Abstract
Background
A run of homozygosity (ROH) is a consecutive tract of homozygous genotypes in an individual that indicates it has inherited the same ancestral haplotype from both parents. Genomic inbreeding can be quantified based on ROH. Genomic regions enriched with ROH may be indicative of selection sweeps and are known as ROH islands. We carried out ROH analyses in five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds; Altay sheep (n = 50 individuals), Large-tailed Han sheep (n = 50), Hulun Buir sheep (n = 150), Short-tailed grassland sheep (n = 150), and Tibetan sheep (n = 50), using genotypes from an Ovine Infinium HD SNP BeadChip.
Results
A total of 18,288 ROH were identified. The average number of ROH per individual across the five sheep breeds ranged from 39 (Hulun Buir sheep) to 78 (Large-tailed Han sheep) and the average length of ROH ranged from 0.929 Mb (Hulun Buir sheep) to 2.544 Mb (Large-tailed Han sheep). The effective population size (Ne) of Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep were estimated to be 81, 78, 253, 238 and 70 five generations ago. The highest ROH-based inbreeding estimate (FROH) was 0.0808 in Large-tailed Han sheep, whereas the lowest FROH was 0.0148 in Hulun Buir sheep. Furthermore, the highest proportion of long ROH fragments (> 5 Mb) was observed in the Large-tailed Han sheep breed which indicated recent inbreeding. In total, 49 ROH islands (the top 0.1% of the SNPs most commonly observed in ROH) were identified in the five sheep breeds. Three ROH islands were common to all the five sheep breeds, and were located on OAR2: 12.2–12.3 Mb, OAR12: 78.4–79.1 Mb and OAR13: 53.0–53.6 Mb. Three breed-specific ROH islands were observed in Altay sheep (OAR15: 3.4–3.8 Mb), Large-tailed Han sheep (ORA17: 53.5–53.8 Mb) and Tibetan sheep (ORA5:19.8–20.2 Mb). Collectively, the ROH islands harbored 78 unique genes, including 19 genes that have been documented as having associations with tail types, adaptation, growth, body size, reproduction or immune response.
Conclusion
Different ROH patterns were observed in five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds, which reflected their different population histories. Large-tailed Han sheep had the highest genomic inbreeding coefficients and the highest proportion of long ROH fragments indicating recent inbreeding. Candidate genes in ROH islands could be used to illustrate the genetic characteristics of these five sheep breeds. Our findings contribute to the understanding of genetic diversity and population demography, and help design and implement breeding and conservation strategies for Chinese sheep.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s40104-021-00608-9.
Keywords: Candidate genes, Genomic inbreeding coefficient, ROH islands, Runs of homozygosity, Sheep
Introduction
Selection is one of the main forces reshaping the genomes of domestic animals. A genomic region subjected to intense selection would leave a footprint as a result of the selection and this is known as a selection signature. These signatures might demonstrate increased frequency of favorable allele(s), and reduced nucleotide diversity around the selected locus [1]. The reduction in genetic variation can be characterized as consecutive segments of homozygous genotypes (i.e. runs of homozygosity; ROH). In animal breeding, selection plays the vital role in achieving genetic gain. Mating among related animals cannot be avoided because only a small proportion of individuals are elite, and these tend to be used more widely than average animals. Inbreeding results in loss of genetic diversity, the emergence of harmful recessive mutations, as well as reducing productive performance, notably fecundity. All these effects impact the profitability and sustainability of livestock and poultry [2, 3].
Traditionally, inbreeding was characterized in terms of the inbreeding coefficient, calculated according to pedigree records (FPED) as proposed by Wright [4]. FPED reflects the probability that a pair of alleles is identical by descent (IBD), which is a statistical expectation [5]. Moreover, FPED is usually underestimated because it assumes the founder animals in the pedigree are unrelated in which case FPED ignores historical inbreeding prior to the founders [6–8]. The availability of genome sequencing data and high-density SNP genotypic data provides an opportunity to evaluate inbreeding at a molecular level. Inbreeding evaluation based on genomic information could reflect the true inbreeding value by directly identifying alleles at a locus that are IBD.
An individual inheriting the same haplotype from both parents exhibits ROH [9]. McQuillan et al. [10] first used ROH to compute the genomic inbreeding coefficient (FROH) in human. In animal genetics, ROH has been used to estimate whole-genome inbreeding at both the individual and population levels [11, 12] and to detect selection signatures [13–15]. Forutan et al. [7] reported that based on simulation FROH provides the closest estimates to true inbreeding [5]. Moreover, the correlations between FPED and FROH were moderate to high (0.62–0.75) [16–18], so FROH was considered as an alternative approach to evaluate the inbreeding degree of an individual [5], particularly when pedigree information is unavailable or might be unreliable.
The length of IBD segments follows an inverse exponential distribution with a mean of 1/2 t Morgans, where t represents the number of generations from a common ancestor [19]. Therefore, the length of ROH can be used to infer inbreeding history. Shorter ROH are the result of more ancient inbreeding, while longer ROH suggest more recent inbreeding [9]. Hence, the detection and characterization of ROH can provide insight into how population history, structure and demography evolved over time [9, 17, 20] and to characterize inbreeding levels [15, 21]. Genomic regions enriched with ROH tend to generate ROH hotspots, which are also called ROH islands [9]. ROH islands could be used to positionally identify genes under natural or artificial selection in past adaptation and breeding processes [14, 15, 17, 22].
The aim of this study was to investigate the occurrence and distribution of ROH in five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds using genotypes assayed from the Ovine Infinium HD SNP BeadChip. These five sheep breeds are regionally disparate and possess breed specific characterizations. Based on ROH, we calculate genomic inbreeding coefficients and identify candidate genes residing in ROH islands in these Chinese indigenous sheep breeds.
Materials and methods
Animal populations and genotype quality control
Samples from a total of 450 sheep were collected representing five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds: Altay sheep (n = 50), Large-tailed Han sheep (n = 50), Hulun Buir sheep (n = 150), Short-tailed grassland sheep (n = 150) and Tibetan sheep (n = 50). Altay sheep were collected from Altay city in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Large-tailed Han sheep from the national Large-tailed Han sheep conservation farm of China, Tibet sheep from Qinghai Tibet Plateau in Tianzhu county, Gansu Province, Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep from the grassland of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. All the animals were genotyped using an Ovine Infinium HD SNP BeadChip which included 604,715 SNPs. Genotype quality control was executed using PLINK v1.90 [23]. The following quality control criteria were used to filter the raw data: (1) locus call rate > 0.90; (2) minor allele frequency (MAF) > 0.01 and no evidence of Hardy Weinberg disequilibrium (P < 0.001); (3) SNPs located on autosomes; (4) call rate for individual > 90%. After quality control, 407 samples including 533,453 SNPs were retained for subsequent analyses. Chromosomal coordinates for each SNP were obtained from ovine genome assembly 3.1 (OAR3.1) (https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/refseq/vertebrate_mammalian/Ovis_aries/all_assembly_versions/suppressed/GCF_000298735.1_Oar_v3.1/). Missing genotypes were imputed using non pedigree methods in Beagle 5.0 software [24].
Estimation of LD and effective population size
In this study, linkage disequilibrium (LD) coefficients (r2) between all pairwise SNPs separated less than 5 Mb in the genome were calculated for each breed using PLINK v1.09 software [23]. The mean r2 was calculated according to different pairwise distance classes as following [0 ~ ≤20; 20 ~ ≤40; 40 ~ ≤60;……; 4,940 ~ ≤4,960; 4,960 ~ ≤4,980; 4,980 ~ ≤5,000 kb].
Historical effective population sizes (Ne) of the five sheep breeds were computed as below by rearranging a formula proposed by Sved [25]:
| 1 |
where Ne(t) is the effective population size t generations prior to the genotyped animals and t is approximately equal to [26]. The parameter c represents the genetic distance between two SNPs expressed in Morgans, such that c = 0.5 represents no linkage between two loci. We relate the sheep linkage map distances between pairwise markers from their physical locations on the same autosome according to the ratio of the total physical distance to the total recombinant genetic distance. The total physical distance and total genetic distance of sheep were obtained from the links https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/refseq/vertebrate_mammalian/Ovis_aries/all_assembly_versions/suppressed/GCF_000298735.1_Oar_v3.1/ and https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/MapView/Ovis_aries/non_sequence/, respectively. E(r2| ct) is the mean values of r2 between all pairwise SNPs spanning specific physical distance across all autosomes. In this study, the average ratio of the total physical distance to the total recombinant genetic distance was 1.415, and c = 0.1 M amounted to the average physical distance between SNP pairs of around 7.06 Mb, which can estimate Ne 5 generations previous to the genotyped animals. To better understand the historical change and trend of Ne for each breed, Ne of 1,000, 500, 200, 100, 50, 20, 10 and 5 generations ago were estimated, respectively.
Identification of runs of homozygosity
The R package detectRUNS was used to detect ROH per individual [27]. The following criteria were set to detect ROH: (1) a sliding window of 50 SNPs; (2) a maximum of one heterozygous genotype per window; (3) the default value 0.05 as the threshold of the sliding window; (4) the maximum gap of 500 kb between two consecutive SNPs in ROH; (5) the minimum SNP density per ROH was set to one SNP every 50 kb; (6) the minimum ROH length was set to 500 Kb to exclude short ROH due to LD; (7) To minimize the number of ROH detected by chance, the minimum number of SNPs that constituted a ROH was set based on the method proposed by Lencz et al. [28]. That is:
| 2 |
where l is the minimum number of SNPs that must be in a ROH, nSNP is the number of SNPs of each individual, ni is the total number of individuals in the whole population, α is the false positive rate of identified ROH (set to 0.05 in the present study) and was the mean heterozygosity of all SNPs. In this study, calculated from our genotypic data, l was equal to 53 SNPs.
ROH size categories
For each sheep breed, the average number of ROH per individual and the average length of ROH were estimated. The identified ROH were divided into five classes based on their length: 0.5–5 Mb, 5–10 Mb, 10–15 Mb, 15–20 Mb and > 20 Mb. Frequency of the ROH numbers in each length category was calculated for the five sheep breeds. For each category, the mean sum of ROH per animal for each breed was calculated by summing all ROH in that category and averaging the sum number of animals in that breed. The ROH number of each chromosome for the five sheep breeds were counted respectively as well as the total length and total number of ROH for each animal.
Estimation of ROH-based inbreeding coefficients
Genomic inbreeding coefficients based on ROH (FROH) were computed for each individual using the equation proposed by McQuillan et al. [10]:
| 3 |
where ∑LROH is the total length of all the ROH identified in an individual, LAUTO is the total length of the autosomes covered by SNPs, which was 2,452 Mb in our study. To investigate differences of FROH on each chromosome, we calculated FROH for each chromosome. Moreover, inbreeding coefficient based on expected number of homozygous genotypes (FHOM) was calculated using PLINK v1.9 [23]. Pearson’s correlation between FROH and FHOM was calculated.
Detection of ROH islands
To identify the genomic regions most commonly associated with ROHs, the percentage of occurrence of SNPs in ROH was calculated by counting the number of times that a SNP was detected in an ROH across all the individuals in each breed. In this study, the top 0.1% of the SNPs observed in ROHs was selected as the threshold for identifying the genomic regions most commonly associated with ROH in each breed. A series of adjacent SNPs that exceeded this threshold formed a genomic region which we refer to as an ROH island. In this study, the breed specific thresholds were 40%, 44%, 37%, 39% and 50% of the individuals sharing the overlapping homozygous regions (ROH islands) in Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively. Gene annotation in ROH islands was performed on the basis of sheep reference genome Ovis_aries.Oar_v3.1. The biological function of the genes residing in ROH islands was conducted by survey of relevant literature.
Results
Estimation of LD and effective population size (Ne)
Figure 1 shows the average r2 per breed plotted against the physical distances between pairwise SNPs in classes of 20 kb, providing an overview of the decline of r2 in each breed. On the whole, Tibetan sheep showed the highest average r2 at all marker distances, followed by Large-tailed Han sheep and Altay sheep. The average r2 of Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep decayed significantly faster than r2 of the other breeds. Moreover, LD decay lines of Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep almost overlapped but the smallest values of average r2 were apparent in Hulun Buir sheep.
Fig. 1.
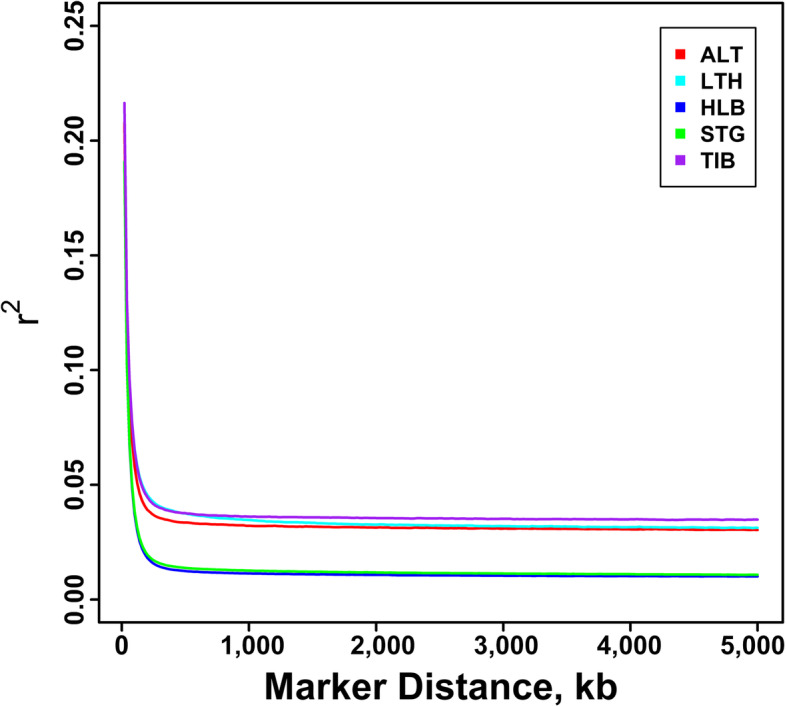
LD decay map measured by r2 over distance between SNPs in five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds. ALT, LTH,HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Estimates of effective population size (Ne) for the five sheep breeds are depicted in Fig. 2. For all five breeds, a declining trend of effective population size (Ne) across generations was observed. For all generations, Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep had larger Ne, relative to other sheep breeds. The Ne of the five sheep breeds at 1,000 generations ago were predicted to be 5,053 (Hulun Buir sheep), 5,013 (Short-tailed grassland sheep), 4,059 (Altay sheep), 3,715 (Large-tailed Han sheep) and 3,697 (Tibetan sheep). In a more recent time frame (5 generations ago), the corresponding estimates of Ne were 253 (Hulun Buir sheep), 237 (Short-tailed grassland sheep), 81 (Altay sheep), 78 (Large-tailed Han sheep) and 70 (Tibetan sheep). The sequences of estimated effective population sizes by generation and breed are shown in Table S1.
Fig. 2.
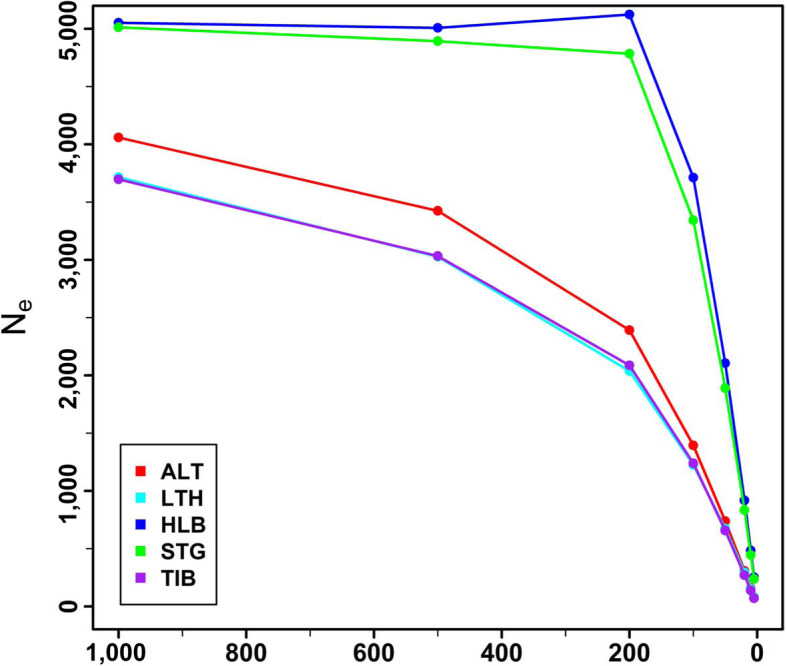
Estimates of effective population sizes (Ne) for Chinese five sheep breeds for 1000–5 ancestral generations ago. ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
ROH detection
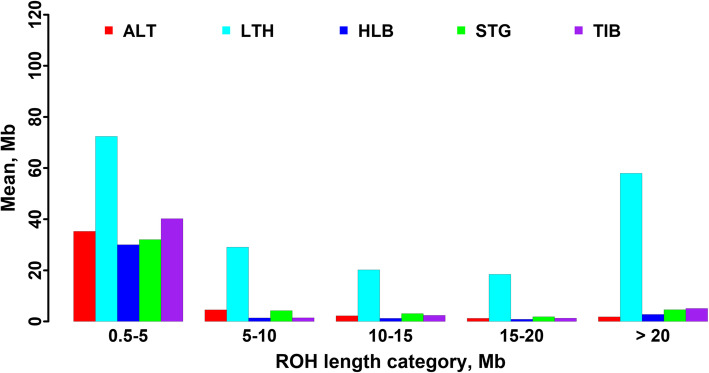
A total of 18,288 ROHs were identified across the five sheep breeds. Table 1 summarizes the average number of ROH per individual and the average length of ROH per sheep breed. The average number of ROH per individual ranged from 78 (Large-tailed Han sheep) to 39 (Hulun Buir sheep), and the average length of ROH each breed ranged from 0.929 Mb (Hulun Buir sheep) to 2.554 Mb (Large-tailed Han sheep). Table 2 shows the percentages of ROH numbers in five length categories of 0.5–5, 5–10, 10–15, 15–20 and > 20 Mb in each breed. Regardless of breed, most ROH were shorter than 5 Mb. Compared with the other four sheep breeds, Large-tailed Han sheep had a higher proportion of long ROHs (> 5 Mb). Fig. 3 illustrates the mean sum of ROH in each length category of the five sheep breeds. Large-tailed Han had the highest mean sum of ROH in all ROH length categories. Especially in the category of > 20 Mb, the gap between Large-tailed Han and other breeds was more prominent. As seen in Fig. 4, the percentages of ROH numbers on autosomes varied but the trends across the five sheep breeds tended to be similar. The highest percentage was observed on OAR2 in all five sheep breeds, while the lowest percentage of ROH number was on OAR24 in Short-tailed grassland sheep and OAR26 in the other four breeds. On the whole, the numbers of ROH per chromosome tended to increase with chromosome length, with the average correlation coefficient of 0.934 across all sheep breeds. Figure 5 depicts the total number and the total length of ROH per individual. Several extreme individuals exhibiting autosomal ROH > 600 Mb were found in Large-tailed Han sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep breeds.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics for ROH and genomic inbreeding coefficients in five sheep breeds
| Breeds | ROH number | ROH length, Mb | FROH | FHOM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| ALT | 42.95 ± 7.52 | 1.053 ± 1.709 | 0.0184 ± 0.0081 | −0.0121 ± 0.00865 | 0.868 |
| LTH | 77.56 ± 22.90 | 2.554 ± 5.647 | 0.0808 ± 0.0810 | 0.0444 ± 0.0847 | 0.997 |
| HLB | 39.08 ± 6.10 | 0.929 ± 1.988 | 0.0148 ± 0.0139 | −0.00334 ± 0.0157 | 0.909 |
| STG | 40.08 ± 7.31 | 1.145 ± 2.386 | 0.0187 ± 0.0266 | −0.000860 ± 0.0286 | 0.950 |
| TIB | 53.70 ± 11.85 | 0.939 ± 1.951 | 0.0206 ± 0.0138 | −0.0163 ± 0.0250 | 0.721 |
| ALL | 44.93 ± 15.25 | 1.278 ± 3.055 | 0.0234 ± 0.0364 | 0.0129 ± 0.0403 | 0.960 |
Note: ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Table 2.
The percentages of ROH number in different length categories in the five sheep breeds
| Categories, Mb | ALT | LTH | HLB | STG | TIB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5–5 | 0.977 | 0.888 | 0.989 | 0.972 | 0.988 |
| 5–10 | 0.016 | 0.054 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.004 |
| 10–15 | 0.004 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.004 |
| 15–20 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| > 20 | 0.002 | 0.023 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.003 |
Note: ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Fig. 3.
The Mean sum of ROH in Mb per animal within each ROH length category. ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Fig. 4.
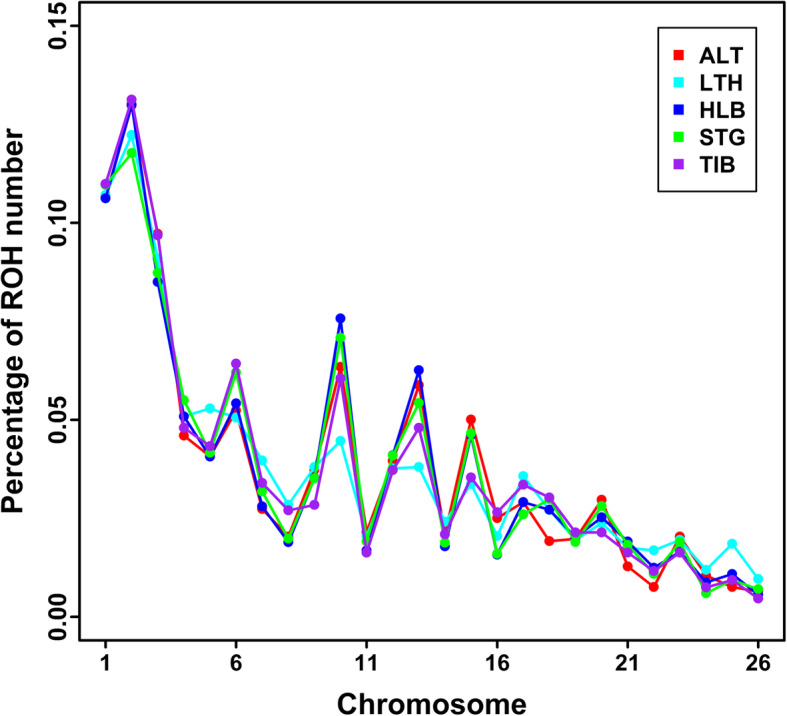
Number of ROH per chromosome in five sheep breeds. ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Fig. 5.
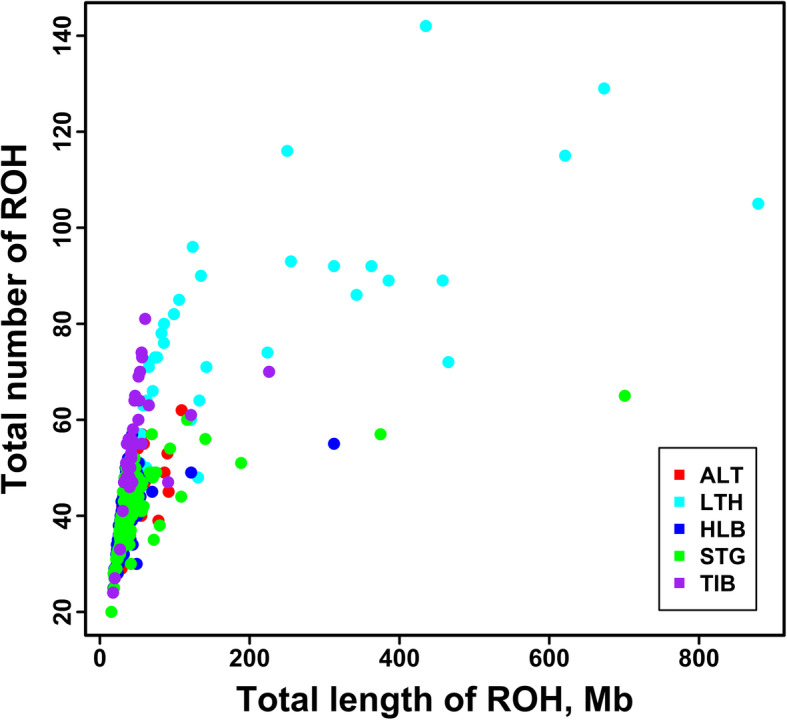
Total number of ROHs and total length of genome (Mb) covered by ROH segments per individual for each sheep breed. ALT, LTH, HLB, and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Genomic inbreeding coefficients
Table 1 shows the two measures of inbreeding (FROH and FHOM) in the five sheep breeds. All the average FROH of the five sheep breeds were bigger than 0.01, while the average FHOM in Altay sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep breeds were negative. The average of FROH of Hulun Buir sheep was the lowest (0.0148) among these five sheep breeds, whereas the average FROH of Large-tailed Han sheep was the highest (0.0808). It should be noted that the FROH of Short-tailed grassland sheep was very close to Hulun Buir sheep breed. The correlations between FROH and FHOM ranged from 0.721 (Tibetan sheep) to 0.997 (Large-tailed Han sheep) in five sheep breeds, and the correlation coefficient across all the animals was 0.960. The FROH per chromosome per breed are illustrated in Fig. 6. The autosomal values of FROH of Large-tailed Han sheep were the highest across all the five breeds.
Fig. 6.
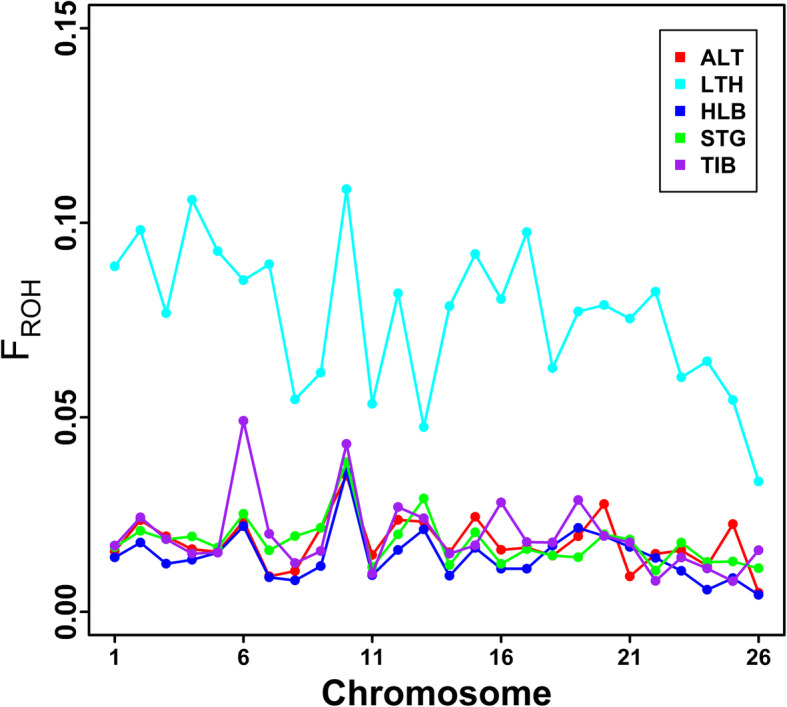
Distribution of FROH on each Ovies aries chromosome (OAR) in five sheep breeds. ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Detection of common ROHs
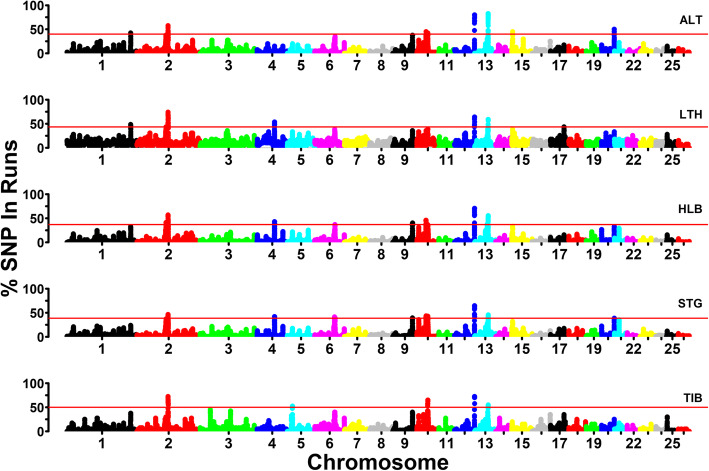
Fig. 7 displays the percentage of occurrence of SNPs in ROH against the position of the SNP along all the autosomes. As seen in Fig. 7, ROH islands were mainly distributed on OARs 2, 9, 10, 12 and 13, with many overlap regions observed among the five sheep breeds. Totally, 49 genomic regions were identified as ROH islands in the five sheep breeds (Table 3). Three of those genomic regions were common to all the five breeds. They were located on OAR2: 12.2–12.3 Mb, OAR12: 78.4–79.1 Mb and OAR13: 53.0–53.6 Mb. In addition, there were three breed-specific ROH islands in Altay sheep (OAR15: 3.4–3.8 Mb), Large-tailed Han sheep (ORA17: 53.5–53.8 Mb) and Tibetan sheep (ORA5:19.8–20.2 Mb). From the genomic regions representing ROH islands in the five sheep breeds, a total of 257 positional candidate genes were annotated. After removing genes that were represented more than once, 76 unique genes remained. Among them, 19 genes were reported in the literature as having been associated with economically important traits (Table 4), whereas the other genes are listed in Table S2.
Fig. 7.
Genome-wide frequency of SNPs occurrence into ROHs for each sheep breed. The red line was the threshold to define the ROH islands. ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Table 3.
List of ROH islands identified in five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds
| Breeds | Chr | Number of SNPs | Start, bp | End, bp | Number of genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT | 1 | 61 | 250,505,889 | 250,968,614 | 2 |
| 2 | 29 | 122,022,456 | 122,196,859 | 0 | |
| 2 | 67 | 122,203,171 | 122,713,621 | 1 | |
| 2 | 49 | 122,789,438 | 123,131,444 | 0 | |
| 10 | 1 | 36,431,208 | 36,431,208 | 1 | |
| 10 | 12 | 42,602,855 | 42,668,804 | 0 | |
| 10 | 2 | 42,864,819 | 42,886,791 | 0 | |
| 10 | 2 | 43,201,824 | 43,218,840 | 0 | |
| 12 | 79 | 78,441,984 | 79,070,188 | 7 | |
| 13 | 104 | 52,983,990 | 53,669,096 | 27 | |
| 15 | 71 | 3,369,761 | 3,860,098 | 1 | |
| 20 | 53 | 49,963,739 | 50,507,014 | 1 | |
| LTH | 1 | 68 | 250,505,243 | 251,024,337 | 2 |
| 2 | 9 | 114,531,332 | 114,582,444 | 0 | |
| 2 | 188 | 122,066,517 | 123,448,890 | 1 | |
| 4 | 86 | 68,604,130 | 69,128,428 | 21 | |
| 12 | 91 | 78,412,601 | 79,070,188 | 7 | |
| 13 | 90 | 53,019,664 | 53,640,527 | 25 | |
| 17 | 33 | 53,546,799 | 53,758,306 | 2 | |
| HLB | 2 | 3 | 114,602,806 | 114,611,225 | 0 |
| 2 | 19 | 115,006,350 | 115,133,173 | 0 | |
| 2 | 146 | 122,203,171 | 123,318,733 | 1 | |
| 4 | 59 | 68,730,153 | 69,128,428 | 21 | |
| 6 | 1 | 79,981,634 | 79,981,634 | 0 | |
| 9 | 61 | 77,276,731 | 77,807,912 | 1 | |
| 10 | 105 | 35,838,530 | 36,431,208 | 10 | |
| 10 | 12 | 42,602,855 | 42,668,804 | 0 | |
| 12 | 79 | 78,441,984 | 79,070,188 | 7 | |
| 13 | 4 | 49,772,494 | 49,800,472 | 0 | |
| 13 | 82 | 53,046,392 | 53,647,951 | 25 | |
| STG | 2 | 67 | 122,203,171 | 122,713,621 | 1 |
| 4 | 55 | 68,730,153 | 69,082,247 | 20 | |
| 6 | 3 | 78,164,118 | 78,171,900 | 0 | |
| 6 | 22 | 78,190,079 | 78,372,681 | 1 | |
| 6 | 5 | 79,989,614 | 80,013,968 | 0 | |
| 6 | 41 | 80,045,125 | 80,283,293 | 0 | |
| 9 | 43 | 77,387,147 | 77,790,278 | 1 | |
| 10 | 47 | 35,839,462 | 36,132,909 | 5 | |
| 10 | 52 | 36,173,170 | 36,431,208 | 6 | |
| 10 | 34 | 42,602,855 | 42,829,373 | 0 | |
| 10 | 29 | 42,862,671 | 43,163,671 | 0 | |
| 12 | 78 | 78,449,224 | 79,070,188 | 7 | |
| 13 | 72 | 53,065,617 | 53,589,429 | 22 | |
| 20 | 7 | 50,349,355 | 50,424,219 | 1 | |
| TIB | 2 | 154 | 122,210,623 | 123,369,957 | 1 |
| 5 | 75 | 19,764,108 | 20,233,040 | 4 | |
| 10 | 168 | 42,182,526 | 43,525,344 | 0 | |
| 12 | 78 | 78,449,224 | 79,070,188 | 7 | |
| 13 | 55 | 53,152,803 | 53,589,429 | 18 |
Note: ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Table 4.
Candidate genes resided in ROH island associated with economic traits of animals
| Breeds | OAR | Position, bp | Candidate genes | Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT, LTH | 1 | 250,958,731 ~ 251,069,283 | PCCB | Growth and carcass |
| LTH, HLB,STG | 4 | 68,858,042 ~ 68,863,494 | HOXA10 | Fat deposition |
| LTH, HLB, STG | 4 | 68,921,977 ~ 68,924,549 | HOXA3 | Embryo development |
| TIB | 5 | 19,737,330 ~ 19,769,293 | P4HA2 | Hypoxic adaptation |
| TIB | 5 | 19,956,144 ~ 19,958,155 | CSF2 | Immunity and inflammation response |
| TIB | 5 | 19,971,457 ~ 19,973,243 | IL3 | Immunity regulation |
| HLB, STG | 10 | 35,862,425 ~ 35,885,746 | LATS2 | Embryonic development |
| HLB, STG | 10 | 36,045,326 ~ 36,103,818 | IFT88 | Inflammatory response |
| HLB, STG | 10 | 36,253,000 ~ 36,253,785 | GJB6 | Body size and development |
| HLB, STG | 10 | 36,271,774 ~ 36,272,454 | GJB2 | Body size and development |
| HLB, STG | 10 | 36,304,573 ~ 36,305,769 | GJA3 | Body size and development |
| ALT, LTH, HLB, STG, TIB | 12 | 78,543,637 ~ 78,552,280 | CSRP1 | Growth and carcass |
| ALT, LTH, HLB, STG, TIB | 12 | 78,591,681 ~ 78,596,742 | TNNI1 | Growth, carcass and meat quality |
| ALT, LTH, HLB, STG | 13 | 53,097,296 ~ 53,098,312 | NPBWR2 | Reproductive activity |
| ALT, LTH,HLB, STG, TIB | 13 | 53,280,623 ~ 53,282,184 | ABHD16B | Male infertility |
| ALT, LTH, HLB, STG, TIB | 13 | 53,482,080 ~ 53,488,365 | EEF1A2 | Muscle development and lipid metabolism |
| LTH | 15 | 3,848,546 ~ 4,133,998 | PDGFD | Lipid metabolism |
| LTH | 17 | 53,560,417 ~ 53,616,466 | P2RX7 | Final weight and backfat thickness |
| LTH | 17 | 53,661,638 ~ 53,752,199 | IFT81 | Spermiogenesis and fertility |
Note: ALT, LTH, HLB, STG and TIB represent Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Tibetan sheep, respectively
Discussion
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) and effective population size (Ne) affected by demography
In this study, we collected five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds with different tail types: short fat-tailed (Short-tailed grassland sheep), medium fat-tailed (Hulun Buir sheep), long fat-tailed (Large-tailed Han sheep), fat-rumped (Altay sheep), and thin-tailed sheep (Tibetan sheep). Large-tailed Han sheep possess the fattiest and largest tails of all Chinese local sheep breeds. The conspicuous feature of Large-tailed Han sheep is their long fat tails, which can reach the ground in some extreme individuals. A remarkable feature of Altay sheep is their fat buttocks. Among all the sheep breeds, the highest value of average r2 was observed in Tibetan sheep, which had the smallest Ne. LD decay lines of Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep almost overlapped and the smallest values of average r2 were showed in Hulun Buir sheep. Short-tailed grassland sheep and Hulun Buir sheep are distributed in Hulun Buir grassland in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region [29]. Their Ne were about 253 and 238 at five generation ago, respectively, which were close to Ne of Sunite sheep (207) at seven generations ago in our previous study [30]. Like Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep, Sunite sheep also originated from Mongolia sheep and had a similar breed history and management system. These results demonstrate the high genetic diversity of Mongolian sheep.
ROH and ROH-based inbreeding coefficient (FROH)
Since the length of ROH can be used to infer when inbreeding happened, the number, length and distribution of ROH can provide valuable information about the demography history. Furthermore, we can further utilize the lengths of ROH to estimate the ROH-based inbreeding coefficients. In the current study, ROH identified in all five sheep breeds were unevenly distributed (Fig. 4), with OAR2 having the largest number of ROH among all sheep populations. The number of ROH had high positive correlation with chromosome length (0.934). Our results were consistent with other sheep breeds [31, 32]. However, the smallest number of ROH per chromosome was on different chromosomes in different sheep breeds [31, 32]. Moreover, the mean numbers of ROH varied in the five sheep breeds as well as the average lengths of ROH. Among these breeds, Large-tailed Han sheep had the highest average number of ROH per animal (77.56), the longest average length of ROH (2.554 Mb), and the highest proportion of long ROH fragments (> 5 Mb), especially ROH > 20 Mb (Fig. 3). Moreover, the most individuals carrying a large number of ROH with a total length ≥ 600 Mb were mainly observed in Large-tailed Han sheep. Furthermore, Large-tailed Han sheep showed the highest FROH in both genome (0.0808) and chromosome level (Fig. 7). These results demonstrate that Large-tailed Han sheep had low genetic diversity, and more recent inbreeding events. This might be due to the uncontrolled mating of related individuals in the national Large-tailed Han sheep conservation of China where we sampled these individuals. On the contrary, the Hulun Buir sheep breeds exhibited the least mean number of ROH per animal (39.08) and the shortest average length of ROH (0.929 Mb). Hulun Buir sheep also showed the lowest FROH, followed by Short-tailed grassland sheep which was consistent with the results of effective population size. These reflected their low level of inbreeding resulting from management systems based on random mating in the grassland. The difference of mean number per animal and average length of ROH may reflect the demography of the different populations. In general, the results of ROH had reflected the inbreeding and population history of the five sheep breeds, and the results of LD and effective population size basically supported and verified the results of ROH. Our results seemed to indicate that ROH can be used as a useful tool for inbreeding evaluation and livestock conservation.
Candidate genes within ROH islands
ROH islands are generated from natural or artificial selection and could be used to identify selection signatures. In the process of long-term domestication and adaptation, sheep breeds have formed breed-specific traits. The high frequency homozygous fragments in the genome representing ROH islands can be used to elucidate the genetic mechanism of the breed specific traits. The thresholds in the present study were more stringent than those of other studies using low-density chips [12, 13], which could avoid false positive results.
There were three breed-specific ROH islands: in Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep and Tibetan sheep. In Altay sheep, the specific ROH island was located on OAR15: 3.4–3.8 Mb. In that genomic region, the fat-tail sheep breeds (Large-tailed Han sheep, Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep) also had peaks close to the top 0.1% threshold line (Fig. 7). This genomic region harbors PDGFD that has been documented as a causal gene for fat deposition in sheep tails [33–37]. Moreover, HOXA10 was identified in overlapped ROH island (OAR4: 68.7–69.1 Mb) of Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Large-tailed Han sheep populations. HOXA10 was identified as a candidate gene related to tail type by selection signature detection [35] and further validated as a candidate gene strongly linked with fat deposition in sheep tail by RNA Seq [38]. In addition, PCCB resided in the overlapped ROH islands of Large-tailed Han sheep and Altay sheep, and is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids in pig [39].
These results were supported by the samples with obvious breed feature in terms of tail types. According to sheep tail morphology, the five sheep breeds can be classified into five classes: long fat-tailed (Large-tailed Han sheep), median fat-tailed (Hulun Buir sheep), short fat-tailed (Short-tailed grassland sheep), fat-rumped (Altay sheep) or thin-tailed sheep (Tibetan sheep). In the Tibetan sheep population, the breed specific ROH island resided in OAR5: 19.8–20.2 Mb. That genomic region harbored P4HA2, which is related to hypoxic adaptation and can be induced to express in hypoxic conditions [40, 41]. This may indicate that P4HA2 gene had been selected in the process of Tibetan sheep adapting to high altitude environment. In Large-tailed Han sheep population, the breed specific ROH island was on the OAR17: 53.5–53.8 Mb. On that region, P2RX7 was also annotated, and that gene had been found to be associated with the final weight and backfat thickness of Landrace pigs [42].
Three ROH islands located on OAR2: 12.2–12.3 Mb, OAR12: 78.4–79.1 Mb and OAR13: 53.0–53.6 Mb were common to all the five sheep breeds. The latter two genomic regions harbored four important candidate genes of TNNI1, CSRP1, EEF1A2 and ABHD16B. TNNI1 has been implicated with carcass, growth and meat quality traits in pigs [43, 44] and cattle [45]. CSRP1 was identified as a strong candidate gene associated with growth and carcass traits through SNV and haplotype analysis in the Chinese beef cattle [46]. EEF1A2 was involved in muscle development and lipid metabolism during fetal development in sheep [47]. Furthermore, GJB2, GJB6 and GJA3 were found in overlapping ROH islands of Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep, and have documented associations with body size and development by selection signature detection of Egyptian sheep and goat populations [48]. ABHD16B is the potential causative protein-altering variant for male infertility in Holstein cattle [49]. Other genes have documented involvement in reproduction. IFT81 was identified from ROH island in Large-tailed Han sheep population, and played an essential role in spermiogenesis and fertility male mice [50]. NPBWR2 was located on the overlapped ROH islands in Altay sheep, Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Large-tailed Han sheep, and play a role in modulating the reproductive activity in the pig [51]. HOXA3 resided in the overlapped ROH island in Hulun Buir sheep, Short-tailed grassland sheep and Large-tailed Han sheep populations and was reported to be expressed in bovine oocytes and early-stage embryos and may influence oocyte maturation and the first stages of embryonic development [52]. LATS2 was located on the overlapped ROH islands in Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep, and plays an essential role in embryonic development, proliferation control and genomic integrity [53].
In addition, we identified several genes related to immune and inflammatory response. We identified CSF2 and IL3 from the ROH islands of Tibetan sheep. Previous study had shown that CSF2 played an important role in immunity regulation, hematopoiesis and inflammation response [54–56]. Furthermore, CSF2 was also reported that played pivotal roles in implantation events during early pregnancy in pigs [57] and influence the reproductive capacity in mice [58]. IFT88 resided in the overlapped ROH islands from Hulun Buir sheep and Short-tailed grassland sheep and had been reported to be involved in the inflammatory response of interleukin-1 [59].
Conclusions
In this study, we used genotypes assayed using an Ovine Infinium HD SNP BeadChip to characterize the pattern of LD, estimate the effective population sizes and investigate the occurrence and distribution of ROH across the genomes of five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds. Different LD and ROH patterns were observed in the five breeds. The large-tailed Han sheep population had the highest genomic inbreeding coefficients and the highest proportion of long ROH fragments which reflect recent inbreeding events. On the contrary, the opposite conditions were present in Hulun Buir sheep. In total, 49 ROH islands were identified. Three ROH islands were common to all the breeds, and three breed-specific ROH islands were in Altay sheep, Large-tailed Han sheep and Tibetan sheep. These ROH islands harbored 78 unique genes, including 19 genes documented as being involved in tail types, adaptation, growth, body size, reproduction or immune response. Our findings contribute to the understanding of genetic diversity, population demography and the underlying genetic mechanism of economically important traits, and help design and implement breeding and conservation strategies for Chinese sheep.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1 The effective population size across generations for each breed. Table S2 ROH hotspots identified in five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds and candidate genes annotated.
Acknowledgements
We thank the researchers at our laboratories for their dedication and hard work. We would like to thank everyone who made this thesis possible.
Authors’ contributions
JXL performed analyses and drafted the manuscript. FPZ contributed to acquisition of data. LYS, YL, LC, DG and FPZ engaged in useful discussion and revised the manuscript. LXW and FPZ conceived and designed the experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 31572357) to FPZ and Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP-IAS02) to LXW.
Availability of data and materials
The genotypic data was available at figshare: 10.6084/m9.figshare.14524332.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiments involving animals were approved by the Science Research Department of the Institute of Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) (Beijing, China). There was no use of human participants, data or tissues.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Jiaxin Liu and Liangyu Shi contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Jiaxin Liu, Email: jiaxinliu2019@126.com.
Liangyu Shi, Email: 82101181190@caas.cn.
Yang Li, Email: 18331279970@163.com.
Liang Chen, Email: chenliang1@pkuschool.edu.cn.
Dorian Garrick, Email: D.Garrick@massey.ac.nz.
Lixian Wang, Email: iaswlx@263.net.
Fuping Zhao, Email: zhaofuping@caas.cn.
References
- 1.Smith JM, Haigh J. The hitch-hiking effect of a favourable gene. Genet Res 2007;89:391–403. 10.1017/s0016672308009579. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Mc Parland S, Kearney JF, Rath M, Berry DP. Inbreeding effects on milk production, calving performance, fertility, and conformation in Irish Holstein-Friesians. J Dairy Sci 2007;90:4411–4419. 10.3168/jds.2007-0227. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Bjelland DW, Weigel KA, Vukasinovic N, Nkrumah JD. Evaluation of inbreeding depression in Holstein cattle using whole-genome SNP markers and alternative measures of genomic inbreeding. J Dairy Sci 2013;96:4697–4706. 10.3168/jds.2012-6435. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Wright S. Coefficients of inbreeding and relationship. Am Nat 1922;56:330–338. 10.1086/279872.
- 5.Keller MC, Visscher PM, Goddard ME. Quantification of inbreeding due to distant ancestors and its detection using dense single nucleotide polymorphism data. Genetics. 2011;189:237. 10.1534/genetics.111.130922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Scraggs E, Zanella R, Wojtowicz A, Taylor JF, Gaskins CT, Reeves JJ, et al. Estimation of inbreeding and effective population size of full-blood Wagyu cattle registered with the American Wagyu cattle association. J Anim Breed Genet. 2014;131:3–10. 10.1111/jbg.12066. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Forutan M, Mahyari SA, Baes C, Melzer N, Schenkel FS, Sargolzaei M. Inbreeding and runs of homozygosity before and after genomic selection in North American Holstein cattle BMC Genomics 2018;19:98. 10.1186/s12864-018-4453-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Saura M., Fernandez A., Varona L., Fernandez A.I., de Cara M.A., Barragan C., et al. Detecting inbreeding depression for reproductive traits in Iberian pigs using genome-wide data. Genet Sel Evol 2015;47:1. 10.1186/s12711-014-0081-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Ceballos F.C., Joshi P.K., Clark D.W., Ramsay M., Wilson J.F. Runs of homozygosity: windows into population history and trait architecture. Nat Rev Genet 2018;19:220–234. 10.1038/nrg.2017.109. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.McQuillan R, Leutenegger AL, Abdel-Rahman R, Franklin CS, Pericic M, Barac-Lauc L, et al. Wilson J.F. Runs of homozygosity in European populations. Am J Hum Genet 2008;83:359–72. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Peripolli E., Munari D.P., Silva M., Lima A.L.F., Irgang R., Baldi F. Runs of homozygosity: current knowledge and applications in livestock. Anim Genet 2017;48:255–271. 10.1111/age.12526. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.Mastrangelo S., Tolone M., Di Gerlando R., Fontanesi L., Sardina M.T., Portolano B. Genomic inbreeding estimation in small populations: evaluation of runs of homozygosity in three local dairy cattle breeds. Animal. 2016;10:746–754. 10.1017/s1751731115002943. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Purfield D.C., Mcparland S., Wall E., Berry D.P. The distribution of runs of homozygosity and selection signatures in six commercial meat sheep breeds. PLoS One 2017;12:e0176780. 10.1371/journal.pone.0176780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Xie R, Shi L, Liu J, Deng T, Wang L, Liu Y, et al. Genome-wide scan for runs of Homozygosity identifies candidate genes in three pig breeds. Animals. 2019;9:518. 10.3390/ani9080518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Shi L, Wang L, Liu J, Deng T, Yan H, Zhang L, et al. Estimation of inbreeding and identification of regions under heavy selection based on runs of homozygosity in a large white pig population. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2020;11:46. 10.1186/s40104-020-00447-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Marras G, Gaspa G, Sorbolini S, Dimauro C, Ajmone-Marsan P, Valentini A, et al. Analysis of runs of homozygosity and their relationship with inbreeding in five cattle breeds farmed in Italy. Anim Genet. 2015;46:110–21. 10.1111/age.12259. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Purfield D.C. Runs of homozygosity and population history in cattle. BMC Genet 2012;13:70. 10.1186/1471-2156-13-70, 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Ferencakovic M., Hamzic E., Gredler B., Solberg T.R., Klemetsdal G., Curik I., et al. Estimates of autozygosity derived from runs of homozygosity: empirical evidence from selected cattle populations. J Anim Breed Genet. 2013;130:286–293. 10.1111/jbg.12012. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 19.Howrigan D.P., Simonson M.A., Keller M.C. Detecting autozygosity through runs of homozygosity: a comparison of three autozygosity detection algorithms. BMC Genomics 2011;12:460. 10.1186/1471-2164-12-460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 20.Herrero-Medrano J.M., Megens H.J., Groenen M.A., Ramis G., Bosse M., Perez-Enciso M., et al. Conservation genomic analysis of domestic and wild pig populations from the Iberian Peninsula. BMC Genet 2013;14:106. 10.1186/1471-2156-14-106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Kim E.S., Sonstegard T.S., Van Tassell C.P., Wiggans G., Rothschild M.F. The relationship between runs of Homozygosity and inbreeding in Jersey cattle under selection. PLoS One 2015;10:e0129967. 10.1371/journal.pone.0129967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Szmatoła T., Gurgul A., Ropka-Molik K., Jasielczuk I., Ząbek T., Bugno-Poniewierska M. Characteristics of runs of homozygosity in selected cattle breeds maintained in Poland. Livest Sci. 2016;188:72–80. 10.1016/j.livsci.2016.04.006.
- 23.Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira M.A.R, Bender D, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:559–75. 10.1086/519795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Browning B.L., Browning S.R. Genotype imputation with millions of reference samples. Am J Hum Genet 2016;98:116–126. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Sved J.A. Linkage disequilibrium and homozygosity of chromosome segments in finite populations. Theor Popul Biol 1971;2:125–141. 10.1016/0040-5809(71)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Hayes B.J., Visscher P.M., McPartlan H.C., Goddard M.E. Novel multilocus measure of linkage disequilibrium to estimate past effective population size. Genome Res 2003;13:635–643. 10.1101/gr.387103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 27.Biscarini F., Marras G., Cozzi P., Gaspa G., detectRUNS: an R package to detect runs of homozygosity and heterozygosity in diploid genomes, 2018.
- 28.Lencz T, Lambert C, DeRosse P, Burdick K.E, Morgan T.V, Kane J.M, et al. Runs of homozygosity reveal highly penetrant recessive loci in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:19942–7. 10.1073/pnas.0710021104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Zhang T, Gao H, Sahana G, Zan Y, Fan H, Liu J, et al. Genome-wide association studies revealed candidate genes for tail fat deposition and body size in the Hulun Buir sheep. J Anim Breed Genet. 2019;136:362–70. 10.1111/jbg.12402. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 30.Zhao F., Wang G., Tao Z., Wei C., Li Z., Wang H., et al. Estimations of genomic linkage disequilibrium and effective population sizes in three sheep populations. Livest Sci 2014;170:22–29. 10.1016/j.livsci.2014.10.015.
- 31.Al-Mamun H.A., Clark S.A., Kwan P., Gondro C. Genome-wide linkage disequilibrium and genetic diversity in five populations of Australian domestic sheep. Genet Sel Evol 2015;47:90. 10.1186/s12711-015-0169-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Mastrangelo S., Tolone M., Sardina M.T., Sottile G., Sutera A.M., Di Gerlando R., et al. Genome-wide scan for runs of homozygosity identifies potential candidate genes associated with local adaptation in Valle del Belice sheep. Genet Sel Evol 2017;49:84. 10.1186/s12711-017-0360-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Wei C, Wang H, Liu G, Wu M, Cao J, Liu Z, et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals population structure and selection in Chinese indigenous sheep breeds. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:194. 10.1186/s12864-015-1384-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Mastrangelo S., Moioli B., Ahbara A., Latairish S., Ciani E. Genome-wide scan of fat-tail sheep identifies signals of selection for fat deposition and adaptation. Anim Prod Sci 2019;59. 10.1071/AN17753.
- 35.Zhao F., Deng T., Shi L., Wang W., Zhang Q., Du L., et al. Genomic scan for selection signature reveals fat deposition in Chinese indigenous sheep with extreme tail types. Animals. 2020;10. 10.3390/ani10050773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 36.Dong K, Yang M, Han J, Ma Q, Han J, Song Z, et al. Genomic analysis of worldwide sheep breeds reveals PDGFD as a major target of fat-tail selection in sheep. BMC Genomics. 2020;21:800. 10.1186/s12864-020-07210-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Li X, Yang J, Shen M, Xie X.L, Liu G.J, Xu Y.X, et al. Whole-genome resequencing of wild and domestic sheep identifies genes associated with morphological and agronomic traits. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2815. 10.1038/s41467-020-16485-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Bakhtiarizadeh M.R., Alamouti A.A. RNA-Seq based genetic variant discovery provides new insights into controlling fat deposition in the tail of sheep. Sci Rep 2020;10:13525. 10.1038/s41598-020-70527-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Poucke M.V., Sjoberg A., Mattheeuws M., Zeveren A.V., Bouquet Y., Chowdhary B.P., et al. Mapping of the ATP2B2 and PCCB genes on porcine chromosome 13. Mamm Genome 1997;8:852–853. 10.1007/s003359900592. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 40.Gilkes D.M., Bajpai S., Chaturvedi P., Wirtz D., Semenza G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) promotes extracellular matrix remodeling under hypoxic conditions by inducing P4HA1, P4HA2, and PLOD2 expression in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 2013;288:10819–10829. 10.1074/jbc.M112.442939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Retracted]
- 41.Hofbauer K.H., Gess B., Lohaus C., Meyer H.E., Katschinski D., Kurtz A. Oxygen tension regulates the expression of a group of procollagen hydroxylases. Eur J Biochem 2003;270:4515–4522. 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03846.x. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Lee Y.S., Shin D., Song K.D. Dominance effects of ion transport and ion transport regulator genes on the final weight and backfat thickness of landrace pigs by dominance deviation analysis. Genes Genomics 2018;40:1331–1338. 10.1007/s13258-018-0728-7. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Xu ZY, Yang H, Xiong YZ, Deng CY, Li FE, Lei MG, et al. Identification of three novel SNPs and association with carcass traits in porcine TNNI1 and TNNI2. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37:3609–13. 10.1007/s11033-010-0010-9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Yang H, Xu ZY, Lei MG, Li FE, Deng CY, Xiong YZ, et al. Association of 3 polymorphisms in porcine troponin I genes (TNNI1 andTNNI2) with meat quality traits. J Appl Genet 2010;51:51–7. 10.1007/BF03195710. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 45.He H., Hu Z., Tserennadmid S., Chen S., Liu X. Novel muscle-specific genes TCAP, TNNI1, and FHL1 in cattle: SNVs, linkage disequilibrium, combined genotypes, association analysis of growth performance, and carcass quality traits and expression studies. Anim Biotechnol 2018;29:259–268. 10.1080/10495398.2017.1377084. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.He H, Liu XL, Zhang HL, Yang J, Niu FB, Li ZX, et al. SNV and haplotype analysis reveals new CSRP1 variants associated with growth and carcass traits. Gene. 2013;522:206–13. 10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 47.Xu L, Zhao F, Ren H, Li L, Lu J, Liu J, et al. Co-expression analysis of fetal weight-related genes in ovine skeletal muscle during mid and late fetal development stages. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10:1039–50. 10.7150/ijbs.9737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 48.Kim E.S., Elbeltagy A.R., Aboul-Naga A.M., Rischkowsky B., Sayre B., Mwacharo J.M., et al. Multiple genomic signatures of selection in goats and sheep indigenous to a hot arid environment. Heredity. 2016;116:255–264. 10.1038/hdy.2015.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Shan S, Xu F, Bleyer M, Becker S, Melbaum T, Wemheuer W, et al. Association of alpha/beta-hydrolase D16B with bovine conception rate and sperm plasma membrane lipid composition. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21. 10.3390/ijms21020627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 50.Qu W, Yuan S, Quan C, Huang Q, Zhou Q, Yap Y, et al. The essential role of intraflagellar transport protein IFT81 in male mice spermiogenesis and fertility. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;318:C1092–C1106. 10.1152/ajpcell.00450.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.Yang S., Ma Z., Suo C., Cheng L., Su J., Lei Z. Cloning and mRNA expression of NPB and its effect on hormone secretion of the reproductive cells in the pig. Gen Comp Endocrinol 2018;261:97–103. 10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Paul D., Bridoux L., Rezsohazy R., Donnay I. Hox genes are expressed in bovine and mouse oocytes and early embryos. Mol Reprod Dev 2011;78:436–449. 10.1002/mrd.21321. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 53.McPherson JP, Tamblyn L, Elia A, Migon E, Shehabeldin A, Matysiak-Zablocki E, et al. Lats2/Kpm is required for embryonic development, proliferation control and genomic integrity. EMBO J. 2004;23:3677–88. 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Gasson J.C. Molecular physiology of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1991;77:1131. 10.1182/blood.V77.6.1131.1131. [PubMed]
- 55.Yang Y.C., Ciarletta A.B., Temple P.A., Chung M.P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J.S., et al. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloningof a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986;47:3–10. 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 56.Otsuka T, Miyajima A, Brown N, Otsu K, Abrams J, Saeland S, et al. Isolation and characterization of an expressible cDNA encoding human IL-3. Induction of IL-3 mRNA in human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988;140:2288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jeong W., Song G. EGF, IGF-I, VEGF and CSF2: effects on Trophectoderm of porcine Conceptus. Reprod Dev Biol 2014;38:21–34. 10.12749/RDB.2014.38.1.21.
- 58.Robertson S.A., Roberts C.T., Farr K.L., Dunn A.R., Seamark R.F. Fertility impairment in granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-deficient mice. Biol Reprod 1999;60:251. 10.1095/biolreprod60.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 59.Wann A. A role for IFT88/the primary cilium in the inflammatory response to interleukin-1. Cilia. 2012;1:P60-P60. 10.1186/2046-2530-1-S1-P60.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1 The effective population size across generations for each breed. Table S2 ROH hotspots identified in five Chinese indigenous sheep breeds and candidate genes annotated.
Data Availability Statement
The genotypic data was available at figshare: 10.6084/m9.figshare.14524332.