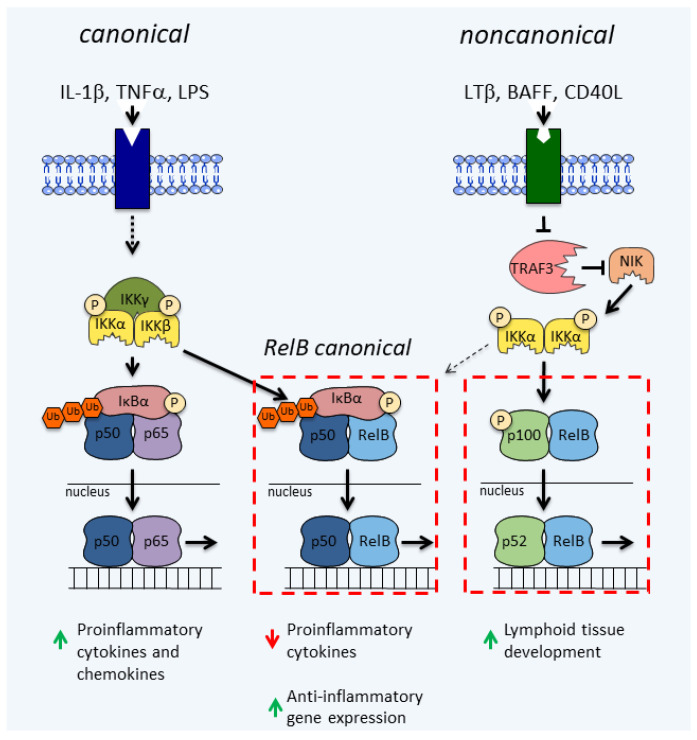
Figure 1.
Activation of RelB by the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathways. The canonical NF-κB pathway is activated by interleukin 1β (IL-1 β), tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), and liposaccharide (LPS). The noncanonical NF-κB pathway is activated by lymphotoxin β (LTβ), B cell activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF), and CD40 ligand (CD40L). The canonical activation of RelB/p50 occurs in cells expressing high levels of RelB (basally or after induction). IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; IKK, IκB kinase; NIK, NF-κB-inducing kinase; P, phosphate; and TRAF3, TNF receptor-associated factor 3.