GRB2 controls radiation-induced DNA damage repair—a predictive biomarker for PARPi and radiation therapy outcome.
Abstract
DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair is initiated by MRE11 nuclease for both homology-directed repair (HDR) and alternative end joining (Alt-EJ). Here, we found that GRB2, crucial to timely proliferative RAS/MAPK pathway activation, unexpectedly forms a biophysically validated GRB2-MRE11 (GM) complex for efficient HDR initiation. GRB2-SH2 domain targets the GM complex to phosphorylated H2AX at DSBs. GRB2 K109 ubiquitination by E3 ubiquitin ligase RBBP6 releases MRE11 promoting HDR. RBBP6 depletion results in prolonged GM complex and HDR defects. GRB2 knockout increased MRE11-XRCC1 complex and Alt-EJ. Reconstitution with separation-of-function GRB2 mutant caused HDR deficiency and synthetic lethality with PARP inhibitor. Cell and cancer genome analyses suggest biomarkers of low GRB2 for noncanonical HDR deficiency and high MRE11 and GRB2 expression for worse survival in HDR-proficient patients. These findings establish GRB2’s role in binding, targeting, and releasing MRE11 to promote efficient HDR over Alt-EJ DSB repair, with implications for genome stability and cancer biology.
INTRODUCTION
Repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs), the most toxic and mutagenic form of DNA damage, involves multiple proteins, but the meiotic recombination 11 homolog (MRE11) complex with RAD50 adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) and NBS1 phospho-binding protein (MRN) complex plays a central initiating and orchestrating role (1, 2). At DSBs, the variant histone H2AX, which is inserted within ~2 to 25% of nucleosome core particles throughout the genome, is constitutively phosphorylated on tyrosine-142 (Y142) by the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)–dependent chromatin remodeling complex Williams syndrome transcription factor (WSTF) (3). In response to DNA damage, serine-139 undergoes phosphorylation (pS139, also known as γH2AX) on both sides of a DNA DSB by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)–related kinases (4), thus providing a critical signal and platform for recruitment of DNA damage repair (DDR) proteins (5). Early DNA damage signaling is dominated by H2AX dually phosphorylated on Y142 and S139 (pH2AX). Yet, around 2 hours after DNA damage, a switch to the γH2AX state of S139 phosphorylation is required to complete repair (3). The transcriptional coactivator eyes absent (EYA) phosphatase facilitates Y142 dephosphorylation (6). MRN is recruited to DSB sites via multiple independent processes. Many cell-based assays show that γH2AX plays a pivotal role in MRN recruitment to chromatin through association of NBS1-MDC1-H2AX (7–10). The NBS1 FHA domain interacts with phosphorylated mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1 (MDC1), which, in turn, binds to γH2AX, establishing a mode of MRN recruitment to DNA damage sites (11, 12). Rad17, through its association with NBS1, also indirectly recruits MRE11 to DSBs at an early stage, independent of MDC1 (13). Evolutionarily conserved complement component 1 Q subcomponent-binding protein (C1QBP) interacts with MRE11-RAD50 to form a complex without NBS1, stabilizing MRE11 but preventing its DNA binding (14). Thus, multiple processes may enrich MRE11 at DSBs, including some not involving MRN complex. Overall, these data show that timely MRE11 recruitment dictates DSB repair initiation and efficiency as critical for cell survival and genome stability (2).
Growth factor receptor–bound protein 2 (GRB2) is a metazoan adapter protein essential for receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)–induced RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation (15, 16). Functionally, GRB2 acts in early signaling complexes (ESCs): Within seconds after RTK activation, a GRB2-SOS complex is recruited by the receptor to the membrane for RAS activation (17). GRB2 is so essential for RTK-induced RAS activation that GRB2-knockout (KO) mice are embryonically lethal due to defective endodermal cell differentiation and epiblast formation (18). Although the nuclear localization of GRB2 was first reported over 20 years ago (19, 20), no function was assigned. Based primarily upon inferential evidence, a GRB2-PTEN signaling axis was recently proposed to act in DNA repair and genomic stability with possible implications in DDR pathways in HeLa and 293T cells (21). Yet, a substantial presence and role of GRB2 in the nucleus and its specific molecular and cellular functions remained uncertain. We therefore set out to define and test the molecular basis for GRB2 as a bona fide DDR protein, including possible nuclear activities, as a foundation for future GRB2 research.
Here, investigation of GRB2 in multiple human cells and tissues provides comprehensive and systematic evidence of its nuclear localization. Whereas we found that GRB2 depletion affects DNA repair, our direct measurements found limited correlation between PTEN and GRB2 in DNA repair. Instead, our results define a previously unidentified nucleoplasmic GRB2-MRE11 (GM) complex as an MRE11 pool possibly distinct from its canonical MRN complex (2). Moreover, GRB2 preferentially promotes homology-directed repair (HDR) and suppresses alternative end joining (Alt-EJ). Furthermore, GRB2-KO was synthetically lethal to the loss of poly(adenosine 5′-diphosphate–ribose) polymerase (PARP) function, and GRB2-mediated MRE11 recruitment to phosphorylated H2AX was indispensable for timely HDR. At DNA damage sites, MRE11 release enabling efficient HDR was regulated by GRB2 ubiquitination on lysine-109 (K109). Release was controlled by the E3 ubiquitin ligase retinoblastoma binding protein 6 (RBBP6), which acts in maintaining common fragile site stability (22). Mutant cell lines with GRB2-KO, reconstitution of GM interaction disrupting GRB2 mutants, and RBBP6 depletion showed HDR defects. This GM molecular and cellular axis for efficient HDR was further supported by data from patients with breast cancer. In our The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) analyses, high GRB2 expression showed worse survival only in HDR-proficient patients with high MRE11 expression. Provocatively, immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of human normal and breast cancer tissues supported correlation between cancer progression stage and nuclear GRB2 (nGRB2), where high levels of nGRB2 occur in late-stage patients. These findings suggest that GRB2 and MRE11 coexpression levels merit testing as a prognostic biomarker in HDR-proficient patients, paving the way to identify patient groups without BRCA mutations who may favorably respond to PARP inhibitor (PARPi). Overall, we find an unexpected GRB2 function in timely and robust recruitment and ubiquitination-regulated release of MRE11 that promotes HDR and suppresses Alt-EJ, suggesting that the GM complex acts in maintaining genome integrity.
RESULTS
nGRB2 is poly-ubiquitinated at K109
To robustly test the potential impact of GRB2 nuclear function, we tested its localization by performing a systematic IHC analysis on representative mouse and human tissues. We found differential GRB2 nuclear localization with broad tissue type specificity. This observation supports and extends reports of GRB2 in the nucleus in some cells (19, 20). Although ubiquitous in the cytoplasm, nGRB2 was highly detected in brain, colon, stomach, and intestine while rarely observed in breast, liver, heart, and muscle (Fig. 1, A and B, and fig. S1, A and B). Immunofluorescence and cell fractionation analyses in representative cancer cell lines also indicated GRB2 presence in nuclei (Fig. 1C and fig. S1C). Intriguingly, nGRB2 showed an apparent higher–molecular weight pattern stereotypical of ubiquitination.
Fig. 1. nGRB2 is poly-ubiquitinated by RBBP6 at the K109 site.
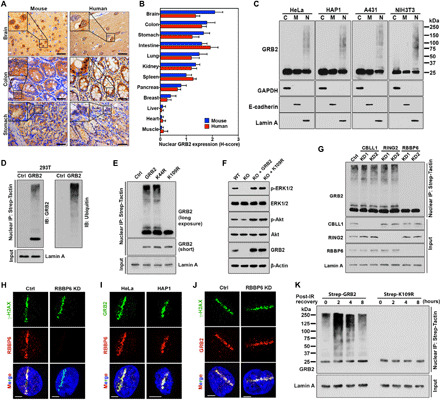
(A) IHC analysis of GRB2 expression in mouse and human tissue samples. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) H-score quantification of nGRB2. (C) GRB2 expression patterns by subcellular fractionations. Cytoplasm (C), plasma membrane (M), and nucleus (N). (D) Strep-GRB2 with Strep-tag alone (Ctrl) was precipitated from the nuclear extracts of human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells and analyzed with GRB2 or ubiquitin antibodies. (E) Strep-tagged K44R or K109R mutant GRB2 was precipitated from the nuclear extracts of HEK293T cells and immunoblotted with anti-GRB2 antibody. (F) Wild-type (WT), GRB2-KO cells, and KO cells reconstituted with WTGRB2 or K109RGRB2 were immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (G) Strep-GRB2 was precipitated from the nuclear extracts of CBLL1-, RING2-, or RBBP6-KD HEK293T cells and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (H) Micro-irradiated RBBP6-KD HeLa cells were analyzed with the indicated antibodies. (I) Micro-irradiated cells analyzed with indicated antibodies. (J) As (H), except with indicated antibodies. (K) HEK293T cells stably expressing either WT or K109R mutant GRB2 were exposed to 5-Gy IR (152 s) and then either immediately lysed (t = 0). Following indicated recovery time, precipitated GRB2 from nuclear extracts was immunoblotted with anti-GRB2 antibody. All data are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bars, 5 μm.
We therefore used Strep-tagged nGRB2 affinity purification and Western blotting. We found a strong correlation in nGRB2 migration patterns with proteins detected by anti-ubiquitin antibody, supporting nGRB2 ubiquitination (Fig. 1D). PhosphoSite database analysis revealed 61 independent mass spectrometry (MS) studies reporting potential GRB2 ubiquitination on lysine-109 (K109) and five reporting ubiquitination on lysine-44 (K44). We therefore created lysine-to-arginine K44R and K109R GRB2 mutants and tested ubiquitination potential. Only the K109R mutation eliminated nGRB2 high–molecular weight protein bands (Fig. 1E), supporting K109 as the major ubiquitin conjugation site.
To test the function of K109R, we generated CRISPR-Cas9 GRB2-KO cells (fig. S2, A and B) reconstituted with either WTGRB2 or K109RGRB2 and measured RAS/MAPK and PI3K activity under normal growth conditions and following RTK activation (Fig. 1F and fig. S2, C and D). The K109RGRB2 showed ubiquitination loss, but no measurable difference in GRB2 dimerization, SOS binding, or cellular localization (fig. S2, E and F). Thus, K109RGRB2 had no quantifiable effect on cytoplasmic signaling and is empirically a separation-of-function mutant for nuclear activity.
RBBP6 ubiquitinates nGRB2 at DNA damage sites
Strep-tagged nGRB2 affinity purification followed by MS identified multiple E3 ubiquitin ligases—RING2, RBBP6, and CBLL1—precipitated with nGRB2 in three independent MS experiments (fig. S2G). Knockdown (KD) of each E3 ligase with two different short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), followed by nuclear extraction, affinity precipitation, and Western blotting, identified RBBP6 as the E3 ubiquitin ligase responsible for nGRB2 ubiquitination (Fig. 1G). Coimmunoprecipitation further verified the interaction between GRB2 and RBBP6 (fig. S2H). Notably, RBBP6 acts in maintenance of genome stability and retention of common fragile sites (22), which are DNA damage hotspots. Ultraviolet laser micro-irradiation (UV-LMI) coupled immunofluorescence analysis showed an obvious enrichment of endogenous RBBP6 at the DNA damage site marked by γH2AX (Fig. 1H). Moreover, nGRB2 also accumulated and colocalized with RBBP6 at the DNA break site, where ubiquitination most likely occurs (Fig. 1I).
We therefore examined recruitment kinetics by RBBP6-KD and UV-LMI. The results showed that RBBP6 does not facilitate GRB2 recruitment to the DNA damage site (Fig. 1J). Instead, Strep-tagged affinity purification and immunoblotting revealed ionizing radiation (IR)–induced transient ubiquitination of WTGRB2 that peaked at 2 hours, but no ubiquitination of K109RGRB2 was detected (Fig. 1K). Investigation with the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 indicated that IR-induced ubiquitinated GRB2 (ubGRB2) was not degraded by the proteasome (fig. S2I). As PSMD14 deubiquitinates GRB2 (23), it is likely responsible for GRB2 deubiquitination. Notably, the detection of ubGRB2 without DNA damage required long exposure times, which can be correlated to the relative intensities of the nonubiquitinated 25-kDa GRB2.
Collectively, these results show that GRB2 localizes to the cell nucleus, and nGRB2 is primarily ubiquitinated at K109. Under normal cell growth conditions, there was a steady-state basal level of nGRB2 ubiquitination, possibly reflecting endogenous DNA damage. Furthermore, E3 ubiquitin ligase RBBP6, which colocalizes with GRB2 at DNA damage sites, ubiquitinates nGRB2. However, exogenous DNA damage stimulated a transient increase in ubGRB2 that was largely deubiquitinated later and not degraded.
nGRB2 forms a GM complex
To examine nGRB2 function, we analyzed its nuclear interactome by MS. We identified its binding partners acting in the DDR (Fig. 2A and fig. S3, A to D). Coimmunoprecipitation confirmed top DDR-related proteins MRE11, RPA70 (also called RPA1), and H2AX as nGRB2 interactors, supporting the MS data (Fig. 2B). Our immunoprecipitation coupled with MS did not identify RAD50 or NBS1 as coprecipitants. Consistently, GRB2 precipitation and Western blotting also identified MRE11 but not RAD50 or NBS1 (Fig. 2C). We further investigated this by NBS1 and RAD50 precipitation followed by Western blot analysis and found the MRN complex but little or no GRB2 (Fig. 2, D and E). We also performed MRE11 precipitation and found RAD50 and NBS1 in addition to GRB2 (Fig. 2F). Provocatively, our data imply that nGRB2-bound MRE11 may be a separate pool of MRE11 from that in MRN complex. In several cultured cell lines, RAD50-KD induced a proportional loss of NBS1 in cells, but not MRE11 (24–26), suggesting that MRE11 can exist separately from MRN.
Fig. 2. Interactions of nGRB2 with DNA damage repair factors.
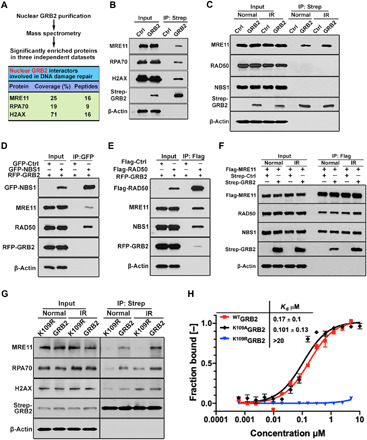
(A) MS identifies DDR protein associated with GRB2. Mean of coverage and unique peptides from three independent data sets are shown. (B) Strep-GRB2 precipitated from HEK293T cells followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (C) Strep-GRB2 expressed HEK293T cells treated with or without 5-Gy IR were lysed immediately followed by Strep-Tactin precipitation and immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (D) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with red fluorescent protein (RFP)–GRB2 and green fluorescent protein (GFP)–NBS1 or GFP alone as control, precipitated with GFP-trap beads, and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (E) HEK293T cells expressing Flag-RAD50 or Flag-Ctrl were cotransfected with RFP-GRB2 for 24 hours. Unperturbed cells were immunoprecipitated with Flag-M2 beads and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (F) HEK293T cells expressing Flag-MRE11 were cotransfected with Strep-GRB2 or Strep-Ctrl for 24 hours. Unperturbed or IR-treated (5 Gy) cells were immunoprecipitated with Flag-M2 beads and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (G) Strep-Tactin precipitation of WT and K109R mutant Strep-GRB2 from HEK293T cells that were unperturbed or IR treated (5 Gy) and lysed, followed by Western blot detection with the indicated antibodies. (H) MST isotherms of 100 nM Atto488–labeled WT, K109R, or K109A mutant to titrating concentrations of human MRE11 (residues 1 to 411). All data are representative of three independent experiments.
Because WTGRB2 can be ubiquitinated while K109RGRB2 cannot, we investigated the role of GRB2 ubiquitination in MRE11 binding and differential protein interaction functions. Strep-tagged WTGRB2 and K109RGRB2 were affinity-purified from cells treated with or without IR, and the coprecipitants were analyzed by Western blotting. IR treatment without a recovery period transiently increased MRE11, RPA70, and H2AX association with WTGRB2. In contrast, K109RGRB2 showed a drastic reduction in MRE11 coprecipitation while retaining unaltered H2AX levels (Fig. 2G). Notably, the K109RGRB2 mutant did not affect GRB2 dimerization, SOS binding, or MAPK signaling (Fig. 1F and fig. S2, C to F).
To test whether ubiquitination is required for GM interaction, we performed microscale thermophoresis (MST), an in vitro binding assay, by using bacterially expressed and purified proteins (fig. S3E) that lack ubiquitination. The binding isotherms revealed that non-ubGRB2 interacted with MRE11 with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 0.17 ± 0.1 μM, while the K109R mutant showed no binding. While a lysine-to-arginine mutation maintains the charge, the bulky arginine guanidinium destabilized GRB2 interaction with MRE11 independent of ubiquitination status (Fig. 2H). This finding uncovered GM interface specificity and the expectation that K109 site ubiquitination would destabilize the GM interaction (see below). In contrast, the K109A mutant, which is ubiquitination defective without steric blocking, showed intact MRE11 binding (Fig. 2H).
Non-canonical GRB2 binding interfaces are specific for DNA repair proteins
GRB2 consists of an SH2 domain flanked by two SH3 domains specializing in protein-protein interactions. To identify individual domains responsible for the observed DDR protein binding, we used a glutathione S-transferase (GST)–fused SH domain (Fig. 3A) to precipitate nuclear proteins. The N-terminal SH3 (nSH3) domain engaged RPA70, while the SH2 domain precipitated H2AX (Fig. 3B). Multiple DDR proteins interact with MRE11, such as the reported direct interaction between PCNA and MRE11 (27); we therefore used bacterially purified MRE11 for the GST pulldown assay and identified the GRB2-SH2 domain as the primary MRE11 interacting domain (Fig. 3C). The C-terminal SH3 (cSH3) domain also precipitated MRE11, albeit with lower efficiency. nSH3 sequence analyses revealed a conserved OB1 fold domain binding motif (DFKATADDE) embedded within the nSH3 domain as a suitable docking site for RPA70 (sequence alignment, Fig. 3D). Using MST, we confirmed direct binding and a comparable Kd for RPA70 N-terminal OB1 domain (RPA70N) with GRB2 and a synthetic peptide corresponding to the putative OB1 sequence of GRB2 (Fig. 3D). Furthermore, double aspartic acid and phenylalanine mutations of GRB2 to alanine (DF/AA) within the GRB2-OB1 binding motif at positions 8 and 9 drastically reduced RPA70 coprecipitation with GRB2. These data support a previously undefined GRB2-RPA70 interaction site in the GRB2 nSH3 domain (Fig. 3E).
Fig. 3. Identification of GRB2 binding interfaces on MRE11, RPA70, and H2AX.
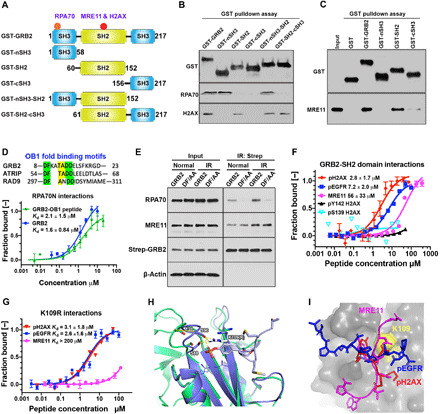
(A) Schematic DDR binding motifs (red circles) on GRB2 within its domain architecture. (B) GST-SH domains pulldown of HEK293T cell extracts followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (C) GST pulldown of bacterially purified human MRE11. (D) OB1 fold binding motif sequence alignment (top). MST isotherms of 50 nM Atto488–labeled RPA70 (residues 1 to 120) with titrating concentrations of GRB2 or GRB2-derived OB1 peptide. (E) Strep-Tactin precipitation of WT and DF/AA mutant from HEK293T cells that were either untreated (normal) or immediately after IR treated (5 Gy) and lysed, followed by Western blot detection with the indicated antibodies. (F) MST-binding isotherms of an Atto488-labeled GRB2-SH2 domain (100 nM) binding to synthetic peptides derived from indicated proteins. (G) MST isotherms of K109R binding to synthetic peptides derived from the indicated proteins. (H) Molecular docking overlay model showing S88 and S90 movement ~4.7 Å when bound to phosphotyrosine peptide. PDB structures used were as follows: 3wa4, purple; 1gri, green. K109R shown modeled (white sticks), which could engage with the loop containing S88 and S90 residues (purple sticks). (I) Docking of pH2AX (red), MRE11 (magenta), and pEGFR (blue) peptide into GRB2 SH2 domain pocket (gray). The relative docking orientation of each peptide is shown. Yellow surface marks the K109 position.
The GM complex targets phosphorylated histone H2AX
The GRB2-SH2 domain interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated motifs in the context of a pYxNx motif, where asparagine at the +2 position provides specificity (28). As our pulldown experiments showed the GRB2-SH2 domain precipitated H2AX (Fig. 3B) and phosphorylated H2AX is a marker for DNA damage (29), we investigated whether H2AX forms a GRB2-SH2 domain binding site. Because dually S139 and Y142 phosphorylated H2AX (pH2AX) dominates early signaling events (3) and GRB2 acts in ESCs, we used a double-phosphorylated peptide for MST binding measurements. Our results revealed that the pH2AX peptide [PSGGKKATQA(pS)QE(pY)] binds the GRB2-SH2 domain with a Kd of 2.8 ± 3.3 μM. Notably, this Kd resembles canonical endothelial growth factor receptor (EGFR)–derived phosphopeptide (pEGFR) binding (7.2 ± 2.0 μM) (Fig. 3F). However, using a H2AX peptide containing single phosphorylation at pS139 or pY142 failed to produce a binding isotherm (pS139 H2AX and pY142 H2AX; Fig. 3F).
SH2 domains are classically known for their affinity for tyrosine phosphorylated protein binding, yet GRB2 interacted with unphosphorylated MRE11 (Figs. 2H and 3C). Focusing upon GRB2’s binding to unstructured flexible regions, we analyzed the human MRE11 crystal structure [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID, 3T1I]. We identified the WVNYQDGNLN sequence missing in the atomic structure due to flexibility (30) and tested whether GRB2-SH2 would bind to the corresponding synthetic peptide. In vitro MST binding studies confirmed the GRB2-SH2 domain bound WVNYQDGNLN with a 33 ± 15 μM affinity (Fig. 3F), similar to the reported binding Kd for GRB2-SOS peptides (31). Peptide binding was weaker than binding to fully folded MRE11, suggesting added stabilizing contacts with the cSH3 domain, with probable sites being solvent-exposed PxxP motifs within residues 323 to 326 and 358 to 361.
As the MRE11 peptide contains a tyrosine, we tested binding of a tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide (WVNpYQDGNLN) to both full-length GRB2 and the SH2 domain and found that phosphorylation had limited impact on the peptide’s binding affinity (fig. S4A). This suggests that GRB2-SH2 interaction with MRE11 is outside the typical SH2 domain phosphotyrosine binding mode. As K109R mutation abrogated GM interactions (Fig. 2H), we tested the K109RGRB2 binding affinity for MRE11 peptide. Measured binding affinity was at least two orders of magnitude weaker. In contrast, K109RGRB2 binding to pEGFR and pH2AX peptides was comparable to that of WTGRB2 (Fig. 3G).
Structurally, K109R is likely to engage S88 and S90, which would obstruct the MRE11 binding groove above K109 predicted by our molecular docking (Fig. 3, H and I). Thus, we envisage that ubiquitin at K109, like K109RGRB2, would sterically block MRE11 binding. Collectively, these data defined individual GRB2 interactions, identified reciprocal binding interfaces, and determined relative binding affinities that establish GRB2 as a nuclear adapter suitable to link MRE11 to H2AX and RPA70.
nGRB2 links MRE11 to phosphorylated H2AX-marked DNA damage sites
As MRE11 is a key nuclease for HDR initiation (32), we investigated whether GRB2 directs green fluorescent protein (GFP)–MRE11 to DNA damage sites by using UV-LMI and live-cell imaging. In control cells, GFP-MRE11 was recruited to the UV laser damage site within 1 min (Fig. 4, A and B, and movie S1). However, GFP-MRE11 recruitment was delayed in GRB2-KO cells, appearing later (after 4 min) and at much lower levels than in control cells (Fig. 4, A and B, and movie S2). Reconstitution of WTGRB2, but not K109RGRB2, restored GFP-MRE11 recruitment kinetics to control levels, indicating that GM interaction enables efficient MRE11 recruitment to the DNA damage site (KO + GRB2 versus KO + K109R; Fig. 4, A and B, and movies S3 and S4). We also tested RPA70 recruitment using UV-LMI and found that it mirrored the MRE11 recruitment profile (Fig. 4C and movies S5 to S8). Because MRE11 is evidently recruited to pH2AX rather than to DSBs per se, we postulate that GRB2 acts in both MRE11 and RPA recruitment, as single-stranded DNA is not yet generated by MRE11. Notably, reconstitution of WTGRB2, but not the MRE11 interaction–defective K109RGRB2, rescued RPA70 recruitment (Fig. 4C and movies S7 and S8). Furthermore, restoration of MRE11 recruitment was sufficient for RPA70 chromatin loading independent of GRB2 binding (fig. S4B).
Fig. 4. GRB2 recruits MRE11 to the DNA damage sites.
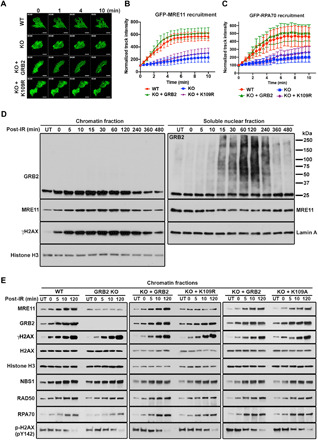
(A) GFP-MRE11 was transfected into the indicated stable cells, followed by UV-LMI imaging. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) GFP-MRE11 track intensity values from 20 cells at every 30 s were quantified with ImageJ, and normalized average intensities are shown with the SD. (C) Kinetics of GFP-RPA70 recruitment to micro-irradiated regions in HeLa cells. GFP-RPA70 was transfected into the indicated stable cells, followed by UV-LMI imaging. Track intensities were calculated as described in (B). (D) HeLa cells exposed to 5-Gy IR (152 s) were either immediately lysed (0 min) or allowed to recover for the indicated time. The chromatin fractions and the soluble nuclear fractions were analyzed with indicated antibodies. (E) Cells were either untreated (UT) or irradiated with 5-Gy IR (152 s) and then lysed immediately (0 min) or allowed to recover for the indicated time. Chromatin fractions were analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies (left). Comparison of GRB2-KO HeLa cells reconstituted with either WT (KO + GRB2) or K109R (KO + K109R) mutant (middle). Comparison of GRB2-KO HeLa cells reconstituted with either WT (KO + GRB2) or K109A (KO + K109A) mutant (right).
Because UV-LMI was conducted in GFP-MRE11–overexpressed cells, we next investigated whether the IR-induced endogenous MRE11 recruitment to DNA damage sites on chromatin can recapitulate our UV-damaged live-cell findings. Chromatin fractions of IR-treated HeLa cells were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting. The results revealed IR-induced transient GRB2 and MRE11 accumulation onto chromatin at the early DDR stage, which coincided with γH2AX phosphorylation (chromatin fractions; Fig. 4D). Analysis of the nucleoplasmic proteins revealed that ubGRB2 was readily detectable 15 min after IR, and ubiquitination reached the maximum level at 2 hours before subsiding (soluble nuclear fractions; Fig. 4D). Notably, increased MRE11 on chromatin correlated with a measurable and proportional decrease in the nucleoplasm (Fig. 4D, second panel). However, changes in GRB2 levels were less clear. We therefore conducted additional cell fractionations to include cytoplasm and plasma membrane. Our results uncovered a measurable redistribution of the cytoplasmic GRB2 in response to IR. The observed GRB2 increase on chromatin following IR correlated with a proportional decrease in cytoplasmic GRB2 (fig. S4C). Immunoblotting of total cell extracts showed no change in overall GRB2 level between control and IR-treated samples (fig. S4D), indicating that the observed reduction in the cytoplasmic GRB2 was due to a redistribution of proteins.
To further understand the role of GRB2 in MRE11 chromatin loading, we directly compared HDR-related protein loading on chromatin between control and GRB2-KO HeLa cells. In control cells, time-dependent accumulation of MRE11 and GRB2 onto chromatin was induced by IR. However, in GRB2-KO cells, IR-induced MRE11 recruitment to chromatin was abrogated (GRB2-KO left column; Fig. 4E). The chromatin loading of DNA damage marker γH2AX and the other MRN complex components NBS1 and RAD50 were unaffected by GRB2 loss. In agreement with our UV-LMI, RPA70 chromatin recruitment was delayed in GRB2-KO cells (RPA70; Fig. 4E). Thus, GRB2 plays an indispensable role in timely IR-induced MRE11 recruitment to the DNA damage site. Because the K109R mutant cannot bind to MRE11 but retains H2AX binding capacity (Fig. 3G), we directly compared the effect of this mutation in MRE11 recruitment. In a reconstitution experiment, the WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2), but not K109RGRB2 mutant (KO + K109R), rescued MRE11 recruitment to the chromatin (Fig. 4E, middle column). The K109AGRB2 mutant, which is MRE11-binding proficient but ubiquitination-defective, rescued MRE11 chromatin recruitment in a manner parallel to the WTGRB2 (Fig. 4E, right column, and see below). Thus, formation of GM complex is vital for efficient MRE11 loading onto chromatin. These results are consistent with the cellular pulldown experiments (Fig. 2, C to F) showing an exclusive GM complex, the observed MRE11 nonbinding to K109RGRB2 (Fig. 2, G and H), and the failure to recruit MRE11 to the UV-LMI site in GRB2-KO and K109R reconstituted cells (Fig. 4, A and B).
We also investigated IR-induced endogenous MRE11 foci formation along with RPA70, NBS1, RAD51, CtIP, and 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) between the control groups and GRB2-KO cells. Cells were either untreated (normal) or IR treated and allowed to recover for 120 min (post-IR) before collection (fig. S3E). Under normal conditions, all tested proteins formed a limited number of foci, but no significant difference between the wild-type (WT) and KO cells was observed. However, following IR treatment, the number of DNA damage foci detected per cell increased in both groups. Quantification analysis of foci-positive cells revealed a measurable reduction in MRE11, NBS1, BrdU, RPA70, and RAD51 foci formation in GRB2-KO cells. However, no difference of CtIP foci formation was observed in these two cell groups (fig. S4E, histograms). Thus, our data support the idea that defective MRE11 recruitment impedes efficient resection and subsequent single-stranded DNA accumulation at damage sites in GRB2-KO cells.
Phosphorylated H2AX is a docking site for GRB2
Having measured high-affinity interaction between the GRB2-SH2 domain and pH2AX (Fig. 3F), we therefore tested the requirement of H2AX for GRB2-mediated MRE11 recruitment onto chromatin. UV-LMI of H2AX-KO mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) with matched controls (WT) showed that H2AX-KO MEF cells were defective in MRE11 recruitment to the DNA damage site (Fig. 5, A and B, and movies S9 and S10). Furthermore, we performed comparative chromatin fractionation time course experiments that showed a time-dependent incremental increase in IR-induced GRB2 on chromatin mirrored by MRE11 and H2AX phosphorylation in control cells (Fig. 5C, control lanes). These data correlate with the observed pattern of IR-induced GRB2 accumulation on chromatin in HeLa cells (Fig. 4E). However, in H2AX-KO MEFs, IR-induced GRB2 enrichment was severely compromised at all tested time periods (Fig. 5C, H2AX KO lanes). The MRN complex recruitment was also measurably decreased in H2AX-KO MEFs. Reconstitution of the WT H2AX (KO + WT) restored GRB2 and MRN recruitment patterns similar to the control. However, reconstitution of S139A or Y142F H2AX mutant only partially rescued IR-induced GRB2 and MRE11 accumulation on chromatin. NBS1 recruitment was abrogated in S139A but not in Y142F reconstituted cells (Fig. 5D). Thus, our collective data demonstrate that H2AX is required for GM complex recruitment following DNA damage and that dual phosphorylation of H2AX on S139 and Y142 is important for efficient GRB2 docking.
Fig. 5. pH2AX creates a platform for GM complex recruitment.
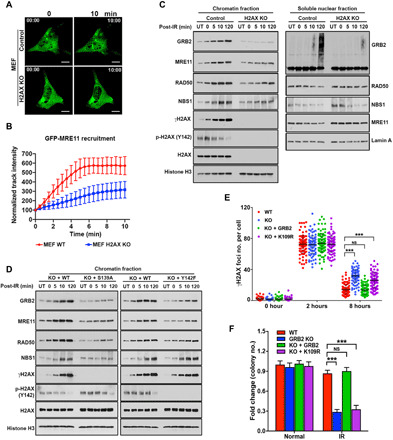
(A) Representative images of live-cell GFP-MRE11 recruitment in WT and H2AX-KO MEFs. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) GFP-MRE11 track intensity values from 20 cells at every 30 s were quantified, and normalized average intensities are shown with SDs. (C) WT and H2AX-KO MEFs were either untreated (UT) or irradiated with 5-Gy IR (152 s) and then lysed immediately (0 min) or allowed to recover for the indicated time. Chromatin and soluble nuclear fractions were analyzed by Western blotting with indicated antibodies. (D) H2AX-KO MEF cells reconstituted with either WT-H2AX or S139A and Y142F mutant were treated as above, and the chromatin fractions were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) Quantitative analysis of γH2AX foci from GRB2-KO HeLa and KO cells stably reconstituted with WT or K109R mutant GRB2, treated with 5-Gy IR, and then fixed at the indicated times. The numbers of γH2AX foci were counted and represented. (F) Colony survival assay of WT HeLa cells, GRB2-KO cells, and stable GRB2-KO cells reconstituted with WT or K109R mutant, cultured for 10 days after exposure to IR (1 Gy). The significance was analyzed by two-sided Student’s t test. ***P ≤ 0.001 and ****P ≤ 0.0001; NS, not significant.
nGRB2 promotes DDR
We found that GRB2 links MRE11 to pH2AX through direct interactions (Fig. 3). UV-LMI treatment of live HeLa cells followed by indirect immunofluorescence revealed enrichment of endogenous GRB2 together with γH2AX at laser-induced damage sites (Fig. 1J). We therefore investigated the consequence of low intracellular GRB2 by focusing on the spatiotemporal regulation of DNA damage foci. Using γH2AX as a marker, control and GRB2-KD cells were treated with IR, and foci longevity was compared. At 2 hours after IR, no measurable difference was observed between control and GRB2-KD cells. However, γH2AX foci in GRB2-KD cells persisted at 8 hours after IR exposure (fig. S5, A to E), suggesting that reduced intracellular GRB2 was sufficient to delay DNA repair.
To further investigate this delay, we used the MRE11 nonbinding K109RGRB2. GRB2-KO (KO) cells reconstituted with either WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2) or K109RGRB2 (KO + K109R), together with control cells (WT), were treated with IR and allowed to recover for designated times. GRB2-KO cells mirrored GRB2-KD results. Reconstitution of WTGRB2 restored cells to the control γH2AX foci phenotype. However, K109RGRB2 reconstitution failed to rescue the GRB2-KO phenotype (Fig. 5E), suggesting that GRB2-mediated MRE11 recruitment is indispensable for a timely DNA repair process. We therefore tested the consequence of this delayed repair on fragmented genomic DNA. A comet assay showed substantial unrepaired damaged DNA in IR-treated GRB2-KD cells, as seen by a longer DNA tail moment compared with controls (fig. S5, F and G), consistent with the observed prolonged γH2AX foci in GRB2-KD and GRB2-KO cells (fig. S5, B to E). Thus, the collective data indicate that timely and robust completion of DSB repair by HDR requires GM interactions.
To further test the functional significance of reduced GM complex formation and consequent prolonged DNA repair, we performed clonogenic cell survival assays. GRB2-KD or GRB2-KO cells exposed to IR showed a drastic reduction in colony survival (Fig. 5F and fig. S5, H to J). Clonogenic assays also linked delayed repair to reduced cell survival in K109RGRB2 reconstituted cells following IR treatment (Fig. 5F). These results showed that nGRB2 improves DNA repair efficiency and that nGRB2 deficiency reduces overall cell viability. Notably, the finding that the K109R mutant, which has intact canonical cytoplasmic functions, failed to rescue GRB2-KO cell survival establishes the biological importance of nGRB2 for genome stability affecting survival.
GRB2 promotes HDR while suppressing Alt-EJ
To further test nGRB2’s role in cellular DNA repair and its importance for HDR in particular, we performed I-SceI–based assays for all major DSB repair processes (33). GRB2-KO in DR-GFP U2OS cells were generated and then reconstituted with either WTGRB2 or K109RGRB2, followed by a comparison of repair efficiency between the four cell lines (fig. S6A). GRB2-KO had an immediate effect on all tested repair processes. We used the K109R reconstitution mutant to separate the GRB2’s DNA repair–related function from the loss of RAS/MAPK signaling. Notably, a significant reduction in HDR occurred in GRB2-KO cells, which was rescued by WTGRB2 but not K109RGRB2 (Fig. 6A and fig. S6B). The observed HDR reduction coincided with an increase in alternative nonhomologous EJ (NHEJ; Alt-EJ) (34). This increase is reduced by either WTGRB2 or K109RGRB2 (Fig. 6B and fig. S6C), suggesting that the GM complex is channeled toward HDR, whereas GRB2-free MRE11 is shunted toward Alt-EJ by interactions with XRCC1. MRE11 complex with XRCC1 and polymerase theta (also known as POLQ) is important for the initiation of Alt-EJ repair at breaks and forks (35, 36). We therefore immunoprecipitated POLQ and detected MRE11 and XRCC1 but not GRB2 in the complex (Fig. 6C). We then directly tested the nature of the XRCC1/MRE11 complex in control, GRB2-KO, and KO cells either reconstituted with WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2) or K109RGRB2 mutant. The results revealed that lack of GRB2 expression in GRB2-KO cells promoted XRCC1/MRE11 complex formation, which was reduced by reconstitution of WTGRB2 (Fig. 6D). Unexpectedly, K109RGRB2, which does not bind MRE11, also partially suppressed the XRCC1/MRE11 complex, in agreement with the Alt-EJ suppression measured by I-SceI–based assay (Fig. 6, B and D). How K109R suppresses the XRCC1/MRE11 complex requires further investigation. Nonetheless, the data provide insight into how GRB2 can promote molecular complexes and dictate pathway choices and outcomes.
Fig. 6. GRB2 KO suppresses HDR.
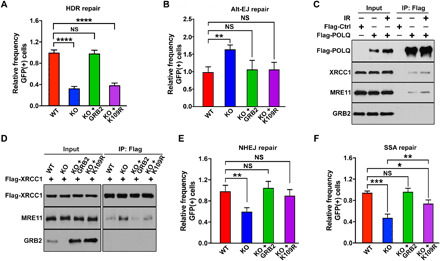
(A) DR-GFP reporter assay for control (WT), GRB2-KO (KO), and indicated reconstituted U2OS cells. The percentage of GFP-positive cells was determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) 72 hours after transfection. Normalized data are shown. (B) Normalized data showing a measurable increase in Alt-EJ in GRB2-KO cells. The up-regulation was suppressed with either WT GRB2 or K109R mutant reconstitution. (C) HEK293T cells overexpressing Flag-tagged POLQ was immunoprecipitated immediately after 5-Gy IR treatment or without treatment and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (D) Parental control (WT), GRB2-KO (KO), WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2), and K109RGRB2 (KO + K109R) reconstituted HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged XRCC1. After 24 hours, XRCC1 was immunoprecipitated and the resulting coimmunoprecipitants were analyzed by Western blotting with indicated antibodies. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (E) Normalized data showing a significant reduction in NHEJ in GRB2-KO cells that was rescued by reconstitution of either WT GRB2 or K109R mutant. (F) Normalized data showing GRB2-KO and reconstituted cells for single-stranded annealing (SSA) repair. The K109R mutant only partially rescued the GRB2-KO phenotype. The significance was analyzed by two-sided Student’s t test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001; NS, not significant.
GRB2-KO cells also showed reduced single-stranded annealing (SSA) and NHEJ repair. Like Alt-EJ, reconstitution with either WTGRB2 or K109RGRB2 was sufficient to restore NHEJ; yet, the mutant only partially rescued SSA (Fig. 6, E and F, and fig. S6, D and E). Our data suggest that the GM complex preferentially promotes HDR and that GRB2-deficient cells are HDR deficient. To further test whether GRB2 and MRE11 are part of the same repair axis, we performed an HDR repair assay in MRE11-KD cells with or without GRB2 using two different shRNAs (Fig. 7A). MRE11-KD showed a drastic reduction in GFP-positive cells, indicating HDR repair deficiencies matching those seen with GRB2-KO cells (Fig. 7B and fig. S6F). MRE11-KD in a GRB2-KO background showed no further reduction in HDR repair efficiency, suggesting that both proteins function in the same repair pathway and a reduction in either one is sufficient to significantly impair HDR.
Fig. 7. GRB2 KO sensitizes cells to PARPi.
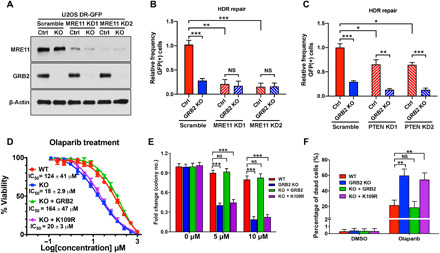
(A) MRE11 depletion levels with two different shRNA (KD1 and KD2) in U2OS cells with normal level of GRB2 (Ctrl) and GRB2-KO. (B) DR-GFP reporter assay in MRE11-KD control (Ctrl) and GRB2-KO U2OS cells. (C) DR-GFP reporter assay in PTEN-KD and/or GRB2-KO U2OS cells. (D) Sulforhodamine B assay of olaparib-induced cytotoxicity in control HeLa cells, GRB2-KO cells, and GRB2-KO cells reconstituted with WT or K109R mutant GRB2. IC50 values are shown. (E) Clonogenic assay evaluating the effect of a PARPi on colony formation of HeLa cells. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of the PARPi olaparib and cultured for 10 days, and then the resulting colonies were visualized with crystal violet staining and counted by GelCount instrument. Parental control (WT), GRB2-KO (KO), WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2), and K109RGRB2 (KO + K109R) reconstituted HeLa cells. (F) Bar graph representing annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) combined labeling and flow cytometry analysis of olaparib-treated control (WT), GRB2-KO, reconstituted WTGRB2 (KO + GRB2), and K109R mutant (KO + K109R) HeLa cells. Cells were treated with either dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 50 μM olaparib for 72 hours. All data are representative of three independent experiments. The significance was analyzed by two-sided Student’s t test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001; NS, not significant.
Recently, GRB2 was suggested to induce PTEN nuclear translocation to suppress micronucleus formation (21). To test whether this proposal is related to our data, we knocked down PTEN (PTEN-KD) in control and GRB2-KO U2OS cells (fig. S6G) and tested HDR repair. Unlike GRB2-KO, which showed a staggering 80% reduction in HDR repair, PTEN-KD had a modest 20% decease. Notably, KO of GRB2 in PTEN-KD cells induced further suppression of HDR (Fig. 7C and fig. S6H), suggesting that PTEN is not required for the GRB2-mediated HDR, and they are not in the same repair axis. We reason that the observed 20% reduction in HDR in PTEN-KD cells could reflect defective global phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling or the previous observation that nuclear PTEN regulates RAD51 expression (37).
Combined GRB2 and PARP defects are synthetically lethal
As HDR deficiency causes synthetic lethality with PARPis (38) and GRB2-KO cells are HDR defective (Fig. 6A), we reasoned that if GRB2 plays a key role in HDR, then GRB2-KO cells would be PARPi sensitive. Therefore, we compared PARPi olaparib sensitivity between control and GRB2-KO cells, along with GRB2-KO cells reconstituted with either WTGRB2 or K109RGRB2. Sulforhodamine B assays revealed that GRB2-KO cells were seven times more sensitive to olaparib treatment [half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50), 18 ± 2.9 μM] than WT control cells (IC50, 124 ± 41 μM). Moreover, reconstitution of WTGRB2 (IC50, 164 ± 47 μM), but not K109RGRB2 (IC50, 20 ± 3 μM), caused desensitization (Fig. 7D). In addition, in clonogenic survival assays, only the GRB2-KO and K109RGRB2 reconstituted cells showed a severe reduction in colony formation in response to low-dose olaparib treatment (Fig. 7E and fig. S6I). UV-LMI experiments demonstrated that PARP1 recruitment to DNA damage sites was unaffected by GRB2 expression levels (fig. S7, A and B, and movies S11 to S14). Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining followed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis showed olaparib-induced apoptosis in 20% of the control (WT) cells, increasing to a notable 60% in GRB2-KO cells, and reconstitution of K109RGRB2 failed to rescue the phenotype (Fig. 7F and fig. S7C). These results correlated with the measured PARP, caspase-3, and caspase-7 cleavage in GRB2-KO and K109RGRB2 reconstituted cells (fig. S7D). Thus, GRB2-KO is synthetically lethal with loss of PARP function, confirming GRB2’s critical role in HDR.
The GM axis correlates with cancer progression and survival
We analyzed TCGA database to investigate whether a functional GM axis can be discerned in the clinical setting and if the efficiency of GM-complex formation can translate into cancer patient outcome. We found that GRB2 expression was up-regulated in about half of the tumor types (Fig. 8A). As described earlier, in normal breast tissues, nGRB2 expression was very low (Fig. 1B), and up-regulation therefore is an indication of malignancy. We further investigated nGRB2 expression with IHC using a human breast cancer tissue array containing clinical tumor samples at different stages (Fig. 8B). Analysis of 100 patient and 10 normal breast tissue samples revealed a correlation between protein expression and nuclear localization with disease progression. In late-stage diseases, more GRB2 expression and nuclear localization were observed compared to early stages or normal tissue (Fig. 8C). This incremental increase of GRB2 expression/nuclear localization suggests a potential predictive biomarker for tracking breast cancer progression.
Fig. 8. GRB2 expression affects survival upon high expression of MRE11 in an HDR-proficient cohort.
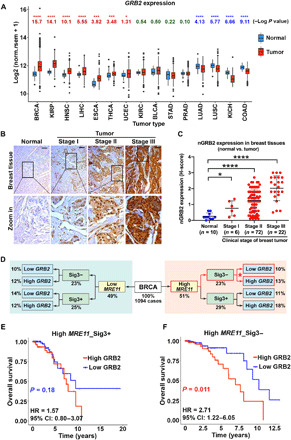
(A) GRB2 expression in TCGA tumors and matched normal tissues. Log P values were from Wilcoxon tests, with greater values indicating stronger differences; GRB2 expression was higher in tumors than in matched controls in BRCA, KIRP, HNSC, LIHC, ESCA, THCA, and UCEC (red) but lower in tumor than in controls in LUAD, LUSC, KICH, and COAD (blue). Datasets with >10 normal samples were included. Box plots display the interquartile range (IQR) from Q1 to Q3 (25 to 75% percentiles), median (center line), whiskers extending to the minimum (Q1 − 1.5*IQR) and maximum (Q3 + 1.5*IQR), and outliers (dots). (B) GRB2 expression in breast tumor tissue array. Scale bars, 50 μm. (C) H-score quantification of nGRB2 IHC staining for 100 BRCA and 10 normal tissue samples. The significance was analyzed by two-sided Student’s t test. *P ≤ 0.05 and ****P ≤ 0.0001. (D) Schematic diagram of BRCA patient stratification according to MRE11 expression and signature 3. (E and F) Kaplan-Meier survival curves and hazard ratios (HR) for TCGA breast cancer patients with high (above mean) MRE11 expression scored positive [n = 285; Sig3+ (E)] or negative [n = 226; Sig3− (F)] for signature 3 mutations and low (at or below mean) or high (above mean) GRB2 expression; P values from log-rank tests. CI, confidence interval.
In breast cancer patients, where GRB2 was most up-regulated relative to matched controls, co–up-regulation of MRE11 with GRB2 was associated with worse clinical outcome (fig. S8, A and B). This poor prognosis was dependent on patients’ HDR status. When breast cancer patients were stratified as HDR proficient and HDR deficient based on their signature 3 mutations (Fig. 8D), a pattern of single-base substitution mutations strongly associated with BRCAness (39), only patients with no signature 3 mutations (HDR-proficient) combined with high MRE11 and high GRB2 expression exhibited increased risk. By contrast, survival was not affected in HDR-defective patients (signature 3 positive) with high MRE11 and high GRB2 (Fig. 8, E and F). Thus, in this context, GRB2 expression alone does not confer poor outcome, unless it is correlated with MRE11 expression and HDR status. These data imply that up-regulated GRB2 expression acting with MRE11 on the DDR specifically affects survival of breast cancer patients. Likewise, survival was independent of HDR status in high GRB2– and low GRB2–expressing patients when either MRE11 expression was low (fig. S8, C and D) or when patients were not stratified according to MRE11 expression (fig. S8, E and F). The collective experimental and bioinformatics data imply that MRE11 and GRB2 are partners in the DDR in cancer, where cells with fully operational HDR may use the GM complex pathway to recover from oncogenic replication stress and DSBs, providing benefit to tumor growth at the expense of patients’ lives. These observations reinforce our molecular findings and suggest that disruption of the GM repair axis may be therapeutically beneficial to the subpopulation of HDR-proficient breast cancer patients with co–up-regulated GRB2 and MRE11.
GRB2 is a key regulator of MRE11 recruitment and release for HDR function
GRB2 chromatin recruitment begins immediately following IR and peaks at 15 to 30 min (Fig. 4, D, left, and E). Ubiquitination of GRB2, on the other hand, was first detected in the nucleoplasm of cells at 15 min and reached maxima at 120 min (Fig. 4D, right). Furthermore, IR-induced increase in nGRB2 correlated with an apparent proportional decrease of GRB2 in the cytoplasm (fig. S4C). These data indicate a dynamic temporal regulation of GRB2 concentration across cellular compartments and the disruption of GM interaction by ubiquitination of GRB2. We therefore tested the effect of GRB2 ubiquitination on MRE11 interaction by co-complex analysis. Strep-tagged GRB2 precipitations were performed in cells treated with IR (time “0”) and then recovered for 2, 4, or 8 hours, and MRE11 coprecipitation was monitored by Western blotting. The results revealed that at the height of GRB2 ubiquitination at 2 hours after IR (Figs. 1K and 4D and fig. S4C), the GM complex was drastically reduced (Fig. 9A). At 4 and 8 hours after IR, when the level of ubGRB2 was decreasing, the GM complex began to recover. Thus, ubGRB2 releases MRE11 and non-ubGRB2 promotes GM complex formation.
Fig. 9. Ubiquitinated GRB2 releases MRE11 at the DSB sites.
(A) HEK293T cells expressing Strep-GRB2 were treated with 5-Gy IR, lysed immediately (0), or allowed to recover for the designated time. Strep-tagged GRB2 was precipitated and immunoblotted with MRE11 antibody. Input controls are shown in the bottom three panels. (B) Control or RBBP6-KD1 HEK293T cells overexpressing Strep-GRB2 were treated with 5-Gy IR, lysed immediately, or allowed to recover for the designated time. Strep-GRB2 was precipitated from total extract and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies along with input controls. (C) Strep-tagged WTGRB2 or K109AGRB2 mutant precipitated from 5-Gy IR–treated (0) or post-recovery (2 hours) and analyzed with indicated antibodies. (D) DR-GFP reporter assay for control (Ctrl) and two RBBP6-KD U2OS cells. (E) DR-GFP reporter assay for control, GRB2-KO (KO), and K109A reconstituted (KO + K109A) U2OS cells. The significance was analyzed by two-sided Student’s t test. **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001. (F) Schematic proposed model depicting the role of GRB2 in the DSB repair. IR creates DSBs and phosphorylation of H2AX, which serves as a docking site for the recruitment of the GM complex. Ubiquitination of GRB2 at K109 by RBBP6 releases GRB2 from MRE11, while deubiquitination of GRB2 possibly by PSMD14 enables GM reassociation.
To further test the role of ubiquitination in GM interaction, we knocked down RBBP6 (RBBP6-KD) from cells and performed the same strep-GRB2 coimmunoprecipitation study. In WT cells, following IR, the GM complex decreased incrementally over time to its lowest level at 2 hours after IR. In RBBP6-KD cells, on the other hand, the GM complex persisted for an extended period of time and was readily detectable at 1 and 2 hours after IR (Fig. 9B, upper two panels; MRE11 levels indicated by *). RBBP6 depletion caused no change in IR-induced GRB2, MRE11, and other HDR protein recruitment to chromatin (fig. S9). Additional coprecipitation experiments with ubiquitination-defective K109AGRB2 mutant revealed that lack of ubiquitination maintained the GM complex at 2 hours after IR treatment (Fig. 9C).
In the absence of RBBP6 ubiquitin ligase, GRB2 ubiquitination was abrogated (Fig. 1G), resulting in lingering GM complexes (Fig. 9B). We investigated the consequence of the prolonged GM complexes in DSB repair using I-SceI–based assays for HDR (33) in RBBP6-KD cells. The results from two different RBBP6 shRNA KDs (KD1 and KD2) revealed significant HDR reduction (Fig. 9D). To further test whether the observed HDR reduction in RBBP6-KD cells was due to GRB2 ubiquitination defects, we used the K109AGRB2 mutant reconstituted GRB2-KO cells to measure HDR efficiency. Consistent with the RBBP6-KD results, K109AGRB2 failed to rescue the HDR defect caused by GRB2-KO (Fig. 9E), suggesting that ubiquitination-mediated MRE11 release at DSBs is important for error-free HDR repair. Collectively, these data revealed a pool of MRE11 in the nucleoplasm bound to GRB2 (the GM complex), which appear to be separate from MRE11 in the canonical MRN complex (2). Immediately following DNA damage, GRB2 efficiently recruits MRE11 to pH2AX-marked DNA damage sites, where MRE11 is released for HDR by ubiquitination of GRB2 at K109 by RBBP6, whereas deubiquitination re-enables the GM complex formation (Fig. 9F).
DISCUSSION
DNA repair and genome fidelity critically depend on timely recruitment and regulated release or handoffs of damage excision enzymes, as initially shown for APE1 in base excision repair (BER) (40). For DSBs, our collective findings unveil GRB2 adapter complex for recruitment and release of MRE11 for efficient HDR. GRB2’s cytoplasmic role in proliferative RAS/MAPK/ERK (extracellular signal–regulated kinase) kinase pathway activation is thus unexpectedly complemented by a nuclear role in targeting MRE11 for DSB repair, as logically associated with replication and proliferative stress. The GRB2-SH2 domain binds MRE11 through a unique binding interface tailored to GRB2 DDR function. As RPA70 binds to a conserved OB1 fold in the nSH3 domain of GRB2, which occurs in many DNA repair proteins [e.g., BRCA2, BLM-complex proteins, and ligase-1 (41)], further studies may test and uncover GRB2 as an adapter for recruitment of other DNA repair proteins. Currently, GRB2 targeting of MRE11 and RPA to γH2AX for efficient HDR has apparent analogies to recruitment of NEIL1 glycosylase to oxidation-susceptible open chromatin sites for efficient BER, as revealed by the notable correspondence between NEIL1 occupancy and mutation rates along the genome (42).
GRB2-KO cells show an immediate measurable downregulation of DSB repair activities except for Alt-EJ. This could partly reflect loss of RAS/MAPK signaling in GRB2-KO cells, but reconstitution with separation-of-function GRB2 mutant suggests otherwise. Also, we found that the adapter protein XRCC1, which forms a repair complex with MRE11 and POLQ that supports Alt-EJ activity (35, 36), is up-regulated in GRB2-depleted cells. Thus, the interplay between nuclear and cytosolic GRB2 redistribution and of GRB2-MRE11 promotion of HDR versus XRCC1-MRE11 enabling Alt-EJ merit future investigation. Notably, K109RGRB2 retains all cytoplasmic GRB2 functions, but it cannot bind to and recruit MRE11 to the DNA damage site. In GRB2-KO cells, elevated Alt-EJ is returned to normal levels, and NHEJ down-regulation is fully rescued by K109RGRB2 reconstitution. K109RGRB2 partially rescues SSA. As EXO1 can potentially substitute for MRE11 in DSB repair, EXO1 may enable resection for SSA (43, 44). K109RGRB2, which is defective in MRE11 binding, and K109AGRB2, which is defective in MRE11 release, both failed to rescue HDR, highlighting the role of GM complex recruitment and release for HDR.
In summary, GRB2 nuclear functions revealed here provide mechanistic insight into MRE11 recruitment to DSB sites with functional consequences for HDR and human cancer. Our TCGA database analysis showed that GRB2 affects survival of patients with both HDR proficiency and high MRE11 expression. Furthermore BRCA-proficient patients with high MRE11 and low GRB2 are a noncanonical HDR-deficient group with cancer progression vulnerability. Both GRB2-KD and GRB2-KO cells are HDR deficient, which causes synthetic lethality to PARPi-treated cells. Overall, our results unveil GRB2’s key role in DDR for efficiently recruiting and releasing MRE11 to initiate HDR rather than Alt-EJ with implications for cancer biology and for targeting synthetic lethality in precision medicine anticancer efforts.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents
Antibodies against p-ERK1/2 (4370S), ERK1/2 (4695S), p-Akt (S473) (4060S), Akt (4685S), ubiquitin (3936S), ubiquitin (3933S), cleaved PARP (Asp214) (5625S), cleaved caspase-3 (Asp175) (9664S), cleaved caspase-7 (Asp198) (8438S), MRE11 (4847S), RPA70 (2267S), H2AX (7631S), p-H2AX (S139) (20E3) (9718S), RAD50 (3427S), NBS1(14956S), XRCC1 (2735S), histone H3 (4499S), and β-actin (3700S) were ordered from Cell Signaling. Antibodies against GRB2 (C-23) (sc-255), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (sc-47724), E-cadherin (sc-21791), lamin A (sc-71481), CBLL1 (sc-517157), RING2 (sc-101109), RBBP6 (M56) (sc-9962), GST (sc-138), GFP (sc-9996), and SOS1 (sc-10803) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Antibodies against γH2AX (S139) (05-636) and p-H2AX (Y142) (07-1590) were ordered from MilliporeSigma. Antibodies against MRE11 (ab214), NBS1 (ab181729), and RAD50 (ab124682) were purchased from Abcam. Antibodies against Strep-tag (A00626), red fluorescent protein (RFP)–tag (A00682), and Flag-tag (A00187) were ordered from GenScript. Antibody against Rad51 (GTX100469) was from GeneTex. Antibody against CtIP (61141) was from Active Motif. Antibody against BrdU (347580) was from BD Biosciences, and antibody against RBBP6 (NBP1-49535) was from Novus Biologicals. CBLL1 shRNA1 (V2LHS_157953), CBLL1 shRNA2 (V3LHS_319113), RING2 shRNA1 (V2LHS_188269), RING2 shRNA2 (V3LHS_640474), RBBP6 shRNA1 (V2LHS_255063), RBBP6 shRNA2 (V3LHS_353550), MRE11 shRNA1 (V2LHS_202468), MRE11 shRNA2 (V2LHS_202464), PTEN shRNA1 (V2LHS_231477), PTEN shRNA2 (V2LHS_192536), and GRB2 shRNA (V2LHS_137365) were ordered from Dharmacon. Flag-MRE11, Flag-RAD50, and Flag-H2AX plasmids were purchased from OriGene. Mutants H2AX S139A, H2AX Y142, GRB2 K109R, GRB2 K109A, and GRB2 DF/AA were generated by site-directed mutagenesis. GFP-MRE11 plasmid was a gift from S. Jackson (University of Cambridge, UK). NBS1-GFP plasmid was a gift from J. Lukas (University of Copenhagen, Denmark). GFP-RPA70 plasmid was provided by M. S. Wold (University of Iowa, USA). Flag-XRCC1 and Flag-POLQ plasmids were provided by S. Mitra (Houston Methodist, USA). Phosphorylated EGFR synthetic peptide FLPVPE(pY)INQSVPKR, MRE11 peptide PWVNYQDGNLN, tyrosine-phosphorylated MRE11 peptide PWVN(pY)QDGNLN, phosphorylated H2AX (pH2AX) peptide PSGGKKATQA(pS)QEY, phosphorylated H2AX (pH2AX) peptide PSGGKKATQASQE(pY), dual-phosphorylated H2AX (pH2AX) peptide PSGGKKATQA(pS)QE(pY), and GRB2 OB1 peptide KYDFKATADDELSFKRG were purchased from GenScript. GFP-trap, Flag agarose beads, and Strep-Tactin beads were purchased from Chromotek (gta-10), MilliporeSigma (A2220), and MilliporeSigma (71592), respectively.
Cell culture
Human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T, NIH3T3, and A431 cells [purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC)] and MEFs and H2AX-KO MEFs (gifts from A. Nussenzweig, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute) were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s high-glucose medium. HeLa cells (ATCC) were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium, and HAP1 cells (Horizon Discovery) were maintained in Iscove’s modified Dulbecco’s medium. U2OS cells (ATCC) were maintained in McCoy’s 5A medium. Media were supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% antibiotic/antimycotic (Lonza) in a humidified incubator with 10% CO2. Stable cells containing Strep-tagged GRB2 or GRB2 mutants were produced as described previously (45). The I-SceI reporter assay (a gift from J. Stark, City of Hope) was performed as described previously (33). The sulforhodamine B cytotoxicity and colony formation assays were performed as described previously (46).
CRISPR-Cas9–mediated GRB2-KO
GRB2 was knocked out by using the CRISPR-Cas9 system according to the protocol described previously (47, 48). The guide RNA (gRNA) targeting GRB2 was designed using an online tool available at http://crispr.mit.edu. DNA primers (forward primer, 5′-CACCGGAGCCGGAAGTCTTCCTC-3′; reverse primer, 5′-AAACGAGGAAGTACTTCCCGGCTCC-3′) for the GRB2 gRNA and reverse complement sequence plus adapters needed for ligation were synthesized from IDT and ligated into the LentiCRISPR v2 (Addgene #52961) or LentiCRISPR v2-Blast (Addgene #83480). Correct insertion of GRB2 gRNA was confirmed by sequencing the constructs. Lentivirus particles were generated in HEK293T cells. Cells were infected with lentivirus and then selected with puromycin or blasticidin. Single clones were picked up, and GRB2-KO was verified by Western blotting. Mixture pools of different clones were used for experiments.
Western blots
Cells were seeded onto 10-cm dishes and grown for at least 24 hours before experiments. Cells were lysed with radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer [20 mM tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 1% IGEPAL, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4, and leupeptin (1 μg/ml)] supplemented with Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Set III (EMD Millipore) to obtain total proteins. Cell fractionation was done using Subcellular Protein Fractionation Kit for Cultured Cells (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Protein expression and purification
Expression and purification of GRB2 from bacteria have been described previously (31). The K109R and K109A mutant GRB2 was generated by site-directed mutagenesis and purified in a manner similar to the WT. Human MRE11 core (residues 1 to 411) purification was described previously (30). The generation of individual GRB2 domains was as described before (49). The purification of RPA70N (1-120) was performed according to a published procedure (50).
Immunofluorescence
Designated cells were grown on coverslips, fixed with the addition of 4% (w/v) paraformaldehyde (pH 8.0) with or without pre-extraction, and washed four times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 8.0). After permeabilization with 0.5% Triton X-100 on ice for 5 min, cells were washed three times with PBS and incubated with blocking buffer [PBS, 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 5% FBS, and 0.5% Triton X-100] for 2 hours at room temperature or overnight at 4°C. Following a further three washes with PBS, cells were incubated with primary antibody overnight in PBS, 3% BSA, and 0.5% Triton X-100. Cells were then washed five or six times with PBS and incubated with the fluorescence-conjugated secondary antibody for 2 to 3 hours. Following another PBS wash, coverslips were mounted onto a slide with mounting medium (0.1% p-phenylenediamine and 75% glycerol in PBS at pH 7.5 to 8.0). For pre-extraction before fixation, cells were treated with cytoskeleton buffer [10 mM Pipes (pH 6.8), 100 mM NaCl, 300 mM sucrose, 3 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, and 0.5% Triton X-100] for 5 min on ice and followed by washing with stripping buffer [10 mM tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 10 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 1% Tween 20, and 0.25% sodium deoxycholate] for 5 min on ice. Cells were imaged using either a Leica SP5 II or Zeiss LSM710 confocal microscope.
UV laser micro-irradiation
UV-LMI was performed as described previously (51): Cells were grown on 35-mm glass-bottom dishes (Matsunami), micro-irradiated with a MicroPoint ablation system (Photonics Instruments) with 60% laser output, and visualized with a Nikon Eclipse TE2000-U inverted microscope.
Alkaline comet assay
Untreated and IR-treated cells embedded in low–melting point agarose were layered over a slide with a thin film of agarose. Cells were then lysed overnight at 4°C in lysis buffer [10 mM tris-HCl (pH 10), 2.5 M NaCl, 100 mM EDTA, 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and 1% Triton X-100]. After equilibration in electrophoresis buffer [300 mM NaOH, 1 mM EDTA (pH > 13)] for 40 min at 4°C, electrophoresis was performed to identify DNA damage by the migration of small fragments of broken DNA away from the nucleus, forming a “tail” to the dense circular comet head of undamaged DNA. Nuclear DNA was visualized by staining with SYBR Gold solution, and images were captured using a Leica SP5 II microscope. The tail moment of each cell was analyzed by OpenComet software.
Annexin V/PI staining assay
To determine the percentage of olaparib-induced apoptotic cells, an annexin V/PI staining assay was used according to the standard protocol (Life Technologies). Briefly, cells were cultured and treated with DMSO or 50 μM olaparib for 72 hours. Then, cells were trypsinized, washed, and resuspended in annexin-binding buffer. Cells were labeled by adding annexin V–Alexa Fluor 647 and PI to each sample. After incubation for 15 min at room temperature in the dark, samples were analyzed on a flow cytometer (FACSCanto II, BD Biosciences) for the detection of annexin V– and PI-positive subpopulations. DMSO-treated cells were used as a control, and each experiment was performed in triplicate. Further data analysis was performed with FlowJo V10 software.
Microscale thermophoresis
MST was measured using the Monolith NT.115 system (Nano Temper). Proteins were fluorescently labeled with Atto 488 according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Labeling efficiency was determined to be 1:1 (protein:dye) by measuring the absorbance at 280 and 488 nm. A solution of peptides or proteins in 0.01 M Hepes (pH 7.4), 0.15 M NaCl, and 0.005% (v/v) Surfactant P20 was serially diluted, typically from about 100 μM to 30 nM, in the presence of 100 nM labeled protein. The samples were loaded into silica capillaries (Polymicro Technologies) after incubation at room temperature for 15 min. Measurements were performed at 22°C using 20% light-emitting diode power and 40% infrared laser power. Measurements were also carried out using 20 and 60% infrared laser power for comparison. Data analyses were performed using Nano Temper Analysis software using the Kd curve fitting function. Raw data were exported and fitting curves were generated using Prism 8 (GraphPad Software) for presentation.
Molecular docking
We used the available GRB2 structure from the PDB (PDB ID, 1GRI). The structure was prepared for docking by eliminating water and cofactors; a monomeric unit was used. The GRB2 coordinates were prepared and minimized using Protein Preparation Wizard (Schrödinger Suite 2019-2). We aimed the molecular docking to the K109 site. We docked ligands (in this specific experimental peptide) with length ≤20 Å with cubic box dimensions of 15 Å. We also generated a mutant of GRB2, K109R, using the function “simply mutate” in Coot model-building software. In this structure, we aimed the docking to R109. We used the peptide docking utility implemented in the Schrödinger Suite; the peptides were added as a sequence in the specific section “Define peptide to dock.” We used the following peptide-derived sequences for MRE11, EGFR, and γH2AX: Mre11-PWVNYQDGN, EGFR-NPVYHNQPL, and H2AX-SQEY, respectively. For the docking experiments, we used Glide (Schrödinger Release 2019-2). The best docking results were selected and compared in superimposed sessions in the PyMOL molecular graphics system (PyMOL 2.0; Schrödinger).
IHC and staining quantification
Breast cancer tumor tissue array slides (BC081116d; Biomax), normal human tissue array slides (MNO961; Biomax), and the paraffin-embedded tissue sections of different mouse tissues were collected for determination of GRB2 distribution. Sections were dewaxed and rehydrated following a standard dewaxing protocol. Then, the samples were exposed to 10 mM citric acid buffer (pH 6.0 for 20 min at 105°C) for heat antigen retrieval and exposed to 3% H2O2 for 12 min to block endogenous peroxidase activity. Subsequently, the samples were blocked with goat serum for 1 hour and incubated with anti-GRB2 primary antibody (1:100) overnight. The VECTASTAIN ABC HRP Kit (peroxidase, rabbit immunoglobulin G) and DAB Substrate Kit (peroxidase, horseradish peroxidase) were used to develop color, followed by nuclear counterstaining with hematoxylin. Last, the slides were mounted and visualized. Representative regions were selected and photographed. Two pathologists were tasked with evaluating IHC staining, and the H-score method was applied for calculating the staining score of each sample. In brief, each sample was assessed by staining intensity (negative, 0; weak, 1; moderate, 2; strong, 3) and staining extent (0 to 100%), with H-score = [1 × (staining extent of weak staining) + 2 × (staining extent of moderate staining) + 3 × (staining extent of strong staining)]. Three samples were used to quantify H-score for each tissue, and the average of H-score and SD for all the cases were calculated and presented.
Mass spectrometry
To identify proteins associated with GRB2 in the nucleus, GRB2 was immunoprecipitated with Strep-Tactin beads (MilliporeSigma #GE28-9355-99) from the nuclear extracts of 293T cells expressing Strep-GRB2 or Strep-Ctrl. Three experimental samples and three matched negative controls were prepared independently for MS. Using the MyriMatch and Sequest search engines, the MS spectra were matched to the human protein database. Scaffold 3 was used to analyze the fold enrichment values of each sample compared to the matched negative control sample. Proteins enriched at least 1.5-fold with a P value of less than 0.05 (Fisher test) as computed by Scaffold 3 were selected and listed. The proteins in the list were used to conduct the pathway and network analysis by BINGO in Cytoscape 3.7.2. Hypergeometric tests were performed and corrected by Benjamini and Hochberg false discovery rate correction. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 8 using multiple t test function.
TCGA data analysis
We retrieved the gene expression and clinical patient data to estimate the Kaplan-Meier survival curves from TCGA using the TCGA-Assembler suite available at https://github.com/compgenome365/TCGA-Assembler-2. For gene expression analyses between tumor and matched controls, we selected datasets with at least 10 matched controls. Data were plotted with the R packages ggpllot2 and ggpubr. Survival curves and hazard ratios were obtained with the survminer, survival, and dplyr R packages. Signature 3 mutations were obtained from https://synapse.org/#!Synapse:syn11801497.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Chen for UV-LMI instrument access, K. Schlacher for discussion, and L. S. Warden and T. M. Link for protein purifications. Editorial assistance was provided by MD Anderson’s Editing Services, Research Medical Library. Funding: This research was supported by the University Cancer Foundation via the Institutional Research Grant program at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (to Z.A.); by Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) grants RP180813 and RP130397; and by NIH grants R01 CA200231, P01 CA092584, R35 CA220430, and 1S10OD012304-01. J.A.T.’s efforts are also supported by a Robert A. Welch Chemistry Chair. Author contributions: Z.A. and J.A.T. directed the research; Z.Y., J.A.T., and Z.A. conceived the research plan; Z.Y., S.X., Y.S., and Z.A. performed the experiments; Z.Y., S.X., Y.S., J.A.T., and Z.A. designed experiments and analyzed results; Y.S. and A.B. contributed to MS and TCGA data analysis; D.M. and C.-L.T. performed computational docking and analysis; A.S., Q.S., G.P., P.G.L., D.E.J., and B.W. provided critical reagents and resources; and Z.Y., S.X., J.A.T., and Z.A. wrote the paper. Competing interests: J.A.T., Z.A., and Z.Y. are inventors on a patent application related to this work filed by The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The authors declare no other competing interests. Data and materials availability: All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper and/or the Supplementary Materials.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/7/32/eabe9254/DC1
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Paull T. T., Deshpande R. A., The Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex: Recent insights into catalytic activities and ATP-driven conformational changes. Exp. Cell Res. 329, 139–147 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Syed A., Tainer J. A., The MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex conducts the orchestration of damage signaling and outcomes to stress in DNA replication and repair. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 87, 263–294 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Xiao A., Li H., Shechter D., Ahn S. H., Fabrizio L. A., Erdjument-Bromage H., Ishibe-Murakami S., Wang B., Tempst P., Hofmann K., Patel D. J., Elledge S. J., Allis C. D., WSTF regulates the H2A.X DNA damage response via a novel tyrosine kinase activity. Nature 457, 57–62 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Blackford A. N., Jackson S. P., ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: The trinity at the heart of the DNA damage response. Mol. Cell 66, 801–817 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Paull T. T., Rogakou E. P., Yamazaki V., Kirchgessner C. U., Gellert M., Bonner W. M., A critical role for histone H2AX in recruitment of repair factors to nuclear foci after DNA damage. Curr. Biol. 10, 886–895 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cook P. J., Ju B. G., Telese F., Wang X., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Tyrosine dephosphorylation of H2AX modulates apoptosis and survival decisions. Nature 458, 591–596 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wu L., Luo K., Lou Z., Chen J., MDC1 regulates intra-S-phase checkpoint by targeting NBS1 to DNA double-strand breaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 11200–11205 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Melander F., Bekker-Jensen S., Falck J., Bartek J., Mailand N., Lukas J., Phosphorylation of SDT repeats in the MDC1 N terminus triggers retention of NBS1 at the DNA damage-modified chromatin. J. Cell Biol. 181, 213–226 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Spycher C., Miller E. S., Townsend K., Pavic L., Morrice N. A., Janscak P., Stewart G. S., Stucki M., Constitutive phosphorylation of MDC1 physically links the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex to damaged chromatin. J. Cell Biol. 181, 227–240 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chapman J. R., Jackson S. P., Phospho-dependent interactions between NBS1 and MDC1 mediate chromatin retention of the MRN complex at sites of DNA damage. EMBO Rep. 9, 795–801 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stucki M., Clapperton J. A., Mohammad D., Yaffe M. B., Smerdon S. J., Jackson S. P., MDC1 directly binds phosphorylated histone H2AX to regulate cellular responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Cell 123, 1213–1226 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lloyd J., Chapman J. R., Clapperton J. A., Haire L. F., Hartsuiker E., Li J., Carr A. M., Jackson S. P., Smerdon S. J., A supramodular FHA/BRCT-repeat architecture mediates Nbs1 adaptor function in response to DNA damage. Cell 139, 100–111 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang Q., Goldstein M., Alexander P., Wakeman T. P., Sun T., Feng J., Lou Z., Kastan M. B., Wang X. F., Rad17 recruits the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex to regulate the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks. EMBO J. 33, 862–877 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bai Y., Wang W., Li S., Zhan J., Li H., Zhao M., Zhou X. A., Li S., Li X., Huo Y., Shen Q., Zhou M., Zhang H., Luo J., Sung P., Zhu W. G., Xu X., Wang J., C1QBP promotes homologous recombination by stabilizing MRE11 and controlling the assembly and activation of MRE11/RAD50/NBS1 complex. Mol. Cell 75, 1299–1314.e6 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chardin P., Camonis J. H., Gale N. W., van Aelst L., Schlessinger J., Wigler M. H., Bar-Sagi D., Human Sos1: A guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras that binds to GRB2. Science 260, 1338–1343 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J., The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell 70, 431–442 (1992). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Aoki K., Yamada M., Kunida K., Yasuda S., Matsuda M., Processive phosphorylation of ERK MAP kinase in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 12675–12680 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cheng A. M., Saxton T. M., Sakai R., Kulkarni S., Mbamalu G., Vogel W., Tortorice C. G., Cardiff R. D., Cross J. C., Muller W. J., Pawson T., Mammalian Grb2 regulates multiple steps in embryonic development and malignant transformation. Cell 95, 793–803 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Verbeek B. S., Adriaansen-Slot S. S., Rijksen G., Vroom T. M., Grb2 overexpression in nuclei and cytoplasm of human breast cells: A histochemical and biochemical study of normal and neoplastic mammary tissue specimens. J. Pathol. 183, 195–203 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yamazaki T., Zaal K., Hailey D., Presley J., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Samelson L. E., Role of Grb2 in EGF-stimulated EGFR internalization. J. Cell Sci. 115, 1791–1802 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hou B., Xu S., Xu Y., Gao Q., Zhang C., Liu L., Yang H., Jiang X., Che Y., Grb2 binds to PTEN and regulates its nuclear translocation to maintain the genomic stability in DNA damage response. Cell Death Dis. 10, 546 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Miotto B., Chibi M., Xie P., Koundrioukoff S., Moolman-Smook H., Pugh D., Debatisse M., He F., Zhang L., Defossez P. A., The RBBP6/ZBTB38/MCM10 axis regulates DNA replication and common fragile site stability. Cell Rep. 7, 575–587 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lv J., Zhang S., Wu H., Lu J., Lu Y., Wang F., Zhao W., Zhan P., Lu J., Fang Q., Xie C., Yin Z., Deubiquitinase PSMD14 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by stabilizing GRB2. Cancer Lett. 469, 22–34 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhong Z. H., Jiang W. Q., Cesare A. J., Neumann A. A., Wadhwa R., Reddel R. R., Disruption of telomere maintenance by depletion of the MRE11/RAD50/NBS1 complex in cells that use alternative lengthening of telomeres. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 29314–29322 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chang E. Y.-C., Tsai S., Aristizabal M. J., Wells J. P., Coulombe Y., Busatto F. F., Chan Y. A., Kumar A., Zhu Y. D., Wang A. Y.-H., Fournier L.-A., Hieter P., Kobor M. S., Masson J.-Y., Stirling P. C., MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 promotes Fanconi anemia R-loop suppression at transcription-replication conflicts. Nat. Commun. 10, 4265 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Millet R., Jolinon N., Nguyen X. N., Berger G., Cimarelli A., Greco A., Bertrand P., Odenthal M., Buning H., Salvetti A., Impact of the MRN complex on adeno-associated virus integration and replication during coinfection with herpes simplex virus 1. J. Virol. 89, 6824–6834 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hogrel G., Lu Y., Laurent S., Henry E., Etienne C., Phung D. K., Dulermo R., Bosse A., Pluchon P. F., Clouet-d’Orval B., Flament D., Physical and functional interplay between PCNA DNA clamp and Mre11-Rad50 complex from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, 5651–5663 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., McGlade J., Olivier P., Pawson T., Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M., Sabe H., Hanafusa H., Yi T., Specific motifs recognized by the SH2 domains of Csk, 3BP2, fps/fes, GRB-2, HCP, SHC, Syk, and Vav. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2777–2785 (1994). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rogakou E. P., Pilch D. R., Orr A. H., Ivanova V. S., Bonner W. M., DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5858–5868 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Park Y. B., Chae J., Kim Y. C., Cho Y., Crystal structure of human Mre11: Understanding tumorigenic mutations. Structure 19, 1591–1602 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ahmed Z., Timsah Z., Suen K. M., Cook N. P., Lee G. R. IV, Lin C.-C., Gagea M., Marti A. A., Ladbury J. E., Grb2 monomer-dimer equilibrium determines normal versus oncogenic function. Nat. Commun. 6, 7354 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shibata A., Moiani D., Arvai A. S., Perry J., Harding S. M., Genois M. M., Maity R., van Rossum-Fikkert S., Kertokalio A., Romoli F., Ismail A., Ismalaj E., Petricci E., Neale M. J., Bristow R. G., Masson J. Y., Wyman C., Jeggo P. A., Tainer J. A., DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice is directed by distinct MRE11 nuclease activities. Mol. Cell 53, 7–18 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gunn A., Stark J. M., I-SceI-based assays to examine distinct repair outcomes of mammalian chromosomal double strand breaks. Methods Mol. Biol. 920, 379–391 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sfeir A., Symington L. S., Microhomology-mediated end joining: A back-up survival mechanism or dedicated pathway? Trends Biochem. Sci. 40, 701–714 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dutta A., Eckelmann B., Adhikari S., Ahmed K. M., Sengupta S., Pandey A., Hegde P. M., Tsai M. S., Tainer J. A., Weinfeld M., Hegde M. L., Mitra S., Microhomology-mediated end joining is activated in irradiated human cells due to phosphorylation-dependent formation of the XRCC1 repair complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, 2585–2599 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Eckelmann B. J., Bacolla A., Wang H., Ye Z., Guerrero E. N., Jiang W., El-Zein R., Hegde M. L., Tomkinson A. E., Tainer J. A., Mitra S., XRCC1 promotes replication restart, nascent fork degradation and mutagenic DNA repair in BRCA2-deficient cells. NAR Cancer 2, zcaa013 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shen W. H., Balajee A. S., Wang J., Wu H., Eng C., Pandolfi P. P., Yin Y., Essential role for nuclear PTEN in maintaining chromosomal integrity. Cell 128, 157–170 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ashworth A., Lord C. J., Synthetic lethal therapies for cancer: What’s next after PARP inhibitors? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15, 564–576 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Angus L., Smid M., Wilting S. M., van Riet J., Van Hoeck A., Nguyen L., Nik-Zainal S., Steenbruggen T. G., Tjan-Heijnen V. C. G., Labots M., van Riel J., Bloemendal H. J., Steeghs N., Lolkema M. P., Voest E. E., van de Werken H. J. G., Jager A., Cuppen E., Sleijfer S., Martens J. W. M., The genomic landscape of metastatic breast cancer highlights changes in mutation and signature frequencies. Nat. Genet. 51, 1450–1458 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mol C. D., Izumi T., Mitra S., Tainer J. A., DNA-bound structures and mutants reveal abasic DNA binding by APE1 and DNA repair coordination. Nature 403, 451–456 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Flynn R. L., Zou L., Oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding fold proteins: A growing family of genome guardians. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 45, 266–275 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bacolla A., Sengupta S., Ye Z., Yang C., Mitra J., De-Paula R. B., Hegde M. L., Ahmed Z., Mort M., Cooper D. N., Mitra S., Tainer J. A., Heritable pattern of oxidized DNA base repair coincides with pre-targeting of repair complexes to open chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, 221–243 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Symington L. S., Mechanism and regulation of DNA end resection in eukaryotes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 51, 195–212 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Williams R. S., Moncalian G., Williams J. S., Yamada Y., Limbo O., Shin D. S., Groocock L. M., Cahill D., Hitomi C., Guenther G., Moiani D., Carney J. P., Russell P., Tainer J. A., Mre11 dimers coordinate DNA end bridging and nuclease processing in double-strand-break repair. Cell 135, 97–109 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ahmed Z., Lin C. C., Suen K. M., Melo F. A., Levitt J. A., Suhling K., Ladbury J. E., Grb2 controls phosphorylation of FGFR2 by inhibiting receptor kinase and Shp2 phosphatase activity. J. Cell Biol. 200, 493–504 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Houl J. H., Ye Z., Brosey C. A., Balapiti-Modarage L. P. F., Namjoshi S., Bacolla A., Laverty D., Walker B. L., Pourfarjam Y., Warden L. S., Babu Chinnam N., Moiani D., Stegeman R. A., Chen M. K., Hung M. C., Nagel Z. D., Ellenberger T., Kim I. K., Jones D. E., Ahmed Z., Tainer J. A., Selective small molecule PARG inhibitor causes replication fork stalling and cancer cell death. Nat. Commun. 10, 5654 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sanjana N. E., Shalem O., Zhang F., Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 11, 783–784 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Shalem O., Sanjana N. E., Hartenian E., Shi X., Scott D. A., Mikkelson T., Heckl D., Ebert B. L., Root D. E., Doench J. G., Zhang F., Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science 343, 84–87 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ahmed Z., George R., Lin C. C., Suen K. M., Levitt J. A., Suhling K., Ladbury J. E., Direct binding of Grb2 SH3 domain to FGFR2 regulates SHP2 function. Cell. Signal. 22, 23–33 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Souza-Fagundes E. M., Frank A. O., Feldkamp M. D., Dorset D. C., Chazin W. J., Rossanese O. W., Olejniczak E. T., Fesik S. W., A high-throughput fluorescence polarization anisotropy assay for the 70N domain of replication protein A. Anal. Biochem. 421, 742–749 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Feng L., Chen J., The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 201–206 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/7/32/eabe9254/DC1


