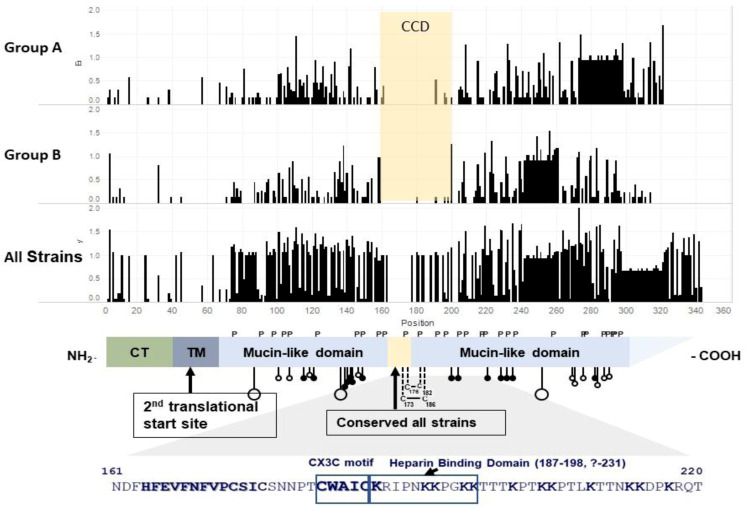
Figure 1.
Schematic of the functional domains of the RSV G protein. The first three panels are entropy plots that indicate variability at each amino acid by height of the bar. Sequences were aligned using mafft 7.471, and Shannon entropy was calculated using the formula , where Pi is the fraction of residues of type I, and M is the total number of residue type (Wootton, J.C. and Federhen, S., Computers & Chemistry, 1993) [37], using Python code from https://gist.github.com/jrjhealey/130d4efc6260dd76821edc8a41d45b6a (accessed on 6 April 2021). The panels were generated using Tableau 2021.1.0. The 1st panel, Group A, is based on 50 sequences representing the different Group A genotypes. Since some Group A viruses have a 23 aa duplication in G, a gap was included in viruses without the duplication to maintain the alignment. The 2nd panel is based on 53 sequences representing the different Group B genotypes. Since some Group B viruses have a 20 aa duplication in G, a gap was included in viruses without the duplication to maintain the alignment. The 3rd panel is based on the 103 Group A and B sequences used in panels 1 and 2. It includes one gap for the 23 aa duplication in Group A and a second gap for the 20 aa duplication in Group B viruses. The 4th panel is a schematic of the structure of the RSV A2 G gene adapted from Teng et al. (with permission) [38]. P indicates prolines and C cysteine. The stalk with large circles indicates sites for N-linked carbohydrates, and stalks with small circles indicate sites, serine open, and threonine closed, for O-linked carbohydrates. The 13 aa, aa 164–176, conserved among all strains is highlighted in beige. The 5th panel shows aa sequences that include CCD, the CX3C motif (aa 182–186), and the HBD (aa 187–198). CCD is defined in this review as the central relatively conserved domain from ~aa 160 to 200 that is relatively conserved within but not between Group A and B strains. CT = cytoplasmic tail. TM = transmembrane domain. The CX3C motif and K (lysine) are in bold print.