Abstract
目的
探究类风湿关节炎(RA)患者长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)Linc00638的表达,及其对RA滑膜成纤维细胞(FLS)炎症、氧化应激的影响。
方法
收集20例正常人(健康对照组)、35例RA患者(RA组)外周血单个核细胞(PBMCs),RT-qPCR法检测Linc00638表达,并研究其与临床指标的相关性;构建Linc00638过表达质粒和小干扰RNA,转染至RA-FLS中;CCK8检测细胞活力;RT-qPCR法检测Linc00638的过表达和干扰效率。ELISA法检测细胞上清液中白介素-4(IL-4)、白介素-6(IL-6)、活性氧(ROS)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)的表达。
结果
与健康对照组相比,RA患者血沉(ESR)、C反应蛋白、类风湿因子(RF)、抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体(Anti-CCP)、IgA、C4显著升高(P < 0.05),Linc00638表达显著降低(P < 0.01);ROC曲线下面积AUC为91.86%,Linc00638的最佳截断值为0.74。Spearman相关性分析表明Linc00638与年龄、病程、DAS28、ESR、C反应蛋白、RF、anti-CCP呈负相关,与IL-4,SOD呈正相关(P < 0.05)。关联规则分析表明Linc00638的下降与年龄(>60岁)、病程(>10年)、ESR、RF、anti-CCP的升高,与IL-4、SOD的降低具有强关联。过表达Linc00638能够抑制细胞活力,干扰Linc00638能够提升细胞活力。过表达Linc00638组能够显著升高Linc00638、IL-4、SOD水平(P < 0.05),降低IL-6、ROS表达(P < 0.05);si-Linc00638组能显著降低Linc00638、IL-4、SOD表达(P < 0.05),升高IL-6、ROS表达(P < 0.05)。
结论
Linc00638在RA患者中低表达,可能通过调控炎症和氧化应激参与疾病进展。
Keywords: 类风湿关节炎, 长链非编码RNA, 炎症, 氧化应激
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the expression of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) Linc00638 in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its regulatory role in inflammation and oxidative stress of synovial fibroblasts in RA patients (RA-FLS).
Methods
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected from 20 healthy individuals and 35 RA patients for detecting the expression of Linc00638 using RT-qPCR to analyze the correlation of Linc00638 expression with the clinical indicators of RA patients. A Linc00638 overexpression plasmid and siRNA targeting Linc00638 were transfected into RA-FLS, and the changes in cell viability was observed using CCK8 assay; the changes in the expression levels of interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-6, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the supernatant were detected using ELISA.
Results
Compared with the healthy control subjects, RA patients had significantly increased ESR, CRP, RF, anti-CCP, IgA, and C4 levels (P < 0.05) and significantly decreased Linc00638 expression in the PBMCs (P < 0.01). The area under the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve of Linc00638 was 91.86% with the best cut-off value of 0.74 for diagnosis of RA. Spearman correlation analysis showed that Linc00638 expression level was negatively correlated with age, course of disease, DAS28, ESR, CRP, RF and anti-CCP, and positively correlated with IL-4 and SOD levels (P < 0.05). Association rule analysis showed that a decreased Linc00638 expression was strongly correlated with an increase of age (>60 years), a longer disease course (>10 years), elevated levels of ESR, RF and anti-CCP, and decreased levels of IL-4 and SOD. In RA-FLS, overexpression of Linc00638 significantly inhibited while Linc00638 interference obviously enhanced the cell viability. Over-expression of Linc00638 also significantly increased the levels of IL-4 and SOD (P < 0.05) and decreased the expressions of IL-6 and ROS (P < 0.05), while interference of Linc00638 produced the opposite effects in the cells (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
RA patients have low expression levels of Linc00638, which may participate in disease progression by regulating inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, long non-coding RNA, inflammation, oxidative stress
类风湿关节炎(RA)是一种以对称性多关节炎为主要临床表现,以关节滑膜慢性炎症、关节的进行性破坏为特征的自身免疫疾病[1-3]。RA发病与遗传、环境、应激等因素有关,能异常诱导激活固有免疫系统和适应性免疫系统,导致免疫耐受破坏而诱发一系列炎症反应[4, 5]。RA病变可累及全身多系统,其全球发病率为0.5%~1.0%,我国大陆发病率为0.42%,具有较高发病率和致残率[6]。RA发病机制虽尚不明确,但氧化应激(OS)及免疫炎症反应在RA发生发展过程中发挥重要作用[7-9]。长链非编码RNA(lncNA)参与RA炎症、凋亡、氧化应激等过程,已成为研究的热点[10, 11]。本团队前期通过高通量测序及生物信息学分析,认为Linc00638是参与RA炎症反应及氧化应激的关键lncRNA[12, 13]。RA体内氧化、抗氧化作用失衡,导致大量氧化中间产物ROS自由基的产生,抗氧化能力减弱,进一步加重炎症反应、引起组织损伤[14, 15]。目前国内外关于Linc00638的研究较少且主要集中于肿瘤方面报导,缺乏Linc00638在RA中研究,以及如何参与RA免疫炎症反应、氧化应激的调控过程。
本研究主要是研究Linc00638在RA患者的表达,分析其与临床指标的的相关性,进一步通过细胞实验,采用RA患者滑膜成纤维细胞(RA-FLS)探究Linc00638干扰或过表达状态下对RA-FLS炎症和氧化应激的影响。
1. 资料和方法
1.1. 临床资料
35例RA患者来自2020年6月~2020年10月安徽中医药大学第一附属医院风湿免疫科住院患者(RA组),其中男性5例,女性30例,年龄56.03±12.43岁;20例正常人为健康对照组(HC组)来自我院健康体检中心,其中男性3例,女性17例,年龄56.25±7.33岁,两组基线差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。本研究经安徽中医药大学第一附属医院伦理委员会批准(2019AH-12)。
选取患者入院后首次检查的实验室指标,具体指标如下:炎症指标:血沉(ESR)、C反应蛋白(CRP);免疫指标:类风湿因子(RF)、抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体(Anti-CCP)、免疫球蛋白A(IgA)、免疫球蛋白G(IgG)、免疫球蛋白M(IgM)、补体C3(C3),补体C4(C4),并计算RA患者DAS28评分。
1.2. 诊断标准
所有患者均符合2010年美国风湿病学会(ACR)联合欧洲抗风湿病联盟(EULAR)提出的RA诊断标准[16]。
1.3. 纳入及排除标准
纳入标准:符合上述诊断标准。排除标准:入院后后无相应实验室指标者;未成年、妊娠期及哺乳期患者;合并其他风湿病,如系统性红斑狼疮、强直性脊柱炎等及合并心血管、血液系统等疾病者。
1.4. RA-FLS培养及转染
RA患者原代滑膜成纤维细胞经SV40过表达慢病毒转染而成的永生化细胞系。在青霉素(终浓度为100 U/mL)和链霉素(终浓度为0.1 mg/mL)的RPMI 1640培养基,5%CO2、37 ℃的细胞培养箱中培养,待细胞融合度达70%即可传代。根据制造商的说明,将pcDNA3.1-Linc00638、si-Linc00638与各自阴性对照用Li-pofectamine2000转染至RA-FLS中,继续孵育48 h。pcDNA3.1-Linc00638、si-Linc00638与各自阴性对照质粒(GenePharma)。
1.5. 实验试剂及仪器
DMEM培养基(Hyclone);白介素4 ELISA试剂盒(武汉基因美),白细胞介素6 ELISA试剂盒(武汉基因美),超氧化物歧化酶ELISA试剂盒(南京建成),A001-1;活性氧(ROS)检测试剂盒(上海贝博);CCK8检测试剂盒(上海贝博),逆转录试剂盒(TaKaRa);荧光定量PCR仪(Thermo Scientific,型号:PIKOREAL 96);高速台式冷冻离心机(安徽嘉文仪器装备有限公司,型号:JW-3021HR);酶标仪(雷杜生命科学股份有限公司,型号:RT-6000)。
1.6. 实验方法
1.6.1. ELISA检测IL-4、IL-6、ROS、SOD表达
收集各组细胞培养上清液,1000 r/min离心10 min,弃去沉淀。将上清液加入酶标板中(每孔100 μL),37 ℃孵育1.5 h,采用ELISA方法,严格按照各试剂盒说明书进行操作,检测IL-4、IL-6、ROS、SOD的表达。
1.6.2. RT-qPCR检测Linc00638的表达
Trizol提取各组RA-FLS总RNA,逆转录反应,进行扩增反应,琼脂糖凝胶电泳,采用Gelpro32凝胶图像分析软件对PCR产物进行半定量分析,以β-actin表达量为参照采用2-△△Ct进行相对定量分析。引物:Linc00638正向引物为5'-CCATAGCCGATTAGCTGTCA',反向引物为5'-AAT GCCGAACTGGAGGTG-3',β-actin正向引物为5'-CC CTGGAGAAGAGCTACGAG-3',反向引物为5'-GGA AGGAAGGCTGGAAGAGT-3'。
1.7. CCK8检测RA-FLS细胞活力
根据制造商的操作说明,用CCK8检测试剂盒检测细胞活力。以每孔3×104 RA-FLSs接种到96孔板中,培养至70%~90%汇合。按上述方法转染对数生长期细胞。每组3孔,分别培养0、24、48 h。在每个时间点,向每个孔中添加10 μL CCK-8溶液,并将细胞在37 ℃下培养1.5 h。酶标仪测定A450nm值来评估细胞活力。
1.8. 统计学分析
SPSS 24. 0软件进行统计学处理,符合正态分布的计量资料采用均数±标准差表示,不合符正态分布,采用四分位数间距表示。正态分布则采用两独立样本t检验,不符合正态分布,则采用秩和检验;采用Spearman进行相关性分析;IBM SPSS Modeler 18.0软件中Apriri模块进行关联规则分析;GraphPad Prism 8.0.1软件绘图,以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1. 受试者临床特征
RA患者的平均DAS28评分为5.16±0.57分,与健康对照组相比,RA患者ESR、CRP、RF、anti-CCP、IgA和C4显著升高(P < 0.05),差异有统计学意义;两组IgG、IgM和C3差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表 1)。
1.
受试者临床指标比较情况
Comparison of the clinical indexes between healthy control (HC) subjects and RApatients
| Index | RA(n=35) | HC(n=20) | P |
| DAS28 | 5.16±0.57 | - | - |
| ESR (mm/h) | 38.09±19.75 | 6.95±3.68 | 0.000 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 23.50 (14.92, 32.77) | 3.97±1.69 | 0.000 |
| RF(U/mL) | 56.00(17.20, 97.90) | 11.11±5.12 | 0.000 |
| anti-CCP(U/mL) | 36.70 (27.70, 45.70) | 2.49±0.88 | 0.000 |
| IGA(g/L) | 2.65 (1.43, 3.80) | 1.62±082 | 0.003 |
| IGG(g/L) | 10.04 (7.19, 13.88) | 8.27±2.34 | 0.071 |
| IGM(g/L) | 0.88 (0.67, 1.45) | 1.27±0.56 | 0.637 |
| C3(g/L) | 1.34±0.29 | 1.18±0.09 | 0.192 |
| C4(g/L) | 0.31±0.10 | 0.25±0.10 | 0.012 |
2.2. Linc00638在RA患者中低表达
为了研究Linc00638在RA患者中的表达,对35例RA组和20例HC组受试者的PBMCs进行RT-qPCR检测。结果显示,在RA中Linc00638的水平下调(图 1A)。进行受试者操作特征(ROC)曲线分析以评估Linc00638的诊断效用,ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.9186(95% CI: 0.85~0.99)。根据Youden指数,区分RA和HC的最佳截断值为0.74,具有88.57%的敏感性和80.00%的特异性(图 1B)。
1.
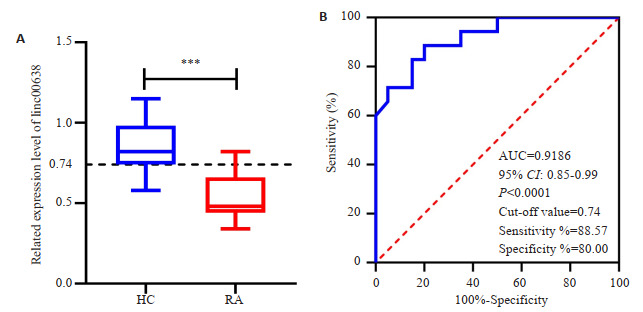
Linc00638在RA患者PBMCs中表达
Expression of Linc00638 in PBMCs of RA patients. A: The expression of Linc00638 in PBMCs from RA patients was decreased (***P < 0.001 vs HC). B: ROC curve analysis of Linc00638 for diagnosis of RA.
2.3. RA患者PBMCs中IL-4、SOD低表达,IL-6、ROS高表达
与健康对照组相比,RA患者PBMCs中IL-4、SOD表达水平显著降低(P < 0.01,图 2A、D),IL-6、ROS表达水平显著升高(P < 0.01,图 2B、C)。
2.
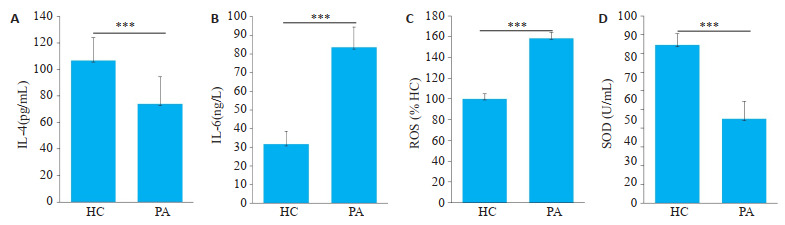
ELISA检测炎症因子、氧化应激指标
Detection of inflammatory factors and oxidative stress indicators by ELISA. A: IL-4 was lowly expressed in PBMCs of RA patients. B: IL-6 was highly expressed in PBMCs of RA patients. C: ROS was highly expressed in PBMCs of RA patients. D: SOD was lowly expressed in PBMCs of RApatients. ***P < 0.01.
2.4. Linc00638与年龄、病程、DAS28及免疫炎症、氧化应激指标存在相关性
Spearman相关性分析结果显示,RA患者Linc00638与年龄、病程、DAS28、ESR、CRP、RF、antiCCP呈负相关(P < 0.05);与IL-4、SOD呈正相关(P < 0.05),与其他指标无相关性(P>0.05,图 3A~I)。
3.
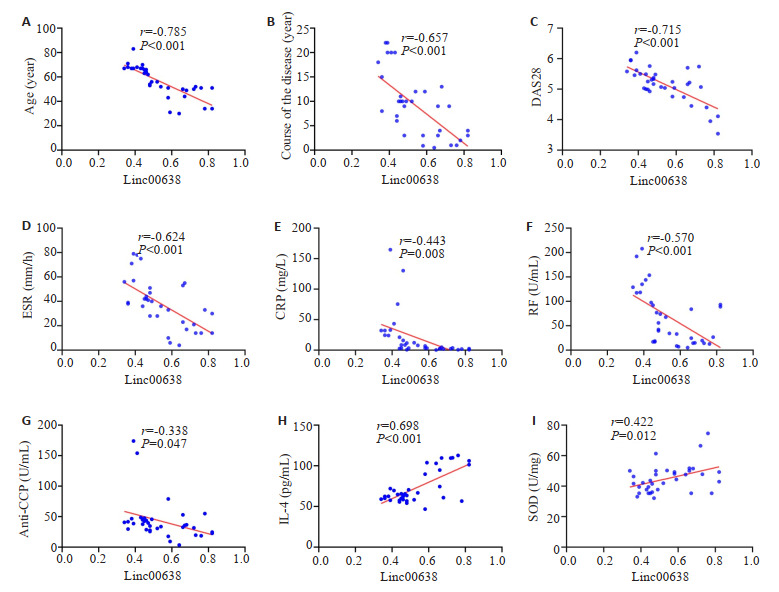
Linc00638与指标的相关性分析
Correlation analysis between Linc00638 and the clinical and biochemical indicators of RA patients. Linc00638 is negatively correlated with age (A), course of the disease (B), DAS28 (C), ESR (D), CRP (E), RF (F), and anti-CCP (G), and positively correlated with IL-4 (H) and SOD (I).
2.5. Linc00638的降低与高龄、长病程、免疫炎症及氧化应激指标具有强关联
RA患者Linc00638的下降与年龄(>60岁)、病程(>10年)、DAS28、ESR、RF、CRP及anti-CCP的升高具强关联,支持度均大于40%,置信度均大于60%;Linc00638的下降与SOD、IL-4指标值的下降具有强关联,支持度均大于65%、置信度均大于75%(表 2)。
2.
Linc00638与年龄、病程、DAS28及实验室指标的关联规则分析
Association rule analysis of Linc00638 with age, course of disease, DAS28 and laboratory indexes
| The former | The latter | Support (%) | Confidence (%) |
| Linc00638↓ | Age>60 years | 67.00 | 83.26 |
| Linc00638↓ | Course of the disease> 10 years | 54.22 | 75.35 |
| Linc00638↓ | ESR↑ | 53.75 | 71.41 |
| Linc00638↓ | DAS28↑ | 57.14 | 64.52 |
| Linc00638↓ | CRP↑ | 42.65 | 75.75 |
| Linc00638↓ | anti-CCP↑ | 63.60 | 83.34 |
| Linc00638↓ | SOD↓ | 80.00 | 90.32 |
| Linc00638↓ | IL-4↓ | 68.57 | 77.42 |
2.6. Linc00638在RA-FLS中的表达及对细胞活力的影响
与pcDNA3.1-NC组相比,Linc00638组Linc00638表达显著升高(P < 0.01);与si-NC组相比,si-Linc00638组Linc00638表达显著降低(P < 0.01,图 4A)。CCK8检测Linc00638对RA-FLS细胞活力的影响,结果显示,与pcDNA3.1-NC组相比,Linc00638组细胞活力明显降低(P < 0.01);与si-NC组相比,si-Linc00638组细胞活力明显降低(P < 0.01,图 4B)。4组中si-Linc00638组细胞活力最高,Linc00638组细胞活力最低(图 4B)。
4.
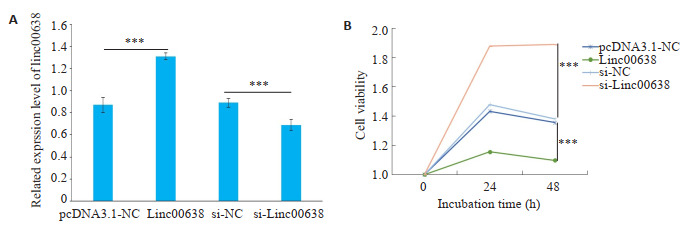
Linc00638在RA-FLS中的表达以及对细胞活力的影响
Expression of Linc00638 in RA-FLS and its effect on cell viability. A: Expression level of Linc00638 in RA-FLS with Linc00638 overexpression or interference. B: Results of CCK8 assay for detecting viability of RA-FLS with Linc00638 overexpression or interference. ***P < 0.01.
2.7. Linc00638对RA-FLS中IL-4、IL-6表达的影响
与pcDNA3.1-NC组相比,Linc00638组IL-4表达显著升高,IL-6表达显著下降(P < 0.05,图 5A、B);与si-NC组相比,si-Linc00638组IL-4表达显著降低,IL-6表达升高(P < 0.05,图 5A、B)。
5.
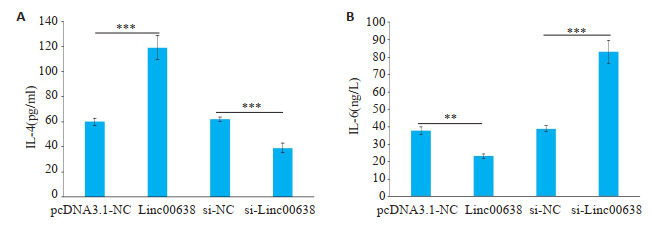
Linc00638对RA-FLS中IL-4、IL-6表达的影响
Effect of Linc00638 overexpression or interference on expressions of IL-4 (A) and IL-6 (B) in RA-FLS. **P < 0.05, ***P < 0.01.
2.8. Linc00638对RA-FLS中ROS、SOD表达的影响
与pcDNA3.1-NC组相比,Linc00638组ROS表达显著降低,SOD表达显著升高(P < 0.05,图 6A、B);与si-NC组相比,si-Linc00638组ROS表达显著升高、SOD表达降低(P < 0.05,图 6A、B)。
6.
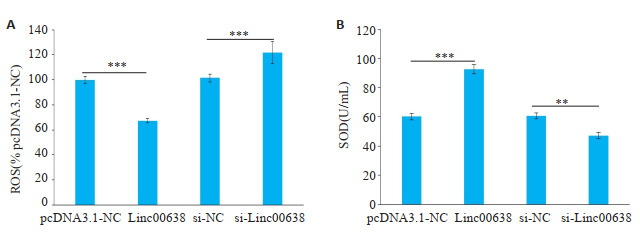
Linc00638对RA-FLS中ROS、SOD表达的影响
Effect of Linc00638 overexpression or interference on expressions of ROS (A) and SOD (B) in RA-FLS. **P < 0.05, ***P < 0.01.
3. 讨论
RA是一种病因复杂的炎症性自身免疫疾病,氧化应激产生的自由基可作为氧化剂和炎症介质参与RA的病理过程[17, 18]。氧化损伤可以诱发RA患者体内炎症反应,产生诸多炎症因子如IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β等,而自由基的增多,可造成氧化剂与抗氧化剂系统的紊乱,导致机体的抗氧化能力减弱,进一步加重炎症反应[19, 20]。本团队以中医学理论为指导,前期通过高通量测序、生物信息学分析及临床验证表明Linc00638是参与RA炎症、氧化应激的关键lncRNA。目前国内外关于Linc00638的研究较少,缺乏在RA患者中的临床及研究。本研究通过临床试验和细胞实验,验证Linc00638在RA湿热痹阻证患者表达情况,以及参与调控炎症与氧化应激的可能机制。
本研究表明Linc00638在RA患者PBMCs中表达显著降低,ROC曲线下面积AUC为91%,表明Linc00638具备较高的诊断价值。细胞因子在RA的发病过程中调节炎症过程,特别是一些促炎细胞因子,并在滑膜炎症和滑膜增生中发挥重要作用,从而导致RA的软骨和骨破坏[21, 22]。秦文等[23]通过基因芯片筛选及生信学分析表明LINC00638、Uc011jsq.2和AK021458有可能参与了炎症来源牙周膜干细胞(PPDLSCs)在力学信号介导下的成骨分化的作用。本研究中RA患者的IL-4、SOD水平降低,IL-6、ROS水平升高,表明患者存在炎症因子失衡、氧化与抗氧化系统紊乱;相关性分析显示Linc00638与年龄、病程、DAS28、ESR、CRP、RF、antiCCP呈负相关,与IL-4、SOD呈正相关,表明Linc00638与临床免疫炎症、氧化应激指标存在相关性。进一步通过关联规则分析,得出同样的结论,表明Linc00638与临床免疫炎症、氧化应激指标存在相关性。研究表明三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)中FOLH1、LINC00638、OAS3等是关于肿瘤预后的重要基因,其机制与T细胞激活免疫调节有关[24];研究发现HCP5、LINC00638、TP53TG1等基因可能作为新生儿败血症的潜在标志物,与调节机体免疫应答过程有关[25]。
RA患者关节滑膜中聚集了大量炎性细胞并产生炎性因子,加重滑膜、软骨的炎症及骨破坏,进一步导致滑膜腔缺氧[26, 27]。而细胞在代谢过程产生的ROS等有害自由基持续升高,产生了高水平的氧化应激。在氧化应激下,脂质过氧化改变细胞膜的渗透性,削弱膜基酶的活性,从而激活抗氧化酶[28-30]。为了进一步探究Linc00638在RA中发挥的潜在机制作用,本研究构建Linc00638的过表达质粒和小干扰RNA,成功转染进入RA-FLS并影响Linc00638的表达。CCK8结果表明Linc00638的过表达质粒能够显著降低RA-FLS细胞活力,而si-Linc00638能够显著提高细胞活力。过表达Linc00638能够显著提升RA-FLS中IL-4、SOD的表达,降低IL-6、ROS的表达;反之,对Linc00638干扰后IL-4、SOD表达明显降低,IL-6、ROS表达明显升高,表明在RA患者中Linc00638可能通过调控患者炎症和氧化应激,参与疾病的发生、发展。Linc00638在不同疾病中,发挥着重要作用,在食管鳞癌的研究中Linc00638与VEGF-C mRNA可直接结合,促进VEGF-C蛋白表达,或与miR-216b相互作用,调控靶基因KRAS的表达,来促进食管癌的进展[31]。LINC00638、hsa_circ_0005139、hsa_circ_0037858等被认为参与为腰椎间盘退行性病变进展的关键基因,参与组织细胞组成、细胞生物合成过程、基因表达和代谢过程的调控[32]。
综上所述,Linc00638在RA患者低表达,与临床指标存在相关性,过表达Linc00638能够降低RA-FLS细胞活力,炎症反应及氧化应激水平。国内外有关Linc00638在RA发生发展中的研究较少。因此,对其在RA中的具体调控机制、下游通路需进一步研究。
Biography
孙艳秋,在读博士研究生,E-mail: 1007900836@qq.com
Funding Statement
科技部国家重点研发计划中医药现代化研究重点专项(2018YFC1705204);国家自然科学基金(81973655,82074373);国自然青年基金(82004102);安徽省高校协同创新项目(GXXT-2020-025);安徽省重点研究和开发计划对外科技合作项目(201904b11020011);安徽省省级质量工程教学研究项目(2018jyxm1068);安徽省名中医刘健工作室建设项目(中医药发展秘[2018] 11号);全国中医药创新骨干人才培训项目(国中医药人教函[2019]128号);安徽省重点研究与开发计划项目(201904a07020004);安徽现代中医内科应用基础与开发研究省级实验室(2016080503B041);安徽省第12批“115”创新团队(皖人才办[2019]1号);安徽省自然科学青年基金(2008085QH386);新安医学教育部重点实验室(2020xayx10)
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81973655, 82074373)
Contributor Information
孙 艳秋 (Yanqiu SUN), Email: 1007900836@qq.com.
刘 健 (Jian LIU), Email: liujianahzy@126.com.
References
- 1.Uthman I, Almoallim H, Buckley CD, et al. Nurse-led care for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the global literature and proposed strategies for implementation in Africa and the Middle East. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(3):529–42. doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04682-6. [Uthman I, Almoallim H, Buckley CD, et al. Nurse-led care for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the global literature and proposed strategies for implementation in Africa and the Middle East [J]. Rheumatol Int, 2021, 41(3): 529-42.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keretsu S, Bhujbal SP, Cho SJ. Molecular modeling studies of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidin-4-amine derivatives as JAK1 inhibitors based on 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) and MM-PBSA calculations. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/338499387_Molecular_modeling_studies_of_pyrrolo23-dpyrimidin-4-amine_derivatives_as_JAK1_inhibitors_based_on_3D-QSAR_molecular_docking_molecular_dynamics_MD_and_MM-PBSA_calculations. J Biom Bolecular Structure Dynam. 2020;59(4):1–26. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1714483. [Keretsu S, Bhujbal SP, Cho SJ. Molecular modeling studies of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidin-4-amine derivatives as JAK1 inhibitors based on 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) and MM-PBSA calculations[J]. J Biom Bolecular Structure Dynam, 2020, 59(4): 1-26.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.巩 勋, 崔 家康, 姜 泉, et al. 1388例类风湿关节炎患者中医证型与疾病活动度特征横断面调查. 中医杂志. 2021;62(4):312–7. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.04.009. [巩勋, 崔家康, 姜泉, 等. 1388例类风湿关节炎患者中医证型与疾病活动度特征横断面调查[J]. 中医杂志, 2021, 62(4): 312-7.] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.覃 桂城, 林 晓吟, 梁 培彬, et al. 高强度炎症反应诱导关节软骨特异性瓜氨酸化抗原表达. http://www.j-smu.com/CN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.08.03. 南方医科大学学报. 2020;40(8):1081–9. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.08.03. [覃桂城, 林晓吟, 梁培彬, 等. 高强度炎症反应诱导关节软骨特异性瓜氨酸化抗原表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(8): 1081-9.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.陈 永和, 苏 宝倡, 尚 孟乔. P2X7受体在类风湿关节炎中的诊断价值及炎症反应中的作用. http://www.j-smu.com/CN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.12.09. 南方医科大学学报. 2018;38(12):1453–8. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.12.09. [陈永和, 苏宝倡, 尚孟乔. P2X7受体在类风湿关节炎中的诊断价值及炎症反应中的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(12): 1453-8.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.中华医学会风湿病学分会 2018中国类风湿关节炎诊疗指南. 中华内科杂志. 2018;40(4):242–51. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2018.04.004. [中华医学会风湿病学分会. 2018中国类风湿关节炎诊疗指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2018, 40(4): 242-51.] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga T. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;24(9746):1094–108. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60826-4. [Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga T. Rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Lancet, 2010, 24(9746): 1094-108.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pope JE, Choy EH. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51(1):219–29. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.11.005. [Pope JE, Choy EH. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2021, 51(1): 219-29.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lin W, Shen P, Song Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species in autoimmune cells: function, differentiation, and metabolism. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/349598904_Reactive_Oxygen_Species_in_Autoimmune_Cells_Function_Differentiation_and_Metabolism/download. Front Immunol. 2021;12(9):635021–9. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.635021. [Lin W, Shen P, Song Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species in autoimmune cells: function, differentiation, and metabolism[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12(9): 635021-9.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fan C, Cui X, Chen S, et al. LncRNA LOC100912373 modulates PDK1 expression by sponging miR-17-5p to promote the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=33437356. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(12):7709–23. [Fan C, Cui X, Chen S, et al. LncRNA LOC100912373 modulates PDK1 expression by sponging miR-17-5p to promote the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Am J Transl Res, 2020, 12(12): 7709-23.] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhu X, Zhu Y, Ding C, et al. LncRNA H19 regulates macrophage polarization and promotes Freund's complete adjuvant-induced arthritis by upregulating KDM6A. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;93:107402–11. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107402. [Zhu X, Zhu Y, Ding C, et al. LncRNA H19 regulates macrophage polarization and promotes Freund's complete adjuvant-induced arthritis by upregulating KDM6A[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 93: 107402-11.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wen JT, Liu J, Wang B, et al. Prediction of self-perception of patient in rheumatoid arthritis with the key RNAs expression profiles. Front Med. 2020;7:567–73. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00567. [Wen JT, Liu J, Wang B, et al. Prediction of self-perception of patient in rheumatoid arthritis with the key RNAs expression profiles[J]. Front Med, 2020, 7: 567-73.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.文 建庭, 刘 健, 万 磊, et al. 类风湿关节炎患者氧化应激关键lncRNAs表达谱的筛选验证及相关性分析. 风湿病与关节炎. 2020;9(6):6–11, 20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4174.2020.06.002. [文建庭, 刘健, 万磊, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者氧化应激关键lncRNAs表达谱的筛选验证及相关性分析[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2020, 9(6): 6-11, 20.] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wójcik P, Gęgotek A, Žarkoviḉ N, et al. Oxidative stress and lipid mediators modulate immune cell functions in autoimmune diseases. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/348472949_Oxidative_Stress_and_Lipid_Mediators_Modulate_Immune_Cell_Functions_in_Autoimmune_Diseases. Int J Molecul Sci. 2021;22(2):13–21. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020723. [Wójcik P, Gęgotek A, Žarkoviḉ N, et al. Oxidative stress and lipid mediators modulate immune cell functions in autoimmune diseases [J]. Int J Molecul Sci, 2021, 22(2): 13-21.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nawaz H, Ali A, Rehman T, et al. Chronological effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40(5):1767–78. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05438-0. [Nawaz H, Ali A, Rehman T, et al. Chronological effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2021, 40(5): 1767-78.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/ European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569–81. doi: 10.1002/art.27584. [Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/ European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62(9): 2569-81.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shen P, Huang Y, Ba X, et al. Si Miao San attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in rats with CIA via the modulation of the Nrf2/ ARE/PTEN pathway. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/349231651_Si_Miao_San_Attenuates_Inflammation_and_Oxidative_Stress_in_Rats_with_CIA_via_the_Modulation_of_the_Nrf2AREPTEN_Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:2843623–9. doi: 10.1155/2021/2843623. [Shen P, Huang Y, Ba X, et al. Si Miao San attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in rats with CIA via the modulation of the Nrf2/ ARE/PTEN pathway[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 2843623-9.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ziadé N, Saad S, Al Mashaleh M, et al. Perceptions of patients with rheumatoid arthritis about self-assessment of disease activity after watching an educational video: a qualitative pilot study from the AUTO-DAS in Middle Eastern Arab countries project. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(4):733–40. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04799-2. [Ziadé N, Saad S, Al Mashaleh M, et al. Perceptions of patients with rheumatoid arthritis about self-assessment of disease activity after watching an educational video: a qualitative pilot study from the AUTO-DAS in Middle Eastern Arab countries project [J]. Rheumatol Int, 2021, 41(4): 733-40.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.郭 锦晨, 刘 健, 张 晓军, et al. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊含药血清对类风湿关节炎患者氧化应激及AMPK, FoxO3a蛋白表达的影响. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZY202013032.htm. 中国中药杂志. 2020;45(13):3228–32. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200427.502. [郭锦晨, 刘健, 张晓军, 等. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊含药血清对类风湿关节炎患者氧化应激及AMPK, FoxO3a蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(13): 3228-32.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ferreira HB, Melo T, Paiva A, et al. Insights in the role of lipids, oxidative stress and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis unveiled by new trends in lipidomic investigations. Antioxidants. 2021;10(1):45–53. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010045. [Ferreira HB, Melo T, Paiva A, et al. Insights in the role of lipids, oxidative stress and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis unveiled by new trends in lipidomic investigations[J]. Antioxidants, 2021, 10(1): 45-53.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schett G, Stach C, Zwerina J, et al. How antirheumatic drugs protect joints from damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(10):2936–48. doi: 10.1002/art.23951. [Schett G, Stach C, Zwerina J, et al. How antirheumatic drugs protect joints from damage in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2008, 58(10): 2936-48.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Luisa DM, Fabrizio C, Angela M, et al. The natural agonist of estrogen receptor β silibinin plays an immunosuppressive role representing a potential therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1903–12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01903. [Luisa DM, Fabrizio C, Angela M, et al. The natural agonist of estrogen receptor β silibinin plays an immunosuppressive role representing a potential therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1903-12.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.秦 文, 严 青, 郭 冬会, et al. 长链非编码RNA在炎症来源牙周膜干细胞力学刺激加载前后的表达谱分析. 临床口腔医学杂志. 2019;35(6):323–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1634.2019.06.002. [秦文, 严青, 郭冬会, 等. 长链非编码RNA在炎症来源牙周膜干细胞力学刺激加载前后的表达谱分析[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2019, 35(6): 323-6.] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.苏 芃, 毛 晓韵, 关 舒, et al. 三阴性乳腺癌肿瘤微环境特征免疫相关生物学标志物筛选及功能预测分析. 中国肿瘤外科杂志. 2020;12(4):348–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4136.2020.04.013. [苏芃, 毛晓韵, 关舒, 等. 三阴性乳腺癌肿瘤微环境特征免疫相关生物学标志物筛选及功能预测分析[J]. 中国肿瘤外科杂志, 2020, 12(4): 348-55.] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Liu L, Wang H, Zhang XF, et al. Identification of potential biomarkers in neonatal Sepsis by establishing a competitive endogenous RNA network. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2020;23(5):369–80. doi: 10.2174/1386207323666200401121204. [Liu L, Wang H, Zhang XF, et al. Identification of potential biomarkers in neonatal Sepsis by establishing a competitive endogenous RNA network[J]. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen, 2020, 23(5): 369-80.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.郭 锦晨, 刘 健, 王 键, et al. 基于AMPK-FoxO3a-MnSOD信号通路探讨类风湿关节炎患者氧化应激的机制及黄芩清热除痹胶囊对其影响. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MYXZ201908008.htm. 免疫学杂志. 2019;35(8):681–90. [郭锦晨, 刘健, 王键, 等. 基于AMPK-FoxO3a-MnSOD信号通路探讨类风湿关节炎患者氧化应激的机制及黄芩清热除痹胶囊对其影响[J]. 免疫学杂志, 2019, 35(8): 681-90.] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Oğul Y, Gür F, Cengiz M, et al. Evaluation of oxidant and intracellular anti-oxidant activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: In vivo and in silico studies. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107654–63. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107654. [Oğul Y, Gür F, Cengiz M, et al. Evaluation of oxidant and intracellular anti-oxidant activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: In vivo and in silico studies [J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 97: 107654-63.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim HJ, Herath K, Dinh D, et al. Sargassum horneri ethanol extract containing polyphenols attenuates PM-induced oxidative stress via ROS scavenging and transition metal chelation. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464621000505. J Functional Foods. 2021;79(2):1307–16. [Kim HJ, Herath K, Dinh D, et al. Sargassum horneri ethanol extract containing polyphenols attenuates PM-induced oxidative stress via ROS scavenging and transition metal chelation[J]. J Functional Foods, 2021, 79(2): 1307-16.] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Das M, Devi KP. Dihydroactinidiolide regulates Nrf2/HO-1 expression and inhibits caspase-3/Bax pathway to protect SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells from oxidative stress induced neuronal apoptosis. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0161813X2100022X. Neurotoxicology. 2021;84(12):53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2021.02.006. [Das M, Devi KP. Dihydroactinidiolide regulates Nrf2/HO-1 expression and inhibits caspase-3/Bax pathway to protect SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells from oxidative stress induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Neurotoxicology, 2021, 84(12): 53-63.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pisoschi AM, Pop A, Iordache F, et al. Oxidative stress mitigation by antioxidants-an overview on their chemistry and influences on health status. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0223523420308631. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;209:112891–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112891. [Pisoschi AM, Pop A, Iordache F, et al. Oxidative stress mitigation by antioxidants-an overview on their chemistry and influences on health status [J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2021, 209: 112891-8.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.王雅丽. 长链非编码RNALINC00638在食管鳞癌中的功能和作用机制研究[D]. 北京协和医学院, 2017.
- 32.Zhang YH, Song J, Shen L, et al. Systematic identification of lncRNAs and circRNAs-associated ceRNA networks in human lumbar disc degeneration. Biotech Histochem. 2019;94:606–16. doi: 10.1080/10520295.2019.1622782. [Zhang YH, Song J, Shen L, et al. Systematic identification of lncRNAs and circRNAs-associated ceRNA networks in human lumbar disc degeneration[J]. Biotech Histochem, 2019, 94: 606-16.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


