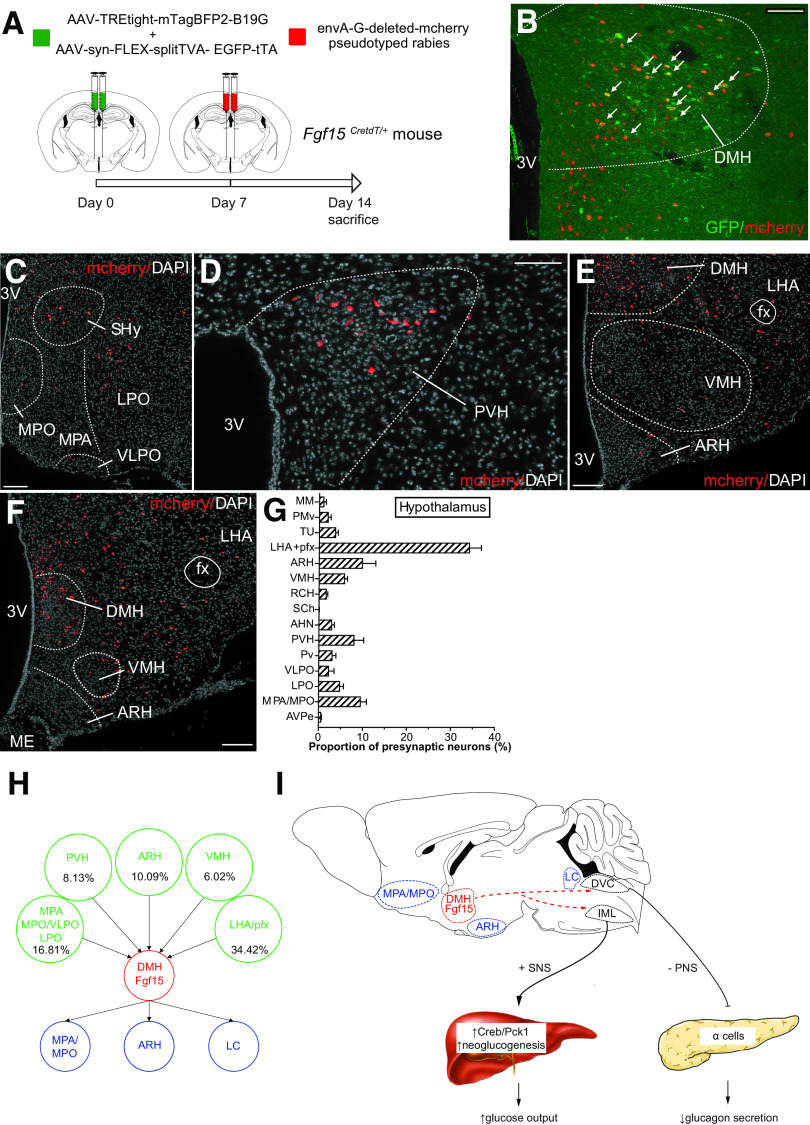
Figure 8.
Retrograde mapping of DMH Fgf15 neuron innervation. A: AAV1-syn-FLEX-splitTVA-EGFP-tTA and AAV1-TREtight-mTagBFP2-B19G were injected bilaterally in the DMH of Fgf15CretdT/+ and an EnvA-G-deleted-mCherry pseudotyped rabies virus 1 week later. B: Immunofluorescence detection of EYFP/mCherry double-positive neurons in the DMH. Scale bar = 50 μm. Immunofluorescence detection of mCherry-positive presynaptic neurons in the septohypothalamic nucleus (SHy), MPO, MPA, ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO), and lateral preoptic area (LPO) (C) (scale bar = 50 μm); the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVH) (D) (scale bar = 50 μm); and the VMH, ARH, and lateral hypothalamic area (LHA) (E and F) (scale bar = 50 μm). G: Quantitative assessment of the neurons innervating DHM Fgf15 neurons based on their brain localization. AHN, anterior nucleus of the hypothalamus; AVPe, anteroventral periventricular nucleus; MM, medial mammillary nucleus, medial part; PMv, premammillary nucleus, ventral part; pfx, perifornical area; Pv, periventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; RCH, retrochiasmatic area; SCh, suprachiasmatic nucleus; TU, tuberal nucleus. H: Graphical summary of the afferent inputs into Fgf15 neurons and their efferent projections. I: Graphical summary of the impact of Fgf15 neurons activation on autonomic nervous activity, glucagon secretion, and hepatic glucose production. DVC, dorsal vagal complex; IML, intermediolateral cell column; LC, locus coeruleus; PNS, parasympathetic nerve, SNS, sympathetic nerve; 3V, third ventricle.