Abstract
The phthalocyanine (Pc) and naphthalocyanine (Nc) nanoagents have drawn much attention as contrast agents for photoacoustic (PA) imaging due to their large extinction coefficients and long absorption wavelengths in the near-infrared region. Many investigations have been conducted to enhance Pc/Ncs' photophysical properties and address their poor solubility in an aqueous solution. Many diverse strategies have been adopted, including centric metal chelation, structure modification, and peripheral substitution. This review highlights recent advances on Pc/Nc-based PA agents and their extended use for multiplexed biomedical imaging, multimodal diagnostic imaging, and image-guided phototherapy.
I. INTRODUCTION
Photoacoustic (PA) imaging is a hybrid imaging modality based on the PA effect that exploits both rich optical contrast and high ultrasonic spatial resolution in deep tissues.1–4 It visualizes optical chromophores in biological tissues where ultrasound (US) signals are generated from light absorption and subsequent thermoelastic expansions. In the last decades, PA imaging has been studied extensively, with many advantages for biomedical imaging. First, unlike traditional optical imaging techniques where imaging depth is limited to few millimeters due to round trip optical attenuation in biological tissues, PA imaging can reach up to a few centimeters of depth in biological tissues, thanks to one-way photon propagation and acoustic detection which suffers far much less attenuation and scattering than optical detection.5–9 Second, the spatial resolution and achievable imaging depth are scalable based on the US detector frequency, thus covering many applications ranging from organelles and cells to small animals and humans.10–16 Third, PA imaging is inherently compatible with many complementary imaging modalities, e.g., conventional US imaging and optical imaging modalities, and thus are highly suitable for multiplexed and multimodal imaging.17–22
The PA imaging exploits both endogenous and exogenous contrast agents to image biological tissues. The endogenous agents include DNA/RNA,23,24 melanin,25–28 oxygenated-/deoxygenated-hemoglobin,29–31 lipid,32–34 and water.35 These agents provide functional, metabolic, and histopathologic information such as blood oxygenation, oxygen metabolism, and vascularity.36,37 A large variety of exogenous contrast agents have been investigated, including inorganic nanomaterials (gold nanostructures, carbon nanotubes, etc.), organic dyes (porphyrine-/cyanine-based dyes), and fluorescent proteins [green/red fluorescent protein (GFP/RFP)].38–42 Gold nanomaterials are one of the most widely investigated PA agents thanks to their surface plasmon resonance properties and biocompatibilities. The plasmonic peaks can be tuned from the visible to the near-infrared (NIR) range depending on their shapes and provide optical contrast,43 but still has limitations for clinical translation due to photoinstability.44 Fluorescent proteins have drawn much attention in live-cell optical imaging.45 GFP, however, has a lower absorption peak wavelength, high fluorescent quantum yield (i.e., low heat conversion efficiency), and shallow imaging depth for in vivo applications.46
The phthalocyanine (Pc) and naphthalocyanine (Nc) are organic dyes that have been explored widely for optical imaging and phototherapy due to their strong extinction coefficients and long absorption wavelengths in the NIR region.47–49 This region is also known as an optical/biological/therapeutic window where light can penetrate deeply in tissues with low phototoxicity. The Pc/Ncs also have attractive traits of good photostability and tunable optical properties through facile chemical modifications.50–53 Low aqueous solubility is the main challenge for Pc/Ncs as a contrast agent, and many attempts have been successfully made to solubilize Pc/Ncs using biocompatible and biodegradable coating (e.g., surfactant modification, micelle/liposome carrier).54–58 Several Pc/Nc derivatives, including aluminum Pc, silicon Pc, and zinc Pc, have either already been through the FDA approval process or are under clinical trials.59,60
In this review, we summarize the recent advances in Pc/Nc-based nanomaterials as PA imaging agents and synergistic applications for using multimodal imaging and theranostics. First, we present design strategies and processes to enhance the functionality of Pc/Ncs, including photophysical properties and targeting ability. We then focus on their biomedical applications, including contrast-enhanced PA imaging, biosensing of tumor and other biomolecules, and cancer theranostics. Finally, we will discuss future directions for Pc/Nc-based PA agents.
II. FUNCTIONALIZING PCS AND NCS AS a PHOTOACOUSTIC CONTRAST AGENT
A. Photophysical property
The two important photophysical properties of nanoparticle for considering them as potential PA contrast agent are: (1) does the peak absorption wavelength ensures sufficient penetrating depth and (2) how the absorbed energy efficiently transfers to thermal expansion, which is directly proportional to photoacoustic signal intensity. These aspects connote two strategies for engineering the nanoparticles; how to tune the wavelength and how to increase the given particle's absorption yield.
1. Absorption spectrum shift
For most biomedical imaging techniques, the allowed penetration depth is under the boundary of the optical ballistic region (< 1 mm). However, the PA imaging crosses over the boundary because the PA technique involves a one-way optical propagation and, independent of scattering, it responds with an acoustic signal. For reaching the maximum penetration depth in tissue, the wavelength of the optical source is generally selected in the specific range of NIR zone (650–1350 nm), named as “NIR window.”61–63 In such wavelength range, the photon gets absorbed less by blood than shorter wavelengths and bypasses the absorption by water, compared to longer wavelengths. In addition, determining the absorption wavelength carefully can lead to accurate multiplex imaging or combinatorial therapy such as photodynamic therapy (PDT) or photothermal therapy (PTT).
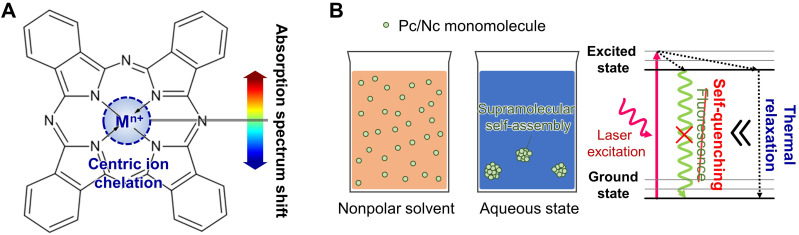
Even though the free-base Pc and Nc have their absorption peak around 670 nm and 750 nm in DMF solution, respectively,64,65 centric ion chelation, at the center of the Pc/Ncs molecule, enables the tuning of the optical absorption band of the agent [Fig. 1(a)].66 Depending on the type of metal, Pc/Nc's absorption peak can be varied through chelation in the range of 650–950 nm. In addition to wavelength tuning, chelation with appropriate diamagnetic metallic ions increases the absorption yield of Pc/Ncs and stabilizes the charge balance, and, consequently, lengthens the molecules' lifetime.67,68
FIG. 1.
Strategies to functionalize photophysical properties of phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine. (a) Absorption spectrum shift with centric ion chelation. (b) Increased absorption yield by supramolecular self-assembly in aqueous condition.
Currently, metallic ions such as zinc (Zn),69 copper (Cu),70 iron (Fe),71 and indium (In)72 are widely favored in research studies with a corresponding peak absorption of 700, 850, 680, and 840 nm, respectively.
Duffy et al. showed through a comprehensive study that Nc particle's central ion change results in maximum PA intensity wavelength shift at 850, 848, 774, and 808 nm, for copper, nickel, silicon, and vanadium ion, respectively.73 The study further identified that central ion change also affected singlet oxygen photoproduction and fluorescence pattern.
In addition to metallic ions, variation with nonmetallic ion chelation can also be used for engineering the nanoparticle's optical response. Chelation with semiconducting elements, such as silicon (Si), exhibits good photothermal conversion efficiency and is capable of both PDT and PTT effect,74 which enables the use of such material as single-agent theranostic nanoprobes.58 Choice of peak absorption to NIR-II window (1000–1700 nm) instead of NIR-I window is advantageous from both aspects: penetration depth and maximum permissible exposure (MPE). Hence, contrast agents with its peak absorption at NIR-II window enlarges the scope of imaging target to deeper organs, which is an important factor to translate from preclinical studies to future clinical application toward human. A number of studies already present the superiority of NIR-II PAI with multi-centimeter penetration depth compared to NIR-I PAI. Together with chicken breast phantom, rodent mammary tumor models, lymphatic mapping, and ultimately with 2.6–5.1-cm-thick compressed human breast, transcendent depth penetrating ability of NIR-II PAI was well validated as well as giving proof to its applicability.75 Having deep penetration depth as its major strength, a number of precedential studies eagerly expect its future potential to extend barrier of PAI application toward gastrointestinal tract, lymphatic system, and excretory system.76 The electron-deficient group 15 elements (P, As, and Sb) and the electron-rich group 16 elements (S, Se, and Te) can also be used as central substituents, which expands the applicable optical band beyond 1000 nm.77 For example, Zhou et al. observed intense absorption at 1000 nm with phosphorus Pc to target deeper imaging depth with PACT.78 Without using a central inorganic semiconducting element or polymer, Pan et al. synthesized NIR-II (1064 nm) agent by arranging four ZnPc molecules into cruciform pentad.56
The representative publications for absorption spectrum shift are summarized in Table I.
TABLE I.
Summary of the representative publications for absorption spectrum shift of phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanaoparticles. , maximum absorption wavelength; , fluorescence quantum yield; FL, fluorescence; , excitation wavelength; , emission wavelength; , molar extinction coefficient; , photothermal conversion coefficient; , singlet oxygen generation quantum yield.
| Group | Central chelation | (nm) | FL / (nm) | (M−1 cm−1) | Major features | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al.69 | ZnPc | ∼700 | ⋯ | 650/715 | ⋯ | • = 31.3 % |
| • = 0.62 | ||||||
| Duffy et al.73 | CuNc | 850 | 0.0003 | ⋯ | 2.10 × 105 | ⋯ |
| NiNc | 848 | < 0.02 | ⋯ | 1.80 × 105 | ⋯ | |
| SiNc | 774 | 0.07 | ⋯ | 5.70 × 105 | ⋯ | |
| VNc | 808 | < 0.02 | ⋯ | 2.40 × 105 | ⋯ | |
| Choi et al.70 | CuNc | 850 | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ |
| He et al.71 | Fe(II)Pc | 680 | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ |
| Lobo et al.72 | InPc | 840 | < 0.001 (at 850 nm) | ⋯ | 9.00 × 104 (at 850 nm) | ⋯ |
| Wei et al.58 | SiNc | 730 | ⋯ | 808/⋯ | ⋯ | • = ∼59.8 % |
| Zhou et al.78 | PPc | 997 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 6.40 × 104 (at 998 nm) | ⋯ |
| Pan et al.56 | Cruciform ZnPc pentad | 1040 | 0.002 | 880/1108 | 3.70 × 105 | • = 58.3 % |
2. Increased absorption yield
Due to the hydrophobic nature, arising from their π-conjugated planar arrangement, Pc and Nc exhibit high self-aggregation in aqueous solution. During the supramolecular self-assembly phase, collective aggregation induces complete FL self-quenching. It blocks radical oxygen species (ROS) generation pathways, leading to a favorable increase in nonradiative thermal relaxation in its excited phase [Fig. 1(b)].79,80 Thus, supramolecular self-assembly can effectively increase PA signal yield compared to its monomolecular application. Liu et al. introduced a polymeric nanosystem for near-infrared multispectral PA imaging, which augmented the self-assembly by using hydrophobized ZnPc and oxazoline block copolymer complex (H-PcZn), to efficiently encapsulate the micelles by self-assembly.81 Li et al. reported a molecular recognition-based supramolecular approach between PcS4 and PcN4, the two water-soluble Pc derivatives, and observed completely quenched fluorescence (FL) and reduced singlet oxygen generation.54
The representative publications for increasing absorption yield are summarized in Table II.
TABLE II.
Summary of the representative publications for increasing absorption yield of phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles. , maximum absorption wavelength; , molar extinction coefficient; O.D., optical density; , zeta potential; FL, fluorescence.
| Group | Nanomaterial | (nm) | Monomer/assembly size (nm) | [O.D.] | Major features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al.81 | Hydrophobized zinc Pc complex | 680 | −/20–100 | 8.9 (P-NP); | • Hydrophobizing characterization with oxazoline block copolymer, |
| 7.4 ( N-NP) | • = P-Pc: +29 mV; N-Pc: −43.8 mV | ||||
| Li et al.54 | PcS4-PcN4 complex | 694 | 0.5–3/30–100 | ⋯ | • Total FL self-quenching identified at 610 nm |
B. Passive delivery
1. Enhanced solubility
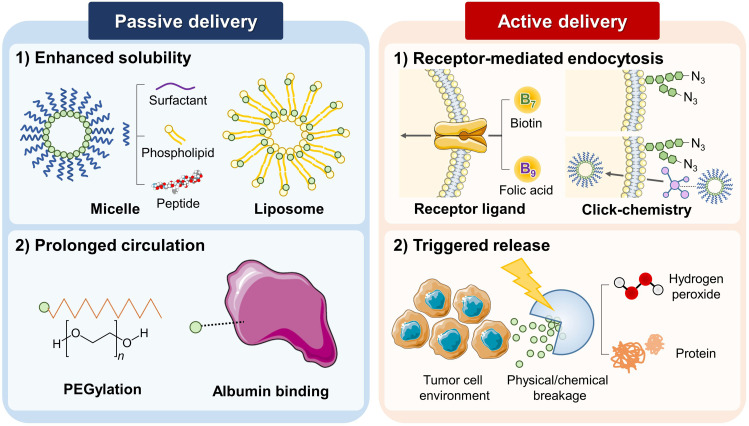
Low water solubility is a frequently mentioned demerit for Pc and Nc nanoparticles for using them as a PA contrast agent. The administered pharmaceutics dissolve in body fluids, e.g., blood, and get delivered to the destination tissue through the circulatory system's capillary network. Therefore, for diagnostic/therapeutic application, low water solubility is a big hurdle for tissue permeability and poses threats to stricture or stenosis. For enhancing the solubility, hydrophobic molecules are mostly coated with hydrophilic functional substances or reprocessed into amphiphilic nanocarriers with biologically suitable surfactants [Fig. 2(a)].82,83
FIG. 2.
Functionalizing phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles for passive and active delivery.
When the molecular complex unit is composed of the hydrophobic part and hydrophilic part, it forms a spherical supramolecular assembly called micelle when dissolved into water. The polarity of the solvent and intermolecular interaction force grants “packing behavior,” arranging hydrophilic parts of the monomer to face the exterior surface of the assembly, and hydrophobic parts cluster toward the center of the assembly.84–86 The aggregates form a colloidal suspension, which leads to a better solubility of the assembly. Pluronic F127, also known as poloxamer 407, is a hydrophilic nonionic block copolymer surfactant. In pharmaceutics, pluronic copolymer micelles are commonly used as a passive drug container to improve the delivery of the hydrophobic drug.87 To enhance the stability of the resulting multifunctional nanodroplets, Choi et al. conjugated their Nc particles with the in particular, developed form of Pluronic F127 and crosslinked with the primary amine of six-arm PEG.70,88 By similar means, to create a lipophilic or amphipathic PC-carrying micelle, Rizvi et al. applied tomamine, another type of commercial surfactant. They identified an induced Pc distortion, which enabled photothermal processes for PA imaging and uncomplicated surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy.89 To accommodate higher loading of Nc/Pc, Zhang et al. introduced novel low-temperature processing called “surfactant-stripped frozen micelle.” Through the removal of free or unbound solubilizing surfactant, this processing increased the drug to surfactant ratio by 2–3 orders of magnitude higher than the conventional method.90 Zhang et al. named their surfactant-stripped high loading Nc micelles as “nanonaps” and introduced its use for multifunctional cancer theranostics.91
Phospholipids are the representative nature-derived amphiphilic surfactant, having hydrophilic phosphate head and two hydrophobic long fatty acid tails. The Pc/Nc enclosed with a monolayer of phospholipid forms phospholipid micelle, and the assembly is reinforced with PEG chains. Wei et al. reported the effective diagnostic nano agents for PA imaging, PTT, and PDT combination therapy.58
The liposome is another variation of a phospholipid-complex vesicle. Contrary to phospholipid micelles, liposomes consist of a lipid bilayer membrane, which can be loaded with hydrophilic nutrients or pharmaceutical drugs in its most inner void.94 Using such an approach, Ma et al. complexed ZnPc with soybean phospholipid using hydrogen bond and intermolecular interaction. The self-assembled liposomal nanoparticles were loaded with doxorubicin to achieve additional chemotherapy.92
Conjugating short hydrophilic peptide onto Pc/Nc particle also increases the water solubility by inducing the supramolecular self-assembly. Furthermore, short peptides may increase cellular uptake during their interaction with cell membranes due to their excellent biocompatibility.95 Li et al. suggested spatiotemporally coupled tumor phototheranostic nanoparticles, composed of easy Pc-peptide conjugation and switchable photoactivity, triggered by cellular membrane interaction.93
The representative publications for nanocarriers enhancing aqueous solubility are summarized in Table III.
TABLE III.
Summary of the representative publications for nanocarriers enhancing aqueous solubility of phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles. , mean diameter; PEG, polyethylene glycol, , maximum absorption wavelength; , molar extinction coefficient; , fluorescence quantum yield; , singlet oxygen generation quantum yield; SERS, Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy; , photothermal conversion coefficient; PDT, photodynamic therapy; PTT, photothermal therapy.
| Group | Nanomaterial | Carrier type | Excipient type | (nm) | Major features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choi et al.70 | Nc/PFH@PCPN | Block copolymer micelle | Six-arm PEG-amine crosslinked Pluronic F127 | 500–2500 | • = 850 nm |
| • 89.4 % 14-day sustainability (37 °C) | |||||
| Rizvi et al.89 | ZnPc (tomamine)n | Block copolymer micelle | Tomamine | 89 ± 8; | • [nm] = 774; 810; 805; 820 |
| 133 ± 7; | • [O.D.] = 3.60; 3.49; 3.38; 3.25 | ||||
| 193 ± 10; | • ≪ 1 | ||||
| 223 ± 9; | • < 0.01 | ||||
| • strong SERS signal | |||||
| Zhang et al.91 | Nanonap | Block copolymer micelle | Pluronic F127 | 29.5 | • Surfactant-stripped micelle |
| • = 860 nm | |||||
| • PTT with upconversion cream, | |||||
| • PET application with 64Cu chelation | |||||
| Wei et al.58 | SiNcOH-DSPE-PEG(NH2) | phospho-lipid micelle | PEG-conjugated phospholipid | 160 | • = 59.8 % |
| • 7-day stability | |||||
| Ma et al.92 | ZnPc-SPC | Liposome | ZnPc-soybean phospholipid complex | 296.9 ± 6.553 | • Drug loading (doxorubicin) |
| • Folate receptor(FRα), | |||||
| • max. 15 day stability | |||||
| Li et al.93 | Pc-petide conjugate self-assembly | Short Petide micelle | L-phenylalanine-L-phenylalanine | 54.8 ± 17.6 (pH 7.0) | • Theranostic application (PDT/PTT) |
| • pH dependent nanoparticle size | |||||
| • Switchable photoactivity with cell membrane interaction |
2. Prolonged circulation
The capillary network delivers the injected nanoparticles into cells via the reticuloendothelial system using the principle of diffusion. The difference between hydraulic pressure inside the capillary wall and intracellular pressure of the recipient cell transfers oxygen and nutrients essential for metabolic events of the cell. The enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR) is a generally accepted phenomenon in vessels surrounding rapidly growing tumor cells. These tumor cells have greater cellular uptake through large fenestrations between endothelial cells and allow nanoparticles to reach the matrix easily than normal cells.96 Thus, the prolonged circulation of the nanoparticle increases the possibility of them reaching the peritumor site, and is necessary for efficient passive delivery of the nanoparticle.
Many methods such as cross-linking with polyethylene glycol (PEG) classes and variants, or PEGylation, are adopted to extend the circulation time of the injected nanoparticles by growing the volume of the nanocarrier, which effectively inhibits the reticuloendothelial uptake.97 In addition, bulky organic ligands on the monomer provides steric hindrance and lowers the critical micellar concentration, which degrades the lower intramolecular aggregation.98 Huang et al. modified an Sn-chelated octabutoxy Nc with PEG, and demonstrated increased blood circulation after intravenous administration to the mouse in in vivo experiment with 24 hours monitoring. The experimental results showed 4 times longer half-life and 10 times greater area under the curve.99
Albumin binding is also a well-preferred method to regulate the circulation time. Human serum albumin is the most abundant protein in human blood plasma; it constitutes about 50%f of serum protein and is produced in the liver. Against the hydraulic pressure that diffuses the solvents to peripheral cells during capillary metabolism, albumin regulates the oncotic pressure of blood by trapping water, cations (e.g., Ca2+, Na+, K+), fatty acids, hormones, bilirubin, tyroxine, thus preventing discharge of pharmaceuticals from microvessels. The passive delivery rate of drugs is often enhanced by binding with albumin in the pharmaceutical field.100 Using inherent biocompatibility and reduced immunogenicity, Jia et al. fabricated a human serum albumin-iron(II) Pc nanoparticle complex as a phototheranostic agent and observed the monotonic increase in PA signal intensity at < 15 hours post-injection.101
The representative publications for absorption spectrum shift are summarized in Table IV.
TABLE IV.
Summary of the representative publications for prolonged circulation of phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles. PA, photoacoustic; , maximum absorption wavelength; AUC, area under the curve; , photothermal conversion coefficient; , mean diameter; , zeta potential.
| Group | Nanomaterial | Ligand type | Max. PA signal elapse (H) | Half lifetime (h) | Mean residence time (h) | Major features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al.99 | PEG-Sn-ONc | PEG | 24 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 8.1 ± 1.8 | • = 930 nm |
| • 4 times longer half-life | ||||||
| • ∼10 times AUC. | ||||||
| Jia et al.101 | HSA-FePc NPs | Human serum albumin | 12 | ⋯ | ⋯ | • = ∼ 44.4% (at 671 nm) |
| • = 55 nm | ||||||
| • = −26.9 mV | ||||||
| • Low long-term toxicity | ||||||
| • Preferential accumulation to tumor site | ||||||
| • ∼51.3 wt% loading efficiency |
C. Active delivery
In addition to the passive delivery, engineering the nanoparticles with targeting or stimulus-triggered release function helps to achieve optimal therapeutic and diagnostic effects [Fig. 2(b)].102 The presence of closed d-shell diamagnetic ions (e.g., Zn2+, Al2+, Ga3+) strengthens Pc/Nc complexes of both high triplet yields and long lifetimes and consequently forms hydroperoxide products (type I), or yield singlet oxygen generation converted from ground-state triplet oxygen (type II).67 Both oxidative reactions degrade cellular components, and the damage level highly depends on the local concentration of the dye and oxygen availability. Excessive dosage into the living matter may adversely occur damage to the nontarget systemic normal cells together with targeting tumor cells and lead to pathologic response.103,104 Therefore, selective Pc/Nc delivery restricted only to the targeting tumor cells becomes important to minimize the dosage needed for the treatment. The designed nanocarriers prevent the excessive release of dosage into the bloodstream and normal tissues and therefore keep up the delivery to desired tumor tissue, resulting in high drug concentration within the tumor. From this section, we explain both concepts into the boundary of “active delivery,” as the technique selectively marks the target tumor cells depending on nanoparticle-cell interaction under specific target cell conditions.105 The representative publications for absorption spectrum shift are summarized in Table V.
TABLE V.
Summary of the representative publications for active delivery of phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles. , photothermal conversion coefficient; , mean diameter; PA, photoacoustic, FL, fluorescence, PDT, photodynamic therapy.
| Group | Material name | Delivery type | Mechanism | Major features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al.110 | Biotin-conjugated ZnPc nanodots | Receptor-mediated endocytosis | Biotin receptor | • = 45.7% |
| • = 80 nm | ||||
| • Max. PA signal in +8 hr post-injection | ||||
| • Increased phototoxicity with receptor-rich HeLa cell | ||||
| Ding et al.57 | PEG-folate/ZnPc nanodots | Receptor-mediated endocytosis | Folic acid receptor | • = 20 nm |
| • Effectively internalized to folate receptor-overexpressed CNE-2 cell | ||||
| Du et al.113 | DBCO-ZnPc-LP | Receptor-mediated endocytosis | Bioorthogonal Metabolic Glycoengineering-Activated Tumor Targeting | • = 78.82 nm |
| • Complete self-quenching | ||||
| • = ∼ 44.39% | ||||
| Xie et al.115 | PCBP | Triggered release | H2O2-triggered self-immolative PEG arms | • = max. ∼350 nm |
| • ∼1.4-fold PA amplitude increase | ||||
| Li et al.116 | NanoPcTB | Triggered release | Photoswitchable protein disassembly | • Biotin receptor-mediated switchable property (FL/PDT) |
| Li et al.93 | Pc-peptide conjugate self-assembly | Phthalocyanine-peptide conjugate self-assembly | Photoswitchable protein disassembly | • L-phenylalanine-L-phenylalanine (FF)—mediated switchable photoactivity (FL/PDT) |
1. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
In active targeting, ligands bonded to the nanoparticle promote receptor-mediated endocytosis specifically to the receptor-acquainted cells. The nanoparticles engineered with active delivery are often multi functionalized not only for the diagnostic imaging purpose but also for the therapeutic purpose. The binding biomolecule, such as biotin (or vitamin B7) or folic acid (or vitamin H), which combines overexpressed receptors on the cell membrane, is considered a promising biomarker for substantially reducing the streak effects of aggressive pharmaceutics.106
Studies have revealed the tendency of biotin receptors to overexpress in tumors than in normal tissues. Besides, the structure of biotin is simple and can be readily functionalized.107–109 Thus, it has the potential to be an active tumor-targeting ligand. Wu et al. produced a tumor-targeting capability of fabricated ZnPc nanodots by conjugating biotin onto the surface.110 Also, Ding et al. equipped tumor-specific delivering property by targeting ligand by coupling ZnPc nanodots with folic acid-conjugated PEG chains.57
To overcome the intrinsic disadvantages of traditional biological molecules, such as a limited number of receptors and tumor heterogeneity, a two-step chemical tumor-targeting concept, composed of metabolic glycoengineering and click chemistry, has been actively applied from the time it was first proposed by Koo et al.111,112 The addition of artificial chemical receptor increases the number of binding nanocarriers significantly on the surface of most tumor cells, regardless of tumor type. Such a strategy was first presented by Du et al. in the photothermal/photoacoustic synergistic therapy application.113
2. Triggered release
The difference between receptor-mediated endocytosis and triggered release is that the latter involves a physical or chemical breakage of nanocarrier structure and is triggered by a specific cell condition. Hydrogen peroxide or H2O2-triggered drug release is designed for exclusive oxidative microenvironment within cancer cells.114 The ROS responsive nanocarrier rapidly disassembles in target cells and promotes rapid intracellular drug release. The four self-immolative PEG arms consisting of the activatable probe, developed by Xie et al., are specifically cleaved with the ROS presence. The increased hydrophobicity promotes the supramolecular regrowth around the tumor cells and gets spatiotemporally highlighted in the photoacoustic image.115
Joining selective recognition of protein as a biomarker and reverse application of self-quenching monomer could lead to the novel design of switchable photoactivity. Li et al. explored biotin-receptor-responsive photoswitchable property from biotin-conjugated Pc-based nanodots.116 The presence of biotin-receptor-like protein triggers the nanoparticle's partial disassembly, resulting in the generation of fluorescence and reactive oxygen species instead of photothermal conversion, inducing PA signal generation and PTT effect. The nanoparticle delivery showed high selectivity toward biotin receptor-positive cancer cells on xenograft models (A549), compared to the receptor-negative cancer cells (WI38-VA13). The switchable photoactivity from short peptide micelle was also reported in aforementioned Li et al.'s work.93
III. BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS OF Pc/Ncs
A. Biomedical Imaging
1. Contrast-enhanced PA imaging
Using endogenous biological chromophores, such as oxy-/deoxy-hemoglobin and melanin, the PA imaging achieves superb optical imaging contrast, high spatial resolution, and a larger depth of penetration compared to pure optical imaging techniques. However, due to strong light absorption and scattering in tissue, light fluence and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) decrease exponentially with increased imaging depth. In addition, some tissues or organs that need to be imaged, such as tumor and lymphatic system, do not possess intrinsic optical contrast. Many Pc/Nc-based materials have been developed as PA imaging contrast agents to visualize such biological targets and improve imaging sensitivity, specificity, and penetration depth.78,99,117–119
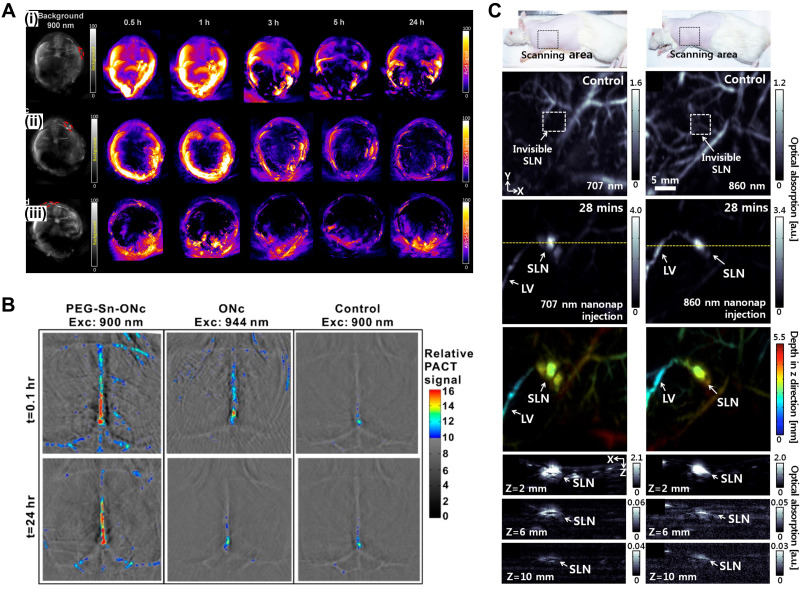
For in vivo PA tumor imaging, Attia et al. investigated three tetrasulfonate phthalocyanine formulations as contrast agents: phthalocyanine tetrasulfonic acid (PcS4), Zn(II) phthalocyanine tetrasulfonic acid (ZnPcS4), and Al(III) phthalocyanine chloride tetrasulfonic acid (AlPcS4).118 They observed high PA imaging contrast in the tumor after intravenous administration of PcS4 [Fig. 3(a)]. Huang et al. synthesized Sn(IV)-chelated octabutoxy Nc (Sn-ONc) with axial conjugation of polyethylene glycol (PEG) for photoacoustic vascular imaging [Fig. 3(b)].99 Introducing Sn and PEG exhibited longer absorption peaks and prolonged circulation time, respectively, enabling noninvasive long-term brain vessel imaging in vivo. A family of organic nano formulated naphthalocyanine was first introduced by Zhang et al.119 The reported nanoparticle was designed using the formulation of frozen micelles to endure a hostile gastrointestinal (GI) environment for real-time PA imaging of GI function. Based on the tunable NIR absorption wavelength of the nanoformulated Nc, Lee et al. developed two nanoformulated Nc dyes with large NIR absorption at 707 nm or 860 nm using 2,11,20,29,tetra-tert-butyl-2,3-naphthlaocyanine or 5,9,14,18,23,27,32,36-octabutoxy,-2,3-naphthalocyanine, respectively. They photoacoustically observed lymphatic vessels and the sentinel lymph node [Fig. 3(c)], which are invisible in label-free PA imaging.117
FIG. 3.
Contrast-enhanced PA images. (a) In vivo PA signals at various time points after tail-vein administration of (i) PcS4, (ii) ZnPcS4, and (iii) AlPcS4. Reprinted with permission from Attia et al., Biomed. Opt. Express 6(2), 591 (2015). Copyright 2015 The Optical Society. (b) Noninvasive photoacoustic images of brain blood vessels of mice administered with PEG-Sn-ONc or ONc at the indicated time points following intravenous injection. Reprinted with permission from Huang et al., Bioconjugate Chem. 27(7), 1574 (2016). Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society. (C) In vivo PA imaging of rat's SLNs with injection of 707 nm (left column) and 860 nm (right column) nanonaps. Reprinted with permission from Lee et al., “Dual-color photoacoustic lymph node imaging using nanoformulated naphthalocyanines,” Biomaterials 73, 142–148. Copyright 2015 Elsevier. PA, photoacoustic; SLN, sentinel lymph node; LV, lymphatic vessel.
2. Multimodal imaging agents
Thanks to the inherent capability of Pc/Nc for high NIR absorption and centric metal ion chelation, Pc/Ncs have great potential to be a contrast agent for complementary multimodal imaging.
The FL is one of the most widely used biological imaging modalities in visualizing living organelles. When a substance absorbs light, the excess energy dissipates through the emission of light, which is FL and/or heat, contributing to PA wave generation. Though FL and PA have competing yield, both are based on high absorbance of light, and thus, many contrast agents have been reported as a bimodal FL and PA imaging agent or FL-PA switchable imaging agent.68,81,92,93,116,120–122 Li et al. developed phthalocyanine-peptide conjugate nanoparticles with switchable photoactivity between PA imaging, associated with photothermal therapy, and FL imaging, associated with photodynamic therapy.93 The switchable photoactivity was observed when the NPs were disassembled by the cell membrane-interaction, which permitted spatiotemporally optimal therapeutic windows via adaptive PA/FL imaging, and achieved precise phototheranostics.
With a nature of PA imaging of combining photon excitation and US detection, the PA imaging can be easily integrated with the conventional US imaging. Choi et al. designed surface crosslinked nanodroplets encapsulating Nc and perfluorohexane for PA/US dual-modal image-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) therapy.70 The accumulation of the developed nanoparticles in the tissue was photoacoustically monitored to confirm the optimal time point of HIFU treatment. The intratherapy monitoring was performed by US imaging visualizing echogenic microbubbles generated under HIFU exposure.
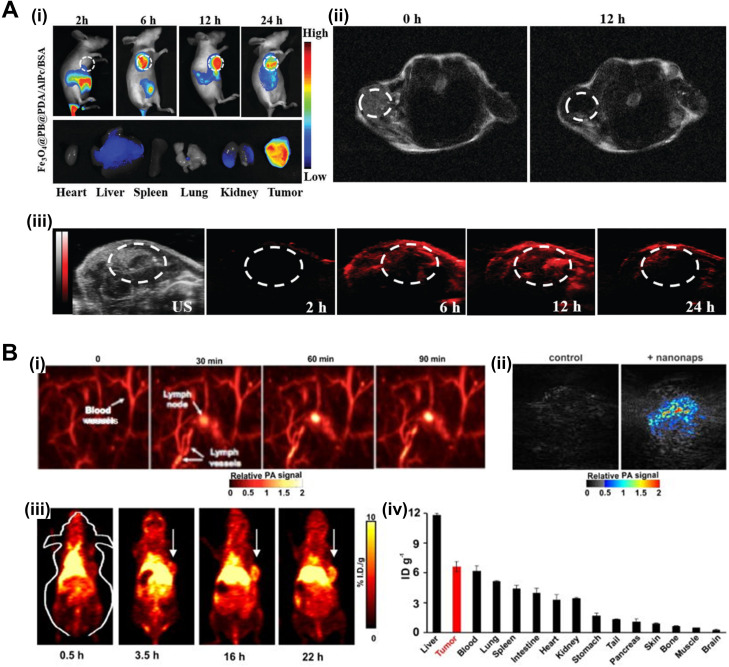
Other imaging modalities have also been explored using Pc/Nc-based PA agents. Wang et al. fabricated polydopamine (PDA)/aluminum Pc (AlPc)/bovine serum albumin (BSA) coated magnetic Prussian blue nanoparticles for triple-modal FL/MR/PA cancer imaging [Fig. 4(a)].120 Lu et al. compared and screened a series of porphyrin Pc and Nc dyes, encapsulated in the interior of nanoparticles through the flash nanoprecipitation (FNP) process, and revealed strong PA responses at high loadings of dyes and combined PA and FL responses at lower loadings of dyes.68 The incorporability of nanoparticles with MR/PET/SPEC imaging agents and therapeutic drugs was also demonstrated. Zhang et al. developed nanoformulated Ncs for in vivo dual-modal PA/PET imaging of lymph nodes and tumors [Fig. 4(b)].91
FIG. 4.
Pc/Ncs for multimodal imaging. (a) (i) In vivo FL images after i.v. injection of Fe3O4@PB@PDA/AlPc/BSA in tumor-bearing mice at 2 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h and ex vivo FL images of AlPc in major organs induced with 660 nm laser irradiation after i.v. injection for 24 h. (ii) MR signals in the tumor before and 12 h after i.v. injection with Fe3O4@PB@PDA/AlPc/BSA. (iii) US and PA images of tumor-bearing mice after i.v. injection with Fe3O4@PB@PDA/AlPc/BSA taken different time points. Republished with permission from Wang et al., J. Mater. Chem. B 6(16), 2460 (2018); permission conveyed through Copyright 2018 Royal Society of Chemistry, Clearance Center, Inc. (B) Nanonaps for PA and PET imaging. (i) PA lymph node imaging using nanonaps. (ii) PA imaging of subcutaneous 4T1 whole tumors in living BALB/c mice with or without i.v. administration of 2.6 mg nanonaps 24 h prior. (iii) Serial PET images of 4T1 subcutaneous breast tumors in BALB/c mice after i.v. injection. Arrows show tumor location. (iv) Biodistribution of 64Cu within nanonaps 24 hours post injection of nanonaps. Republished with permission from Zhang et al., Nanoscale 9(10), 3391 (2017); permission conveyed through Copyright 2017 Royal Society of Chemistry Clearance Center, Inc. FL, fluorescence; i.v., intravenous; MR, magnetic resonance; US, ultrasound; PA, photoacoustic; PET, positron emission tomography.
The representative publications for biomedical imaging application are summarized in Table VI.
TABLE VI.
Summary of the representative publications for biomedical imaging application of phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles. , excitation wavelength; PA, photoacoustic; GI, gastrointestinal tract; NP, nanoparticle; FL, fluorescence; PTT, photothermal therapy; PDT, photodynamic therapy; US, ultrasound; HIFU, high-intensity focused ultrasound; MR, magnetic resonance; PET, positron emission tomography.
| Group | Agent | (nm) | Imaging modality | Application | Major features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al.99 | PEG-Sn-ONc | 900, 944 | PA | Blood circulation (brain) | • Absorbance shift from 860 nm to 930 nm via Tin chelation |
| • Prolonged circulation time via axial PEGylation | |||||
| Zhou et al.78 | P-Pc | 1064 | PA | Tumor imaging, GI tract | • High absorbance (>1000) at 1000 nm |
| • Imaging depth: 11.6 cm (chicken breast tissues), 5 cm (human arm) | |||||
| Lee et al.117 | 2,11,20,29,tetra-tert-butyl-2,3-Nc or 5,9,14,18,23,27,32,36-octabutoxy,-2,3-Nc | 707, 860 | PA | Lymphatic system imaging | • Dual-color PA imaging of two separate lymphatic systems |
| • Spectrally stable at a very high concentration | |||||
| Li et al.116 | PF NP | 680 | PA/FL | Bimodal image-guided PTT/PDT | • Switchable PTT+PA and PDT+FL theranostics |
| • Highly selective for biotin receptor-positive cancer cells (e.g. A549) | |||||
| Choi et al.70 | Nc/PFH@PCPN | 850 | PA/US | Bimodal image-guide HIFU therapy | • 0 US imaging contrast when vaporized under HIFU ablation |
| Wang et al.120 | Fe3O4@PB @PDA/AlPc/BSA | 660 | PA/FL/MR | Trimodal image-guided PTT/PDT | • Fe3O4-based MR contrast |
| • Prussian blue (PB) modification for PA-guided PTT | |||||
| • Synergistic FL-guided PDT with AlPc photosensitizer | |||||
| Zhang et al.91 | Surfactant-stripped ONc nanonap | 860 | PA/PET | Lymphatic mapping, tumor imaging | • 64Cu-based PET contrast |
B. Probing biological processes
1. Tumor detection
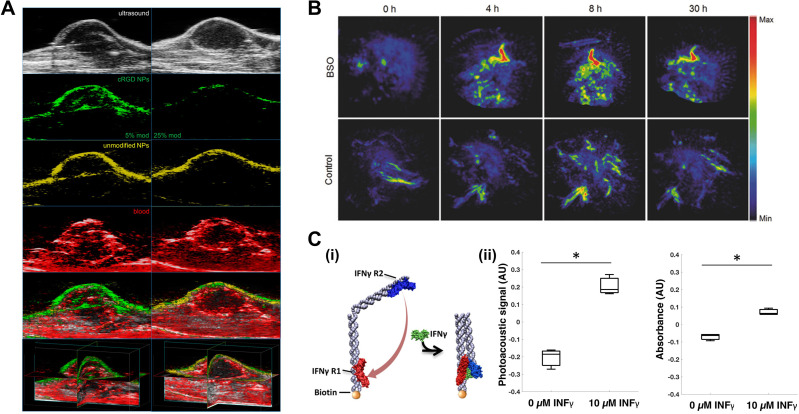
Active targeting for anticancer is essential for delivering theragnostic agents to the region of interest while avoiding normal tissues. Several Pc/Nc derivatives have been introduced as an active cancer diagnostic probe or to deconvolute passive vs active targeting effects. As an actively targeted cancer theragnostic agent, Ma et al. presented a zinc phthalocyanine soybean phospholipid (ZnPc-SPC),92 which showed high sensitivity to FRα over-expressed tumor cells. The ZnPc-SPC complex presented multiphase theranostics: (1) PTT associated with PA imaging in the early phase and (2) PDT with FL images in the late phase accompanied by pH-sensitive drug release in the tumor. Lu et al. developed multiplexed PA imaging agents of cRGD-modified nanoparticles, which can bind to αVβ3 integrin expressed in Lewis lung carcinoma tumors, and unmodified nanoparticles based on Pc/Nc macrocycles, which can internally normalize active ligand targeting effects from passive targeting such as EPR effect.123 PA imaging of the two spectrally separable nanoparticles showed the distinct distribution of agents in the tumor site [Fig. 5(a)]. Du et al. investigated tumor-targeting Pc compounded with dual-targeting effect via metabolic glycoengineering and click chemistry.113 The PA signal in the tumor region was substantially higher in the mice group injected with the proposed dual-targeting nanoagent intravenously than in the control group with a passive-targeting agent.
FIG. 5.
Pc/Nc-based agents for probing biological processes. (a) Multiplexed in vivo tumor PA imaging. Representative 2D slice images exhibiting US (first row), cRGD NP PA (second row), unmodified NP PA (third row), blood PA (fourth row), and overlaid signals (fifth row), and example 3D reconstruction (sixth row) of mice tumors, 48 h after tail vein inoculation with 5% cRGD NPs + 0% cRGD NPs (left column) and 25% cRGD NPs + 0% cRGD NPs (right column), respectively. Reprinted with permission from Lu et al., ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 3(3), 443 (2017). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society. (b) Representative PA MAP images of tumors for BSO-pretreated and untreated mice after systemic administration of PCBP (30 μg per mouse) through tail vein. Republished with permission from Xie et al., Adv. Mater. 29(44), 1703693 (2017). Permission conveyed through Copyright 2017 John Wiley and Sons Clearance Center, Inc. (C) (i) Schematic of the nanosensor 2-step binding mechanism between IFNγ and its receptors. (ii) Response of the IFNγ nanosensor (780 nm) to buffer and 10 μM IFNγ (169 μg/ml) in buffer. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent trials. Reprinted with permission from Morales et al., ACS Sens. 4(5), 1313 (2019). Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. PA, photoacoustic; US, ultrasound.
2. Biomolecule detection
Tracking biomolecules in the body is critically important in many fields ranging from basic science research to medical health care. The tracking helps significantly in understanding biological/physiological processes in living organisms, diagnosing diseases, or monitoring pre-/in-/post-treatment responses. Recently, Morales et al. developed a DNA-based PA nanosensor to detect interferon-gamma (IFNγ) that plays a critical role in activating immunity against infections.124 In the presence of IFNγ, the DNA structure's arms were folded to induce stacking of Pc dye, achieving a 55% increase in PA signal [Fig. 5(c)]. Toriumi et al. reported tautomeric benziphthalocyanines, by introducing free hydroxyl group with esterase- or H2O2-labile markers, for activatable PA detection of esterase or H2O2.55 Xie et al. designed Pc-based semiconducting macromolecule, which first underwent ROS-induced cleavage process of PEG and then subsequently the residual Pcs self-assembled into large nanoparticles, showing enhanced PA signal [Fig. 5(b)] in the presence of ROS.115
The representative publications for probing biological processes with Pc/Ncs are summarized in Table VII.
TABLE VII.
Summary of the representative publications for probing biological processes with phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles. PTT, photothermal therapy; PA, photoacoustic; PDT, photodynamic therapy; FL, fluorescence; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
| Group | Agent | Targeting/Probing strategy | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ma et al.92 | ZnPc-SPC | FRα receptor | • FRα over-expressed tumor cell detection (e.g. 4T1) |
| • Multiphase phototheranostics (Phase I: PTT/PA → Phase II: PDT/FL) | |||
| • pH-sensitive drug release in tumor | |||
| Lu et al.123 | PEG-coated Pc/Nc with tert-butyl or butoxy functional groups with/without cRGD surface modification | αVβ3 integrin | • Multiplexed PA imaging |
| • Lewis lung carcinoma tumor detection | |||
| Du et al.113 | DBCO-ZnPc-LP | Metabolic glycoengineering + click chemistry | • PA tumor imaging |
| • PA image-guided PTT/PAT | |||
| Morales et al.124 | DNA-based nanostructure conjugated with Pc and IFNγ receptors | IFNγ receptors (IFNγR1, IFNγR2) | • IFNγ detection |
| Toriumi et al.55 | BPcs derivatives | Free hydroxyl group with esterase-/H2O2-labile markers | • Activatable PA detection of esterase or H2O2 |
| Xie et al.115 | Macromoleuclar PCBP | Four PEG arms with ROS-responsive linker, inducing self-assembling upon ROS-induced cleavage of PEG | • PA detection of ROS during drug treatment |
C. Therapeutic agents
1. Photothermal therapy
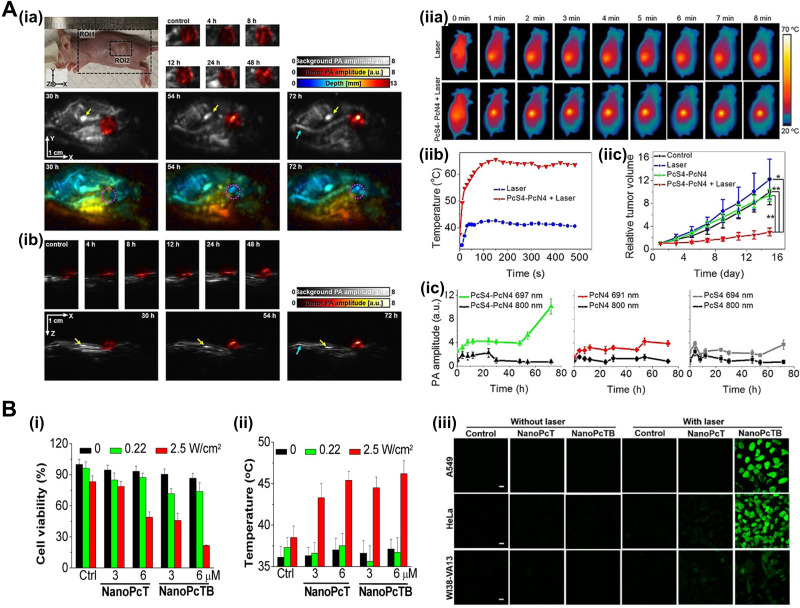
Since PA imaging is based on high optical absorption and local heat conversion, many Pc/Ncs investigated for PA imaging agents inherently have great potential for PTT, which is based on local heat generation at a specific excitation band. The Pc/Ncs, mainly due to strong absorbance at long wavelengths, possess attractive traits of theranostics such as deeper penetrability, lower photon energy, and much safer to adjacent normal cells/tissues. In 2020, Li et al. reported a nanostructured theranostic agent for both PA imaging and PTT through supramolecular self-assembly of two water-soluble Pc derivatives.54 The Pc assemblies showed completely quenched FL and strong PA/photothermal responses, resulting in high contrast PA imaging of cancer tumors and efficient anticancer PTT in vivo [Fig. 6(a)]. To further exploit the advantages of maximum permissible exposure (MPE) of laser and deep penetration in tissues, a phototheranostic agent in the second near-infrared (NIR-II) window was proposed by Pan et al.56 The agent was developed based on an organic molecular material, cruciform Pc pentad. The in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated strong PA signals and PTT effect at 1064 nm. Du et al. developed a tumor-targeting nanoagent, dibenzyl cyclooctyne zinc(II)-Pc lipid-poly(ethylene glycol) (DBCO-ZnPc-LP), for multifunctional phototheranostics of PTT and PA therapy, which is a recently emerged phototherapy to eradicate tumor cells using PA shockwave.113
FIG. 6.
Pc/Nc-based agents for PA image-guided phototherapy. (a) In vivo PA (ia) top-view and (ib) side-view MAP images of 4T1-bearing mice before and after intraperitoneal injection of PcS4-PcN4. The gray-scale image represents background PA amplitude, color-scale images represent PA amplitude in the tumor region and depth along the z axis. (ic) In vivo PA amplitude changes in the tumor region over time before and after the injection of PcS4, PcN4, and PcS4-PcN4. (iia) Thermal IR imaging of 4T1-bearing mice with the indicated treatments. (iib) Temperature change curves of 4T1 tumors in mice after the indicated treatments. (iic) Growth curves of tumors in mice after the indicated treatments. Republished with permission, from Li et al., Angew. Chem. 59(22), 8630–8634 (2020). Copyright 2020 John Wiley and Sons Clearance Center, Inc. (b) In vitro anticancer effect. (i) Cytotoxic effects and (ii) temperature of the HeLa cells incubated with NanoPcT and NanoPcTB for 2 h without or with 655 nm laser irradiation. (iii) ROS generation induced by NanoPcT and NanoPcTB in the A549, HeLa, and WI38-VA13 cells in the presence of laser irradiation. Scale bar = 20 μm. Reprinted with permission from Li et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(31), 10880 (2017). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society. PA, photoacoustic; MAP, maximum amplitude projection; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
2. Photodynamic therapy
The Pc/Ncs have been widely exploited as photosensitizers in PDT due to strong absorption at long wavelengths and easily tunable photochemical properties. Ding et al. synthesized zinc(II)-phthalocyanine (ZnPc) nanodot by cryodesiccation-driven crystallization for PA image-guided cancer PDT.57 In addition to the PDT capability, with cytotoxic singlet oxygen generation, the nanodots showed excellent water-soluble and stealth properties with the surface modified using PEG2000-folate and Pluronic F127. Li et al. developed nanostructured Pc assemblies as a PDT agent, which are activatable in biotin receptor-positive cancer cells.116 The Pc assemblies displayed synergistic phototheranostic capability with intrinsic PA and PTT properties and cancer-specific FL and PDT properties [Fig. 6(b)]. The two-photon excited PDT (TPE-PDT) was introduced by Mauriello-Jimenez et al. for precise cancer treatment.122 Similar to two-photon excitation microscopy, The TPE-PDT allows deep penetration with longer wavelengths and superb spatiotemporal resolution. Bridged silsesquioxane nanoparticles were designed from tetrasilylated porphyrin and Pc, showing excellent TPE-PDT performance and strong PA imaging contrast in vivo.
The representative publications for phototherapy with Pc/Nc nanoparticles are summarized in Table VIII.
TABLE VIII.
Summary of the representative publications for phototherapy with phthalocyanine/naphthalocyanine nanoparticles. PA, photoacoustic; PTT, photothermal therapy; FL, fluorescence; NIR, near infrared; PAT, photoacoustic therapy; PDT, photodynamic therapy.
| Group | Agent | Phototherapy parameters | Application | Major features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al.54 | PcS4-PcN4 | 660 nm, 2 W·cm−2, 8 min | PA image-guided PTT | • Completely quenched FL, leading to strong PA/PTT responses |
| Pan et al.56 | Zn4-H2Pc/DP NPs | 1064 nm, 0.6 W·cm−2, 10 min | PA image-guided PTT | • Phototheranostic agent in NIR-II window |
| Du et al.113 | DBCO-ZnPc-LP | 808 nm, 0.1 W·cm−2, 5 min | PA image-guided PTT/PAT | • Strong heat energy transfer for PTT |
| • Thermal-enhanced ultrasonic shockwave for PAT | ||||
| Ding et al.57 | FA-ZnPcNDs | 808 nm, 0.5 W·cm−2, 3 min | PA image-guided PDT | • Excellent water solubility and stealth properties |
| Li et al.116 | NanoPcTBs | 655 nm, 2.0 W·cm−2, 1 min. + 0.22 W·cm−2, 5 min | PA/FL image-guided PTT/PDT | • Activatable in biotin receptor-positive cancer cells |
| • Intrinsic PA+PTT properties | ||||
| • Cancer-specifically activating FL+PDT properties | ||||
| Mauriello-Jimenez et al.122 | BSPOR, BSPHT | 750 nm, 800 nm, 3 W, 1.57 s | PA image-guided PDT | • Two-photon excited PDT for precise treatment in deep tissues. |
IV. CONCLUSIONS AND OUTLOOK
In this review, we summarized recent advances in nanoformulated Pc/Nc agents for PA imaging, synergetic biomedical imaging, biochemical sensing, and phototherapy. Due to strong extinction coefficients at long wavelengths ( > 105 M−1 cm−1, > 650 nm), Pc/Ncs inherently possess high contrast for PA imaging in deep tissues. Diverse metal chelation can also be performed to modulate their optical properties to further increase the extinction coefficients (1) for high-sensitive PA imaging, (2) to enable multiplexing imaging by sharpening and separating the absorption peak, and (3) to explore multimodal imaging such as64Cu PET imaging. A large variety of chemical substituents have been reported in the literature, which can easily conjugate on Pc/Nc peripheries and induce targeting ability, switchable/activatable properties, enhanced stability, and improved water solubility. Many Pc/Ncs have also been used as PA image-guided phototheranostic agents in addition to their conventional use as photosensitizers in phototherapy. Rich absorption over NIR-I window has well verified its suitability as an angiographic contrast agent, and breaking its barrier to NIR-II window has overlooked its application to reveal unseen physiological findings from important deeply located organs as (1) gastrointestinal tract, (2) lymphatic system, and (3) excretory system. Intestinal motility disorder is one of the common factors that may deteriorate to severe bacterial infection and diabetes.125 Sentinel lymph node biopsy is a decisive process to staging of metastatic cancer and plays a critical role in future treatment and prognosis.126 Venous pyelogram is a test to check for abnormalities in kidney function, stones in the kidneys and ureters, and cancer.127 While application sites are inaccessible with noninvasive optical imaging techniques, aforementioned diagnostic protocols involve incision or cumbersome minimal invasive catheterized/endoscopic technique, otherwise heavily rely on ionizing radiation procedures as X-ray and computed tomography. As being a noninvasive, nonionizing process, NIR-II PAI possess high functional potential to innovate conventional diagnostic protocol of unreachable organs. Strong NIR absorption and photostability are their true strengths as multi-modal bioimaging and phototherapy agents. To achieve successful clinical translation and commercialization, rigorous and systemic studies must precede the approval showing further improvements in biocompatibility, solubility, clearance, and diagnostic/therapeutic efficacy. With the current emerging trends and continuous developments, we believe Pc/Ncs could serve as a vital tool for biomolecular imaging and theranostics in the near future.
AUTHORS' CONTRIBUTIONS
E.Y.P. and D.O. contributed equally to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. NRF-2019R1A2C2006269), National R&D Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT (No. 2020M3H2A1078045), and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2020R1A6A1A03047902). It was also supported by BK21 FOUR project.
Note: This paper is part of the special issue on Functional Biomaterials.
DATA AVAILABILITY
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
- 1. Xu M. and Wang L. V., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77(4), 041101 (2006). 10.1063/1.2195024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Beard P., Interface Focus 1(4), 602 (2011). 10.1098/rsfs.2011.0028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Wang L. V., Photoacoustic Imaging and Spectroscopy ( CRC Press, 2017). [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kim J., Lee D., Jung U., and Kim C., Ultrasonography 34(2), 88 (2015). 10.14366/usg.14062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kim C., Erpelding T. N., Jankovic L., Pashley M. D., and Wang L. V., Biomed. Opt. Express 1(1), 278 (2010). 10.1364/BOE.1.000278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Yao J. and Wang L. V., Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 6(5), 332 (2011). 10.1002/cmmi.443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Yao J. and Wang L. V., Photoacoustics 2(2), 87 (2014). 10.1016/j.pacs.2014.04.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Wang L. V., IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 14(1), 171 (2008). 10.1109/JSTQE.2007.913398 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Jeon S., Kim J., Lee D., Baik J. W., and Kim C., Photoacoustics 15, 100141 (2019). 10.1016/j.pacs.2019.100141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Kim J., Park E.-Y., Park B., Choi W., Lee K. J., and Kim C., Exp. Biol. Med. 245(4), 321 (2020). 10.1177/1535370219889968 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Choi W., Park E.-Y., Jeon S., and Kim C., Biomed. Eng. Lett. 8(2), 139 (2018). 10.1007/s13534-018-0062-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kim J., Park S., Jung Y., Chang S., Park J., Zhang Y., Lovell J. F., and Kim C., Sci. Rep. 6(1), 35137 (2016). 10.1038/srep35137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Kim J. Y., Lee C., Park K., Lim G., and Kim C., Sci. Rep. 5(1), 7932 (2015). 10.1038/srep07932 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Jeon M., Kim J., and Kim C., Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 54(2–3), 283 (2016). 10.1007/s11517-014-1182-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Park E. Y., Lee D., Lee C., and Kim C., IEEE Access 8, 160915 (2020). 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3020559 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wang L. V., Nat. Photonics 3(9), 503 (2009). 10.1038/nphoton.2009.157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kim C., Song K. H., Gao F., and Wang L. V., Radiology 255(2), 442 (2010). 10.1148/radiol.10090281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Wang Y., Maslov K., Kim C., Hu S., and Wang L. V., IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57(10), 2576 (2010). 10.1109/TBME.2010.2059026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Park E.-Y., Park S., Lee H., Kang M., Kim C., and Kim J., Photonics 8(1), 13 (2021). 10.3390/photonics8010013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Jeon M. and Kim C., IEEE Trans. Multimedia 15(5), 975 (2013). 10.1109/TMM.2013.2244203 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Galanzha E. I., Shashkov E. V., Kelly T., Kim J.-W., Yang L., and Zharov V. P., Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(12), 855 (2009). 10.1038/nnano.2009.333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Zhang W., Li Y., Yu Y., Derouin K., Qin Y., Nguyen V. P., Xia X., Wang X., and Paulus Y. M., Photoacoustics 20, 100194 (2020). 10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Yao D.-K., Maslov K., Shung K. K., Zhou Q., and Wang L. V., Opt. Lett. 35(24), 4139 (2010). 10.1364/OL.35.004139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Kim H., Baik J. W., Jeon S., Kim J. Y., and Kim C., Opt. Lett. 45(24), 6755 (2020). 10.1364/OL.404041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Zhou Y., Xing W., Maslov K. I., Cornelius L. A., and Wang L. V., Opt. Lett. 39(16), 4731 (2014). 10.1364/OL.39.004731 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Galanzha E. I., Shashkov E. V., Spring P. M., Suen J. Y., and Zharov V. P., Cancer Res. 69(20), 7926 (2009). 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4900 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Park B., Bang C. H., Lee C., Han J. H., Choi W., Kim J., Park G. S., Rhie J. W., Lee J. H., and Kim C., J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 35(3), 669–676 (2021). 10.1111/jdv.16985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Kim J., Kim Y. H., Park B., Seo H.-M., Bang C. H., Park G. S., Park Y. M., Rhie J. W., Lee J. H., and Kim C., Br. J. Dermatol. 179(3), 780 (2018). 10.1111/bjd.16677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Zhang H. F., Maslov K., Sivaramakrishnan M., Stoica G., and Wang L. V., Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(5), 053901 (2007). 10.1063/1.2435697 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Wang X., Xie X., Ku G., Wang L. V., and Stoica G., J. Biomed. Opt. 11(2), 024015 (2006). 10.1117/1.2192804 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Kim J., Kim J. Y., Jeon S., Baik J. W., Cho S. H., and Kim C., Light: Sci. Appl. 8(1), 103 (2019). 10.1038/s41377-019-0220-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sangha G. S., Phillips E. H., and Goergen C. J., Biomed. Opt. Express 8(2), 736 (2017). 10.1364/BOE.8.000736 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Allen T. J., Beard P. C., Hall A., Dhillon A. P., and Owen J. S., J. biomedical optics 17(6), 061209 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.061209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Dasa M. K., Nteroli G., Bowen P., Messa G., Feng Y., Petersen C. R., Koutsikou S., Bondu M., Moselund P. M., and Podoleanu A., Photoacoustics 18, 100163 (2020). 10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Diot G., Metz S., Noske A., Liapis E., Schroeder B., Ovsepian S. V., Meier R., Rummeny E., and Ntziachristos V., Clinical Cancer Res. 23(22), 6912 (2017). 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Jeon S., Song H. B., Kim J., Lee B. J., Managuli R., Kim J. H., Kim J. H., and Kim C., Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1 (2017). 10.1038/s41598-017-04334-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Yao J., Maslov K. I., Zhang Y., Xia Y., and Wang L. V., J. Biomed. Opt. 16(7), 076003 (2011). 10.1117/1.3594786 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Yavuz M. S., Cheng Y., Chen J., Cobley C. M., Zhang Q., Rycenga M., Xie J., Kim C., Song K. H., Schwartz A. G., Wang L. V., and Xia Y., Nat. Mater. 8(12), 935 (2009). 10.1038/nmat2564 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Lovell J. F., Jin C. S., Huynh E., Jin H., Kim C., Rubinstein J. L., Chan W. C. W., Cao W., Wang L. V., and Zheng G., Nat. Mater. 10(4), 324 (2011). 10.1038/nmat2986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Filonov G. S., Krumholz A., Xia J., Yao J., Wang L. V., and Verkhusha V. V., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 51(6), 1448 (2012). 10.1002/anie.201107026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Lee W. J., Park E.-Y., Choi D., Lee D., Koo J., Min J. G., Jung Y., Hong S. B., Kim K., Kim C., and Kim S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(29), 32270 (2020). 10.1021/acsami.0c05650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Noh I., Kim MSik, Kim J., Lee D., Oh D., Kim J., Kim C., Jon S., and Kim Y.-C., J. Controlled Release 320, 283 (2020). 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hu M., Chen J., Li Z.-Y., Au L., Hartland G. V., Li X., Marquez M., and Xia Y., Chem. Soc. Rev. 35(11), 1084 (2006). 10.1039/b517615h [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Cavigli L., Khlebtsov B. N., Centi S., Khlebtsov N. G., Pini R., and Ratto F., Nanomaterials 11(1), 116 (2021). 10.3390/nano11010116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Giepmans B. N. G., Adams S. R., Ellisman M. H., and Tsien R. Y., Science 312(5771), 217 (2006). 10.1126/science.1124618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Laufer J., Jathoul A., Pule M., and Beard P., Biomed. Opt. Express 4(11), 2477 (2013). 10.1364/BOE.4.002477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Josefsen L. B. and Boyle R. W., Theranostics 2(9), 916 (2012). 10.7150/thno.4571 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. de la Torre G., Claessens C. G., and Torres T., Chem. Commun. 2007(20), 2000. 10.1039/B614234F [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Song L., Li H., Sunar U., Chen J., Corbin I., Yodh A. G., and Zheng G., Int. J. Nanomed. 2(4), 767 (2007). [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Davidson A. T., J. Chem. Phys. 77(1), 168 (1982). 10.1063/1.443636 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Chitgupi U. and Lovell J. F., Biomed. Eng. Lett. 8(2), 215 (2018). 10.1007/s13534-018-0059-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Zhang Y. and Lovell J. F., Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 9(1), e1420 (2017). 10.1002/wnan.1420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Ali H. and Lier J. E. V., Chem. Rev. 99(9), 2379 (1999). 10.1021/cr980439y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Li X., Park E. Y., Kang Y., Kwon N., Yang M., Lee S., Kim W. J., Kim C., and Yoon J., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 59(22), 8630 (2020). 10.1002/anie.201916147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Toriumi N., Asano N., Ikeno T., Muranaka A., Hanaoka K., Urano Y., and Uchiyama M., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 58(23), 7788 (2019). 10.1002/anie.201903303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Pan H., Li S., Kan J. L., Gong L., Lin C., Liu W., Qi D., Wang K., Yan X., and Jiang J., Chem. Sci. 10(35), 8246 (2019). 10.1039/C9SC02674F [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Ding H., Cai Y., Chen J., Lu T., Wen W., Nie G., and Wang X., Microchim. Acta 186(4), 237 (2019). 10.1007/s00604-019-3286-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Wei J.-P., Chen X.-L., Wang X.-Y., Li J.-C., Shi S.-G., Liu G., and Zheng N.-F., Chin. Chem. Lett. 28(6), 1290 (2017). 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.01.007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Jiang Z., Shao J., Yang T., Wang J., and Jia L., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 87, 98 (2014). 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.05.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Schreiver I., Hutzler C., Laux P., Berlien H.-P., and Luch A., Sci. Rep. 5(1), 12915 (2015). 10.1038/srep12915 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Kenry, Duan Y., and Liu B., Adv. Mater. 30(47), 1802394 (2018). 10.1002/adma.201802394 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Hong G., Antaris A. L., and Dai H., Nat. Biomed. Eng. 1(1), 0010 (2017). 10.1038/s41551-016-0010 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Luo S., Zhang E., Su Y., Cheng T., and Shi C., Biomaterials 32(29), 7127 (2011). 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.06.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Tedesco A. C., Primo F. L., and Carvalho de Jesus P. d. C., in Multifunctional Systems for Combined Delivery, Biosensing and Diagnostics, edited by Grumezescu A. M. ( Elsevier, 2017), p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- 65. Macor L., Fungo F., Tempesti T., Durantini E. N., Otero L., Barea E. M., Fabregat-Santiago F., and Bisquert J., Energy Environ. Sci. 2(5), 529 (2009). 10.1039/b822954f [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Yasin A., Sevim A. M., Hamuryudan E., and Ahmet G., Dyes Pigments 68(2), 129 (2006). 10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.01.019 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67. van Lier J. E. and Spikes J. D., “The chemistry, photophysics and photosensitizing properties of phthalocyanines,” in Ciba Foundation Symposium 146-Photosensitizing Compounds: Their Chemistry, Biology and Clinical Use: Photosensitizing Compounds: Their Chemistry, Biology and Clinical Use: Ciba Foundation Symposium 146 ( Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK, 2007), pp. 17–39. 10.1002/9780470513842.ch3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Lu H. D., Lim T. L., Javitt S., Heinmiller A., and Prud'homme R. K., ACS Comb. Sci. 19(6), 397 (2017). 10.1021/acscombsci.7b00031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Wang Z., Gai S., Wang C., Yang G., Zhong C., Dai Y., He F., Yang D., and Yang P., Chem. Eng. J. 361, 117 (2019). 10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Choi H., Choi W., Kim J., Kong W. H., Kim K. S., Kim C., and Hahn S. K., Biomacromolecules 20(10), 3767 (2019). 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00842 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. He Y., Wang M., Fu M., Yuan X., Luo Y., Qiao B., Cao J., Wang Z., Hao L., and Yuan G., Int. J. Nanomedicine 15, 5927 (2020). 10.2147/IJN.S254108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Lobo C. S., Tomé V. A., Schaberle F. A., Calvete M. J., Pereira M. M., Serpa C., and Arnaut L. G., Inorg. Chim. Acta 514, 119993 (2021). 10.1016/j.ica.2020.119993 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Duffy M. J., Planas O., Faust A., Vogl T., Hermann S., Schäfers M., Nonell S., and Strassert C. A., Photoacoustics 9, 49 (2018). 10.1016/j.pacs.2017.12.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Taratula O. R., Taratula O., Han X., Jahangiri Y., Tomozawa Y., Horikawa M., Uchida B., Albarqi H. A., Schumann C., Bracha S., Korzun T., and Farsad K., J. Vasc. Interv Radiol. 30(9), 1480 (2019). 10.1016/j.jvir.2019.03.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Chitgupi U., Nyayapathi N., Kim J., Wang D., Sun B., Li C., Carter K., Huang W.-C., Kim C., Xia J., and Lovell J. F., Adv. Mater. 31(40), 1902279 (2019). 10.1002/adma.201902279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Park B., Lee K. M., Park S., Yun M., Choi H.-J., Kim J., Lee C., Kim H., and Kim C., Theranostics 10(6), 2509 (2020). 10.7150/thno.39403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Furuyama T., Satoh K., Kushiya T., and Kobayashi N., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(2), 765 (2014). 10.1021/ja411016f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Zhou Y., Wang D., Zhang Y., Chitgupi U., Geng J., Wang Y., Zhang Y., Cook T. R., Xia J., and Lovell J. F., Theranostics 6(5), 688 (2016). 10.7150/thno.14555 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Kostka M., Zimcik P., Miletin M., Klemera P., Kopecky K., and Musil Z., J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 178(1), 16 (2006). 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2005.06.014 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80. George R. D., Snow A. W., Shirk J. S., and Barger W. R., J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 2(1), 1–7 (1998). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Liu K., Wang X., Ntziachristos V., Marsch S., and Hunziker P., Eur. Polym. J. 88, 713 (2017). 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.03.008 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Bottari G., Trukhina O., Ince M., and Torres T., Coord. Chem. Rev. 256(21–22), 2453 (2012). 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.03.011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Bottari G., Suanzes J. A., Trukhina O., and Torres T., J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(8), 905 (2011). 10.1021/jz200241k [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Sibata M. N., Tedesco A. C., and Marchetti J. M., Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 23(2), 131 (2004). 10.1016/j.ejps.2004.06.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Coimbra M., Isacchi B., van Bloois L., Torano J. S., Ket A., Wu X., Broere F., Metselaar J. M., Rijcken C. J., and Storm G., Int. J. Pharm. 416(2), 433 (2011). 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.01.056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Gao D. and Lo P.-C., J. Controlled Release 282, 46 (2018). 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.04.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Ottenbrite R. M. and Javan R., in Encyclopedia of Condensed Matter Physics, edited by Bassani Franco, Liedl Gerald L., and Wyder P. ( Elsevier, Oxford, 2005), p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- 88. Choi W., Choi H., Kim J., Kim C., and Hahn S. K., “Surface-crosslinked multi-functional nanodroplets for photoacoustic/ultrasound image-guided high intensity focused ultrasound therapy,” in Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing (International Society for Optics and Photonics), Vol. 11240, p. 1124040. 10.1117/12.2543696 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Rizvi W., Berisha N., Farley C., Bhupathiraju N., Andreou C., Khwaja E., Fuentes G. V., Kircher M. F., Gao R., and Drain C. M., Chem.–A Eur. J. 25(64), 14517 (2019). 10.1002/chem.201903463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Zhang Y., Song W., Geng J., Chitgupi U., Unsal H., Federizon J., Rzayev J., Sukumaran D. K., Alexandridis P., and Lovell J. F., Nat. Commun. 7(1), 10.1038/ncomms11649 (2016). 10.1038/ncomms11649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Zhang Y., Hong H., Sun B., Carter K., Qin Y., Wei W., Wang D., Jeon M., Geng J., Nickles R. J., Chen G., Prasad P. N., Kim C., Xia J., Cai W., and Lovell J. F., Nanoscale 9(10), 3391 (2017). 10.1039/C6NR09321C [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Ma J., Chen D., Li Y., Chen Y., Liu Q., Zhou X., Qian K., Li Z., Ruan H., Hou Z., and Zhu X., J Control Release 284, 1 (2018). 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.06.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Li S., Zhao L., Chang R., Xing R., and Yan X., Chem.–A Eur. J. 25(58), 13429 (2019). 10.1002/chem.201903322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Mohammed A. R., Weston N., Coombes A. G. A., Fitzgerald M., and Perrie Y., Int. J. Pharm. 285(1–2), 23 (2004). 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. He R., Finan B., Mayer J. P., and DiMarchi R. D., Molecules 24(10), 1855 (2019). 10.3390/molecules24101855 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Blanco E., Shen H., and Ferrari M., Nat. Biotechnol. 33(9), 941 (2015). 10.1038/nbt.3330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Verhoef J. J. and Anchordoquy T. J., Drug Delivery Transl. Res. 3(6), 499 (2013). 10.1007/s13346-013-0176-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Parrott M. C. and DeSimone J. M., Nat. Chem. 4(1), 13 (2012). 10.1038/nchem.1230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Huang H., Wang D., Zhang Y., Zhou Y., Geng J., Chitgupi U., Cook T. R., Xia J., and Lovell J. F., Bioconjugate Chem. 27(7), 1574 (2016). 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Chrysanthakopoulos M., Giaginis C., and Tsantili-Kakoulidou A., J. Chromatogr. A 1217(37), 5761 (2010). 10.1016/j.chroma.2010.07.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Jia Q., Ge J., Liu W., Zheng X., Wang M., Zhang H., and Wang P., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(25), 21124 (2017). 10.1021/acsami.7b04360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Loomis K., McNeeley K., and Bellamkonda R. V., Soft Matter 7(3), 839 (2011). 10.1039/C0SM00534G [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Liu M. O., Tai C-h, Sain M-z, Hu A. T., and Chou F-i, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 165(1–3), 131 (2004). 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2004.03.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Kolarova H., Nevrelova P., Bajgar R., Jirova D., Kejlova K., and Strnad M., Toxicol. Vitro 21(2), 249 (2007). 10.1016/j.tiv.2006.09.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Huo M., Chen Y., and Shi J., Expert Opin. Drug Delivery 13(9), 1195 (2016). 10.1080/17425247.2016.1213241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Gocheva G. and Ivanova A., Mol. Pharm. 16(8), 3293 (2019). 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Chen S., Zhao X., Chen J., Chen J., Kuznetsova L., Wong S. S., and Ojima I., Bioconjugate Chem. 21(5), 979 (2010). 10.1021/bc9005656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Davies-Venn C. A., Angermiller B., Wilganowski N., Ghosh P., Harvey B. R., Wu G., Kwon S., Aldrich M. B., and Sevick-Muraca E. M., Mol. Imag. Biol. 14(3), 301 (2012). 10.1007/s11307-011-0499-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Wang H., Chang J., Shi M., Pan W., Li N., and Tang B., Angew. Chem. 131(4), 1069 (2019). 10.1002/ange.201811273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Wu F., Yue L., Cheng K., Chen J., Wong K.-L., Wong W.-K., and Zhu X., ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 6(9), 5230 (2020). 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c00684 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Koo H., Huh M. S., Sun I.-C., Yuk S. H., Choi K., Kim K., and Kwon I. C., Acc. Chem. Res. 44(10), 1018 (2011). 10.1021/ar2000138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Lee S., Koo H., Na J. H., Han S. J., Min H. S., Lee S. J., Kim S. H., Yun S. H., Jeong S. Y., and Kwon I. C., ACS Nano 8(3), 2048 (2014). 10.1021/nn406584y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Du L., Qin H., Ma T., Zhang T., and Xing D., ACS Nano 11(9), 8930 (2017). 10.1021/acsnano.7b03226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Liu J., Pang Y., Zhu Z., Wang D., Li C., Huang W., Zhu X., and Yan D., Biomacromolecules 14(5), 1627 (2013). 10.1021/bm4002574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Xie C., Zhen X., Lyu Y., and Pu K., Adv. Mater. 29(44), 1703693 (2017). 10.1002/adma.201703693 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Li X., Kim C. y, Lee S., Lee D., Chung H.-M., Kim G., Heo S.-H., Kim C., Hong K.-S., and Yoon J., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(31), 10880 (2017). 10.1021/jacs.7b05916 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Lee C., Kim J., Zhang Y., Jeon M., Liu C., Song L., Lovell J. F., and Kim C., Biomaterials 73, 142 (2015). 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.09.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Attia A. B. E., Balasundaram G., Driessen W., Ntziachristos V., and Olivo M., Biomed. Opt. Express 6(2), 591 (2015). 10.1364/BOE.6.000591 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Zhang Y., Jeon M., Rich L. J., Hong H., Geng J., Zhang Y., Shi S., Barnhart T. E., Alexandridis P., Huizinga J. D., Seshadri M., Cai W., Kim C., and Lovell J. F., Nat. Nanotechnol. 9(8), 631 (2014). 10.1038/nnano.2014.130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Wang Y., Pang X., Wang J., Cheng Y., Song Y., Sun Q., You Q., Tan F., Li J., and Li N., J. Mater. Chem. B 6(16), 2460 (2018). 10.1039/C8TB00483H [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Lee S., Li X., Lee D., Yoon J., and Kim C., “Photoacoustic imaging of tumor targeting with biotin conjugated nanostructured phthalocyanine assemblies,” in Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing (International Soc. for Optics and Photonics, 2018), Vol. 10494, p. 1049467. 10.1117/12.2292784 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Mauriello-Jimenez C., Henry M., Aggad D., Raehm L., Cattoën X., Wong Chi Man M., Charnay C., Alpugan S., Ahsen V., Tarakci D. K., Maillard P., Maynadier M., Garcia M., Dumoulin F., Gary-Bobo M., Coll J.-L., Josserand V., and Durand J.-O., Nanoscale 9(43), 16622 (2017). 10.1039/C7NR04677D [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Lu H. D., Wilson B. K., Lim T. L., Heinmiller A., and Prud'homme R. K., ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 3(3), 443 (2017). 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00645 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Morales J., Pawle R. H., Akkilic N., Luo Y., Xavierselvan M., Albokhari R., Calderon I. A. C., Selfridge S., Minns R., Takiff L., Mallidi S., and Clark H. A., ACS Sens. 4(5), 1313 (2019). 10.1021/acssensors.9b00209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Keller J., Bassotti G., Clarke J., Dinning P., Fox M., Grover M., Hellström P. M., Ke M., Layer P., and Malagelada C., Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15(5), 291 (2018). 10.1038/nrgastro.2018.7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Sivasubramanian K., Periyasamy V., and Pramanik M., J. Biophotonics 11(1), e201700061 (2018). 10.1002/jbio.201700061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Lipkin M. E., Mancini J. G., Zilberman D. E., Raymundo M. E., Yong D., Ferrandino M. N., Miller M. J., Yoshizumi T. T., and Preminger G. M., J. Endourol. 25(4), 563 (2011). 10.1089/end.2010.0431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.