Abstract
Purpose
To measure the diagnostic accuracy and inter-observer agreement with the use of COVID-19 Reporting and Data System (CO-RADS) for detection of COVID-19 on CT chest imaging.
Methods
This retrospective study included 164 consecutive patients with clinical suspicion of COVID-19 in whom a CT chest examination was performed at a single institution between April 2020 and July 2020. Of them, 101 patients was RT-PCR positive for COVID-19. Six readers with varying radiological experience (two each of chest radiologists, general radiologists, and radiologists in training) independently assigned a CO-RADS assessment category for each CT chest study. The Fleiss’ K was used to quantify inter-observer agreement. The inter-observer agreement was also assessed based on the duration of onset of symptoms to CT scan. ROC curve analysis was used to determine the diagnostic accuracy of CO-RADS. The area under curve was calculated to determine the reader accuracy for detection of COVID-19 lung involvement with RT-PCR as reference standards. The data sets were plotted in ROC space, and Youden’s J statistic was calculated to determine the threshold cut-off CO-RADS category for COVID-19 positivity.
Results
There was overall moderate inter-observer agreement between all readers (Fleiss’ K 0.54 [95% CI 0.54, 0.54]), with substantial agreement among chest radiologists (Fleiss’ K 0.68 [95% CI 0.67, 0.68]), general radiologists (Fleiss’ K 0.61 [95% CI 0.61, 0.61]), and moderate agreement among radiologists-in-training (Fleiss’ K 0.56 [95% CI 0.56, 0.56]). There was overall moderate inter-observer agreement in early disease (stages 1 and 2), with cumulative Fleiss’ K 0.45 [95% CI 0.45, 0.45]). The overall AUC for CO-RADS lexicon scheme to accurately diagnose COVID-19 yielded 0.92 (95% CI 0.91, 0.94) with strong concordance within and between groups, of chests radiologists with AUC of 0.91 (95% CI 0.88, 0.94), general radiologists with AUC 0.96 (95% CI 0.94, 0.98), and radiologists in training with AUC of 0.90 (95% CI 0.87, 0.94). For detecting COVID-19, ROC curve analysis yielded CO-RADS > 3 as the cut-off threshold with sensitivity 90% (95% CI 0.88, 0.93), and specificity of 87% (95% CI 0.83, 0.91).
Conclusion
Readers across different levels of experience could accurately identify COVID-19 positive patients using the CO-RADS lexicon with moderate inter-observer agreement and high diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, CO-RADS
Key points
CO-RADS lexicon scheme has a high diagnostic accuracy to detect lung involvement in COVID-19 with RT-PCR as reference standard (AUC 0.92 [95% CI 0.91, 0.94]).
CO-RADS lexicon demonstrated moderate inter-observer agreement among readers with different levels of expertise (Fleiss’ K 0.54 [95% CI 0.54, 0.54]).
The threshold of CO-RADS category > 3 had a sensitivity and specificity of 90% [95% CI 0.88, 0.93], and 87% [95% CI 0.83, 0.91], respectively.
Introduction
Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is straining the health systems around the globe. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is regarded as the standard reference in diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. There are times when the turnaround time for RT-PCR test result reaching up to 72 h or multiple RT-PCR test being needed for confirming the presence of disease when there is a high clinical index of suspicion [1].
The practice pattern and ordering imaging for the diagnosis and workup of COVID-19 vary universally. The utility of CT chest in the diagnosis and follow up of COVID-19 is controversial [2]. Many radiological societies have advised not to use CT chest for disease screening, especially in asymptomatic patients, as the CT scan has low specificity in differentiating other non-COVID-19 lung infections that could have similar CT chest findings [3, 4]. However, recent Cochrane systematic review reported a sensitivity of 87.9% and a higher specificity of 80% in diagnosis of COVID-19 indicating that accuracy may be sufficient for there to be a role for CT in the diagnostic pathway for COVID-19 patients [5].
Imaging has an important role in solving clinical dilemma, and to ascertain disease-related complications. With the intention of providing a clear communication without ambiguity to facilitate appropriate patient care, multiple reporting lexicon has been suggested by different societies including CO-RADS [6], RSNA consensus guidelines for CT chest reporting in COVID-19 [7], and BSTI COVID-19 reporting template. The authors have recommended an extensive validation of their proposals, especially with radiologists of different levels of experience. Thus, the purpose of this study is to assess the inter-rater reproducibility of using CO-RADS across radiologists of different level of experience and specialization and to assess its diagnostic accuracy.
Materials and methods
This retrospective study performed in a single centre was approved by institution review board (study protocol MRC-01-20-1142), with waiver of informed consent. The study was compliant with Standards for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy (STARD) initiative recommendations [8]
Study design and study population
We performed an imaging database search for ‘CT Chest’ examinations during the period April 1 2020, to July 30, 2020, using picture archiving and communication system (PACS) keyword search. In keeping with international guidelines, CT chest was not performed as a first-line diagnostic modality in our institution, but as a problem-solving tool at times of clinical ambiguity while suspecting COVID-19, but also other disease that may have similar clinical presentations such as bacterial pneumonia, malignancies, or to rule out COVID-19 complications such as pulmonary embolism. We included consecutive patients who underwent CT chest during the study period with clinical suspicion for COVID-19. We excluded patients in whom there is (a) technically insufficient CT scan due to motion artefact, (b) those without a RT-PCR result, and (c) CT chest done primarily for the work up of diseases other than suspected COVID-19. All COVID-19 positive patients in our study sample had both clinical diagnosis and at least one RT-PCR positive result for COVID-19. Patients with initial RT-PCR negative result but CT chest shows features suspicious for COVID-19 underwent at least two RT-PCR testing within the next 7 days following the CT scan.
Furthermore, depending on the onset of symptoms to CT scan [9], COVID-19 positive patients were classified into stage 1 (0 to 4 days), stage 2 ( 5 to 9 days), stage 3 (10 to 14 days), stage 4 (15 to 21 days), stage 5 (22 to 28 days), and stage 6 (more than 28 days). The inter-observer agreement was compared based on the stage of the disease.
CT chest Image acquisition parameters
All CT chest scans were performed using a 640-detector CT scanner (Canon Acquilion one). All patients were scanned supine, during single end deep inspiration breath hold. The scanning range was from the apex of the lung to bilateral adrenals. CT scan parameters are as follows: X-ray tube parameter with automatic tube current modulation with kVp range 100–120, with automatic tube current modulation, rotation time 0.5s, a pitch of 1.388, 0.5 and 3 mm section thickness, collimation 0.5×80, and intersection space 0.8 for the volume scan.
Radiology readers and lexicon implementation
The CT Chest studies were independently assessed by 6 readers, divided into 3 groups based on their radiological expertise. Fellowship trained chest radiologists R1 and R2 (AN, DK) with experience of reporting more than 200 COVID-19 CT chests; general radiologists without any sub-speciality fellowships R3 and R4 (PG, HS) with reporting experience of 100 to 150 COVID-19 CT chest cases; and radiologist in training R5 and R6 (SB, HZ) in PGY-5 with reporting experience of less than 100 COVID-19 CT chests. A training set comprising 50 COVID-19 positive CT chest with CO-RADS scoring independent of the study cohort was provided to each reader after two online training sessions of 1 h each done 2 weeks prior to the start of the study.
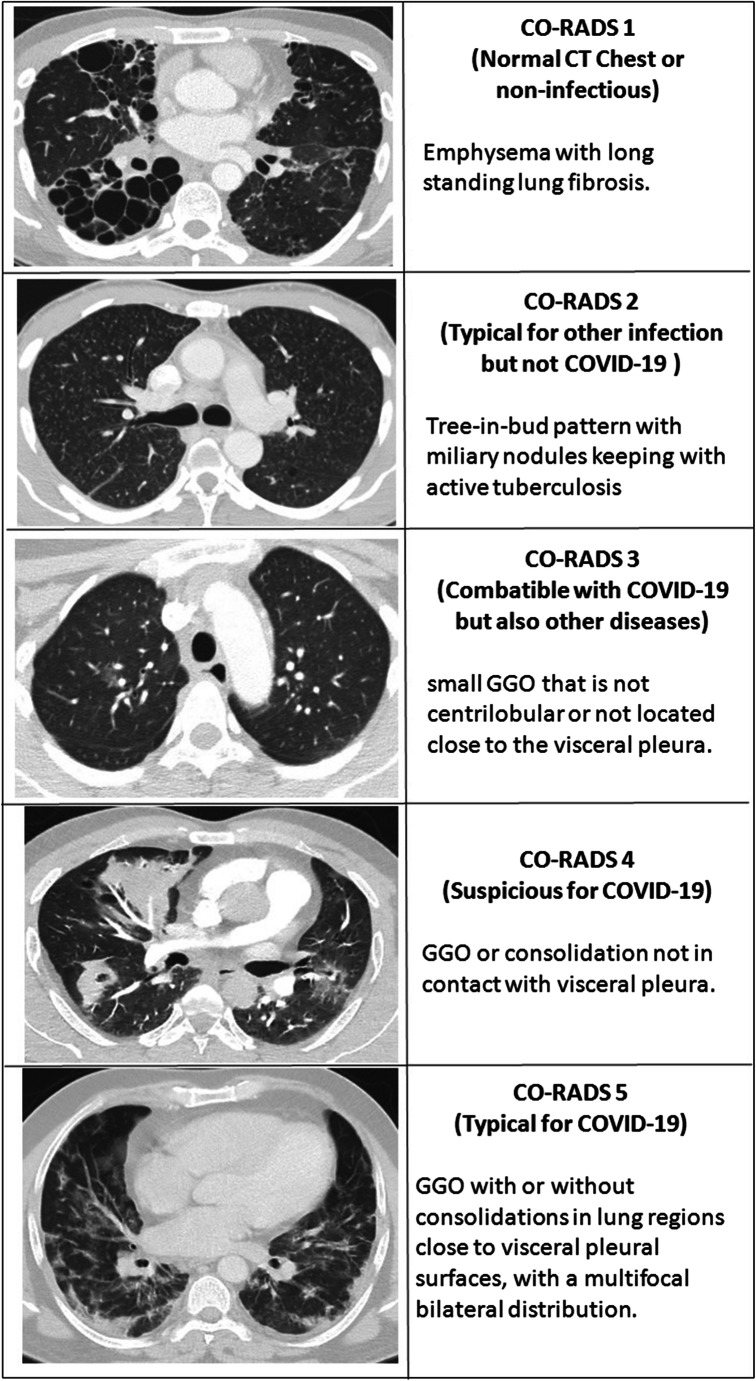
Six readers independently reviewed all CT scans using PACS stations with standard settings for CT chest reading. All readers were blinded to the clinical diagnosis, CT reports including the RT-PCR results. The readers assigned one category from 0 to 5, using the CO-RADS lexicon depending on their overall suspicion of lung involvement in COVID-19. The CO-RADS category 0 (un-interpretable scans) was removed at the start of the study with the application of exclusion criteria. Since the six reading radiologists were blinded to CT reports including the RT-PCR test outcome, there was no provision to assign CO-RADS 6 category (RT-PCR confirmed positive). The CO-RADS lexicon is summarized in Fig. 1. For detailed insights into CO-RADS, refer to the original work from Prokop et al. [6].
Fig. 1.
Pictorial representation of CT chest studies illustrating typical characteristics of different CO-RADS categories from our study sample. COVID-19, Corona Virus disease 2019; GGO, ground glass opacities
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are expressed as mean, median, standard deviation (SD), or interquartile range and categorical variables as frequencies or percentage. Fleiss’ K statistic were used for analysis of inter-observer agreement [10] (<0 indicates poor agreement, 0.01 to 0.20 indicates slight agreement, 0.21 to 0.40 as fair agreement, 0.41 to 0.60 as moderate agreement, 0.61 to 0.80 as substantial agreement, and 0.81–1.00 as almost perfect agreement). Median Fleiss’ K with 95% confidence interval from three reader groups was assessed with pair wise comparison to determine the statistical significance of inter-observer agreement between the groups. The receiver operating characteristics curve (ROC) and AUC were assessed for each reader by using DeLong et al. method [11] for assessing the diagnostic performance of CO-RADS lexicon. Accuracy of the CO-RADS lexicon was compared with RT-PCR as standard of reference. The datasets were plotted in ROC space and Youden’s J statistic was used to estimate the diagnostic accuracy for CO-RADS > 3 and CO-RADS > 4 being taken as a threshold reference for discriminating COVID-19 positive cases. P value <0.05 was considered for statistical significance. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS V 26.0 software (IBM SPSS, USA).
Results
Patient selection
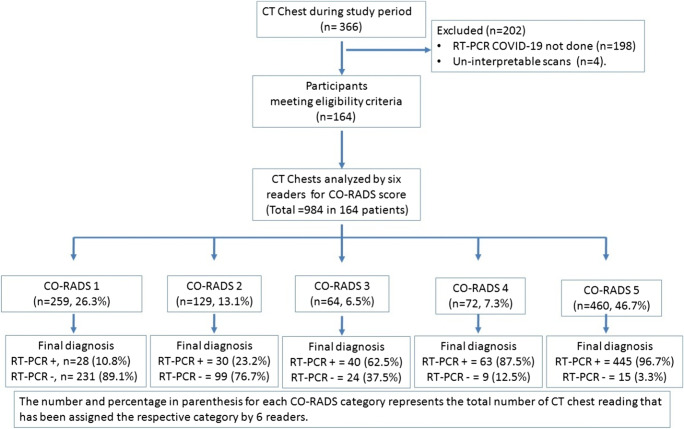
A total of 164 patients meeting the inclusion criteria were included in the study (Fig. 2). The mean age of study sample was 49 +15 (standard deviation), and 139 (84 %) were males. Of the patients included, 101 patients (61.5 %) were RT-PCR confirmed COVID-19 positive and 63 patients (38.4 %) were RT-PCR negative. The median time interval for performing a CT chest from the symptom onset was 11 days (IQR 7–17) and the median time interval between CT chest and RT-PCR was 6 days (IQR 4 to 10). Of the 101 positive, 6 patients (5.9%) underwent more than one RT-PCR tests to confirm the positivity. The final diagnosis to those patients who tested negative, when available, were viral or bacterial pneumonia, lung metastasis, primary lung carcinoma, tuberculosis, right or left heart failure, bronchial asthma exacerbation, or acute pulmonary embolism. Table 1 depicts the baseline characteristics of the included 164 study subjects and Table 2 depicts the CT chest findings of 101 patients with RT-PCR positive COVID-19.
Fig. 2.
Flow diagram of patient inclusion and exclusion in the present study. COVID-19, Corona Virus disease 2019; RT-PCR +, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction positive; RT-PCR−, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction negative
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patient study group
| Parameter | Value (n=164) |
|---|---|
| Age (years)* | 49±15 |
| Male sex | 139 (84) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Diabetes | 43 (26) |
| Lung disease | 6 (4) |
| Cancer | 4 (2) |
| Cardiovascular | 39 (24) |
| Duration of symptoms (days)† | 11 (7–17) |
| Positive PT-PCR | 101 (61) |
| Number of PT-PCR assays | |
| 1 | 48 (29) |
| 2 | 45 (27) |
| 3 | 31 (19) |
| 4 | 29 (18) |
| 5 | 11 (7) |
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, data are number of patients and data in parenthesis are percentages
*Data are mean ± standard deviation
†Data are median with interquartile range (in parenthesis)
Table 2.
CT chest findings of COVID-19 positive patients
| CT findings | Number of patients with COVID-19 (n=101) |
|---|---|
| GGO and consolidation | |
| Absence of both GGO and consolidation | 4 (4) |
| Presence of GGO with consolidation | 63 (62.3) |
| Presence of GGO without consolidation | 21 (20.8) |
| Presence of consolidation without GGO | 13 (12.9) |
| Bronchiectasis | 4 (4) |
| Vascular enlargement of the involved area | 50 (49.5) |
| Crazy paving with interlobar septal thickening | 11 (10.9) |
| Air bronchogram sign | 65 (64.4) |
| Air trapping | 5 (5) |
| Reverse halo sign | 1 (1) |
| Discrete pulmonary nodules | |
| With halo | 4 (4) |
| Without halo | 7 (6.9) |
| Pleural effusion | 16 (15.8) |
| Pneumomediastinum | 11 (10.9) |
| Pneumothorax | 4 (4) |
| Mediastinal lymphadenophaty | 27 (26.7) |
| Disease geography | |
| Central or perihilar | 3 (3) |
| Peripheral predominance | 94 (93.1) |
| Dorsal predominance | 92 (91.1) |
| Ventral predominance | 5 (5) |
Data are numbers (percentage %)
CT, computed tomography; COVID-19, corona virus disease 2019; GGO, ground glass opacities
Inter-observer agreement
Overall, there was moderate agreement among all observers (Fleiss’ K= 0.548 [95% CI 0.547, 0.549]). For various CO-RADS categories, the agreement was substantial in CO-RADS category 1 (Fleiss’ K= 0.718 [95% CI 0.717, 0.719]), substantial agreement in CO-RADS category 5 (Fleiss’ K= 0.675 [95% CI 0.674, 0.676]), and moderate agreement in CO-RADS 2 (Fleiss’ K= 0.463 [95% CI 0.462, 0.464]). There was slight agreement in CO-RADS 3 (Fleiss’ K= 0.171 [95% CI 0.170, 0.172]), and slight agreement in CO-RADS 4 (Fleiss’ K= 0.077 [95% CI 0.076, 0.078]). Regarding inter-observer agreement among radiologists groups with different expertise, the chest radiologists group had substantial agreement (Fleiss’ K= 0.682 [95% CI 0.679, 0.685]), general radiologist group had substantial agreement (Fleiss’ K= 0.614 [95% CI 0.611, 0.617]), and radiologists in training group had moderate agreement (Fleiss’ K= 0.563 [95% CI 0.561, 0.566]). When Fleiss’ K was compared between the groups, there was no statistical significance (p 0.80). Table 3 summarizes inter-observer agreement and performance among different readers relative to different CO-RADS categories.
Table 3.
CO-RADS inter-observer agreement and performance
| CO-RADS assessment score | Fleiss’ K overall for all readers | Fleiss’ K for chest radiologists (R1 and R2) | Fleiss’ K for general radiologist (R3 and R4) | Fleiss’ K for radiologists in training (R5 and R6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO-RADS 1 | 0.71 (0.71, 0.72) | 0.81 (0.80, 0.81) | 0.80 (0.80, 0.81) | 0.76 (0.76, 0.77) |
| CO-RADS 2 | 0.46 (0.46, 0.46) | 0.70 (0.70, 0.71) | 0.26 (0.25, 0.26) | 0.54 (0.54, 0.55) |
| CO-RADS 3 | 0.17 (0.17, 0.17) | 0.31 (0.31, 0.32) | 0.10 (0.10, 0.11) | 0.37 (0.37, 0.38) |
| CO-RADS 4 | 0.07 (0.07, 0.07) | 0.14 (0.14, 0.15) | 0.33 (0.33, 0.34) | 0.18 (0.17, 0.18) |
| CO-RADS 5 | 0.67 (0.67, 0.67) | 0.79 (0.78, 0.79) | 0.73 (0.72, 0.73) | 0. 61 (0.61, 0.62) |
| Overall | 0.54 (0.54, 0.54) | 0.68 (0.67, 0.68) | 0.61 (0.61, 0.61) | 0.56 (0.56, 0.56) |
The inter-observer agreement for various CO-RADS category, overall among all readers and within the groups. Data in parenthesis are 95% confidence interval
When CO-RADS assessment category > 3 was considered positive, there was overall almost perfect agreement among the six readers (Fleiss’ K= 0.86 [95% CI 0.81, 0.92]), and almost perfect agreement in all the three groups, among the chest radiologists group (Fleiss’ K= 0.88 [95% CI 0.80, 0.95]), general radiologists (Fleiss’ K= 0.83 [95% CI 0.75, 0.92]), and radiologists-in-training (Fleiss’ K= 0.84 [95% CI 0.76, 0.92]). When CO-RADS assessment category > 4 was considered positive, there was overall almost perfect agreement among the six readers (Fleiss’ K= 0.85 [95% CI 0.73, 0.98]), and almost perfect agreement among the chest radiologists group (Fleiss’ K= 0.83 [95% CI 0.75, 0.92]), and general radiologists (Fleiss’ K= 0.86 [95% CI 0.78, 0.94]). While there was substantial agreement among the radiologists-in-training group (Fleiss’ K= 0.78 [95% CI 0.68, 0.87]). The overall inter-observer agreement was marginally better when CO-RADS category > 3 was considered positive than CO-RADS category > 4. When Fleiss’ K was compared between the groups, above these threshold cut-off categories, there was no statistical significance (p 0.2).
Diagnostic performance of CO-RADS
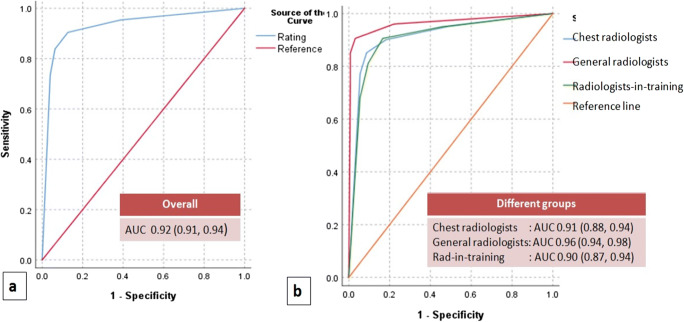
When all datasets from six readers were plotted in ROC space, ROC curve analysis yielded an overall area under curve of 0.929 (95%CI 0.911, 0.947) (Fig. 3). CO-RADS category > 3 score as threshold yielded a sensitivity of 90% (95% CI 0.88, 0.93), specificity of 87% (95% CI 0.83, 0.91), and Youden’s J statistic of 0.777. The threshold of 3 or more had a higher Youden’s J statistic than while using a threshold cut-off CO-RADS category of >4 with sensitivity of 83% (95% CI 0.81, 0.87), specificity of 93% (95% CI 0.91, 0.96), and Youden’s J statistic of 0.775.
Fig. 3.
Receiver operating characteristic curve a AUC for all readers obtained by plotting of all datasets in ROC space; b AUC comparison for different experience groups. AUC-Area under curve
Considering the optimal cut-off to differentiate COVID-19 positive from negative as CO-RADS >3, the blended AUC for chest radiologists yielded AUC of 0.91 (95%CI 0.88, 0.94) with a sensitivity of 90% (95% CI 0.85, 0.94) and specificity of 82% (95% CI 0.75, 0.88); in general radiologists group, AUC yielded 0.96 (95%CI 0.94, 0.98) with a sensitivity of 91% (95% CI 0.87, 0.95) and specificity of 97% (95% CI 0.93, 0.99); and radiologists in training group yielded AUC of 0.90 (95%CI 0.87, 0.94) with a sensitivity of 91% (95% CI 0.86, 0.95) and specificity of 83% (95% CI 0.76, 0.89) (Fig. 3). Table 4 summarizes the diagnostic performance of all readers by using CO-RADS category of 3 or more and CO-RADS category of 4 or more as cut-off. Table 5 summarizes the reader’s diagnostic performance by using CO-RADS to detect COVID-19 in CT chest when CO-RADS category of 3 or more is considered threshold positive. Table 6 summarizes the diagnostic performance of readers relative to each CO-RADS category.
Table 4.
Readers diagnostic performance by using CO-RADS to detect COVID-19 in CT chest when CO-RADS category of 3 or more and 4 or more is considered as threshold positive
| Readers | CO-RADS cut off ≥ 3 | CO-RADS cut off ≥ 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
| R1 | 88 (0.82, 0.94) | 83 (0.73, 0.92) | 83 (0.76, 0.90) | 90 (0.83, 0.98) |
| R2 | 92 (0.87, 0.97) | 81 (0.71, 0.90) | 87 (0.81, 0.94) | 92 (0.85, 0.94) |
| R3 | 88 (0.82, 0.94) | 100 (1, 1) | 85 (0.78, 0.92) | 100 (1, 1) |
| R4 | 93 (0.92, 0.99) | 94 (0.87, 0.99) | 85 (0.78, 0.92) | 98 (0.95, 1.0) |
| R5 | 90 (0.84, 0.96) | 79 (0.69, 0.89) | 82 (0.75, 0.90) | 86 (0.77, 0.94) |
| R6 | 91 (0.85, 0.96) | 89 (0.79, 0.95) | 80 (0.72, 0.88) | 94 (0.89, 1.0) |
The diagnostic performance among various readers for diagnosing COVID-19 positivity when using CO-RADS 3 and 4 as cut-off. Data in parenthesis are 95% confidence intervals
Table 5.
Readers diagnostic performance by using CO-RADS to detect COVID-19 in CT chest when CO-RADS category of 3 or more is considered as threshold positive
| Groups | Reader No. | AUC vs RT-PCR | Fleiss’ K within groups for CO-RADS ≥ 3 | AUC within groups for CO-RADS ≥ 3 | Sensitivity within groups for CO-RADS ≥ 3 | Specificity within groups for CO-RADS ≥ 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest radiologists | R1 | 0.90 (0.85, 0.95) | 0.88 (0.80, 0.95) | 0.91 (0.88, 0.94) | 0.90 (0.85, 0.94) | 0.82 (0.75, 0.88) |
| R2 | 0.92 (0.87, 0.96) | |||||
| General radiologists | R3 | 0.97 (0.95, 0.99) | 0.83 (0.75, 0.92) | 0.96 (0.94, 0.98) | 0.91 (0.87, 0.95) | 0.97 (0.93, 0.99) |
| R4 | 0.95 (0.92, 0.98) | |||||
| Radiologists in training | R5 | 0.89 (0.83, 0.94) | 0.84 (0.76, 0.92) | 0.90 (0.87, 0.90) | 0.91 (0.86, 0.95) | 0.83 (0.76, 0.89) |
| R6 | 0.93 (0.89, 0.97) | |||||
| Overall | 0.92 (0.91, 0.94) | 0.84 (0.76, 0.92) | 0.92 (0.91, 0.94) | 0.90 (0.88, 0.93) | 0.87 (0.83, 0.91) |
Note: The area under the curve for each observer is compared to reference standard defined by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) positivity. The inter-observer agreement, area under the curve, sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy within the various groups when threshold for COVID-19 positivity is defined by CO-RADS ≥ 3. Data in parenthesis are 95% confidence intervals
Table 6.
Readers diagnostic performance for each CO-RADS category to detect COVID-19 in CT Chest
| Reader | CO-RADS 1 | CO-RADS 2 | CO-RADS 3 | CO-RADS 4 | CO-RADS 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Sensitivity | Specificity | Sensitivity | Specificity | Sensitivity | Specificity | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
| R1 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.95 | 0.52 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.90 | 0.78 | 0.93 |
| R2 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.95 | 0.50 | 0.92 | 1.81 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.95 |
| R3 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.97 | 0.77 | 0.88 | 0.1 | 0.85 | 1.0 | 0.78 | 1.0 |
| R4 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.95 | 0.77 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 0.98 |
| R5 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.95 | 0.52 | 090 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.90 |
| R6 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 0.57 | 0.98 |
Influence of stage of disease on inter-observer agreement
Overall, there was moderate agreement among all readers in stage 1 (0 to 4 days), Fleiss’ K= 0.46 [95% CI 0.45, 0.46], and stage-2, (5 to 9 days), Fleiss’ K= 0.41 [95% CI 0.40, 0.41], with a cumulative Fleiss’ K of 0.45 [95% CI 0.45, 0.45]) in stages 1 and 2. The overall agreement was fair in stage 4 (15 to 21 days), Fleiss’ K= 0.36 [95%CI 0.36, 0.36], and slight agreement in stage 3 (10 to 14 days), stage 5 (21 to 28 days), and stage 6 (more than 28 days). The overall agreement among the readers for different stages was statistically significant in stages 1, 2, and 4 (p 0.000), stage 3 (0.026), and stage 6 (p 0.001) and insignificant in stage 5 (p 0.815). The inter-observer agreement depending on the stage of disease is summarized in Table 7.
Table 7.
CO-RADS inter-observer agreement depending on the stage of COVID-19 lung involvement
| Stage of diseases | Number of study subjects (n=101) | Overall Fleiss’ K | Fleiss’ K for chest radiologists | Fleiss’ K for general radiologists | Fleiss’ K for radiologists in training |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 (0–4 days) | 7 | 0.46 (0.45, 0.46) | 0.79 (0.78, 0.81) | 0.20 (0.18, 0.21) | 0.41 (0.40, 0.42) |
| Stage 2 (5–9 days) | 35 | 0.41 (0.40, 0.41) | 0.67 (0.66, 0.68) | 0.29 (0.28, 0.30) | 0.55 (0.55, 0.56) |
| Stage 3 (10–14 days) | 26 | 0.08 (0.08, 0.09) | 0.17 (0.16, 0.18) | 0.26 (0.24, 0.27) | −0.13 (−0.14, −0.12) |
| Stage 4 (14–21 days) | 14 | 0.36 (0.36, 0.36) | 0.54 (0.53, 0.55) | 0.30 (0.29, 0.32) | 0.63 (0.62, 0.64) |
| Stage 5 (22–28 days) | 8 | 0.01 (0.01, 0.01) | −0.06 (−0.08, −0.04) | 0.23 (0.22, 0.25) | 0.07 (0.06, 0.09) |
| Stage 6 (> 28 days) | 11 | 0.17 (0.17, 0.17) | 0.52 (0.51, 0.51) | 0.24 (0.22, 0.25) | 0.17 (0.15, 0.18) |
The inter-observer agreement for COVID-19 positive patients depending on stage of disease overall among all readers and within the group. Data in parenthesis are 95% confidence intervals
Post lexicon re-analysis
A post lexicon re-analysis was performed to identify the false positive and false negative cases reported with CO-RADS in a total 984 readings among the six readers. In the RT-PCR COVID-19 negative group with a total of 378 reading, there were 24 false positive readings (6.3%, in 13 patients) that were erroneously assigned CO-RADS 4 and 5 and identified as a CO-RADS 1 and 2 on post-lexicon re-analysis. Among the RT-PCR COVID-19 positive group with 606 readings, there were 34 false negative readings (5.6%, in 16 patients) that were erroneously assigned CO-RADS 1 and 2 and correctly identified as a CO-RADS 4 and 5 on post-lexicon re-analysis. Twenty-four readings (3.9%, in 4 patients) had a normal CT chest despite clinical and RT-PCR positive diagnosis for COVID-19.
Discussion
This study evaluated the inter-observer agreement between the readers of varying experiences, and the diagnostic performance of CO-RADS lexicon scheme in accurately identifying COVID-19 lung involvement on CT chest. Overall, there was moderate inter-observer agreement between radiologists of different levels of experience. We observed that a threshold category of CO-RADS 3 and above can reliably differentiate COVID-19 infection from other non-COVID lung diseases. Our results indicate that a standardized reporting lexicon for lung involvement for COVID-19 can be reliably used in clinical practice to enhance communication with the attending physician.
Since the introduction of CO-RADS [6], only a relatively small number of studies have evaluated the reproducibility and performance of the CO-RADS scoring system [12][13]. Overall, these studies have shown that CO-RADS is a reliable method for identifying COVID-19 lung disease, across the radiologists of different levels of experience, but with varying inter-observer agreement. In our study, the overall inter-observer agreement for CO-RADS categories among the six readers was moderate (Fleiss’ K = 0.548 [95% CI 0.547, 0.549]). Similar observations were noted in prior studies by Bellini et al. [13] among 12 readers with an overall moderate inter-observer agreement (Fleiss’ K = 0.43 [95% CI 0.42, 0.44]), and Prokop et al. [6] reported an overall moderate inter-observer agreement among their 8 readers (Fleiss’ K = 0.47 [95% CI 0.45, 0.49]). However, a recent study by Atta et al. reported an overall substantial agreement among 3 readers (Fleiss’ K = 0.78 [95% CI 0.59, 0.91]) [12]. The higher agreement observed in this study could be due to small number of readers and more experienced readers contributing to a higher inter-observer agreement. Furthermore, in our study, there was no significant difference in inter-observer agreement between the chest radiologists, general radiologists, or radiologist in training, and our findings support the applicability of using CO-RADS lexicon within a structured radiology report.
The CO-RADS assessment category that is considered positive for COVID-19 may also affect the reader accuracy. The CO-RADS 1 and 2 are assigned when there is no radiological suspicion for COVID-19, and CO-RADS 4 and 5 are assigned when there is a high radiological suspicion for COVID-19. Prokop et al. noted that CO-RADS 3 is an indeterminate suspicion category, that has overlapping features of COVID-19 lung disease with other viral pneumonia or non-infectious causes [6]. In our study, we estimated that a threshold of CO-RADS 3 or more had a marginally higher diagnostic accuracy and higher inter-observer agreement compared to CO-RADS 4 or more being used to determine COVID-19 lung involvement. Our findings are in contrast to the observations by Bellini et al. [13], in the study they estimated that a CO-RADS category of 4 or more as a reliable cut-off to discriminate RT-PCR positive from negative, with a high accuracy and moderate inter-rater agreement. However, in routine clinical practice, the knowledge of disease prevalence, availability of past medical records, clinical history, and higher experience in dealing with COVID-19 chest CTs may decrease the number of cases assigned with CO-RADS category 3, either by upgrading the level of suspicion to 4 or 5 or downgrading the level of suspicion to CO-RADS categories 1 and 2. Using a threshold of CO-RADS 3, although the general radiologists group had a higher AUC, specificity and sensitivity to detect COVID-19, the inter-observer agreement was higher within chest radiologists group, likely influenced by diverse practice pattern, varied CT chest findings related to COVID-19, or ambiguity in differentiating COVID-19 from other infections or diseases.
The lung involvement with COVID-19 evolves rapidly at early stages of disease and the CT chest findings vary depending on the time of onset of symptoms [14]. Ding et al. [9] noted that the lung changes evolve rapidly in early stage of disease (stages 1 and 2), and stabilizes in the later stages to remain for a longer period. Despite these, Atta et al. [12] observed no significant impact on the time of onset of symptoms, while assessing the lungs for scoring with CO-RADS. In the current study, we observed that the overall inter-observer agreement was moderate for early stage of disease in stage 1 and stage 2, while in later stages of disease process when the disease process stabilizes within the lungs, there was a slight or fair inter-observer agreement. This could be attributable to the rapid changes of disease process happening within the lungs, with interstitial and alveolar oedema setting in with stage 3 and above thereby creating ambiguity in differentiating COVID-19 from other lung infections. However, there was no statistical significance in the inter-observer agreement between the radiologists groups of different levels of experience to suggest if this would influence the lexicon categorization based on the stage of disease.
The study has few limitations. First, this study is from a single centre and is retrospective in nature; further prospective studies with sequential inclusion of CT chests are still needed to validate the observations. Second, there could have been a selection bias in our institutional use of CT scan as a problem solving tool rather than a method of primary diagnosis of COVID-19. Thus, the study sample included only symptomatic patients, and there could have been a bias towards severe disease spectrum, thereby affecting the diagnostic accuracy estimate of CO-RADS. Moreover, CO-RADS lexicon has been recommended for use specifically in suspected COVID-19 patients with moderate to severe symptoms. Third, RT-PCR is reported to have considerable false negative rates [15–17] and the limitations on the use of RT-PCR as a reference standard needs to be recognized. However, in our study, 116 study samples (70.7%) had more than one RT-PCR results which would reduce the probability of false negative cases for the reference standard.
In conclusion, the CO-RADS lexicon scheme serves to identify features typical for COVID-19 and can reliably differentiate it from other infections or alternative diagnosis. In places where RT-PCR testing is limited or delayed, CT chest can be used as a reliable tool in differentiating COVID-19 from other non-COVID-19 lung diseases.
Abbreviations
- CO-RADS
COVID-19 Reporting and Data System
- COVID-19
Corona virus disease-2019
- CT
Computed tomography
- RT-PCR
Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
- SARS-COV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2
Author contribution
Guarantor of integrity of the study, study concept and design, manuscript drafting, and revision for important intellectual content, A.N. Final version of manuscript approved by all authors. Literature research, H.S., P.S., H.Z., S.W., D.K., M.H., M.M. CO-RADS lexicon scoring, S.W.,H.Z., P.S.,H.S.,D.K., A.N.; data manager and data collection: B.J.; methodology and statistical analysis, M.M., D.S, A.N. Manuscript editing, B.J.,D.S., M.M., A.N.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
7/27/2021
Co-authors email addresses were removed per request.
References
- 1.Waller J, Kaur P, Tucker A, et al. Diagnostic tools for coronavirus disease (COVID-19): comparing CT and RT-PCR viral nucleic acid testing. Am Roentgen Ray Soc. 2020;215(4):834–838. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.23418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nair AV, Kumar D, Yadav SK, Nepal P, Jacob B, Al-Heidous M. Utility of visual coronary artery calcification on non-cardiac gated thoracic CT in predicting clinical severity and outcome in COVID-19. Clin Imaging. 2021;74:123–130. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.01.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.ACR Recommendations for the use of Chest Radiography and Computed Tomography (CT) for Suspected COVID-19 Infection | American College of Radiology [Internet]. [cited 2021 May 12]. Available from: https://www.acr.org/Advocacy-and-Economics/ACR-Position-Statements/Recommendations-for-Chest-Radiography-and-CT-for-Suspected-COVID19-Infection
- 4.Rubin GD, Ryerson CJ, Haramati LB, Sverzellati N, Kanne JP, Raoof S, Schluger NW, Volpi A, Yim JJ, Martin IBK, Anderson DJ, Kong C, Altes T, Bush A, Desai SR, Goldin, Goo JM, Humbert M, Inoue Y, Kauczor HU, Luo F, Mazzone PJ, Prokop M, Remy-Jardin M, Richeldi L, Schaefer-Prokop CM, Tomiyama N, Wells AU, Leung AN. The role of chest imaging in patient management during the covid-19 pandemic: a multinational consensus statement from the fleischner society. Radiology. 2020;296(1):172–180. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020201365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Islam N, Ebrahimzadeh S, Salameh JP, Kazi S, Fabiano N, Treanor L et al (2021) Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19, vol 2021. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, John Wiley and Sons Ltd [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Prokop M, Van Everdingen W, Van Rees VT, Van Ufford HQ, Stöger L, Beenen L et al (2020 Aug 1) CO-RADS: A Categorical CT Assessment Scheme for Patients Suspected of Having COVID-19-Definition and Evaluation. Radiology. 296(2):E97–E104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Simpson S, Kay FU, Abbara S, Bhalla S, Chung JH, Chung M, Henry TS, Kanne JP, Kligerman S, Ko JP, Litt H. Radiological Society of North America expert consensus document on reporting chest CT findings related to COVID-19: endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020;2(2):e200152. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2020200152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Bruns DE, Glasziou PP, Irwig L, et al. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies1. Radiology. 2015;277(3):826–832. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ding X, Xu J, Zhou J, Long Q. Chest CT findings of COVID-19 pneumonia by duration of symptoms. Eur J Radiol. 2020;1:127. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Crewson PE (2005) Reader agreement studies. American Journal of Roentgenology. American Roentgen Ray Society, In, pp 1391–1397 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845. doi: 10.2307/2531595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Atta H, Hasan HA, Elmorshedy R, Gabr A, Abbas WA, El-Barody MM. Validation of imaging reporting and data system of coronavirus disease 2019 lexicons CO-RADS and COVID-RADS with radiologists’ preference: a multicentric study. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 2021;52(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s43055-021-00485-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bellini D, Panvini N, Rengo M, Vicini S, Lichtner M, Tieghi T, Ippoliti D, Giulio F, Orlando E, Iozzino M, Ciolfi MG, Montechiarello S, d’Ambrosio U, d’Adamo E, Gambaretto C, Panno S, Caldon V, Ambrogi C, Carbone I. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver variability of CO-RADS in patients with suspected coronavirus disease-2019: a multireader validation study. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(4):1932–1940. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07273-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sultan OM, Al-Tameemi H, Alghazali DM, Abed M, Ghniem MNA, Hawiji DA, et al. Pulmonary ct manifestations of COVID-19: changes within 2 weeks duration from presentation. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 2020;51(1):1–7. doi: 10.1186/s43055-019-0116-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xu B, Xing Y, Peng J, Zheng Z, Tang W, Sun Y, Xu C, Peng F. Chest CT for detecting COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. Eur Radiol. 2020;30(10):5720–5727. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06934-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fang Y, Zhang H, Xie J, Lin M, Ying L, Pang P, et al. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Vol. 296, Radiology. Radiological Society of North America Inc.; 2020. p. E115–7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Xie X, Zhong Z, Zhao W, Zheng C, Wang F, Liu J. Chest CT for typical coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia: relationship to negative RT-PCR testing. Radiology. 2020;296(2):E41–E45. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]