Abstract
Objectives
Pharmacists are increasingly providing patient-focused services in community pharmacies, including in the area of sexual and reproductive health (SRH). Specific SRH areas have been the focus of research, but a broader perspective is needed to position pharmacists as SRH providers. This review explored research that described and evaluated professional pharmacy services across a broad range of SRH areas.
Design
Scoping review
Data sources
Medline, EMBASE, CINAHL, Web of Science, Scopus and Cochrane Library (January 2007–July 2020).
Study selection
Studies reporting on the description and evaluation of professional pharmacy SRH services provided by community pharmacists.
Data extraction
Two investigators screened studies for eligibility, and one investigator extracted the data. Data were analysed to primarily describe professional pharmacy services and intervention outcomes.
Results
Forty-one studies were included. The main SRH areas and professional pharmacy services reported were sexually transmitted and bloodborne infections (63%) and screening (39%), respectively. Findings showed that pharmacists’ delivery of SRH services was feasible, able to reach vulnerable and high-risk groups, and interventions were highly accepted and valued by users. However, integration into daily workflow, pharmacist remuneration, cost and reimbursement for patients, and policy regulations were some of the barriers identified to implementing SRH services. Studies were primarily in specific areas such as chlamydia screening or hormonal contraception prescribing, while studies in other areas (ie, medical abortion provision, long-acting reversible contraception prescribing and vaccine delivery in pregnant women) were lacking.
Conclusion
This scoping review highlights the expansion of pharmacists’ roles beyond traditional product-focused services in a number of SRH areas. Given the potential feasibility, users’ acceptability and reach, pharmacists are ideally situated to enhance SRH care access. Future research describing implementation and evaluation of professional pharmacy services in all SRH areas is needed to promote access to these services through community pharmacies and position pharmacists as SRH providers worldwide.
Keywords: reproductive medicine, sexual medicine, hiv & aids, public health
Strengths and limitations of this study.
This is the first scoping review to systematically identify and synthesise research that described and evaluated professional pharmacy services across a broad range of sexual and reproductive health (SRH) areas.
A broad and comprehensive search strategy was conducted in six peer-reviewed databases.
This review may help to guide the implementation of SRH services and inform new policies in high-income countries where pharmacists’ scope of practice is expanding.
We summarised challenges and barriers associated with provision of professional pharmacy services in SRH for studies that met our inclusion criteria; however, this review may not include all the barriers reported in the literature.
A critical appraisal of the literature was undertaken to highlight gaps and potential future research areas, but no quality assessment was performed in this scoping review.
Introduction
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is recognised as essential to a person’s overall health and well-being.1 Over the past two decades, considerable progress has been made in advancing the global agenda focused on ensuring access to high-quality SRH services.2 However, accessibility remains inadequate in many countries due to limited resources, infrastructure, education, awareness of services or environmental barriers.2 The far-reaching impact of unsafe abortions, unintended pregnancies, reproductive cancers and sexually transmitted and bloodborne infections (STBBI) on countries’ health and socioeconomic development cannot be overemphasised.
Globally, pharmacists’ roles have become more patient-focused and service-based in recent years, as compared to traditional roles that were more product focused.3 4 The convenient location of community pharmacies allows pharmacists to engage directly with several communities and promote access to healthcare services.5–7 Legislative, policy and educational changes have enabled pharmacists to expand their scope of practice to address different and new health challenges.8–10 However, pharmacy practice and pharmacy education, as well as legal and regulatory frameworks guiding pharmacy practice differ considerably worldwide.11 12 Traditional pharmacy services are those typically provided in all pharmacies and include compounding and dispensing of prescription medications, providing drug information and supporting patient self-care with over-the-counter medications and products.11 Various terms have been used in the literature to describe patient-focused pharmacy services, making international comparisons challenging. Professional pharmacy services is a broad term that refers to applying specialised health knowledge ‘to optimise the process of care with the aim to improve health outcomes and the value of healthcare’.13 Examples of professional pharmacy services include administering vaccines and other injectable medications, prescribing or renewing medications, smoking cessation, medication therapy management and disease screening or testing.11–13
While the model and scope of pharmacy practice differ between countries, the shift towards delivery of patient-focused services provides the opportunity to address the burden on primary healthcare systems and poor accessibility, especially in SRH. As one of the most accessible and trusted health professionals,14 15 pharmacists are well positioned to take on a more significant role in delivering SRH services by removing practical barriers and connecting with other care providers.15
Examples of policy and regulatory changes to support improved access to SRH through community pharmacies can be seen around the globe. In many cases, pharmacists’ roles in SRH have evolved from primarily dispensing to include professional pharmacy services such as patient education programmes, preventive, screening and referral services, according to regulations in each jurisdiction.15–21 As an example, non-prescription progestin-only emergency contraception (EC) has been available at community pharmacies for more than 15 years in various European countries, Canada, the USA, Australia and New Zealand22 23; and ulipristal acetate (EC approved in 2009) was switched from prescription to non-prescription status in 2015 by the European Commission.24 Further changes in several Canadian provinces and jurisdictions in the USA granted authority for pharmacists to prescribe hormonal contraception.25 26 Pharmacists are also authorised to administer injections, such as injectable contraceptives and vaccines, in many parts of the world, including Canada, the USA, UK, Australia and New Zealand.27
Previous literature reviews on pharmacists’ roles in SRH are focused on specific SRH areas or experiences related to SRH services. These include reviews of pharmacists’ role in the supply of EC,22 medical abortion provision,28 HIV prevention29 and STBBI screening.30 Other reviews have also focused on pharmacists’ and users’ knowledge, attitudes, experiences and perspectives related to contraception as well as a broader spectrum of SRH services.31–36 Overall, the available literature highlights positive users’ experiences, implementation is feasible, and also some challenges for pharmacy staff and users. However, these reviews have not addressed the topic from the service organisation, implementation and delivery perspective.
Although interest in SRH has increased in recent years, there is little research synthesising professional pharmacy services across a broad spectrum of SRH areas.33–36 Clarity is needed with respect to pharmacists’ roles in SRH as well as the types of professional pharmacy services that may be delivered in community pharmacies to better serve the needs of the community. Addressing this gap in the literature is critical to position pharmacists as SRH providers, especially now that access issues have been exacerbated during the COVID-19 pandemic, and pharmacists are perceived as crucial in emergency response.37 Therefore, this review aimed to identify research that described and evaluated professional pharmacy services provided by pharmacists across a broad range of SRH areas.
Methods
Study design
Scoping review’s framework and methodology are an excellent option for exploring SRH services offered at community pharmacies, pharmacists’ roles in providing these services, and identifying knowledge gaps within the existing literature. The outcomes of this scoping review were to (1) identify the professional pharmacy services in SRH provided by pharmacists in community practice and (2) report on service description and evaluation.
The work was structured around the five stages of the framework recommended by Arksey and O’Malley38 and enhanced by Levac et al39: (1) identifying the research question, (2) identifying relevant studies, (3) study selection, (4) charting the data and (5) collecting, summarising, and reporting the results. The review was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses protocol extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines.40 The PRISMA-ScR checklist can be found in online supplemental file 1.
bmjopen-2020-047034supp001.pdf (1.3MB, pdf)
Search strategy
The search strategy was developed in consultation with a research librarian. Six health-science databases were searched for relevant peer-reviewed literature: Medline (Ovid), EMBASE (Ovid), CINAHL (Ebsco), Web of Science Core Collection (Clarivate), Scopus (Elsevier) and Cochrane Library (Wiley). We searched ProQuest Dissertations & Abstracts for grey literature, and handsearched the reference lists of selected papers to identify any additional studies. There were no limits on language of publication. The search included studies published from 1 January 2007 to 22 July 2020. The time frame for inclusion was determined based on the publication dates of previous reviews in this field, and the scope of pharmacist practice and policy changes in high-income countries worldwide that have impacted current practice. The articles were retrieved from each database and imported into EndNote (V.9, Clarivate Analytics) for management and screening.
Keywords included: pharmacists, sexual health, reproductive health, pregnancy, sexually transmitted disease* or sexually transmitted infection* or STD* or STI or STIs, prescriptions, screening, patient education, service (online supplemental file 2).
bmjopen-2020-047034supp002.pdf (89.6KB, pdf)
Screening and study selection
Study selection focused on peer-reviewed literature that described and evaluated delivery of professional pharmacy services in SRH. To be included, studies had to describe and evaluate (eg, assessed feasibility, uptake, or acceptability from users’ perspective) an intervention. Articles were excluded if they did not describe how the intervention was organised, implemented or delivered, the setting was not a community pharmacy, a community pharmacist was not part of the intervention, outcomes reported were only about experiences, knowledge or attitudes of pharmacists, or if the research was incomplete or yet to be published (eg, conference abstracts). Studies conducted in low-income and middle-income countries were also excluded due to differences in health systems and regulation of community pharmacies and pharmacy professionals as compared with high-income countries (table 1).41
Table 1.
Eligibility criteria for studies included
| Aspects of study design | Eligibility criteria |
| Population | People of all ages from high-income countries. Referred to as users, patients or individuals. |
| Intervention | Professional pharmacy services focused on SRH. Face-to-face interaction between provider and user. |
| Outcome | Description and evaluation of SRH services provided to real users of the services; mystery clients or simulated patients were excluded. |
| Setting | Community pharmacy; specialised pharmacy or pharmacy based in a hospital/clinic were excluded. |
| Provider | Community pharmacists had to participate in the intervention directly; services provided by clinical pharmacists or residents only were excluded. |
| Study design | Qualitative, mixed methods and quantitative. Descriptive studies (retrospective, cross-sectional or prospective), comparative and non-comparative studies were included; abstracts, protocols, reviews, letters, commentaries, editorials, opinions, meta-analysis and reviews were excluded. |
| Year | Articles published after 2007. |
| Language | No language restrictions. |
SRH, sexual and reproductive health.
Articles were screened in two phases. Two investigators (JN and CAH) independently screened titles and abstracts of studies for eligibility. Both investigators (JN and CAH) reviewed the full text of articles identified as potentially relevant. Discrepancies were discussed until consensus was reached.
Data extraction and synthesis
A data extraction tool was developed in Excel (V.16.39, Microsoft) to record key information of included articles. Data were extracted by JN and reviewed by a second investigator for accuracy (NY, TJS or CAH).
A descriptive analysis including a numerical overview of the amount, type, and distribution of included articles, and a narrative synthesis were performed to fulfil the study objectives (JN, NY, TJS and CAH). Articles were grouped and synthesised by SRH areas and professional pharmacy services uncovered in the scoping review. Characteristics of studies and key findings were summarised, and studies were compared.
Patient and public involvement
No patient involved.
Results
Figure 1 summarises study selection. The initial search yielded 6559 results after the removal of duplicates (figure 1). After screening titles and abstracts, 77 articles were retrieved for full-text review. From these, 41 articles were included in the review (online supplemental file 3).
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow chart and search results. PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; SRH, sexual and reproductive health.
bmjopen-2020-047034supp003.pdf (163.6KB, pdf)
Study characteristics
In terms of research design, 27 studies were quantitative (non-randomised), 2 were cluster randomised and 2 were randomised controlled trials. Mixed methods were used in nine studies, and one study was qualitative. About 66% of studies reported additional training was provided to pharmacists in order to offer SRH services. Table 2 outlines characteristics of the studies included.
Table 2.
Summary characteristics of studies included (n=41)
| Characteristics | Studies n (%) |
| Region | |
| USA | 20 (48.8) |
| UK | 13 (31.7) |
| Australia | 3 (7.3) |
| Canada | 1 (2.4) |
| Spain | 1 (2.4) |
| Greece and Spain | 1 (2.4) |
| Puerto Rico | 1 (2.4) |
| Norway | 1 (2.4) |
| Research design | |
| Quantitative (non-randomised) | 27 (65.9) |
| Quantitative cluster randomised trial | 2 (4.9) |
| Quantitative randomised controlled trial | 2 (4.9) |
| Mixed methods | 9 (22.0) |
| Qualitative | 1 (2.4) |
| SRH area | |
| STBBI | 26 (63.4) |
| Chlamydia | 9 (34.6) |
| HIV | 7 (26.9) |
| HPV | 5 (19.2) |
| Hepatitis C | 5 (19.2) |
| Contraception | 12 (29.2) |
| Hormonal contraceptives | 7 (58.3) |
| Injectable contraceptives | 3 (25.0) |
| Emergency contraception | 2 (16.7) |
| Pregnancy | 2 (4.9) |
| Sexual dysfunction | 1 (2.4) |
| Reported additional training for pharmacists | |
| Yes | 27 (65.9) |
| No | 14 (34.1) |
| Professional pharmacy service | |
| Screening | 16 (39.0) |
| Prescribing | 7 (17.0) |
| Injection administration | 6 (14.6) |
| HPV vaccine | 3 (50.0) |
| Injectable contraceptives | 3 (50.0) |
| Provision of medication by pharmacist | 6 (14.6) |
| Specific protocol | 4 (66.7) |
| Pharmacists only medication | 2 (33.3) |
| Education programmes | 4 (9.8) |
| Screening and treatment | 2 (4.9) |
HPV, Human papillomavirus; SRH, sexual and reproductive health; STBBI, sexually transmitted and bloodborne infections.
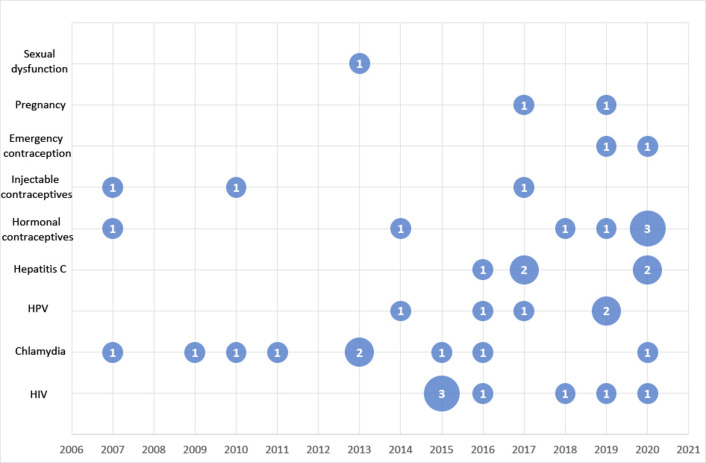
Most of the studies were conducted in the USA (n=20) or UK (n=13). Twenty-six (63%) studies focused on STBBI, 12 (29%) on contraception, 2 (5%) on pregnancy and 1 (2%) on sexual dysfunction. The most common professional pharmacy services provided by pharmacists were screening (39%), prescribing (17%), administration of injections (15%) and provision of medication by pharmacists (15%). Provision of medication was through specific protocol (eg, patient group directions or study protocol) or pharmacist only medications. Provision of medication through specific protocol included pharmacists who provided medications because the legal framework allowed them (eg, vouchers for chlamydia treatment) while pharmacists only medication refers to medications that can be provided by pharmacists without a prescription (eg, EC). Other activities included education programmes and screening and treatment (as one service) (table 2). More than two-thirds of studies (71%) were published between 2015 and 2020. Figure 2 shows the number of articles included for each SRH area by year of publication.
Figure 2.
Systematic map—SRH topic and year of publication. Area of points are proportional to absolute values of number of studies. HPV, human papillomavirus; SRH, sexual and reproductive health.
SRH areas and services
Studies were categorised into four main SRH areas: STBBI, contraception, pregnancy and sexual dysfunction (online supplemental file 3). An overview of these studies is described in further detail below.
Sexually transmitted and bloodborne infections
Twenty-six studies evaluated STBBI services provided by pharmacists; 9 (35%) were Chlamydia trachomatis related, 7 (27%) were focused on HIV, 5 (19%) on human papillomavirus (HPV) and 5 (19%) on hepatitis C virus (HCV).
Chlamydia
Four of the nine studies evaluated pharmacists’ involvement in chlamydia screening,42–45 two evaluated screening along with treatment services,46 47 and three evaluated treatment services only.48–50 Screening for chlamydia was offered through distribution of chlamydia test kits,42 44 46 or by collection of urine samples that were stored at the pharmacy and shipped to a pathology provider for analysis.43 45 In one study, it was not clear how screening was performed.47 Of the studies which evaluated treatment services only, two focused on treatment of partners,48 50 and one focused on the treatment of index cases.49
In terms of studies that assessed chlamydia screening, the target population and sample size varied (online supplemental file 3). Studies using home test kits reported 18% and 28% of samples returned for testing.42 44 In comparison, one study offered on-site screening (collection of samples) with an incentive for participants and pharmacists.43 In this study, 75% of unique samples were returned to the pharmacy.43 Positivity rates reported for chlamydia ranged from 0% to 9.8%.42–44 46 47 Studies focused on treatment services used redeemable vouchers for free chlamydia treatment at participating community pharmacies. Cameron et al found 40% of the treatment vouchers were redeemed by partners of index cases.48 Slutsker et al reported similar results; 41% of vouchers were redeemed even when the medication was free of charge.50 Another study used the same methodology but for index cases with uncomplicated chlamydia and found that 87% of vouchers were redeemed.49
Overall, users reported a high level of satisfaction with the services provided.44 45 47 48 Convenience,44 45 47 location,45 short waiting times and no appointments needed44 45 47 48 and a non-judgemental approach47 were reported as benefits. Barriers or challenges were also noted, including users’ low awareness of service,42 44 concerns regarding confidentiality and privacy,44 45 47 and in some cases, inconvenience of returning specimens to designated pharmacies or laboratories.42 44
HIV
Among the seven studies focused on HIV, one evaluated pharmacist-led pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP),51 and the remainder focused on HIV screening at the community pharmacy.52–57
Havens et al implemented a pilot whereby individuals started on HIV PrEP could choose to be followed by a pharmacist for ongoing sexually transmitted infections (STI)/HIV screening, follow-up, and PrEP prescribing.51 Although the authors described logistical challenges related to STI screening, results indicated that implementing a pharmacist-led PrEP programme was feasible and achieved high satisfaction rates among participants.51 The studies reporting HIV screening in community pharmacies varied in terms of duration, tests performed, and whether screening was offered as part of a pilot or an established programme. Most studies used rapid point-of-care testing (POCT) with finger-prick blood samples for screening,52 54 55 57 and one used oral fluid samples.56 Five studies reported referral and confirmatory testing for individuals with reactive results.52 54–57 The authors reported 0.8%,52 57 0.9%55, 1.5%54 and 1.6%56 of HIV rapid tests performed were reactive. Fernández-Balbuena et al reported findings from three programmes in Spain involving 110 pharmacies and found that pharmacy testing contributed to identifying 10% of new HIV cases in the region; a high percentage of heterosexual men were tested.55
Studies that focused on HIV screening demonstrated pharmacists are capable of reaching high-risk groups and individuals not previously tested.52–57 Crawford et al evaluated uptake of HIV testing when part of comprehensive disease screening implementation in low access and minority communities.53 Kelly et al and Fernández-Balbuena et al found as low as 27% and as high as 52% of individuals reported they were not previously tested for HIV (or were unsure).55 57
Some studies reported positive experiences with HIV screening at community pharmacies.54 57 However, challenges were also reported, including recruitment and advertising,54 56 57 obtaining the sample,54 57 integration into the daily workflow,57 pharmacists’ remuneration,54 57 costs56 and referral and linkage to care.52 Havens et al also described similar challenges for HIV PrEP services, such as integration into the daily workflow, pharmacist compensation, and cost for users and reimbursement policies.51
Human papillomavirus
Five studies explored professional pharmacy services focused on HPV vaccination. Two studies evaluated the implementation of HPV vaccination services at community pharmacies,58 59 two focused on educational strategies and impact on vaccination rates,60 61 and one focused on a patient assistance programme for university students and vaccination uptake.62 Three studies targeted adolescents and/or younger adults,58 61 62 one targeted individuals between 9 and 26 years old filling acne or birth control prescriptions at the pharmacy,60 and one did not specify the target group (online supplemental file 3).59
HPV vaccination service was offered directly through the pharmacy,58 60–62 or by a health clinic that promoted a community pharmacy as an alternate setting to complete the vaccination series.59 Regarding service promotion, different strategies were described. Calo et al included direct mailing to families with eligible children, radio and newspaper advertisements, posting fliers and promotion in the pharmacy using posters, bag stuffers, handouts, roadside signs and direct patient approach.58 Other authors described similar strategies, with direct patient approach most commonly used.59–62
There were, however, important barriers reported in these studies. In some states in the USA, community pharmacies are not included as qualified vaccine provider sites for vaccinating age-eligible adolescents.58 As a consequence, this limits the reach to young people and the integration of the service into primary care systems.58 Parental beliefs about vaccination,59 61 62 awareness of pharmacists’ immunisation training58 and information about available services58 62 were also challenges reported.
Hepatitis C
All five studies focused on HCV screening services in community pharmacies.63–67 In one study, pharmacists performed HCV-antibody rapid POCT,65 and in four studies dried blood spot testing (DBST) was used.63 64 66 67 One study reported DBST samples were tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV), HIV, and syphilis in addition to HCV, although results for these infections were not reported.64 Two other studies reported testing samples for HCV, HBV and HIV.66 67
The screening services in these studies aimed to reach primarily high-risk groups, including individuals attending for needle exchange,64 opiate substitution therapy64 66 67 and those with limited access to care.65 The percentage of tests completed that were reactive was reported to be 1.2%,65 7%63 64 and 28%.66 As part of the service, pharmacists consulted or referred patients with reactive tests to specialist care.63–67 In two articles, Buchanan et al reported implementation in more than 20 community pharmacies a ‘point-of-diagnosis’ consultation with the pharmacist and a hepatologist for individuals with confirmed HCV infection.63 64 Pharmacist services extended beyond screening to support patients’ care following diagnosis. Buchanan et al reported that most patients remained actively engaged in care, and some of them started HCV treatment.63 64 Radley et al reported that more patients in the pharmacist-led pathway for HCV initiated treatment and achieved HCV cure as compared with the conventional care pathway.67
Reported challenges implementing HCV screening services included motivating people to get tested,65 careful time management by pharmacists to balance workload63 65 66 and pharmacist remuneration.65
Contraception
Of the 12 studies focused on contraception, six studies assessed prescribing hormonal contraception,68–73 three focused on injectable contraceptive administration74–76 and two on EC provision.77 78 One study compared two interventions, pharmacist-provision of 1 month of a bridging method of contraception or pharmacist referral to a family planning clinic, to standard care in women seeking EC.79
Five studies focused on the implementation of policies which support direct pharmacy access in some US states, and enable pharmacists to independently prescribe contraceptives for Medicaid-insured women.68 70–73 Anderson et al found that community pharmacists in Oregon issued 10% of new contraceptive prescriptions (oral or transdermal methods) during 2016–2017.68 In addition, Lu et al reported that pharmacists in Oregon and California prescribed different contraceptive methods, including oral (95.7%), patch (1.6%), vaginal ring (2.6%) and injectable (0.1%).70 However, Gibbs and Harvey assessed the impact of this type of policy in Oregon during the first 2 years following implementation and concluded there was no significant increase in contraceptive use.73 Still, they noted that women’s satisfaction, convenience, cost, equity and impact on access and unintended pregnancy rates should be studied in the future when the demand for these services increases.73
Effective and consistent use of contraception is strongly related to access and supply. Rodriguez et al showed that pharmacists’ prescription service was associated with improved contraception continuation rates as pharmacists were significantly more likely to prescribe a 6-month supply than other prescribers.72 Pharmacists may also enhance access to contraceptive and SRH services through referral to other healthcare professionals and clinics for further care.69 75 77 79 Mantzourani et al noted that 31% of EC consultations included a referral to a sexual health clinic or a general practitioner.77 Monastersky Maderas and Landau found that pharmacy and clinic partnerships to expand access to injectable contraception resulted in reciprocal referrals.75 Michie et al concluded that referral by pharmacists to a family planning clinic and pharmacists’ provision of progestogen-only contraceptive pill were valuable and could increase the uptake of effective contraception after EC.79
Compared with other contraceptive methods, injectable contraceptives require more visits to clinics, which may be inconvenient for some individuals.74 75 Pharmacists can assist women by administering injectable contraceptives at the time of picking up their refill.74 75 Heller et al suggested that a pharmacy-based injection service for users of injectable contraceptives may be feasible, but the public viewed pharmacist availability as a barrier for access.74 Some authors explored the potential of this service in partnership with a clinic. Picardo and Ferreri randomised women to receive the injection at a community pharmacy or clinic,76 and Monastersky Maderas and Landau gave women the option to continue receiving the injections at the clinic or a community pharmacy.75 Convenient access to community pharmacies made this service feasible with high acceptance rates by women.74–76
Community pharmacies provide an important option for women to access EC.77 78 According to 5-year trends, Mantzourani et al described consistent provision of a free pharmacy-based EC service in the UK to women of a wide age range.77 Turnbull et al showed that users of over the counter EC preferred community pharmacies for the ease and speed of access and convenience.78 Disadvantages included less personalised service by the pharmacist and subsequent need for EC.78 Women in this study suggested enhancements including increased privacy and consultation to expand pharmacists’ role in the provision of contraception.78
Pregnancy
Two studies addressed pregnancy and preconception care.80 81 One of these tested the feasibility of a pharmacist consultation in early pregnancy.81 The women reported high satisfaction rates, emphasising the importance of a telephone consultation, and the majority would recommend the service to other pregnant women.81 DiPietro Mager et al demonstrated that pharmacists could offer targeted medication reviews to provide preconception education including folic acid use, medications that may cause fetal harm, and recommended vaccines in pregnancy.80 This study found that community pharmacists rapidly integrated the service process and that a sustainable reimbursement model was feasible.80
Sexual dysfunction
One study assessed pharmacists’ ability to detect erectile dysfunction (ED) and encourage individuals to seek medical advice.82 Pharmacists used a questionnaire to gather clinical and behavioural questions and patients completed the validated Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) to identify those who might have ED (SHIM score ≤21). The results showed that 77% of men included in the study had a SHIM score ≤21 indicating ED, however only a minority of these men were able to be contacted by phone to determine if they visited a physician.82 The authors concluded that pharmacists’ roles in detecting, evaluating and motivating individuals to follow up with a physician need to be evaluated further.82
Discussion
This scoping review aimed to identify and synthesise research that described and evaluated professional pharmacy services provided by pharmacists in SRH. Our results reveal pharmacists are engaged in a wide range of activities beyond traditional pharmacy services, signalling that pharmacists play a more significant role in delivering services in a number of SRH areas.
Generally, studies included in this review found the provision of SRH services by pharmacists enhanced access to care, users’ experiences and the uptake of services. Our results are consistent with previous SRH research addressing users’ experiences with pharmacy services, which have similarly reported the location of the pharmacy, extended opening hours, and no necessary appointments, as some of the pharmacies’ advantages.32 35 36 In a systematic review, Chirewa and Wakhisi found that young women considered obtaining EC through community pharmacies in the UK as convenient and easy to access.32 In addition, a non-judgemental approach, receiving services from helpful pharmacists and free and confidential services, were considerations when choosing community pharmacies over other settings.32 Similarly, Gauly et al reported in a systematic review that pharmacy users appreciated the convenience and easy access of pharmacies for SRH services and felt comfortable discussing sexual health with the pharmacist.36 However, Gauly et al noted conflicting results about individuals’ views on privacy. Some patients appreciated the privacy level provided in pharmacies while others expressed concerns about being overheard by other clients when talking to the pharmacist.36
SRH services provided by pharmacists at community pharmacies reached vulnerable and high-risk groups. The analysis of studies reporting interventions highlighted variable findings. Since positivity rates of STBBI vary depending on study and intervention designs, testing technology, jurisdictions, risk behaviours, population groups and year of implementation,83 the variability in findings reported by the studies included in this review is not surprising. However, the advantages of reaching a significant proportion of first-time testers and high-risk populations increases STBBI awareness. Community pharmacies have been described as a healthcare ‘hub’,84 and opportunities exist to promote and integrate SRH services to enhance access for underserved populations.35 This is particularly relevant to emphasise now, as the COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically impacted public health, and SRH and rights are no exception. The pandemic has had repercussions on access to routine and preventive services, shortage of products and supplies and service delivery capacity.85–87 This situation is likely to impact the most vulnerable populations disproportionately.85 88 89 Positioning pharmacists as SRH providers could translate into the development of strategies using community pharmacies as an access point for patient-focused SRH care.
Legislative changes, availability of technology for screening and sample collection and partnerships, were found to be important enablers for pharmacists to deliver professional pharmacy services. For example, the availability of hormonal contraceptives and progestin-only EC pill in community pharmacies is due to approved legislation in some states in the USA and Canada.90–93 For STBBI, a community pharmacy is usually more conveniently located than a clinical testing site,94 95 and advances in POCT, DBST and home test kits technologies enabled pharmacists to offer screening services for HIV, HCV and chlamydia outside traditional settings.96 Similarly, care delivery models, including partnerships with sexual health clinics as well as physicians (eg, collaborative practice agreements), were also crucial for service establishment in some cases.
Our results also indicate several barriers to implementing SRH services at community pharmacies. Integration of services into the daily workflow,57 59 66 pharmacists’ remuneration,51 57 63–65 cost and reimbursement for patients51 55 56 62 and policy regulations61 are commonly reported challenges. Introducing new policy approaches to boost and enhance community pharmacists’ roles in SRH is still needed. For example, pharmacists are authorised to administer injections in every state in the US. However, state laws may limit pharmacists’ ability to administer HPV vaccines based on the age of individuals and conditions under which they can administer HPV vaccines, such as independent authority, collaborative practice agreement, or another health professional prescription.58 61 Additionally, parents’ and patients’ awareness of pharmacists’ training and services,42 44 50 54 56 57 62 concerns about pharmacists providing safe and high-quality services,69 and motivation to opt into the services (eg, voluntarily ask for any STBBI screening service)42 44 65 are some of the other challenges to overcome. In order for SRH services through community pharmacies to be sustainable and affordable, these barriers are paramount to address.
The findings from this review could help pharmacists visualise and understand their role in SRH and promote the value of professional pharmacy services. This review may also help support the implementation of SRH services in the community and the development of new policies in countries to expand pharmacists’ roles in providing professional pharmacy services. The evidence supports the evolution of pharmacists’ roles in SRH, from traditional product-focused to offering different professional pharmacy services. Given the potential feasibility, users’ acceptability and reach, pharmacists are ideally situated to enhance access to SRH services now and in the future to better meet the needs of the public in areas such as contraception,97 98 medical abortion99 and STBBI treatment and prevention.100
As previously described, most studies focused on specific SRH areas. None of the studies evaluated the delivery of SRH services addressing patient needs in the areas of medical abortion provision, prescribing or referral for intrauterine contraceptive devices and subdermal implants, vaccine education and delivery in pregnant women (eg, tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis vaccine), nutritional advice in pregnant women and screening and treatment for other STI, such as gonorrhoea and syphilis. Studies on community pharmacy delivery of SRH services to lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer/questioning individuals in the community, who may face health disparities mainly related to SRH,101 were not found. These gaps identified may be due in part to our search dates and inclusion criteria. However, these gaps highlight future research opportunities to examine pharmacists’ roles in the delivery of comprehensive SRH services tailored to diverse populations which may better position pharmacists as SRH providers.
We developed the search strategy and set the eligibility criteria to capture evidence from real-life scenarios, which effectively represented what pharmacists may offer to the public. However, this approach may have limited the identification of contributory articles evaluating professional pharmacy SRH services since some studies may have explored this topic using mystery clients or simulated patients. Based on the studies included, we reported challenges and barriers that were highlighted. We considered it relevant to summarise similar reports across different SRH areas. Since we did not include articles focused on attitudes or experiences, the barriers acknowledged in this review may not represent all the barriers reported in the literature. Lastly, deciding to conduct a scoping review was based on the analytical approach which aims to map the data, the broad research question we identified, and the less restrictive inclusion of studies in terms of design and quality. A quality assessment of articles, as typically performed in a systematic review, was not completed. Future work might conduct a quality assessment of studies in this research area by taking the findings from this scoping review as a precursor of a systematic review.
Conclusions
Given that accessibility to SRH services remains an issue in many countries, it is relevant to recognise pharmacists as SRH providers. This scoping review has identified that pharmacists’ roles have expanded beyond traditional product-focused services and the delivery of professional pharmacy services in a number of SRH areas is feasible and highly accepted by users. Still, the available evidence suggests several challenges need to be addressed to position pharmacists as sustainable and affordable providers of SRH services in high-income countries worldwide. Based on identified gaps, studies describing the implementation and evaluating the impact of a full spectrum of professional pharmacy services may promote access to SRH care through community pharmacies and position pharmacists as SRH providers.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
JN acknowledges the National Agency for Research and Development (ANID)/Scholarship program for supporting her research (Master Becas Chile/2018 – 73190318). The authors wish to acknowledge Meghan Sebastianski (PhD) and Diana Keto-Lambert (MLIS) from the Alberta Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research (SPOR) SUPPORT Unit Knowledge Translation Platform for their support with the search strategy and database searches, and Dary Chen for his help during the data extraction stage.
Footnotes
Twitter: @ca_hughes9
Contributors: JN: conceptualisation, methodology, investigation, analysis, writing-original draft. NY and TJS: analysis, writing-review and editing. CAH: conceptualisation, methodology, investigation, analysis, supervision, writing-original draft, review and editing. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information. No additional data available.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not required.
References
- 1.Galati JA. Onward to 2030: sexual and reproductive health and rights in the context of the sustainable development goals. In: Guttmacher Policy Review. 18. Washington, DC: Guttmacher Institute, 2015. https://www.guttmacher.org/sites/default/files/article_files/gpr1807715.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 2.Starrs AM, Ezeh AC, Barker G, et al. Accelerate progress-sexual and reproductive health and rights for all: report of the Guttmacher-Lancet Commission. Lancet 2018;391:2642–92. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30293-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bragazzi NL, Mansour M, Bonsignore A, et al. The role of hospital and community pharmacists in the management of COVID-19: towards an expanded definition of the roles, responsibilities, and duties of the pharmacist. Pharmacy 2020;8. 10.3390/pharmacy8030140. [Epub ahead of print: 07 Aug 2020]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ilardo ML, Speciale A. The community pharmacist: perceived barriers and patient-centered care communication. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020;17:536. 10.3390/ijerph17020536 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Taylor JG, Joubert R. Pharmacist-Led minor ailment programs: a Canadian perspective. Int J Gen Med 2016;9:291–302. 10.2147/IJGM.S99540 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Buss VH, Shield A, Kosari S, et al. The impact of clinical services provided by community pharmacies on the Australian healthcare system: a review of the literature. J Pharm Policy Pract 2018;11:22. 10.1186/s40545-018-0149-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Agomo CO. The role of community pharmacists in public health: a scoping review of the literature. J Pharm Health Serv Res 2012;3:25–33. 10.1111/j.1759-8893.2011.00074.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bates I, Bader LR, Galbraith K. A global survey on trends in advanced practice and specialisation in the pharmacy workforce. Int J Pharm Pract 2020;28:173–81. 10.1111/ijpp.12611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Goode J-V, Owen J, Page A, et al. Community-based pharmacy practice innovation and the role of the community-based pharmacist practitioner in the United States. Pharmacy 2019;7:106. 10.3390/pharmacy7030106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Anderson S. Community pharmacy and public health in Great Britain, 1936 to 2006: how a Phoenix rose from the ashes. J Epidemiol Community Health 2007;61:844–8. 10.1136/jech.2006.055442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.World Health Organization . The legal and regulatory framework for community pharmacies in the WHO European region. Denmark, 2019. Available: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/326394/9789289054249-eng.pdf
- 12.International pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) . Advanced practice and specialization in pharmacy: global report 2015. The Hague 2015. https://www.fip.org/file/1397 [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moullin JC, Sabater-Hernández D, Fernandez-Llimos F, et al. Defining professional pharmacy services in community pharmacy. Res Social Adm Pharm 2013;9:989–95. 10.1016/j.sapharm.2013.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Maderas NM, Landau SC, Taylor-McGhee B. The continuum of care: a case for pharmacists as key members of the reproductive health care team. Contraception 2008;77:139–42. 10.1016/j.contraception.2007.11.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pfaff A, Rafie S. Expanding pharmacy capacity for patient-centered reproductive health services. Pharmacy 2020;8:236. 10.3390/pharmacy8040236 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ribeiro N, Mota-Filipe H, Guerreiro MP, et al. Primary health care policy and vision for community pharmacy and pharmacists in Portugal. Pharm Pract 2020;18:2043. 10.18549/PharmPract.2020.3.2043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hermansyah A, Wulandari L, Kristina SA, et al. Primary health care policy and vision for community pharmacy and pharmacists in Indonesia. Pharm Pract 2020;18:2085. 10.18549/PharmPract.2020.3.2085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Anderson C, Sharma R. Primary health care policy and vision for community pharmacy and pharmacists in England. Pharm Pract 2020;18:1870. 10.18549/PharmPract.2020.1.1870 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rafie S, Stone RH, Wilkinson TA, et al. Role of the community pharmacist in emergency contraception counseling and delivery in the United States: current trends and future prospects. Integr Pharm Res Pract 2017;6:99–108. 10.2147/IPRP.S99541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Department of health and social care . The pharmacy offer for sexual health, reproductive health and HIV. In:. 25. London: Public Health England, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gale A, Watson MC. The provision of current and future sexual health services from community pharmacies in Grampian, Scotland. Int J Clin Pharm 2011;33:183–90. 10.1007/s11096-010-9458-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Anderson C, Blenkinsopp A. Community pharmacy supply of emergency hormonal contraception: a structured literature review of international evidence. Hum Reprod 2006;21:272–84. 10.1093/humrep/dei287 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cleland K, Bass J, Doci F, et al. Access to emergency contraception in the over-the-counter era. Womens Health Issues 2016;26:622–7. 10.1016/j.whi.2016.08.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Italia S, Brand H. Status of emergency contraceptives in Europe one year after the European medicines Agency's recommendation to switch Ulipristal acetate to non-prescription status. Public Health Genomics 2016;19:203–10. 10.1159/000444686 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee R, McCarthy L. Canadian "minor ailments" programs: unanswered questions. Can Pharm J 2015;148:302–4. 10.1177/1715163515611144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sachdev G, Kliethermes MA, Vernon V, et al. Current status of prescriptive authority by pharmacists in the United States. J Am Coll Clin Pharm 2020;3:807–17. 10.1002/jac5.1245 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Houle SKD, Carter CA, Tsuyuki RT, et al. Remunerated patient care services and injections by pharmacists: an international update. J Am Pharm Assoc 2019;59:89–107. 10.1016/j.japh.2018.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sneeringer RK, Billings DL, Ganatra B, et al. Roles of pharmacists in expanding access to safe and effective medical abortion in developing countries: a review of the literature. J Public Health Policy 2012;33:218–29. 10.1057/jphp.2012.11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Deas C, McCree DH. Pharmacists and HIV/AIDS prevention: review of the literature. J Am Pharm Assoc 2010;50:411–5. 10.1331/JAPhA.2010.09039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wood H, Gudka S. Pharmacist-Led screening in sexually transmitted infections: current perspectives. Integr Pharm Res Pract 2018;7:67–82. 10.2147/IPRP.S140426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Eckhaus LM, Ti AJ, Curtis KM, et al. Patient and pharmacist perspectives on pharmacist-prescribed contraception: a systematic review. Contraception 2021;103:66–74. 10.1016/j.contraception.2020.10.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chirewa B, Wakhisi A. Emergency hormonal contraceptive service provision via community pharmacies in the UK: a systematic review of pharmacists' and young women's views, perspectives and experiences. Perspect Public Health 2020;140:108–16. 10.1177/1757913919867356 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Taylor B. Developments in pharmacy-based sexual health services. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 2008;34:143–5. 10.1783/147118908784734747 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chin KL. Sexual/reproductive health and the pharmacist: what is known and what is needed? J Pharm Health Serv Res 2011;2:65–9. 10.1111/j.1759-8893.2011.00050.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gonsalves L, Hindin MJ. Pharmacy provision of sexual and reproductive health commodities to young people: a systematic literature review and synthesis of the evidence. Contraception 2017;95:339–63. 10.1016/j.contraception.2016.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gauly J, Ross J, Hall I, et al. Pharmacy-based sexual health services: a systematic review of experiences and attitudes of pharmacy users and pharmacy staff. Sex Transm Infect 2019;95:488–95. 10.1136/sextrans-2019-054096 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) . Call to action to support pharmacists and pharmacy workers on the coronavirus COVID-19 frontline, 2020. Available: https://www.fip.org/files/content/publications/2020/FIP-call-to-action-to-support-pharmacists-and-pharmacy-workers-on-the-coronavirus-COVID-19-frontline.pdf
- 38.Arksey H, O'Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 2005;8:19–32. 10.1080/1364557032000119616 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Levac D, Colquhoun H, O'Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci 2010;5:69. 10.1186/1748-5908-5-69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med 2018;169:467–73. 10.7326/M18-0850 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hamid H, Masood RA, Tariq H, et al. Current pharmacy practices in low- and middle-income countries; recommendations in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Drugs Ther Perspect 2020:1–3. 10.1007/s40267-020-00745-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brabin L, Thomas G, Hopkins M, et al. Delivery of Chlamydia screening to young women requesting emergency hormonal contraception at pharmacies in Manchester, UK: a prospective study. BMC Womens Health 2009;9:7. 10.1186/1472-6874-9-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Currie MJ, Deeks LS, Cooper GM, et al. Community pharmacy and cash reward: a winning combination for Chlamydia screening? Sex Transm Infect 2013;89:212–6. 10.1136/sextrans-2011-050357 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gudka S, Marshall L, Creagh A, et al. To develop and measure the effectiveness and acceptability of a pharmacy-based Chlamydia screening intervention in Australia. BMJ Open 2013;3:e003338. 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003338 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Parker RM, Bell A, Currie MJ, et al. 'Catching Chlamydia': combining cash incentives and community pharmacy access for increased Chlamydia screening, the view of young people. Aust J Prim Health 2015;21:79–83. 10.1071/PY12135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Anderson C, Thornley T. A pharmacy-based private Chlamydia screening programme: results from the first 2 years of screening and treatment. Int J Clin Pharm 2011;33:88–91. 10.1007/s11096-010-9460-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Baraitser P, Pearce V, Holmes J, et al. Chlamydia testing in community pharmacies: evaluation of a feasibility pilot in South East London. Qual Saf Health Care 2007;16:303–7. 10.1136/qshc.2006.020883 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cameron ST, Glasier A, Muir A, et al. Expedited partner therapy for Chlamydia trachomatis at the community pharmacy. BJOG 2010;117:1074–9. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2010.02573.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.McClure KS, Cameron ST. An audit of expedited treatment for uncomplicated Chlamydia trachomatis index cases at the community pharmacy. Int J STD AIDS 2016;27:1016–8. 10.1177/0956462416633969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Slutsker JS, Tsang L-YB, Schillinger JA. Do prescriptions for expedited partner therapy for Chlamydia get filled? findings from a multi-jurisdictional evaluation, United States, 2017-2019. Sex Transm Dis 2020;47:376–82. 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Havens JP, Scarsi KK, Sayles H, et al. Acceptability and feasibility of a pharmacist-led HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PreP) program in the midwestern United States. Open Forum Infect Dis 2019;6:ofz365. 10.1093/ofid/ofz365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Collins B, Bronson H, Elamin F, et al. The "no wrong door" approach to HIV testing: Results from a statewide retail pharmacy-based HIV testing program in Virginia, 2014-2016. Public Health Rep 2018;133:34S–42. 10.1177/0033354918801026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Crawford ND, Dean T, Rivera AV, et al. Pharmacy intervention to improve HIV testing uptake using a comprehensive health screening approach. Public Health Rep 2016;131 Suppl 1:139–46. 10.1177/00333549161310S116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Darin KM, Klepser ME, Klepser DE, et al. Pharmacist-provided rapid HIV testing in two community pharmacies. J Am Pharm Assoc 2015;55:81–8. 10.1331/JAPhA.2015.14070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fernández-Balbuena S, Belza MJ, Zulaica D, et al. Widening the access to HIV testing: the contribution of three in-pharmacy testing programmes in Spain. PLoS One 2015;10:e0134631. 10.1371/journal.pone.0134631 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Weidle PJ, Lecher S, Botts LW, et al. HIV testing in community pharmacies and retail clinics: a model to expand access to screening for HIV infection. J Am Pharm Assoc 2014;54:486–92. 10.1331/JAPhA.2014.14045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kelly DV, Kielly J, Hughes C, et al. Expanding access to HIV testing through Canadian community pharmacies: findings from the approach study. BMC Public Health 2020;20:639. 10.1186/s12889-020-08719-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Calo WA, Shah PD, Gilkey MB, et al. Implementing pharmacy-located HPV vaccination: findings from pilot projects in five U.S. states. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2019;15:1831–8. 10.1080/21645515.2019.1602433 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Doucette WR, Kent K, Seegmiller L, et al. Feasibility of a coordinated human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination program between a medical clinic and a community pharmacy. Pharmacy 2019;7:91. 10.3390/pharmacy7030091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hohmeier KC, Randolph DD, Smith CT, et al. A multimodal approach to improving human papillomavirus vaccination in a community pharmacy setting. SAGE Open Med 2016;4:205031211668212. 10.1177/2050312116682128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jiménez-Quiñones EM, Melin K, Jiménez-Ramírez FJ. Impact of a pharmacist conducted educational program on human papilloma virus vaccination rates in a low socioeconomic population in the city of Lares, PR. P R Health Sci J 2017;36:67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Navarrete JP, Padilla ME, Castro LP, et al. Development of a community pharmacy human papillomavirus vaccine program for underinsured university students along the United States/Mexico border. J Am Pharm Assoc 2014;54:642–7. 10.1331/JAPhA.2014.13222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Buchanan R, Cooper K, Grellier L, et al. The testing of people with any risk factor for hepatitis C in community pharmacies is cost-effective. J Viral Hepat 2020;27:36–44. 10.1111/jvh.13207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Buchanan R, Hassan-Hicks P, Noble K, et al. Integrating community pharmacy testing for hepatitis C with specialist care. Pharm J 2016;8. 10.1211/PJ.2016.20201549 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Dong BJ, Lopez M, Cocohoba J. Pharmacists performing hepatitis C antibody point-of-care screening in a community pharmacy: a pilot project. J Am Pharm Assoc 2017;57:510–5. 10.1016/j.japh.2017.04.463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Radley A, Melville K, Tait J, et al. A quasi-experimental evaluation of dried blood spot testing through community pharmacies in the Tayside region of Scotland. Frontline Gastroenterol 2017;8:221–8. 10.1136/flgastro-2016-100776 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Radley A, de Bruin M, Inglis SK, et al. Clinical effectiveness of pharmacist-led versus conventionally delivered antiviral treatment for hepatitis C virus in patients receiving opioid substitution therapy: a pragmatic, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;5:809–18. 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30120-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Anderson L, Hartung DM, Middleton L, et al. Pharmacist provision of hormonal contraception in the Oregon Medicaid population. Obstet Gynecol 2019;133:1231–7. 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gardner JS, Downing DF, Blough D, et al. Pharmacist prescribing of hormonal contraceptives: results of the direct access study. J Am Pharm Assoc 2008;48:212–26. 10.1331/JAPhA.2008.07138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lu S, Rafie S, Hamper J, et al. Characterizing pharmacist-prescribed hormonal contraception services and users in California and Oregon pharmacies. Contraception 2019;99:239–43. 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rodriguez MI, Edelman AB, Skye M, et al. Reasons for and experience in obtaining pharmacist prescribed contraception. Contraception 2020;102:259–61. 10.1016/j.contraception.2020.05.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Rodriguez MI, Edelman AB, Skye M, et al. Association of pharmacist prescription with dispensed duration of hormonal contraception. JAMA Netw Open 2020;3:e205252. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.5252 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gibbs SE, Harvey SM, Marie Harvey S. Pharmacist prescription and access to hormonal contraception for Medicaid-insured women in Oregon. Contraception 2020;102:262–6. 10.1016/j.contraception.2020.07.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Heller R, Johnstone A, Cameron ST. The feasibility of contraceptive injections at the community pharmacy. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care 2017;22:327–33. 10.1080/13625187.2017.1357808 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Monastersky Maderas NJ, Landau SC. Pharmacy and clinic partnerships to expand access to injectable contraception. J Am Pharm Assoc 2007;47:527–31. 10.1331/JAPhA.2007.06112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Picardo C, Ferreri S. Pharmacist-administered subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Contraception 2010;82:160–7. 10.1016/j.contraception.2010.01.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mantzourani E, Hodson K, Evans A, et al. A 5-year evaluation of the emergency contraception enhanced community pharmacy service provided in Wales. BMJ Sex Reprod Health 2019;45:275–82. 10.1136/bmjsrh-2018-200236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Turnbull G, Scott RH, Mann S. Accessing emergency contraception pills from pharmacies: the experience of young women in London. BMJ Sex Reprod Health 2020:23. 10.1136/bmjsrh-2019-200339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Michie L, Cameron ST, Glasier A, et al. Pharmacy-based interventions for initiating effective contraception following the use of emergency contraception: a pilot study. Contraception 2014;90:447–53. 10.1016/j.contraception.2014.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.DiPietro Mager NA, Bright DR, Markus D, et al. Use of targeted medication reviews to deliver preconception care: a demonstration project. J Am Pharm Assoc 2017;57:90–4. 10.1016/j.japh.2016.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Truong MB-T, Ngo E, Ariansen H, et al. Community pharmacist counseling in early pregnancy-results from the SafeStart feasibility study. PLoS One 2019;14:e0219424–14. 10.1371/journal.pone.0219424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Martin Morales A, Hatzichristou D, Ramon Lladós J, et al. Community pharmacy detection of erectile dysfunction in men with risk factors or who seek treatment or advice but lack a valid prescription. J Sex Med 2013;10:2303–11. 10.1111/jsm.12238 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Leichliter JS, Dittus PJ, Copen CE, et al. Trends in factors indicating increased risk for STI among key subpopulations in the United States, 2002-2015. Sex Transm Infect 2020;96:121–3. 10.1136/sextrans-2019-054045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.McMillan SS, Wheeler AJ, Sav A, et al. Community pharmacy in Australia: a health hub destination of the future. Res Social Adm Pharm 2013;9:863–75. 10.1016/j.sapharm.2012.11.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Church K, Gassner J, Elliott M. Reproductive health under COVID-19 - challenges of responding in a global crisis. Sex Reprod Health Matters 2020;28:1–3. 10.1080/26410397.2020.1773163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hussein J. COVID-19: what implications for sexual and reproductive health and rights globally? Sex Reprod Health Matters 2020;28:1746065. 10.1080/26410397.2020.1746065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Tang K, Gaoshan J, Ahonsi B, et al. Sexual and reproductive health (SRH): a key issue in the emergency response to the coronavirus disease (COVID- 19) outbreak. Reprod Health 2020;17:59. 10.1186/s12978-020-0900-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Desai S, Samari G. COVID-19 and immigrants' access to sexual and reproductive health services in the United States. Perspect Sex Reprod Health 2020;52:69–73. 10.1363/psrh.12150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lindberg LD, Bell DL, Kantor LM. The sexual and reproductive health of adolescents and young adults during the COVID ‐19 pandemic. Perspect Sex Reprod Health 2020;52:75–9. 10.1363/psrh.12151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Tak CR, Kessler LT, Scott MA, et al. Pharmacist-prescribed hormonal contraception: a review of the current landscape. J Am Pharm Assoc 2019;59:633–41. 10.1016/j.japh.2019.05.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Stone RH, Rafie S, Ernest D, et al. Emergency contraception access and counseling in urban pharmacies: a comparison between states with and without pharmacist prescribing. Pharmacy 2020;8:105. 10.3390/pharmacy8020105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Chaumont A, Foster AM. The not so over-the-counter status of emergency contraception in Ontario: a mixed methods study with pharmacists. FACETS 2017;2:429–39. 10.1139/facets-2017-0024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wong K, Hum S, McCarthy L, et al. Beyond plan B: a qualitative study of Canadian pharmacists' emergency contraception counselling practices. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2017;39:1021–7. 10.1016/j.jogc.2017.04.042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Buss VH, Deeks LS, Shield A, et al. Analytical quality and effectiveness of point-of-care testing in community pharmacies: a systematic literature review. Res Social Adm Pharm 2019;15:483–95. 10.1016/j.sapharm.2018.07.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Weber NC, Klepser ME, Akers JM, et al. Use of CLIA-waived point-of-care tests for infectious diseases in community pharmacies in the United States. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2016;16:253–64. 10.1586/14737159.2015.1116388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kehrer JP, James DE. The role of pharmacists and pharmacy education in point-of-care testing. Am J Pharm Educ 2016;80:129–8. 10.5688/ajpe808129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Black A, Costescu D, Guilbert E. Contraception consensus: updated guidance during pandemics and periods of social disruption, 2020. Available: https://sogc.org/common/Uploaded%20files/2020-04%20Contraception%20Consensus%20-%20Final%20Submitted.pdf
- 98.Action Canada for Sexual Health & Rights . Prioritizing the neglected areas of SRHR in Canada’s global COVID-19 response, 2020. Available: https://www.actioncanadashr.org/resources/policy-briefs-submissions/2020-04-15-prioritizing-neglected-areas-srhr-canadas-global-covid-19-response [Accessed 11 Oct 2020].
- 99.Costescu D, Guilbert E, Wagner M-S, et al. Induced abortion: updated guidance during pandemics and periods of social disruption, 2020. Available: https://sogc.org/common/Uploaded%20files/Induced%20Abortion%20-%20Pandemic%20Guidance%20-%20FINAL.PDF
- 100.Cohen MA, Powell AM, Coleman JS, et al. Special ambulatory gynecologic considerations in the era of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and implications for future practice. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2020;223:372–8. 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Maxwell E, Salch S, Boliko M, et al. Discrepancies in lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender patient care and how pharmacists can support an evolved practice. Am J Pharm Educ 2017;81:4. 10.5688/ajpe8176181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2020-047034supp001.pdf (1.3MB, pdf)
bmjopen-2020-047034supp002.pdf (89.6KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2020-047034supp003.pdf (163.6KB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information. No additional data available.