Abstract
Ceramide is a bioactive sphingolipid involved in numerous cellular processes. In addition to being the precursor of complex sphingolipids, ceramides can act as second messengers, especially when they are generated at the plasma membrane of cells. Its metabolic dysfunction may lead to or be a consequence of an underlying disease. Recent reports on transcriptomics and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis have demonstrated the variation of specific levels of sphingolipids and enzymes involved in their metabolism in different neurodegenerative diseases. In the present review, we highlight the most relevant discoveries related to ceramide and neurodegeneration, with a special focus on Parkinson’s disease.
Keywords: ceramide, sphingolipids, Parkinson’s disease, neurodegeneration, sphingomyelinase, ceramide synthase, β-GCase, sphingolipidomics
1. Introduction
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease [1]. PD affects 1% of the population over 60 years of age, with a higher risk of developing the disease in males [2,3]. The annual economic burden of PD in the European healthcare system per patient ranges from €2600 to €10,000 [4]. The disease presents with symptoms of motor impairment such as bradykinesia, rigidity, tremor, postural instability, and difficulty in speaking and swallowing. As for non-motor symptoms, patients present sleep disturbance, depression, cognitive impairment, sensory abnormalities, or autonomic dysfunction [1,2].
PD is characterized by the accumulation of misfolded α-synuclein (α-syn) in inclusions called Lewy bodies located in the substantia nigra of the central nervous system, resulting in the loss of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta and striatal dopamine, which are responsible for the motor symptoms of the disease. Lewy bodies have also been found in other areas of the brain such as raphe nuclei, locus coeruleus, brainstem reticular formation, the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve, amygdala, hippocampus and nucleus basalis of Meynert, to which non-motor symptomatology is attributed [1,2].
As for the mechanisms responsible for PD, neuronal death and neurodegeneration have been linked to oxidative stress, vascular disfunction, tumor progression, altered mitochondrial, autophagy and proteolysis functions, inflammation, excitotoxicity and lysosomal storage disorders (LSD) [2,5]. In addition, it was reported that alterations in sphingolipid metabolism in the early stages of the disease may be linked to an increased risk of developing PD with dementia, while regulating the levels of certain sphingolipids by enzymatic regulation can slow the development of the disease [6].
Sphingolipids are widely distributed in the organism, including the central and peripheral nervous system [7,8]. The closest association of sphingolipids with neurodegenerative diseases was related to their structural function, especially the glycosphingolipids, as the main component of the plasma membrane of oligodendrocytes and myelin [9]. However, several studies have demonstrated the implication of sphingolipids in several key biological processes such as cellular proliferation and migration, differentiation, autophagy, apoptosis, senescence, and inflammation [8,10,11,12,13,14]. Recent works on transcriptomics and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis (sphingolipidomics) have demonstrated the variation of specific levels of sphingolipids and enzymes involved in their metabolism in different neurodegenerative diseases [15,16,17].
Ceramides (Cers) have a dual role in cell biology since they are precursors of complex sphingolipids and second messengers to regulate cell homeostasis [7,8]. Ceramide (Cer) is highly expressed in neurons and modulates neuronal signaling, synaptic transmission, cell metabolism, neuron-glia interaction and cell survival [18,19,20]. The intracellular accumulation of Cer has been noticed as a critical step to neurodegeneration [21]. Neurodegenerative diseases and aging have a direct connection with oxidative stress. The increase in oxidative stress induces stimulation of the sphingomyelinase (SMase) activity and the consequent elevation of intracellular Cer concentration in neurons and oligodendrocytes [21,22]. Furthermore, mutations in different enzymes involved in the metabolism of Cer have been implicated in the development of neurodegenerative diseases. It should be noted that part of lipid metabolism takes place in lysosomal compartments. Thus, it is important to discriminate between lysosomal enzyme alterations, which would be part of LSD and non-lysosomal enzymes [23]. In this review, we will discuss the involvement of sphingolipids in neurodegeneration with special emphasis on PD.
2. Sphingolipid Metabolism
Cers are considered the central hub of sphingolipid metabolism and can regulate key metabolic functions. In particular, Cers are potent inducers of cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death [13,24], and are implicated in inflammatory responses related to microbial infection, asthma, cardiovascular diseases or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [25,26]. Moreover, an unbalance of intracellular Cer levels can lead to neurological and neuroinflammatory diseases. Cers are synthesized mainly by three major pathways. Furthermore, Cer can be synthesized by the dephosphorylation of ceramide 1-phosphate (C1P) by ceramide 1-phosphate phosphatase (CPP). In addition to producing Cer, the metabolites of complex sphingolipid catabolism lead to the production of another bioactive molecules, such as sphingosine 1-phosphate (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Sphingolipid metabolism. Solid arrows represent single reactions, whereas dashed arrows represent various step reactions. Interrogation marks with dashed arrows indicate unidentified mechanisms. Sphingomyelinase (SMase), sphingomyelin synthase (SMS), acid-sphingomyelinase (aSMase), Ceramide 1-phosphate phosphatase (C1PP), ceramide kinase (CERK), Serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT), 3-ketosphinganine reductase (KDR), Ceramide Synthase (CerS), sphingosine kinase (SphK), sphingosine 1-phosphate phosphatase (SPP), Sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase (S1P lyase) are represented by their acronyms.
2.1. The de novo Pathway
This pathway takes place in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) catalyzes the condensation of palmitate and serine to form 3-ketosphinganine (also called 3-ketodehydrosphingosine). Recent structural studies on SPT revealed a symmetrical dimer protein anchored to the ER membrane by six α-helices. The complex is formed by a single molecule of SPTLC1, SPTLC2, ssSPTa/b (two small subunits that enhance enzyme activity and also specify acyl-CoA substrate) and four regulatory subunits, ORMDLs (homologs of the yeast and plant Orms) [27]. Then, 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase (KDR) produces sphinganine. Ceramide synthase (CerS) can then catalyze the formation of dihydroceramide (dhCer) through the incorporation of acyl-CoA of different chain lengths to sphinganine. There are six different isoforms of CerS (CerS1-6) identified in mammals and plants [28]. Specifically, CerS1 is highly expressed in the nervous system and skeletal muscles, but is almost undetectable in other types of tissue. CerS1 mainly generates 18 carbon chain Cer (C18-Cer), whereas CerS2 produces C22/24-Cer, CerS3 produces C26-Cer, CerS4 generates C18/20-Cer, CerS5 synthesizes C14/16-Cer and CerS6 forms C14/16-Cer. Cers with different acyl chain lengths have been detected in the mitochondria of the brain [29,30]. Furthermore, in brain tissue, CerS1, CerS2 and CerS6 enzymes were localized to the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane, and can induce the synthesis of C18-Cer, C22-Cer and C16-Cer, respectively [31]. Interestingly, mitochondrial CerS was associated with mitochondrial injury in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion with increased production of Cer [31]. The last step of this pathway is catalyzed by a dihydroceramide desaturase (DEGS), which introduces a double bond in position 4-5 trans of dhCer. DEGS is localized to the cytosolic leaflet of the ER membrane. In particular, genetic manipulation of the DEGS gene by tissue-specific deletion reduced hepatic steatosis and attenuated insulin resistance [32]. DEGS polymorphisms have been associated with the develop of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia [33]. Recently, DEGS mutation has been described to produce hypomyelination and degeneration of both central and peripheral nervous systems [34].
2.2. The Sphingomyelinase (SMase) Pathway
SMases are enzymes that hydrolyze sphingomyelin (SM) at the plasma membrane of cells to generate Cer and phosphocholine. SM hydrolysis is considered a fast mechanism for the production of Cer. There are five different types of SMases [35], and these have been classified according to their ion dependence, location and optimal pH. These include lysosomal and plasma membrane acid SMase (aSMase) [36], endoplasmic reticulum/nucleus and plasma membrane neutral Mg2+-dependent and neutral Mg2+-independent SMase (nSMase) [37], alkaline SMase (alkSMase), which is present in the intestinal tract and human bile [35,38], and a Zn2+-dependent secreted form of aSMase [39]. Meanwhile, aSMase and nSMase are implicated in cellular signaling, whereas alkSMase is implicated in the degradation of SM incorporated in the diet. It should be noted that aSMase and nSMase increase their activity by the action of pro-inflammatory stimuli, such as Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α), Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) or cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), and it leads to elevation of intracellular Cer concentrations [40,41,42,43]. In addition, these enzymes are activated by some anticancer drugs, and by irradiation of cells with ultraviolet (UV) or ionizing radiation [44]. Mutations in the aSMase (SMPD1) gene results in disfunction of cholesterol and lipids metabolism, leading to Niemann-Pick’s disease [45,46].
There are different nSMase isoforms that have been characterized under different experimental settings [47]. The nSMase1 isoform (SPMD2 gene) is expressed in all cell types and highly enriched in the kidney. The nSMase2 isoform (SPMD3 gene) has a different domain structure than nSMase1. Contrary to nSMase 2, nSMase1 has two transmembrane domains, and instead has one collagen-like domain and two hydrophobic domains [48]. Of interest, nSMase2 is highly expressed in brain tissue [49]. Lastly, nSMase3 (SMPD4 gene) is ubiquitously expressed in all cell types. All of these SMase isoforms are Mg2+-dependent for expression of their activity. Dysregulation or stimulation of nSMase activity has been related to PD, Alzheimer’s disease, cognitive dysfunction or cerebral ischemia recovery [47,48,50,51,52].
2.3. The Salvage Pathway
This pathway involves a series of catabolic reactions that result in degradation of complex sphingolipids in acidic compartments, such as lysosomes. Complex sphingolipids, such as gangliosides (GM1, GM2 or GM3) or globosides, can be degraded to Lactosyl-ceramide (LacCer) by different reactions. Then, LacCer can be converted to Glucosyl-Ceramide (GlcCer) by LacCer hydrolase. Acid β-glucosidase 1 (β-GCase), encoded by GBA1 gene, converts GlcCer to lysosomal Cer. Deficiencies or dysfunction of this enzyme can lead to the accumulation of GlcCer and the development of the lysosomal storage disease known as Gaucher’s disease. Moreover, mutations in the GBA1 gene with loss of function have been linked to PD [53,54]. Contrarily, glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) transforms Cer into GlcCer. Once generated, Cer can be converted to sphingosine (Sph) by ceramidases. These enzymes differ in their optimal pH. There are three alkaline ceramidases (ACER1, ACER2 and ACER3), an acidic ceramidase (ASAH1) and a neutral ceramidase (ASAH2) [55,56]. ASAH1 is ubiquitously expressed in lysosomal compartments while ASAH2 is localized in plasma membranes, and mainly expressed in the small intestine and colon [55]. Sph is released to the cytosol and transformed to Cer by the activity of CerS in ER.
2.4. Ceramide Kinase/Ceramide 1-Phosphate Phosphatase (CerK/CPP) and Sphingosine Kinase/Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Phosphatase (SphK/SPP) Axis
Another relevant enzyme is Ceramide kinase (CerK), which phosphorylates Cer to produce Ceramide 1-phosphate (C1P). C1P is a key regulator of cell proliferation, survival and inflammation. The signaling pathways involved in C1P actions include mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)/extracellularly regulated kinases (ERKs) 1/2, the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt, or protein kinase C-α [57,58,59], c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) [60], or stimulation of vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) secretion [61]. Additionally, C1P-promoted cell survival implicates upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression [62], direct inhibition of aSMase [63,64] or SPT [65] and activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway [66]. It should be noted that C1P is implicated in the regulation of autophagy [67].
Sph that is released from the lysosomes to the cytosol in the Salvage pathway can be phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase (SK) to form S1P. It is one of the most studied sphingolipids. S1P has been described as a potent regulator of inflammatory processes through its union with specific membrane receptors. Thus far, five S1P receptors (S1PR1-5) have been described [68]. It is worth highlighting its involvement in glia activation processes, ischemic stroke and inflammatory processes in the vascular endothelium [69,70,71].
Dephosphorylation of S1P to Sph is due to the activity of S1P phosphatase (SPP) or by lipid phosphate phosphatase (LPP) activity [13]. However, S1P can be catalyzed by S1P lyase to produce hexadecenal and phosphoethanolamine in ER [72]. Of interest, it was observed, in both in vitro and in vivo models with a lack of S1P lyase an accumulation of β-amyloid and α-syn, promoting dysfunction of neuronal autophagy. In addition, the treatment with phosphoethanolamine restored autophagy, decreasing the deposits of β-amyloid and α-syn [73].
3. Neurodegeneration and Sphingolipid Metabolism
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease. It is characterized by extracellular deposits of β-amyloid (previously cleaved by secretases), called senile plaques, and intracellular build-up of hyperphosphorylated Tau protein in neurofibrillary tangles [74,75]. High levels of different species of Cer have been found in human samples from AD patients [76,77,78]. In addition, senile plaques were enriched in C18:1/18:0 and C18:1/20:0-Cer [79]. Likewise, aSMase and nSMase2 were found overexpressed in AD brain samples, correlated with increased Cer levels in blood [77]. Moreover, treatment with a cell-permeable analog of Cer (C6-Cer) or stimulation of endogenous Cer by nSMase activation stabilized β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) increasing β-amyloid accumulation [80]. Interestingly, β-amyloid has been reported to stimulate SMase activity in neurons [43,81,82], oligodendrocytes [83], dendritic [82] and endothelial cells [84], stimulating Cer accumulation and, thereby cell death. Additionally, overexpression of S1P lyase has been described to reduce β-amyloid production in N2a neuroblastoma cells [85]. Furthermore, it was observed a significant reduction of SphK1 and an increase of S1P lyase in AD human brain samples [86].
Different genetic diseases disrupt the metabolism of several molecules in the lysosomes, knowns as Lysosomal storage diseases (LSD). One of the main causes is lipid metabolism dysfunction, due to the alteration of enzymes such as aSMase or β-GCase [23,87,88,89]. LSD include different diseases, such as Niemann-Pick’s disease, Gaucher’s disease, Farber’s disease, Krabbe’s disease, Fabry’s disease, Tay-Sach’s disease, Sandhoff’s disease and ganglioside synthase deficiency. Lysosomal lipid storage occurs in all types of the disease, again highlighting the link between altered sphingolipid metabolism and neurodegeneration.
Niemann-Pick’s disease is a genetic disease that can be caused by two different types of mutations. Mutations in the SMPD1 gene lead to build-up of SM and the develop of Niemann-Pick’s disease type A and B [45,90]. Meanwhile, mutations in NPC Intracellular Cholesterol Transporter 1 or 2 (NPC1 or NPC2) alter cellular cholesterol trafficking and lipid metabolism disruption, leading to Niemann-Pick’s disease type C1 and C2 [91]. Recently, Torres et al. have shown that ASAH1 is downregulated in patients with Niemann-Pick’s disease type C1 [92]. They have also observed that the overexpression of ASAH1 improves mitochondrial function and reduces oxidative stress by decreasing STARD1.
Gaucher’s disease is due to a mutation in the gene encoding β-GCase (GBA), resulting in a deficit of the lysosomal enzyme, leading to an accumulation of GlcCer mainly in macrophages [53]. Elevated levels of glucosylsphingosine (GlcSph) were also found in the brain and were correlated with the phenotype of the disease [93]. Gaucher disease is associated with an increased risk of PD and dementia, since GBA deficiency increase α-syn aggregates [5].
Faber’s disease is caused by mutations in the ASAH1 gene, leading to an accumulation of Cer and cerebral atrophy. Interestingly, a rare epileptic disorder known as spinal muscular atrophy with progressive myoclonic epilepsy (SMA-PME) is also associated with ASAH1 deficit [94]. Recently, C26-Cer was proposed as a biomarker for Faber’s disease diagnosis [95].
Krabbe’s disease is a genetic disease characterized by extensive demyelination, apoptosis of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells and neurodegeneration due to mutations in the GALC gene that encode for galactocerebrosidase [96]. Recently, the possible link of greater cognitive impairment in PD patients with mutations in GALC gene was evidenced [97].
Huntington’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease strongly correlated with the expansion of CAG trinucleotide repeat within the huntingtin gene (HTT). It is characterized by progressive neurodegeneration and cognitive, motor and behavioral disturbances. Different studies carried out in in vivo models of Huntington’s disease have discovered a dysregulation in ganglioside metabolism [98,99]. Furthermore, a recent work has described a downregulation of SPT and CerS in mouse models, with a decrease in dihydroSphingosine, dihydroSphingosine-1-phosphate and dihydroCeramide (C18) [100].
Multiple sclerosis, also known as encephalomyelitis disseminate, is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the central nervous system characterized by demyelination and subsequent degeneration leading to neuronal damage and axonal loss. Its underlying etiology is unknown; however, genetic and environmental risks related to its development have been described [101]. CerS2 was found upregulated in monocytes and neutrophils isolated from mouse models [102]; meanwhile, CerS6 was increased in monocytes/macrophages [103,104]. Their overexpression has been associated with an increase in granulocyte stimulating factor (G-CSF)-induced C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 2 (CXCR2) expression [103]. Additionally, downregulation of CerS2 and CerS6 were shown to inhibit the migration capacity of macrophages and neutrophils [103,104]. Therefore, CerS2 and CerS6 may represent a promising target for multiple sclerosis treatment. Moreover, plasma levels of C16-Cer, C24:1-Cer, C16-GlcCer and C24:1-GlcCer were increased and C16-LacCer was decreased in multiple sclerosis patients compared to healthy controls [105]. Furthermore, increased levels of C16:0- and C24:0-Cer were found in the cerebrospinal fluid samples from patients with multiple sclerosis [106].
Vascular dysfunction has been associated with the risk of neurodegeneration [107]. Notably, cerebral ischemia has been linked to pro-inflammatory processes in endothelial cells and loss of the integrity of the blood–brain barrier [108,109]. Sphingolipid metabolism has been described as a key factor in the progression and prognosis of brain ischemia. SMS1 was expressed in a time-dependent manner with a decrease in the first 24 h and recuperation at 72 h after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) in rats [110]. Additionally, mice lacking aSMase exhibited a reduction in the infarct size in tMCAO, related to a decrease in Cer levels [111]. Moreover, a recent study demonstrated that aSMase protects against mild focal cerebral ischemia [112]. In preclinical studies, the levels of ceramides were increased 24 h after tMCAO in the ipsilateral hemisphere, especially in long-chain Cers, and decreased in SM [113]. Furthermore, recent studies in stroke patients showed elevated levels of long-chain Cers, while S1P and very long-chain Cers were decreased. Interestingly, high levels of long-chain Cers were associated with poor outcome at 48–72 h [114,115].
Glioblastoma is the most common and aggressive malignant brain tumor diagnosed in adults. The sphingolipids metabolism has emerged as a potential target for tumor cancer [116]. SPT inhibition by myriocin or specific siRNA inhibited the proliferation of human U87MG glioblastoma cells [117]. Des1 inhibitors such as γ-tocotrienol, phenoxodiol, or celecoxib have been described to induce autophagy in T98G and U87MG glioblastoma cell lines by dhCer accumulation [118]. Furthermore, N-[(1R,2S)-2-hydroxy-1-hydroxymethyl-2-(2-tridecyl-1-cyclopropenyl)ethyl]octanamide (GT11), another specific inhibitor of Des1, has been found to activate autophagy and apoptosis of the human U87MG glioma cell line [119]. Additionally, treatment with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) produced an alteration of the lipid composition in the endoplasmic reticulum and reduction of Des1 expression, promoting autophagy and apoptosis in human U87MG glioma cells [119]. Interestingly, a correlation between SphK1 and poor survival has been observed in a clinical study with patients with glioblastoma [120]. Moreover, specific inhibition of SphK1 or SphK2 resulted in a cell-cycle arrest in U-1242 and U-87MG glioblastoma [120]. In addition, chemical or transcriptional down-regulation of SphK1 induces apoptosis and suppresses the growth of human glioblastoma cells and xenografts [121].
4. Ceramide Metabolism Alterations in Parkinson’s Disease
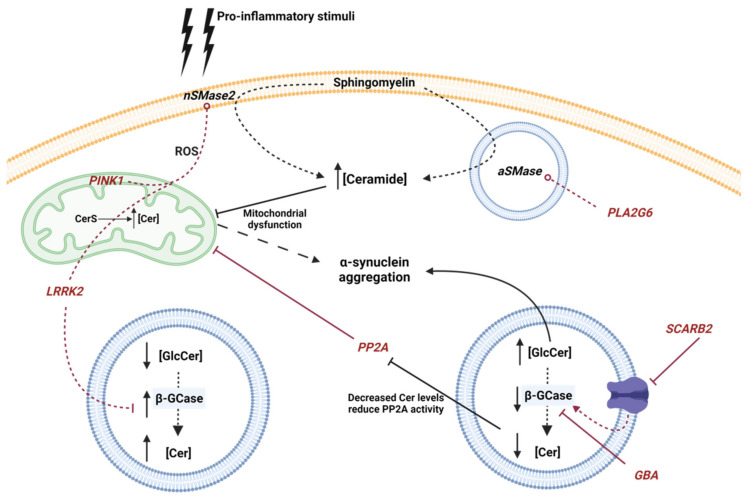
The causes of PD are not completely understood and vary, from environmental factors such as exposure to toxins, such as rotenone [122] or l-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) [123], to genetic factors. About 15 percent of patients with PD have a family history of the condition [3]. Family linked cases can be a consequence of genetic modifications, considered as genetic risk factors, in some of the genes described so far, such as GBA, LRRK2, PLA2G6, PINK1 or SNCA genes (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the influence of genetic mutations involved in PD with Cer metabolism. Genes are represented in italics and red color. Red lines circled at the end indicate increased activity, while a traversed lines at the end indicate inhibition or dysfunction. Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2), acid sphingomyelinase (aSMase), Ceramide Synthase (CerS), acid β-glucosidase (β-GCase), Ceramide (Cer), GlucosylCeramide (GlcCer) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are represented by their acronyms.
4.1. Genetic Risks
4.1.1. GBA
GBA gene mutations are the most common autosomal dominant genetic cause of PD [124]. This gene encodes the lysosomal enzyme β-GCase, a lysosomal hydrolase that degrades GlcCer into Cer and glucose, and alternatively, degrades GlcSph and potentially other β-glucosides. Mutations in this gene that cause loss of expression or functionality in neurons or glia lead to Gaucher’s disease, belonging to Lysosomal Storage Diseases (LSD), by GlcCer accumulation [53,125,126]. Moreover, heterozygous mutations increase the lifetime risk to PD, since increased levels of GlcCer stimulate α-syn pathology [124,127,128]. In addition, recently, it was observed that in a GBA mutant (N370S, L444P, KO) crossed with α-syn transgenic mouse there is a correlation between GlcSph accumulation and α-syn aggregation, indicating that GlcSph promotes α-syn assemblage [129]. Their interconnection is so tight that α-syn has also been shown to reduce β-GCase activity [130]. In fact, elevated levels of GlcCer can lead to α-syn accumulation and, conversely, α-syn can reduce β-GCase activity establishing a bidirectional pathogenic loop [130]. Recently, Jong Kim et al. showed that β-GCase deficiency leads to C18-Cer reduction and alters Rab8a location, a small cytosolic GTPase implicated in secretory autophagy [131]. In this work, the authors also demonstrated that ASAH1 inhibition increased C18-Cer and reduced GlcSph levels and oxidized α-syn [131]. The latter studies demonstrated the possible efficiency of a targeted therapy against GlcCer accumulation. Sardi et al. demonstrated that the use of a specific GCS inhibitor (GZ667161) in α-synucleinopathy transgenic mice reduced GlcCer and GlcSph levels, correlating with the reduction of α-syn aggregates and cognitive improvement [132].
A new small molecule (S-181) that increases β-GCase activity has recently been developed. In human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived dopaminergic neurons from PD patients carrying mutations in GBA, LRRK2, DJ-1 or PARKIN, it was found that S-181 reduced β-GCase activity. Furthermore, S-181 partially restored lysosomal function, and consequently, reduced oxidized dopamine, GlcCer levels and α-syn accumulation. Moreover, S-181 treatment of Gba1D409V/- mice resulted in an increased wild-type β-GCase activity and consequent reduction of α-syn accumulation [133]. These results are in agreement with previous studies in which overexpression of β-GCase carried out by Adenovirus Vector (AAV) Gene Therapy observed a reduction of the α-syn aggregation [134,135].
Interestingly, GBA deficiency promotes a down-regulation of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) leading to an inhibition of autophagy and thus an accumulation of α-syn [136]. This result could be related to a stimulation of PP2A activity by Cer [137,138]. Additionally, it was observed that in lung epithelial cells, the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α stimulates the concentration of intracellular Cer, promoting the stimulation of PP2A activity. Moreover, PP2A was described as modulator of c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and p38 pathways, stimulating the production of interleukin 8 (IL-8) and along with a pro-inflammatory cascade [139]. Therefore, a low concentration of Cer, due to a deficiency in GBA might produce a decrease in the activity of PP2A.
It is well established that α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPAR) are the major receptors responsible for synaptic plasticity in neurons. In neurodegenerative diseases, this ability of neurons to adapt fails, leading to cognitive impairments [140]. Among all the proteins that regulate vesicular traffic and AMPAR activation in synapses, PP2A is a relevant enzyme. This phosphatase regulates the dephosphorylation of AMPARs and thus the inactivation and endocytosis of the receptors [141,142]. Furthermore, it has been reported that Cer reduces neuronal AMPAR levels in synapses after a treatment with pro-inflammatory molecules, such as IL-1β [143] or TNF-α [144]. These observations suggest that Cer regulates the activity of AMPARs through PP2A, although these aspects require further investigation.
Another point of interest is the fact that Cer stimulates autophagy via inhibition of protein kinase B (PKB, also known as Akt) and activation of a mammalian tumor suppressor called Beclin-1 (BENC1), reducing the levels of Cer in GBA deficient neurons, which also produces a decrease in autophagy through this pathway [145].
4.1.2. LRRK2
LRRK2 is a member of the leucine-rich repeat kinase family of genes. Certain mutations associated with PD have been described, representing 1–2% of cases. Mutations in this autosomal dominant gene lead to an increase of LRRK2 activity [146]. Furthermore, different LRRK2 mutations have been associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, stimulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, dysfunction in fission and fusion processes, mitophagy and dysregulation of cytoskeleton dynamics and mitochondria trafficking [147]. The predominant mutation is the modification of a glycine in the 2019 residue for a serine (LRRK2-G2019S) [148]. Recently, Boecker et al. demonstrated that hyperactivation of LRRK2 kinase activity increases phosphorylation of Rab GTPases and recruits the motor adaptor JNK-interacting protein 4 (JIP4) to the autophagosome membrane, leading to a disruption of autophagosome transport [149]. These observations were made in human iPSC-derived neurons gene-edited to express the G2019S mutation, and the results were reversed by genetic or pharmacological inhibition of LRRK2, making it a hopeful target for PD.
LRRK2 mutations have also been observed in patients with GBA mutations. However, the phenotype associated with carriers of individual GBA or LRRK2 mutations and the two joint mutations is not clear. A study with a cohort of 236 participants showed that the LRRK2 mutation together with GBA rescued from further mental degeneration [150]. Meanwhile, a recent study with a cohort of 1193 Ashkenazi Jewish population showed no differences between genotypes [151].
Ferrazza et al. demonstrated that LRRK2 activity is involved in the regulation of Cer metabolism. The authors observed that Lrrk2-/- transgenic mice showed increased β-GCase activity with elevated Cer levels in the brain [152]. Furthermore, increased β-GCase activity was determined in blood samples from patients with LRRK2-G2019S-PD [127]. This observation could be explained by the release of the lysosomal vesicles to the extracellular compartment [127]. Additionally, recent studies in neurons derived from PD patients with mutations in LRRK2 have shown that LRRK2 regulates β-GCase activity through the small GTPase Rab10. Moreover, treatment with specific LRRK2 inhibitors (in clinical phase trials) increased β-GCase activity improving cognition functions in PD patients [153].
It is well established that LRRK2 regulates mitochondrial homeostasis by Dynamin-related protein (Drp-1) and ROS production [154,155]. In addition, Drp-1 modifies Cer distribution in the outer membrane of the mitochondria, preventing mitophagy [156]. As mentioned above, there is a high expression of mitochondrial CerS in the brain [31]. Interestingly, genetic modifications of CerS in C. elegans have been linked to alterations in the inclusion of α-syn [157]. This result could be one of the explanations for the different species of Cer found in patient samples, in both blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), as well as brain biopsies (elegantly reviewed by Pujol-Lereis [22]).
4.1.3. PLA2G6
PLA2G6 gene encodes a calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2-VIA). This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids, producing free fatty acids, including pro-inflammatory polyunsaturated arachidonic acid (AA), and lysophospholipids. Earlier, it was observed that mutations in this gene produce abnormal growth of neuronal axons [158], early onset PD [159,160], and association with PD develop [159]. Additionally, it was also observed that these mutations caused dysregulation of Ca2+ homeostasis, leading to autophagic dysfunction and loss of dopaminergic neurons [161]. Interestingly, the loss of iPLA2-VIA results in a build-up of Cer [162], by a possible mechanism that alters the plasma composition. In fact, PLA2G6 binds to VPS35 (also mutated in some PD patients [163]) and VPS26, stimulating plasma membrane recycling. This process could stimulate the production of Cer in the lysosomes by aSMase. It should be noted that production of lysosomal Cer leads to α-syn accumulation [87].
Since Cer is the substrate for CerK, C1P concentration can be enhanced by increasing Cer levels. However, C1P levels in the blood of PD patients carrying the GBA mutations are reduced in comparison with non-carrier PD patients [164]. Nonetheless, the implication of CerK in PD requires further investigation.
4.1.4. PINK1
The PINK1 gene encodes for phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced putative kinase protein 1 (PINK1), a mitochondrial-targeted serine/threonine kinase [165]. This protein is implicated in the maintenance of mitochondrial homeostasis. When the mitochondrial membrane suffers a depolarization due to oxidative stress, PINK1 recruits the E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin protein from the cytosol, initiating a process of mitochondrial degradation called mitophagy [166]. One of the most important consequences is the dysfunction of Na+/Ca2+ exchange regulation [167]. Mutations in the PINK1 gene are the most common cause of recessive familial PD [165]. Gandhi et al. demonstrated that kinase-dead mutant K219M-PINK1 promotes a dysfunction of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger with the consequent accumulation of Ca2+ in the mitochondria [167]. Calcium overload in the mitochondria stimulates NAPDH oxidase and the production of ROS. The disruption of the electron chain also causes a decrease in glucose transporters in the membrane of neurons by decreasing cellular metabolism. Different studies have shown that the accumulation of ROS stimulates the activity of nSMase2 and the production of Cer [168,169]. Interestingly, the elevation of Cer levels can also take place in the mitochondria by the action of ASAH1 and ASAH2. Moreover, Cer was described to stimulate mitophagy by a mechanism that involves the recruitment of the PINK1/Parkin complex to the mitochondrial membrane [170].
As mentioned previously, PP2A is involved in the regulation of mitochondrial autophagy. In mouse striatum neurons infected with PINK1 gene silencing lentivirus vectors (LVs) an increase in the phosphorylation of PP2A was observed at residue tyrosine 307 (Y307). This phosphorylation resulted in an inactive form of PP2A in dopaminergic cells and striatum tissues, which indicates the involvement of PP2A in the maintenance of mitochondrial homeostasis by PINK1 [171]. Hannun’s group has already shown that the administration of exogenous short-chain Cer (C2-Cer) stimulates the activity of PP2A [172]. In the mentioned work, the authors described that the incubation of PINK1-silenced in differentiated dopaminergic MN9D cells with C2-Cer activated PP2A and thus reduced autophagy levels in a B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)-dependent mechanism, a protein implicated in mitochondrial permeabilization and apoptotic processes [171].
4.1.5. SCARB2
SCARB2 gene encodes to lysosomal integral membrane protein 2 (LIMP2), a protein responsible for transporting β-GCase from the ER to the lysosome through interaction with mannose-6-phosphate receptor [88,173]. Different genetic studies have determined the implication of mutations in this gene in the development of PD [174,175,176,177,178]. Moreover, overexpression of α-syn in ASOTg/Tg mouse models showed reduced levels of mannose-6-phosphate receptor type I (also known as MPR300) [179]. Interestingly, Rothaug et al. demonstrated that the loss of LIMP-2 causes a reduction in β-GCase activity that results in a build-up of α-syn, and thus neurotoxicity in dopaminergic neurons [180].
4.2. Enviromental Risks
Different neurotoxic agents have been described to affect dopaminergic neurons. In this section, a brief summary of some of these agents will be made, and their relationship with Cer metabolism will be addressed.
MPTP is a chemical compound able to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Once in the brain, monoamine oxidase B enzyme (MAOB) catalyzes MPTP to produce a 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+), a toxic metabolite that accumulates in dopaminergic neurons and inhibits mitochondrial complex I [181]. As a consequence, there is a reduction in ATP levels and generation of free radicals. Furthermore, MPP+ increase vesicular dopamine in cytoplasm, where it can also produce ROS [182]. However, this PD model does not present Lewy bodies, one of the characteristic hallmarks of PD. Meanwhile, Rotenone is a lipophilic pesticide found in some tropical plants. Due to its chemical characteristics, it can cross the BBB and internalize in dopaminergic neurons. Like MPP+, Rotenone blocks mitochondrial complex I and stimulates ROS production. In addition, Rotenone also inhibits antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase or glutathione (GSH). This increase in ROS and the inhibition of enzymes involved in their reduction causes degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra with develop of Lewy Bodies. Moreover, it has also been reported that Rotenone induces inflammation, depolarization of microtubules and inhibition of autophagy [183].
In the hippocampus of PD mouse models induced by MPTP was observed that nSMase was down-regulated [50]. Previously, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 was described as activator of SMase activity [184]. In vitro studies in hippocampal PD mice neurons induced by MPTP with consequent upregulation of iNOS and downregulation of nSMase, showed a reduced levels of SM by upregulation of nSMase by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, related with an improve in synaptic plasticity [50]. Interestingly, treatment with MPP+ showed a significant alteration in SphKs and S1P lyase expression in SH-SY5Y dopaminergic neuronal cells [185,186].
Several reports have shown evidence suggesting a critical role of the Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) in inflammatory responses and neuronal death [187,188,189,190]. Both the microglia- mediated inflammatory pathway and aggregated α-syn activate different mechanisms to stimulate inflammation and contribute to neurodegenerative progression in PD via upregulation of TLR2 and TLR4 [191]. Recent studies in TLR4 knockout mice showed protection against MPTP toxicity, with attenuation of motor deficits and a reduction in α-syn dysfunction and neuroinflammation [187]. Interestingly, another study with these mice described an increase in the expression of nSMase that led to a decrease in SM levels and an increase in Cer, which causes a higher sensitivity to MPTP [192].
Rotenone has been described to inhibit PP2A, preventing the dephosphorylating of α-syn and, in turn increasing its aggregation [193]. Furthermore, C2-Cer activates PP2A and counteracted the neurotoxic effects derived from Rotenone treatment and decrease α-syn aggregation [193]. Additionally, in erythrocytes that are known to lack mitochondria, treatment with Rotenone stimulates apoptosis due to an increase in Cer levels, by a mitochondrial-independent mechanism [194]. As showed above, Rotenone inhibits also GSH. Studies in hepatocytes demonstrated that the decrease in GSH activity was correlated with increases in the activity of nSMase2, and this was related to an IL-1β hyperresponsiveness, increasing the pro-inflammatory response [195]. Interestingly, recent study has demonstrated that ASAH1 overexpression increase GSH levels and reduce oxidative stress in fibroblasts derived from Niemann-Pick’s disease type C1 [92].
5. Human Sphingolipidomics of Ceramide Metabolism in PD
In recent years, studies on sphingolipid levels by mass spectrometry (sphingolipidomics) have gained importance in different fields of medicine and scientific research [196] (Table 1). It has been reported that sphingolipids metabolism is related to the progression of different carcinogenic processes, as well as resistance to anti-cancer treatments [197,198,199]. Therefore, the study of the evolution of the different species will allow a more effective diagnosis and treatment. Regarding PD, differences in the levels of Cer, SM and GM1, among other sphingolipids, have been described in post-mortem brain samples, blood and CSF from patients with different neuronal degeneration [17,22,200].
PD post-mortem brain tissue from the anterior cingulate cortex showed a drastic reduction in long-chain Cer (such as C24:1 and C24:0-Cer) levels. Interestingly, an upregulation of CerS1 and CerS4 was observed, which could be due to a compensation system to increase certain Cer species [201]. Meanwhile, comparing plasma samples from patients with GBA mutations and non-carrier patients, an increase in Cer and LacCer levels were described, in addition to a decrease in C1P levels [164]. Additionally, in a recent study of post-mortem CSF samples have been described an increase in Cer and SM levels, which correlated with neuropathological staging and disease duration, a fact that further supports the ability of sphingolipids as biomarkers [202]. Moreover, plasma C14:0 and C24:1-Cer levels were significantly higher in PD with dementia than in PD with no cognitive impairment and normal controls. Interestingly, C22:0, C20:0 and C18:0-Cer were associated with hallucinations, anxiety and disturbances of sleep behavior, respectively [203]. Along with these observations, also plasma Cer (C16:0, C18:0, C20:0, C22:0 and C24:1) species were found elevated in PD non-GBA mutation carriers, with higher levels associated with worse cognitive function [204].
A general increase of long chain SM and Cer levels was also detected in the primary visual cortex [205], as well as, an increase of SM levels in the substantia nigra but only in male PD patients [206]. However, no changes in sphingolipids were observed in the putamen or cerebellum of GBA PD patients [207]. Nonetheless, one study reported reduced plasma levels of SM (d30:1, 32:1 and 39:1) in early PD patients compared to controls [208].
Some GlcCer species, including C18:0, C 20:0, C 22:0, C 24:1 and C 24:0 GlcCer in brain tissue, revealed a correlation between increased levels of these metabolites and PD severity [209]. In addition, plasma GlcCer (C16:0, C22:0 and C24:0) species were increased in PD non-GBA mutation carriers, and were correlated with greater cognitive impairment [204]. In contrast, GlcCer C24:1 was selectively decreased in PD patients with a reduction of C18:1-Cer in frontal cortex [210]. Moreover, no significant differences have been found between the different PD groups and controls in CSF samples [211].
Gangliosides are complex sphingolipids involved in the regulation of inflammatory processes. Their involvement in PD development has been observed in several studies, although the mechanisms are still uncertain [212]. GM1 can increase the internalization process of α-syn by the glia, increasing α-syn clearance [213] and inhibit the aggregation [214]. By contrast, GM3 accelerates α-syn aggregation by a mechanism dependent on the biophysical conditions of both molecules [215].
Ganglioside GM1 has been reported to be decreased in dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra of PD patients versus age-matched controls [216]. In plasma from PD patients with GBA mutations and/or LRRK2-G2019S mutations, increased levels of ganglioside-NANA-3 (a precursor of complex sphingolipids) were observed, possibly due to a reduction in the activity of β-GCase [217]. In addition, in non-carriers of GBA or LRRK2-G2019S mutations PD patients, GM3 species (d18:1/24:1 and d18:1/26:0) were found elevated in comparation with controls, correlated with high levels of GlcCer species in plasma [218].
Table 1.
Summary table of human sphingolipidomics. The up arrows refer to an increase in levels compared to the controls, while the down arrows refer to a reduction. The asterisk (*) indicates that the data were not statistically significant. Ceramide (Cer), ceramide 1-phosphate (C1P), sphingomyelin (SM), glucosyl-ceramide (GlcCer) and lactosyl-ceramide (LacCer).
| Sphingolipid Species | Levels | Source | Type of PD | Notes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cer | ↑ | Serum | GBA mutation | Possible early development of PD and worsening of symptoms | [164] |
| ↑ | Post-mortem CSF | Not specified | Correlation with neuropathological staging and disease duration | [202] | |
| ↑ | Primary visual cortex | Sporadic | Contribution to neuronal dysfunction | [205] | |
| Long-chain Cer (such as C24:1 and C24:0-Cer) | ↓ | Anterior cingulate cortex | Impartment of salvage pathway by increased CerS1 expression | [201] | |
| C14:0-Cer | ↑ | Plasma | PD with dementia | Association with delayed free recall and cognition | [203] |
| C16:0-Cer | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204] |
| C18:0-Cer | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204] |
| ↑ * | PD with dementia | Association with sleep behaviour disturbance | [203] | ||
| C18:1-Cer | ↓ | Frontal cortex | Not specified | Increased formation of diacylglycerols (DAGs) | [210] |
| C20:0-Cer | ↑ * | Plasma | PD with dementia | Association with anxiety | [203] |
| ↑ | Non-GBA mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204] | ||
| C22:0-Cer | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204] |
| ↑ * | PD with dementia | Association with hallucination | [203] | ||
| C24:1-Cer | ↑ | Plasma | PD with dementia | Association with the score of immediate verbal recall and delayed free recall | [203] |
| ↑ | Non-GBA mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204] | ||
| GlcCer | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA or Non-LRRK2 G2019S mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204,218] |
| GlcCer C16:0 | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204] |
| GlcCer C18:0 | ↑ * | Temporal cortex | Not specified | Correlation with PD severity | [209] |
| GlcCer C20:0 | ↑ * | Temporal cortex | Not specified | Correlation with PD severity | [209] |
| GlcCer C22:0 | ↑ * | Temporal cortex | Not specified | Correlation with PD severity | [209] |
| ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA mutation | Tendency to association with worse cognition | [204] | |
| GlcCer C24:0 | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA mutation | Association with worse cognition | [204] |
| ↑ * | Temporal cortex | Not specified | Correlation with PD severity | [209] | |
| GlcCer C24:1 | ↑ * | Temporal cortex | Not specified | Correlation with PD severity | [209] |
| ↓ | Frontal cortex | Not specified | Increased formation of DAGs | [210] | |
| LacCer | ↑ | Serum | GBA mutation | Proposed as novel biomarker for increased risk of PD develop | [164] |
| C1P | ↓ | Serum | GBA mutation | Proposed as novel biomarker for increased risk of PD develop | [164] |
| SM | ↑ | Post-mortem CSF | Not specified | Correlation with neuropathological staging and disease duration | [205] |
| ↑ | Substantia nigra | Male PD | Caused by enrichment in Lewy bodies | [206] | |
| Long-chain SM | ↑ | Primary visual cortex | Sporadic | Contribution to neuronal dysfunction | [205] |
| SM d30:1 | ↓ * | Plasma | Not specified | Due to dysregulation of sphingolipids metabolism. Possibly involved in demyelination | [208] |
| SM d32:1 | ↓ * | Plasma | Not specified | Due to dysregulation of sphingolipids metabolism. Possibly involved in demyelination | [208] |
| SM d39:1 | ↓ * | Plasma | Not specified | Due to dysregulation of sphingolipids metabolism. Possibly involved in demyelination | [208] |
| GM1 | ↓ | Substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons | Sporadic | Loss of neuroprotection and acceleration of α-syn formation | [216] |
| Ganglioside-NANA-3 | ↑ | Plasma | GBA or/and LRRK2 G2019S mutation | Acceleration of α-syn formation | [217] |
| GM3 d18:1/24:1 | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA or Non-LRRK2 G2019S mutation | Acceleration of α-syn formation | [218] |
| GM3 d18:1/26:0 | ↑ | Plasma | Non-GBA or Non-LRRK2 G2019S mutation | Acceleration of α-syn formation | [218] |
6. Concluding Remarks
The dual function of sphingolipids as structural molecules and second messengers makes them vitally important molecules for the maintenance of cell and tissue homeostasis. It has been demonstrated that alterations of sphingolipid metabolism are related to PD progression, and its aggressiveness by a large number of studies carried out in different animal models, in vitro studies and human samples. However, the molecular mechanisms that give rise to this alteration remain incompletely understood. Studies in which the therapeutic targets are the enzymes involved in the metabolism of sphingolipids are of vital importance.
In recent years, sphingolipidomic studies in patient samples have emerged as a new tool to evaluate the aggressiveness and establish specific treatments of certain diseases, including PD. Moreover, sphingolipid levels in PD patients with different symptoms and progress have demonstrated the viability of sphingolipidomics for both diagnosis and specific treatments. These data support the potential of sphingolipids as biomarkers of PD. Furthermore, transcriptional studies have shown variations in the expression of different enzymes involved in sphingolipid metabolism. However, only a few studies have been conducted to determine their involvement in neurological impairment in PD.
Future experiments that aim to understand the involvement of sphingolipids in the development of PD will be of vital importance for the development of therapies and an early diagnosis.
Acknowledgments
Figure 1 was made with BioRender.com software.
Funding
This study was partially supported by grants from the Xunta de Galicia (Consellería de Economía e Industria: IN607A2018/3 & IN607D 2020/09), and Science Ministry of Spain (RTI2018-102165-B-I00 & RTC2019-007373-1). Furthermore, this study was also supported by grants from the INTERREG Atlantic Area (EAPA_791/2018_ NEUROATLANTIC project), INTERREG V A España Portugal (POCTEP) (0624_2IQBIONEURO_6_E) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). Work in AGM lab is supported by grant IT-1106-16 from “Departamento de Educación, Universidades e Investigación” (Gobierno Vasco, Gasteiz-Virtoria, Spain). Moreover, M. Aramburu-Núñez (IFI18/00008) is recipient of iPFIS contract, and Sobrino (CPII17/00027) is recipient of a research contract from the Miguel Servet Program from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Tysnes O.B., Storstein A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017;124:901–905. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1686-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dextera D.T., Jenner P. Parkinson Disease: From Pathology to Molecular Disease Mechanisms. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013;62:132–144. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Blauwendraat C., Nalls M.A., Singleton A.B. The Genetic Architecture of Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:170–178. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30287-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Von Campenhausen S., Winter Y., e Silva A.R., Sampaio C., Ruzicka E., Barone P., Poewe W., Guekht A., Mateus C., Pfeiffer K.-P., et al. Costs of Illness and Care in Parkinson’s Disease: An Evaluation in Six Countries. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011;21:180–191. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Indellicato R., Trinchera M. The Link between Gaucher Disease and Parkinson’s Disease Sheds Light on Old and Novel Disorders of Sphingolipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:3304. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Alessenko A.V., Albi E. Exploring Sphingolipid Implications in Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurol. 2020;11:1–11. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Iqbal J., Walsh M.T., Hammad S.M., Hussain M.M. Sphingolipids and Lipoproteins in Health and Metabolic Disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017;28:506–518. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gomez-Larrauri A., Presa N., Dominguez-Herrera A., Ouro A., Trueba M., Gomez-Munoz A. Role of Bioactive Sphingolipids in Physiology and Pathology. Essays Biochem. 2020;64:579–589. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Giussani P., Prinetti A., Tringali C. The Role of Sphingolipids in Myelination and Myelin Stability and Their Involvement in Childhood and Adult Demyelinating Disorders. J. Neurochem. 2021;156:403–414. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Quinville B.M., Deschenes N.M., Ryckman A.E., Walia J.S. A Comprehensive Review: Sphingolipid Metabolism and Implications of Disruption in Sphingolipid Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:5793. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ouro A., Arana L., Gangoiti P., Gomez-Muñoz A. Role of Ceramide 1-Phosphate in the Regulation of Cell Survival and Inflammation. Biochemistry. 2012;4 doi: 10.5772/32849. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Arana L., Gangoiti P., Ouro A., Trueba M., Gomez-Munoz A., Gómez-Muñoz A. Ceramide and Ceramide 1-Phosphate in Health and Disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2010;9:1–12. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gangoiti P., Camacho L., Arana L., Ouro A., Granado M.H., Brizuela L., Casas J., Fabrias G., Abad J.L., Delgado A., et al. Control of Metabolism and Signaling of Simple Bioactive Sphingolipids: Implications in Disease. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010;49:316–334. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2010.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hannun Y.A., Obeid L.M. Principles of Bioactive Lipid Signalling: Lessons from Sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:139–150. doi: 10.1038/nrm2329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mielke M.M., Haughey N.J., Bandaru V.V.R., Zetterberg H., Blennow K., Andreasson U., Johnson S.C., Gleason C.E., Blazel H.M., Puglielli L., et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Sphingolipids, β-Amyloid, and Tau in Adults at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2014;35:2486–2494. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.05.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lin G., Wang L., Marcogliese P.C., Bellen H.J. Sphingolipids in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019;30:106–117. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2018.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Van Kruining D., Luo Q., van Echten-Deckert G., Mielke M.M., Bowman A., Ellis S., Oliveira T.G., Martinez-Martinez P. Sphingolipids as Prognostic Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration, Neuroinflammation, and Psychiatric Diseases and Their Emerging Role in Lipidomic Investigation Methods. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020;159:232–244. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gulbins A., Grassm H., Hoehn R., Wilker B., Soddemann M., Kohnen M., Edwards M.J., Kornhuber J., Gulbins E. Regulation of Neuronal Stem Cell Proliferation in the Hippocampus by Endothelial Ceramide. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016;39:790–801. doi: 10.1159/000447789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schultz A., Larsson C. Ceramide Influences Neurite Outgrowth and Neuroblastoma Cell Apoptosis Regulated by Novel Protein Kinase C Isoforms. J. Neurochem. 2004;89:1427–1435. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cruciani-Guglielmacci C., López M., Campana M., le Stunff H. Brain Ceramide Metabolism in the Control of Energy Balance. Front. Physiol. 2017;8:787. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jana A., Hogan E.L., Pahan K. Ceramide and Neurodegeneration: Susceptibility of Neurons and Oligodendrocytes to Cell Damage and Death. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009;278:5–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2008.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pujol-Lereis L.M. Alteration of Sphingolipids in Biofluids: Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:3564. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Platt F.M. Sphingolipid Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Nature. 2014;510:68–75. doi: 10.1038/nature13476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Watters R.J., Kester M., Tran M.A., Loughran T.P., Liu X. Development and Use of Ceramide Nanoliposomes in Cancer. Methods Enzymol. 2012;508:89–108. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391860-4.00005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gomez-Muñoz A., Presa N., Gomez-Larrauri A., Rivera I.G., Trueba M., Ordoñez M. Control of Inflammatory Responses by Ceramide, Sphingosine 1-Phosphate and Ceramide 1-Phosphate. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016;61:51–62. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2015.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Albeituni S., Stiban J. Roles of Ceramides and Other Sphingolipids in Immune Cell Function and Inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019;1161:169–191. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-21735-8_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wattenberg B.W. Kicking off Sphingolipid Biosynthesis: Structures of the Serine Palmitoyltransferase Complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021;28:229–231. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00562-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim J.L., Mestre B., Shin S.-H., Futerman A.H. Ceramide Synthases: Reflections on the Impact of Dr. Lina M. Obeid. Cell. Signal. 2021;82:109958. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mignard V., Dubois N., Lanoé D., Joalland M.P., Oliver L., Pecqueur C., Heymann D., Paris F., Vallette F.M., Lalier L. Sphingolipids Distribution at Mitochondria-Associated Membranes (MAM) upon Induction of Apoptosis. J. Lipid Res. 2020;61:1025–1037. doi: 10.1194/jlr.RA120000628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Novgorodov S.A., Gudz T.I. Ceramide and Mitochondria in Ischemic Brain Injury. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011;2:347–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yu J., Novgorodov S.A., Chudakova D., Zhu H., Bielawska A., Bielawski J., Obeid L.M., Kindy M.S., Gudz T.I. JNK3 Signaling Pathway Activates Ceramide Synthase Leading to Mitochondrial Dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:25940–25949. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701812200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chaurasia B., Tippetts T.S., Monibas R.M., Liu J., Li Y., Wang L., Wilkerson J.L., Sweeney C.R., Pereira R.F., Sumida D.H., et al. Targeting a Ceramide Double Bond Improves Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis. Science. 2019;365:386–392. doi: 10.1126/science.aav3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ohi K., Ursini G., Li M., Shin J.H., Ye T., Chen Q., Tao R., Kleinman J.E., Hyde T.M., Hashimoto R., et al. DEGS2 Polymorphism Associated with Cognition in Schizophrenia Is Associated with Gene Expression in Brain. Transl. Psychiatry. 2015;5:e550. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Karsai G., Kraft F., Haag N., Korenke G.C., Hänisch B., Othman A., Suriyanarayanan S., Steiner R., Knopp C., Mull M., et al. DEGS1-Associated Aberrant Sphingolipid Metabolism Impairs Nervous System Function in Humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2019;129:1229–1239. doi: 10.1172/JCI124159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Goi F.M., Alonso A. Sphingomyelinases: Enzymology and Membrane Activity. FEBS Lett. 2002;531:38–46. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03482-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gorelik A., Illes K., Heinz L.X., Superti-Furga G., Nagar B. Crystal Structure of Mammalian Acid Sphingomyelinase. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:1–9. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Clarke C.J., Snook C.F., Tani M., Matmati N., Marchesini N., Hannun Y.A. The Extended Family of Neutral Sphingomyelinases. Biochemistry. 2006;45:11247–11256. doi: 10.1021/bi061307z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cataldi S., Borrelli A., Ceccarini M.R., Nakashidze I., Codini M., Belov O., Ivanov A., Krasavin E., Ferri I., Conte C., et al. Acid and Neutral Sphingomyelinase Behavior in Radiation-Induced Liver Pyroptosis and in the Protective/Preventive Role of RMnSOD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:3281. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kornhuber J., Rhein C., Müller C.P., Mühle C. Secretory Sphingomyelinase in Health and Disease. Biol. Chem. 2015;396:707–736. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2015-0109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jenkins R.W., Canals D., Idkowiak-Baldys J., Simbari F., Roddy P., Perry D.M., Kitatani K., Luberto C., Hannun Y.A. Regulated Secretion of Acid Sphingomyelinase: Implications for Selectivity of Ceramide Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:35706–35718. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Becker K.A., Riethmuller J., Luth A., Doring G., Kleuser B., Gulbins E. Acid Sphingomyelinase Inhibitors Normalize Pulmonary Ceramide and Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010;42:716–724. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0174OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gomez-Muñoz A., Gangoiti P., Arana L., Ouro A., Rivera I.G., Ordoñez M., Trueba M. New Insights on the Role of Ceramide 1-Phosphate in Inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids. 2013;1831:1060–1066. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Malaplate-Armand C., Florent-Béchard S., Youssef I., Koziel V., Sponne I., Kriem B., Leininger-Muller B., Olivier J.L., Oster T., Pillot T. Soluble Oligomers of Amyloid-β Peptide Induce Neuronal Apoptosis by Activating a CPLA2-Dependent Sphingomyelinase-Ceramide Pathway. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006;23:178–189. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2006.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Morad S.A.F., Cabot M.C. Ceramide-Orchestrated Signalling in Cancer Cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012;13:51–65. doi: 10.1038/nrc3398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Horinouchi K., Erlich S., Perl D.P., Ferlinz K., Bisgaier C.L., Sandhoff K., Desnick R.J., Stewart C.L., Schuchman E.H. Acid Sphingomyelinase Deficient Mice: A Model of Types A and B Niemann–Pick Disease. Nat. Genet. 1995;10:288–293. doi: 10.1038/ng0795-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schuchman E.H., Wasserstein M.P. Types A and B Niemann-Pick Disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015;29:237–247. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2014.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wu B.X., Clarke C.J., Hannun Y.A. Mammalian Neutral Sphingomyelinases: Regulation and Roles in Cell Signaling Responses. NeuroMolecular Med. 2010;12:320–330. doi: 10.1007/s12017-010-8120-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Shamseddine A.A., Airola M.V., Hannun Y.A. Roles and Regulation of Neutral Sphingomyelinase-2 in Cellular and Pathological Processes. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015;57:24–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hofmann K., Tomiuk S., Wolff G., Stoffel W. Cloning and Characterization of the Mammalian Brain-Specific, Mg2+-Dependent Neutral Sphingomyelinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:5895–5900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.11.5895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cataldi S., Arcuri C., Hunot S., Légeron F.P., Mecca C., Garcia-Gil M., Lazzarini A., Codini M., Beccari T., Tasegian A., et al. Neutral Sphingomyelinase Behaviour in Hippocampus Neuroinflammation of MPTP-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease and in Embryonic Hippocampal Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017;2017 doi: 10.1155/2017/2470950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tabatadze N., Savonenko A., Song H., Bandaru V.V.R., Chu M., Haughey N.J. Inhibition of Neutral Sphingomyelinase-2 Perturbs Brain Sphingolipid Balance and Spatial Memory in Mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010;88:2940–2951. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gu L.Z., Huang B.S., Shen W., Gao L., Ding Z.Z., Wu H.W., Guo J. Early Activation of NSMase2/Ceramide Pathway in Astrocytes Is Involved in Ischemia-Associated Neuronal Damage via Inflammation in Rat Hippocampi. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013;10:1–16. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hruska K.S., LaMarca M.E., Scott C.R., Sidransky E. Gaucher Disease: Mutation and Polymorphism Spectrum in the Glucocerebrosidase Gene (GBA) Hum. Mutat. 2008;29:567–583. doi: 10.1002/humu.20676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Velayati A., Yu W.H., Sidransky E. The Role of Glucocerebrosidase Mutations in Parkinson Disease and Lewy Body Disorders. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2010;10:190–198. doi: 10.1007/s11910-010-0102-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Coant N., Hannun Y.A. Neutral Ceramidase: Advances in Mechanisms, Cell Regulation, and Roles in Cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2019;71:141–146. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2018.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Romiti E., Meacci E., Tani M., Nuti F., Farnararo M., Ito M., Bruni P. Neutral/Alkaline and Acid Ceramidase Activities Are Actively Released by Murine Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000;275:746–751. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gangoiti P., Granado M.H., Arana L., Ouro A., Gomez-Muñoz A., Gomez-Munoz A. Activation of Protein Kinase C-Alpha Is Essential for Stimulation of Cell Proliferation by Ceramide 1-Phosphate. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:517–524. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.11.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gangoiti P., Bernacchioni C., Donati C., Cencetti F., Ouro A., Gómez-Muñoz A., Bruni P., Gomez-Munoz A., Bruni P. Ceramide 1-Phosphate Stimulates Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts. Biochimie. 2012;94:597–607. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ouro A., Arana L., Gangoiti P., Rivera I.G., Ordoñez M., Trueba M., Lankalapalli R.S., Bittman R., Gomez-Muñoz A. Ceramide 1-Phosphate Stimulates Glucose Uptake in Macrophages. Cell. Signal. 2013;25:786–795. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gangoiti P., Granado M.H., Wei S., Kong J.Y., Steinbrecher U.P., Gómez-muñoz A. Ceramide 1-Phosphate Stimulates Macrophage Proliferation through Activation of the PI3-Kinase / PKB, JNK and ERK1 / 2 Pathways. Cell. Signal. 2008;20:726–736. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ouro A., Arana L., Riazy M., Zhang P., Gomez-Larrauri A., Steinbrecher U., Duronio V., Gomez-Muñoz A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Mediates Ceramide 1-Phosphate-Stimulated Macrophage Proliferation. Exp. Cell Res. 2017;361:277–283. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gangoiti P., Granado M.H., Arana L., Ouro A., Gómez-Muñoz A. Involvement of Nitric Oxide in the Promotion of Cell Survival by Ceramide 1-Phosphate. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:2263–2269. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gomez-Munoz A., Kong J., Salh B., Steinbrecher U.P. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Inhibits Acid Sphingomyelinase and Blocks Apoptosis in Macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2003;539:56–60. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Newcomb B., Rhein C., Mileva I., Ahmad R., Clarke C.J., Snider J., Obeid L.M., Hannun Y.A. Identification of an Acid Sphingomyelinase Ceramide Kinase Pathway in the Regulation of the Chemokine CCL5. J. Lipid Res. 2018;59:1219–1229. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M084202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Granado M.H., Gangoiti P., Ouro A., Arana L., Gómez-Muñoz A. Ceramide 1-Phosphate Inhibits Serine Palmitoyltransferase and Blocks Apoptosis in Alveolar Macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1791:263–272. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gomez-Munoz A., Kong J.Y., Parhar K., Wang S.W., Gangoiti P., Gonzalez M., Eivemark S., Salh B., Duronio V., Steinbrecher U.P. Ceramide-1-Phosphate Promotes Cell Survival through Activation of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3744–3750. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.05.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Mishra S.K., Gao Y.G., Deng Y., Chalfant C.E., Hinchcliffe E.H., Brown R.E. CPTP: A Sphingolipid Transfer Protein That Regulates Autophagy and Inflammasome Activation†. Autophagy. 2018;14:862–879. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1393129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Goetzl E.J., Wang W., McGiffert C., Huang M.C., Graler M.H. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate and Its G Protein-Coupled Receptors Constitute a Multifunctional Immunoregulatory System. J. Cell Biochem. 2004;92:1104–1114. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gaire B.P., Choi J.W. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors in Cerebral Ischemia. NeuroMol. Med. 2021;23:211–223. doi: 10.1007/s12017-020-08614-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Calise S., Blescia S., Cencetti F., Bernacchioni C., Donati C., Bruni P. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Stimulates Proliferation and Migration of Satellite Cells: Role of S1P Receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012;1823:439–450. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Cartier A., Leigh T., Liu C.H., Hla T. Endothelial Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors Promote Vascular Normalization and Antitumor Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:3157–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1906246117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Saba J.D. Fifty Years of Lyase and a Moment of Truth: Sphingosine Phosphate Lyase from Discovery to Disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019;60:456–463. doi: 10.1194/jlr.S091181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mitroi D.N., Karunakaran I., Gräler M., Saba J.D., Ehninger D., Ledesma M.D., van Echten-Deckert G. SGPL1 (Sphingosine Phosphate Lyase 1) Modulates Neuronal Autophagy via Phosphatidylethanolamine Production. Autophagy. 2017;13:885–899. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1291471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Duyckaerts C., Delatour B., Potier M.C. Classification and Basic Pathology of Alzheimer Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118:5–36. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Atri A. The Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Spectrum: Diagnosis and Management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019;103:263–293. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2018.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Mielke M.M., Bandaru V.V.R., Haughey N.J., Xia J., Fried L.P., Yasar S., Albert M., Varma V., Harris G., Schneider E.B. Serum Ceramides Increase the Risk of Alzheimer Disease: The Women’s Health and Aging Study II. Neurology. 2012;79:633–641. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318264e380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Filippov V., Song M.A., Zhang K., Vinters H.V., Tung S., Kirsch W.M., Yang J., Duerksen-Hughes P.J. Increased Ceramide in Brains with Alzheimer’s and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012;29:537–547. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-111202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Czubowicz K., Jęśko H., Wencel P., Lukiw W.J., Strosznajder R.P. The Role of Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019;56:5436–5455. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1448-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Panchal M., Gaudin M., Lazar A.N., Salvati E., Rivals I., Ayciriex S., Dauphinot L., Dargère D., Auzeil N., Masserini M., et al. Ceramides and Sphingomyelinases in Senile Plaques. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014;65:193–201. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Puglielli L., Ellis B.C., Saunders A.J., Kovacs D.M. Ceramide Stabilizes β-Site Amyloid Precursor Protein-Cleaving Enzyme 1 and Promotes Amyloid β-Peptide Biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:19777–19783. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300466200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Desbène C., Malaplate-Armand C., Youssef I., Garcia P., Stenger C., Sauvée M., Fischer N., Rimet D., Koziel V., Escanyé M.-C., et al. Critical Role of CPLA2 in Aβ Oligomer-Induced Neurodegeneration and Memory Deficit. Neurobiol. Aging. 2012;33:1123.e17–1123.e29. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Jana A., Pahan K. Fibrillar Amyloid-β-Activated Human Astroglia Kill Primary Human Neurons via Neutral Sphingomyelinase: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2010;30:12676–12689. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1243-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lee J.T., Xu J., Lee J.M., Ku G., Han X., Yang D.I., Chen S., Hsu C.Y. Amyloid-β Peptide Induces Oligodendrocyte Death by Activating the Neutral Sphingomyelinase-Ceramide Pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2004;164:123–131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200307017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yang D.I., Yeh C.H., Chen S., Xu J., Hsu C.Y. Neutral Sphingomyelinase Activation in Endothelial and Glial Cell Death Induced by Amyloid Beta-Peptide. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004;17:99–107. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2004.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Takasugi N., Sasaki T., Suzuki K., Osawa S., Isshiki H., Hori Y., Shimada N., Higo T., Yokoshima S., Fukuyama T., et al. BACE1 Activity Is Modulated by Cell-Associated Sphingosine-1-Phosphate. J. Neurosci. 2011;31:6850–6857. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6467-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ceccom J., Loukh N., Lauwers-Cances V., Touriol C., Nicaise Y., Gentil C., Uro-Coste E., Pitson S., Maurage C.A., Duyckaerts C., et al. Reduced Sphingosine Kinase-1 and Enhanced Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Lyase Expression Demonstrate Deregulated Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014;2:1–10. doi: 10.1186/2051-5960-2-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Paciotti S., Albi E., Parnetti L., Beccari T. Lysosomal Ceramide Metabolism Disorders: Implications in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:594. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Zhao Y., Ren J., Padilla-Parra S., Fry E.E., Stuart D.I. Lysosome Sorting of β-Glucocerebrosidase by LIMP-2 Is Targeted by the Mannose 6-Phosphate Receptor. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:1–12. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Foo J.N., Liany H., Bei J.X., Yu X.Q., Liu J., Au W.L., Prakash K.M., Tan L.C., Tan E.K. A Rare Lysosomal Enzyme Gene SMPD1 Variant (p.R591C) Associates with Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2013;34:2890.e13–2890.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Conte C., Arcuri C., Cataldi S., Mecca C., Codini M., Ceccarini M.R., Patria F.F., Beccari T., Albi E. Niemann-Pick Type a Disease: Behavior of Neutral Sphingomyelinase and Vitamin D Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:2365. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Vanier M.T. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Volume 113. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2013. Niemann-Pick diseases; pp. 1717–1721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Torres S., Solsona-Vilarrasa E., Nuñez S., Matías N., Insausti-Urkia N., Castro F., Casasempere M., Fabriás G., Casas J., Enrich C., et al. Acid Ceramidase Improves Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease by Repressing STARD1 Expression and Mitochondrial Cholesterol Accumulation. Redox Biol. 2021:102052. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Orvisky E., Park J.K., LaMarca M.E., Ginns E.I., Martin B.M., Tayebi N., Sidransky E. Glucosylsphingosine Accumulation in Tissues from Patients with Gaucher Disease: Correlation with Phenotype and Genotype. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2002;76:262–270. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7192(02)00117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Yu F.P.S., Amintas S., Levade T., Medin J.A. Acid Ceramidase Deficiency: Farber Disease and SMA-PME. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018;13:1–19. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0845-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Cozma C., Iurașcu M.-I., Eichler S., Hovakimyan M., Brandau O., Zielke S., Böttcher T., Giese A.-K., Lukas J., Rolfs A. C26-Ceramide as Highly Sensitive Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Farber Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06604-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Spratley S.J., Hill C.H., Viuff A.H., Edgar J.R., Skjødt K., Deane J.E. Molecular Mechanisms of Disease Pathogenesis Differ in Krabbe Disease Variants. Traffic. 2016;17:908–922. doi: 10.1111/tra.12404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Marshall M.S., Bongarzone E.R. Beyond Krabbe’s Disease: The Potential Contribution of Galactosylceramidase Deficiency to Neuronal Vulnerability in Late-Onset Synucleinopathies. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016;94:1328–1332. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Maglione V., Marchi P., di Pardo A., Lingrell S., Horkey M., Tidmarsh E., Sipione S. Impaired Ganglioside Metabolism in Huntington’s Disease and Neuroprotective Role of GM1. J. Neurosci. 2010;30:4072–4080. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6348-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Alpaugh M., Galleguillos D., Forero J., Morales L.C., Lackey S.W., Kar P., di Pardo A., Holt A., Kerr B.J., Todd K.G., et al. Disease-modifying Effects of Ganglioside GM1 in Huntington’s Disease Models. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017;9:1537–1557. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201707763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Di Pardo A., Basit A., Armirotti A., Amico E., Castaldo S., Pepe G., Marracino F., Buttari F., Digilio A.F., Maglione V. De Novo Synthesis of Sphingolipids Is Defective in Experimental Models of Huntington’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2017;11:698. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yamout B.I., Alroughani R. Multiple Sclerosis. Semin. Neurol. 2018;38:212–225. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1649502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Barthelmes J., de Bazo A.M., Pewzner-Jung Y., Schmitz K., Mayer C.A., Foerch C., Eberle M., Tafferner N., Ferreirós N., Henke M., et al. Lack of Ceramide Synthase 2 Suppresses the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Impairing the Migratory Capacity of Neutrophils. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015;46:280–292. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Eberle M., Ebel P., Mayer C.A., Barthelmes J., Tafferner N., Ferreiros N., Ulshöfer T., Henke M., Foerch C., de Bazo A.M., et al. Exacerbation of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Ceramide Synthase 6 Knockout Mice Is Associated with Enhanced Activation/Migration of Neutrophils. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015;93:825–836. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Schiffmann S., Ferreiros N., Birod K., Eberle M., Schreiber Y., Pfeilschifter W., Ziemann U., Pierre S., Scholich K., Grösch S., et al. Ceramide Synthase 6 Plays a Critical Role in the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2012;188:5723–5733. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kurz J., Brunkhorst R., Foerch C., Blum L., Henke M., Gabriel L., Ulshöfer T., Ferreirós N., Parnham M.J., Geisslinger G., et al. The Relevance of Ceramides and Their Synthesizing Enzymes for Multiple Sclerosis. Clin. Sci. 2018;132:1963–1976. doi: 10.1042/CS20180506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Vidaurre O.G., Haines J.D., Sand I.K., Adula K.P., Huynh J.L., Mcgraw C.A., Zhang F., Varghese M., Sotirchos E., Bhargava P., et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Ceramides from Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Impair Neuronal Bioenergetics. Brain. 2014;137:2271–2286. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Sashindranath M., Nandurkar H.H. Endothelial Dysfunction in the Brain: Setting the Stage for Stroke and Other Cerebrovascular Complications of Covid-19. Stroke. 2021;52:1895–1904. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kahl A., Blanco I., Jackman K., Baskar J., Mohan H.M., Rodney-Sandy R., Zhang S., Iadecola C., Hochrainer K. Cerebral Ischemia Induces the Aggregation of Proteins Linked to Neurodegenerative Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:1–8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21063-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kuźma E., Lourida I., Moore S.F., Levine D.A., Ukoumunne O.C., Llewellyn D.J. Stroke and Dementia Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018;14:1416–1426. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.06.3061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Dmitrieva V.G., Torshina E.V., Yuzhakov V.V., Povarova O.V., Skvortsova V.I., Limborska S.A., Dergunova L.V. Expression of Sphingomyelin Synthase 1 Gene in Rat Brain Focal Ischemia. Brain Res. 2008;1188:222–227. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.10.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Yu Z.F., Nikolova-Karakashian M., Zhou D., Cheng G., Schuchman E.H., Mattson M.P. Pivotal Role for Acidic Sphingomyelinase in Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Ceramide and Cytokine Production, and Neuronal Apoptosis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2000;15:85–97. doi: 10.1385/JMN:15:2:85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Hagemann N., Yusuf A.M., Martiny C., Zhang X., Kleinschnitz C., Gunzer M., Kolesnick R., Gulbins E., Hermann D.M. Homozygous Smpd1 Deficiency Aggravates Brain Ischemia/ Reperfusion Injury by Mechanisms Involving Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils, Whereas Heterozygous Smpd1 Deficiency Protects against Mild Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2020;115:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-00823-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Chao H.C., Lee T.H., Chiang C.S., Yang S.Y., Kuo C.H., Tang S.C. Sphingolipidomics Investigation of the Temporal Dynamics after Ischemic Brain Injury. J. Proteome Res. 2019;18:3470–3478. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Gui Y.-K., Li Q., Liu L., Zeng P., Ren R.F., Guo Z.F., Wang G.H., Song J.G., Zhang P. Plasma Levels of Ceramides Relate to Ischemic Stroke Risk and Clinical Severity. Brain Res. Bull. 2020;158:122–127. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Lee T.H., Cheng C.N., Chao H.C., Lee C.H., Kuo C.H., Tang S.C., Jeng J.S. Plasma Ceramides Are Associated with Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Tea M.N., Poonnoose S.I., Pitson S.M. Targeting the Sphingolipid System as a Therapeutic Direction for Glioblastoma. Cancers. 2020;12:111. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Bernhart E., Damm S., Wintersperger A., Nusshold C., Brunner A.M., Plastira I., Rechberger G., Reicher H., Wadsack C., Zimmer A., et al. Interference with Distinct Steps of Sphingolipid Synthesis and Signaling Attenuates Proliferation of U87MG Glioma Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015;96:119–130. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Casasampere M., Ordóñez Y.F., Casas J., Fabrias G. Dihydroceramide Desaturase Inhibitors Induce Autophagy via Dihydroceramide-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017;1861:264–275. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.11.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Hernández-Tiedra S., Fabriàs G., Dávila D., Salanueva Í.J., Casas J., Montes L.R., Antón Z., García-Taboada E., Salazar-Roa M., Lorente M., et al. Dihydroceramide Accumulation Mediates Cytotoxic Autophagy of Cancer Cells via Autolysosome Destabilization. Autophagy. 2016;12:2213–2229. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1213927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Van Brooklyn J.R., Jackson C.A., Pearl D.K., Kotur M.S., Snyder P.J., Prior T.W. Sphingosine Kinase-1 Expression Correlates with Poor Survival of Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme: Roles of Sphingosine Kinase Isoforms in Growth of Glioblastoma Cell Lines. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005;64:695–705. doi: 10.1097/01.jnen.0000175329.59092.2c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Kapitonov D., Allegood J.C., Mitchell C., Hait N.C., Almenara J.A., Adams J.K., Zipkin R.E., Dent P., Kordula T., Milstien S., et al. Targeting Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibits Akt Signaling, Induces Apoptosis, and Suppresses Growth of Human Glioblastoma Cells and Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2009;69:6915–6923. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Greenamyre J.T., Betarbet R., Sherer T.B. The Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Genes, Environment and Mitochondria. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2003;9:59–64. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(03)00023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Schneider J.S. MPTP-induced Parkinsonism: Acceleration of Biochemical and Behavioral Recovery by GM1 Ganglioside Treatment. J. Neurosci. Res. 1992;31:112–119. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490310116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Gan-Or Z., Liong C., Alcalay R.N. GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease and Other Synucleinopathies. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018;18:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s11910-018-0860-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Chiasserini D., Paciotti S., Eusebi P., Persichetti E., Tasegian A., Kurzawa-Akanbi M., Chinnery P.F., Morris C.M., Calabresi P., Parnetti L. Selective Loss of Glucocerebrosidase Activity in Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015;10:1–6. doi: 10.1186/s13024-015-0010-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Parnetti L., Paciotti S., Eusebi P., Dardis A., Zampieri S., Chiasserini D., Tasegian A., Tambasco N., Bembi B., Calabresi P. Cerebrospinal Fluid β-Glucocerebrosidase Activity Is Reduced in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Mov. Disord. 2009;34:1423–1431. doi: 10.1002/mds.27136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Alcalay R.N., Levy O.A., Waters C.C., Fahn S., Ford B., Kuo S.H., Mazzoni P., Pauciulo M.W., Nichols W.C., Gan-Or Z., et al. Glucocerebrosidase Activity in Parkinson’s Disease with and without GBA Mutations. Brain. 2015;138:2648–2658. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Murphy K.E., Gysbers A.M., Abbott S.K., Tayebi N., Kim W.S., Sidransky E., Cooper A., Garner B., Halliday G.M. Reduced Glucocerebrosidase Is Associated with Increased α-Synuclein in Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Brain. 2014;137:834–848. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Taguchi Y.V., Liu J., Ruan J., Pacheco J., Zhang X., Abbasi J., Keutzer J., Mistry P.K., Chandra S.S. Glucosylsphingosine Promotes α-Synuclein Pathology in Mutant GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2017;37:9617–9631. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1525-17.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Mazzulli J.R., Xu Y.H., Sun Y., Knight A.L., McLean P.J., Caldwell G.A., Sidransky E., Grabowski G.A., Krainc D. Gaucher Disease Glucocerebrosidase and α-Synuclein Form a Bidirectional Pathogenic Loop in Synucleinopathies. Cell. 2011;146:37–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Kim M.J., Jeon S., Burbulla L.F., Krainc D. Acid Ceramidase Inhibition Ameliorates α-Synuclein Accumulation upon Loss of GBA1 Function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018;27:1972–1988. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Sardi S.P., Viel C., Clarke J., Treleaven C.M., Richards A.M., Park H., Olszewski M.A., Dodge J.C., Marshall J., Makino E. Glucosylceramide Synthase Inhibition Alleviates Aberrations in Synucleinopathy Models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:2699–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616152114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Burbulla L.F., Jeon S., Zheng J., Song P., Silverman R.B., Krainc D. A Modulator of Wild-Type Glucocerebrosidase Improves Pathogenic Phenotypes in Dopaminergic Neuronal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019;11 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau6870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Morabito G., Giannelli S.G., Ordazzo G., Bido S., Castoldi V., Indrigo M., Cabassi T., Cattaneo S., Luoni M., Cancellieri C., et al. AAV-PHP.B-Mediated Global-Scale Expression in the Mouse Nervous System Enables GBA1 Gene Therapy for Wide Protection from Synucleinopathy. Mol. Ther. 2017;25:2727–2742. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Rocha E.M., Smith G.A., Park E., Cao H., Brown E., Hayes M.A., Beagan J., McLean J.R., Izen S.C., Perez-Torres E., et al. Glucocerebrosidase Gene Therapy Prevents α-Synucleinopathy of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015;82:495–503. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Du T.T., Wang L., Duan C.L., Lu L.L., Zhang J.L., Gao G., Qiu X.B., Wang X.M., Yang H. GBA Deficiency Promotes SNCA/α-Synuclein Accumulation through Autophagic Inhibition by Inactivated PPP2A. Autophagy. 2015;11:1803–1820. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1086055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Mukhopadhyay A., Saddoughi S.A., Song P., Sultan I., Ponnusamy S., Senkal C.E., Snook C.F., Arnold H.K., Sears R.C., Hanniui Y.A., et al. Direct Interaction between the Inhibitor 2 and Ceramide via Sphingolipid-protein Binding Is Involved in the Regulation of Protein Phosphatase 2A Activity and Signaling. FASEB J. 2009;23:751–763. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-120550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Salinas M., López-Valdaliso R., Martín D., Alvarez A., Cuadrado A. Inhibition of PKB/Akt1 by C2-Ceramide Involves Activation of Ceramide- Activated Protein Phosphatase in PC12 Cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000;15:156–169. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1999.0813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Cornell T.T., Hinkovska-Galcheva V., Sun L., Cai Q., Hershenson M.B., Vanway S., Shanley T.P. Ceramide-Dependent PP2A Regulation of TNFα-Induced IL-8 Production in Respiratory Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009;296:L849–L856. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90516.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Lleó A., Núñez-Llaves R., Alcolea D., Chiva C., Balateu-Paños D., Colom-Cadena M., Gomez-Giro G., Muñoz L., Querol-Vilaseca M., Pegueroles J., et al. Changes in Synaptic Proteins Precede Neurodegeneration Markers in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid*. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019;18:546–560. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.001290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Launey T., Endo S., Sakai R., Harano J., Ito M. Protein Phosphatase 2A Inhibition Induces Cerebellar Long-Term Depression and Declustering of Synaptic AMPA Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:676–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0302914101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Gao J., Hu X.D., Yang H., Xia H. Distinct Roles of Protein Phosphatase 1 Bound on Neurabin and Spinophilin and Its Regulation in AMPA Receptor Trafficking and LTD Induction. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018;55:7179–7186. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0886-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Tong L., Prieto G.A., Cotman C.W. IL-1β Suppresses CLTP-Induced Surface Expression of GluA1 and Actin Polymerization via Ceramide-Mediated Src Activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018;15:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1158-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Furukawa K., Mattson M.P. The Transcription Factor NF-ΚB Mediates Increases in Calcium Currents and Decreases in NMDA- and AMPA/Kainate-Induced Currents Induced by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Hippocampal Neurons. J. Neurochem. 1998;70:1876–1886. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70051876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Scarlatti F., Bauvy C., Ventruti A., Sala G., Cluzeaud F., Vandewalle A., Ghidoni R., Codogno P. Ceramide-Mediated Macroautophagy Involves Inhibition of Protein Kinase B and Up-Regulation of Beclin 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:18384–18391. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313561200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Nguyen A.P.T., Tsika E., Kelly K., Levine N., Chen X., West A.B., Boularand S., Barneoud P., Moore D.J. Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration Induced by Parkinson’s Disease-Linked G2019S LRRK2 Is Dependent on Kinase and GTPase Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:17296–17307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922184117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Singh A., Zhi L., Zhang H. LRRK2 and Mitochondria: Recent Advances and Current Views. Brain Res. 2019;1702:96–104. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Tolosa E., Vila M., Klein C., Rascol O. LRRK2 in Parkinson Disease: Challenges of Clinical Trials. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020;16:97–107. doi: 10.1038/s41582-019-0301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Boecker C.A., Goldsmith J., Dou D., Cajka G.G., Holzbaur E.L.F. Increased LRRK2 Kinase Activity Alters Neuronal Autophagy by Disrupting the Axonal Transport of Autophagosomes. Curr. Biol. 2021;31:2140–2154.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.02.061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Yahalom G., Greenbaum L., Israeli-Korn S., Fay-Karmon T., Livneh V., Ruskey J.A., Roncière L., Alam A., Gan-Or Z., Hassin-Baer S. Carriers of Both GBA and LRRK2 Mutations, Compared to Carriers of Either, in Parkinson’s Disease: Risk Estimates and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019;62:179–184. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Ortega R.A., Wang C., Raymond D., Bryant N., Scherzer C.R., Thaler A., Alcalay R.N., West A.B., Mirelman A., Kuras Y., et al. Association of Dual LRRK2 G2019S and GBA Variations with Parkinson Disease Progression. JAMA Netw. Open. 2021;4:e215845. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Ferrazza R., Cogo S., Melrose H., Bubacco L., Greggio E., Guella G., Civiero L., Plotegher N. LRRK2 Deficiency Impacts Ceramide Metabolism in Brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016;478:1141–1146. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Ysselstein D., Nguyen M., Young T.J., Severino A., Schwake M., Merchant K., Krainc D. LRRK2 Kinase Activity Regulates Lysosomal Glucocerebrosidase in Neurons Derived from Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:1–9. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13413-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Weindel C.G., Bell S.L., Vail K.J., West K.O., Patrick K.L., Watson R.O. LRRK2 Maintains Mitochondrial Homeostasis and Regulates Innate Immune Responses to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. eLife. 2020;9:e56214. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Saez-Atienzar S., Bonet-Ponce L., Blesa J.R., Romero F.J., Murphy M.P., Jordan J., Galindo M.F. The LRRK2 Inhibitor GSK2578215A Induces Protective Autophagy in SH-SY5Y Cells: Involvement of Drp-1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Mitochondrial-Derived ROS Signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1368. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Fugio L.B., Coeli-Lacchini F.B., Leopoldino A.M. Sphingolipids and Mitochondrial Dynamic. Cells. 2020;9:581. doi: 10.3390/cells9030581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Van Ham T.J., Thijssen K.L., Breitling R., Hofstra R.M.W., Plasterk R.H.A., Nollen E.A.A.C. Elegans Model Identifies Genetic Modifiers of α-Synuclein Inclusion Formation during Aging. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Khateeb S., Flusser H., Ofir R., Shelef I., Narkis G., Vardi G., Shorer Z., Levy R., Galil A., Elbedour K., et al. PLA2G6 Mutation Underlies Infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006;79:942–948. doi: 10.1086/508572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Tomiyama H., Yoshino H., Ogaki K., Li L., Yamashita C., Li Y., Funayama M., Sasaki R., Kokubo Y., Kuzuhara S., et al. PLA2G6 Variant in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2011;56:401–403. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2011.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Shen T., Hu J., Jiang Y., Zhao S., Lin C., Yin X., Yan Y., Pu J., Lai H.Y., Zhang B. Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease Caused by Pla2g6 Compound Heterozygous Mutation, a Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Neurol. 2019;10:915. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Zhou Q., Yen A., Rymarczyk G., Asai H., Trengrove C., Aziz N., Kirber M.T., Mostoslavsky G., Ikezu T., Wolozin B., et al. Impairment of PARK14-Dependent Ca2+ Signalling Is a Novel Determinant of Parkinson’s Disease. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:1–14. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Lin G., Lee P.-T., Chen K., Lin W.-W., Wang L., Bellen Correspondence H.J. Phospholipase PLA2G6, a Parkinsonism-Associated Gene, Affects Vps26 and Vps35, Retromer Function, and Ceramide Levels, Similar to Alpha-Synuclein Gain. Cell Metab. 2018;28:605–618. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Follett J., Norwood S.J., Hamilton N.A., Mohan M., Kovtun O., Tay S., Zhe Y., Wood S.A., Mellick G.D., Silburn P.A., et al. The Vps35 D620N Mutation Linked to Parkinson’s Disease Disrupts the Cargo Sorting Function of Retromer. Traffic. 2014;15:230–244. doi: 10.1111/tra.12136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Guedes L.C., Chan R.B., Gomes M.A., Conceição V.A., Machado R.B., Soares T., Xu Y., Gaspar P., Carriço J.A., Alcalay R.N. Serum Lipid Alterations in GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017;44:58–65. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Ge P., Dawson V.L., Dawson T.M. PINK1 and Parkin Mitochondrial Quality Control: A Source of Regional Vulnerability in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020;15:1–18. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00367-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Kitagishi Y., Nakano N., Ogino M., Ichimura M., Minami A., Matsuda S. PINK1 Signaling in Mitochondrial Homeostasis and in Aging (Review) Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017;39:3–8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Gandhi S., Wood-Kaczmar A., Yao Z., Plun-Favreau H., Deas E., Klupsch K., Downward J., Latchman D.S., Tabrizi S.J., Wood N., et al. PINK1-Associated Parkinson’s Disease Is Caused by Neuronal Vulnerability to Calcium-Induced Cell Death. Mol. Cell. 2009;33:627–638. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Sawada M., Nakashima S., Kiyono T., Nakagawa M., Yamada J., Yamakawa H., Banno Y., Shinoda J., Nishimura Y., Nozawa Y., et al. P53 Regulates Ceramide Formation by Neutral Sphingomyelinase through Reactive Oxygen Species in Human Glioma Cells. Oncogene. 2001;20:1368–1378. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.García-Ruiz C., Colell A., Marí M., Morales A., Fernández-Checa J.C. Direct Effect of Ceramide on the Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Leads to Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species: Role of Mitochondrial Glutathione. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:11369–11377. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.17.11369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Ausman J., Abbade J., Ermini L., Farrell A., Tagliaferro A., Post M., Caniggia I. Ceramide-Induced BOK Promotes Mitochondrial Fission in Preeclampsia. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1–18. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0360-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Qi Z., Yang W., Liu Y., Cui T., Gao H., Duan C., Lu L., Zhao C., Zhao H., Yang H. Loss of PINK1 Function Decreases PP2A Activity and Promotes Autophagy in Dopaminergic Cells and a Murine Model. Neurochem. Int. 2011;59:572–581. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Dobrowsky R.T., Kamibayashi C., Mumby M.C., Hannuns Y.A. Ceramide Activates Heterotrimeric Protein Phosphatase 2A. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:15523–15530. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)82288-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Malini E., Zampieri S., Deganuto M., Romanello M., Sechi A., Bembi B., Dardis A. Role of LIMP-2 in the Intracellular Trafficking of β-Glucosidase in Different Human Cellular Models. FASEB J. 2015;29:3839–3852. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-271148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Usenko T.S., Bezrukova A.I., Bogdanova D.A., Kopytova A.E., Senkevich K.A., Gracheva E.V., Timofeeva A.A., Miliukhina I.V., Zakharova E.Y., Emelyanov A., et al. Genetics Variants and Expression of the SCARB2 Gene in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease in Russia. Neurosci. Lett. 2021;741:135509. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Bras J., Guerreiro R., Darwent L., Parkkinen L., Ansorge O., Escott-Price V., Hernandez D.G., Nalls M.A., Clark L.N., Honig L.S., et al. Genetic Analysis Implicates APOE, SNCA and Suggests Lysosomal Dysfunction in the Etiology of Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014;23:6139–6146. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Do C.B., Tung J.Y., Dorfman E., Kiefer A.K., Drabant E.M., Francke U., Mountain J.L., Goldman S.M., Tanner C.M., Langston J.W., et al. Web-Based Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Two Novel Loci and a Substantial Genetic Component for Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Blauwendraat C., Heilbron K., Vallerga C.L., Bandres-Ciga S., von Coelln R., Pihlstrøm L., Simón-Sánchez J., Schulte C., Sharma M., Krohn L., et al. Parkinson’s Disease Age at Onset Genome-Wide Association Study: Defining Heritability, Genetic Loci, and α-Synuclein Mechanisms. Mov. Disord. 2019;34:866–875. doi: 10.1002/mds.27659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Nalls M.A., Pankratz N., Lill C.M., Do C.B., Hernandez D.G., Saad M., Destefano A.L., Kara E., Bras J., Sharma M., et al. Large-Scale Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Data Identifies Six New Risk Loci for Parkinson’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2014;46:989–993. doi: 10.1038/ng.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Matrone C., Dzamko N., Madsen P., Nyegaard M., Pohlmann R., Søndergaard R.V., Lassen L.B., Andresen T.L., Halliday G.M., Jensen P.H., et al. Mannose 6-Phosphate Receptor Is Reduced in -Synuclein Overexpressing Models of Parkinsons Disease. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0160501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Rothaug M., Zunke F., Mazzulli J.R., Schweizer M., Altmeppen H., Lüllmann-Rauche R., Kallemeijn W.W., Gaspar P., Aerts J.M., Glatzel M., et al. LIMP-2 Expression Is Critical for β-Glucocerebrosidase Activity and α-Synuclein Clearance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:15573–15578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405700111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Subramaniam S.R., Chesselet M.F. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013;106–107:17–32. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Weng M., Xie X., Liu C., Lim K.L., Zhang C.W., Li L. The Sources of Reactive Oxygen Species and Its Possible Role in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinson’s Dis. 2018;2018 doi: 10.1155/2018/9163040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Radad K., Al-Shraim M., Al-Emam A., Wang F., Kranner B., Rausch W.D., Moldzio R. Rotenone: From Modelling to Implication in Parkinson’s Disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2019;57:317–326. doi: 10.5114/fn.2019.89857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Magrassi L., Adorni L., Montorfano G., Rapelli S., Butti G., Berra B., Milanesi G. Vitamin D Metabolites Activate the Sphingomyelin Pathway and Induce Death of Glioblastoma Cells. Acta Neurochir. 1998;140:707–714. doi: 10.1007/s007010050166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Pyszko J.A., Strosznajder J.B. The Key Role of Sphingosine Kinases in the Molecular Mechanism of Neuronal Cell Survival and Death in an Experimental Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2014;52:260–269. doi: 10.5114/fn.2014.45567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Pyszko J., Strosznajder J.B. Sphingosine Kinase 1 and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Oxidative Stress Evoked by 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium (MPP+) in Human Dopaminergic Neuronal Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014;50:38–48. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8622-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Shao Q.-H., Chen Y., Li F.-F., Wang S., Zhang X.-L., Yuan Y.-H., Chen N.-H. TLR4 Deficiency Has a Protective Effect in the MPTP/Probenecid Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019;40:1503–1512. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0280-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Zhao X.D., Wang F.X., Cao W.F., Zhang Y.H., Li Y. TLR4 Signaling Mediates AP-1 Activation in an MPTP-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016;32:96–102. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Mariucci G., Pagiotti R., Galli F., Romani L., Conte C. The Potential Role of Toll-Like Receptor 4 in Mediating Dopaminergic Cell Loss and Alpha-Synuclein Expression in the Acute MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018;64:611–618. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Conte C., Roscini L., Sardella R., Mariucci G., Scorzoni S., Beccari T., Corte L. Toll Like Receptor 4 Affects the Cerebral Biochemical Changes Induced by MPTP Treatment. Neurochem. Res. 2017;42:493–500. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Kaur G., Behl T., Sehgal A., Singh S., Sharma N., Kumar A., Arora S., Bungau S. Role of TLR2 and TLR4 Signaling in Parkinson’s Disease: An Insight into Associated Therapeutic Potential. J. Mol. Neurosci. MN. 2021:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01811-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Albi E., Cataldi S., Codini M., Mariucci G., Lazzarini A., Ceccarini M.R., Ferri I., Laurenti M.E., Arcuri C., Patria F., et al. Neutral Sphingomyelinase Increases and Delocalizes in the Absence of Toll-Like Receptor 4: A New Insight for MPTP Neurotoxicity. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019;142:46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2019.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Wang Y., Liu J., Chen M., Du T., Duan C., Gao G., Yang H. The Novel Mechanism of Rotenone-Induced α-Synuclein Phosphorylation via Reduced Protein Phosphatase 2A Activity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016;75:34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Lupescu A., Jilani K., Zbidah M., Lang F. Induction of Apoptotic Erythrocyte Death by Rotenone. Toxicology. 2012;300:132–137. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Rutkute K., Asmis R.H., Nikolova-Karakashian M.N. Regulation of Neutral Sphingomyelinase-2 by GSH: A New Insight to the Role of Oxidative Stress in Aging-Associated Inflammation. J. Lipid Res. 2007;48:2443–2452. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700227-JLR200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Merrill A.H. Sphingolipid and Glycosphingolipid Metabolic Pathways in the Era of Sphingolipidomics. Chem. Rev. 2011;111:6387–6422. doi: 10.1021/cr2002917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Grammatikos G., Schoell N., Ferreirós N., Bon D., Herrmann E., Farnik H., Köberle V., Piiper A., Zeuzem S., Kronenberger B., et al. Serum Sphingolipidomic Analyses Reveal an Upregulation of C16-Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:18095–18105. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Alberg A.J., Armeson K., Pierce J.S., Bielawski J., Bielawska A., Visvanathan K., Hill E.G., Ogretmen B. Plasma Sphingolipids and Lung Cancer: A Population-Based, Nested Case-Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013;22:1374–1382. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Govindarajah N., Clifford R., Bowden D., Sutton P.A., Parsons J.L., Vimalachandran D. Sphingolipids and Acid Ceramidase as Therapeutic Targets in Cancer Therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019;138:104–111. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Belarbi K., Cuvelier E., Bonte M.A., Desplanque M., Gressier B., Devos D., Chartier-Harlin M.C. Glycosphingolipids and Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020;15:1–16. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00408-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Abbott S.K., Li H., Muñoz S.S., Knoch B., Batterham M., Murphy K.E., Halliday G.M., Garner B. Altered Ceramide Acyl Chain Length and Ceramide Synthase Gene Expression in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2014;29:518–526. doi: 10.1002/mds.25729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Fernández-Irigoyen J., Cartas-Cejudo P., Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta M., Santamaría E. Alteration in the Cerebrospinal Fluid Lipidome in Parkinson’s Disease: A Post-Mortem Pilot Study. Biomedicines. 2021;9:491. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Xing Y., Tang Y., Zhao L., Wang Q., Qin W., Ji X., Zhang J., Jia J. Associations between Plasma Ceramides and Cognitive and Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Parkinson’s Disease Dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016;370:82–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.09.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Mielke M.M., Maetzler W., Haughey N.J., Bandaru V.V.R., Savica R., Deuschle C., Gasser T., Hauser A.-K., Ber-Sultan S.G., Schleicher E., et al. Plasma Ceramide and Glucosylceramide Metabolism Is Altered in Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease and Associated with Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE. 2013;9:e0073094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Cheng D., Jenner A.M., Shui G., Cheong W.F., Mitchell T.W., Nealon J.R., Kim W.S., McCann H., Wenk M.R., Halliday G.M. Lipid Pathway Alterations in Parkinson’s Disease Primary Visual Cortex. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e0017299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Seyfried T.N., Choi H., Chevalier A., Hogan D., Akgoc Z., Schneider J.S. Sex-Related Abnormalities in Substantia Nigra Lipids in Parkinson’s Disease. ASN Neuro. 2018;10:1–10. doi: 10.1177/1759091418781889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Gegg M.E., Sweet L., Wang B.H., Shihabuddin L.S., Sardi S.P., Schapira A.H.V. No Evidence for Substrate Accumulation in Parkinson Brains with GBA Mutations. Mov. Disord. 2015;30:1085–1089. doi: 10.1002/mds.26278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Stoessel D., Schulte C., Santos M.C., Scheller D., Rebollo-Mesa I., Deuschle C., Walther D., Schauer N., Berg D., Costa A. Promising Metabolite Profiles in the Plasma and CSF of Early Clinical Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:1–14. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Boutin M., Sun Y., Shacka J.J., Auray-Blais C. Tandem Mass Spectrometry Multiplex Analysis of Glucosylceramide and Galactosylceramide Isoforms in Brain Tissues at Different Stages of Parkinson Disease. Anal. Chem. 2016;88:1856–1863. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Wood P.L., Tippireddy S., Feriante J., Woltjer R.L. Augmented Frontal Cortex Diacylglycerol Levels in Parkinson’s Disease and Lewy Body Disease. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0191815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Niimi Y., Mizutani Y., Akiyama H., Watanabe H., Shiroki R., Hirabayashi Y., Hoshinaga K., Mutoh T. Cerebrospinal Fluid Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease: No Accumulation of Glucosylceramide, but Significant Downregulation of Active Complement C5 Fragment. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2021;11:221–232. doi: 10.3233/JPD-202310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Wu G., Lu Z.H., Kulkarni N., Amin R., Ledeen R.W. Mice Lacking Major Brain Gangliosides Develop Parkinsonism. Neurochem. Res. 2011;36:1706–1714. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0437-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Park J.Y., Kim K.S., Lee S.B., Ryu J.S., Chung K.C., Choo Y.K., Jou I., Kim J., Park S.M. On the Mechanism of Internalization of α-Synuclein into Microglia: Roles of Ganglioside GM1 and Lipid Raft. J. Neurochem. 2009;110:400–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Schneider J.S., Aras R., Williams C.K., Koprich J.B., Brotchie J.M., Singh V. GM1 Ganglioside Modifies α-Synuclein Toxicity and Is Neuroprotective in a Rat α-Synuclein Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42847-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Gaspar R., Pallbo J., Weininger U., Linse S., Sparr E. Ganglioside Lipids Accelerate α-Synuclein Amyloid Formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018;1866:1062–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Wu G., Lu Z.H., Kulkarni N., Ledeen R.W. Deficiency of Ganglioside GM1 Correlates with Parkinson’s Disease in Mice and Humans. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012;90:1997–2008. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Zhang J., Zhang X., Wang L., Yang C. High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Based Quantitative Lipidomics Study of Ganglioside-NANA-3 Plasma to Establish Its Association with Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017;23:5345–5353. doi: 10.12659/MSM.904399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Chan R.B., Perotte A.J., Zhou B., Liong C., Shorr E.J., Marder K.S., Kang U.J., Waters C.H., Levy O.A., Xu Y., et al. Elevated GM3 Plasma Concentration in Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: A Lipidomic Analysis. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0172348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]