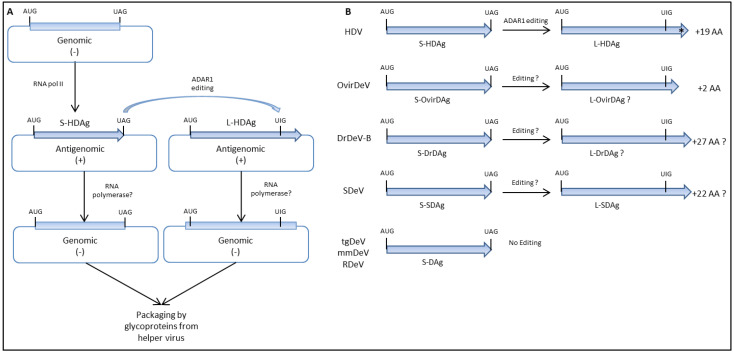
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of RNA editing during deltaviruses replication (A) and putative L-DAgs generated via ADAR1 (B). The incoming viral genome, a circular ssRNA molecule of negative polarity (genomic RNA), serves as a template for the synthesis of DAg encoding mRNAs and circular RNAs of antigenomic polarity. The mRNA produced at the early stages of deltaviruses replication contains an amber stop codon (UAG) and produces the small form of DAgs. In a fraction of the antigenomic RNAs, the adenosine in the amber stop codon is deaminated to inosine (UIG) by the host RNA editing enzyme ADAR1. The edited mRNAs contain a tryptophan (W) codon instead of the amber stop codon and additional codons are translated to yield the large form of DAgs. The asterisk depicts the presence of a CXXQ motif in the C-terminus of L-HDAg required for isoprenylation.