Immune regulation of metabolic homeostasis in health and disease. Cell 161, 146–160 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kohlgruber A. & Lynch L. Adipose tissue inflammation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep 15, 92 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lynch L. et al. Regulatory iNKT cells lack expression of the transcription factor PLZF and control the homeostasis of Treg cells and macrophages in adipose tissue. Nat. Immunol 16, 85–95 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lynch L. et al. Adipose tissue invariant NKT cells protect against diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorder through regulatory cytokine production. Immunity 37, 574–587 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Molofsky AB et al. Innate lymphoid type 2 cells sustain visceral adipose tissue eosinophils and alternatively activated macrophages. J. Exp. Med 210, 535–549 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nussbaum JC et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells control eosinophil homeostasis. Nature 502, 245–248 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lynch L. et al. iNKT cells induce FGF21 for thermogenesis and are required for maximal weight loss in GLP1 therapy. Cell Metab. 24, 510–519 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brestoff JR et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote beiging of white adipose tissue and limit obesity. Nature 519, 242–246 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Feuerer M. et al. Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat. Med 15, 930–939 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cipolletta D. et al. PPAR-γ is a major driver of the accumulation and phenotype of adipose tissue Treg cells. Nature 486, 549–553 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vasanthakumar A. et al. The transcriptional regulators IRF4, BATF and IL-33 orchestrate development and maintenance of adipose tissue-resident regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol 16, 276–285 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bapat SP et al. Depletion of fat-resident Treg cells prevents age-associated insulin resistance. Nature 528, 137–141 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cipolletta D. Adipose tissue-resident regulatory T cells: phenotypic specialization, functions and therapeutic potential. Immunology 142, 517–525 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Panduro M, Benoist C. & Mathis D. Tissue Tregs. Annu. Rev. Immunol 34, 609–633 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kolodin D. et al. Antigen- and cytokine-driven accumulation of regulatory T cells in visceral adipose tissue of lean mice. Cell Metab. 21, 543–557 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Molofsky AB et al. Interleukin-33 and interferon-γ counter-regulate group 2 innate lymphoid cell activation during immune perturbation. Immunity 43, 161–174 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mathis D. IL-33, imprimatur of adipocyte thermogenesis. Cell 166, 794–795 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Odegaard JI et al. Perinatal licensing of thermogenesis by IL-33 and ST2. Cell 166, 841–854 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee M-W et al. Activated type 2 innate lymphoid cells regulate beige fat biogenesis. Cell 160, 74–87 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jackson-Jones LH et al. Fat-associated lymphoid clusters control local IgM secretion during pleural infection and lung inflammation. Nat. Commun 7, 12651 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pichery M. et al. Endogenous IL-33 is highly expressed in mouse epithelial barrier tissues, lymphoid organs, brain, embryos, and inflamed tissues: in situ analysis using a novel Il-33-LacZ gene trap reporter strain. J. Immunol 188, 3488–3495 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Paget C. et al. CD3bright signals on γδ T cells identify IL-17A-producing Vγ6Vδ1+ T cells. Immunol. Cell Biol 93, 198–212 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ribot JC et al. CD27 is a thymic determinant of the balance between interferon-γ- and interleukin 17-producing γδ T cell subsets. Nat. Immunol 10, 427–436 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kreslavsky T. et al. TCR-inducible PLZF transcription factor required for innate phenotype of a subset of γδ T cells with restricted TCR diversity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 12453–12458 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lu Y, Cao X, Zhang X. & Kovalovsky D. PLZF controls the development of fetal-derived IL-17+Vγ6+ γδ T cells. J. Immunol 195, 4273–4281 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Savage AK et al. The transcription factor PLZF directs the effector program of the NKT cell lineage. Immunity 29, 391–403 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Alonzo ES & Sant’Angelo DB Development of PLZF-expressing innate T cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol 23, 220–227 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vantourout P. & Hayday A. Six-of-the-best: unique contributions of γδ T cells to immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol 13, 88–100 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wei Y-L et al. A highly focused antigen receptor repertoire characterizes γδ T cells that are poised to make IL-17 rapidly in naive animals. Front. Immunol 6, 118 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Roark CL et al. Subset-specific, uniform activation among Vγ6/Vδ1+ γδ T cells elicited by inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol 75, 68–75 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Van Dyken SJ et al. Chitin activates parallel immune modules that direct distinct inflammatory responses via innate lymphoid type 2 and γδ T cells. Immunity 40, 414–424 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vannella KM et al. Combinatorial targeting of TSLP, IL-25, and IL-33 in type 2 cytokine-driven inflammation and fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med 8, 337ra65 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schiering C. et al. The alarmin IL-33 promotes regulatory T-cell function in the intestine. Nature 513, 564–568 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kuswanto W. et al. Poor repair of skeletal muscle in aging mice reflects a defect in local, interleukin-33-dependent accumulation of regulatory T cells. Immunity 44, 355–367 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hepworth MR Innate lymphoid cell regulation: meeting the long-lost cousin. Trends Immunol. 38, 873–874 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zúñiga LA et al. IL-17 regulates adipogenesis, glucose homeostasis, and obesity. J. Immunol 185, 6947–6959 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wood IS, Wang B. & Trayhurn P. IL-33, a recently identified interleukin-1 gene family member, is expressed in human adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 384, 105–109 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zeyda M. et al. Severe obesity increases adipose tissue expression of interleukin-33 and its receptor ST2, both predominantly detectable in endothelial cells of human adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 37, 658–665 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Martin NT & Martin MU Interleukin 33 is a guardian of barriers and a local alarmin. Nat. Immunol 17, 122–131 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References
- 40.Kovalovsky D. et al. The BTB-zinc finger transcriptional regulator PLZF controls the development of invariant natural killer T cell effector functions. Nat. Immunol 9, 1055–1064 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wagers AJ, Sherwood RI, Christensen JL & Weissman IL Little evidence for developmental plasticity of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Science 297, 2256–2259 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Okada K. et al. Thioesterase superfamily member 1 suppresses cold thermogenesis by limiting the oxidation of lipid droplet-derived fatty acids in brown adipose tissue. Mol. Metab 5, 340–351 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kim D, Langmead B. & Salzberg SL HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–360 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li H. et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Trapnell C. et al. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol 28, 511–515 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Trapnell C. et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc 7, 562–578 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Trapnell C. et al. Differential analysis of gene regulation at transcript resolution with RNA-seq. Nat. Biotechnol 31, 46–53 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
RNA-seq expression data have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus database under accession number GSE103742. The data that support the findings of this study are additionally available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.