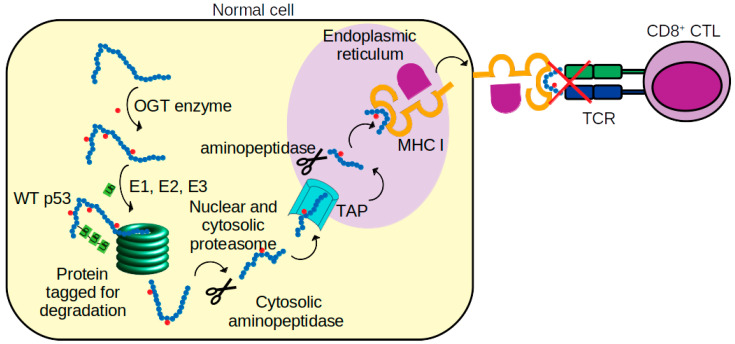
Figure 7.
Schematic of p53 peptide presentations to cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). p53 protein is first glycosylated (small red filled circles) by O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) [64]. The glycosylated p53 is then tagged by ubiquitin (Ub chains) by ubiquitin-activating (E1), ubiquitin-conjugating (E2), and ubiquitin-protein ligase (E3) enzymes. Next, the protein is digested into peptides by proteasomes and aminopeptidase enzymes. The peptides are later translocated, via transporters associated with antigen processing (TAP), into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In the ER, the peptides are again trimmed by aminopeptidase and loaded on to nascent MHC class I molecules [65]. MHC class I-peptide complexes are then translocated to the surface of the tumor cell and recognized by the T cell receptor (TCR) of CD8+ CTL cell. Our simulations suggest that in some normal cells, the glycosylated p53 peptide in the complex with MHC I is not recognized by TCR.