Abstract
Assessment of absolute myocardial hydroxydimethylene diphosphonate–technetium-99m uptake using standardized uptake value with a single-photon emission computed tomography–computed tomography cadmium zinc telluride camera (Discovery NM/CT 670CZT, GE Healthcare, Chicago, Illinois) in a patient with cardiac transthyretin-related amyloidosis treated with tafamidis showed a decrease in hydroxydimethylene diphosphonate cardiac uptake. This imaging technique should be helpful in monitoring therapy and evaluating prognosis. (Level of Difficulty: Intermediate.)
Key Words: chronic heart failure, hybrid imaging, treatment
Abbreviations and Acronyms: ATTR, transthyretin-related [amyloidosis]; HMDP-99mTc, hydroxydimethylene diphosphonate–technetium-99m; IVS, interventricular septum; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NT-ProBNP, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide; NYHA, New York Heart Association; SPECT, single-photon emission computed tomography; SUV, standardized uptake value; SUVmax, maximum standardized uptake value
Graphical abstract

A 90-year-old man with a diagnosis of transthyretin-related (ATTR) cardiac amyloidosis was treated with tafamidis for 6 months and had his first follow-up with bone scintigraphy quantification using standardized uptake value (SUV).
Tafamidis is the first treatment to improve symptoms and survival in patients with ATTR amyloidosis and heart failure (1). Cardiac uptake of hydroxydimethylene diphosphonate–technetium-99m (HMDP-99mTc) is widely used to diagnose cardiac ATTR amyloidosis (2). Visual assessment of cardiac uptake (Perugini grading) on planar imaging is applied in clinical practice, and this new tool should be helpful to manage this first effective drug.
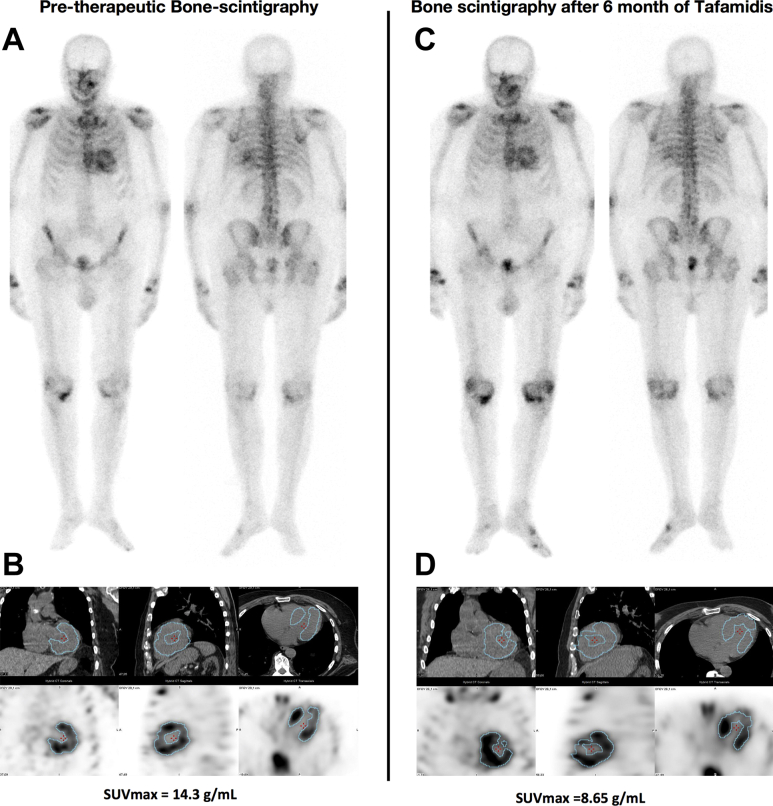
The pre-therapeutic examination revealed New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II heart failure, with peripheral edema, left ventricular hypertrophy with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF], 55%; interventricular septal [IVS], 18 mm; N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide [NT-proBNP], 3,500 ng/l), and significant HMDP-99mTc cardiac uptake noted on bone scintigraphy (Perugini grade 2) (Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
Pre-Therapeutic Bone Scintigraphy
(A) High hydroxydimethylene diphosphonate–technetium-99m visual cardiac uptake (Perugini grade 2) supporting the diagnosis of cardiac transthyretin-related amyloidosis. (B) Absolute quantification (maximum standardized uptake value [SUVmax]) measured in the myocardial volume of interest was 14.3 g/ml, using a single-photon emission computed tomography–computed tomography cadmium zinc telluride camera (Discovery NM 670CZT, GE Healthcare, Chicago, Illinois). (C and D) After 6 months of tafamidis, (D) quantitative measurement of hydroxydimethylene diphosphonate–technetium-99m in cardiac volume of interest showed a decrease of uptake (SUVmax, 8.6 g/ml), whereas (C) visual assessment was unchanged.
Examination at 6 months after treatment showed moderate improvement (New York Heart Association functional class II; IVS, 14; LVEF, 51%; NT-proBNP, 2,265 ng/l). Bone scintigraphy findings were similar (Perugini grade 2) (Figure 1C).
Absolute quantification of HMDP-99mTc cardiac uptake by means of maximum (SUVmax) was performed with a whole-body single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (qMetrix, Charlotte, North Carolina)–computed tomography (CT) cadmium zinc telluride camera (Discovery NM/CT 670CZT, GE Healthcare, Chicago, Illinois) in both examinations (Figures 1B and 1D).
Quantitative measurement of HMDP-99mTc uptake showed a decrease in SUVmax (8.6 g/ml vs, 14.3 g/ml) after 6 months of tafamidis, whereas qualitative assessment (Perugini grading) was unchanged.
Quantitative SPECT seems to be a promising tool for the assessment of therapeutic response and for managing treatment of cardiac ATTR amyloidosis.
Author Disclosures
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Footnotes
The authors attest they are in compliance with human studies committees and animal welfare regulations of the authors’ institutions and Food and Drug Administration guidelines, including patient consent where appropriate. For more information, visit the Author Center.
References
- 1.Maurer M.S., Schwartz J.H., Gundapaneni B., Elliott P.M., Merlini G., Waddington-Cruz M. Tafamidis treatment for patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1007–1016. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1805689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gillmore J.D., Maurer M.S., Falk R.H. Nonbiopsy diagnosis of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis. Circulation. 2016;133:2404–2412. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]