Abstract
背景与目的
肺癌是临床上最为常见的恶性肿瘤,晚期患者预后差,5年生存率低,因此早期诊断成为提高患者预后的关键。近年来随着分子生物学技术的发展,一些关键驱动基因的异常修饰如甲基化成为肺癌早期诊断的重要方法。本研究旨在采用循证医学方法量化评价矮小同源盒基因(short stature homeobox 2, SHOX2)启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺癌价值。
方法
系统检索MEDLINE、EMBASE、Ovid、Web of Science、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)中涉及SHOX2基因启动子区域甲基化与肺癌关系的相关文献,并根据纳入与排除标准进行文献筛选。提取原始研究中SHOX2启动子甲基化相关数据,计算以SHOX2启动子甲基化为参考诊断肺癌的敏感性、特异性及受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)下面积。
结果
最终纳入本次meta分析的文献13篇,各项研究间存在明显的统计学异质性(P < 0.05),数据合并均采用随机效应模型。SHOX2基因启动子甲基化诊断肺癌的敏感性为0.75(95%CI: 0.74-0.77)、特异性为0.89(95%CI: 0.88-0.91);阳性预测值为6.75(4.56-9.99),阴性预测值为0.36(0.25-0.52);诊断优势比为23.16(11.34-47.31),ROC曲线下面积为0.9。
结论
SHOX2基因启动子高甲基化在肺癌患者血清、支气管灌洗液和胸腔积液中发生率均较高,可作为辅助诊断肺癌的生物学标志物。
Keywords: 肺肿瘤, SHOX2基因, 启动子, 甲基化, Meta分析
Abstract
Background and objective
Lung cancer is the most common malignant tumor in clinic. The prognosis of advanced patients is poor, and the 5-year survival rate is low. Therefore, early diagnosis becomes the key to improve the prognosis of patients. In recent years, with the development of molecular biology technology, aberrant modification of some driver genes, such as methylation, has become an important method for early diagnosis of lung cancer. The purpose of the present work was to quantitatively evaluate the diagnostic value of abnormal hypermethylation in short state homeobox 2 (SHOX2) promoter region in lung cancer by evidence-based medicine.
Methods
We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Ovid, Web of Science and CNKI for literatures related to the relationship between SHOX2 gene promoter hypermethylation and lung cancer. The data of SHOX2 promoter hymethylation in the original study were extracted. The diagnostic sensitivity, specificity and area under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of SHOX2 promoter methylation were calculated.
Results
Finally, 13 publications were included in this meta-analysis, and due to significant statistical heterogeneity among the studies (P < 0.05) the data was pooled by random effect model. The diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of SHOX2 promoter hypermethylation in the diagnosis of lung cancer were 0.75 (95%CI: 0.74-0.77) and 0.89 (95%CI: 0.88-0.91), respectively; The positive likelihood ratio value was 6.75 (4.56-9.99), and the negative predictive value was 0.36 (0.25-0.52); The diagnostic odds ratio was 23.16 (11.34-47.31), and the area under the ROC curve was 0.9.
Conclusion
SHOX2 gene promoter hypermethylation is high in serum, broncholavage fluid and pleural effusion of lung cancer patients, which can be used as a biomarker for auxiliary diagnosis of lung cancer.
Keywords: Lung neoplasms, SHOX2 gene, Promoter, Methylation, Meta-analysis
肺癌是临床上最为常见的恶性肿瘤,也是男性恶性肿瘤死亡的第一位。流行病学数据[1]显示,2021年北美预测肺癌新发病例为235, 760例,死亡131, 880例。肺癌已成为发病率和死亡率最高的恶性肿瘤[2]。早期肺癌患者进行以手术为主的综合治疗预后较好,而晚期肺癌预后差,5年生存率低。因此,对肺癌进行早期准确的诊断十分重要[3]。
矮小同源框2(short stature homeobox 2, SHOX2)也称为同源框蛋白Og12X或配对相关同源框蛋白SHOT基因,SHOX2基因编码的蛋白是同源框基因家族的一员,该家族编码含有代表DNA结合域的60个氨基酸残基。同源框蛋白被认为在生物体内广泛表达的转录调节因子,具有复杂的生物功能。近年来有研究[4]报道,SHOX2基因启动子区域异常高甲基化与肺癌的发生发展有关,该基因异常高甲基化可能发生在肺癌早期并与高甲基化后该基因的失活有关。陆续有研究报道了SHOX2基因启动子高甲基化发生频率在肺癌患者与正常对照人群的发生情况;有研究[4]显示,肺癌患者血清等组织中SHOX2基因启动子高甲基化发生率高于对照组人群。但关于SHOX2基因启动子高甲基化作为肺癌患者诊断生物学标志物的可行性研究鲜有道报。本研究采用循证医学的方法量化评价SHOX2启动子区域甲基化诊断肺癌价值。
1. 材料与方法
1.1. 文献检索
系统检索Medline、EMBASE、Ovid、Web of Science、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)中涉及SHOX2基因启动子区域甲基化与肺癌关系的相关文献,检索语种为英语和汉语。以“SHOX2”、“Short stature homeobox 2”、“OG12”、“SHOT”、“OG12X”、“non-small cell lung cancer”、“lung cancer”、“lung neoplasm”为自由词,检索Medline、EMBASE、Ovid、Web of Science等英文数据库;以“肺癌”、“肺肿瘤”、“非小细胞”、“矮小同源盒基因基因”、“SHOX2”为关键词或题名检索CNKI中文数据库。同时,我们对已纳入的研究的参考文献进行进一步评估,以发现可能符合要求的研究。
1.2. 入选标准
① 研究设计:临床病例对照、队列研究或观察性研究;②研究对象:肺癌患者经病理学或细胞学明确确诊;③检测方法:组织标本中SHOX2基因启动子甲基化水平采用甲基化特异性PCR(methylation specific PCR, MSP)方法检测;④结果:原始研究中给出或可间接计算出肺癌患者和对照患者各个组织标本中的SHOX2基因启动子甲基化频率。
1.3. 数据提取
两位研究者刘强、王帅对纳入的原始研究进行分别阅读提取数据和基本信息,提取的内容包括:纳入研究的一般情况,包括第一作者、国家、发表时间、杂志名称;纳入研究的基本特征,包括原始研究中肺癌患者及对照组的人种、样本量、甲基化检测方法;原始研究结果部分指标,包括原始研究中给出或可间接计算出肺癌患者和对照患者各个组织标本中的SHOX2基因启动子甲基化频率。
1.4. 文献质量评价
以观察性流行病学研究报告规范(strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology, STROBE)中所列举出的必需项目清单为标准,依次对纳入研究的题目、摘要、前言、方法、结果、讨论6个部分22个项目进行质量评价,每个项目1分,满分为22分。
1.5. 统计学方法
数据采用meta-DiSc1.4(http://www.biomedsearch.com)统计软件进行分析。在汇集数据之前各个研究间的统计学异质性采用I2检验,当I2 > 50%时,认为存在统计学异质性采用随机效应模型,反之采用固定效应模型进行数据合并,P < 0.05为存在统计学差异。
2. 结果
2.1. 检索结果
检索相关数据库初步获得868篇相关文献,首先经过查重,剔除重复发表文献44篇,通过阅读标题和摘要剔除明显不符合要求文献800篇,最后通过阅读全文剔除不符合要求的文献11篇,最终纳入本次meta分析的文献13篇[5-17](图 1),13篇文献的基本情况见表 1。
图 1.
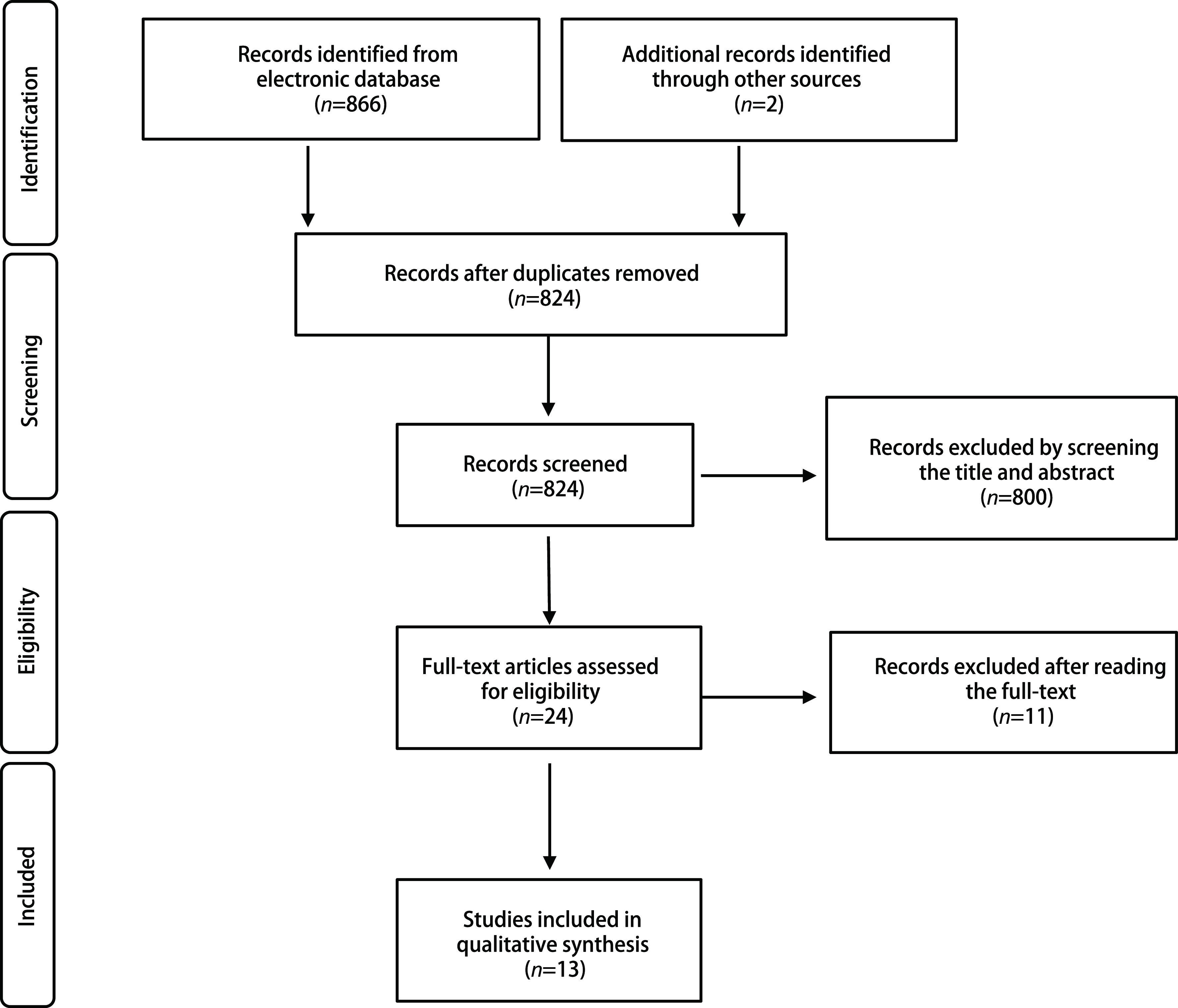
文献检索及纳入与排除相关研究流程图
Flow chart of literature retrieval according to inclusion and exclusion criteria
表 1.
纳入研究的基本特征
General characteristics of the included studies
| Author | Time | Sample size | Cancer | Control | TNM | Tissue | Country | STROBE |
| (M+/M-) | (M+/M-) | |||||||
| BLAF: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; NA: not available; M+/M-: methylation positive/methylation negative; TNM: tumor node metastasis; STROBE: strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology. | ||||||||
| Wang N[5] | 2018 | 120 | 57/23 | 1/39 | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | Serum | China | 9 |
| Rong QP[6] | 2018 | 48 | 18/20 | 2/8 | Ⅲ/Ⅳ | Serum | China | 11 |
| Zhang YM[7] | 2016 | 277 | 98/32 | 34/113 | NA | BLAF | China | 9 |
| Ren M[8] | 2017 | 253 | 79/44 | 10/120 | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | BLAF | China | 14 |
| Schmidt B[9] | 2010 | 523 | 190/91 | 12/230 | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | BLAF | German | 12 |
| Kneip C[10] | 2011 | 343 | 112/76 | 16/139 | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | Serum | German | 14 |
| Dietrich D[11] | 2012 | 204 | 78/22 | 4/100 | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | BLAF | German | 13 |
| Konecny M[12] | 2016 | 63 | 31/6 | 4/22 | NA | BLAF | German | 11 |
| Konecny M[12] | 2016 | 59 | 20/11 | 6/22 | NA | Serum | German | 13 |
| Wang CH[13] | 2016 | 243 | 79/44 | 8/112 | NA | BLAF | China | 8 |
| Ilse P[14] | 2014 | 118 | 48/27 | 1/42 | NA | BLAF | German | 12 |
| Dietrich D[15] | 2013 | 114 | 7/51 | 0/56 | NA | Pleural effusion | German | 14 |
| Li SF[16] | 2014 | 47 | 10/18 | 0/9 | NA | Pleural effusion | China | 10 |
| Ilse P[17] | 2013 | 719 | 138/138 | 70/373 | NA | Pleural effusion | German | 13 |
表 2.
纳入各个研究中真阳性、假阳性、假阴性和真阴性数据分布情况
The TP, FP, FN and TN distribution of the include studies
| Author | Time | Sample size | TP | FP | FN | TN |
| TP: true positive; FP: false positive; FN: false negative; TN: true negative. | ||||||
| Wang N[5] | 2018 | 120 | 57 | 1 | 23 | 39 |
| Rong QP[6] | 2018 | 48 | 18 | 2 | 20 | 8 |
| Zhang YM[7] | 2016 | 277 | 982 | 34 | 32 | 113 |
| Ren M[8] | 2017 | 253 | 79 | 10 | 44 | 120 |
| Schmidt B[9] | 2010 | 523 | 190 | 12 | 91 | 230 |
| Kneip C[10] | 2011 | 343 | 112 | 16 | 76 | 139 |
| Dietrich D[11] | 2012 | 204 | 78 | 4 | 22 | 100 |
| Konecny M[12] | 2016 | 63 | 31 | 4 | 6 | 22 |
| Konecny M[12] | 2016 | 59 | 20 | 6 | 11 | 22 |
| Wang CH[13] | 2016 | 243 | 79 | 8 | 44 | 112 |
| Ilse P[14] | 2014 | 118 | 48 | 1 | 27 | 42 |
| Dietrich D[15] | 2013 | 114 | 7 | 0 | 51 | 56 |
| Li SF[16] | 2014 | 47 | 10 | 0 | 18 | 9 |
| Ilse P[17] | 2013 | 719 | 138 | 70 | 138 | 373 |
2.2. 异质性检验
SHOX2基因启动子高甲基化诊断肺癌的敏感性、特异性、阳性预测值、阴性预测值及诊断优势为效应指标行统计学异质性检验,均存在统计学异质性(P < 0.05),数据合并均采用随机效应模型。
2.3. Meta分析
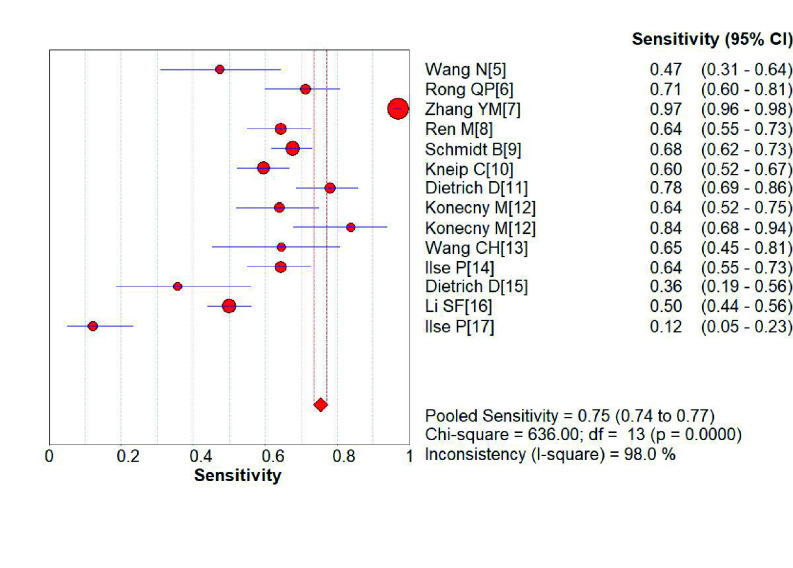
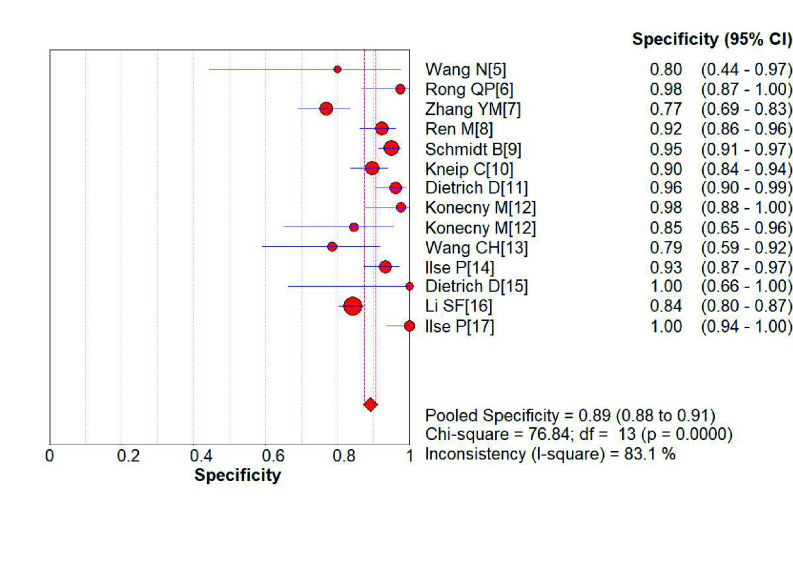
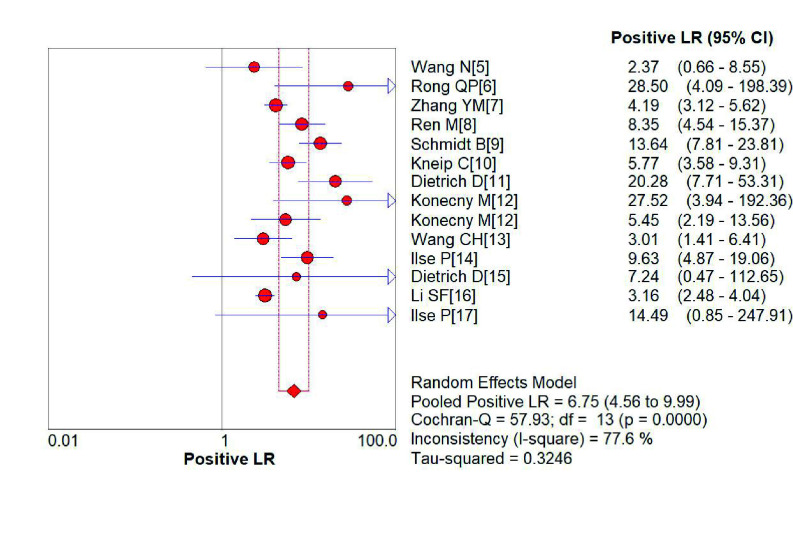
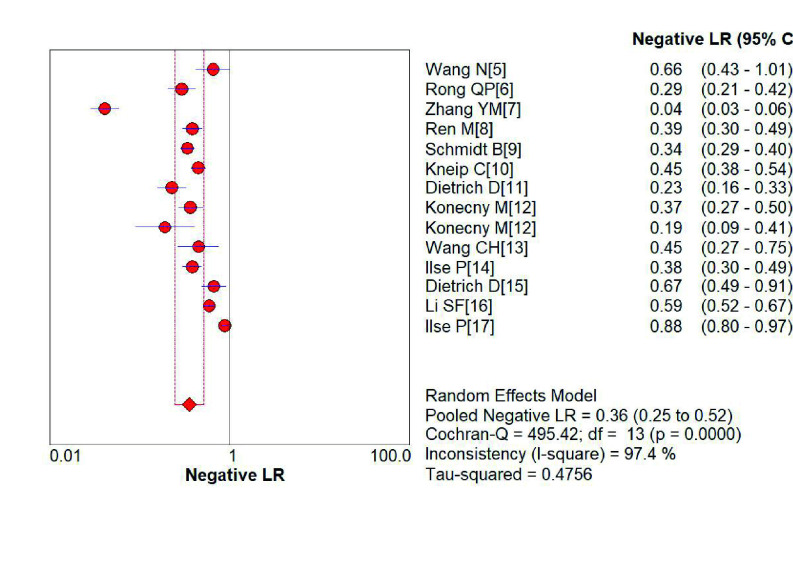
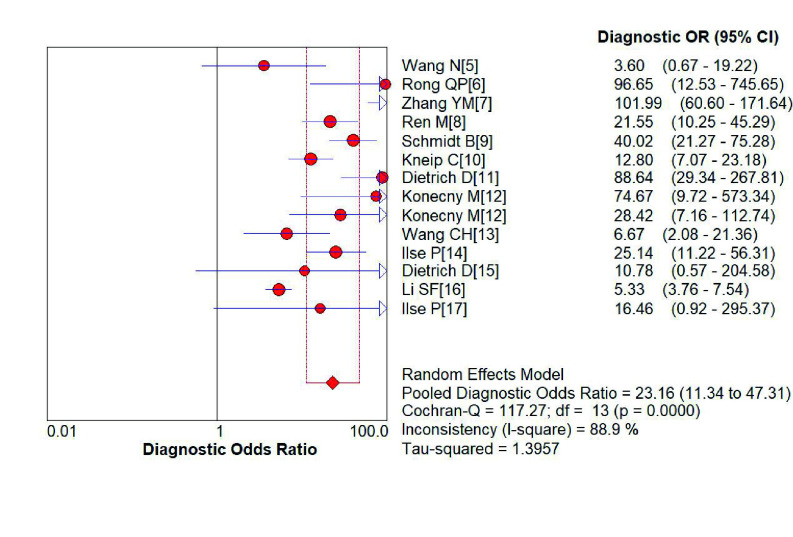
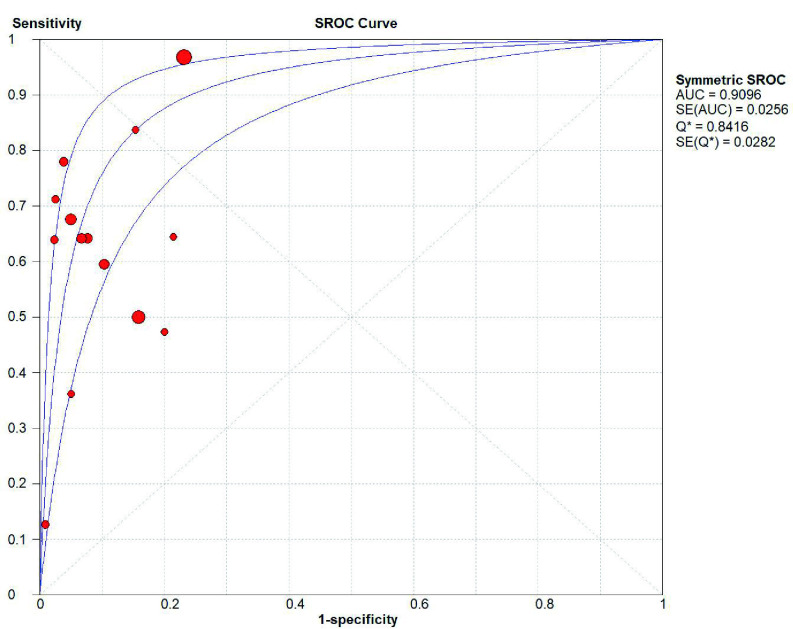
SHOX2基因启动子高甲基化诊断肺癌的敏感性为0.75(95%CI: 0.74-0.77)(图 2)、特异性分别为0.89(95%CI: 0.88-0.91)(图 3);阳性预测值为6.75(4.56-9.99)(图 4),阴性预测值为0.36(0.25-0.52)(图 5);诊断优势比为23.16(11.34-47.31)(图 6),受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)下面积为0.91(图 7)。根据检测换组织标本的不同,进行了亚组分析,具体见表 3。
图 2.
SHOX2基因启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺癌敏感性的森林图
Forest plot of SHOX2 gene hypermethylation for lung cancer diagnostic sensitivity
图 3.
SHOX2基因启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺癌特异性的森林图
Forest plot of SHOX2 gene hypermethylation for lung cancer diagnostic specificity
图 4.
SHOX2基因启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺阳性预测值性的森林图
Forest plot of SHOX2 gene hypermethylation for lung cancer diagnostic positive likelihood ratio
图 5.
SHOX2基因启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺阴性预测值性的森林图
Forest plot of SHOX2 gene hypermethylation for lung cancer diagnostic negative likelihood ratio
图 6.
SHOX2基因启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺诊断优势比的森林图
Forest plot of SHOX2 gene hypermethylation for lung cancer diagnostic odds ratio
图 7.
SHOX2基因甲基化诊断肺癌的ROC曲线
Summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of SHOX2 gene hypermethylation for lung cancer diagnosis
表 3.
SHOX2启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺癌价值的亚组分析
Subgroup analysis of SHOX2 gene hypermethylation for lung cancer
| Group | SEN | SPE | +LR | -LR | DOR | AUC |
| SEN: sensitivity; SPE: specificity; +LR: positive likelihood ratio; -LR: negative likelihood ratio; DOR: diagnostic odds ratio; AUC: area under ROC curve; SHOX2; short stature homeobox 2; ROC: receiver operating characteristic. | ||||||
| Serum | 0.61 (0.56-0.67) | 0.89 (0.85-0.93) | 4.73 (2.26-9.90) | 0.44 (0.33-0.59) | 11.37 (4.33-29.84) | 0.62 |
| BLAF | 0.85 (0.83-0.86) | 0.91 (0.89-0.93) | 9.12 (5.39-15.46) | 0.23 (0.14-0.39) | 44.62 (25.31-78.65) | 0.94 |
| Pleural effusion | 0.43 (0.38-0.48) | 0.86 (0.83-0.89) | 3.22 (2.53-4.11) | 0.71 (0.48-1.04) | 5.47 (3.88-7.70) | 0.70 |
3. 讨论
本研究通过循证医学方法量化分析了SHOX2启动子区域甲基化诊断肺癌的价值。结果共纳入了13项研究,显示SHOX2基因启动子甲基化诊断肺癌的敏感性为0.75(95%CI: 0.74-0.77)、特异性为0.89(95%CI: 0.88-0.91);阳性预测值为6.75(4.56-9.99),阴性预测值为0.36(0.25-0.52);诊断优势比为23.16(11.34-47.31),ROC曲线下面积为0.9。我们的研究结果提示,SHOX2基因启动子甲基化在肺癌患者血清、支气管灌洗液和胸腔积液等体液中的发生率均较高,可作为辅助诊断肺癌的生物学标志物。
肺癌是目前世界上最常见的恶性肿瘤[18]。迄今,用于肺癌早期诊断和筛查的有效和廉价的方法较少[19]。虽然组织学和细胞学检查是诊断肺癌的金标准,但确诊时患者往往处于晚期。因此,迫切需要新的诊断方法来提高早期诊断率,提高确诊率,降低死亡率。SHOX2基因甲基化分析被认为是一个具有广泛临床应用前景的诊断方法[4]。SHOX2基因甲基化检测,与组织学、细胞学检测及影像诊断相结合可提高肺癌的确诊率,并有可能成为早期诊断的有效工具。SHOX2是同源框基因家族的一员,该家族编码含有60个氨基酸残基的蛋白。同源异型盒基因作为转录调节因子广泛存在于无脊椎动物和脊椎动物中[20]。近年来,越来越多的研究关注SHOX2基因启动子甲基化在肺癌早期诊断中的价值。然而,SHOX2基因启动子甲基化在肺癌发生、发展中的生物学意义目前仍未完全阐明。大多数研究[20, 21]认为,SHOX2基因被证实是多种癌症信号通路的调控子或效应子,可促进肿瘤的发生和发展。SHOX2基因甲基化检测在肺癌的发生、发展、转移、耐药和复发过程中起重要作用。SHOX2基因甲基化检测联合影像学等其他诊断学方法被认为是筛查和监测肺癌的一种很好的方法,具有较高的敏感性和特异性。
在本研究中,我们对SHOX2基因启动子高甲基化作为肺癌辅助诊断生物学标志物的价值进行了量化评价,研究认为SHOX2基因启动子诊断肺癌的敏感性和特异性均较高,可作为辅助诊断标志物。但研究本身也存在一定的局限性,首先该meta分析仅纳入13项符合要求的原始研究,样本量相对较小,统计学效能不高;其次,只纳入了发表语言为英文和中文的文献,其他语言发表的文献未进行筛选和纳入;第三,诊断的敏感性、特异性及ROC曲线下面积等指标均存在统计学异质性,采用了随机效应模型。因此,后续应及时对发表的文献进行更新检索,并纳入更多符合要求的相关研究,对SHOX2启动子区域异常高甲基化诊断肺癌价值进行进一步的评估,提供更为充分有力的循证医学证据。同时,单纯依靠检测SHOX2基因启动子甲基化作为肺癌诊断标准,其临床应用价值有限,应结合其他影像学等诊断方法进行综合判断,提高诊断准确性。
Footnotes
【Competing interests】The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author contributions
Liu Q and Huang YQ conceived and designed the study. Liu Q and Wang S performed the experiments. Liu Q, Pei GT and Yang YS analyzed the data. Liu Q, Wang S, and Yang YS contributed analysis tools. Liu Q, Wang S, Pei GT, Yang YS and Huang YQ provided critical inputs on design, analysis, and interpretation of the study. All the authors had access to the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer. 2021 doi: 10.1002/ijc.33588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guan YZ, Ren M, Guo DL, et al. Research progress on lung cancer screening. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020;23(11):954–960. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.101.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; 管 雅喆, 任 萌, 郭 冬利, et al. 肺癌筛查研究进展. 中国肺癌杂志. 2020;23(11):954–960. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.101.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Song L, Yu H, Li Y. Diagnosis of lung cancer by SHOX2 gene methylation assay. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015;19(3):159–167. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wang N, Li ZL, Xie X, et al. Analysis of the SHOX2 gene methylation by droplet digital PCR in plasma from patients with lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2018;25(17):1241–1246. [Google Scholar]; 王 南, 李 卓伦, 谢 昕, et al. 肺癌患者血浆SHOX2基因甲基化微滴数字PCR检测临床意义. 中华肿瘤防治杂志. 2018;25(17):1241–1246. doi: 10.16073/j.cnki.cjcpt.2018.17.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rong QP. Diagnostic significance and clinical features of Shox2 gene methylation in non-small cell lung cancer. Guangdong: Guangdong Medical College, 2016.; 容秋萍. 非小细胞肺癌SHOX2基因甲基化的诊断意义及其临床特征. 广东: 广东医学院, 2016.
- 7.Zhang YM, Wang ML, Wu J, et al. Combined detection of SHOX2 and RASSF1A gene methylation in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of lung cancer. Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi. 2016;22(12):1032–1036. [Google Scholar]; 张 毅敏, 王 明丽, 吴 杰, et al. 肺泡灌洗液中SHOX2和RASSF1A基因甲基化联合检测对肺癌的诊断价值. 肿瘤学杂志. 2016;22(12):1032–1036. doi: 10.11735/j.issn.1671-170X.2016.12.B010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ren M, Wang C, Sheng D, et al. Methylation analysis of SHOX2 and RASSF1A in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for early lung cancer diagnosis. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017;27:57–61. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schmidt B, Liebenberg V, Dietrich D, et al. SHOX2 DNA methylation is a biomarker for the diagnosis of lung cancer based on bronchial aspirates. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:600. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kneip C, Schmidt B, Seegebarth A, et al. SHOX2 DNA methylation is a biomarker for the diagnosis of lung cancer in plasma. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6(10):1632–1638. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318220ef9a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dietrich D, Kneip C, Raji O, et al. Performance evaluation of the DNA methylation biomarker SHOX2 for the aid in diagnosis of lung cancer based on the analysis of bronchial aspirates. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(3):825–832. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Konecny M, Markus J, Waczulikova I, et al. The value of SHOX2 methylation test in peripheral blood samples used for the differential diagnosis of lung cancer and other lung disorders. Neoplasma. 2016;63(2):246–253. doi: 10.4149/210_150419N208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang CH. Detection of Shox2 and RASSF1A methylation in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the diagnosis of lung cancer. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017.; 王春华. 支气管肺泡灌洗液SHOX2、RASSF1A甲基化检测在肺癌诊断中的研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.
- 14.Ilse P, Biesterfeld S, Pomjanski N, et al. SHOX2 DNA methylation is a tumour marker in pleural effusions. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2013;10(5):217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dietrich D, Jung M, Puetzer S, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of SHOX2 and SEPT9 DNA methylation and cytology in benign, paramalignant and malignant pleural effusions. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li SF. Relations pleural effusion SHOX2 gene methylation and lung cancer. Yi Yao Yu Bao Jian. 2014;22(2):3–6. [Google Scholar]; 栗 少飞. 胸水中SHOX2基因甲基化程度与肺癌的关系. 医药与保健. 2014;22(2):3–6. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ilse P, Biesterfeld S, Pomjanski N, et al. Analysis of SHOX2 methylation as an aid to cytology in lung cancer diagnosis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2014;11(5):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(3):145–164. doi: 10.3322/caac.21601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fu F, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, et al. Lung cancer screening strategy for non-high-risk individuals: a narrative review. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021;10(1):452–461. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li N, Zeng Y, Huang J. Signaling pathways and clinical application of RASSF1A and SHOX2 in lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020;146(6):1379–1393. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03188-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hu W, Xin Y, Zhao Y, et al. Shox2: The role in differentiation and development of cardiac conduction system. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018;244(3):177–186. doi: 10.1620/tjem.244.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]