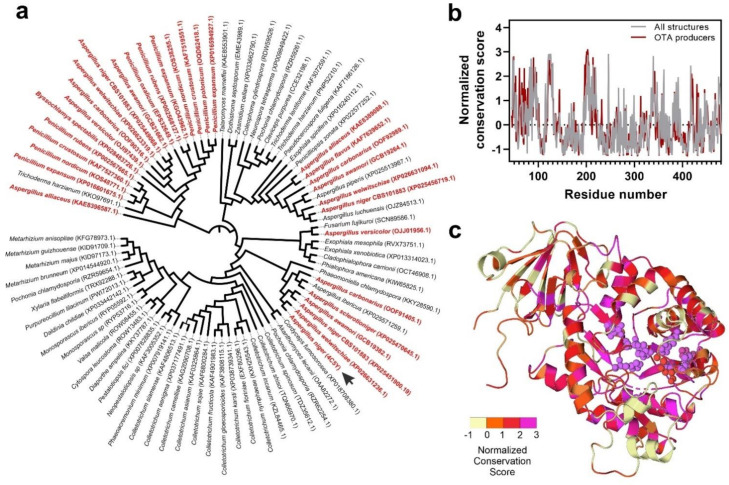
Figure 4.
Structure comparison of the selected set of fungal ochratoxinase-like atomic models. (a) Unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed by the iTOL software [43] and based on the structural superposition of all the atomic models using the Caretta algorithm [42]. The enzyme models are identified by the source microorganism and the ID code from the Uniprot database. Names in red color are enzymes belonging to already characterized ochratoxin producers, whereas the remaining sequences were extracted from proteomes of other fungal strains. The position of A. niger ochratoxin is labeled with an arrow. (b) Normalized conservation score of the whole family of selected proteins calculated by the ConSurf 2016 server [44] using the previous structural superposition and plotted over the sequence of A. niger ochratoxinase. The ConSurf conservation score calculated for the ochratoxinase-like enzymes extracted from ochratoxin-producing fungal proteomes (red line) is compared with the same score calculated for all the cohort of proteins (grey line). (c) Spatial representation of the normalized conservation scores of the ochratoxinase-like enzymes from ochratoxin-producing fungi over the atomic model of A. niger ochratoxinase (PDB code: 4C5Y). The residues involved in the catalytic activity of the protein are highlighted and represented by atomic spheres.