Figure 5.
scGlycan-seq analysis of hiPSCs, hFibs, and NPCs
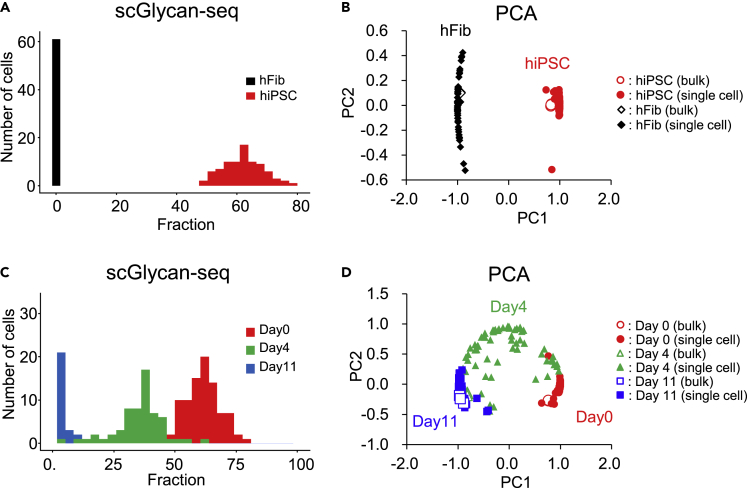
(A) Binding of DNA-barcoded rBC2LCN to hiPSCs and hFibs analyzed by scGlycan-seq. The histogram of rBC2LCN signal levels measured for hiPSCs (n = 83, red) and hFibs (n = 61, black) is shown. There was statistical significance in the distribution of rBC2LCN between the two cell types (p < 0.001, Brunner-Munzel test with Bonferroni correction).
(B) PCA of bulk (100 cells, n = 3 for each cell type) and single cells (n = 96 for each cell type) of hiPSCs (filled circle: single cell, open circle: bulk) and hFibs (filled triangle: single cell, open triangle: bulk). PC1: principal component 1. PC2: principal component 2.
(C) Binding of DNA-barcoded rBC2LCN to hiPSCs after differentiation to NPCs analyzed by scGlycan-seq. The histogram of rBC2LCN signal levels measured for hiPSCs after differentiation to NPCs for 0 (n = 84, red), 4 (n = 61, blue), and 11 days (n = 57, green) is shown. There was statistical significance in the distribution of rBC2LCN between the two cell types (day 0 vs day 4; p < 0.001, day 4 vs day 11; p < 0.001, day 0 vs day 11; p < 0.001, Brunner-Munzel test with Bonferroni correction).
(D) PCA of bulk (100 cells, n = 3 for each cell type) and single cells (n = 96 for each cell type) of hiPSCs after differentiation to NPCs for 0 (open circle: bulk, filled circle: single cell), 4 (open triangle: bulk, filled triangle: single cell), and 11 days (open square: bulk, filled square: single cell). DNA barcode derived from each lectin was divided by DNA barcode of all lectins and multiplied by 100. Glycan-seq data are available in Tables S2–S5. PC1: principal component 1. PC2: principal component 2. See also Figures S7 and S8.