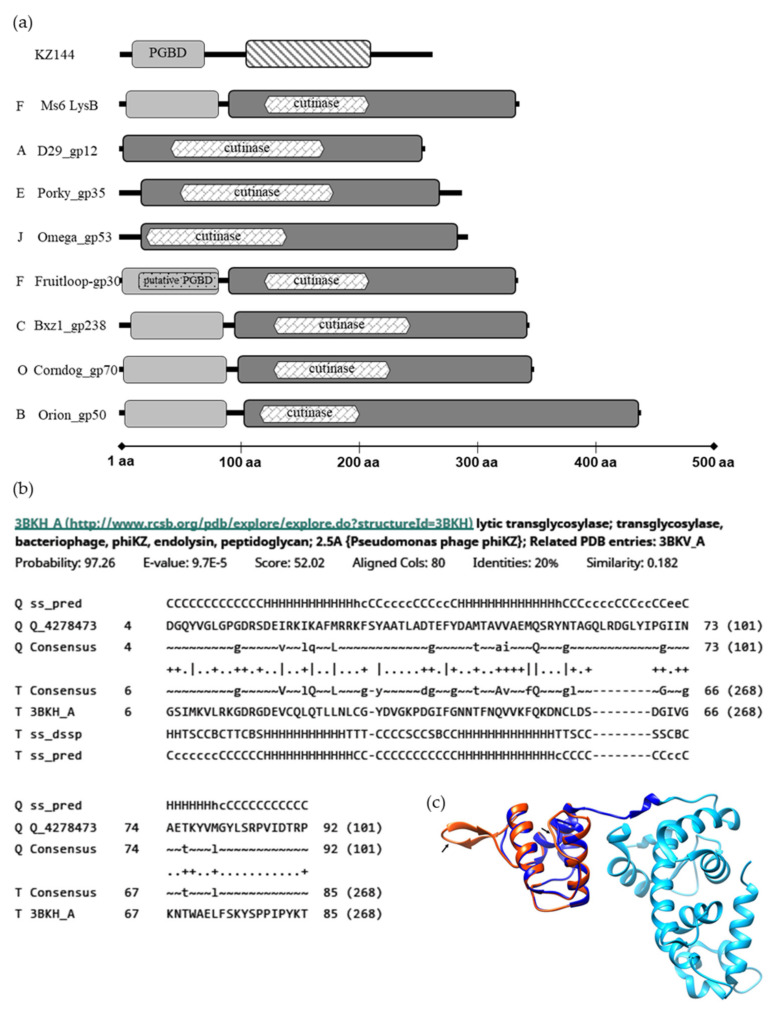
Figure 1.
In silico analysis of LysB proteins. (a) Modular structure of KZ144 and representative mycobacteriophage’s LysB proteins. Regions with structural similarity to the KZ144 PGBD are shown in light grey blocks and a predicted catalytic region similar to D29 LysB in dark grey. φKZ gp144 lytic transglycosylase domain is marked with a strip pattern. The predicted PGBD in Fruitloop_gp30 is marked with a dot pattern. Each phage cluster is indicated by the letters on the left. The data shown are the result of a HHpred analysis for each depicted mycobacteriophage LysB. Predicted cutinase domains with MOTIF Finder are indicated within the LysBs catalytic region. (b) Alignment between the N-terminus of Ms6 LysB and the PGBD of φKZ endolysin as obtained from HHPred. (c) Structural model of Ms6 LysB using KZ144 (PDB ID-3BKH) as the template obtained from the SWISS-MODEL server. Catalytic and N-terminal domains of KZ144 are represented in light and dark blue, respectively. The generated structure of the N-terminal sequence of Ms6 LysB is represented in red. The sequences with lower similarity with target (low scored) are indicated by an arrow. Image was created with UCSF Chimera [44] and by superposing the PDB structure 3BKH and the constructed Ms6 LysB model.