Abstract
Background
Analgesia and sedation therapy are commonly used for critically ill patients, especially mechanically ventilated patients. From the initial nonsedation programs to deep sedation and then to on-demand sedation, the understanding of sedation therapy continues to deepen. However, according to different patient’s condition, understanding the individual patient’s depth of sedation needs remains unclear.
Methods
The public open source critical illness database Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III was used in this study. Latent profile analysis was used as a clustering method to classify mechanically ventilated patients based on 36 variables. Principal component analysis dimensionality reduction was used to select the most influential variables. The ROC curve was used to evaluate the classification accuracy of the model.
Results
Based on 36 characteristic variables, we divided patients undergoing mechanical ventilation and sedation and analgesia into two categories with different mortality rates, then further reduced the dimensionality of the data and obtained the 9 variables that had the greatest impact on classification, most of which were ventilator parameters. According to the Richmond-ASS scores, the two phenotypes of patients had different degrees of sedation and analgesia, and the corresponding ventilator parameters were also significantly different. We divided the validation cohort into three different levels of sedation, revealing that patients with high ventilator conditions needed a deeper level of sedation, while patients with low ventilator conditions required reduction in the depth of sedation as soon as possible to promote recovery and avoid reinjury.
Conclusion
Through latent profile analysis and dimensionality reduction, we divided patients treated with mechanical ventilation and sedation and analgesia into two categories with different mortalities and obtained 9 variables that had the greatest impact on classification, which revealed that the depth of sedation was limited by the condition of the respiratory system.
Keywords: Mechanical ventilation, Clustering, Sedation and analgesia, Latent profile analysis, ICU
Background
The use and development of critical care medicine aims to provide comprehensive and effective life support for nonterminal critical patients with multiple organ dysfunction to save the patients’ lives and recover their quality of life to the greatest extent. After entering the ICU, the patients suffer obvious discomfort and pain due to the disease itself, such as hypoxia, shock, high fever, and surgery. In addition, since they lack a complete understanding of the disease status, treatment plan and prognosis, coupled with the various examinations, treatment measures and noisy medical environments, patients in the ICU can easily become anxious, irritable, painful and even delirious. This state not only causes tremendous pressure on the patient’s mental state but also leads to changes in the patient’s physiological state, even increasing the burden of related organ functions and worsening the condition in severe cases.
Analgesia and sedation therapy refer specifically to the application of medications to eliminate pain, relieve anxiety and restlessness, hypnotize and induce antegrade amnesia. Timely and dynamic assessments of the patients' anxiety, pain, and delirium, the provision of appropriate treatment based on disease state and diagnosis, and the delivery of appropriate analgesic and sedative medications have become the cornerstone for the smooth implementation of all other treatments in the ICU [1–3].
Currently recognized sedation treatment plans are based on analgesia; that is, the pain is evaluated first, and after appropriate treatment, a decision is made regarding the use of sedative drugs according to the patient’s needs.
However, Shehabi et al. found that many patients were deeply sedated within 48 h after entering the ICU, which constitutes an independent risk factor for prolonged mechanical ventilation and increased mortality in mechanically ventilated patients [4, 5]. Therefore, providing deep sedation to mechanically ventilated patients without evaluation and analysis, whether or not it is early in the patient’s care, may worsen the patient's condition, which of course we cannot see clearly.
For patients with severe lung disease, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or spontaneously deep breathing, which leads to an increase in transpulmonary pressure, leading to lung injury, it is also unreasonable to administer light sedation. Instead, deeper sedation may be required to control the drastic changes in transpulmonary pressure to better protect the lungs.
Judging from the historical evolution of analgesia and sedation, the general consensus is to give on-demand sedation treatment to patients on mechanical ventilation in the ICU. From the initial plan involving no sedation to deep sedation and then to on-demand sedation, the understanding of sedation therapy continues to deepen. However, according to different patient’s condition, understanding the individual patient’s depth of sedation needs remains unclear. In this study, we used machine learning methods to identify patients who had received mechanical ventilation and undergone analgesia and sedation treatment into clinical subtypes and analyzed clinical features that affect the classification in an attempt to find a standard that determines the depth of sedation treatment needs for the patients.
Methods
An overview of the primary analysis plan is outlined in Fig. 1. Briefly, latent profile analysis (LPA) was conducted on the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC III) dataset, and the resultant phenotypes based on 36 variables served as the standard for developing stepwise logistic regression variable selection. The dataset was split into a training dataset (80%) and a verification dataset (20%). To reduce the number of variables and simplify the model, principal component analysis (PCA) dimensionality reduction was used for selecting important variables. The most important variables were, in turn, used to develop stepwise logistic regression classifier models. The models were compared with other machine-learning models in terms of comprehensive model performance to verify the optimal model. The model-derived phenotypes were generated and analyzed.
Fig. 1.
Overview of the primary analysis plan
Dataset
The MIMIC-III dataset is a large, freely available database comprising deidentified health-related data associated with over forty thousand patients who stayed in the critical care units of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center between 2001 and 2012. The database includes information such as demographics, vital sign measurements made at the bedside, laboratory test results, procedures, medications, caregiver notes, imaging reports, and mortality [6, 7].
This study used the data from a total of 5935 adults from the MIMIC III database who had received mechanical ventilation and were administered sedative analgesics during their ICU stay. The enrolled patients’ data were extracted from the MIMIC-III database according to the following criteria:
Mechanically ventilated patients: patients with a non-null value for the positive expiratory end pressure (PEEP) were included.
Use of sedative and analgesic drugs: Considering the real data available in the database and clinical experiences, we selected five sedative or analgesic drugs, fentanyl, midazolam, morphine, propofol, and dexmedetomidine. Patients who had used one of them (that is, the corresponding dose value was not empty) were included in the study cohort.
Statistical methods
In total of 36 candidate feature variables associated with mechanical ventilation were selected for statistical analysis, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Thirty-six feature variables and classifications related to mechanical ventilation
| Demographic characteristics and scores | Age, SAPS II, SOFA scores, Richmond-ASS scores |
| Laboratory values | White blood cell (WBC), Hemoglobin (Hb), Hematocrit, Platelet, Urea Nitrogen (BUN), pH, pO2, pCO2, Bicarbonate (HCO3−), Lactate (Lac), Potassium (K), Sodium (Na), Chlorine (Cl), Total calcium (TotalCa), Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) |
| Persistent variables | Fluid balance |
| Life support equipment variables | Positive expiratory end pressure (PEEP), Oxygen concentration in the inhalation gas (FiO2), Tidal volume (VT), Peak airway pressure (Ppeak), Mean airway pressure (Pmean), Platform pressure (Pplat), Respiratory rate (RR) |
| Monitoring data | Heart rate (HR), Mean arterial pressure (MAP), Temperature, Pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2%) |
| Sedative and analgesic drugs | Dexmedetomidine, Fentanyl, Midazolam, Morphine, Propofol |
For each variable, the average value over the first 24 h after analgesia and sedation administration was calculated and used; the exceptions were total calcium, fluid balance and sedative and analgesic drugs, for which the total amount during the first day was used. To explore the subphenotypes of patients given analgesia and sedation, we first evaluated the distributions, absence and correlations of candidate feature variables.
For the preprocessing of missing values and outliers, given the scarcity of samples, we did not simply adopt variable removal and mean replacement. Instead, we used chain equations for multiple imputation for missing data [8] and logarithmic transformation. For the sedative and analgesic drugs, we filled null values with 0 according to the actual situation. In the correlation evaluation, we used the ranking statistics from sensitivity analysis to exclude highly correlated variables.
Latent profile analysis (LPA)
We used the unsupervised clustering method commonly used in medical research in our study. Consensus clustering [9] and latent profile analysis (LPA) were used within a Gaussian mixture model. Latent profile analysis is a probabilistic or model-based technique that is a variant of traditional cluster analysis [10, 11].
To better visualize the results, multiple types of graphs were used for analysis and display: (1) Box plots were used to show the difference in phenotypes through the means and standard deviations of the variables; (2) T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) was used to reduce multidimensional variables to two dimensions to visualize the subphenotypes; and (3) survival analysis curves were used to demonstrate the 28-day survival curve of each phenotype.
To describe the potential relationship between the analgesia and sedation phenotypes and the 36 features, we also compared the means, standard deviations and proportion of each phenotype for these characteristics. At the same time, we performed the χ2 test on the cumulative mortality of each phenotype at 28 days to determine whether there were significant differences.
Variable selection based on principal component analysis (PCA)
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a common data analysis method that is often used for dimensionality reduction of high-dimensional data and can be used to extract the main feature components of the data. In this study, we applied the PCA dimensionality reduction method to find and verify the variables that had the greatest impact on the effect of model classification, which may guide clinical application in the future. First, the original feature set was transformed by PCA, and then the weights of the original features in the transformation were obtained by analyzing the transformation matrix. The final feature subset was selected according to the order of the weights from high to low. To limit the complexity of our model, the ten most important variables were chosen for the next step in the model analysis.
Logistic regression model
The top ten variables identified by PCA were used in forward stepwise regression using the dataset. Logistic regression models of increasing complexity were generated by sequential addition of variables. The order in which the variables were entered into the model was determined by the findings of the stepwise regression analysis. Model performance was assessed by generating receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and calculating the area under the ROC curve (AUROC).
To confirm the advancement of our model, we compared the performance of the logistic regression model and other classifiers, such as XGBoost, random forest, and decision tree. Accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score and AUC (area under curve) were used to evaluate the performance of the classifiers.
Analysis of analgesia and sedation and the effect of mechanical ventilation
The Richmond-ASS [12] reflects the degree of sedation of the patient. The lower the score, the better the sedation effect is. Based on previous clinical studies and experiences, we divided patients into three categories with different degrees of sedation according to the Richmond-ASS: [− 5, − 3], (− 3, 0], and (0, 3]. It is generally considered that patients with 0 points and below have higher levels of sedation. In Richmond-ASS table, 4 is the highest score which stands for combative. Among our patients included in the cohort, the highest score was 3, so the patients who were unsuccessfully sedated are classified as (0, 3].
Results
Statistical description of patient information
We included data from a total of 5,935 patients who had received mechanical ventilation during their ICU stay and extracted their feature data from within 24 h after admission to the ICU. Data from 4747 patients were selected as the training set, and data from 1188 patients were selected as the validation set. Table 2 shows the statistical description of the two data sets.
Table 2.
Statistical description of the training set and validation set in the study
| Features (mean ± SD) | Training set (n = 4747) | Validation set (n = 1188) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 63.83 ± 16.37 | 63.22 ± 16.29 |
| SAPS II | 40.21 ± 15.04 | 39.56 ± 14.85 |
| SOFA scores | 5.49 ± 3.53 | 5.36 ± 3.48 |
| White blood cell (WBC) | 12.52 ± 8.98 | 12.44 ± 6.27 |
| Hemoglobin (Hb) | 10.67 ± 1.90 | 10.74 ± 1.93 |
| Hematocrit | 31.91 ± 5.51 | 32.07 ± 5.48 |
| Platelet | 210.77 ± 109.94 | 210.00 ± 108.69 |
| Urea nitrogen (BUN) | 25.31 ± 20.39 | 24.95 ± 20.04 |
| pH | 7.37 ± 0.07 | 7.37 ± 0.07 |
| pO2 | 189.14 ± 85.98 | 191.54 ± 89.92 |
| pCO2 | 41.91 ± 8.66 | 41.53 ± 8.06 |
| Bicarbonate (HCO3−) | 23.62 ± 4.21 | 23.57 ± 4.01 |
| Lactate (Lac) | 2.23 ± 1.45 | 2.26 ± 1.52 |
| Potassium (K) | 4.22 ± 0.54 | 4.22 ± 0.57 |
| Sodium (Na) | 138.17 ± 4.04 | 138.17 ± 4.16 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | 105.33 ± 5.29 | 105.28 ± 5.37 |
| Total calcium (TotalCa) | 8.24 ± 0.74 | 8.23 ± 0.73 |
| Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) | 35.81 ± 15.29 | 36.14 ± 15.82 |
| Fluid balance | 4580.69 ± 9379.25 | 4687.70 ± 4268.08 |
| Positive expiratory end pressure (PEEP) | 5.99 ± 2.01 | 5.87 ± 1.90 |
| Oxygen concentration in the inhalation gas (FiO2) | 56.06 ± 13.29 | 55.37 ± 12.74 |
| Tidal volume (VT) | 520.06 ± 178.15 | 517.18 ± 159.60 |
| Peak airway pressure (Ppeak) | 20.28 ± 5.62 | 20.36 ± 5.50 |
| Mean airway pressure (Pmean) | 9.45 ± 2.85 | 9.40 ± 2.77 |
| Platform pressure (Pplat) | 18.29 ± 4.18 | 18.23 ± 3.97 |
| Heart rate (HR) | 86.06 ± 15.41 | 86.05 ± 15.63 |
| Mean arterial pressure (MAP) | 78.35 ± 11.68 | 78.42 ± 11.28 |
| Respiratory rate (RR) | 18.76 ± 3.71 | 18.62 ± 3.85 |
| Temperature | 36.83 ± 0.68 | 36.84 ± 0.67 |
| Pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2%) | 97.55 ± 2.26 | 97.61 ± 2.19 |
| Richmond-ASS scores | − 1.59 ± 1.49 | − 1.59 ± 1.55 |
| Dexmedetomidine | 0.12 ± 0.77 | 0.12 ± 0.64 |
| Fentanyl | 3.52 ± 11.43 | 3.12 ± 9.97 |
| Midazolam | 65.45 ± 296.75 | 55.62 ± 208.40 |
| Morphine | 15.23 ± 84.53 | 13.07 ± 38.04 |
| Propofol | 3929.18 ± 8581.78 | 4066.48 ± 9464.44 |
Clustering for clinical phenotypes
After data preprocessing, we used consensus clustering to classify 2–10 phenotypes to confirm the optimal number of phenotypes. According to Fig. 2, we found that dividing the data into two phenotypes was the best fit.
Fig. 2.

Matrix heatmap (k = 2) shows that clustering into 2 categories is the best fit
Considering that the data types of the candidate feature variables were all numerical, we then used the Gaussian mixture model to perform potential profile analysis [13] to cluster the data into two phenotypes. Figure 3 shows the two-dimensional clustering status shown by the t-SNE diagram.
Fig. 3.

t-SNE plot of phenotype assignments
As shown in Fig. 4a and Table 3, the variables were scaled for each phenotype. Broad differences were observed in the distributions of the scaled variables across phenotypes. Of the 36 variables measured, 29 were significantly different across phenotypes in the training set with P < 0.05. Figure 4b shows the 28-day survival curves of the two phenotypes in the training set. The validation set shows the same trend (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4.
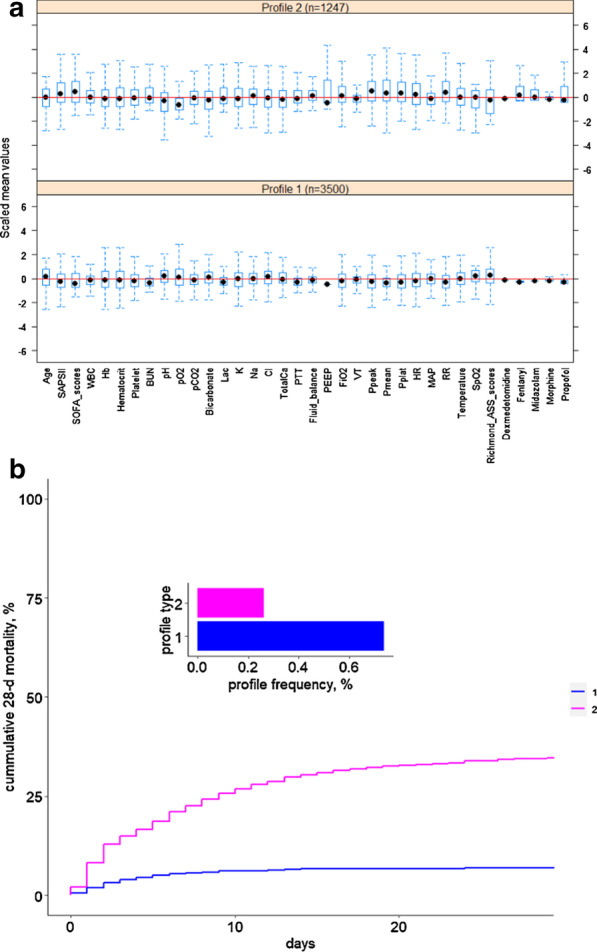
The box plot (a) and 28-day survival curve (b) of the two phenotypes obtained with the 36 variables in the training set
Table 3.
Statistical description of the two phenotypes of the training set
| Features (mean ± SD) | Profile1 (n = 3500) | Profile2 (n = 1247) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 64.57 ± 16.19 | 61.77 ± 16.70 | < 0.001 |
| SAPS II | 37.92 ± 13.47 | 46.63 ± 17.22 | < 0.001 |
| SOFA scores | 4.88 ± 3.00 | 7.20 ± 4.28 | < 0.001 |
| White blood cell (WBC) | 11.78 ± 4.64 | 14.59 ± 15.52 | < 0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (Hb) | 10.65 ± 1.81 | 10.75 ± 2.13 | 0.122 |
| Hematocrit | 31.77 ± 5.18 | 32.28 ± 6.33 | 0.005 |
| Platelet | 207.19 ± 101.90 | 220.82 ± 129.40 | < 0.001 |
| Urea Nitrogen (BUN) | 22.49 ± 15.99 | 33.20 ± 27.95 | < 0.001 |
| pH | 7.38 ± 0.06 | 7.34 ± 0.09 | < 0.001 |
| pO2 | 203.65 ± 85.69 | 148.41 ± 72.72 | < 0.001 |
| pCO2 | 41.49 ± 7.34 | 43.08 ± 11.52 | < 0.001 |
| Bicarbonate (HCO3−) | 23.95 ± 3.64 | 22.67 ± 5.41 | < 0.001 |
| Lactate (Lac) | 2.01 ± 0.93 | 2.85 ± 2.25 | < 0.001 |
| Potassium (K) | 4.21 ± 0.51 | 4.26 ± 0.62 | 0.003 |
| Sodium (Na) | 138.13 ± 3.65 | 138.28 ± 4.96 | 0.245 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | 105.49 ± 4.88 | 104.88 ± 6.29 | 0.001 |
| Total calcium (TotalCa) | 8.27 ± 0.63 | 8.18 ± 0.99 | < 0.001 |
| Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) | 34.06 ± 12.31 | 40.74 ± 20.78 | < 0.001 |
| Fluid balance | 4023.84 ± 3505.98 | 6143.63 ± 17,240.77 | < 0.001 |
| Positive expiratory end pressure (PEEP) | 5.56 ± 1.24 | 7.20 ± 3.01 | < 0.001 |
| Oxygen concentration in the inhalation gas (FiO2) | 54.52 ± 11.58 | 60.39 ± 16.45 | < 0.001 |
| Tidal volume (VT) | 504.45 ± 91.65 | 563.87 ± 307.72 | < 0.001 |
| Peak airway pressure (Ppeak) | 19.21 ± 4.72 | 23.29 ± 6.73 | < 0.001 |
| Mean airway pressure (Pmean) | 8.76 ± 1.88 | 11.40 ± 3.99 | < 0.001 |
| Platform pressure (Pplat) | 17.53 ± 3.43 | 20.44 ± 5.22 | < 0.001 |
| Heart rate (HR) | 84.46 ± 13.91 | 90.54 ± 18.27 | < 0.001 |
| Mean arterial pressure (MAP) | 78.46 | 78.05 ± 17.84 | 0.288 |
| Respiratory rate (RR) | 18.04 ± 3.13 | 20.79 ± 4.40 | < 0.001 |
| Temperature | 36.84 ± 0.58 | 36.79 ± 0.92 | 0.037 |
| Pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2%) | 97.84 ± 1.54 | 96.72 ± 3.43 | < 0.001 |
| Richmond-ASS scores | − 1.39 ± 1.34 | − 2.15 ± 1.74 | < 0.001 |
| Dexmedetomidine | 0.01 ± 0.05 | 0.42 ± 1.47 | < 0.001 |
| Fentanyl | 0.57 ± 1.26 | 11.82 ± 19.99 | < 0.001 |
| Midazolam | 8.29 ± 23.13 | 225.89 ± 546.80 | < 0.001 |
| Morphine | 7.27 ± 12.10 | 37.56 ± 161.65 | < 0.001 |
| Propofol | 2219.76 ± 3271.76 | 8727.05 ± 14,805.89 | < 0.001 |
Fig. 5.

The box plot (a) and 28-day survival curve (b) of two phenotypes obtained with the 36 variables in the validation set
The most influential variables according to PCA
The 10 most important variables obtained from PCA are presented in Fig. 6. They include Pmean, Pplat, PEEP, Ppeak, SOFA score, SAPS II, pH, respiratory rate (RR), FiO2, pO2.
Fig. 6.
The 9 most important variables identified by PCA
Forward stepwise regression did not eliminate any of the ten variables. Increasing the model complexity via the sequential addition of variables led to improved model performance. From Table 4, we can see that there was a relative plateauing by the time the 9-variable and 10-variable models were created. Considering the best balance between classification accuracy and model simplicity, the 9-variable model was defined as the best classifier model in our research. Figure 7 shows the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the 9-variable model, and the area under the curve (AUC) reached 0.77.
Table 4.
Logistic regression model composition and accuracy with the dataset
| Pmean | Pplat | PEEP | Ppeak | SOFA scores | SAPS II | pH | RR | pO2 | FiO2 | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model1 | Yes | 0.70 | |||||||||
| Model2 | Yes | Yes | 0.70 | ||||||||
| Model3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.70 | |||||||
| Model4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.70 | ||||||
| Model5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.72 | |||||
| Model6 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.73 | ||||
| Model7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.74 | |||
| Model8 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.75 | ||
| Model9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.77 | |
| Model10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.77 |
Fig. 7.
ROC curve of the 9-variable model
To confirm the advancement of our model, we compared its performance with that of XGBoost, random forest and decision tree in terms of several parameters, such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score and AUC. As Table 5 shows, random forest has the highest precision with 0.7947, and XGBoost has the highest recall with 0.6574, but our logistic regression model has the highest accuracy, F1-score, and AUC with 0.7997, 0.6771, and 0.7725, respectively. Thus, we believe the logistic regression model performed better than other classifiers.
Table 5.
Performance of different classifiers
| Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic regression | 0.7997 | 0.7625 | 0.6550 | 0.6771 | 0.7725 |
| XGBoost | 0.7870 | 0.7245 | 0.6574 | 0.6753 | 0.7464 |
| Random forest | 0.7921 | 0.7947 | 0.6130 | 0.6265 | 0.7684 |
| Decision tree | 0.7012 | 0.6168 | 0.6247 | 0.6200 | 0.6247 |
Based on the 9 most influential variables obtained by PCA, we also obtained two phenotypes, and the corresponding box plot and the 28-day survival curve of the validation set are shown in Fig. 8. The 9 variables were significantly different between the two phenotypes.
Fig. 8.
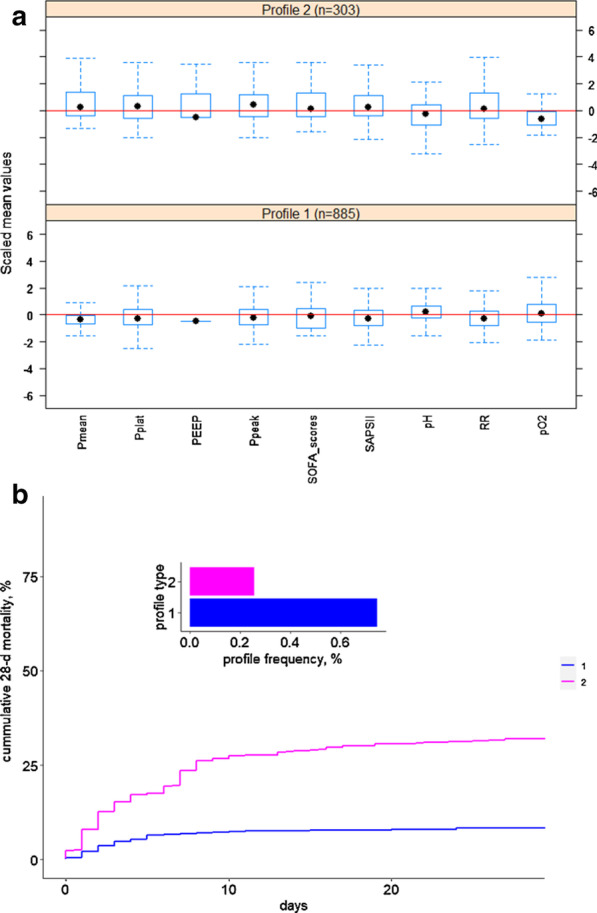
The box plot (a) and 28-day survival curve (b) of the two phenotypes obtained with the 9 most important variables in the validation set
To further explore the relationship between different phenotypes and the degree of sedation and analgesia, the data of the two phenotypes from the validation set were then divided into three different levels of sedation according to the Richmond-ASS score, where [− 5, − 3] stands for deep sedation, (− 3, 0] stands for light sedation and (0, 3] stands for unsuccessful sedation treatment, as shown in Fig. 9. From this figure, Profile 1 accounted for 66.42% (n = 182) in the deep sedation [− 5, − 3] group, which indicated that these patients maybe reduce the depth of sedation. Profile 2 accounted for 25.47% (n = 215) in the light sedation (− 3, 0], which indicated that these patients need deeper sedation to meet their breathing needs. The proportion of unsuccessful sedation treatment (0, 3] patients is relatively small.
Fig. 9.
The validation set was further divided into three levels of sedation: deep sedation, light sedation and unsuccessful sedation. The corresponding RASS scores are [− 5 − 3], (− 3 0] and (0 3]
Discussion
This study divided mechanically ventilated patients who were administered analgesia and sedation into two categories. By reducing the dimensionality of the PCA, we can see that the obvious difference between the two types lies in the ventilator-based parameters. This shows that sedation is necessary for mechanically ventilated patients, who need to be administered sedation therapy to assist in lung self-treatment. By dividing the validation cohort into three categories, the result showed that patients with higher ventilator conditions require deeper levels of sedation. If the patient’s respiratory system disease is improving, the patient can be identified in time according to the model. Patients with profile1 require reduction in the level of sedation earlier or transition to the awake state in time, and patients with profile2 may need to continue with a deeper sedation mode to continue treatment.
Mechanical ventilation remains the main indication for continuous sedation in the ICU. For example, given the severity of ARDS, the needs of patients with regard to analgesia and sedation will be substantially different. Yoshida et al. [14] conducted a controlled study of spontaneous breathing and muscle relaxation therapy by making animal models of acute experimental lung injury of different severities. The results showed that with mild lung injury, spontaneous respiration can maintain a lower peak airway pressure and lead to more obvious histological improvement, while with severe lung injury, a lower peak airway pressure can be maintained when there is no spontaneous respiration; that is, under muscle relaxation, lower peak pressure and better histological improvement can be achieved. Papazian et al. [15] also confirmed that for patients with severe ARDS, deep analgesia and sedation combined with muscle relaxants can improve their 90-day survival rate and shorten the time of mechanical ventilation and do not increase the incidence of muscle weakness. That is, for patients with severe ARDS, retaining spontaneous breathing and maintaining mild sedation may be harmful. The mechanism is related to the deep analgesia, sedation and muscle relaxation used to improve human–machine synchronization, reduce transpulmonary pressure, and reduce ventilator-related lung damage. However, as the condition of the ARDS patient improves, the continuous implementation of deep sedation strategies for patients with mild ARDS becomes more harmful. Shehabi et al. [16] suggested that the proportion of patients with excessive sedation within 48 h of mechanical ventilation in the ICU is as high as 68%. The disadvantages of long-term deep sedation are as follows: the patient's consciousness cannot be judged in time; it increases complications (such as muscle atrophy and weakness), ventilator dependence, venous thromboembolism, pressure ulcers and delirium; it inhibits circulation and gastrointestinal motility; it prolongs weaning time and length of ICU hospital stay; and it increases the risk of acquired ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). [17]. In particular, coma caused by sedative drugs may increase the mortality rate of ICU patients, prolong intubation time and ICU hospitalization time, and cause long-term neuropsychological dysfunction [18]. For ICU patients, shallow sedation can effectively prevent excessive sedation, ensure that the patient is comfortable, safe and sufficiently awake and responsive, make it easy to determine whether to wean and extubate, and assess pain, delirium, and the ability to carry out early activities [19]. By establishing this model, the dose ranges of sedative drugs can be determined according to the parameters of the ventilator used during treatment. In other words, for the patient, what kind of ventilator parameters require deep sedation or light sedation? In this way, mechanically ventilated patients with serious pulmonary disease were found to need appropriate sedation therapy, while for recovery after treatment, the degree of sedation can be reduced, in turn reducing the secondary harm of mechanical ventilation to the patients.
There are some limitations in this study. First, MIMIC III was built in 2012, and there was insufficient knowledge about analgesia and sedation at that time. Second, respiratory waveforms and other information were not available; thus, although the score reached the standard, it was not clear whether the ventilator still allowed spontaneous breathing after sedation (this would aggravate the injuries related to mechanical ventilation). Third, the effects of muscle relaxation on mechanical ventilation patients were not analyzed in this study. In the future, it may be necessary to conduct related research by incorporating other databases, such as MIMIC IV.
Conclusion
The patients in the MIMIC III database who underwent mechanical ventilation therapy and took sedative and analgesic drugs during their ICU stay were selected as the research sample. Based on 36 variables, we applied latent profile analysis to divide these patients into two categories with different mortalities. To further identify the key variables that affected the classification, we applied dimensionality reduction to select the 9 most critical variables, most of which were parameters associated with mechanical ventilation. After that, we divided the patients into three subphenotypes, deep sedation, light sedation and unsuccessful sedation, according to the degree of sedation and analgesia and correlated them with the critical parameters of mechanical ventilation. That is, patients with profile1 were more suitable for reduced sedation, and patients with profile2 were more suitable for maintaining deeper sedation. We look forward to adjusting the parameters of mechanical ventilation according to the degree of sedation in the future to achieve fine individualized treatment in the ICU.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
About this supplement
This article has been published as part of BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making Volume 21, Supplement 2 2021: HealthBig Data and Artificial Intelligence. The full contents of the supplement are available at https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/supplements/volume-21-supplement-2.
Abbreviations
- ICU
Intensive care unit
- MIMIC III
Medical information mart for intensive care III
- ARDS
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- LPA
Latent profile analysis
- PCA
Principal component analysis
- PEEP
Positive expiratory end pressure
- t-SNE
T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC
Area under curve
- AUROC
Area under the ROC curve
- RR
Respiratory rate
- SOFA score
Sequential organ failure assessment score
- SAPS II
Simplified acute physiology score II
- RASS
Richmond agitation-sedation scale
- VAP
Ventilator-associated pneumonia
Authors' contributions
NH, XZ and YL are corresponding authors and take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, from the inception to the published article; LS, CL and FC contributed equally; LS and CL are responsible for the study design and conception; CL, FC, BT, LH, HJ, NH, and WZ are responsible for the data management and statistical analysis; and LS and CL drafted the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the following: Beijing Nova Program from Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (No. Z201100006820126) and Capital Characteristic Clinic Project of Beijing (No. Z181100001718209), grant recipient Longxiang Su, MD. PhD. China International Medical Exchange Foundation Special Fund for Young and Middle-aged Medical Research, award number Z-2018-35-1902, grant recipient Xiang Zhou MD. China Health Information and Health Care Big Data Association Severe Infection Analgesia and Sedation Big Data Special Fund, award number Z-2019-1-001, grant recipient Yun Long MD. The Undergraduate Teaching Reform of Peking Union Medical College Hospital (2020zlgc0109), recipient Longxiang Su.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of supporting data
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Longxiang Su, Chun Liu and Fengxiang Chang have contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Na Hong, Email: hongna@dchealth.com.
Xiang Zhou, Email: zx_pumc@163.com.
Yun Long, Email: ly_icu@aliyun.com.
References
- 1.Jones CGR, Humphris G, et al. Memory, delusions, and the development of acute post-traumatic stress disorder-related symptoms after intensive care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:573–580. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200103000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lewis KSWJ, Michael KA, et al. Effect of analgesic treatment on the physiological consequences of acute pain. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1994;51:1539–1554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schelling GSC, Meoer M, et al. Health-related quality of life and post-traumatic stress disorder in survivors of adult respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1998;26:651–659. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199804000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Mehta S, Riker R, Takala J. Intensive care sedation: the past, present and the future. Crit Care. 2013;17(3):322–322. doi: 10.1186/cc12679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Reade MC, Finfer S. Sedation and delirium in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(5):444–454. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1208705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mehta N, Kalra A, Nowacki AS, Anjewierden S, Han Z, Bhat P, Carmona-Rubio AE, Jacob M, Procop GW, Harrington S, et al. Association of use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with testing positive for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5:745–747. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Johnson AEWPT, Shen L, Lehman L, Feng M, Ghassemi M, Moody B, Szolovits P, Celi LA, Mark RG. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci Data. 2016;3:160035. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2016.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.OgnjenGajic SID, Mendez JL, Adesanya AO, et al. Ventilator-associated lung injury in patients without acute lung injury at the onset of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(9):1817–1824. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000133019.52531.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mardani R, Ahmadi Vasmehjani A, Zali F, Gholami A, Mousavi Nasab SD, Kaghazian H, Kaviani M, Ahmadi N. Laboratory parameters in detection of COVID-19 patients with positive RT-PCR; a diagnostic accuracy study. Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2020;8(1):e43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tein JY, Coxe S, Cham H. Statistical power to detect the correct number of classes in latent profile analysis. Struct Equ Model A Multidiscip J. 2013;20(4):640–657. doi: 10.1080/10705511.2013.824781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rosenberg J, Beymer P, Anderson D, Schmidt J. tidyLPA: an R package to easily carry out latent profile analysis (LPA) using open-source or commercial software. J Open Source Softw. 2018;3:978. doi: 10.21105/joss.00978. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Curtis N, Sessler MSG, Grap MJ, et al. The Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(10):1338–1344. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2107138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fernández-Pérez ER, Sprung J, Afessa B, Warner DO, Vachon CM, Schroeder DR, Brown DR, Hubmayr RD, Gajic O. Intraoperative ventilator settings and acute lung injury after elective surgery: a nested case control study. Thorax. 2009;64(2):121. doi: 10.1136/thx.2008.102228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.TakeshiYoshida AU, Matsuura N, Mashimo T, Fujino Y. The comparison of spontaneous breathing and muscle paralysis in two different severities of experimental lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(2):536–545. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182711972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.LaurentPapazian J-MF, Gacouin A, Penot-Ragon C, et al. Neuromuscular blockers in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(12):1107–1116. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1005372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shehabi YBR, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, McArthur CJ, Seppelt IM, Webb SA, Weisbrodt L. Sedation Practice in Intensive Care Evaluation (SPICE) Study Investigators; ANZICS Clinical Trials Group. Early intensive care sedation predicts long-term mortality in ventilated critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186(8):724–731. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201203-0522OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yahya Shehabi LC, Kadiman S, Alias A, Ismail WN. Sedation depth and long-term mortality in mechanically ventilated critically ill adults: a prospective longitudinal multicentre cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(5):910–918. doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-2830-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Juliana Barr GLF, Puntillo K, Wesley Ely E. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(1):263–306. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182783b72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Juliana Barr PPP. The pain, agitation, and delirium care bundle: synergistic benefits of implementing the 2013 Pain, Agitation, and Delirium Guidelines in an integrated and interdisciplinary fashion. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(9 suppl 1):S99–115. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182a16ff0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






