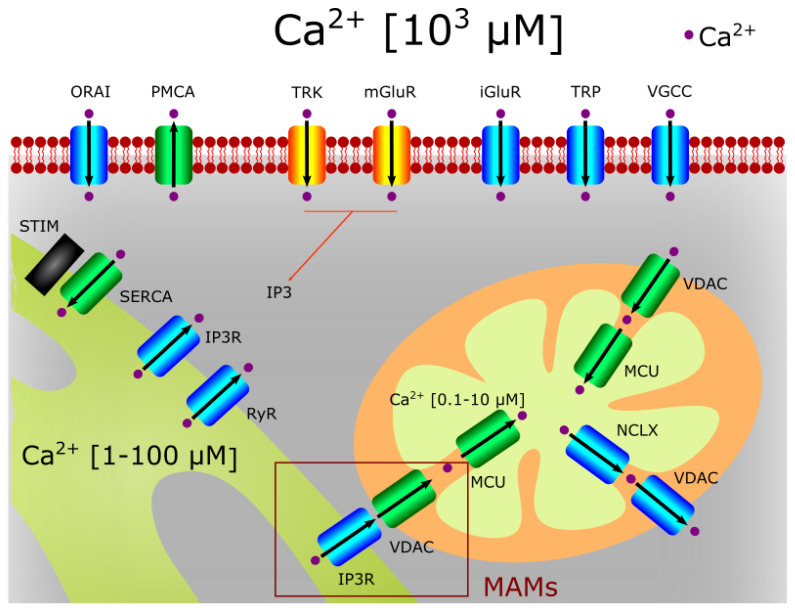
Figure 4.
Ca2+ homeostasis in neurons. The entrance of extracellular Ca2+ into neurons is due to the direct activation of neurotransmitter and neurotrophin receptors (such as NMDAR and TRK) and cationic channels (such as TRPs or voltage activated Ca2+ channels). The VDAC channel can import or export Ca2+ in the mitochondria when associated to MCU or NCLX, respectively. IP3R and VDAC channels found in MAMs can also transport Ca2+ from the ER to the mitochondria. The Ca2+ extrusion to the extracellular medium is mediated by ATPases (i.e., PMCA).