In the molecular structure of the title compound, the urethane function and the benzoyl group are almost perpendicular to each other [dihedral angle 88.97 (5)°]. In the crystal structure, infinite supramolecular layers in the bc plane are formed by weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, urethanes, carbamates, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds
Abstract
In the molecular structure of the title compound, C15H21NO3, the urethane function and the benzoyl group are almost perpendicular to each other [dihedral angle 88.97 (5)°]. In the crystal structure, infinite supramolecular layers in the bc plane are formed by weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Chemical context
Phenacyl and desyl compounds have been a subject of interest for many years due to their use as photoremovable protecting groups (PPGs) (Givens et al., 2012 ▸; Kammari et al., 2007 ▸; Klán et al., 2013 ▸; Sheehan & Umezawa, 1973 ▸). Carbamates are used for the protection of carboxylic acids and may also act as suitable protecting groups for amines (Speckmeier et al., 2018 ▸). Speckmeier and co-workers synthesized several phenacyl urethanes, but the protection of diisopropylamine by a phenacyl group has not been reported so far. The title compound was synthesized according to reported routes (Speckmeier et al., 2018 ▸).
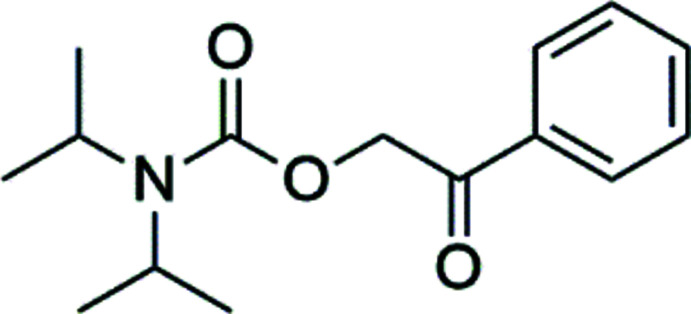
Structural commentary
As expected, the carbamate functional moiety (N1/C3/O3/O2) is essentially planar (maximum deviation of 0.01 Å for C3). The same is true for the benzoyl group (C1/O1/C10–C15, maximum deviation of 0.05 Å for O1). These two planes subtend a dihedral angle of 88.97 (5)° and therefore an almost perpendicular arrangement (Fig. 1 ▸). Otherwise, the bond lengths and angles are of expected values with C3—N1 [1.348 (2) Å] and C3—O2 [1.368 (2) Å] being slightly shorter than a typical C—O or C—N single bond due to the partial double-bond character of the respective bonds in a carbamate.
Figure 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
The crystal structure of the title compound features weak hydrogen bonds (Desiraju & Steiner, 2001 ▸) of the C—H⋯O type, as shown in Table 1 ▸. The interaction C5—H5B⋯O3 links molecules of the title compound into infinite chains parallel to the c-axis direction. Additional C2—H2B⋯O1 and C9—H9B⋯O2 interactions link these infinite chains to a supramolecular sheet parallel to the bc plane (Fig. 2 ▸). The latter interaction is accompanied by a short C9—H9B⋯C3 contact, which makes the contact look like a non-classical hydrogen bond towards the π-system of a C=O double bond, again showing the partial double-bond character of the respective bond.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2B⋯O1i | 0.99 | 2.70 | 3.605 (2) | 152 |
| C5—H5B⋯O3ii | 0.98 | 2.62 | 3.578 (2) | 167 |
| C9—H9B⋯O2iii | 0.98 | 2.68 | 3.599 (2) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y-1, z; (ii) x, -y+{\script{3\over 2}}, z+{\script{1\over 2}}; (iii) x, y+1, z.
Figure 2.
Crystal structure of the title compound showing layers of molecules along the bc plane that are built up by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Database survey
In the CSD (ConQuest Version 2020.3.0; Groom et al., 2016 ▸), only one other carbamate with a CH2–C(O)-Ph group attached to the carbamate oxygen atom is reported (NIWQUI; Jiang et al., 2019 ▸). The respective compound shows a diethylamino group and a p-chlorophenyl substituent instead of the diisopropylamino group and the non-substituted phenyl group in the title compound. In contrast to the title compound, the carbamate plane and the benzoyl plane are almost coplanar. The carbonyl oxygen atoms show numerous short contacts towards different C—H groups of neighboring molecules, leading to a dense three-dimensional network.
Synthesis and crystallization
Diisopropylamine (0.05 mol, 5.05 g) and 1 equiv. of cesium carbonate (0.05 mol, 16.55 g) were placed in a Schlenk tube and dissolved in anhydrous DMSO (150 mL). The tube was sealed with a septum and two balloons filled with CO2 were bubbled through the reaction mixture within one h while stirring. After the addition of CO2, 1.1 equiv. of 2-bromo-1-phenylethan-1-one (0.055 mol, 10.95 g) dissolved in a small amount of DMSO was added in one portion. The consumption of 2-bromo-1-phenylethan-1-one was monitored by TLC and after 30 min the reaction mixture was poured on ice to quench the reaction. After extraction with dichloromethane (3×), the combined organic phases were washed with brine, separated and dried over Na2SO4. The solvent was removed in vacuo and the crude product was recrystallized from n-hexane/ethanol (4:1) to afford the title compound (12.90 g; 98%) as a colorless solid, m.p. 347.5°C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) [ppm]: δ = 7.90 (dd, 2H), 7.55 (ddt, 1H), 7.45 (dd, J = 8.4, 7.1 Hz, 2H), 5.33 (s, 2H), 3.97 (hept, 2H), 1.25 (d, 12H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) [ppm]: δ = 193.91 (C=O), 154.80 (NC=O), 134.69, 133.65, 128.84, 127.83 (C ar), 66.36 (O=C—O), 46.32 [(H3C)2 CH–], 20.99 [(H3 C)2CH–].
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All hydrogen atoms were placed in idealized positions (C—H = 0.95–0.99Å) and refined using a riding model with isotropic displacement parameters calculated as U iso(H) = 1.2×U eq(C) for methylene and hydrogen atoms of the phenyl group or 1.5×U eq(C) for methyl groups.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C15H21NO3 |
| M r | 263.33 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 133 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 18.4574 (8), 5.7020 (2), 14.8058 (6) |
| β (°) | 113.468 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1429.33 (10) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.10 × 0.10 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Nonius KappaCCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.674, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 13968, 3280, 2464 |
| R int | 0.040 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.049, 0.113, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3280 |
| No. of parameters | 177 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.27, −0.21 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021006927/zl5014sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021006927/zl5014Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021006927/zl5014Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2094771
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Financial support of the PhD project of VM by Lohmann GmbH & Co. KG, Neuwied, Germany, is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C15H21NO3 | F(000) = 568 |
| Mr = 263.33 | Dx = 1.224 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 18.4574 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 13968 reflections |
| b = 5.7020 (2) Å | θ = 2.8–27.5° |
| c = 14.8058 (6) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 113.468 (1)° | T = 133 K |
| V = 1429.33 (10) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.10 × 0.10 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 2464 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| phi + ω – scans | Rint = 0.040 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.8° |
| Tmin = 0.674, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −23→23 |
| 13968 measured reflections | k = −5→7 |
| 3280 independent reflections | l = −19→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.113 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0368P)2 + 0.6743P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3280 reflections | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 177 parameters | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2018/3 (Sheldrick 2015) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0093 (16) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.38605 (6) | 0.7949 (2) | 0.38826 (9) | 0.0338 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.27936 (6) | 0.4581 (2) | 0.32610 (8) | 0.0280 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.24228 (6) | 0.6202 (2) | 0.17458 (8) | 0.0285 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.17054 (7) | 0.6836 (3) | 0.26709 (9) | 0.0285 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.41005 (8) | 0.6137 (3) | 0.36687 (11) | 0.0234 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.35448 (8) | 0.4079 (3) | 0.32488 (12) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.348514 | 0.377390 | 0.256450 | 0.031* | |
| H2B | 0.376866 | 0.265560 | 0.364461 | 0.031* | |
| C3 | 0.23136 (8) | 0.5945 (3) | 0.24965 (11) | 0.0249 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.16762 (9) | 0.6747 (4) | 0.36534 (12) | 0.0371 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.211633 | 0.570586 | 0.407718 | 0.044* | |
| C5 | 0.18152 (13) | 0.9155 (5) | 0.41331 (15) | 0.0605 (7) | |
| H5A | 0.228794 | 0.985787 | 0.409862 | 0.091* | |
| H5B | 0.188987 | 0.899895 | 0.482386 | 0.091* | |
| H5C | 0.135734 | 1.015930 | 0.378631 | 0.091* | |
| C6 | 0.09072 (11) | 0.5665 (4) | 0.36026 (15) | 0.0452 (5) | |
| H6A | 0.046572 | 0.670305 | 0.322993 | 0.068* | |
| H6B | 0.093071 | 0.545940 | 0.427083 | 0.068* | |
| H6C | 0.083000 | 0.413759 | 0.327431 | 0.068* | |
| C7 | 0.11069 (9) | 0.8271 (3) | 0.19039 (11) | 0.0278 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.074178 | 0.887235 | 0.220031 | 0.033* | |
| C8 | 0.06055 (9) | 0.6780 (3) | 0.10240 (12) | 0.0319 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.019602 | 0.775918 | 0.054376 | 0.048* | |
| H8B | 0.035643 | 0.551161 | 0.124422 | 0.048* | |
| H8C | 0.094128 | 0.610990 | 0.071729 | 0.048* | |
| C9 | 0.14496 (11) | 1.0413 (3) | 0.16096 (14) | 0.0405 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.176297 | 0.991762 | 0.124230 | 0.061* | |
| H9B | 0.178789 | 1.126741 | 0.220191 | 0.061* | |
| H9C | 0.101940 | 1.143637 | 0.119443 | 0.061* | |
| C10 | 0.49370 (8) | 0.5861 (3) | 0.37810 (11) | 0.0248 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.51983 (9) | 0.3863 (3) | 0.34607 (12) | 0.0315 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.484354 | 0.260546 | 0.317232 | 0.038* | |
| C12 | 0.59781 (10) | 0.3710 (4) | 0.35634 (13) | 0.0420 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.615586 | 0.234665 | 0.334388 | 0.050* | |
| C13 | 0.64925 (10) | 0.5519 (4) | 0.39804 (13) | 0.0478 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.702529 | 0.540331 | 0.404875 | 0.057* | |
| C14 | 0.62389 (10) | 0.7512 (4) | 0.43024 (13) | 0.0437 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.659736 | 0.876252 | 0.458872 | 0.052* | |
| C15 | 0.54637 (9) | 0.7686 (3) | 0.42078 (12) | 0.0327 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.529143 | 0.904967 | 0.443406 | 0.039* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0316 (6) | 0.0311 (6) | 0.0386 (7) | 0.0050 (5) | 0.0140 (5) | −0.0076 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0204 (5) | 0.0369 (6) | 0.0260 (6) | 0.0011 (5) | 0.0087 (4) | 0.0069 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0261 (5) | 0.0375 (7) | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0108 (4) | 0.0031 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0433 (8) | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0081 (5) | 0.0037 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0080 (6) | 0.0014 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0264 (8) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0095 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0310 (8) | 0.0211 (7) | −0.0038 (6) | 0.0055 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0257 (8) | 0.0627 (13) | 0.0251 (8) | 0.0034 (8) | 0.0125 (7) | 0.0044 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0611 (13) | 0.0909 (18) | 0.0325 (10) | −0.0377 (13) | 0.0217 (10) | −0.0224 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0487 (11) | 0.0512 (12) | 0.0475 (11) | −0.0061 (9) | 0.0314 (9) | 0.0003 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0218 (7) | 0.0317 (9) | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0065 (6) | −0.0008 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0251 (7) | 0.0352 (9) | 0.0289 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0041 (7) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0418 (10) | 0.0327 (10) | 0.0417 (10) | −0.0035 (8) | 0.0108 (8) | 0.0002 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0335 (9) | 0.0174 (7) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0069 (6) | 0.0035 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0404 (10) | 0.0257 (8) | 0.0066 (7) | 0.0101 (7) | 0.0001 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0672 (13) | 0.0276 (9) | 0.0201 (9) | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0047 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0923 (17) | 0.0311 (10) | 0.0091 (10) | 0.0111 (7) | 0.0159 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0265 (8) | 0.0666 (14) | 0.0318 (10) | −0.0123 (9) | 0.0051 (7) | 0.0068 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0288 (8) | 0.0404 (10) | 0.0252 (8) | −0.0038 (7) | 0.0068 (7) | 0.0003 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.2149 (19) | C7—C9 | 1.517 (2) |
| O2—C3 | 1.3684 (18) | C7—C8 | 1.522 (2) |
| O2—C2 | 1.4230 (17) | C7—H7 | 1.0000 |
| O3—C3 | 1.2148 (18) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C3 | 1.348 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C7 | 1.4764 (19) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C4 | 1.478 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C10 | 1.494 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.519 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C10—C15 | 1.392 (2) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C10—C11 | 1.392 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.520 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.389 (2) |
| C4—C6 | 1.522 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 1.0000 | C12—C13 | 1.371 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9800 | C13—C14 | 1.384 (3) |
| C5—H5C | 0.9800 | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9800 | C14—C15 | 1.385 (2) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9800 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6C | 0.9800 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C3—O2—C2 | 114.64 (12) | N1—C7—C8 | 111.27 (13) |
| C3—N1—C7 | 119.12 (13) | C9—C7—C8 | 112.63 (14) |
| C3—N1—C4 | 122.37 (13) | N1—C7—H7 | 106.3 |
| C7—N1—C4 | 117.83 (13) | C9—C7—H7 | 106.3 |
| O1—C1—C10 | 121.89 (14) | C8—C7—H7 | 106.3 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 120.45 (14) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C10—C1—C2 | 117.64 (13) | C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O2—C2—C1 | 110.00 (13) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O2—C2—H2A | 109.7 | C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.7 | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O2—C2—H2B | 109.7 | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.7 | C7—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.2 | C7—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O3—C3—N1 | 125.75 (14) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O3—C3—O2 | 122.46 (14) | C7—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—O2 | 111.72 (13) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—C5 | 111.30 (16) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—C6 | 111.37 (14) | C15—C10—C11 | 119.50 (15) |
| C5—C4—C6 | 111.69 (16) | C15—C10—C1 | 118.42 (15) |
| N1—C4—H4 | 107.4 | C11—C10—C1 | 122.07 (14) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 107.4 | C12—C11—C10 | 119.92 (17) |
| C6—C4—H4 | 107.4 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.25 (18) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C12—C13—C14 | 120.29 (16) |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C4—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C4—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.11 (18) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C4—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C14—C15—C10 | 119.93 (18) |
| H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| N1—C7—C9 | 113.40 (13) | C10—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2B···O1i | 0.99 | 2.70 | 3.605 (2) | 152 |
| C5—H5B···O3ii | 0.98 | 2.62 | 3.578 (2) | 167 |
| C9—H9B···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.68 | 3.599 (2) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iii) x, y+1, z.
References
- Desiraju, G. R. & Steiner, T. (2001). The Weak Hydrogen Bond. Oxford Science Publications.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Givens, R. S., Rubina, M. & Wirz, J. (2012). Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 11, 472–488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H., Zhang, H., Xiong, W., Qi, C., Wu, W., Wang, L. & Cheng, R. (2019). Org. Lett. 21, 1125–1129. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kammari, L., Plíštil, L., Wirz, J. & Klán, P. (2007). Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 6, 50–56. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Klán, P., Šolomek, T., Bochet, C. G., Blanc, A., Givens, R., Rubina, M., Popik, V., Kostikov, A. & Wirz, J. (2013). Chem. Rev. 113, 119–191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Sovago, I., Cottrell, S. J., Galek, P. T. A., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Platings, M., Shields, G. P., Stevens, J. S., Towler, M. & Wood, P. A. (2020). J. Appl. Cryst. 53, 226–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Nonius (1998). COLLECT. Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sheehan, J. C. & Umezawa, K. (1973). J. Org. Chem. 38, 3771–3774.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Speckmeier, E., Klimkait, M. & Zeitler, K. (2018). J. Org. Chem. 83, 3738–3745. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021006927/zl5014sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021006927/zl5014Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021006927/zl5014Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2094771
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




